Effect of the Quality Property of Table Grapes in Cold Chain Logistics-Integrated WSN and AOW
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WSN Nodes
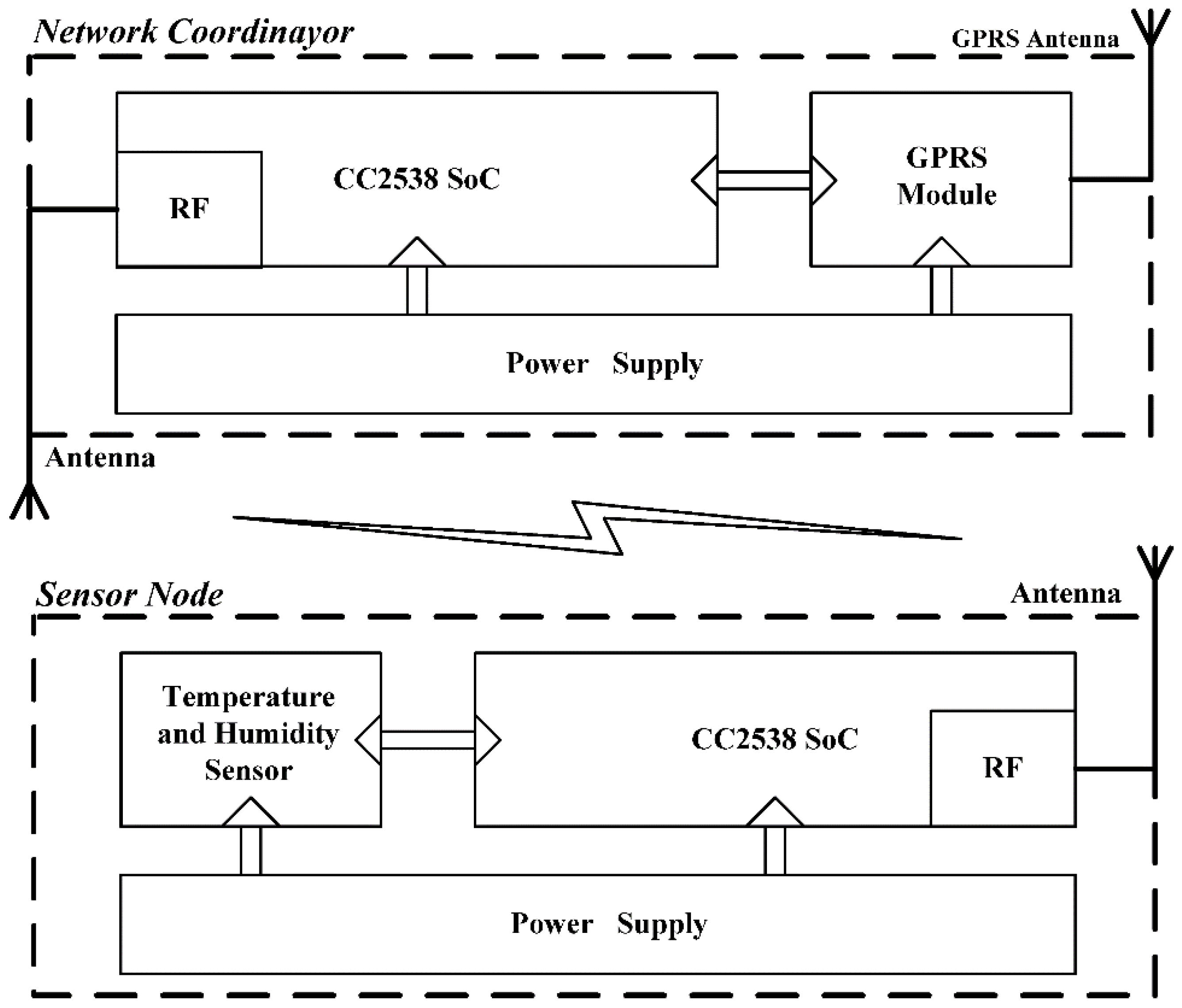
2.2. Optimal Weighted Data Fusion
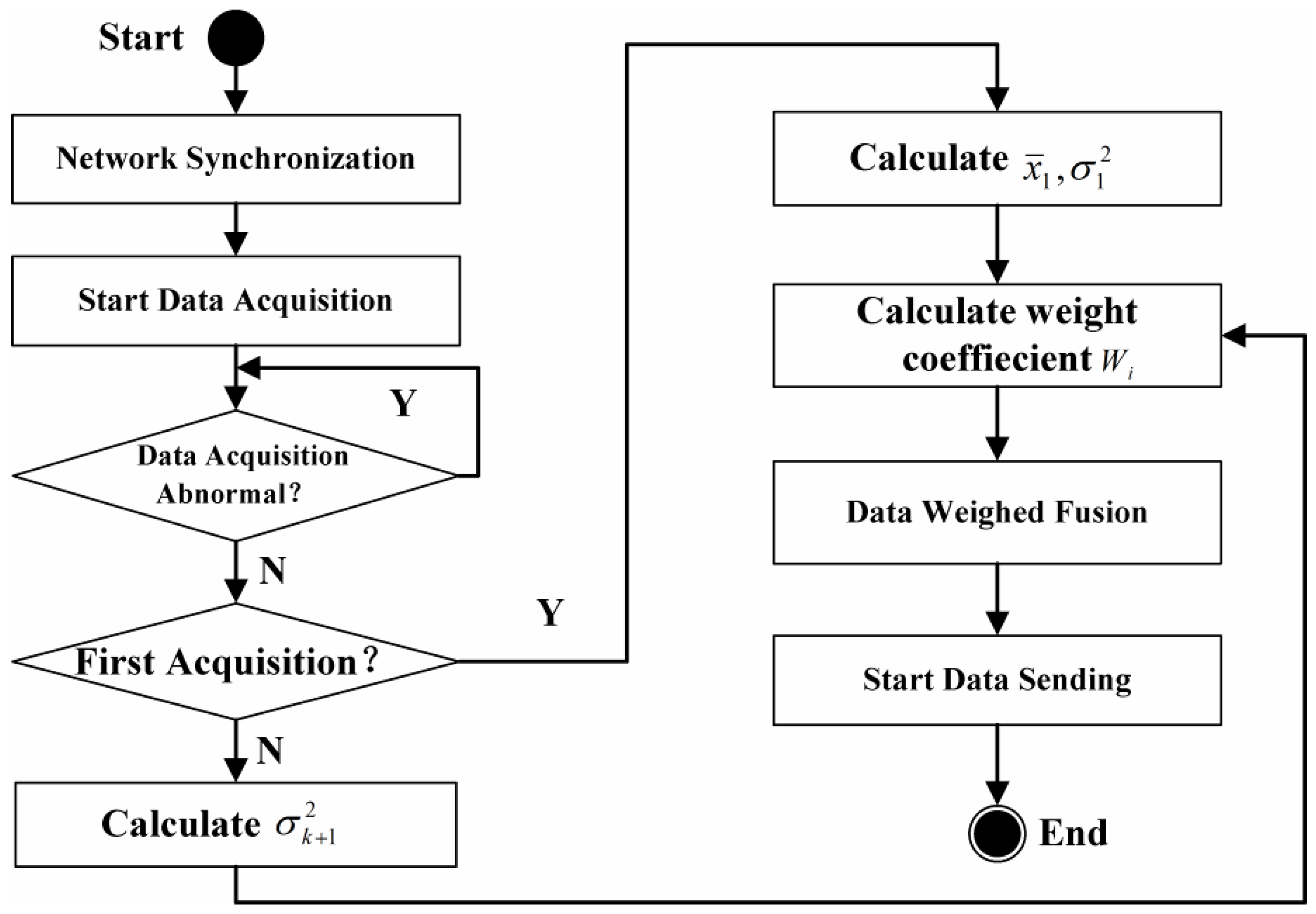
2.3. Dynamic Adjustment of Weight Coefficient
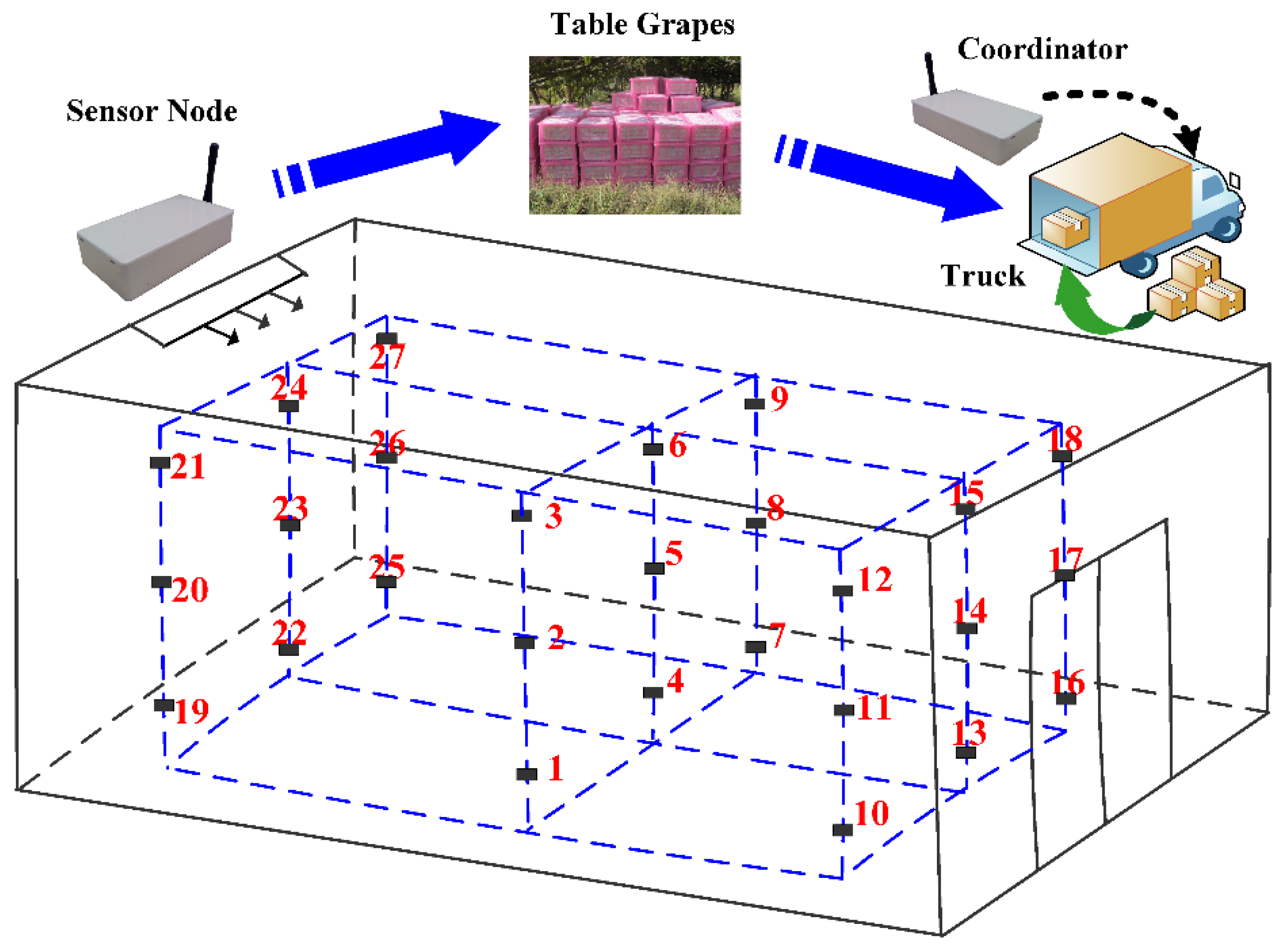
2.4. Implementation Scenario
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Process Analysis of Table Grapes’ Cold Chain Logistics

| Step | Operation | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Picking and Packing | Table grapes should be picked when fully ripe in the evening with dry weather conditions and packed into boxes. | Temperature and relative humidity varied with the ambient temperature. |
| 2 | Ordinary Transportation | Table grapes are transported to cold storage by ordinary truck. | Temperature and relative humidity varied with the ambient temperature. |
| 3 | Pre-cooling | Pre-cooling for the picked table grapes because they are still in the metabolism. | Temperature of 0 °C or lower and relative humidity of 90% or higher. |
| 4 | Storage | Table grapes are stored at a low and stable temperature and relative humidity for cold chain storage. | Temperature of 0 °C or lower and relative humidity of 90% or higher with about 3 days or more. |
| 5 | Loading | Table grapes are loaded. | About 6 h or lower. |
| 6 | Refrigerated Transportation | Table grapes are transported in a low and stable temperature and relative humidity condition. | Temperature of 0 °C or lower and relative humidity of 90% or higher with about 5 days or more. |
