Integrated SOM Multi-Attribute Optimization and Seismic Waveform Inversion for Thin Sand Body Characterization: A Case Study of the Paleogene Lower E3d2 Sub-Member in the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
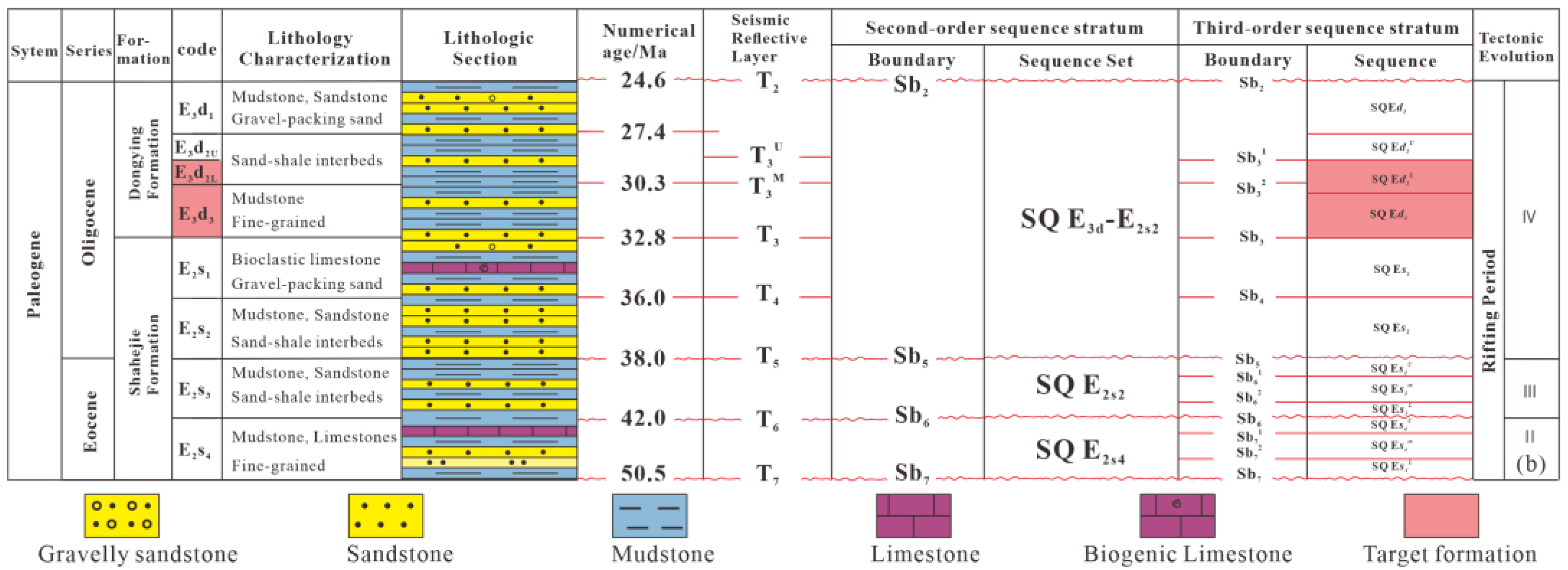
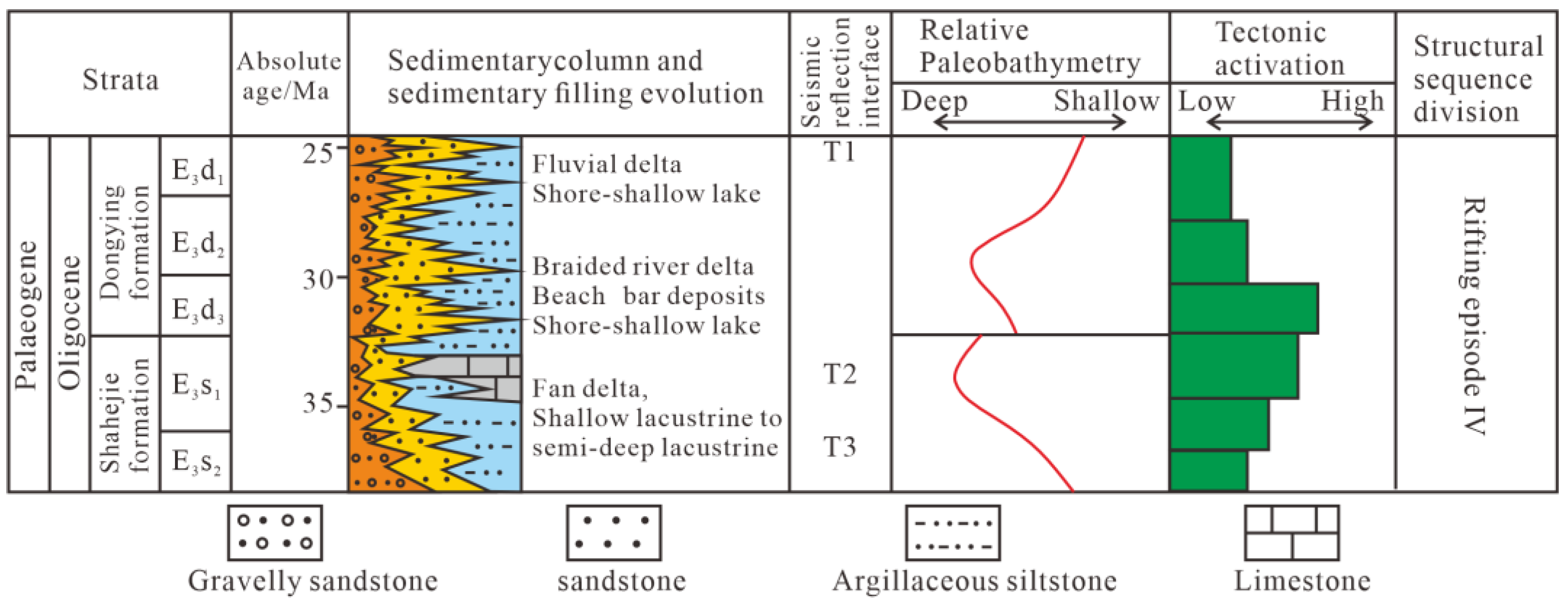
2. Regional Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Seismic Data Quality Analysis
