Text-Guided Refinement for Referring Image Segmentation
Abstract
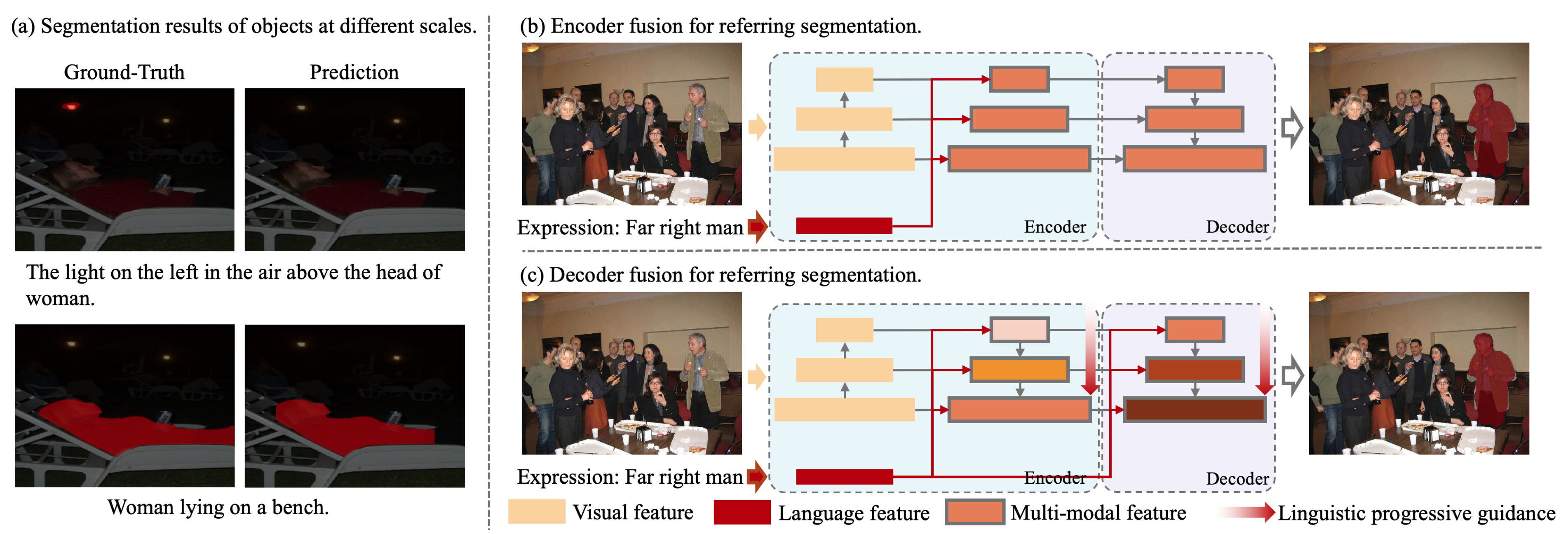
1. Introduction
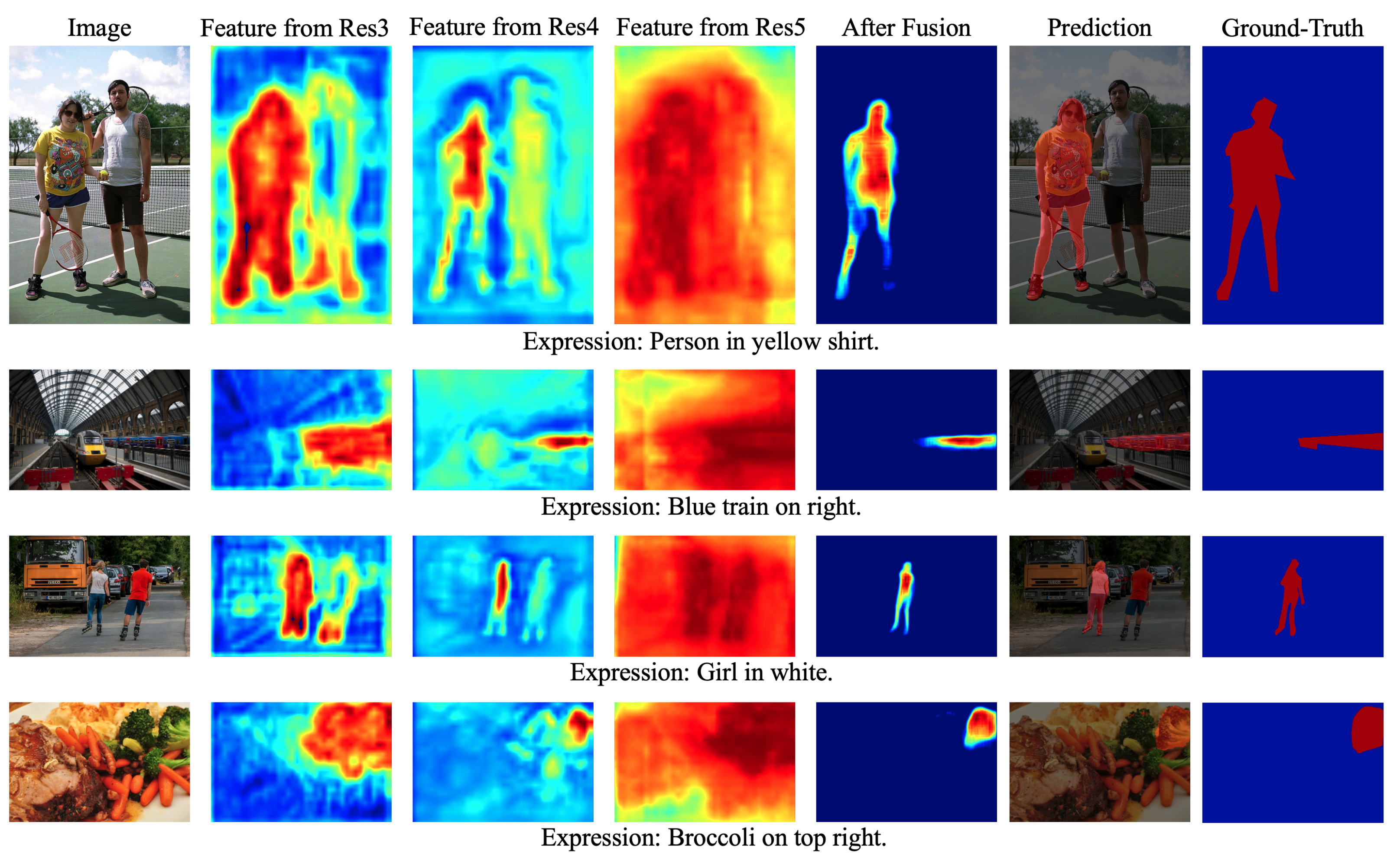
- We propose the Text-Guided Refinement Network, which utilizes a novel text-guided multi-scale feature decoding approach, integrating hierarchical image features through a dynamic gating mechanism. This approach reduces irrelevant information and ensures precise feature alignment, addressing key challenges in segmentation.
- We designed a cascaded pyramid structure, consisting of TGFusionNet and RefineNet, to enhance the network’s ability to perceive and represent objects of varying scales. This structure ensures robustness in segmenting targets of diverse sizes and progressively refines fine details, addressing the challenge of accurate edge prediction.
- Extensive experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our method, achieving significant improvements over baselines, including a +7.82% gain on the UNC dataset.