| 7 | Unloading | Table grapes are unloaded for sale. | About 6 h or lower. |
| 8 | Sale | Table grapes are sold in the market. | Temperature and relative humidity varied with the ambient temperature. |
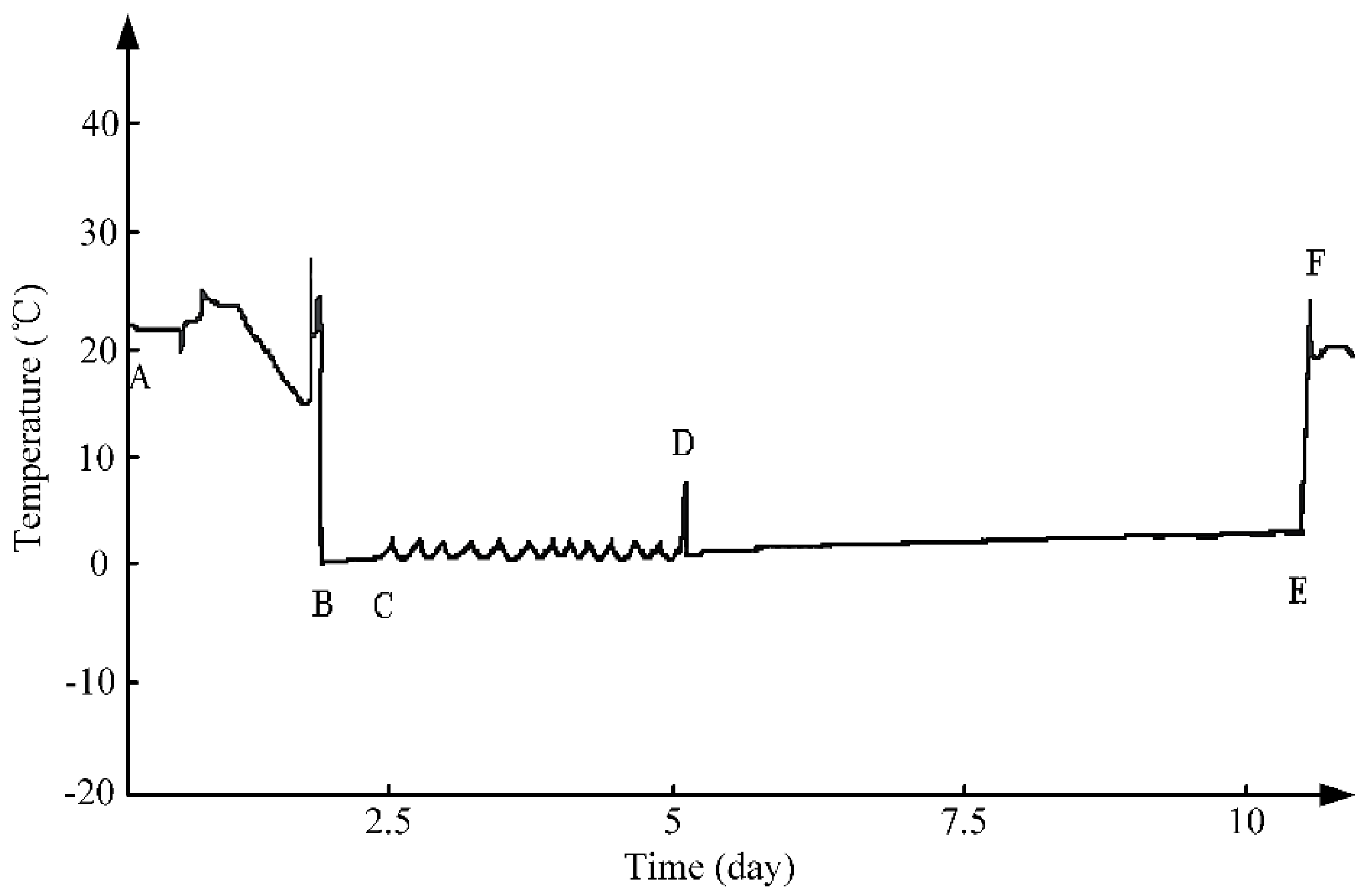
3.2. Adaptive Data Fusion Analysis of Table Grapes’ Cold Chain Logistics
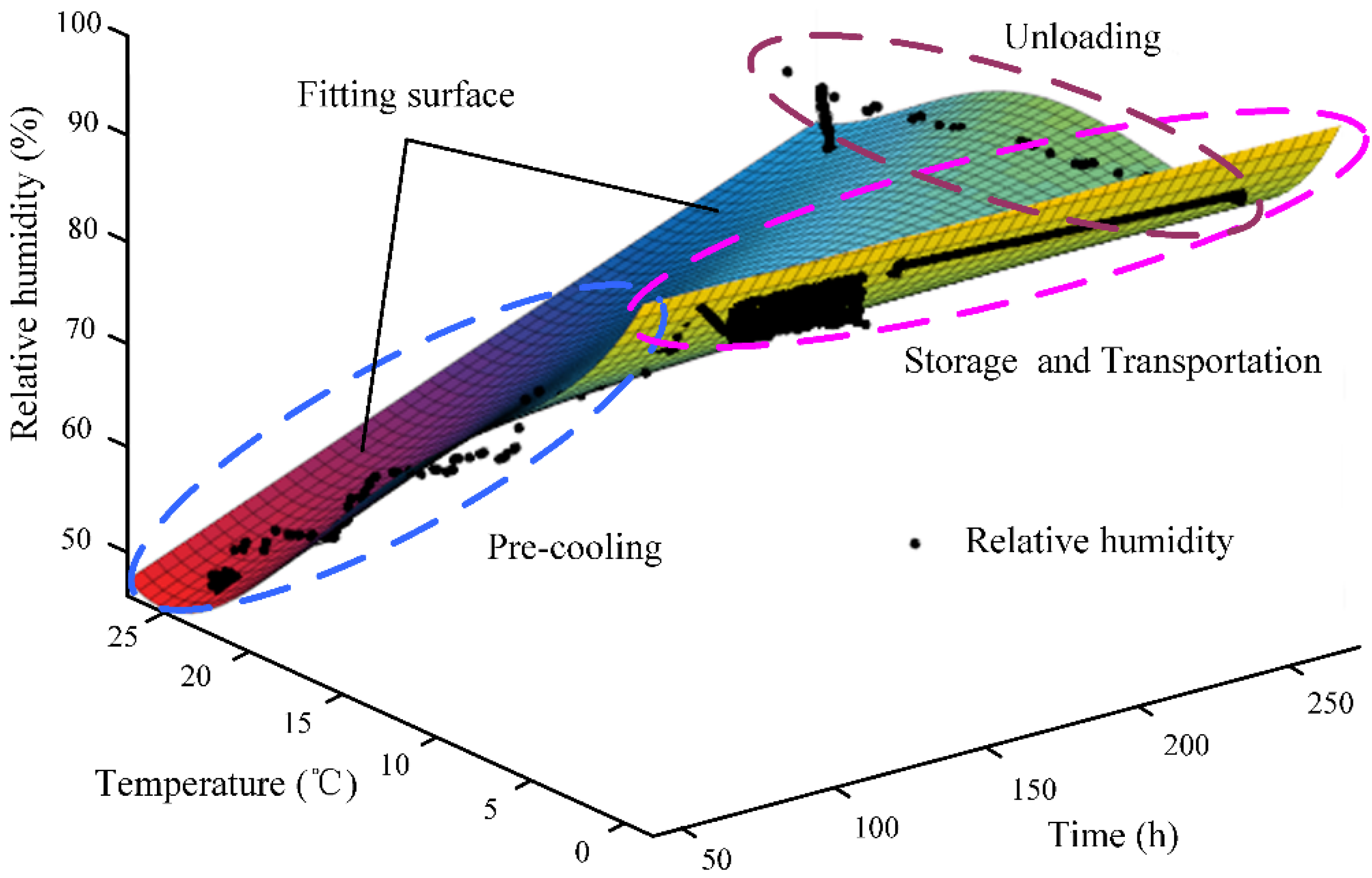
| Parameters | Mean Absolute Error | Mean Relative Error | Run Time | Mean Battery Charge Status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Relative humidity | Temperature | Relative humidity | |||
| Arithmetic Mean | 0.35 °C | 1.56% | 19.54% | 2.99% | 1.508 s | 93.2% |
| AOW | 0.06 °C | 0.12% | 8.61% | 0.23% | 1.594 s | 91.5% |
3.3. Firmness Analysis of Table Grapes’ Cold Chain Logistics
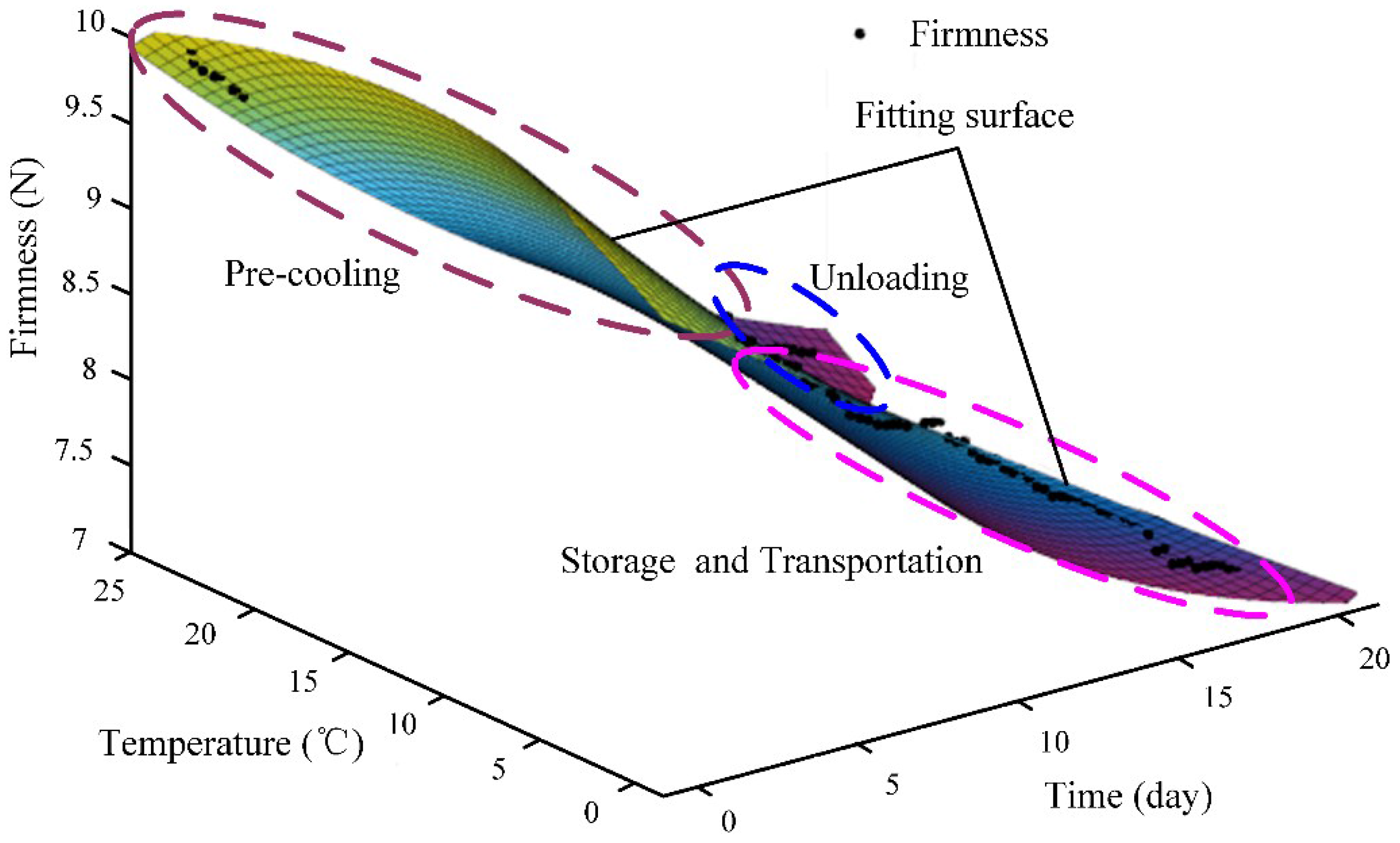
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Hu, J. Design on wireless SO2 sensor node based on CC2530 for monitoring table grape logistics. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2013, 11, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z.; Mu, W. Assessment of consumers’ perception and cognition toward table grape consumption in China. Br. Food J. 2014, 116, 611–628. [Google Scholar]
- Ngcobo, M.E.K.; Opara, U.L.; Thiart, G.D. Effects of packaging liners on cooling rate and quality attributes of table grape (cv. Regal Seedless). Packag. Technol. Sci. 2012, 25, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xu, M.; Fu, Z.; Mira, T.; Zhang, X. (CSLDS)-S-2: A WSN-based perishable food shelf-life prediction and LSFO strategy decision support system in cold chain logistics. Food Control 2014, 38, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, V.; Ndoye, F.T.; el Jabri, M.; le Page, J.F.; Hezard, B.; Lintz, A.