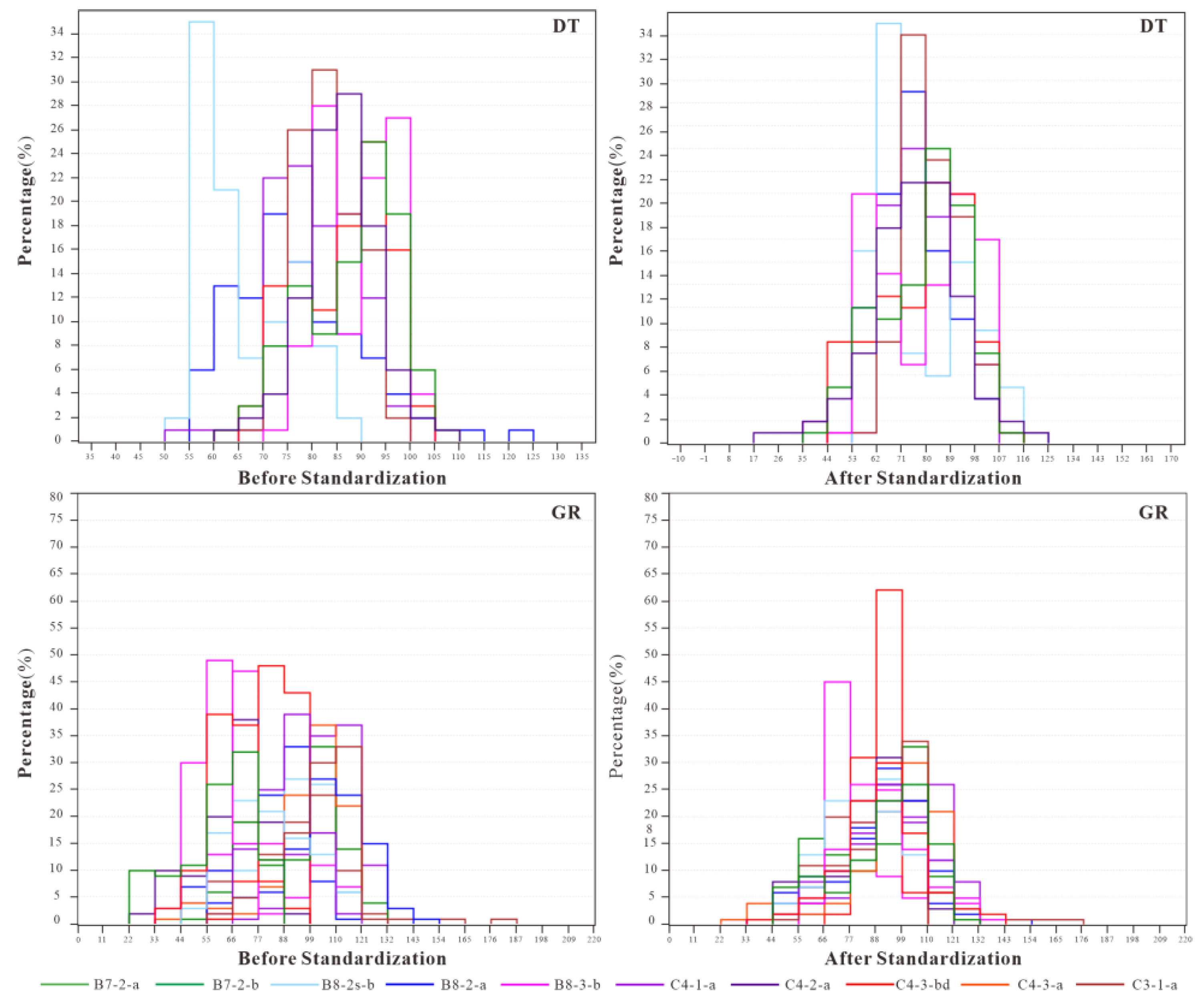
3.2. Well Logging Data Preprocessing
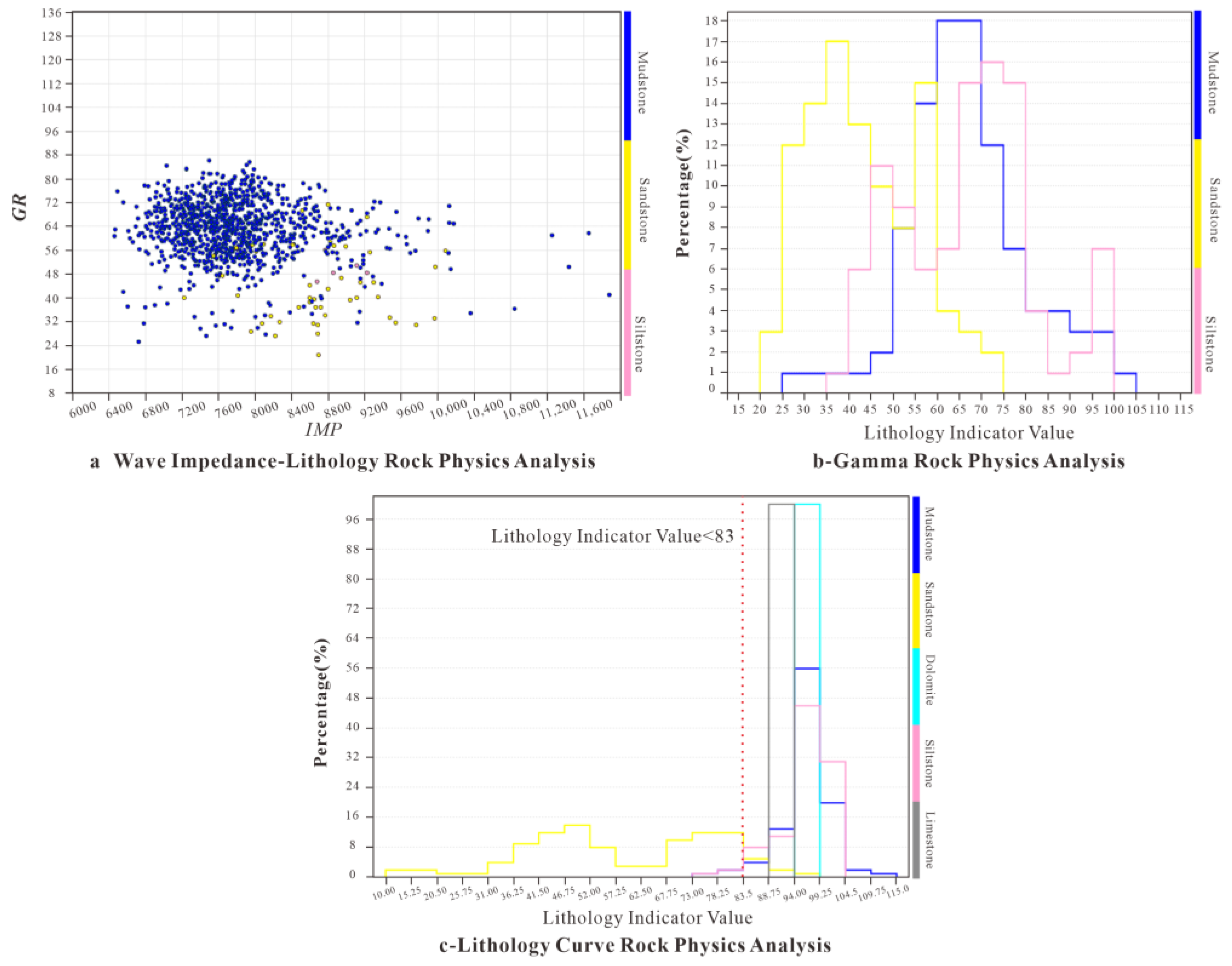
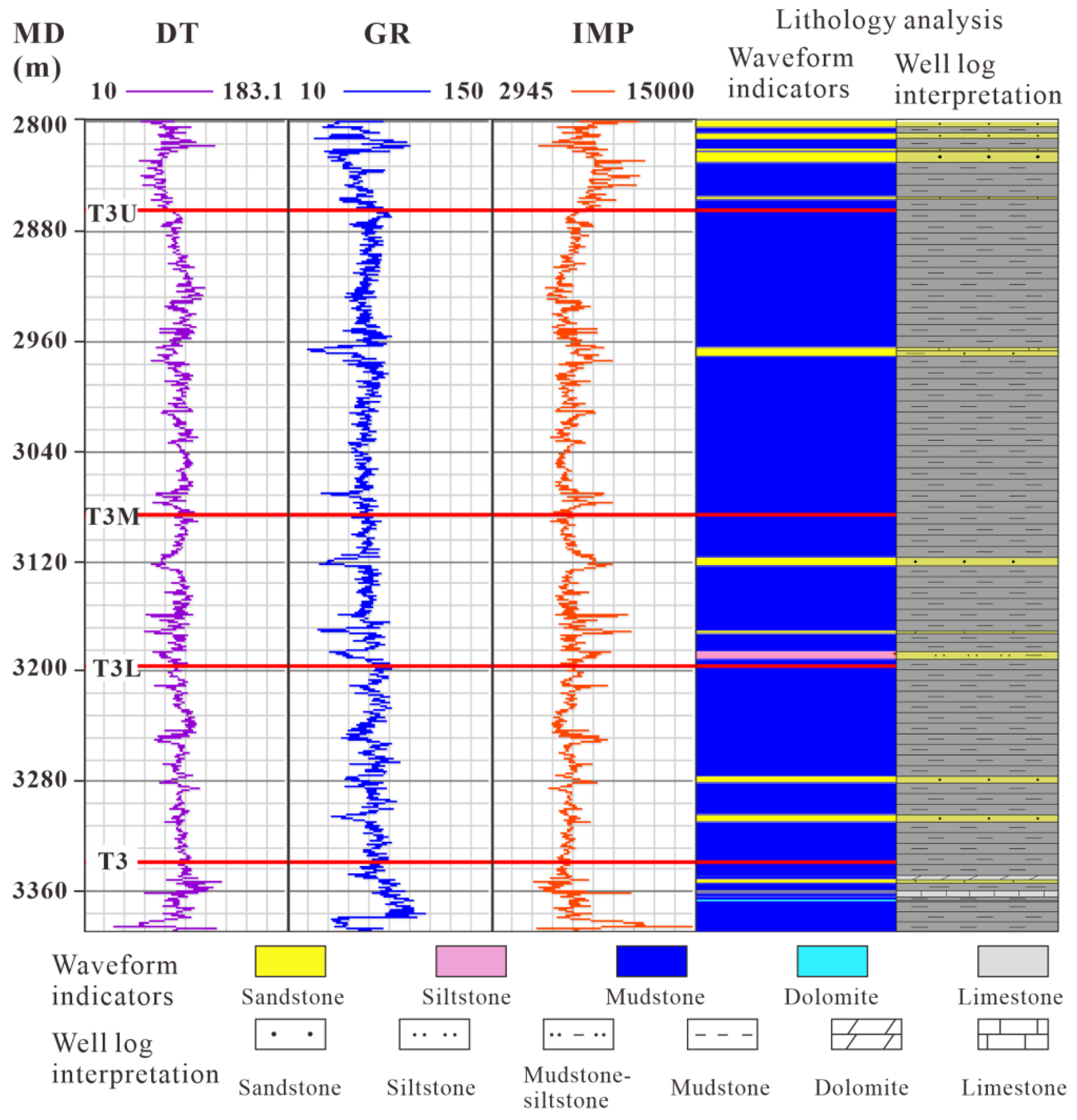
3.3. Petrophysical Analysis
4. Principles of Technical Methods
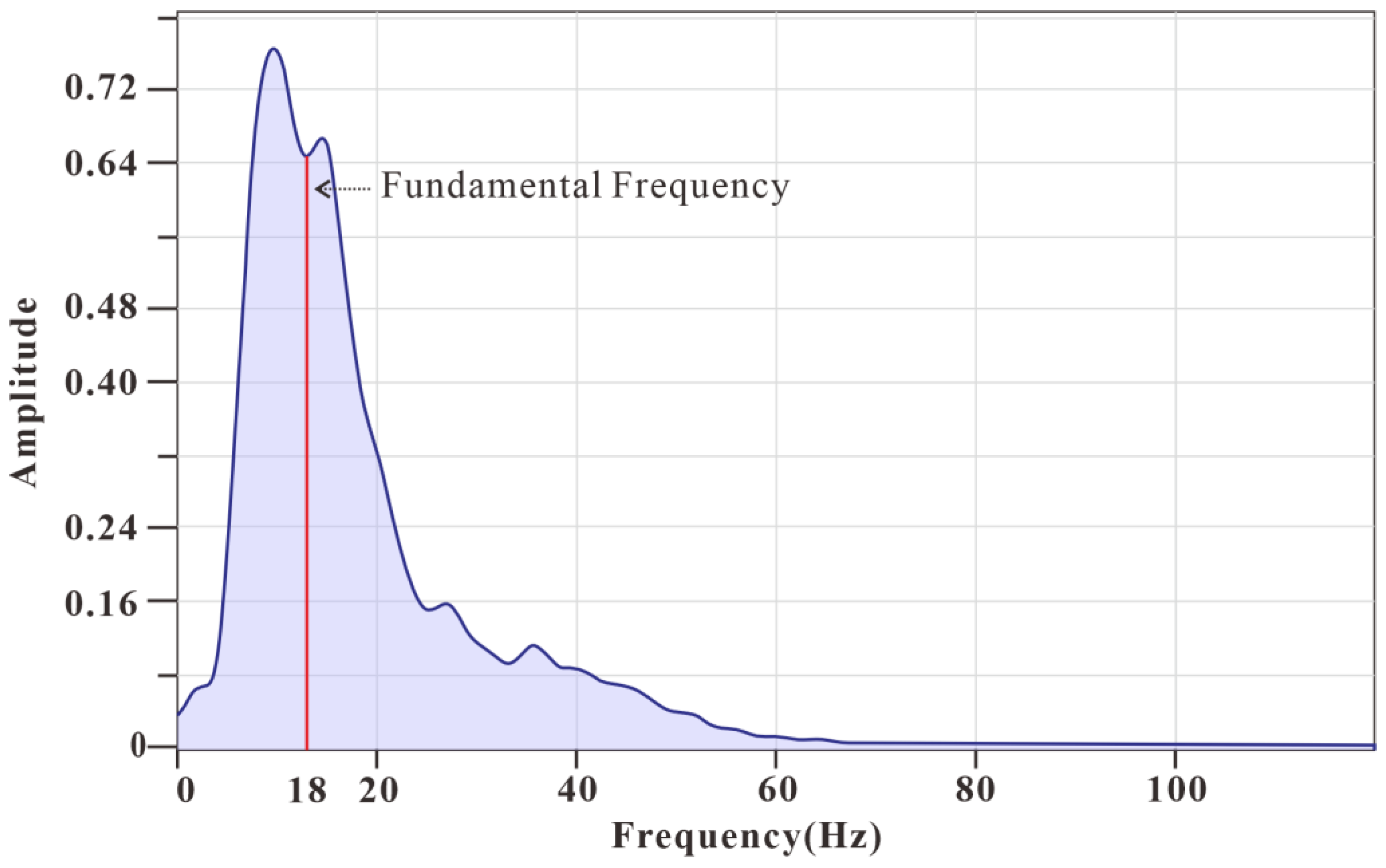
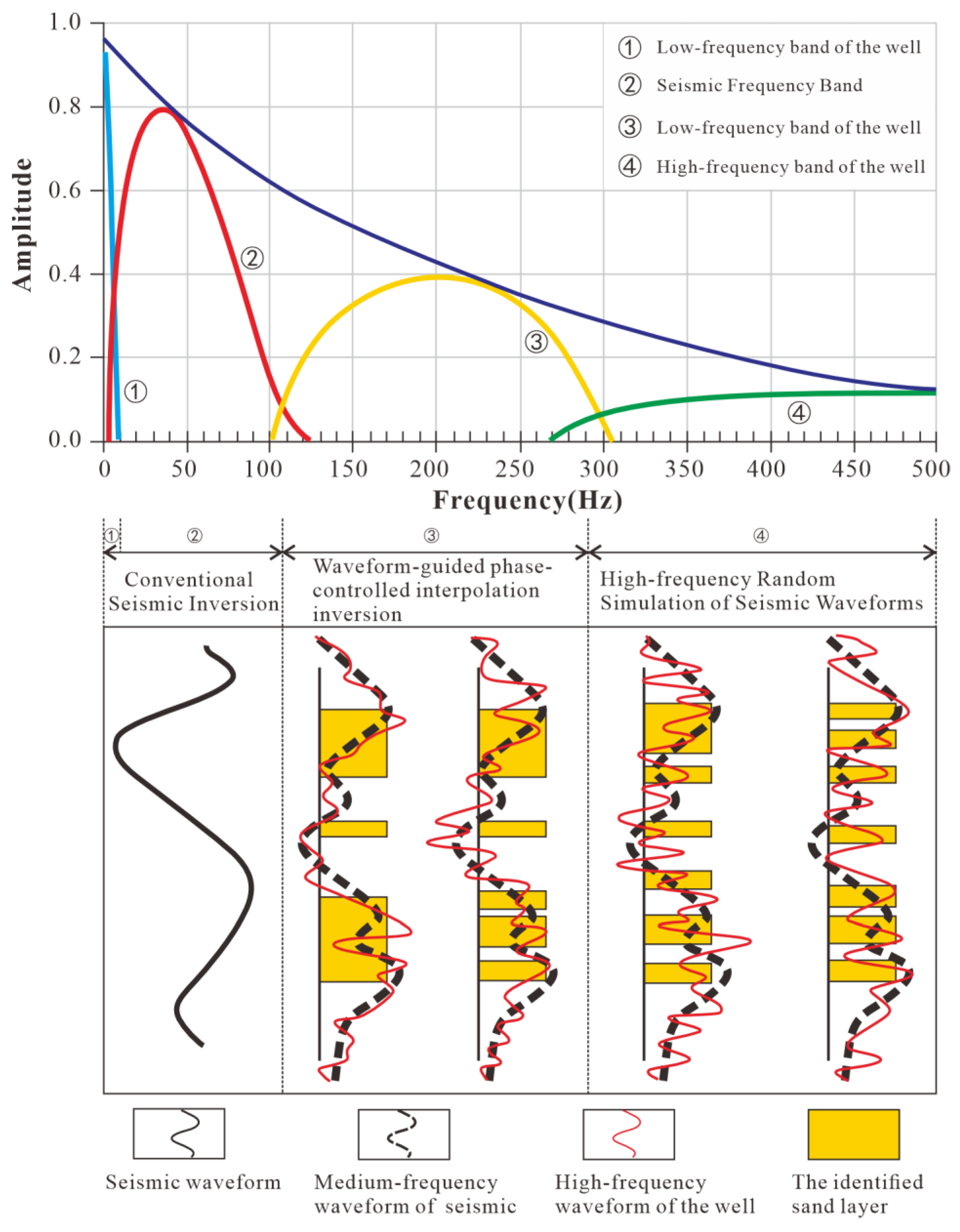
4.1. Seismic Waveform Inversion
