A Contribution to the Temperature Particles Method—Implementation of a Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) Model for the Temperature Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
3. Numerical Solution: The Temperature Particles Method (TPM)
3.1. Particles Generation
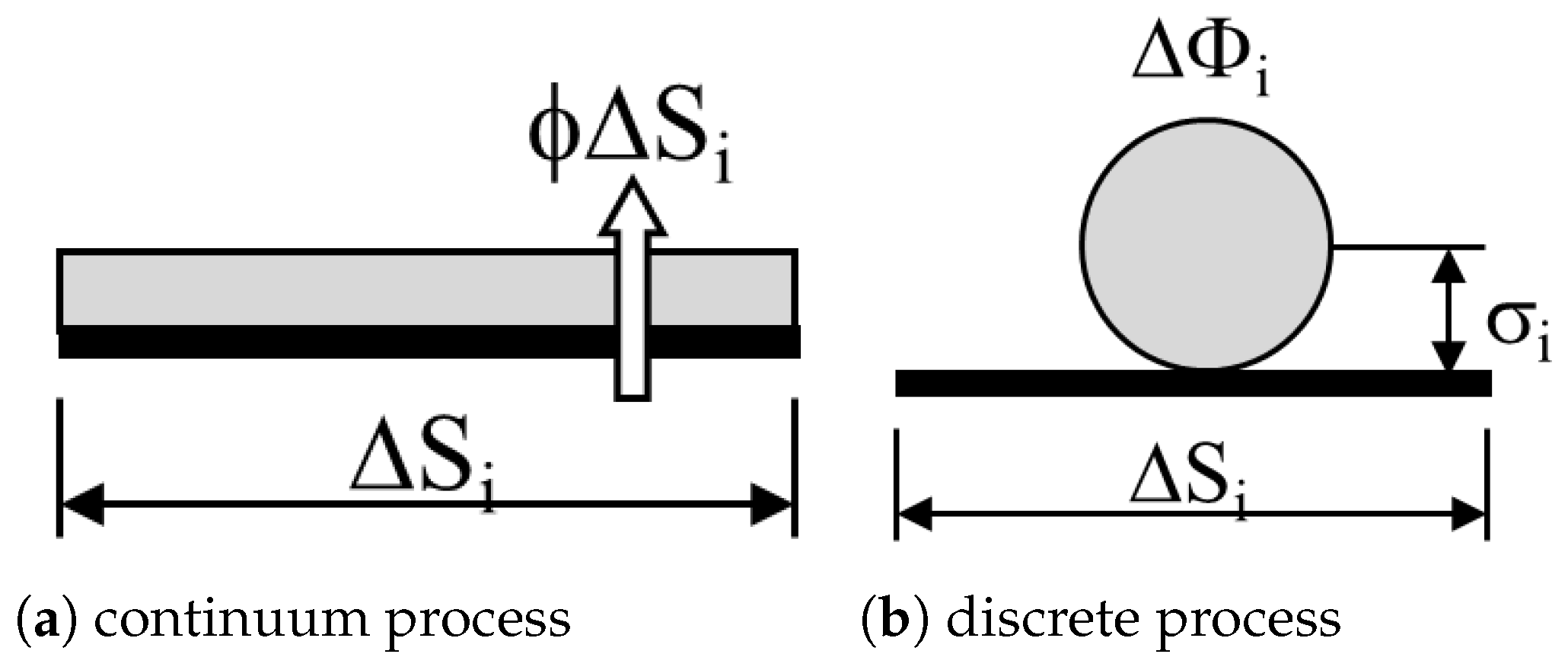
3.2. Solid Surface Representation
3.3. Viscous Splitting Algorithm
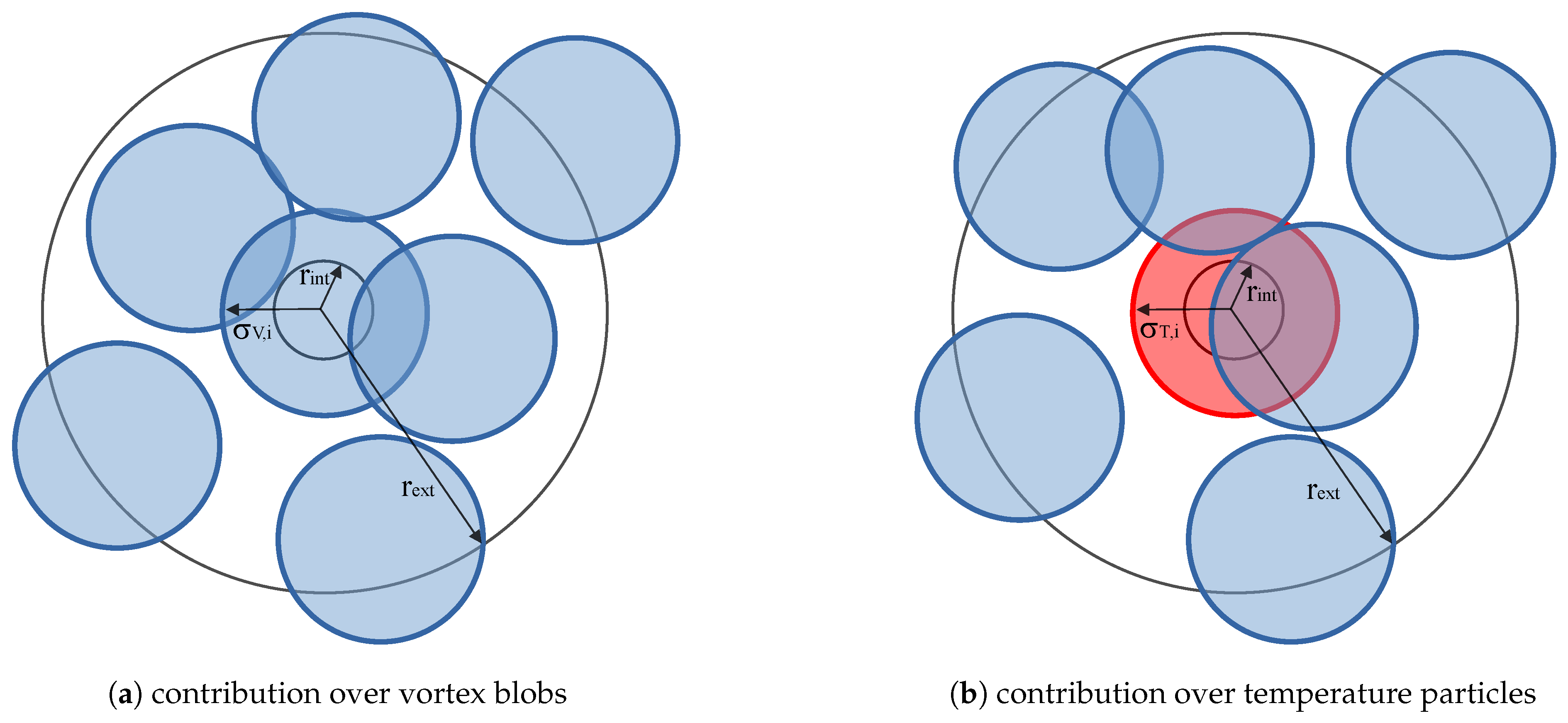
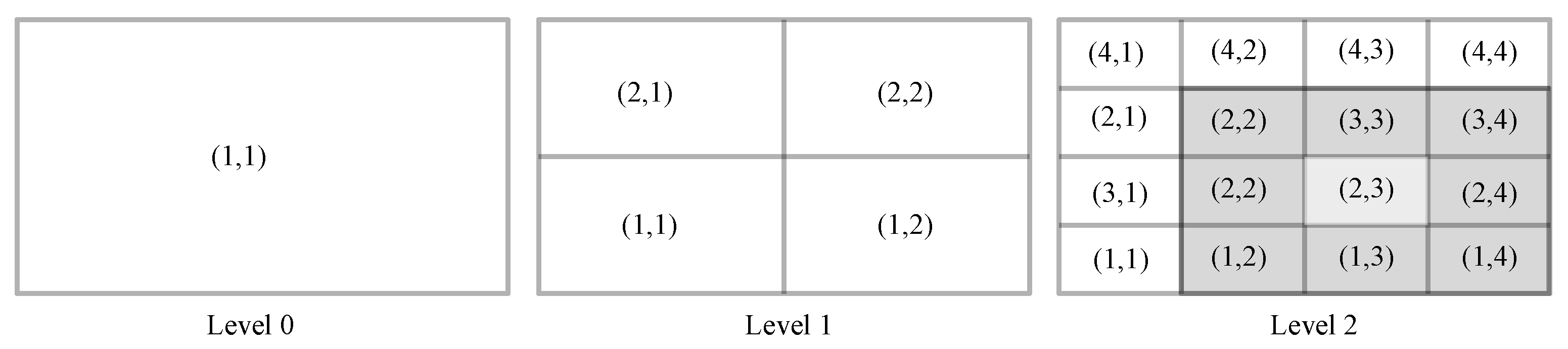
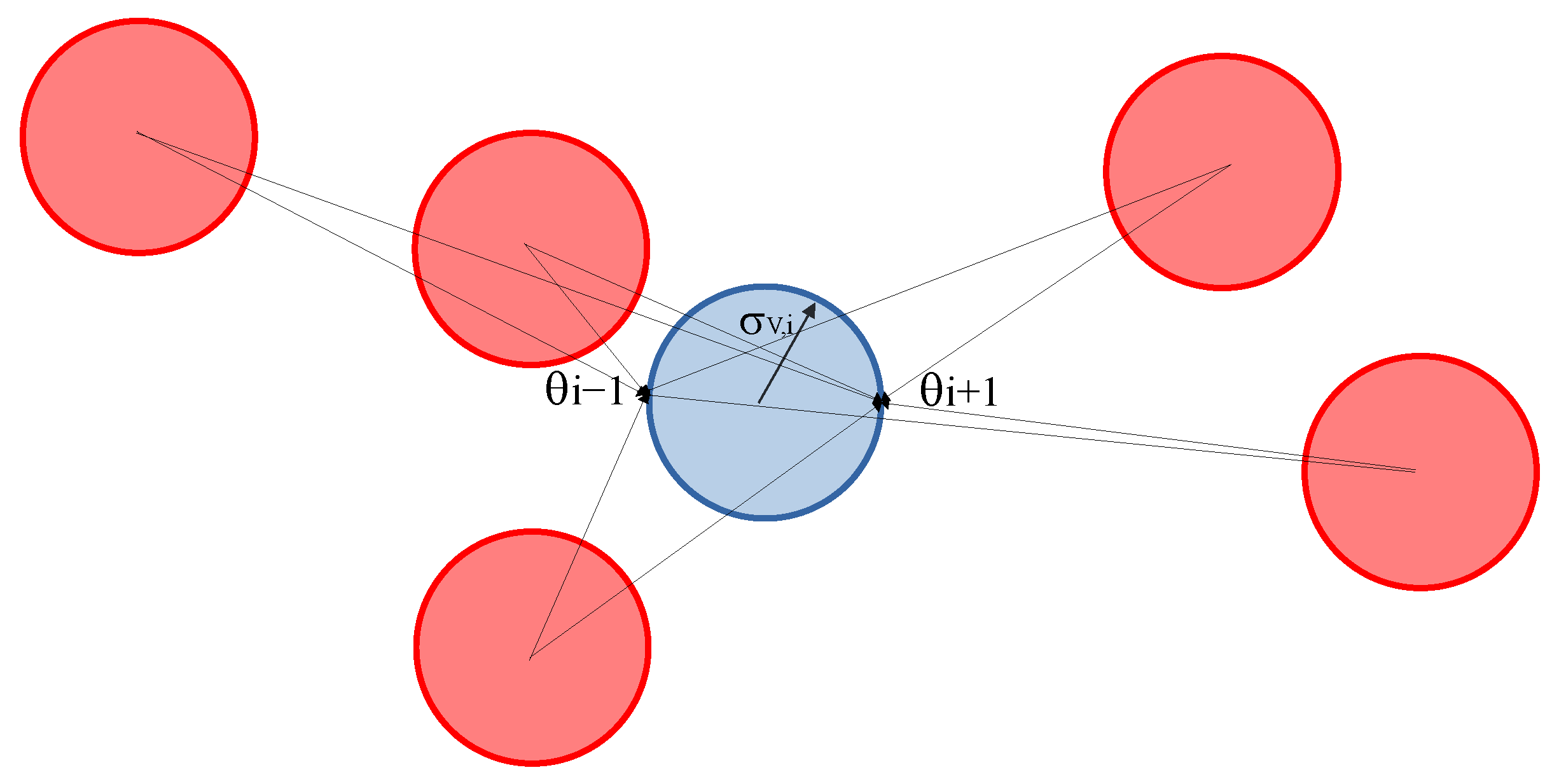
3.4. Turbulence Modeling
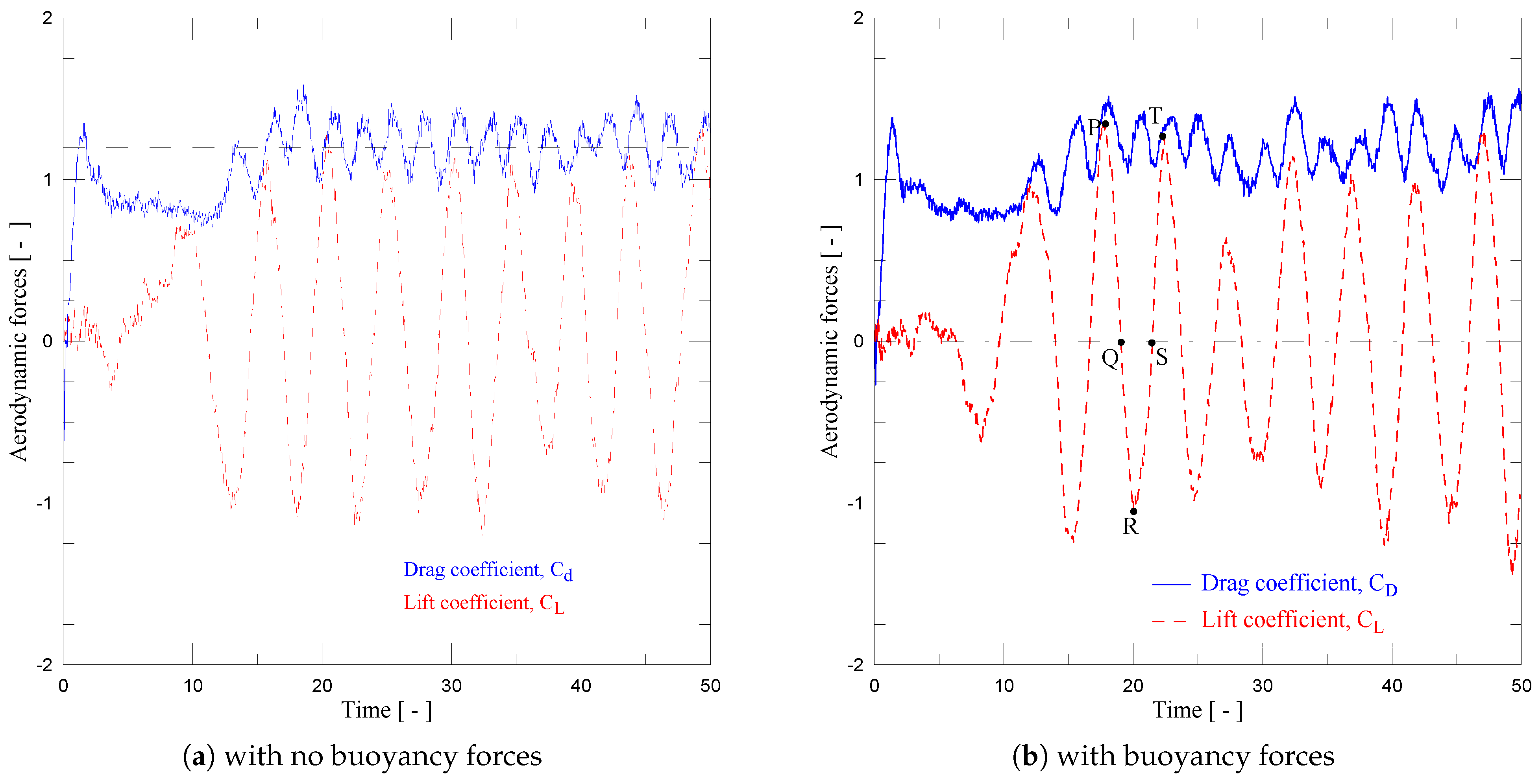
3.5. Buoyancy Forces
3.6. Pressure Field and Aerodynamic Forces
4. Results and Discussion
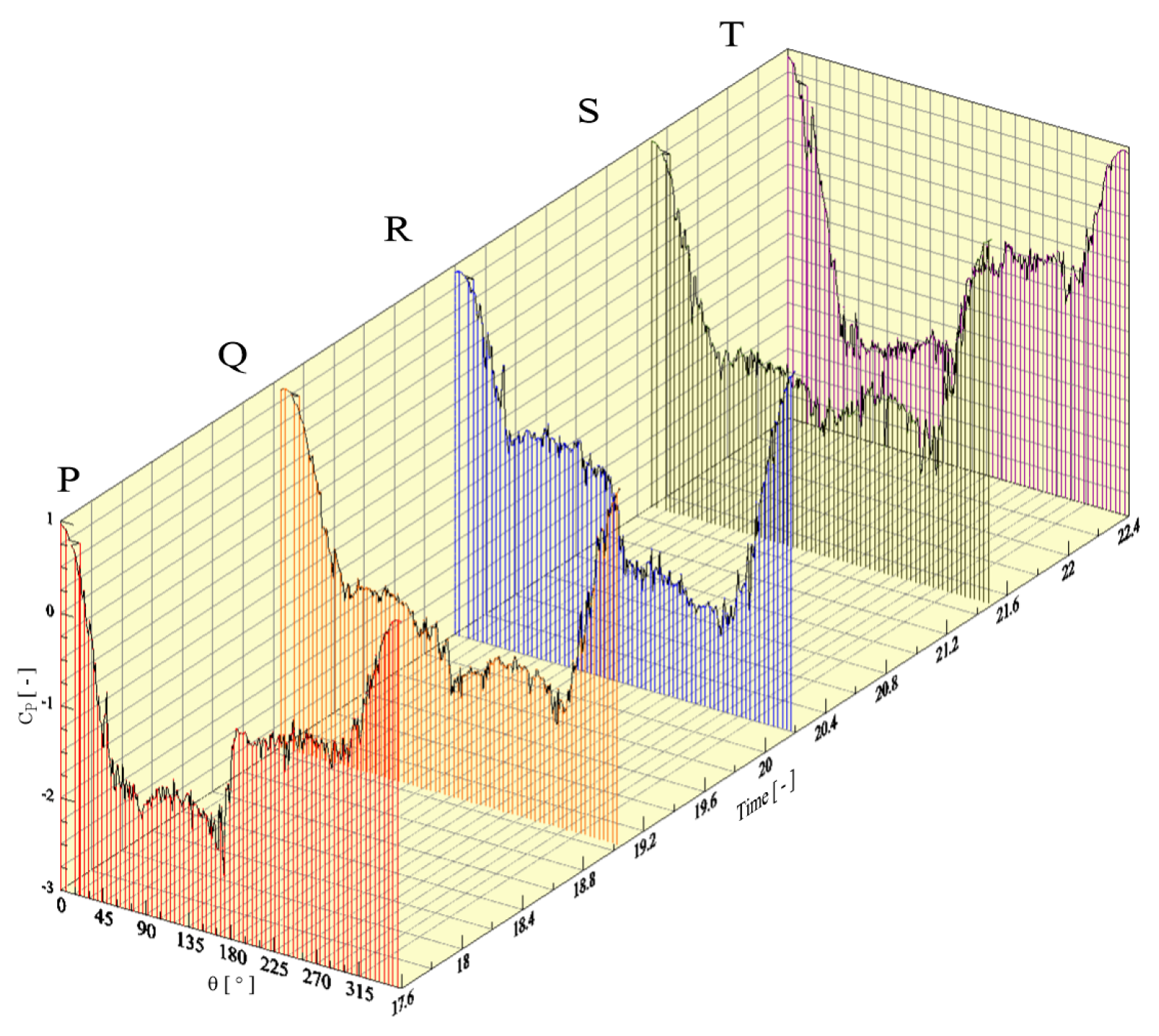
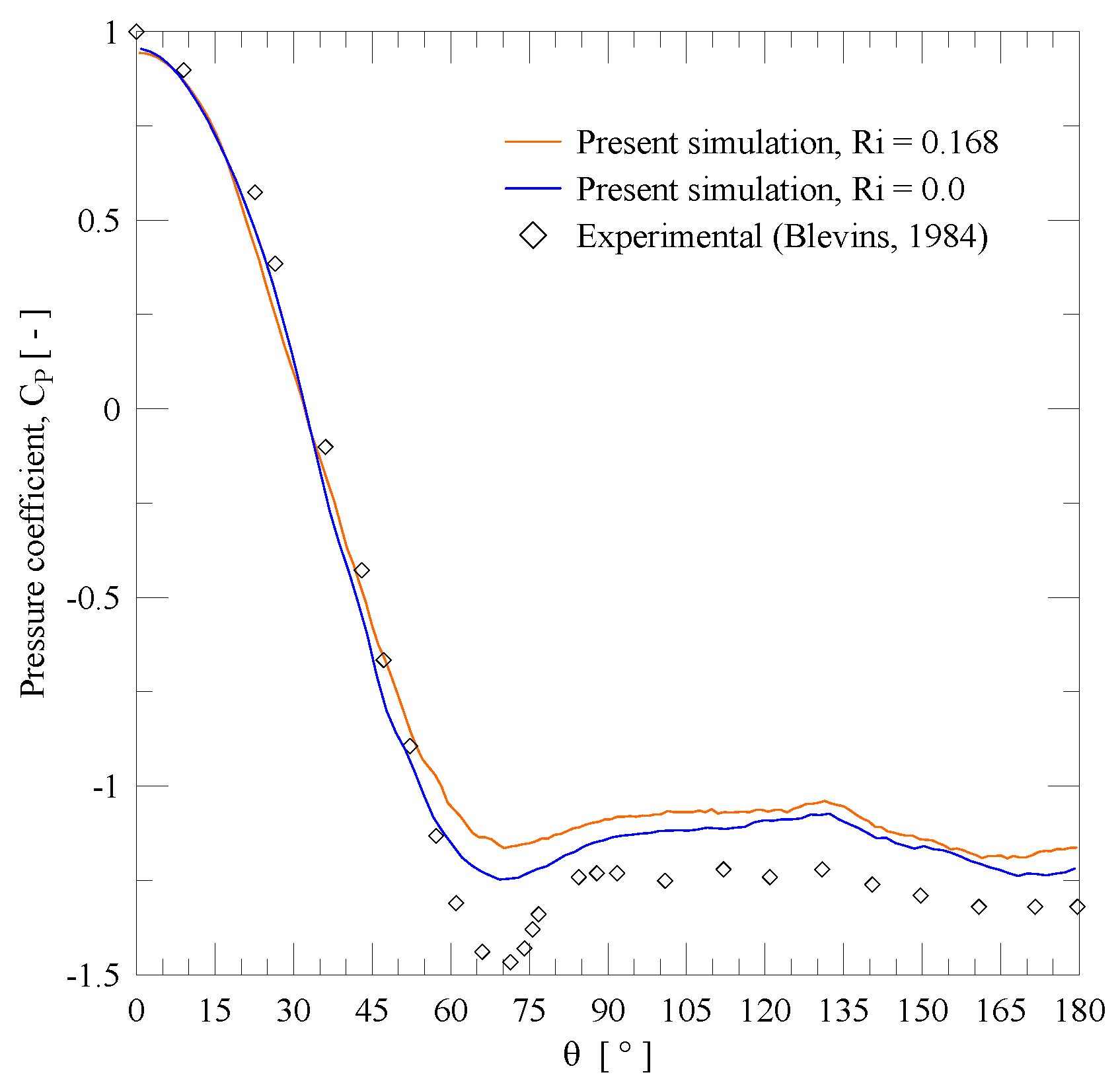
4.1. Single Circular Cylinder
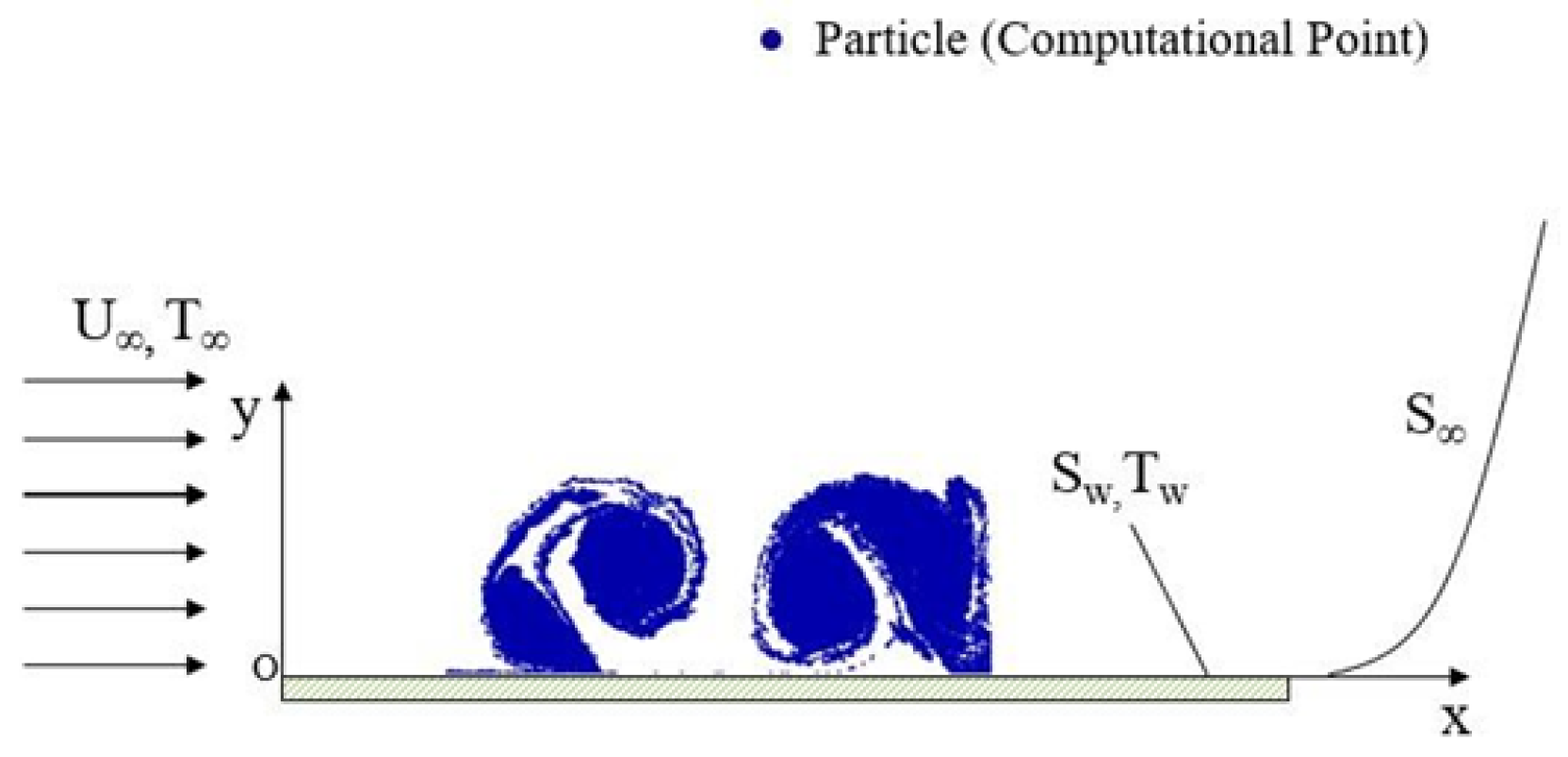