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Alvarez, G.; Thuault, D. Safety and quality assessment of ready-to-eat pork products in the cold chain. J. Food Eng. 2015, 148, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Fu, Z. Real time monitoring system for aquatic cold-chain logistics based on WSN. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2012, 43, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.-J.; Lien, T.-W.; Hisao, B.-R.; Wang, H.-S.; Yang, C.-F.; Tarng, J.-H.; Nien, C.-C.; Chiu, T.-C. Sensor integrated antenna design for applications in cold chain logistic services. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Tian, S. Physiological responses and quality attributes of table grape fruit to chitosan preharvest spray and postharvest coating during storage. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Qi, L.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, X. Monitoring method for cold chain logistics of table grape based on compressive sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Yao, M.; Ma, C.; Qi, L.; Zhang, X. Applicability of a chemical time temperature indicator as a quality indicator for table grape. J. China Agric. Univ. 2013, 18, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, W.; Fu, Y. Preservation of Kyoho grapes stored in active, slow-releasing pasteurizing packaging at room temperature. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-W.; Sun, D.-W.; Xiao, H.-W.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Gao, Z.-J. Novel high-humidity hot air impingement blanching (HHAIB) pretreatment enhances drying kinetics and color attributes of seedless grapes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.R.; Aung, M.M.; Chang, Y.S.; Makatsoris, C. Freshness Gauge based cold storage management: A method for adjusting temperature and humidity levels for food quality. Food Control 2015, 47, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balic, I.; Ejsmentewicz, T.; Sanhueza, D.; Silva, C.; Peredo, T.; Olmedo, P.; Barros, M.; Verdonk, J.C.; Paredes, R.; Meneses, C.; et al. Biochemical and physiological study of the firmness of table grape berries. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 93, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno, I.; Antonio Cabezas, J.; Martinez-Mora, C.; Arroyo-Garcia, R.; Luis Cenis, J.; Martinez-Zapater, J.M.; Carreno, J.; Ruiz-Garcia, L. Quantitative genetic analysis of berry firmness in table grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Tree Genet. Genom. 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyom, K.; Kraus, S.; Mato, R.B.; Gaukel, V.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Jose Cocero, M. Dielectric properties of grape marc: Effect of temperature, moisture content and sample preparation method. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabale, R.; Shabeer, T.P.A.; Utture, S.C.; Banerjee, K.; Jadhav, M.R.; Oulkar, D.P.; Adsule, P.G.; Deshmukh, M.B. Dissipation kinetics, safety evaluation, and assessment of pre-harvest interval (PHI) and processing factor for kresoxim methyl residues in grape. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanpour, H. Effect of Aloe vera gel coating on antioxidant capacity, antioxidant enzyme activities and decay in raspberry fruit. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; You, X.; Wen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Wei, P.; Li, L.; Li, C. Preservation quality and physiological biochemical characteristics of abscission fruit of grape during cold storage. J. South. Agric. 2014, 45, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Arazuri, S.; Diezma, B.; Blanco, R.; Garcia-Ramos, F.J. Comparison of different pre-treatments to improve accuracy of total soluble solids content prediction models in grapes using a portable NIR spectrophotometer. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2014, 12, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez de Lerma, N.; Moreno, J.; Peinado, R.A. Determination of the optimum sun-drying time for Vitis vinifera L. cv. tempranillo grapes by E-nose analysis and characterization of their volatile composition. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Oh, Y.A.; Lee, H.; Bin Song, K.; Min, S.C. Grape berry coatings of lemongrass oil-incorporating nanoemulsion. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Fish product quality evaluation based on temperature monitoring in cold chain. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 9, 6146–6151. [Google Scholar]
- Badia-Melis, R.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Garcia-Hierro, J.; Villalba, J.I.R. Refrigerated fruit storage monitoring combining two different wireless sensing technologies: RFID and WSN. Sensors 2015, 15, 4781–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Zhang, J.; Mark, X.; Fu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. Developing WSN-based traceability system for recirculation aquaculture. Mathem. Comput. Model. 2011, 53, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayev, Y.; Chen, F.; Hou, Y.; Johnson, M.P.; Bar-Noy, A.; la Porta, T.F.; Leung, K.K. Throughput maximization in mobile WSN scheduling with power control and rate selection. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 4066–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadevara, N.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kelly, S.D.T.; Gill, S.P.S. WSN-based smart sensors and actuator for power management in intelligent buildings. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Tian, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Z. Sensing data compression method based on SPC for agri-food cold-chain logistics. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2011, 42, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, R.W.; Delwiche, M.J.; Broad, A.; Holler, M. Wireless sensor network with irrigation valve control. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 96, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia-Melis, R.; Garcia-Hierro, J.