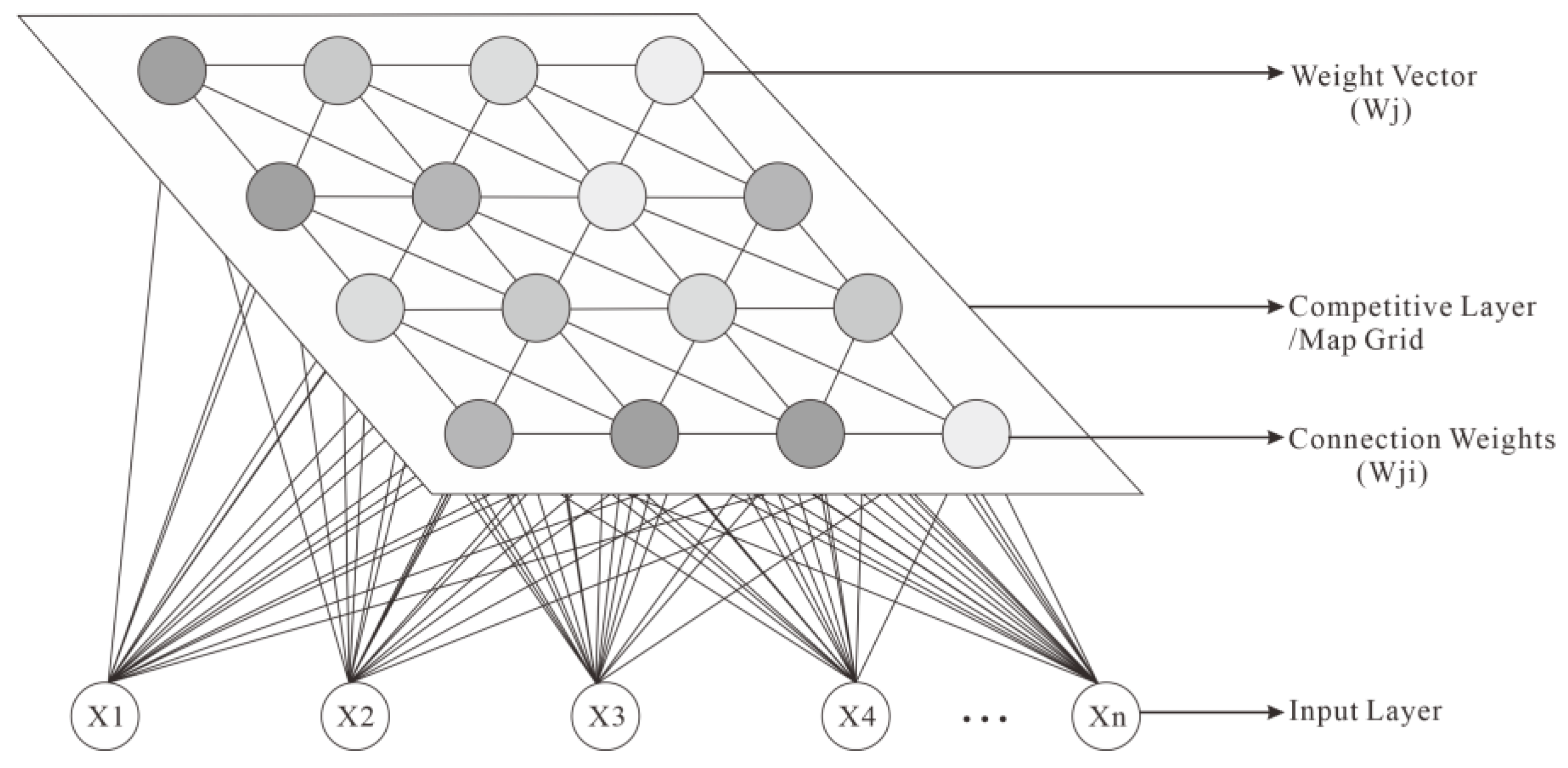
4.2. SOM-Based Seismic Attribute Clustering Analysis
4.3. Technical Workflow for Thin-Bedded Sandbody Boundary Delineation
5. Applications and Discussion
5.1. Geological and Geophysical Characteristics
5.2. Results of Rock Physics Analysis
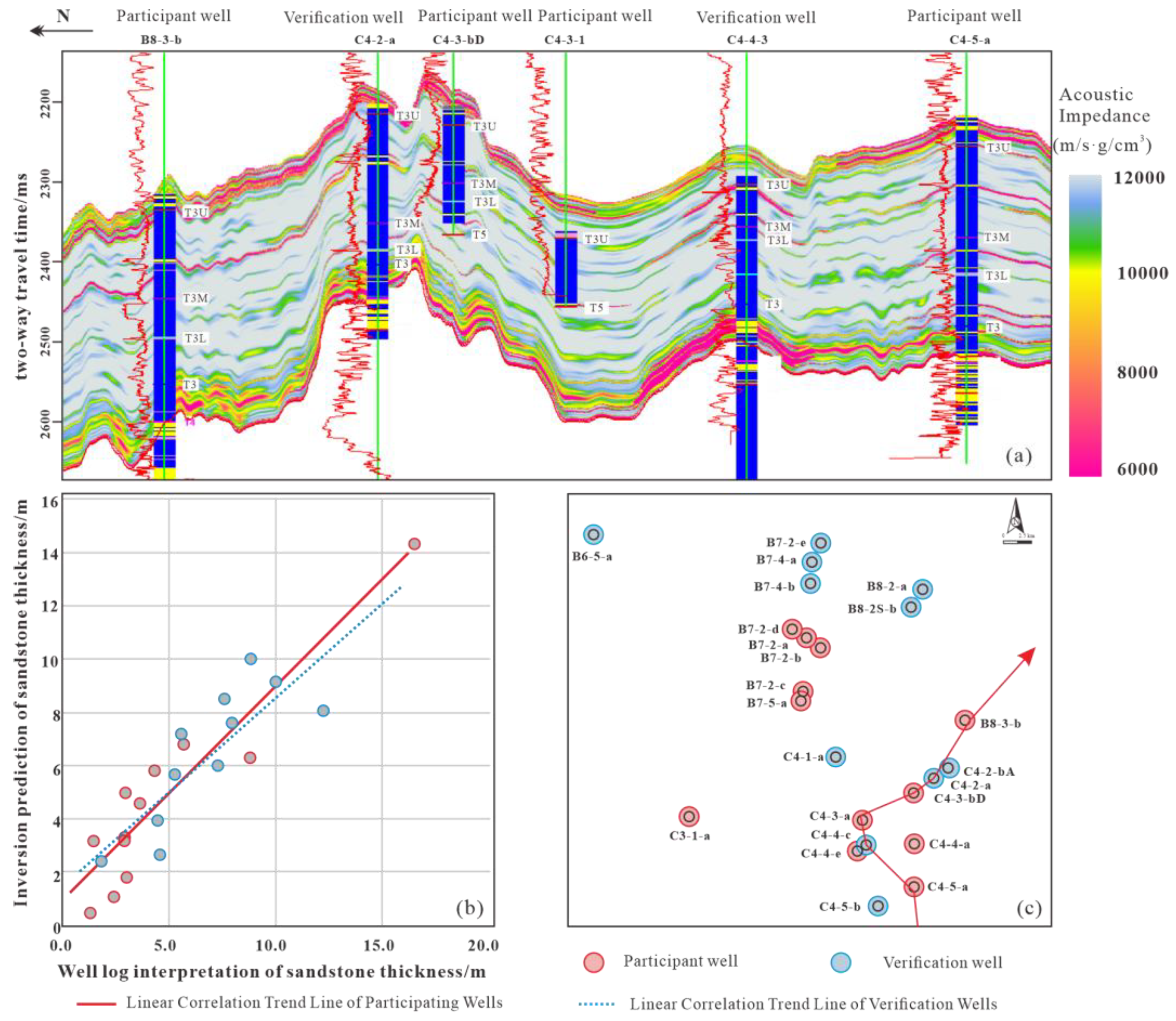
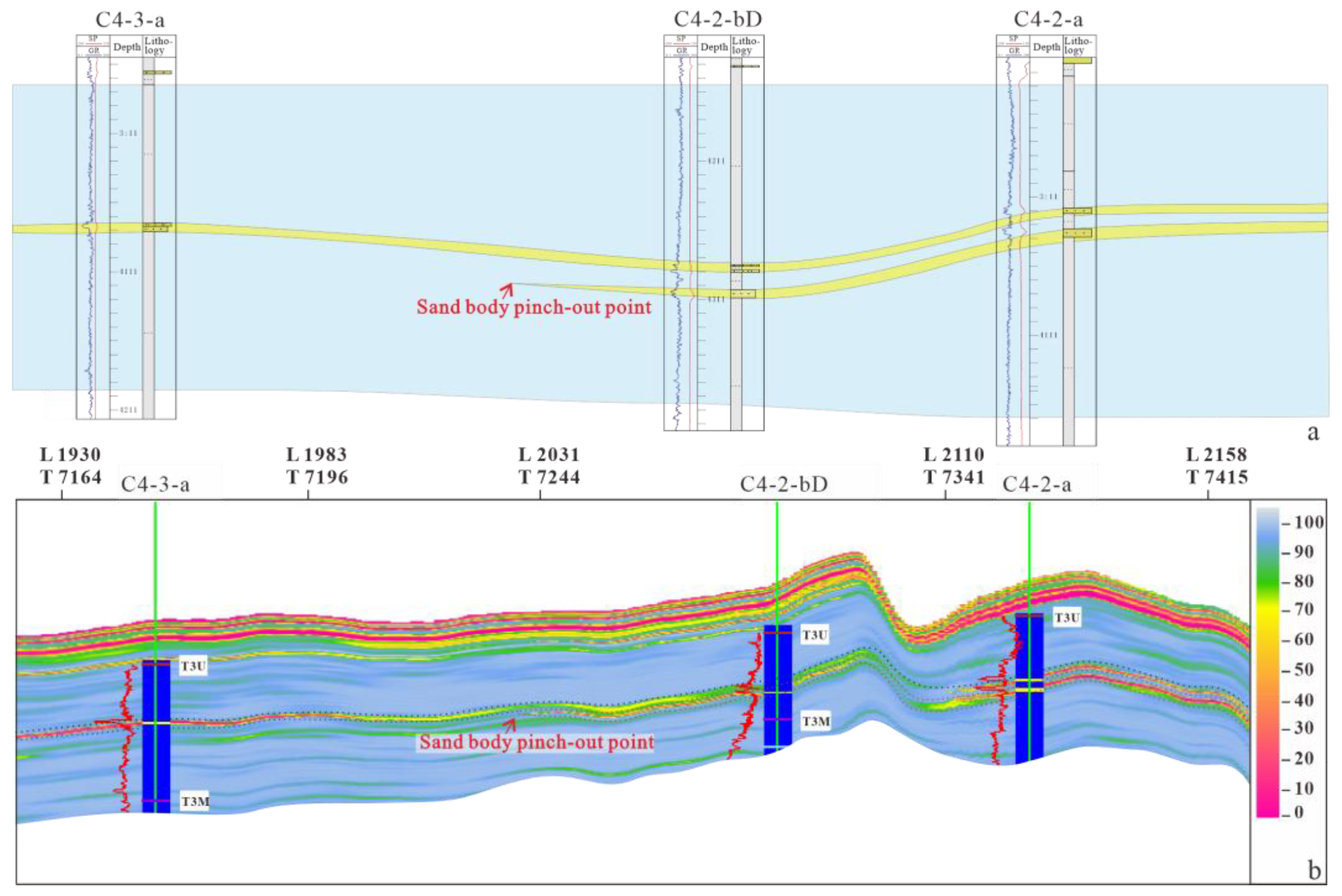
5.3. Cross-Section Inversion Results