2. Related Work
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Referring Expression Grounding
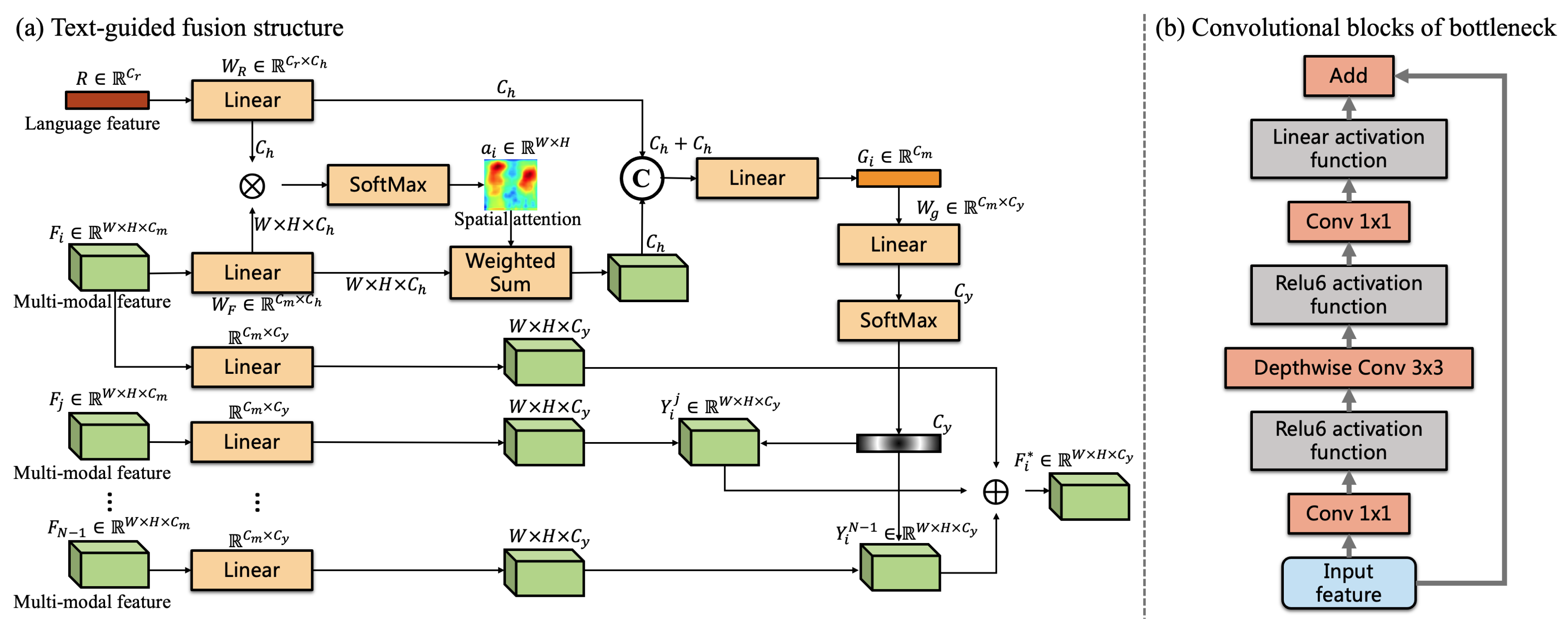
3. Method
3.1. Cascaded Pyramid Structure
3.2. Text-Guided Gating Mechanism
3.3. Language-Embedded Visual Encoder
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Arts
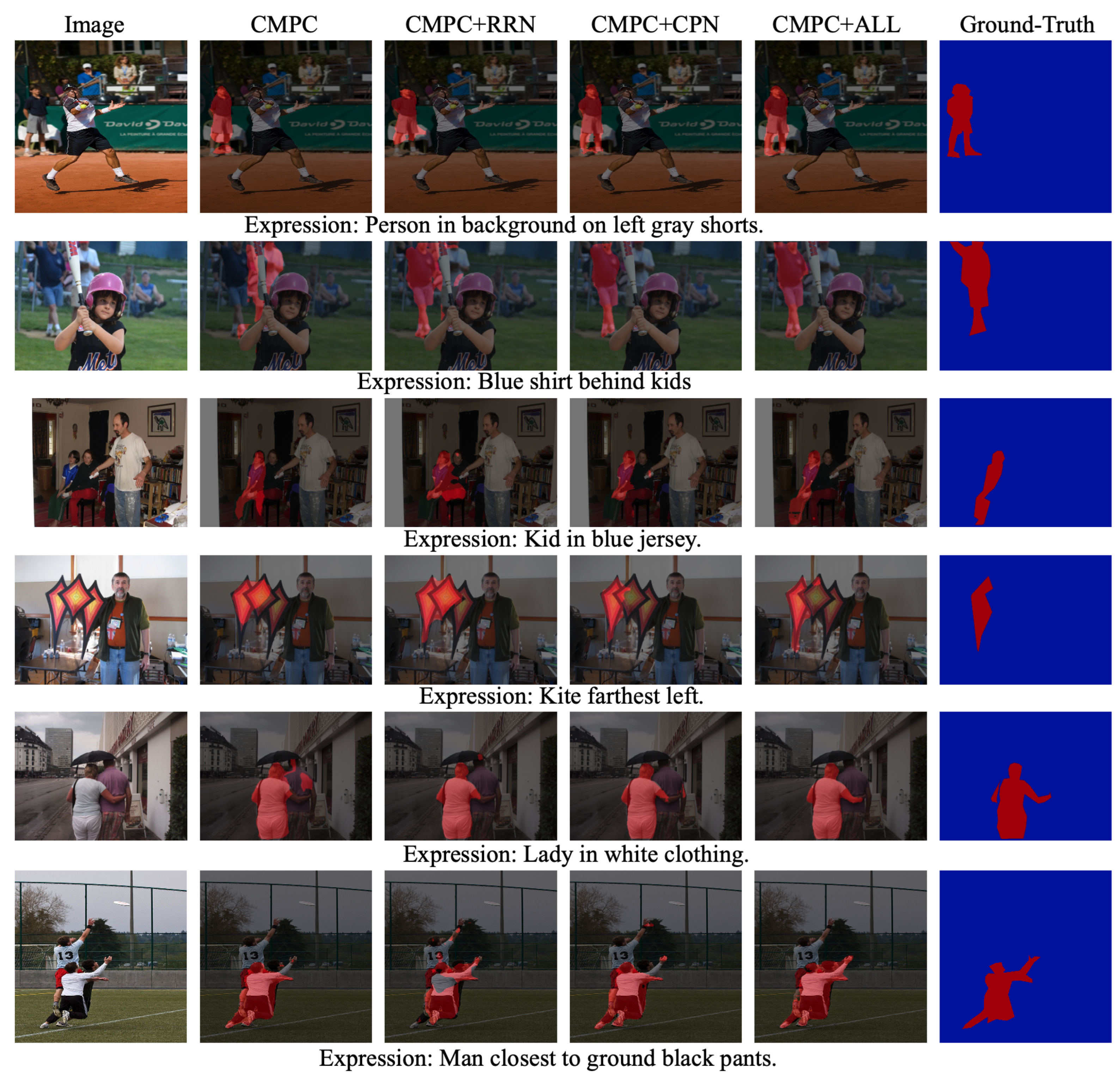
4.5. Ablation Study
- Baseline: Since this method primarily focuses on designing a multi-scale feature fusion decoder, the encoder from the widely used CMPC method [35] was chosen for multi-modal feature encoding. To evaluate the necessity of multi-scale information fusion, segmentation predictions were made using only the multi-modal feature.
- Baseline + RRN: This model incorporates the RRN method [2] following the encoder of the CMPC model. The multi-modal features from three different scales are sequentially fed into a convLSTM network for multi-scale feature fusion.
- Baseline + CPN: This model denotes the addition of a cascaded pyramid structure for multi-scale information fusion based on the baseline model. In this model, features of different scales are not fused by a gate function but are achieved by simple feature addition.
- Baseline + CPN + TG: This model extends the previous one by adding the text-guided gating mechanism (TG) for enhanced fusion within the cascaded pyramid structure.
- Baseline + ALL: This model incorporates language-embedded visual encoder for subsequent processing, building upon the previous model. Also, the model includes the ASPP module to enhance the network’s ability to capture fine-grained image details, thus forming the complete network structure proposed in this paper.