4.2. Airplane Wingtip Vortices
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUDA | Compute Unified Device Architecture |
| DVM | Discrete Vortex Method |
| FMM | Fast Multipoles Method |
| FSI | Fluid–Structure Interaction |
| LES | Large-Eddy Simulation |
| RWM | Random-Walk Method |
| SGS | Sub-Grid-Scale |
| TPM | Temperature Particles Method |
| VIV | Vortex-Induced Vibrations |
References
- Kamemoto, K. On contribution of advanced vortex element methods toward virtual reality of unsteady vortical flows in the new generation of CFD. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2004, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Alcântara Pereira, L.; Recicar, J.; Moura, W. High Reynolds number oscillations of a circular cylinder. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2008, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, R.; Narumi, T.; Sakamaki, R.; Kameoka, S.; Obi, S.; Yasuoka, K. Fast Multipole Methods on a Cluster of GPUs for the Meshless Simulation of Turbulence. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, S.; Lakkis, I. An Adaptive Error-Controlled Hybrid Fast Solver for Regularized Vortex Methods. J. Comput. Phys. 2022, 468, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchevsky, I.; Ryatina, E.; Kolganova, A. Fast Barnes-Hut-Based Algorithm in 2D Vortex Method of Computational Hydrodynamics. Comput. Fluids. 2023, 366, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; He, X.; Tong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, B. Neural Vortex Method: From Finite Lagrangian Particles to Infinite Dimensional Eulerian Dynamics. Comput. Fluids 2023, 258, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, A. Numerical