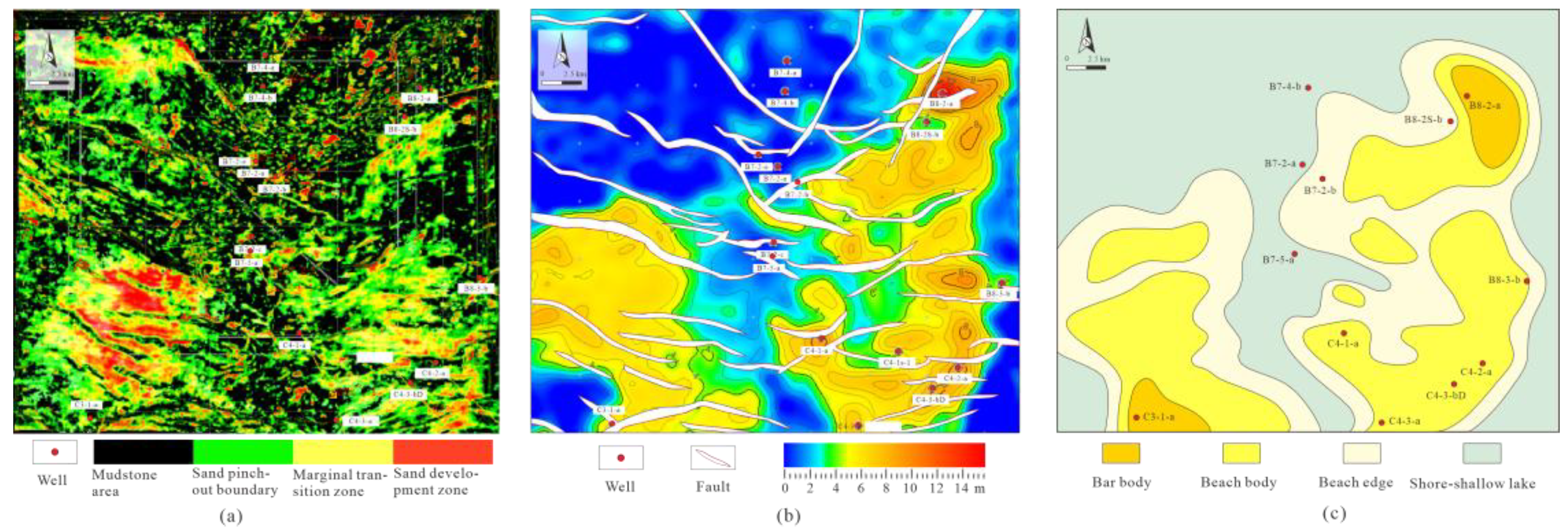
5.4. Planar Sedimentary Microfacies
6. Conclusions
- The lithological types in the study area predominantly consist of sandstone, siltstone, mudstone, limestone, and dolomite. A single logging curve is inadequate for reservoir identification. Therefore, a lithology indicator curve was developed to effectively identify sandstone, utilizing a cutoff value of less than 83. Subsequently, seismic waveform inversion was employed to predict thin sand bodies, which can be identified vertically at depths of 3 to 8 m and laterally with distinct boundaries. The validation results of the inversion demonstrate a coincidence rate exceeding 90% with the participating wells and over 80% with the verification wells.