4.6. Generalizability Analysis
4.7. Computational Analysis
4.8. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, R.; Rohrbach, M.; Darrell, T. Segmentation from natural language expressions. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, K.; Kuo, Y.C.; Shu, M.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Jia, J. Referring Image Segmentation via Recurrent Refinement Networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Yuille, A. Recurrent Multimodal Interaction for Referring Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.07939. [Google Scholar]
- Margffoy-Tuay, E.; Pérez, J.C.; Botero, E.; Arbeláez, P. Dynamic Multimodal Instance Segmentation guided by natural language queries. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.02257. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Li, H.; Meng, F.; Wu, Q. Key-Word-Aware Network for Referring Expression Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.02611. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Shen, C.; Van Den Hengel, A.; Reid, I. Efficient piecewise training of deep structured models for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 3194–3203. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, B.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, G. Scene segmentation with dag-recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Feng, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Bi-directional relationship inferring network for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 4424–4433. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, T.; Liu, S.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Yu, S.; Zhang, F.; Han, J. Linguistic structure guided context modeling for referring image segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020; Proceedings, Part X; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Rochan, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Cross-modal self-attention network for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10502–10511. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Torr, P.H. Lavt: Language-aware vision transformer for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 18155–18165. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X. VLT: Vision-language transformer and query generation for referring segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 7900–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Tao, X.; Guo, Y.; Gong, M.; Liu, T. Cris: Clip-driven referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 11686–11695. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Kim, D.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Kwak, S. Restr: Convolution-free referring image segmentation using transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 18145–18154. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Xiao, H.; Shi, H.; Jie, Z.; Feng, J.; Huang, T.S. Revisiting Dilated Convolution: A Simple Approach for Weakly-and Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Jiang, X.; Shuai, B.; Liu, A.Q.; Wang, G. Context contrasted feature and gated multi-scale aggregation for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2393–2402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Hawaii, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D.; Jia, J. Psanet: Point-wise spatial attention network for scene parsing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, J. Co-occurrent features in semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 548–557. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzoli, G.; Shenaj, D.; Zanuttigh, P. Source-free domain adaptation for rgb-d semantic segmentation with vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Hawaii, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2024; pp. 615–624. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Wang, W.; Guo, R.; Wang, R.; Tang, S. Asymformer: Asymmetrical cross-modal representation learning for mobile platform real-time rgb-d semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 7608–7615. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Xu, H.; Rohrbach, M.; Feng, J.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Natural language object retrieval. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.H. Referring expression generation and comprehension via attributes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4856–4864. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, W.; Xu, D.; Li, P.; Cai, Y.; Huang, Q. Rethinking Two-Stage Referring Expression Comprehension: A Novel Grounding and Segmentation Method Modulated by Point. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 7487–7495. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Li, R.; Feng, F.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X. LGR-NET: Language Guided Reasoning Network for Referring Expression Comprehension. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 7771–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Qian, C.; Li, B. A real-time cross-modality correlation filtering method for referring expression comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10880–10889. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.J.; Jia, S.; Lo, Y.C.; Chen, H.T.; Liu, T.L. See-through-text grouping for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7454–7463. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Hui, T.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Wei, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, L.; Li, B. Referring image segmentation via cross-modal progressive comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10488–10497. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.W.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yang, M.H. Referring expression object segmentation with caption-aware consistency. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.04748. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wei, Y.; Wei, S. Referring image segmentation by generative adversarial learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, C.; Yan, J.; Tao, D. Asymmetric cross-guided attention network for actor and action video segmentation from natural language query. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3939–3948. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Poirson, P.; Yang, S.; Berg, A.C.; Berg, T.L. Modeling context in referring expressions. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 10–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Zurich, Switzerlan, 5–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Bansal, M.; Berg, T.L. Mattnet: Modular attention network for referring expression comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1307–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Hui, T.; Huang, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, B.; Li, G. Cross-Modal Progressive Comprehension for Referring Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 4761–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Encoder fusion network with co-attention embedding for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15506–15515. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, W. Referring Image Segmentation via Text Guided Multi-Level Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Dalian, China, 10–12 August 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, M.; Luo, B.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, F.; Kong, M. Text-Vision Relationship Alignment for Referring Image Segmentation. Neural Process. Lett. 2024, 56, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Kong, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Tan, T. Locate then segment: A strong pipeline for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9858–9867. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Cao, L.; Wu, C.; Deng, C.; Ji, R. Multi-task collaborative network for joint referring expression comprehension and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10034–10043. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Ding, H. Instance-specific feature propagation for referring segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 3657–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xue, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; Yu, C. DCMFNet: Deep Cross-Modal Fusion Network for Different Modalities with Iterative Gated Fusion. In Proceedings of the 50th Graphics Interface Conference, Halifax, NS, Canada, 3–6 June 2024; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X. Multi-modal mutual attention and iterative interaction for referring image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 3054–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Methods | Vis.Encoder | Lang.Encoder | UNC | UNC+ | G-Ref | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | testA | testB | val | testA | testB | val | |||
