Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing for Power Systems: State of the Art, Architecture, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Systematic Literature Review: A systematic review is conducted to analyze the role of EC in energy distribution systems, addressing its potential advantages and limitations in comparison to other computing paradigms.
- Technical Comparison of Computing Architectures: EC is critically compared with CC and FC in terms of essential criteria such as latency, computational efficiency, data transmission, and security, emphasizing their contextual applicability in power systems.
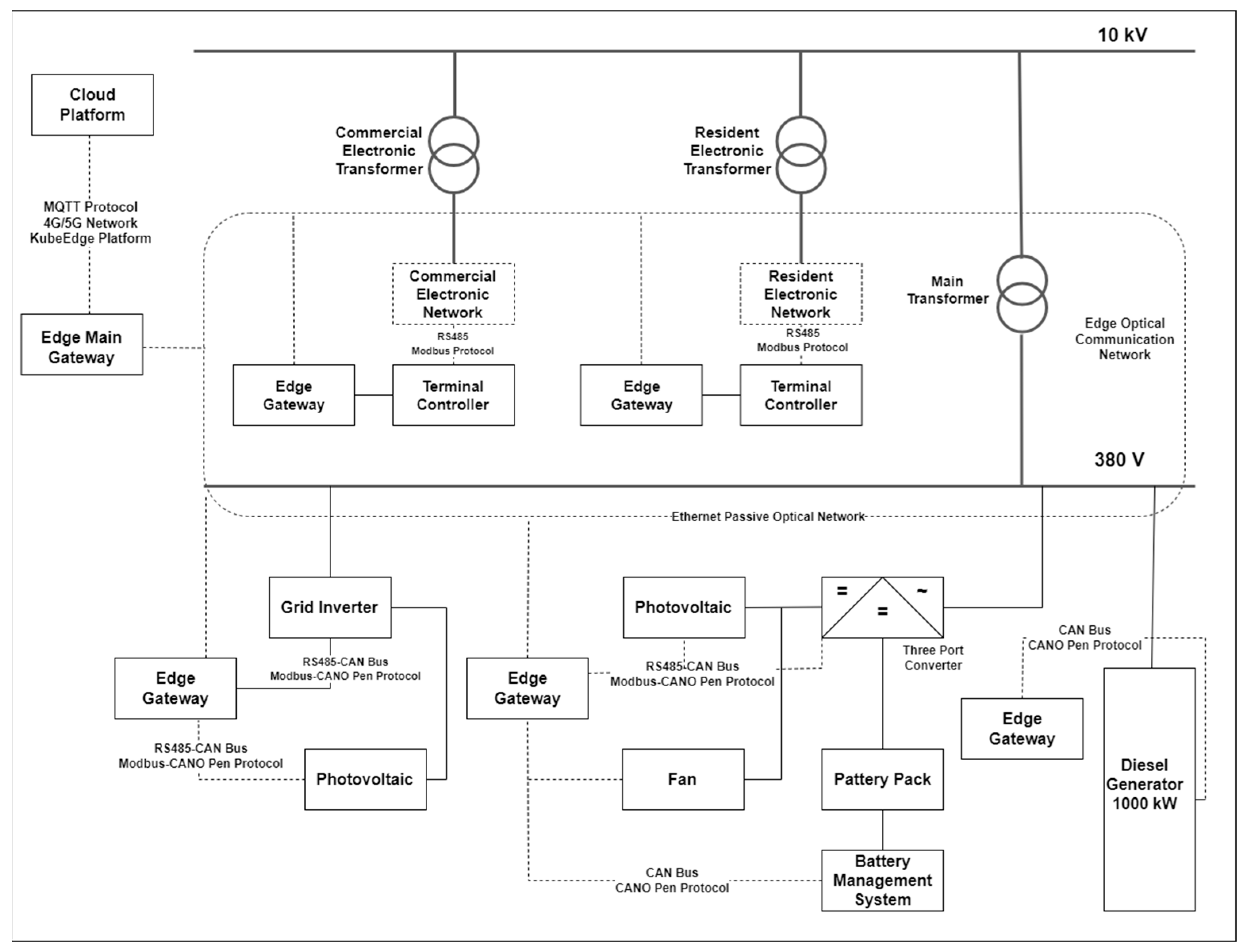
- Real-Time Data Processing and Optimization Techniques: The integration of EC with communication protocols such as Minimum Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) and Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP), container technologies like Docker and Kubernetes, and AI-driven predictive maintenance models is explored. The study also analyzes the role of EC in sensor data processing to enhance fault prediction accuracy and optimize demand-side management in energy systems.
- Technological Components and Infrastructure: The role of hardware and software architectures in EC-enabled energy systems is analyzed. The study explores computational frameworks, edge devices, virtualization technologies, and distributed resource allocation strategies that contribute to the efficient deployment of EC.
- Applications in Power Systems: The advantages of EC in various power system applications, including data transmission, real-time monitoring and control, microgrid systems, smart metering, anomaly detection, state estimation, energy management, and fault detection, are assessed in terms of their contributions to grid stability, operational efficiency, and system reliability. The study evaluates how EC-based solutions improve energy consumption modeling, enable decentralized energy management, optimize grid stability, and enhance system reliability.
- Security and Privacy Solutions: By identifying major vulnerabilities in EC-powered energy systems, the paper proposes mitigation strategies including decentralized authentication, hybrid encryption, and secure transmission protocols to strengthen system resilience.
- Future Research Directions: Key areas requiring further investigation are highlighted, including scalable EC architectures, energy-efficient edge processors, advanced data management techniques, and the integration of distributed AI applications to enhance the resilience and efficiency of energy systems.
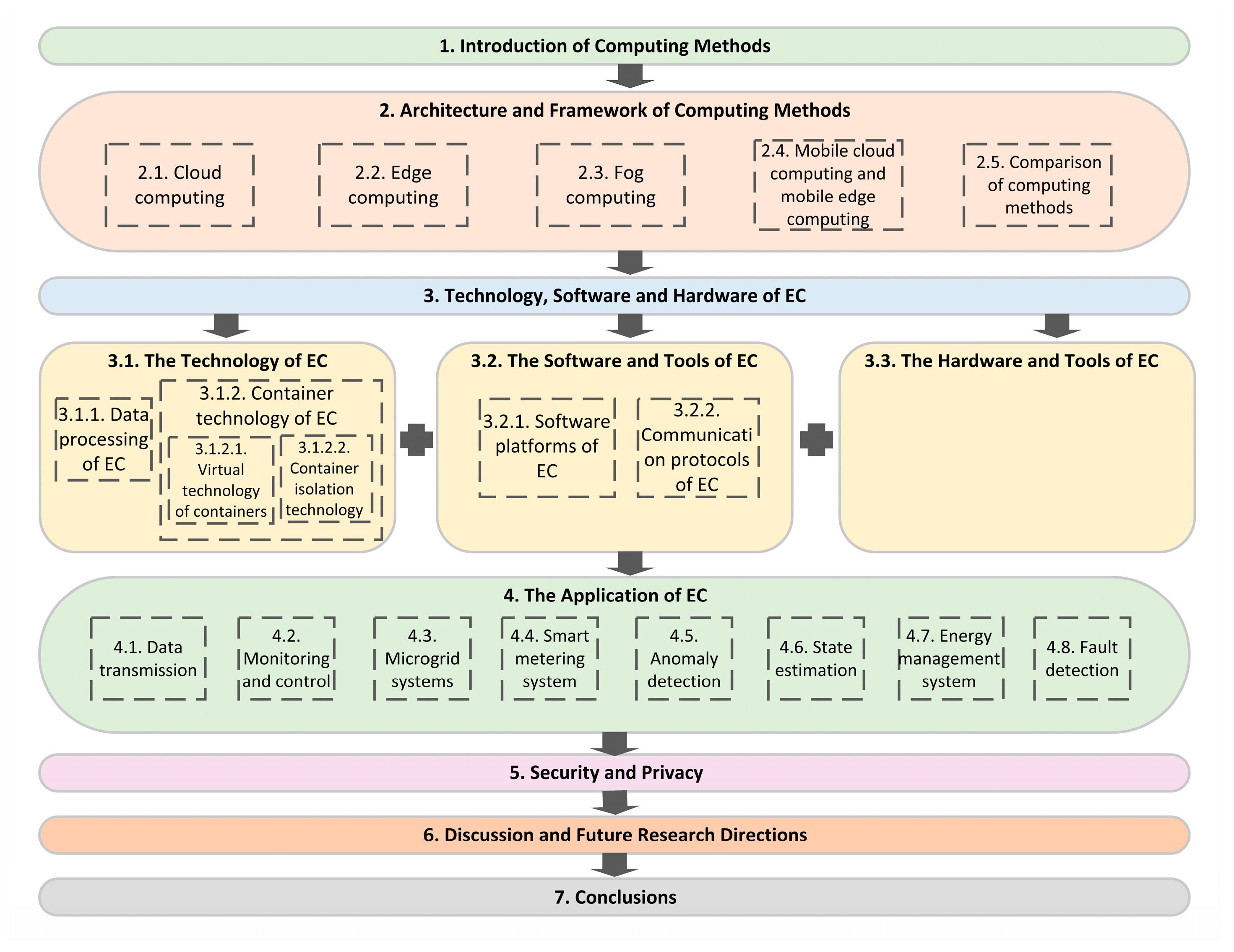
2. Architecture and Framework of Computing Methods
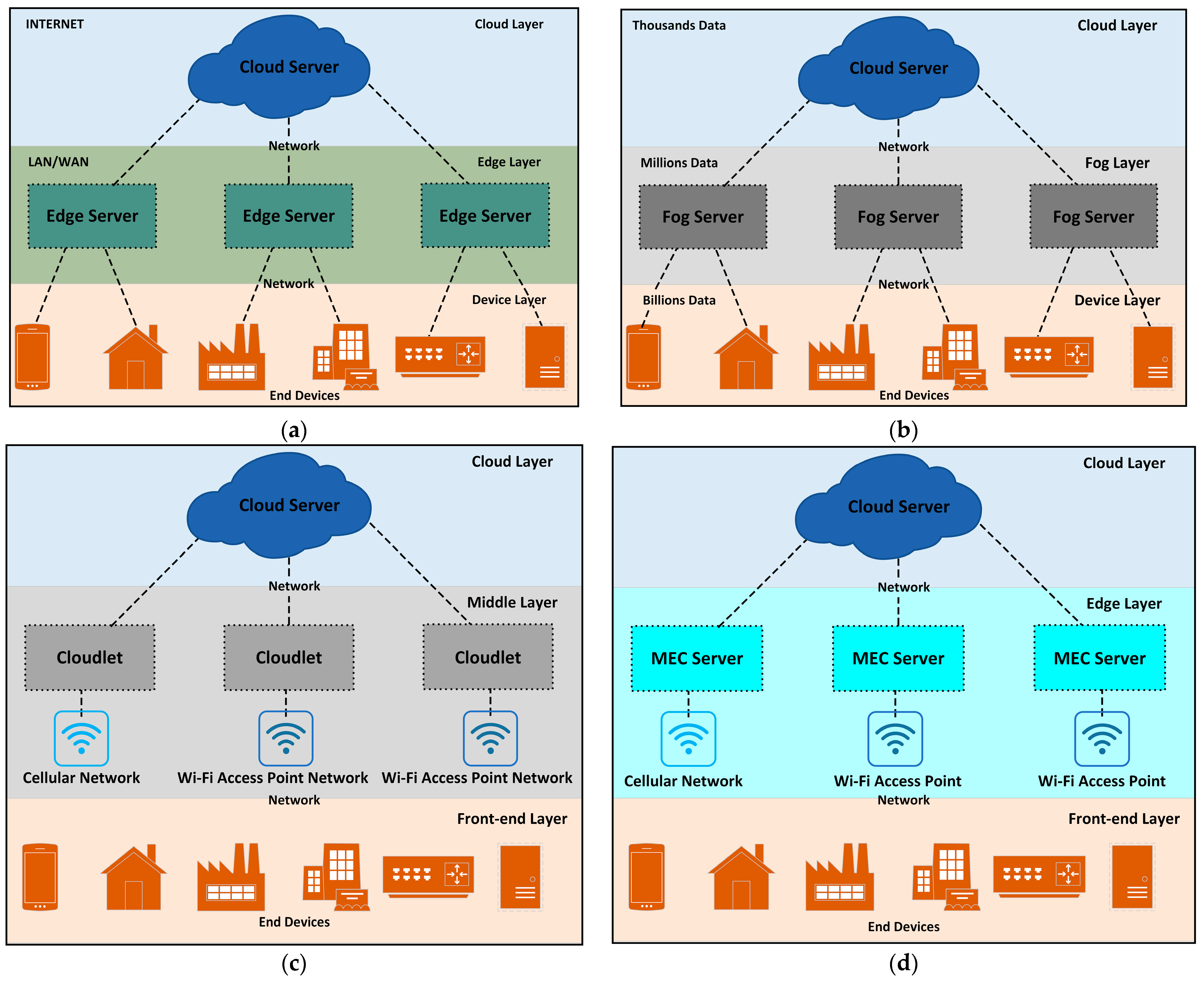
2.1. Cloud Computing
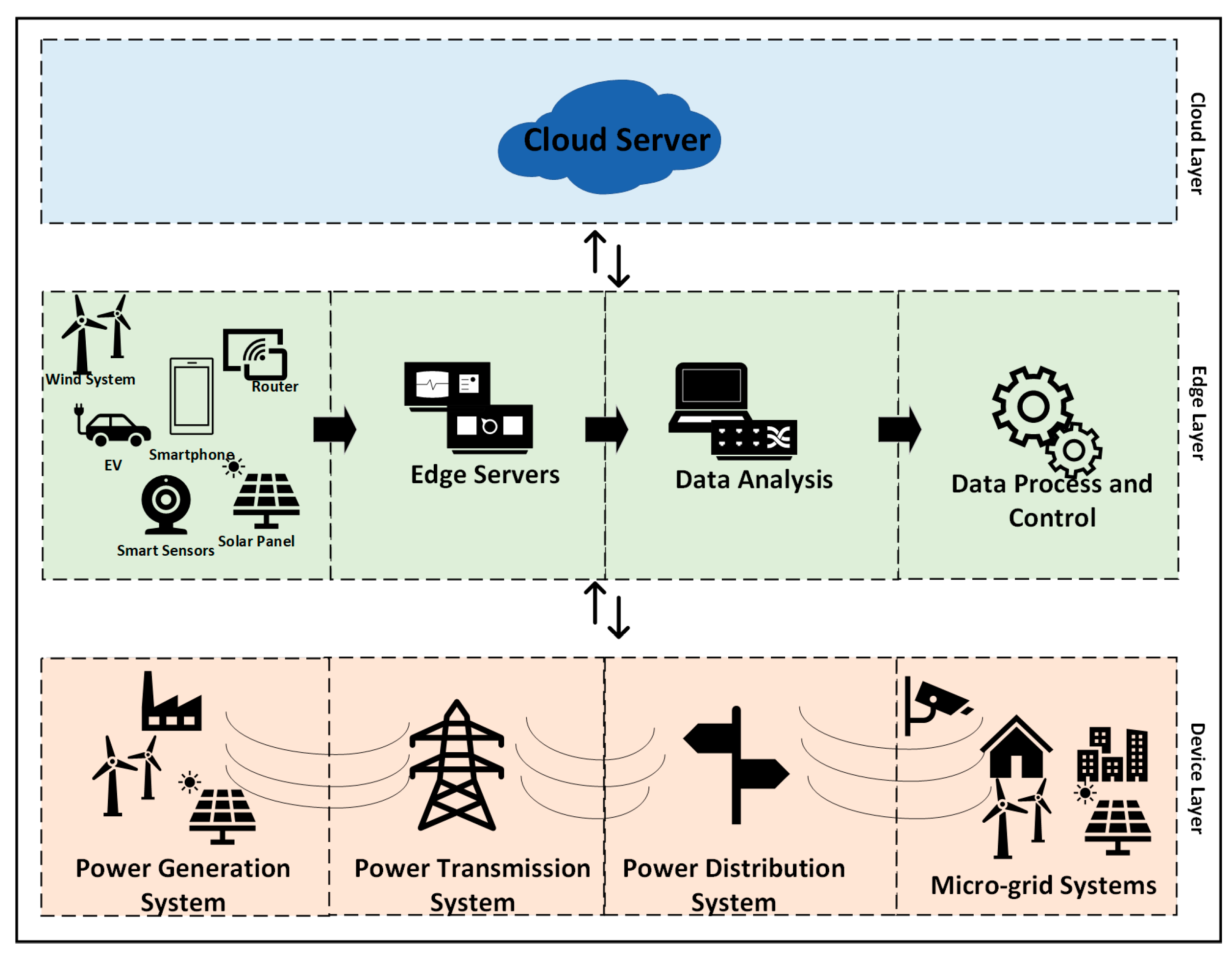
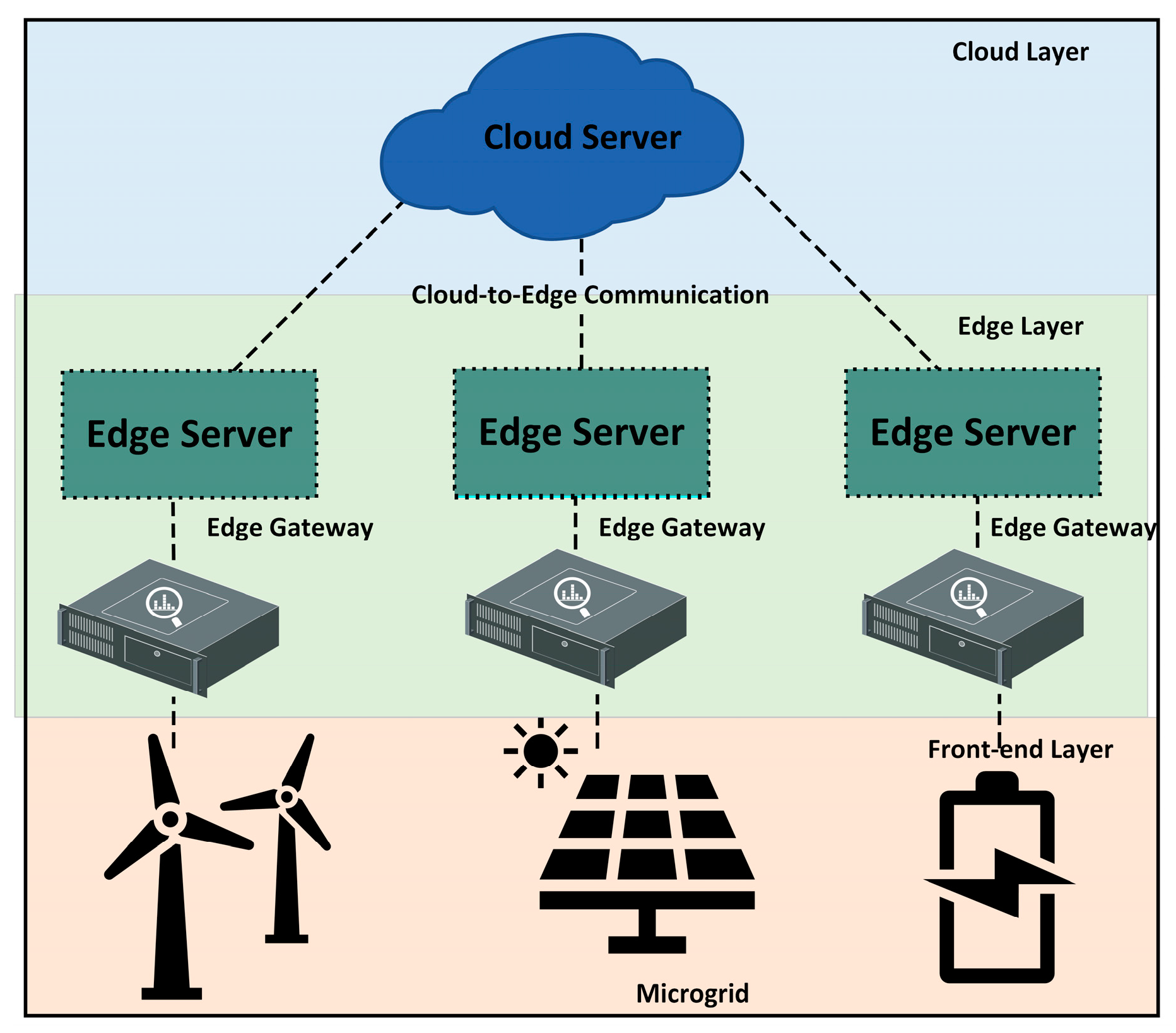
2.2. Edge Computing
2.3. Fog Computing
2.4. Mobile Cloud Computing and Mobile Edge Computing
2.5. Comparison of Computing Methods
3. Technology, Hardware and Software of Edge Computing
3.1. The Technology of Edge Computing
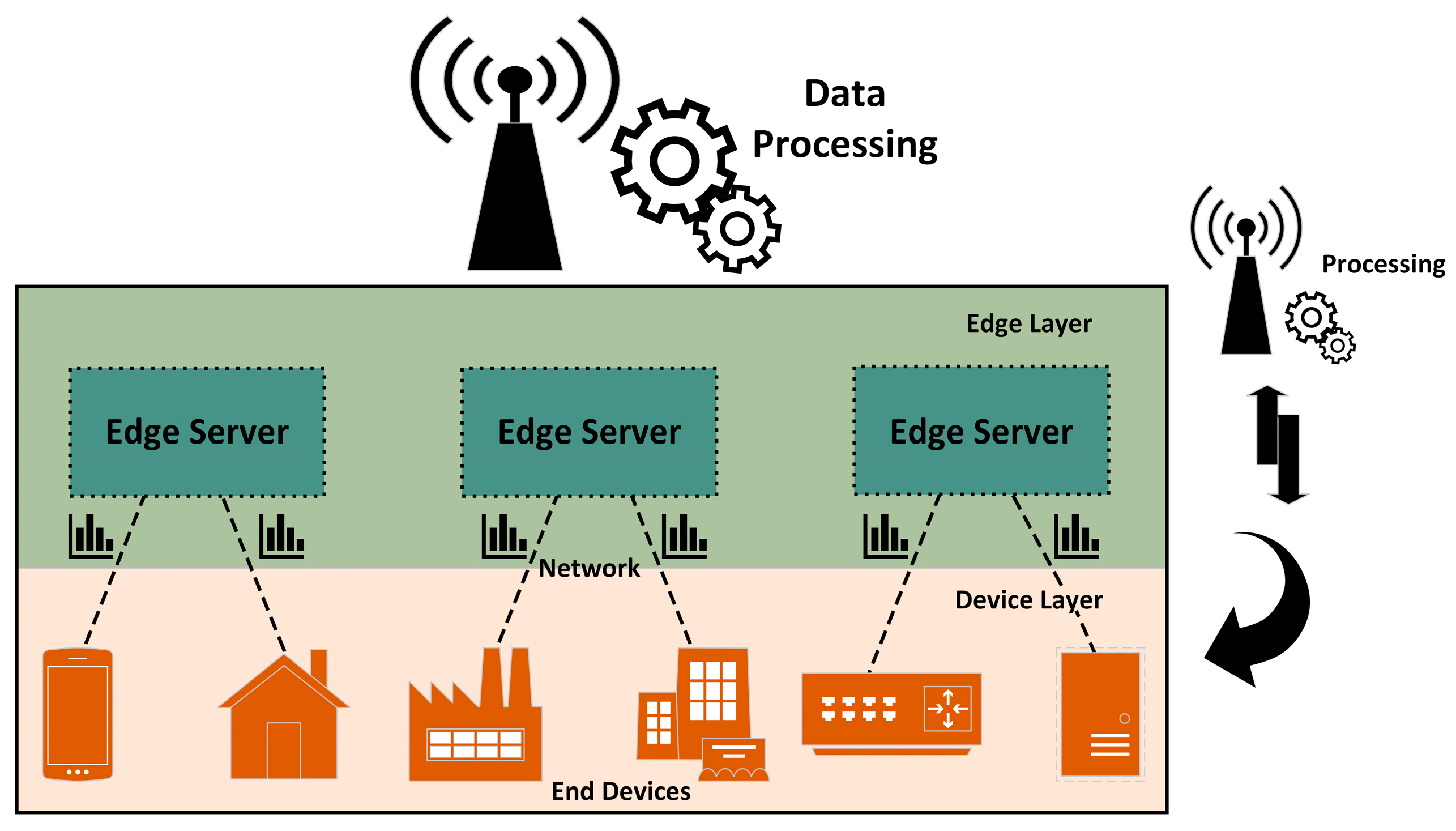
3.1.1. Data Processing of Edge Computing
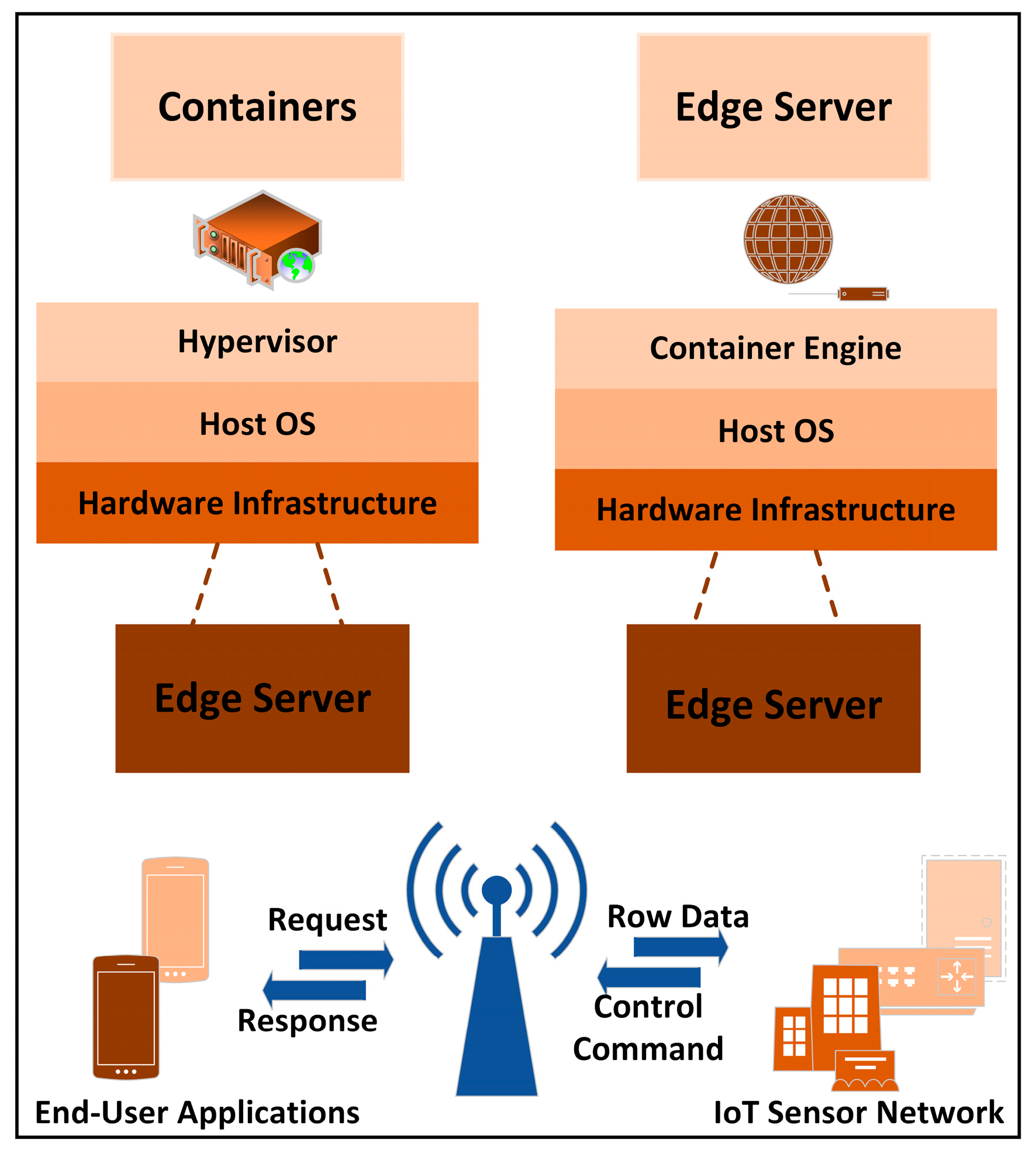
3.1.2. Container Technology
Virtual Technology of Containers
Container Isolation Technology
3.2. The Software and Tools of Edge Computing
3.2.1. Software Platforms
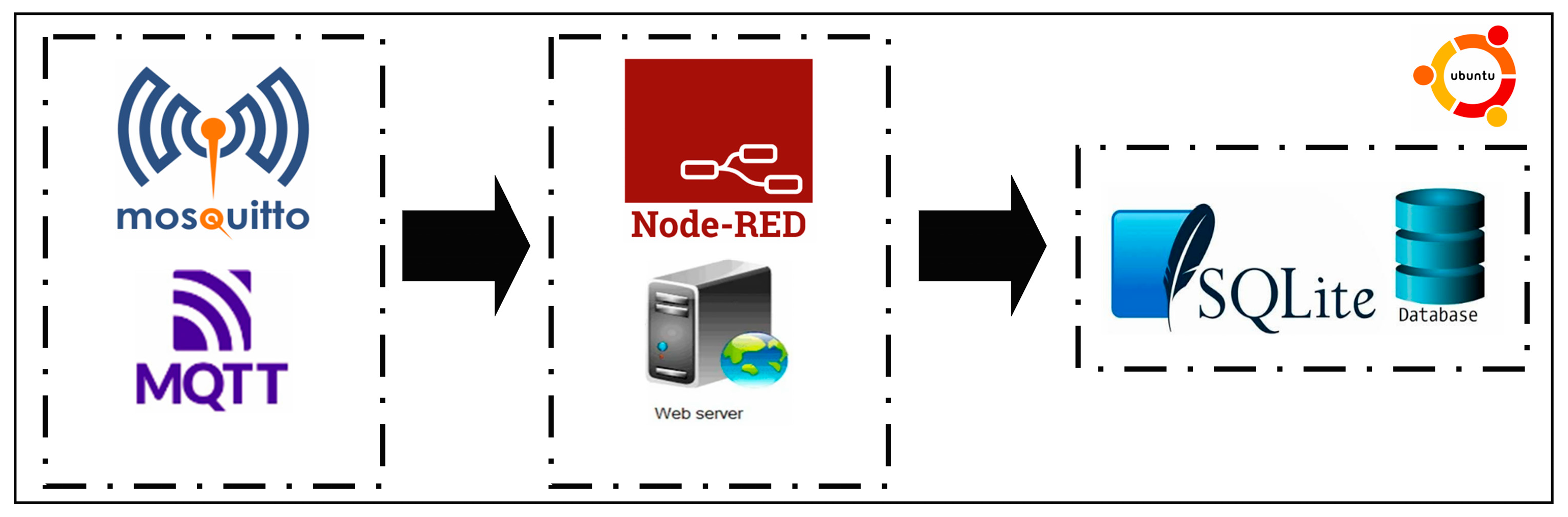
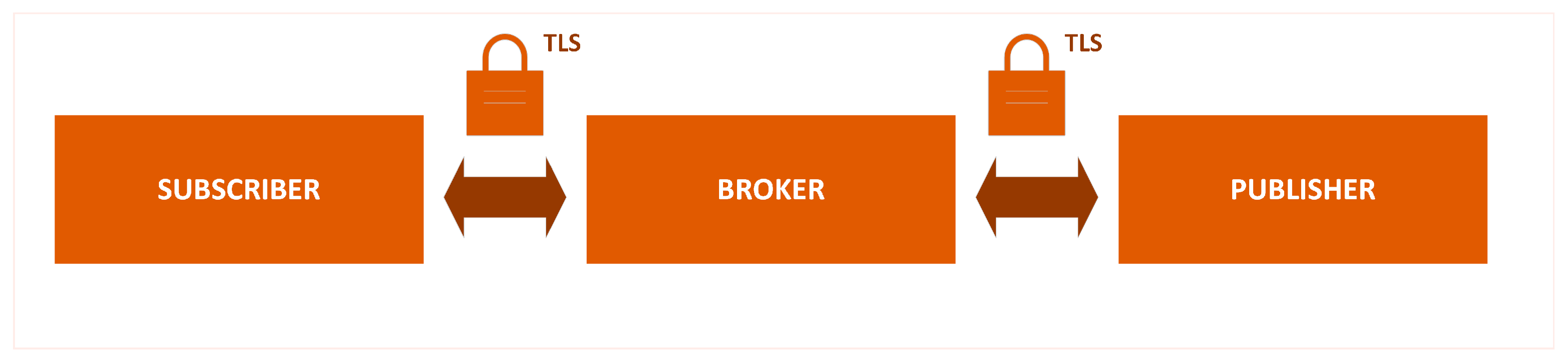
3.2.2. Communication Protocols
3.3. The Hardware and Tools of Edge Computing
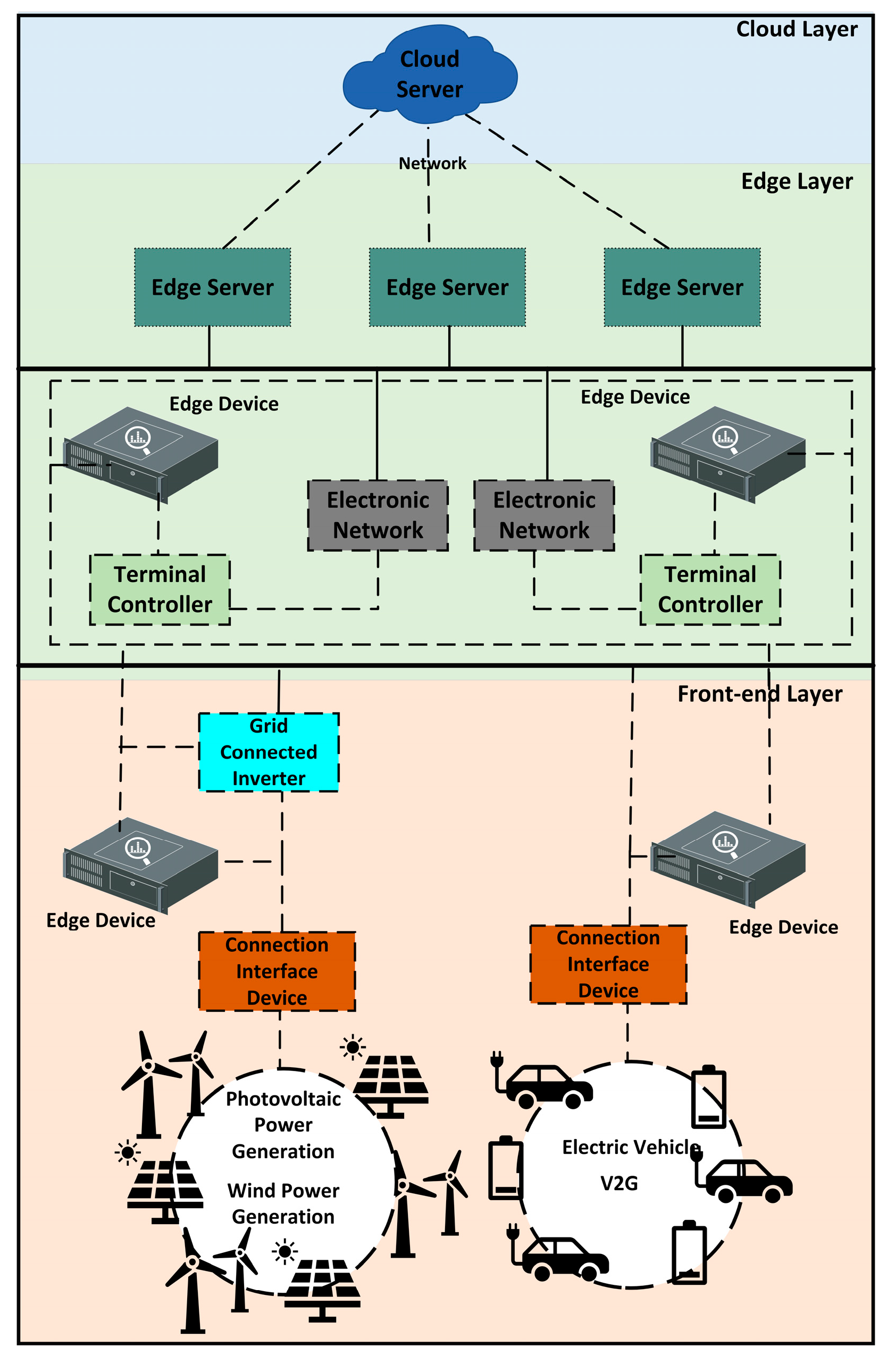
4. The Application of Edge Computing System
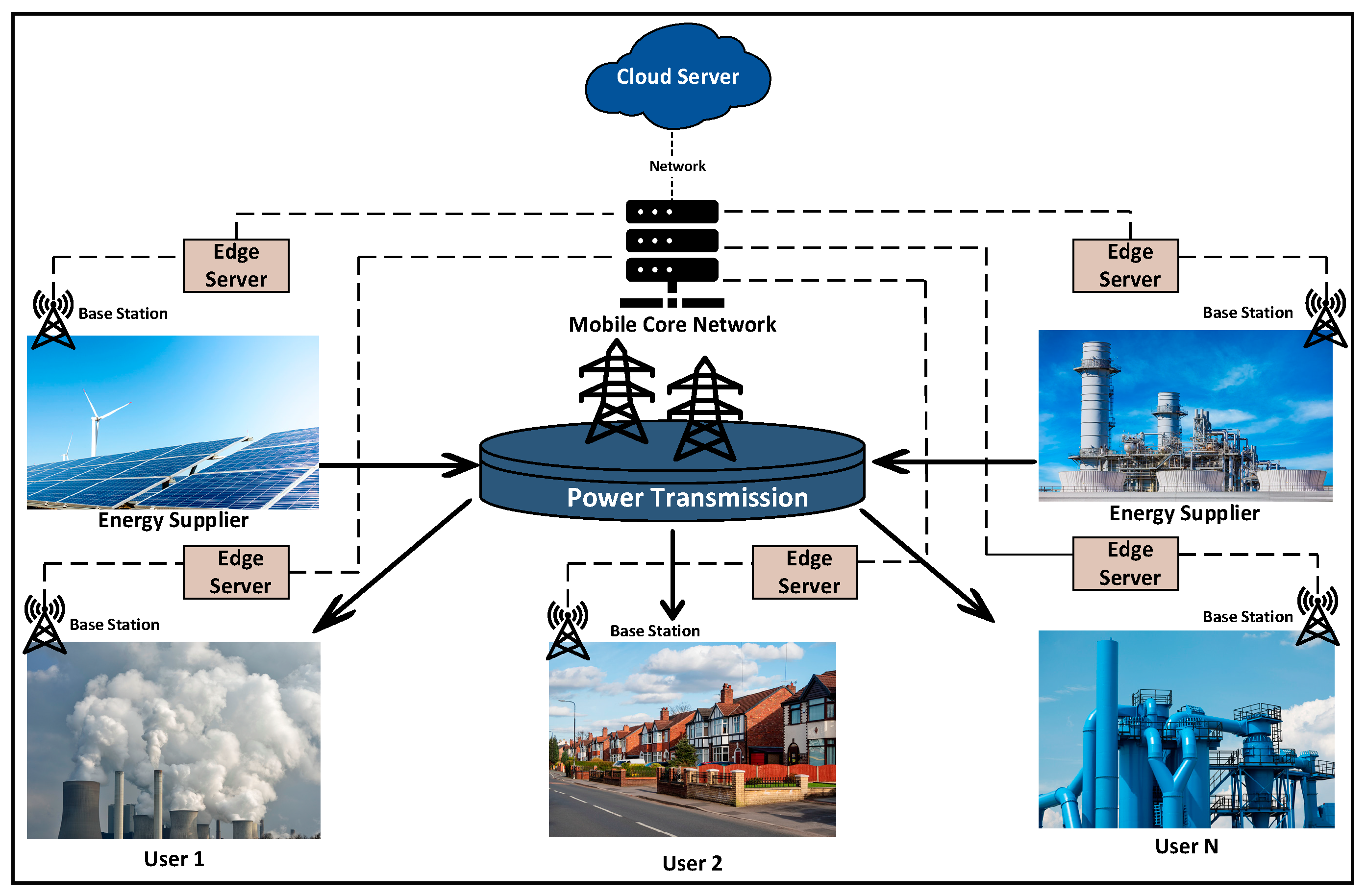
4.1. Data Transmission
4.2. Monitoring and Control
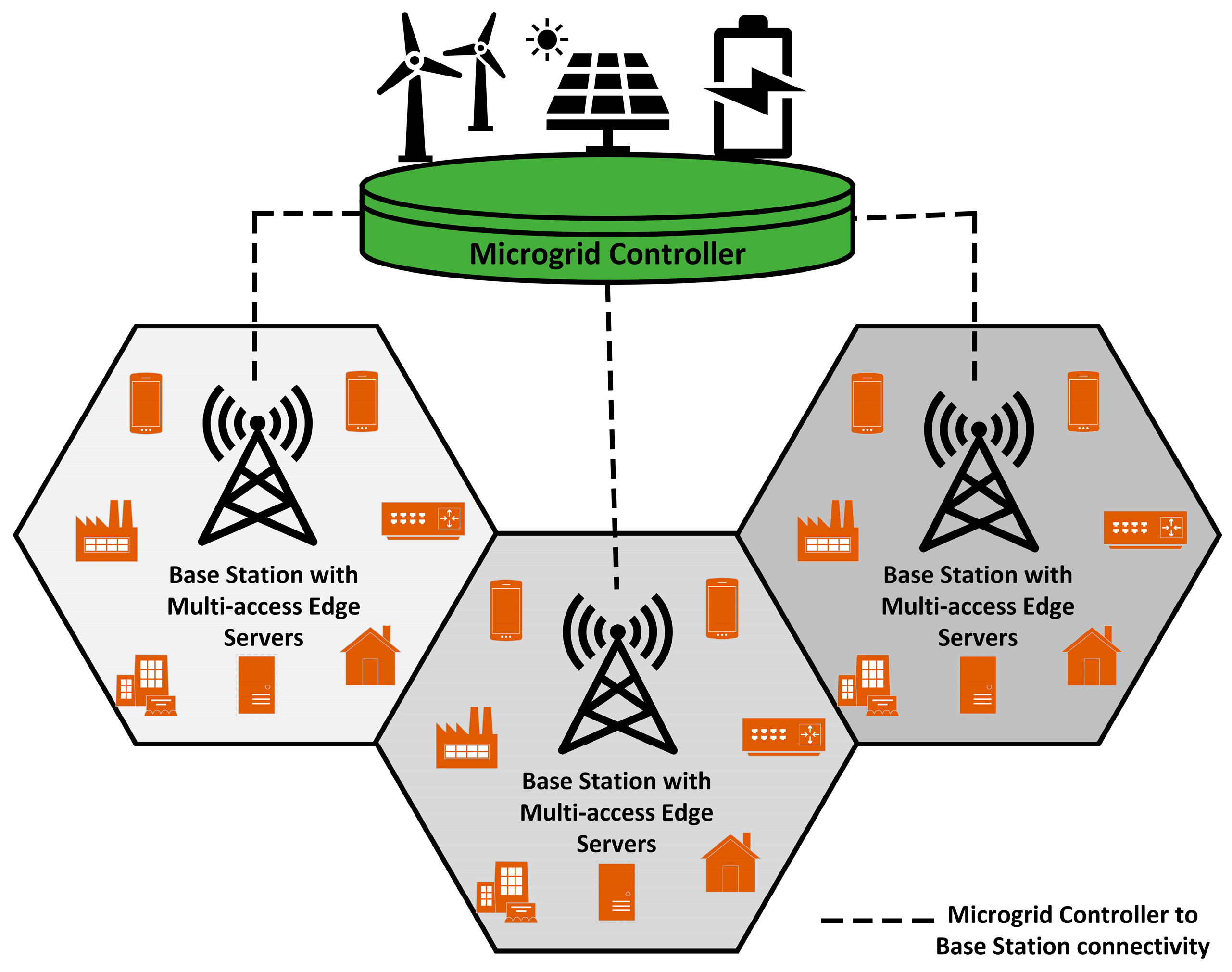
4.3. Microgrid System
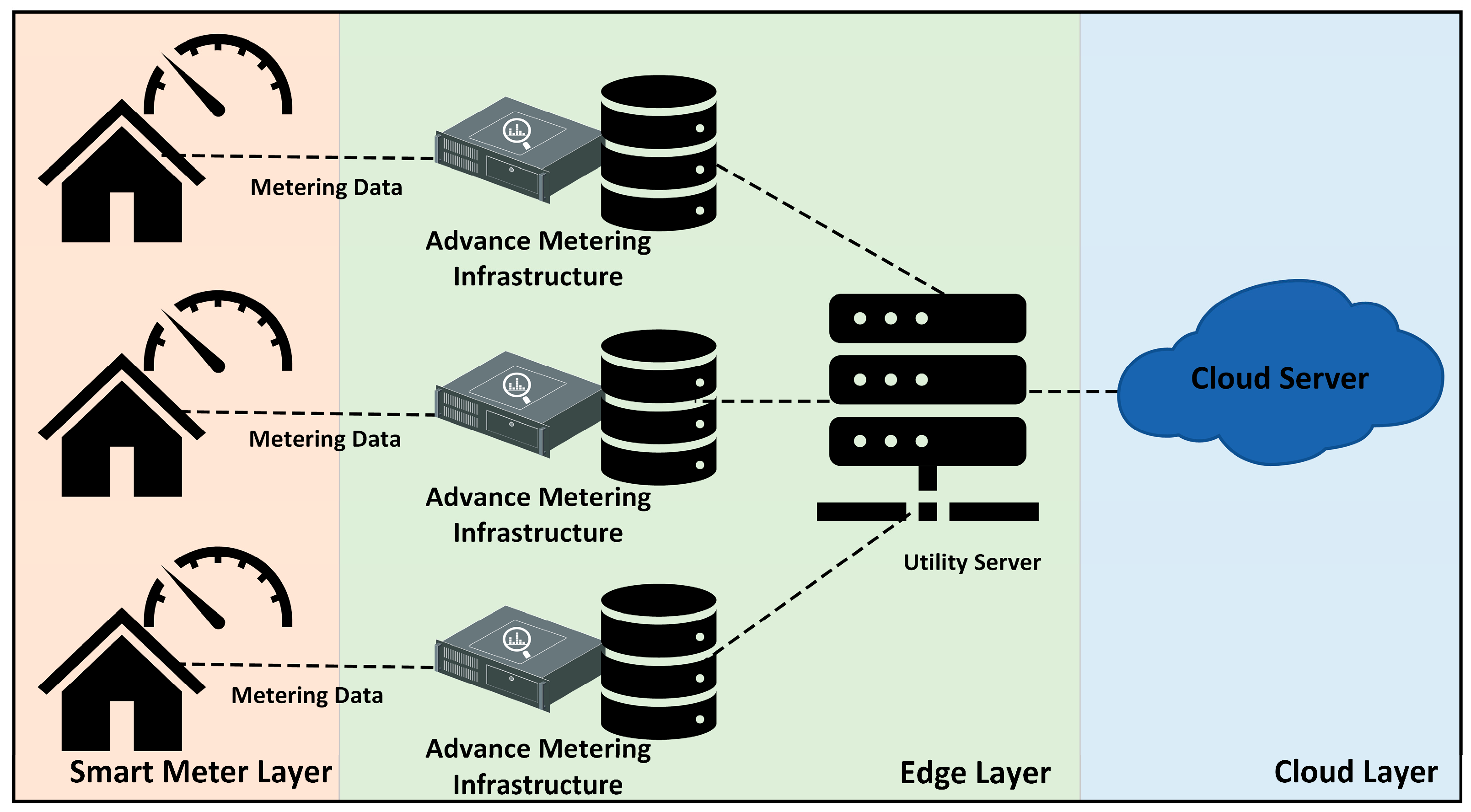
4.4. Smart Metering System
4.5. Anomaly Detection
4.6. State Estimation
4.7. Energy Management System
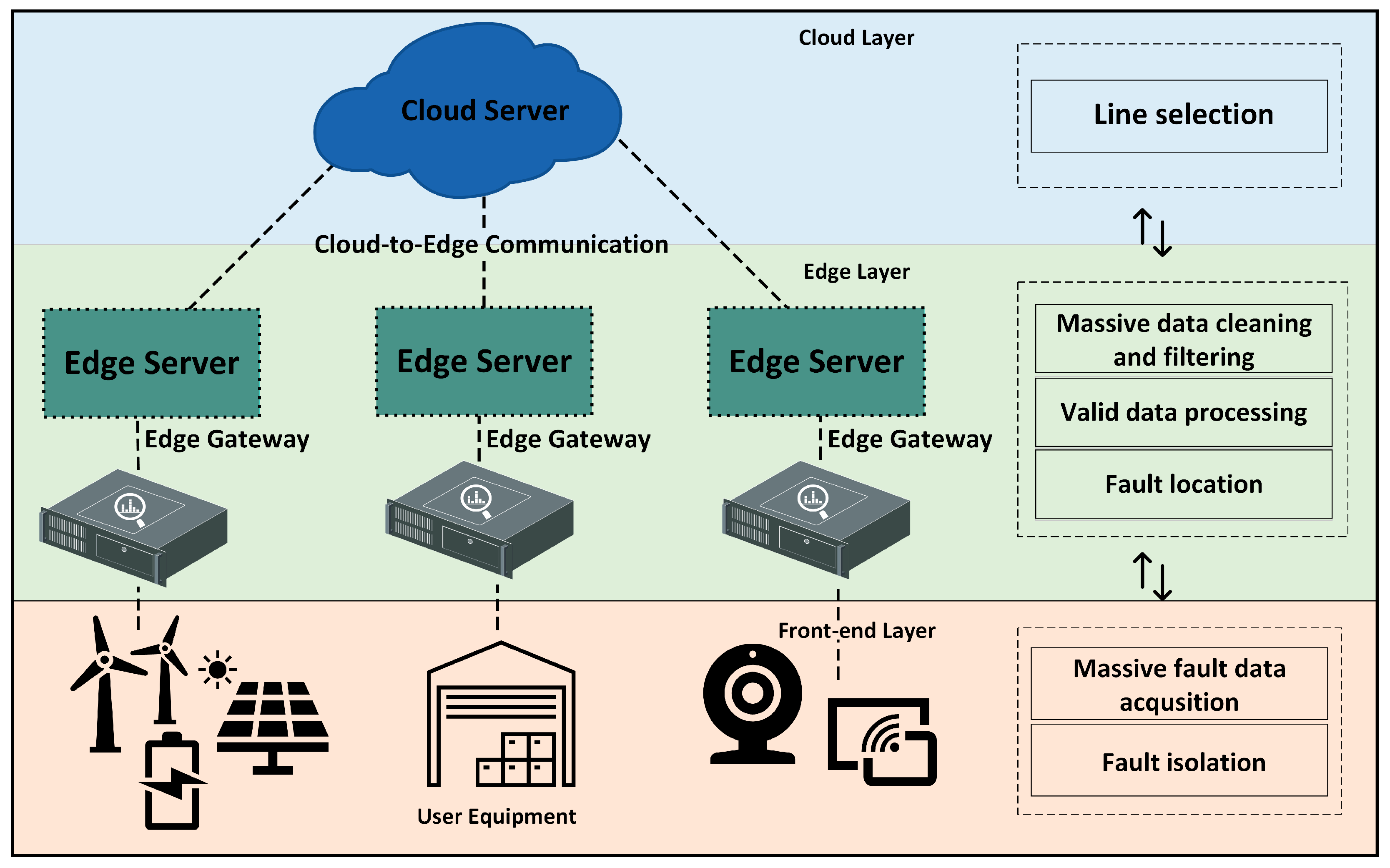
4.8. Fault Location
5. The Security and Privacy of Edge Computing
6. Discussion and Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| EC | Edge Computing |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| IED | Improvised Explosive Devices |
| CC | Cloud Computing |
| CI | Computational Intelligence |
| DMLS | Distributed Multi-level Storage |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| MEC | Multi-access Edge Computing |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |
| FCN | Fog Computing Network |
| ILP | Integer Linear Programming |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| MCC | Mobile Cloud Computing |
| QoE | Quality of Experience |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| P2P | Peer-to-peer |
| NFV | Network Function Virtualisation |
| CVT | Container-based Virtualisation Technology |
| VM | Virtual Machine |
| CLI | Command Line Interface |
| JTSC | Joint Task Scheduling and Containerisation |
| BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy |
| CoAP | Constrained Application Protocol |
| MQTT | Minimum Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| TLS | Transport Layer Security |
| AMQP | Advanced Message Queuing Protocol |
| XMPP | Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| AioT | AI of Things |
| TATSR | Time Average Transmission Success Rate |
| SG | Smart Grid |
| 6LoWPAN | Low Power Personal Area Network |
| DER | Distributed Energy Resources |
| DG | Distributed Generators |
| SPVI | Smart PV-based Inverters |
| FDI | False Data Injection |
| SE | State Estimation |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| VVC | Voltage/VAR Control |
| IoS | Internet of Services |
| MADRL | Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| AMI | Advanced Metering Infrastructure |
| NILM | Non-intrusive Load Monitoring |
| MDMS | Meter Data Management System |
| HAN | Home Area Network |
| SM | Smart Metering |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbor |
| AMI | Advanced Metering Infrastructure |
| LV | Low Voltage |
| DTU | Distribution Transformer Unit |
| PMU | Phasor Measurement Data |
| DSSE | Distribution System State Estimation |
| DMS | Distribution Management System |
| VAR | Vector Autoregression |
| FDIA | False Data Injection Attack |
| HEMS | Home Energy Management System |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| ECCREM | Edge-cloud Collaboration-based Residential Energy Management |
| SDN | Software-Defined Network |
| TATSR | Time Average Transmission Success Ratio |
| PD-IoT | Power Distribution Internet of Things |
| MDRL | Model-based Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| LoRa | Long Range |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| VVC | Volt/var Control |
| PD-IoT | Power Distribution Internet of Things |
| FL | Federated Learning |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| HDTG | Hierarchical Decision-making Strategy Based on Prediction Strategy and Task Grading |
| LoRa | Long Range |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| TWAM | Traveling Wave Acquisition Module |
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| DT | Digital Twins |
| SLG | Single-Phase Ground |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| CPS | Cyber-Physical Systems |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
References
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D. Using the internet of things in smart energy systems and networks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 68, 102783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Chowdhury, P.; Yeassin, R.; Hasan, M.; Ahmad, T.; Chowdhury, N.U.R. Impacts of digitalization on smart grids, renewable energy, and demand response: An updated review of current applications. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 24, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.S.; Kumar, C. A Green and Reliable Internet of Things. Commun. Netw. 2013, 5, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravandi, B.; Papapanagiotou, I. A Self-Learning Scheduling in Cloud Software Defined Block Storage. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge to Core and the Internet of Things|Dell Technologies Info Hub. Available online: https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/t/edge-to-core-and-the-internet-of-things-2/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Cisco Annual Internet Report-Cisco Annual Internet Report (2018–2023) White Paper-Cisco. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/executive-perspectives/annual-internet-report/white-paper-c11-741490.html (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Google and IBM Announce Academic Data Center Collaboration-DCD. Available online: https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/news/google-and-ibm-announce-academic-data-center-collaboration/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Nieuwenhuis, L.J.M.; Ehrenhard, M.L.; Prause, L. The shift to Cloud Computing: The impact of disruptive technology on the enterprise software business ecosystem. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 129, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Yadav Yanamala, A.; Pointe Blvd, O. Emerging Challenges in Cloud Computing Security: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2024, 4, 448–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ometov, A.; Molua, O.L.; Komarov, M.; Nurmi, J. A Survey of Security in Cloud, Edge, and Fog Computing. Sensors 2022, 22, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Nayyar, A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A. Fog computing: From architecture to edge computing and big data processing. J. Supercomput. 2018, 75, 2070–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Edge Computing: Vision and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Negi, N.; Chauhan, R. Integration of edge computing with cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Computing and Communication Technologies (ICETCCT), Dehradun, India, 17–18 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Nishi, H.; Vyatkin, V.; Huang, V.; Shi, Y.; Guan, X. Industrial Edge Computing: Enabling Embedded Intelligence. EEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2019, 13, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.L.P. Edge computing and its role in Industrial Internet: Methodologies, applications, and future directions. Inf. Sci. 2021, 557, 34–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooi, H.B.; Wang, T.; Tang, Y. Edge Intelligence for Smart Grid: A Survey on Application Potentials. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, C.; Xiang, Y.; Li, F. Edge-cloud Computing Systems for Smart Grid: State-of-the-art, Architecture, and Applications. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, Q.N.; Nguyen, V.H.; Quy, V.K.; Ngoc, L.A.; Chehri, A.; Jeon, G. Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid: The Future of Energy. Energies 2022, 15, 6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Buyya, R.; Kim, H. Securing Cloud-Based Internet of Things: Challenges and Mitigations. Sensors 2025, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour, A.; Fung, C.; Nguyen, T.; Kadiyala, K.; Jalali, F.; Niakanlahiji, A.; Kong, J.; Jue, J.P. All One Needs to Know about Fog Computing and Related Edge Computing Paradigms: A Complete Survey. J. Syst. Archit. 2019, 98, 289–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y. A Review of Edge Computing Technology and Its Applications in Power Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, Y.; Babar, M.A. A review of edge computing: Features and resource virtualization. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2021, 150, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mell, P.; Grance, T. The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing, Special Publication (NIST SP); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, R.A.A.; Nasaruddin, F.; Gani, A.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Ahmed, E.; Imran, M. Real-time big data processing for anomaly detection: A Survey. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 45, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Dong, N.; Li, W.; Cao, J. Edge Computing with Artificial Intelligence: A Machine Learning Perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Jumaili, A.H.A.; Muniyandi, R.C.; Hasan, M.K.; Paw, J.K.S.; Singh, M.J. Big Data Analytics Using Cloud Computing Based Frameworks for Power Management Systems: Status, Constraints, and Future Recommendations. Sensors 2023, 23, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburukba, R.O.; AliKarrar, M.; Landolsi, T.; El-Fakih, K. Scheduling Internet of Things requests to minimize latency in hybrid Fog–Cloud computing. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 111, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiza, G.; Saeteros, M.; Oñate, W.; Garcia, M.V. Fog Computing at Industrial Level, Architecture, Latency, Energy, and Security: A Review. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Misra, S.; Xue, G.; Yang, D. Managing smart grid information in the cloud: Opportunities, model, and applications. IEEE Netw. 2012, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popeangă, J. Cloud Computing and Smart Grids. Database Syst. J. 2012, III, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Shen, C. CloudPSS: A high-performance power system simulator based on cloud computing. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Jumaili, A.H.A.; Mashhadany, Y.I.A.; Sulaiman, R.; Alyasseri, Z.A.A. A Conceptual and Systematics for Intelligent Power Management System-Based Cloud Computing: Prospects, and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Jumaili, A.H.A.; Muniyandi, R.C.; Hasan, M.K.; Singh, M.J.; Paw, J.K.S.; Amir, M. Advancements in intelligent cloud computing for power optimization and battery management in hybrid renewable energy systems: A comprehensive review. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 2206–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahvirdizadeh, Y.; Moghaddam, M.P.; Shayanfar, H. A survey on cloud computing in energy management of the smart grids. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2019, 29, e12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, L.; Shahinzadeh, H.; Shayeghi, H.; Dejamkhooy, A.; Bayindir, R.; Iranpour, M. Integration of Cloud Computing and IoT (CloudIoT) in Smart Grids: Benefits, Challenges, and Solutions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Smart Power System and Sustainable Energy, CISPSSE 2020, Keonjhar, India, 29–31 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, C.; Psannis, K.E.; Kim, B.G.; Gupta, B. Secure integration of IoT and Cloud Computing. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bi, Z.; Da Xu, L. IoT and cloud computing in automation of assembly modeling systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What is Edge Computing?|Cloudflare. Available online: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/serverless/glossary/what-is-edge-computing/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Satyanarayanan, M. The emergence of edge computing. Computer 2017, 50, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Wang, Y. Edge Computing Technology: Development and Countermeasures. Chin. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 20, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.Z.; Ahmed, E.; Hakak, S.; Yaqoob, I.; Ahmed, A. Edge computing: A survey. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is Edge Computing? Introduction to Edge Computing. Available online: https://stlpartners.com/articles/edge-computing/what-is-edge-computing/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Leung, V.C.M. An Edge Computing Framework for Real-Time Monitoring in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet, ICII 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, G.; Pattanaik, K.K.; Sharma, G.K. Towards edge computing in intelligent manufacturing: Past, present and future. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 588–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, P.Q. A Review on Computational Intelligence Techniques in Cloud and Edge; Computing. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2020, 4, 742–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Dai, H.; Yu, Z. A distributed multi-level model with dynamic replacement for the storage of smart edge computing. Syst. Arch. 2018, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcas, G.I.; Cioara, T.; Anghel, I.; Lazea, D.; Hangan, A. Edge Offloading in Smart Grid. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 680–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Meng, G.; Sun, Q. An Overview on Edge Computing Research. EEE Access 2020, 8, 85714–85728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, I.; Harjula, E.; Glisic, S.; Lorenzo, B.; Ylianttila, M. Cloud and Edge Computation Offloading for Latency Limited Services. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 55764–55776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwarafy, A.; Al-Thelaya, K.A.; Abdallah, M.; Schneider, J.; Hamdi, M. A Survey on Security and Privacy Issues in Edge-Computing-Assisted Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 4004–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gill, S.S. Edge AI: A survey. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.; Zhang, T. Fog and IoT: An Overview of Research Opportunities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, F.; Milito, R.; Zhu, J.; Addepalli, S. Fog computing and its role in the internet of things. In Proceedings of the MCC’12-Proceedings of the 1st ACM Mobile Cloud Computing Workshop, New York, NY, USA, 17 August 2012; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Reference Architecture Is a Leap Forward for Fog Computing-Cisco Blogs. Available online: https://blogs.cisco.com/innovation/new-reference-architecture-is-a-leap-forward-for-fog-computing (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Baktyan, A.; Zahary, A. A Review on Cloud and Fog Computing Integration for IoT: Platforms Perspective. EAI Endorsed Trans. Internet Things 2018, 4, 156084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouradian, C.; Naboulsi, D.; Yangui, S.; Glitho, R.H.; Morrow, M.J.; Polakos, P.A. A Comprehensive Survey on Fog Computing: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 20, 416–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolui, K.; Datta, S.K. Comparison of edge computing implementations: Fog computing, cloudlet and mobile edge computing. In Proceedings of the GIoTS 2017-Global Internet of Things Summit, Proceedings, Geneva, Switzerland, 6–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebortta, S.; Tripathy, S.S.; Modibbo, U.M.; Ali, I. An optimal fog-cloud offloading framework for big data optimization in heterogeneous IoT networks. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 8, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Yang, R.; Garraghan, P.; Lin, T.; Xu, J.; Rovatsos, M. Fog orchestration for internet of things services. IEEE Internet Comput. 2017, 21, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, S.; Gill, S.S.; Song, C.; Xu, M.; Aslanpour, M.S.; Toosi, A.N.; Du, J.; Wu, H.; Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, D.; et al. AI-based fog and edge computing: A systematic review, taxonomy and future directions. Internet Things 2023, 21, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeshu, A.; Chilamkurti, N. Deep Learning: The Frontier for Distributed Attack Detection in Fog-To-Things Computing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, S.; Mahmud, R.; Tuli, S.; Buyya, R. FogBus: A Blockchain-based Lightweight Framework for Edge and Fog Computing. J. Syst. Softw. 2019, 154, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Yang, L.T.; Wang, L.; Vinel, A. Internet of Things. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2012, 25, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Zhang, Y.; Taherkordi, A.; Skeie, T. Mobile Edge Computing: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Patel, M.; Sabella, D.; Sprecher, N.; Young, V. ETSI White Paper #11 Mobile Edge Computing—A Key Technology Towards 5G; ETSI: Valbonne, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akherfi, K.; Gerndt, M.; Harroud, H. Mobile cloud computing for computation offloading: Issues and challenges. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2018, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, T.H.; Zeadally, S.; Alfazi, A.; Sheng, Q.Z. Mobile cloud computing: Challenges and future research directions. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 115, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A Survey on Mobile Edge Computing: The Communication Perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TKiendrébéogo; Ouédraogo, I.Z.; Pousga, S.; Barry, D.; Kaboré-Zoungrana, C.Y. Effects of Rations Containing Maggot Concentrate as a Fish Substitute on the Technical and Economic Performance of Large White’s Piglets in Burkina Faso. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 10, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QasemJaber, Z.; Issam Younis, M. Design and Implementation of Real Time Face Recognition System (RTFRS). Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 94, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Shuwaili, A.; Simeone, O. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Mobile Edge Computing-Based Augmented Reality Applications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2017, 6, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanovnik, S.; Cankar, M. On the Similarities and Differences Between the Cloud, Fog and the Edge; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); LNCS; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 11997, pp. 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrust, M.; Fox, A.; Griffith, R.; Joseph, A.D.; Katz, R.H.; Konwinski, A.; Lee, G.; Patterson, D.A.; Rabkin, A. Above the Clouds: A Berkeley View of Cloud Computing; EECS Department, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dayong, W.; Bin Abu Bakar, K.; Isyaku, B.; Abdalla Elfadil Eisa, T.; Abdelmaboud, A. A Comprehensive Review on Internet of Things Task Offloading in Multi-Access Edge Computing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Application of Edge Computing in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering, ICBAIE 2022, Xi’an, China, 15–17 July 2022; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Dutta, S.; Ksentini, A.; Iqbal, M.; Flinck, H. Mobile edge computing potential in making cities smarter. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, T.; Rashed, A.; Dustdar, S. Optimized container scheduling for data-intensive serverless edge computing. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 114, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulkinbekov, K.; Kim, D.H. Blockchain-Enabled Approach for Big Data Processing in Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 18473–18486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Song, J. Data Processing Delay Optimization in Mobile Edge Computing. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 6897523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Zeadally, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Vehicular delay-tolerant networks for smart grid data management using mobile edge computing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.J.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, W.; Xu, A.; Wen, H.; Chen, S. A P2P network based edge computing smart grid model for efficient resources coordination. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.F.; Qureshi, N.M.F.; Chowdhry, B.S.; Uqaili, M.A. Edge-node-aware adaptive data processing frameworfor smart grid. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 106, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Gu, D.; Zhang, J.; Xue, J.; Wang, H. Privacy-preserving statistical analysis over multi-dimensional aggregated data in edge computing-based smart grid systems. J. Syst. Arch. 2022, 127, 102508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.I.; Martín, A.; Parejo, A.; Larios, D.F.; Molina, F.J.; León, C. A General-Purpose Distributed Analytic Platform Based on Edge Computing and Computational Intelligence Applied on Smart Grids. Sensors 2023, 23, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, G.; Xu, C. Multi source data security protection of smart grid based on edge computing. Meas. Sens. 2024, 35, 101288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modupe, O.T.; Otitoola, A.A.; Oladapo, O.J.; Abiona, O.O.; Oyeniran, O.C.; Adewusi, A.O.; Komolafe, A.M.; Obijuru, A. Reviewing the Transformational Impact of Edge Computing on Real-Time Data Processing and Analytics. Sci. IT Res. J. 2024, 5, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Liu, T.; Hou, B.; Gao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, H. A Low-Latency RDP-CORDIC Algorithm for Real-Time Signal Processing of Edge Computing Devices in Smart Grid Cyber-Physical Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Luo, H.; Tang, Z.; Jia, W.; Zhao, W. Efficient Container Assignment and Layer Sequencing in Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2022, 16, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skourtis, D.; Rupprecht, L.; Tarasov, V.; Megiddo, N. Carving Perfect Layers out of Docker Images. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Conference on Hot Topics in Cloud Computing (HotCloud′19), Renton, WA, USA, 8 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.C.; Lee, C.S.; Chen, J.L. Mobile Edge Computing Platform with Container-Based Virtualization Technology for IoT Applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 102, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, R. Virtualization on internet of things edge devices with container technologies: A performance evaluation. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8835–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprolu, M.; Di Pietro, R.; Lombardi, F.; Raponi, S. Edge Computing Perspectives: Architectures, Technologies, and Open Security Issues. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing (EDGE), Edge Computing (EDGE), Milan, Italy, 8–13 July 2019; pp. 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, S.R.U.; Mukkala, L.; Westerlund, T.; Plosila, J. Virtualization at the network edge: A technology perspective. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing, FMEC 2018, Barcelona, Spain, 23–26 April 2018; pp. 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, R.; Cozzolino, V.; Ding, A.Y.; Beijar, N.; Ott, J. Consolidate IoT Edge Computing with Lightweight Virtualization. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A. Container-Based IoT Sensor Node on Raspberry Pi and the Kubernetes Cluster Framework. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2016; pp. 8–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabahi, F. Secure Virtualization for Cloud Environment Using Hypervisor-Based Technology. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2012, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yin, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Luo, H. Container-based fog computing architecture and energy-balancing scheduling algorithm for energy IoT. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Mangat, V.; Kumar, K. A Review on Virtualized Infrastructure Managers with Management and Orchestration Features in NFV Architecture. Comput. Netw. 2022, 217, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Sinnott, R.O. Benchmarking Container Technologies For IoT Environments. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing, FMEC 2022, Paris, France, 12–15 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Rufino, J.; Ferreira, J.; Ahmed, S.H.; Shah, N.; Chen, Y. Orchestration of Microservices for IoT Using Docker and Edge Computing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, J.; Li, B. KubeHICE: Performance-aware Container Orchestration on Heterogeneous-ISA Architectures in Cloud-Edge Platforms. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking (ISPA/BDCloud/SocialCom/SustainCom), New York City, NY, USA, 30 September–3 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Taherkordi, A.; Eliassen, F.; Liu, L.; Delbruel, S.; Dustdar, S.; Yang, Y. Task Partitioning and Orchestration on Heterogeneous Edge Platforms: The Case of Vision Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 7418–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.M.; Vidal, I.; Valera, F. Enabling the Orchestration of IoT Slices through Edge and Cloud Microservice Platforms. ensors 2019, 19, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, S.; Haq, M.S.; Tosun, A.S.; Korkmaz, T. Container Technologies for ARM Architecture: A Comprehensive Survey of the State-of-the-Art. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 84853–84881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, P. Navigating ARM-Based Application Adoption: Software Engineer’s Insights on Challenges and Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking, WiSPNET 2024, Chennai, India, 21–23 March 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raho, M.; Spyridakis, A.; Paolino, M.; Raho, D. KVM, Xen and Docker: A performance analysis for ARM based NFV and cloud computing. In Proceedings of the Advances in Information, Electronic and Electrical Engineering, AIEEE 2015-Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 3rd Workshop, Riga, Latvia, 13–14 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.S.; Tosun, A.S.; Korkmaz, T. Security Analysis of Docker Containers for ARM Architecture. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-2022 IEEE/ACM 7th Symposium on Edge Computing, SEC 2022, Seattle, WA, USA, 5–8 December 2022; pp. 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemashkin, F.Y.; Drobintsev, P.D.; Zhilenkov, A.A. Research of Clustering Methods of ARM Devices Based for Edge Computing Use Cases. In Proceedings of the Seminar on Information Systems Theory and Practice, ISTP 2023, Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation, 30 November 2023; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubernetes. Available online: https://kubernetes.io/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Ning, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, F.; Yang, L.T. Heterogeneous edge computing open platforms and tools for internet of things. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 106, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Anantharaj, K.; Subramani, K. Containerized architecture for edge computing in smart home: AAA consistent architecture for model deployment. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics, ICCCI 2020, Coimbatore, India, 22–24 January 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavapeddy, A.; Mortier, R.; Rotsos, C.; Scott, D.; Singh, B.; Gazagnaire, T.; Smith, S.; Hand, S.; Crowcroft, J. Unikernels. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Arch. News 2013, 41, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, M. Evolving Container to Unikernel for Edge Computing and Applications in Process Industry. Processes 2021, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Ghosal, A.; Margaria, T.; Pesch, D. DSLs for model driven development of secure interoperable automation systems with EdgeX foundry. In Proceedings of the 2021 Forum on Specification & Design Languages (FDL), Antibes, France, 8–10 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, T.L. EdgeX Foundry|#1 Open Source Edge Platform. Available online: https://www.edgexfoundry.org (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Amento, B.; Balasubramanian, B.; Hall, R.J.; Joshi, K.; Jung, G.; Purdy, K.H. FocusStack: Orchestrating edge clouds using location-based focus of attention. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-1st IEEE/ACM Symposium on Edge Computing, SEC 2016, Washington, DC, USA, 27–28 October 2016; pp. 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akraino Edge Stac–LF EDGE: Building an Open Source Framework for the Edge. Available online: https://lfedge.org/category/akraino-edge-stack/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- GitHub-Azure/Iotedge: The IoT Edge OSS Project. Available online: https://github.com/Azure/iotedge (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- KubeEdge. Available online: https://kubeedge.io/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- CORD Archives-Open Networking Foundation. Available online: https://opennetworking.org/tag/cord/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- IoT Edge’de Zeka-AWS IoT Greengrass-AWS. Available online: https://aws.amazon.com/tr/greengrass/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- GitHub-Baetyl/Baetyl: Extend Cloud Computing, Data and Service Seamlessly to Edge Devices. Available online: https://github.com/baetyl/baetyl (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Hung, C.C.; Ananthanarayanan, G.; Bodik, P.; Golubchik, L.; Yu, M.; Bahl, P.; Philipose, M. VideoEdge: Processing camera streams using hierarchical clusters. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-2018 3rd ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing, SEC 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–27 October 2018; pp. 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqaisi, O.I.; Tosun, A.S.; Korkmaz, T. Performance Analysis of Container Technologies for Computer Vision Applications on Edge Devices. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 41852–41869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojabri, M.; Dersch, U.; Papaemmanouil, A.; Bosshart, P. A Comprehensive Survey on Phasor Measurement Unit Applications in Distribution Systems. Energies 2019, 12, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Ge, T.; Wang, X.; Hwang, T. Joint Task Scheduling and Containerizing for Efficient Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 32, 2086–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Luo, J.; Li, K. An Optimal Image Storage Strategy for Container-Based Edge Computing in Smart Factory. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 7204–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, M.; Xiao, T.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. MXNet: A Flexible and Efficient Machine Learning Library for Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. December 2015. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.01274v1 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- TensorFlow. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Demosthenous, G.; Vassiliades, V. Continual Learning on the Edge with TensorFlow Lite. May 2021. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2105.01946 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Core ML|Apple Developer Documentation. Available online: https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Caffe2|A New Lightweight, Modular, and Scalable Deep Learning Framework. Available online: https://caffe2.ai/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- PyTorch. Available online: https://pytorch.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- TensorRT SDK|NVIDIA Developer. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Amento, B.; Hall, R.J.; Joshi, K.; Purdy, K.H. FocusStack: Orchestrating Edge Clouds Using Focus of Attention. IEEE Internet Comput. 2017, 21, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liao, X.; Jin, H.; Li, P. Computation Offloading Toward Edge Computing. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1584–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Barijough, K.M.; Gerstlauer, A. DeepThings: Distributed adaptive deep learning inference on resource-constrained IoT edge clusters. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 2348–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendki, P. Docker container based analytics at IoT edge Video analytics usecase. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-2018 3rd International Conference On Internet of Things: Smart Innovation and Usages, IoT-SIU 2018, Bhimtal, India, 23–24 February 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apache MXNet|A Flexible and Efficient Library for Deep Learning. Available online: https://mxnet.apache.org/versions/1.9.1/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. March 2016. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.04467v2 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Jha, D.N.; Alwasel, K.; Alshoshan, A.; Huang, X.; Naha, R.K.; Battula, S.K.; Garg, S.; Puthal, D.; James, P.; Zomaya, A.; et al. IoTSim-Edge: A simulation framework for modeling the behavior of Internet of Things and edge computing environments. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2020, 50, 844–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.A.V.; Laureano, E.V.; Betancourt, R.O.J.; Álvarez, E.N. An open source IoT edge-computing system for monitoring energy consumption in buildings. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lim, J.; Kwon, T.L. MQTLS: Toward Secure MQTT Communication with an Untrusted Broker. In Proceedings of the ICTC 2019-10th International Conference on ICT Convergence: ICT Convergence Leading the Autonomous Future, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A. AMQP and beyond. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Smart Applications, Communications and Networking, SmartNets 2021, Glasgow, UK, 22–24 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Andre, P.; Houri, A.; Hildebrand, J. Interworking between the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP): Instant Messaging. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fuqaha, A.; Guizani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aledhari, M.; Ayyash, M. Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2347–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsgaard, H.J.; Ometov, A.; Nurmi, J. Approximation Opportunities in Edge Computing Hardware: A Systematic Literature Review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Liu, S.; Xiong, X.; Cai, Z.; Tu, G. A Survey of Recent Advances in Edge-Computing-Powered Artificial Intelligence of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13849–13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taigman, Y.; Yang, M.; Ranzato, M.; Wolf, L. DeepFace: Closing the Gap to Human-Level Performance in Face Verification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ding, Y.; Strbac, G.; Kang, C. Smart grid encounters edge computing: Opportunities and applications. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X.; Hatcher, W.G.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. A Survey on the Edge Computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 6900–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Wan, J.; Liu, C.; Imran, M. Adaptive transmission optimization in SDN-based industrial internet of things with edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhai, C. Dynamic Power Control for Cell-Free Industrial Internet of Things with Random Data Arrivals. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4138–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Beaulieu, N.C.; Li, Z.; Si, J.; Qi, P. Energy-Efficient Optimal Power Allocation for Fading Cognitive Radio Channels: Ergodic Capacity, Outage Capacity, and Minimum-Rate Capacity. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 15, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, S.B. Prosumer in smart grids based on intelligent edge computing: A review on Artificial Intelligence Scheduling Techniques. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Ramezani, M.; Xiao, Y. Artificial Neural Networks for Volt/VAR Control of DER Inverters at the Grid Edge. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 10, 5564–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, A.R.; Annaswamy, A.M.; Shah, J. Hierarchical Hybrid Architecture for Volt/Var Control of Power Distribution Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 35, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.Y.; Shadmand, M.B. Multitimescale Three-Tiered Voltage Control Framework for Dispersed Smart Inverters at the Grid Edge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 57, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, C.; Hu, H.; Wang, F. Design of a Power Transmission Line Monitoring System Based upon Edge Computing and Zigbee Wireless Communication. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 9379789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccadoro, P. Smart Grids Empowerment with Edge Computing: An Overview. September 2018. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1809.10060 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Zhang, J. Online Monitoring System of Electromechanical Transient Simulation Data of Distribution Network Based on Edge Computing. Scalable Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 25, 5151–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, D. Design of Reactive Power Online Monitoring System of Intelligent Distribution Transformer Based on Edge Computing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2532, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbao, X.; Yan, L.; Mingshun, Y.; Xi, C. Design of Intelligent Monitoring System for Power Distribution Equipment Based on Cloud Edge Collaborative Computing. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Precision Machining, Non-Traditional Machining and Intelligent Manufacturing (PNTIM 2019), Xi′an, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, S.; Gao, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. Research on Multi-Parameter Data Monitoring System of Distribution Station Based on Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd Asia Energy and Electrical Engineering Symposium, AEEES 2021, Chengdu, China, 26–29 March 2021; pp. 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, S.; Deng, S.; Liu, G. Service Scheduling Based on Edge Computing for Power Distribution IoT. Mater. Contin. 2020, 62, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, Y.; Yin, C.; Xi, J.; Bai, L.; Hui, Z. A Real-Time Monitoring and Warning System for Power Grids Based on Edge Computing. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8719227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Bai, H.; Huo, C.; Zhang, G. An Intelligent Integrated Terminal Based on Edge Computing for Power Distribution and Metering. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering Technology, CCET 2021, Beijing, China, 13–15 August 2021; pp. 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, J. A Power-Grid-Mapping Edge Computing Structure for Digital Distributed Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 15, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Y. Power distribution network management based on edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Shanghai, China, 7–9 April 2021; Volume 2021, pp. 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Bao, Y.; Zeng, L. Research on Edge-Computing-Based High Concurrency and Availability ‘Cloud, Edge, and End Collaboration’ Substation Operation Support System and Applications. Energies 2023, 17, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cui, H. An Edge Computing Architecture and Application Oriented to Distributed Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking (ISPA/BDCloud/SocialCom/SustainCom), New York City, NY, USA, 30 September–3 October 2021; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9644694/ (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Munir, M.S.; Abedin, S.F.; Tran, N.H.; Hong, C.S. When Edge Computing Meets Microgrid: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7360–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.S.; Abedin, S.F.; Kim, D.H.; Tran, N.H.; Han, Z.; Hong, C.S. A multi-agent system toward the green edge computing with microgrid. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.S.; Abedin, S.F.; Tran, N.H.; Han, Z.; Huh, E.N.; Hong, C.S. Risk-Aware Energy Scheduling for Edge Computing with Microgrid: A Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021, 18, 3476–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, C.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, S. Power flow adjustment for smart microgrid based on edge computing and multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. J. Cloud Comput. 