- Guided by seismic sedimentary theory, a Self-Organizing Map (SOM)-based multi-attribute optimization analysis was conducted utilizing three seismic attributes sensitive to lithological characteristics: Root Mean Square Amplitude (RMS), Total Energy (TE), Average Energy (AE), Amplitude Envelope (ENV), and Peak Amplitude (PA). SOM operations were employed for correlation and clustering analyses to identify a subset of data that reflects lithological features. In conjunction with well-seismic calibration, a threshold for sandstone distribution was established, non-sandstone areas were excluded, and a spatial hollowing-out map of the Lower Member of the Second East Sandstone Formation was produced. The visual representation of this map, in comparison to single attributes, emphasizes the distribution of beach-bar sand bodies and facilitates clearer identification and delineation of the sandbody edges.
- Seismic waveform inversion, which embodies phase-controlled principles, operates independently of the quantity and distribution of wells. The Self-Organizing Map (SOM) algorithm is effectively employed for comprehensive attribute clustering analysis. The integration of these two techniques in the study of beach-bar microfacies within the Lower Member of the Second East Sandstone Formation in the HHK Depression reveals a strong correlation between sandstone thickness pinch-out lines and the boundaries of attribute amplitude anomalies. By predicting sandbody thickness through waveform inversion and integrating litho-electric characteristics with seismic responses, three microfacies types are delineated: bar body, beach body, and beach edge. The thickness of the bar body sandbody is approximately 8 to 14 m, the beach body ranges from 3 to 8 m, and the beach edge measures between 0 and 3 m.
- Guided by geological principles and seismic sedimentology theory, high-resolution waveform indicator inversion is employed in well-controlled areas to enhance the accuracy of thin-sandstone predictions. In regions lacking well control, Self-Organizing Map (SOM) based seismic attribute clustering mitigates the limitations of inversion precision by clarifying the spatial distribution of sand bodies. This integrated methodology addresses two critical challenges in seismic interpretation: the low vertical resolution of seismic data and the complexities associated with lithological identification. By combining the high-resolution capabilities of waveform inversion with the pattern recognition advantages of SOM clustering, this approach offers a novel solution for predicting thin sandstones and delineating boundaries in sparsely sampled areas.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, T.; Zhang, Q. Deepwater Bottom Current Rework Sand (BCRS) in Lacustrine Basins:Sedimentary Characteristics, Identification Criterion, Formation Mechanism and Its Significance for Unconventional Oil/Gas Exploration. Nat. Gas. Geosci. 2014, 25, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Sun, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, A.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S.; et al. Advances and Trends in Sedimentological Research in Oil and Gas Exploration and Development in China. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2025, 43, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhang, G.S.; Yang, Z.; Tao, S.Z.; Hou, L.H.; Zhu, R.K.; Yuan, X.J.; Ran, Q.Q.; Li, D.H.; Wang, Z.P. Geological concepts, characteristics, resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon:on unconventional petroleum geology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Han, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, L. Sedimentary succession and recognition marks of lacustrine gravel beach-bars, a case study from the Qinghai Lake, China. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlonienė, D.; Pupienis, D.; Jarmalavičius, D.; Dubikaltinienė, A.; Žilinskas, G. The Impact of Coastal Geodynamic Processes on the Distribution of Trace Metal Content in Sandy Beach Sediments, South-Eastern Baltic Sea Coast (Lithuania). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, B.P.; Durand, B.; Espitalie, J. Influence of nature and diagenesis of organic matter in formation of petroleum. AAPG Bull. 1974, 58, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Pu, X.; Zhou, L.; Jin, F.; Han, G.; Shi, Z.; Han, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; et al. Enrichment theory, exploration technology and prospects of shale oil in lacustrine facies zone of deep basin:a case study of the Paleogene in Huanghua depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z. Diversity in the lithofacies assemblages of marine and lacustrine shale strata and significance for unconventional petroleum exploration in China. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Han, G.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X. A Study on a Novel Production Forecasting Method of Unconventional Oil and Gas Wells Based on Adaptive Fusion. Processes 2024, 12, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Pang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Sedimentary characteristics and reservoir origin of the mound and shoal microfacies of the Ma51+2 submember of the Majiagou Formation in the Jingbian area. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 108041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; You, X.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, J. The Sequence Stratigraphy and Sedimentary Evolution of the Guantao Formation in the Binxian Uplift Area, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.S.; Shuhab, D.K.; Janok, P.B.; Craig, G.; Darsel, S. Thin-bedded reservoir analogs in an ancient delta using terrestrial laser scanner and high-resolution ground-based hyperspectral cameras. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 342, 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Ye, S. Sedimentary Succession and Model of Gravel Beach-Bars in The Southeastern Qinghai Lake. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 300, 022156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Dai, X. Seismic Characterization Technology and Practice in the Hydrocarbon Reservoirs. Petroleum industry press: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X. Review on extension of geophysical technology to reservoir development and road ahead. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2025, 64, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, G.; Liu, F.; Wu, Q. Reservoir characteristics and seismic identification techniques for shallowgas reservoirs in the South China Sea. Comput. Tech. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 47, 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Ren, G.; Liu, L.; Du, Y.; Lin, J. Overview and Analysis of Several Common Spatial Interpolation Analysis Methods in Watershed Ecological Environment Analysis. Territ. Nat. Resour. Study 2025, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Cheng, G.; Lu, L. Comparison of spatial interpolation methods. Adv. Earth Sci. 2000, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, P.; Sepahvand, K.; Guist, C.; Bär, J.; Peplow, A.; Marburg, S. Matching experimental and three dimensional numerical models for structural vibration problems with uncertainties. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 417, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Su, N.; Yang, S.; Yao, R.; Chu, S. Sedimentary characteristics of thick layer lacustrine beach-bars in the Cenozoic Banqiao Sag of the Bohai Bay Basin, East China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 151, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, T.; Liu, E.; Chen, S.; Jiang, P. Sedimentary Characteristics of Lacustrine Beach-Bars and Their Formation in the Paleogene Weixinan Sag of Beibuwan Basin, Northern South China Sea. Energies 2022, 15, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kra, K.L.; Qiu, L.; Yang, B.; Ahmed, K.S.; Donald, K.K.A.; Qiao, Y.; Habulashenmu, Y. Elaborated Porosity and High-Quality Reservoirs in Deeply Buried Coarse-Grained Sediment: Insight of the Sublacustrine Sandy Conglomerates in the Eocene Shehejie Formation (Es4), Dongying Subbasin, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xing, H. Vertical resolution of broadband, wide-azimuth and high-density seismic data. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 53, 520–527. [Google Scholar]
- Ling Yun Study Group. Application of amplitude tuning in surveying geologic target thickness less than1/4wavelength. Oil Geophys. Prospect 2003, 38, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Liu, S. Analysis on the spatial resolution in common offset gather of seismic data. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2013, 52, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Ajanaku, B.S.; Akintorinwa, O.J. Determination of gas reservoir (s) using AVO inversion within “XY” field offshore Niger Delta. Pet. Res. 2019, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, Y.; Kemerli, D.B.; Yılmaz, T.; Saral, M.; Göknar, E.C.; Korkmaz, E. Reconstruction of subsurface potential hydrocarbon reservoirs through 3D seismic automatic interpretation and attribute analysis. Phys. Chem. Earth 2024, 136, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel Gavidia, J.C.; Furlan Chinelatto, G.; Basso, M.; da Ponte Souza, J.P.; Soltanmohammadi, R.; Campane Vidal, A.; Goldstein, R.H.; Mohammadizadeh, S.M. Utilizing integrated artificial intelligence for characterizing mineralogy and facies in a pre-salt carbonate reservoir, Santos Basin, Brazil, using cores, wireline logs, and multi-mineral petrophysical evaluation. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 231, 212303. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xue, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qu, J. Lithological identification based on high-frequency vibration signal analysis. Measurement 2023, 221, 113534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yang, D.; Zhu, H. Optimal Transport Map with Prescribed Direction Indicator for Seismic Full-Waveform Inversion. J. Geophys. Res. 2024, 129, e2023JB027342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y. Stochastic inversion method based on compressed sensing frequency division waveform indication prior. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 12, 1505682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y. Analysis of seismic inversion imaging and its technical core issues. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2015, 54, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Bai, X.; Li, J.; Ding, Y. 3D visualization and attribute analysis applied in seismic data interpretationof Doshan Area. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 53, 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Bu, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y. Establishment of classification and evaluation criteria for tight reservoirs based on characteristics of microscopic pore throat structure and percolation: A case study of Chang 7 reservoir in Longdong area, Ordos Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2019, 41, 451–460. [Google Scholar]