Study of Slightly Viscous Flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1973, 57, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoniem, A.F.; Sherman, F.S. Grid-free simulation of diffusion using random walk methods. J. Comput. Phys. 1985, 61, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamemoto, K.; Miyasaka, T. Development of a Vortex and Heat Elements Method and its Application to Analysis of Unsteady Heat Transfer around a Circular Cylinder in a Uniform Flow. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Vortex Method, Kobe, Japan, 4–5 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ogami, Y. Simulation of heat-fluid motion by the vortex method. JSME Int. J. 2001, 44, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.G.d.; Oliveira, M.A.d.; Bimbato, A.M.; Alcântara Pereira, L.A. A Lagrangian Description of Buoyancy Effects on Aircraft Wake Vortices from Wing Tips near a Heated Ground Plane. Energies 2022, 15, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimeau, C.; Mortazavi, I. A Review of Vortex Methods and Their Applications: From Creation to Recent Advances. Fluids 2021, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsipur, S.; Ramesh, K.; Gopalarathnam, A.; Edwards, J.R. Discrete vortex modeling of perching and hovering maneuvers. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2023, 37, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J. Discrete Vortex Method-Based Fish-Like Locomotion Modeling. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 49, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Padhee, S.S.; Samanta, D. Aerodynamic performance and flow mechanism of 3D flapping wing using discrete vortex method. J. Fluids Struct. 