2021, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nammouchi, A.; Aupke, P.; Kassler, A.; Theocharis, A.; Raffa, V.; Di Felice, M. Integration of AI, IoT and Edge-Computing for Smart Microgrid Energy Management. In Proceedings of the 21st IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2021 5th IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power System Europe, EEEIC/I and CPS Europe 2021-Proceedings, Bari, Italy, 7–10 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, W.; Zomaya, A.Y. Machine-Learning-Based Real-Time Economic Dispatch in Islanding Microgrids in a Cloud-Edge Computing Environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13703–13711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wen, H.; Wu, J.; Lei, W.; Hou, W.; Liu, W.; Xu, A.; Jiang, Y. Internet of Things Based Smart Grids Supported by Intelligent Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74089–74102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gupta, B.B.; Tian, Z. An Edge-AI Based Forecasting Approach for Improving Smart Microgrid Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7946–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, J.; Cui, D. Artificial-intelligence-based algorithms in multi-access edge computing for the performance optimization control of a benchmark microgrid. Phys. Commun. 2021, 44, 101240. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1874490720303177 (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Prajeesha; Anuradha, M. EDGE Computing Application in SMART GRID-A Review. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems, ICESC 2021, Coimbatore, India, 4–6 August 2021; pp. 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokomme, D.N.; Chabalala, C.S.; Bokoro, P.N. A review of cognitive radio smart grid communication infrastructure systems. Energies 2020, 13, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.; Hossain, J.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Khamfroush, H.; Rahnamay-Naeini, M.; Ghani, N. A framework for edge intelligent smart distribution grids via federated learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Athens, Greece, 19–22 July 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guerrero, J.; Vasquez, J.C. Digitalization and decentralization driving transactive energy Internet: Key technologies and infrastructures. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 126, 106593. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142061520328210 (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Tom, R.J.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Aggregator based RPL for an IoT-fog based power distribution system with 6LoWPAN. China Commun. 2020, 17, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupis, J.; Rodrigues, R.; Razeghi-Jahromi, M.; Melese, A.; Xavier, J.I. Hierarchical Distribution Grid Intelligence: Using Edge Compute, Communications, and IoT Technologies. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2023, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, J. Deep Learning for Edge Computing Applications: A State-of-the-Art Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58322–58336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, V.; Mehmeti, F.; He, T.; La Porta, T.F.; Khamfroush, H.; Wang, S.; Chan, K.S.; Poularakis, K. Service placement and request scheduling for data-intensive applications in edge clouds. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2021, 29, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.; Lee, S.; Abbas, A.; Bashir, A.K. Optimizing lifespan and energy consumption by smart meters in green-cloud-based smart grids. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20934–20945. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8046004/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Al-Turjman, F.; Abujubbeh, M. IoT-enabled smart grid via SM: An overview. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Mishra, R.; Gupta, H.P.; Gupta, H.P.; Dutta, T.; Das, S.K. An energy efficient smart metering system using edge computing in LoRa network. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2022, 7, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Rojas, J.C.; Reyes-Archundia, E.; Gutiérrez-Gnecchi, J.A.; Molina-Moreno, I.; Téllez-Anguiano, A.C.; Cerda-Jacobo, J. Smart metering system data analytics platform using multicore edge computing. Int. J. Reconfigurable Embed. Syst. 2021, 10, 11. Available online: https://ijres.iaescore.com/index.php/IJRES/article/view/20308 (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liang, C.; He, Q. Remote malfunctional smart meter detection in edge computing environment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 67436–67443. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9057452/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Utomo, D.; Sensors, P.H. A multitiered solution for anomaly detection in edge computing for smart meters. Sensors 2020, 20, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Wang, H. Anomaly detection and visualization of school electricity consumption data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data Analysis (ICBDA), Beijing, China, 10–12 March 2017; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8078707/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Liang, H.; Ye, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H. Anomaly detection based on edge computing framework for AMI. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics Technology (ICEEMT), Qingdao, China, 2–4 July 2021; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9601888/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Wei, S.; Meng, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Qi, L.; Xu, X. Edge-enabled federated sequential recommendation with knowledge-aware Transformer. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 148, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Yu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Min, G. Federated Continual Learning for Edge-AI: A Comprehensive Survey. 2024. Available online: https://3d43585e923c69c05fe5cddbdcda4e642ae7fbed.vetisonline.com/contentitem/edsarx:edsarx.2411.13740?sid=ebsco:plink:crawler&id=ebsco:edsarx:edsarx.2411.13740&crl=c (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, H.; Su, S. Edge Computing Based Electricity-Theft Detection of Low-Voltage Users. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 892541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.; Pegoraro, P.; Atzori, L.; Benigni, A.; Sulis, S. Cloud-based IoT solution for state estimation in smart grids: Exploiting virtualization and edge-intelligence technologies. Comput. Netw. 2018, 130, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraganti, C.K.; Robert, B.P.; Gurrala, G.; Puthuparambil, A.B.; Sundaresan, R. A distributed hierarchy based framework for validating edge devices performing state estimation in a power system. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power Systems Technology (POWERCON), Bangalore, India, 14–16 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y. Incentive edge-based federated learning for false data injection attack detection on power grid state estimation: A novel mechanism design approach. Appl. Energy 2022, 314, 118828. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261922002707 (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.N.; Pota, H.R.; Tran, Q.N.; Hu, J. Designing Constraint-Based False Data-Injection Attacks against the Unbalanced Distribution Smart Grids. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 9422–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Xu, Z.; Wong, B.; Qian, H.; Ju, L.; Jiang, W. Switch state identification in distribution network based on edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Sustainable Power and Energy Conference (iSPEC), Nanjing, China, 23–25 December 2021; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9736010/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Yuan, L.; Gu, J.; Ma, J.; Wen, H.; Jin, Z. Optimal Network Partition and Edge Server Placement for Distributed State Estimation. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayakumar, R.; Mahesh, B.; Sathiyakala, R.; Thandapani, K.; Choubey, A.; Khurramov, A. An Integrated Deep Learning and Edge Computing Framework for Intelligent Energy Management in IoT-Based Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference for Technological Engineering and its Applications in Sustainable Development (ICTEASD), Al-Najaf, Iraq, 14–15 November 2023; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10585232/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Ferreira, L.C.B.C.; Da Rosa Borchardt, A.; Cardoso, G.D.S.; Lemes, D.A.M.; de Sousa, G.R.D.R.; Neto, F.B. Edge computing and microservices middleware for home energy management systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 109663–109676. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9917529/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wan, Y.; Qin, J.; Kang, Y.; Li, L. Privacy-preserving optimal energy management for smart grid with cloud-edge computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 4029–4038. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9546650/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Sánchez, S.; Calvo-Gallego, J.; Erbad, A.; Ibrar, M.; Fernandez, J.H.; Houchati, M.; Corchado, J.M. Enhancing building energy management: Adaptive edge computing for optimized efficiency and inhabitant comfort. Electronics 2023, 12, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicirelli, F.; Gentile, A.F.; Greco, E.; Guerrieri, A.; Spezzano, G.; Vinci, A. An energy management system at the edge based on reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM 24th International Symposium on Distributed Simulation and Real Time Applications (DS-RT), Prague, Czech Republic, 14–16 September 2020; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9213697/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Ruan, L.; Yan, Y.; Guo, S.; Wen, F.; Qiu, X. Priority-based residential energy management with collaborative edge and cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 1848–1857. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8790769/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y. A method for distribution network line selection and fault location based on a hierarchical fault monitoring and control system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 123, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, S.N.; Gouglidis, A.; Farshad, A.; Hutchison, D. The extended cloud: Review and analysis of mobile edge computing and fog from a security and resilience perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2586–2595. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8060526/ (accessed on 24 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Samdanis, K.; Mada, B.; Flinck, H.; Dutta, S.; Sabella, D. On multi-access edge computing: A survey of the emerging 5G network edge cloud architecture and orchestration. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1657–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yao, C.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, G.; Song, L. Joint task assignment, transmission, and computing resource allocation in multilayer mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 2872–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, P.; Becvar, Z. Mobile edge computing: A survey on architecture and computation offloading. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1628–1656. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7879258/ (accessed on 24 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J. Edge computing terminal equipment planning method for real-time online monitoring service of power grid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chengdu, China, 20–22 December 2019; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8997885/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Huo, W.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L. Research on Distributed Power Distribution Fault Detection Based on Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 24643–24652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukabayeva, T.; Zholshiyeva, L.; Karabayev, N.; Khan, S.; Alnazzawi, N. Cybersecurity Solutions for Industrial Internet of Things–Edge Computing Integration: Challenges, Threats, and Future Directions. Sensors 2025, 25, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayed, A.; Lin, J.; Li, F.; Luo, B. Cyber-physical systems security—A survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1802–1831. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7924372/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ranaweera, P.; Jurcut, A.D.; Liyanage, M. Survey on multi-access edge computing security and privacy. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1078–1124. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9364272/ (accessed on 22 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.R.; Singh, J. Edge Computing and IoT in Smart Cities-An Overview; National Foundation for Entrepreneurship Development (NFED): Tamil Nadu, India, 2024; Volume 11, ISBN 978-81-954930-4-3. [Google Scholar]
- Veeramachaneni, V. Edge Computing: Architecture, Applications, and Future Challenges in a Decentralized Era. Recent Trends Comput. Graph. Multimed. Technol. 2024, 7, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sulthana, R.; Shewale, T.; Chamola, V.; Benslimane, A.; Sikdar, B. Machine-Learning-Assisted Security and Privacy Provisioning for Edge Computing: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 236–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.; Siddiqui, F.; Sezer, S. Enhancing security and privacy of next-generation edge computing technologies. In Proceedings of the 2019 17th International Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST), Fredericton, NB, Canada, 26–28 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge Driven Digital Twins in Distributed Energy Systems Role and Opportunities for Hybrid Data Driven Solutions Release 1.0 AIOTI WG Energy. 2024. Available online: https://ecs-org.eu/?publications=ecso-technical-paper-on-cybersecurity-scenarios-and-digital-twins (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Zhou, Z.; Jia, Z.; Liao, H.; Lu, W.; Mumtaz, S.; Guizani, M.; Tariq, M. Secure and Latency-Aware Digital Twin Assisted Resource Scheduling for 5G Edge Computing-Empowered Distribution Grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4933–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Xu, L.; Li, D.; Wu, W. Edge Computing Integrated with Blockchain Technologies; Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); LNCS; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12000, pp. 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, J.; Du, X. A Multiple-Blockchains based Service Monitoring Framework in Edge-Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 23rd Int Conf on High Performance Computing & Communications; 7th Int Conf on Data Science & Systems; 19th Int Conf on Smart City; 7th Int Conf on Dependability in Sensor; Cloud & Big Data Systems & Application (HPCC/DSS/SmartCity/DependSys), Haikou, China, 20–22 December 2021; pp. 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Matam, R.; Shu, L.; Maglaras, L.; Ferrag, M.A.; Choudhury, N.; Kumar, V. Security and Privacy in Fog Computing: Challenges. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19293–19304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, O.A.; Khafajah, N.M. Efficient hybrid centralized and blockchain-based authentication architecture for heterogeneous IoT systems. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, C.; Turcu, C.; Chiuchisan, I. Blockchain and Its Potential in Education. March 2019. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.09300v1 (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Edge Intelligence and Blockchain Empowered 5G Beyond for the Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, F.; Qi, J.; Wang, J.; Sangaiah, A.K. Identity Management and Access Control Based on Blockchain under Edge Computing for the Industrial Internet of Things. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, A.; Ravi, L.; Devarajan, M.; Vairavasundaram, S.; Selvalakshmi, A.; Kotecha, K.; Abraham, A. A Decentralized Resource Allocation in Edge Computing for Secure IoT Environments. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 117177–117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, A. Blockchain Based Distributed Control System for Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 21st International Conference on Control Systems and Computer, CSCS 2017, Bucharest, Romania, 29–31 May 2017; pp. 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Wu, Q.; Fan, Q.; Fan, P.; Li, Z.; Fan, J. A Power Allocation Scheme for MIMO-NOMA and D2D Vehicular Edge Computing Based on Decentralized DRL. Sensors 2023, 23, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mobile Edge Computing | Mobile Cloud Computing | |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution/Deployment | Requires simple configuration and planning | Requires complex configuration and planning |
| Distance to End Users | Close to users | Remote to users |
| Server Hardware | Compact data centers | Large-scale data centers |
| Server Location | Wireless gateways | Servers are located in large areas |
| Use of Backhaul | Relieves network congestion | The risk of network congestion is high |
| System Management | Centralized and distributed | Centralized |
| Latency | Very low latency | High latency |
| Cloud Computing | Fog Computing | Edge Computing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location of data collection, processing, storage | A cluster of data center servers hosted on the internet | Near-edge and core networking, network edge devices, and core networking devices | Network edge, edge devices |
| Computing power | Strong (depend on server cluster) | Weak (depend on network edge device network) | Common (depend on edge device) |