- Matilda, T.D.; Alba, M.R.; Pablo, L.H. Functional PCA and cluster analysis for determining temperature patterns in Chile. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2025, 156, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, H.E.; Mustafa, E.; Essam, A.M.; Hatem, S.R.; György, C.; Attila, K.; Péter, S. Application of stable isotopes, mixing models, and K-means cluster analysis to detect recharge and salinity origins in Siwa Oasis. Egypt Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101124. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P. Applications of hierarchical cluster analysis (CLA) and principal component analysis (PCA) in feed structure and feed molecular chemistry research, using synchrotron-based Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) microspectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7115–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Qi, Y.; Gong, F. Recognition of Sand Bodies Based on Their Characteristics and Lithology. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2023, 59, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, L.; Ahmed, A.R.; Amir, I.; Emad, A.E. Evidence for active generation and seepage of sub-salt natural gas/condensate blend in the east offshore Nile Delta, Egypt: Integrated geochemical, petrophysical and seismic attribute approaches. Pet. Sci. 2025, 22, 130–150. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, L. Modern sedimentation in the wave-dominated delta beach bar sedimentary system of the Fenghe River in Jiaonan, Qingdao. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Szabó, P.N.; Abdelrhim, E.; Péter, S. An integrated workflow combining machine learning and wavelet transform for automated characterization of heterogeneous groundwater systems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, N.; Seyed, R.M.; Mohammad, R.R. Integrating physics of the problem into data-driven methods to enhance elastic full-waveform inversion with uncertainty quantification. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2025, 472, 134518. [Google Scholar]
- Northrup, C.J.; Royden, L.H.; Burchfiel, B.C. Motion of the Pacific plate relative to Eurasia and its potential relation to Cenozoic extension along the eastern margin of Eurasia. Geology 1995, 23, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, E. Sedimentary Environment Reconstruction and Organic Matter Enrichment Mechanisms in Various Lithofacies of the Lacustrine Shale: A Case Study of the Da’anzhai Member, Central Sichuan Basin, China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krampe, V.; Edme, P.; Maurer, H. Optimized experimental design for seismic full waveform inversion: A computationally efficient method including a flexible implementation of acquisition costs. Geophys. Prospect. 2020, 69, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Meng, C. Predicting gas content in coalbed methane reservoirs using seismic waveform indication inversion: A case study from the Upper Carboniferous Benxi Formation, eastern Ordos Basin, China. Acta Geophys. 2022, 70, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lei, C.; Yin, Y.; Xu, Z. Sedimentary architecture of thin-layer beach bar sand bodies in the G. oilfield, Niger. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1394612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Application of Seismic Motion Inversion in the Third Member of the Shahejie Formation in the Northeastern Kenli. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1176, 042078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, S. Artificial Intelligence in Geophysical Exploration. Science Press: Beijing, China, 2025; pp. 103–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, P.; Yan, W.; Wei, H.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Z. A deep-learning framework for borehole formation properties prediction using heterogeneous well-logging data: A case study of a carbonate reservoir in the Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, China. Geophysics 2024, 89, WA295–WA308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, H.; Miao, L.; Muhammad, A.; Syed, N.R.R.; Harith, F.K.; Nafees, A.; Salah, A.A. Advanced Permeability Prediction Through Two-Dimensional Geological Feature Image Extraction with CNN Regression from Well Logs Data. Math. Geosci. 2025, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, R. Sedimentary characteristics and formation mechanisms of lacustrine beach-bars in the fourth member of the Shahejie Formation in the Shubei area, western depression of the Liaohe Oilfield, China. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. Application of Seismic Waveform Indication Inversion in Fluvial Facies Sand Body Prediction. J. Res. Sci. Eng. 2022, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, B. Application of Seismic Attribute Clustering Method Based on PCA-SOM in Identification of Paleochannels. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2834, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, B.; Zhu, J. Prediction of the petroliferous area in WZ6–1 structure of Beibu Gulf Basin in the South China Sea based on PCA-SOM model. Earth Sci. Inform. 2025, 18, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, K.; Wang, C.; Zheng, R.; Wu, Y.; Mi, X. Seismic Sequence and Source Analysis of Typical Sandstone Reservoirs. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2024, 60, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarbary, Z.; Bassiouni, M.E.A.A.; Boukhary, M.; Spieß, V.; El-Barkooky, A.N.; Ewida, H.F. Integrating seismic attributes, post-stack seismic inversion, and static modeling for assessing the Pliocene-Pleistocene hydrocarbon potentialities, Offshore North Sinai Field, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 206, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Shi, P.; Dai, L.; LI, S.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution and geomorphologic restoration of the west section of Bonan low uplift, Bohai Bay basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-Organized Formation of Topologically Correct Feature Maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-Organizing Maps, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Song, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q. Architectural characteristics of beach-bar reservoirs in the lower submember of the 2nd member of the Paleogene Dongying Formation in block SC7, Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2024, 45, 486–501. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.K.; Heping, P.; Sinan, F.; Shazia, A.; Yao, Y.Z.; Chengxiang, D.; Nasir, K. Capability of self-organizing map neural network in geophysical log data classification: Case study from the CCSD-MH. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 118, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Pei, M. Seismic waveform based sequence framework and study on shale lithofacies characteristics: A case study of No. 5 test zone of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2024, 29, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, D. Sedimentary system analysis using seismic multi-attribute techniques in areas lacking well data: An example from the Shahajie Formation in the BZ3–1 Block of the western slope of the Bozhong Sag. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2012, 32, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Sedimentary facies analysis using seismic attributes via k-means clustering algorithm in low-exploration areas: A case study of Wenchang Formation in Baiyun Sag. Mar. Geol. Front. 2018, 34, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Song, J.; Yu, Q.; Kong, F. Generalized distribution reconstruction based on the inversion of characteristic function curve for structural reliability analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 229, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, C.; Fu, Z. Standardization method of logging curves based on petrophysical model of clastic rock. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2025, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Feng, L.; Du, Y. Application of the wave impedance inversion based on the characteristic curve reconstruction in the complex reservoir prediction. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2019, 19, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Meng, F.; Deng, J.; Zhao, P.; Liao, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q. Well logs reconstruction based on automatic machine learning technology. Nat. Gas. Ind. 2024, 44, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, C.; Peng, W.; Li, A.; Cao, D. Research and application of porosity inversion method based on elastic impedance statistical petrophysical model. Comput. Tech. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 47, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ohakwere, E.M.; Igboekwe, M.; Chukwu, G. Petrophysical evaluation and lithology delineation usingcross-plots analysis from some onshore wellsin the Nigerian-delta, west Africa. Int. J. Adv. Geosci. 