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Jiménez-Ariza, T.; Villalba, J.I.R.; Barreiro, P. Assessing the dynamic behavior of WSN motes and RFID semi-passive tags for temperature monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 103, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, J.; Krogh, B.H.; Small, M.J.; Sinopoli, B. An approach to leak detection using wireless sensor networks at carbon sequestration sites. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2012, 9, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of wireless sensor networks in marine environment monitoring: A survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 16932–16952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Zhang, T.; Gidlund, M.; Dobslaw, F. SAS-TDMA: A source aware scheduling algorithm for real-time communication in industrial wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 2013, 19, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhu, T.; Qi, L.; Moga, L.M.; Zhang, X. MS-BWME: A wireless real-time monitoring system for brine well mining equipment. Sensors 2014, 14, 19877–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niri, E.D.; Farhidzadeh, A.; Salamone, S. Adaptive multisensor data fusion for acoustic emission source localization in noisy environment. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 2013, 12, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Hong, M.; Zheng, W.; Sun, L.-M.; Ge, X. Multi-sensor data fusion based on consistency test and sliding window variance weighted algorithm in sensor networks. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2013, 10, 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shen, M. Research of WSN-based data fusion in water quality monitoring. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2014, 50, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Chandrakasan, A.P.; Stojanovic, V.M. Design and analysis of a hardware-efficient compressed sensing architecture for data compression in wireless sensors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhou, R. Efficient data gathering with network coding coupled compressed sensing for wireless sensor networks. Inf. Technol. J. 2013, 12, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Javadi, S.H.; Peiravi, A. Fusion of weighted decisions in wireless sensor networks. IET Wirel. Sensor Syst. 2015, 5, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, E.; Li, J. Effect of the Quality Property of Table Grapes in Cold Chain Logistics-Integrated WSN and AOW. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 747-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040747
Xiao X, Wang X, Zhang X, Chen E, Li J. Effect of the Quality Property of Table Grapes in Cold Chain Logistics-Integrated WSN and AOW. Applied Sciences. 2015; 5(4):747-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Xinqing, Xiang Wang, Xiaoshuan Zhang, Enxiu Chen, and Jun Li. 2015. "Effect of the Quality Property of Table Grapes in Cold Chain Logistics-Integrated WSN and AOW" Applied Sciences 5, no. 4: 747-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040747
APA StyleXiao, X., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Chen, E., & Li, J. (2015). Effect of the Quality Property of Table Grapes in Cold Chain Logistics-Integrated WSN and AOW. Applied Sciences, 5(4), 747-760. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040747