| RMI [3] | DL-101 | LSTM | 45.18 | 45.69 | 45.57 | 29.86 | 30.48 | 29.50 | 34.52 |
| ASGN [37] | DL-101 | LSTM | 50.46 | 51.20 | 49.27 | 38.41 | 39.79 | 35.97 | 41.36 |
| RRN [2] | DL-101 | LSTM | 55.33 | 57.26 | 53.95 | 39.75 | 42.15 | 36.11 | 36.45 |
| MAttNet [45] | M-RCN | LSTM | 56.51 | 62.37 | 51.70 | 46.67 | 52.39 | 40.08 | - |
| CMSA [12] | DL-101 | LSTM | 58.32 | 60.61 | 55.09 | 43.76 | 47.60 | 37.89 | 39.98 |
| CAC [36] | R-101 | LSTM | 58.90 | 61.77 | 53.81 | - | - | - | 44.32 |
| STEP [34] | DL-101 | LSTM | 60.04 | 63.46 | 57.97 | 48.19 | 52.33 | 40.41 | 46.40 |
| BCAM [10] | DL-101 | LSTM | 61.35 | 63.37 | 59.57 | 48.57 | 52.87 | 42.13 | 48.04 |
| CMPC [35] | DL-101 | LSTM | 61.36 | 64.53 | 59.64 | 49.56 | 53.44 | 43.23 | 49.05 |
| LSCM [11] | DL-101 | LSTM | 61.47 | 64.99 | 59.55 | 49.34 | 53.12 | 43.50 | - |
| CMPC+ [46] | DL-101 | LSTM | 62.47 | 65.08 | 60.82 | 50.25 | 54.04 | 43.47 | 49.89 |
| EFN [47] | R-101 | GRU | 62.76 | 65.69 | 59.67 | 51.50 | 55.24 | 43.01 | 51.93 |
| TGMI [48] | DL-101 | LSTM | 62.47 | 65.17 | 60.30 | 49.36 | 53.37 | 43.62 | 50.07 |
| RBVL [49] | DL-101 | LSTM | 62.89 | 65.01 | 61.52 | 51.99 | 54.27 | 45.34 | 50.14 |
| TGRN | DL-101 | LSTM | 63.82 | 66.76 | 61.93 | 51.65 | 56.18 | 44.21 | 51.63 |
| Methods | Vis.Encoder | Lang.Encoder | UNC | UNC+ | G-Ref | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | testA | testB | val | testA | testB | val | |||
| MCN [52] | DN-53 | GRU | 62.44 | 64.20 | 59.71 | 50.62 | 54.99 | 44.69 | 49.22 |
| ISFP [53] | DN-53 | GRU | 65.19 | 68.45 | 62.73 | 52.70 | 56.77 | 46.39 | 52.67 |
| LTS [50] | DN-53 | GRU | 65.43 | 67.76 | 63.08 | 54.21 | 58.32 | 48.02 | 54.40 |
| VLT [14] | DN-53 | GRU | 65.65 | 68.29 | 62.73 | 55.50 | 59.20 | 49.36 | 52.99 |
| DCMFNet [54] | DN-53 | LSTM | 65.84 | 69.34 | 63.09 | 54.78 | 60.03 | 49.30 | 51.99 |
| M3Dec [55] | DN-53 | GRU | 67.88 | 70.82 | 65.02 | 56.98 | 61.26 | 50.11 | 54.79 |
| TGRNcoco | DL-101 | LSTM | 68.59 | 70.39 | 66.10 | 57.28 | 61.44 | 50.66 | 55.83 |
| Methods | Pr@0.5 | Pr@0.6 | Pr@0.7 | Pr@0.8 | Pr@0.9 | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 62.87 | 54.91 | 44.16 | 28.43 | 7.24 | 56.00 |
| Baseline + RRN | 70.78 | 63.25 | 52.54 | 35.55 | 9.42 | 60.42 |
| Baseline + CPN | 72.05 | 65.45 | 55.38 | 39.30 | 12.32 | 61.23 |
| Baseline + CPN + TG | 74.45 | 60.34 | 57.42 | 35.35 | 11.34 | 62.45 |
| Baseline + ALL | 76.13 | 69.62 | 60.15 | 44.96 | 15.83 | 63.82 |
| Baseline | 70.60 | 61.59 | 48.98 | 28.09 | 4.67 | 59.77 |
| Baseline + RRN | 75.38 | 68.29 | 57.20 | 38.02 | 8.84 | 62.84 |
| Baseline + CPN | 76.83 | 70.59 | 60.65 | 41.86 | 11.84 | 64.22 |
| Baseline + CPN + TG | 77.44 | 71.46 | 61.45 | 43.65 | 13.65 | 65.34 |
| Baseline + ALL | 80.35 | 74.97 | 65.12 | 47.78 | 14.72 | 66.76 |
| Baseline | 60.65 | 51.03 | 37.98 | 22.32 | 4.71 | 54.12 |
| Baseline + RRN | 67.91 | 59.41 | 48.87 | 33.27 | 11.03 | 58.70 |
| Baseline + CPN | 67.11 | 60.08 | 51.56 | 38.00 | 15.31 | 59.23 |
| Baseline + CPN + TG | 71.19 | 62.96 | 53.23 | 41.61 | 16.18 | 60.96 |
| Baseline + ALL | 72.13 | 64.72 | 56.26 | 42.71 | 17.56 | 61.93 |
| UNC | Methods | Pr@0.5 | Pr@0.6 | Pr@0.7 | Pr@0.8 | Pr@0.9 | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | CMSA | 66.44 | 59.70 | 50.77 | 35.52 | 10.96 | 58.32 |
| CMSA + ALL | 72.26 | 66.11 | 57.38 | 42.51 | 14.79 | 61.69 | |
| testA | CMSA | 70.28 | 63.64 | 54.07 | 38.38 | 11.21 | 60.61 |
| CMSA + ALL | 77.18 | 71.42 | 62.03 | 45.36 | 13.42 | 65.13 | |
| testB | CMSA | 61.51 | 53.60 | 45.40 | 32.40 | 12.90 | 55.09 |
| CMSA + ALL | 68.42 | 61.12 | 51.14 | 37.31 | 14.90 | 59.16 |
| Methods | IoU | Training Time (h) | Testing Time (ms) | Memory Costs (kb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMPC | 64.53 | 18.46 | 85 | 1,057,705 |
| TGRN | 66.76 | 20.30 | 103 | 1,080,341 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, S.; Zhang, S.; Ruan, T. Text-Guided Refinement for Referring Image Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095047
Qiu S, Zhang S, Ruan T. Text-Guided Refinement for Referring Image Segmentation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095047
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Shuang, Shiyin Zhang, and Tao Ruan. 2025. "Text-Guided Refinement for Referring Image Segmentation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095047
APA StyleQiu, S., Zhang, S., & Ruan, T. (2025). Text-Guided Refinement for Referring Image Segmentation. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095047