2018, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rao, Y. Seismic Full Waveform Inversion Accelerated by Overlapping Data Input and Computation. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 3517–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, O.; Syed, I.; Adel, M.J.; Amer, A. Boosting Reservoir Prediction Accuracy: A Hybrid Methodology Combining Traditional Reservoir Simulation and Modern Machine Learning Approaches. Energies 2025, 18, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. The genesis of authigenic minerals and the porosity evolution of various lithologies and their implications for identifying high-quality reservoirs in the fourth member of Xujiahe Formation (Northeast-Sichuan Basin, China). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.M.A.; Ahmed A., M.; Sohaib R., A. RockDNet: Deep Learning Approach for Lithology Classification. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Romanowicz, B. Accelerating full-waveform inversion using source stacking: Synthetic experiments at the global scale in a realistic 3-D earth model. Geophys. J. Int. 2024, 236, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, R.; Yue, Y.; Liao, S.; Qian, F. Qian F.Robust prestack seismic facies analysis using shearlet transform-based deep learning. J. Geophys. Eng. 2022, 19, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessam, M.S.; Mohammad, A.R.; Majid, N.B.; Seyedmohsen, S. Integrating Bayesian classification and ANN for lithofacies classification using well and seismic data: Bahregansar case study. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Pang, X.; Song, Y. Whole petroleum system and ordered distribution pattern of conventional and unconventional oil and gas reservoirs. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Du, X.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Huo, M.; Mu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. Sedimentary Paleoenvironment and Organic Matter Enrichment Characteristics of Lacustrine Shahezi Shale in Songliao Basin: Insights from Continental Scientific Drilling. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 21097–21115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cao, J.; He, W.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Huang, L. The whole petroleum system with ordered coexistence of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons: Case from the Junggar Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2024, 108, 1261–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Shu, H.; Luo, Y.; Liu, T.; Hua, Z. The heterogeneity of lithofacies types, combination modes, and sedimentary model of lacustrine shale restricted by high-frequency sequence. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 3720–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikara, D.; Khanna, V. Application of a Deep Learning Network for Joint Prediction of Associated Fluid Production in Unconventional Hydrocarbon Development. Processes 2022, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, J. Application of basin modeling method coupling sedimentary filling evolution with petroleum system in simulating ultra-deep oil-gas accumulations:a case study of Sinian Dengying Formation in central Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1445–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Antonietta, M.E.; Walter, D.C.; Giovanni, M.; Flora, G. Efficient SOM’s Application to Seismic Fumarolic Tremor for the Detection of Anomalous Hydrothermal Activity in Campi Flegrei Volcano (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Hu, F.; Yang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Linearized waveform inversion for vertical transversely isotropic elastic media: Methodology and multi-parameter crosstalk analysis. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, A.; Sen, M.K.; Biswas, R. Facies-constrained transdimensional amplitude versus angle inversion using machine learning assisted priors. Geophys. Prospect 2023, 71, 1321–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. AVO Inversion Based on Transfer Learning and Low-Frequency Model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 3004605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tiwari, G. An efficient Bayesian multi-model framework to analyze reliability of rock structures with limited investigation data. Acta Geotech. 2023, 19, 3299–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qian, G.; Xu, C.; Gao, Y.; Kang, R. Sandstone Distribution and Reservoir Characteristics of Shahejie Formation in Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 3068–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y. Clustering algorithm based on improved SOM model. Comput. Sci. 2024, 1–15. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1075.TP.20241101.1447.032.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Janina, H.; Szabolcs, B.; János, G. Cluster defined sedimentary elements of deep-water clastic depositional systems and their 3D spatial visualization using parametrization: A case study from the Pannonian-basin. Geol. Croat. 2017, 70, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ronen, S.; Schultz, P.S.; Hattori, M. Seismic-guided estimation of log properties. Part 2: Using artificial neural networks for nonlinear attribute calibration. Lead. Edge 1994, 13, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, D.; Chen, B. Fine Characterization of Braided River Reservoir Architecture with Sparse Well Patterns Based on Intelligent Fusion of Multiple Seismic Attributes: A Case Study of the Guantao Formation from C-6 oilfield, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, X.; Ren, H.; Tao, L.; Jiang, J.; Wang, T.; Cheng, M.; Ding, S.; Du, R. Seismic Facies Analysis Using the Multiattribute SOM-K-Means Clustering. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 1, 1688233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Quieren, J.; Schuelke, J. Chapter 10 Self-Organizing Map (SOM) network for tracking horizons and classifying seismic traces. Handb. Geophys. Explor. Seism. Explor. 2001, 30, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, J. Application of SOM Neural Network in Lithology Recognition. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 3744, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, G. Multi-waveform classification for seismic facies analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 101, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzanejad, M.; Tran, K.T.; McVay, M.; Horhota, D.; Wasman, S.J. Deep void detection with 3D full waveform inversion of surface-based and in-depth source seismic wavefields. Eng. Geol. 2021, 294, 106407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavur, M.; Moraga, J.; Duzgun, H.S.; Soydan, H.; Jin, G. Displacement Analysis of Geothermal Field Based on PSInSAR And SOM Clustering Algorithms A Case Study of Brady Field, Nevada—USA. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Core Advantages | Limitations | Applicable Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional deterministic impedance inversion | High vertical resolution, fast computation | Low lateral resolution, multiple solutions | Preliminary exploration of well-controlled areas |
| Seismic Waveform Inversion | High resolution, multi-data integration | Complex computation, data sensitivity | Detailed prediction of complex reservoirs |
| SOM | Unsupervised clustering, low computational demand | Limited capability in handling nonlinear structures | Attribute classification and real-time processing |
| Kriging | Spatial modeling, uncertainty quantification | Complex computation, model dependency | Heterogeneous attribute interpolation |
| Single-attribute thresholding | Simple and fast | Singular information, poor adaptability | Rapid screening and simple environments |
| Participant Well | Sandstone Thickness/m | Verification Well | Sandstone Thickness/m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well Log Interpretation | Inversion Prediction | Well Log Interpretation | Inversion Prediction | ||
| B7-2-b | 1.3 | 0.5 | B8-2S-b | 1.8 | 2.3 |
| B7-2-d | 1.5 | 3.2 | C4-2-a | 8 | 7.6 |
| B7-2-a | 2.4 | 1.1 | C-5-b | 4.5 | 3.9 |
| C4-3-bD | 2.9 | 3.4 | B7-2-e | 4.6 | 2.6 |
| C4-4-e | 2.9 | 3.3 | C4-1-a | 5.3 | 5.6 |
| C4-3-a | 3.0 | 5 | B6-5-a | 5.6 | 7.1 |
| B7-2-c | 3.1 | 1.8 | B7-4-a | 7.3 | 6 |
| C4-5-a | 3.6 | 4.6 | B7-4-b | 7.7 | 8.5 |
| B8-3-b | 4.3 | 5.8 | B8-2-a | 8.8 | 10.0 |
| C3-1-a | 16.5 | 14.3 | C4-4-c | 10.1 | 9.1 |
| C4-4-a | 5.7 | 6.8 | C4-2-bA | 12.3 | 8 |
| B7-5-a | 8.8 | 6.3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Guan, D.; Huang, X.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Liu, R.; Feng, B. Integrated SOM Multi-Attribute Optimization and Seismic Waveform Inversion for Thin Sand Body Characterization: A Case Study of the Paleogene Lower E3d2 Sub-Member in the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095134
Wang J, Guan D, Huang X, He Y, Li H, Xu W, Liu R, Feng B. Integrated SOM Multi-Attribute Optimization and Seismic Waveform Inversion for Thin Sand Body Characterization: A Case Study of the Paleogene Lower E3d2 Sub-Member in the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):5134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Dayong Guan, Xiaobo Huang, Youbin He, Hua Li, Wei Xu, Rui Liu, and Bin Feng. 2025. "Integrated SOM Multi-Attribute Optimization and Seismic Waveform Inversion for Thin Sand Body Characterization: A Case Study of the Paleogene Lower E3d2 Sub-Member in the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 5134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095134
APA StyleWang, J., Guan, D., Huang, X., He, Y., Li, H., Xu, W., Liu, R., & Feng, B. (2025). Integrated SOM Multi-Attribute Optimization and Seismic Waveform Inversion for Thin Sand Body Characterization: A Case Study of the Paleogene Lower E3d2 Sub-Member in the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 5134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095134