| Responsible for the type of task | Large computation, or long-term storage task | Preprocessing | Real-time processing |
| Focus | Clusters level | Infrastructures level | Things level |
| Handling multiple IoT applications | Supported | Supported | Unsupported |
| Resource contention | Slight | Sligh | Serious |
| Latency | High | Low | Ultra-low |
| Privacy and Security | Low | Low | High |
| Cloud Computing | Fog Computing | Edge Computing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Low (high energy consumption due to data transmission and processing at large-scale data centers) | Medium (optimized for regional energy use) | High (minimizes transmission energy, efficient local processing) |
| Data Transmission Cost | High (large amounts of data sent to cloud centers) | Medium (aggregates and pre-processes data before sending to cloud) | Low (only critical data are sent, reducing bandwidth usage) |
| Scalability | High (scales based on cloud provider infrastructure) | Medium (limited by regional computing capacity) | High (scales as more edge devices are deployed) |
| Resilience to Network Failures | Low (dependent on continuous connectivity) | Medium (operates even if the cloud connection is lost) | High (independent operation with local processing) |
| Uninterrupted Power and Resilience | Requires stable power for data centers; failure may impact multiple applications | Provides flexibility in managing energy at a regional level | Can operate during grid outages, ensuring continuous data processing |
| Integration with Renewable Energy Sources | Supports large-scale renewable energy integration, but with delays in response | Manages regional renewable energy fluctuations, optimizing local usage | Directly interfaces with local renewable sources like microgrids and DERs |
| Data Aggregation and Preprocessing | Minimal (raw data sent to the cloud for analysis) | Moderate (aggregates and filters data before sending) | High (processes critical data locally, reducing transmission needs) |
| Support for Smart Grids | Used for large-scale smart grid analytics and decision-making | Supports regional smart grid operations and energy management | Essential for real-time control of smart grids, managing demand-response programs |
| Support for Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) | Centralized monitoring and optimization of DERs | Enables coordination of distributed energy assets | Direct integration with DERs for local optimization and real-time adjustments |
| Support for Demand Response (DR) Programs | Delayed responses due to cloud processing times | Supports aggregated demand response strategies | Real-time, automated demand response capabilities |
| Ref. No | Container Technology | Edge Node Hardware | ARM Architecture |
|---|---|---|---|
| [91] | Docker | Raspberry Pi 3 Model B | Not specified |
| [99] | Docker, Containerd | Raspberry Pi 4 Model B and Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ | ARM v8 |
| [100] | Docker | Raspberry Pi 3s | ARM Cortex-A53 |
| [101] | KubeEdge, Kubernetes, Docker | ARM64 4-core CPU | ARM64 |
| [102] | KubeEdge | Jetson AGX Xavier, Raspberry Pi 3 | ARM64 |
| [103] | Kubernetes | Raspberry Pi | Not specified |
| [104] | Docker | Raspberry Pi 4 | ARM64 |
| [105] | Container (Not specified) | Apple Mac Mini M1 2020 with Raspberry Pi and 16GB memory | ARM64 |
| [106] | Docker | A Samsung Exynos 5250 SoC with 1.7 GHz Cortex A15 CPU and a non-virtualized host with 2 GB of memory | ARMv7 |
| [107] | Kubernetes (K3S), Docker | Raspberry Pi 4 B+ | ARM,x86 |
| [108] | Kubernetes | Raspberry Pi | ARM |
| Platform | Virtualization Technique | Owners |
|---|---|---|
| EdgeX over Kubernetes [114,115] | Container | Linux (San Francisco, CA, USA) |
| FocusStack [116] | Container | Not specified |
| Akraino Edge Stack [117] | Container and Virtual Machine | Linux (San Francisco, CA, USA) |
| Azure IoT Edge [118] | Container | Microsoft (Redmond, WA, USA) |
| KubeEdge [119] | Container | Huawei (Shenzhen, China) |
| Cord [120] | Container and Virtual Machine | Open Network Foundation (Menlo Park, CA, USA) |
| AWS IoT Greengrass [121] | Container | Amazon (Seattle, WA, USA) |
| OpenEdge [122] | Container | Not specified |
| VideoEdge [123] | Container | Microsoft (Redmond, WA, USA) |
| Application Protocol | Publish/Subscribe | Request/Response | Transport | Security | Quality of Service(QoS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constrained Application Protocol (COAP) | Yes | Yes | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) | DTLS (Datagram Transport Layer Security) | Yes |
| Minimum Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) | Yes | No | TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) | Yes |
| Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) | Yes | No | TCP | SSL | Yes |
| Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) | Yes | Yes | TCP | SSL | No |
| Productions | Owners |
|---|---|
| TPU | |
| DianNao family | Cambrain |
| Turing GPUs | NVIDIA Corporation |
| 7 Series FPGA | Xilinx |
| HiSilicon Ascend Series | Huawei |
| Exynos 9820 | Samsung |
| Xeon D-2100 | Intel |
| TrueNorth | IBM |
| Ref. No | Scenarios | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| [152] | Data Transmission | Centralized Software Defined Network (SDN) and EC |
| [153] | Data Transmission | TATSR |
| [154] | Data Transmission | Optimal Power Allocation Strategy with Transmission Power Constraints |
| [155] | Data Transmission | Information/Digital Technologies and Artificial Intelligence Planning Techniques |
| [156] | Data Transmission | ANN and VVC and EC |
| [157] | Data Transmission | VVC and Reactive Power Control |
| [158] | Data Transmission | Voltage Stability |
| [159] | Data Transmission | Zigbee Wireless Communication and EC |
| [161] | Monitoring and Control | Transient Electromechanical Simulation |
| [162] | Monitoring and Control | Reactive Power Condition Online Monitoring and EC |
| [163] | Monitoring and Control | A priori Frequent Item Set Algorithm and EC |
| [165] | Monitoring and Control | PD-IoT System |
| [217] | Monitoring and Control | A GA Based on Predator Search Strategy |
| [172] | Microgrid System | Model-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning (MDRL) and EC |
| [173] | Microgrid System | MADRL |
| [174] | Microgrid System, Fault Location | Radial Basis Neural Network Function |
| [175] | Microgrid System, Fault Location | DRL and EC |
| [176] | Microgrid System | ML Algorithm and EC |
| [178] | Microgrid System, Smart Metering System | Hierarchical Decision-Making Strategy Based on Prediction Strategy and Task Grading (HDTG) and Real-Time Electricity Price Forecast |
| [179] | Microgrid System | Edge-AI Algorithm |
| [180] | Microgrid System | Neural-Network-Based Identification Scheme |
| [183] | Smart Metering System | NILM |
| [185] | Smart Metering System | 6LoWPAN Protocol and EC |
| [187] | Smart Metering System | DL and EC |
| [189] | Smart Metering System | Knowledge-based Usage Strategy for Smart Meters |
| [191] | Smart Metering System | EC in Long Range (LoRa) and DL Based Compression–Decompression Model |
| [193] | Anomaly Detection | DT to Filter the Abnormal Data |
| [195] | Anomaly Detection | Polynomial Regression and Gaussian Distribution |
| [196] | Anomaly Detection | KDDCUP99 Datasets |
| [202] | State Estimation | FL Framework for False Data Injection |
| [204] | State Estimation | Data-Driven Algorithm |
| [205] | State Estimation | Genetic Algorithm III (NSGA-III) |
| [208] | Energy Management System | Privacy-Preserving Average Consensus Algorithm |
| [209] | Energy Management System | FL and DRL Algorithms |
| [210] | Energy Management System | Reinforcement Learning Algorithm |
| [211] | Energy Management System | Stackelberg and Lyapunov Algorithms |
| [212] | Fault Location | TWAM |
| [218] | Fault Location | Power Signal Fault Signal Analysis and EC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yıldırım, F.; Yalman, Y.; Bayındır, K.Ç.; Terciyanlı, E. Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing for Power Systems: State of the Art, Architecture, and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084592
Yıldırım F, Yalman Y, Bayındır KÇ, Terciyanlı E. Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing for Power Systems: State of the Art, Architecture, and Applications. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084592
Chicago/Turabian StyleYıldırım, Fatma, Yunus Yalman, Kamil Çağatay Bayındır, and Erman Terciyanlı. 2025. "Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing for Power Systems: State of the Art, Architecture, and Applications" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084592
APA StyleYıldırım, F., Yalman, Y., Bayındır, K. Ç., & Terciyanlı, E. (2025). Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing for Power Systems: State of the Art, Architecture, and Applications. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084592