2024, 127, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, H.C.; Gao, D.L.; Li, R. Numerical simulation of vortex-induced vibration of deepwater drilling riser based on discrete vortex method. Pet. Sci. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.F.M.d.; Vidille, M.F.; Bimbato, A.M.; Alcântara Pereira, L.A. Lagrangian Vortices Interactions Using Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) and Surface Roughness Model—Application for Aircraft Wake Vortices with Crosswind. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métais, O.; Lesieur, M. Spectral large-eddy simulation of isotropic and stably stratified turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 239, 157–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcântara Pereira, L.; Hirata, M.; Silveira Neto, A. Vortex Method with Turbulence Sub-Grid Scale Modelling. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2003, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.; Plotkin, A. Low Speed Aerodynamics: From Wing Theory to Panel Methods; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, P.K. Fluid Mechanics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fourier, J.B. Theorie Analytique de la Chaleur (1822); Freeman, A., Translator; Dover Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Ferziger, J.H. Numerical Methods for Engineering Application; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Shintani, M.; Akamatsu, T. Investigation of Two Dimensional Discrete Vortex Method with Viscous Diffusion Model. Comput. Fluid Dyn. J. 1994, 3, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerrard, J.H. The mechanics of the formation region of vortices behind bluff bodies. J. Fluid Mech. 1966, 25, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumer, B.; Fredsøe, J. Hidrodynamics around Cylindrical Structures. Adv. Ser. Ocean. Eng. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Zindashti, G.; Kurç, O. Flow past rotating cylinders using deterministic vortex method. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 291, 116342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranay, A.; Demirhan, A.; Dobrucali, E.; Kinaci, K.O. A review on vortex-induced vibrations in confined flows. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 285, 115309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameshwaran, R.; Dhulipalla, S.; Yendluri, D. Fluid-structure Interactions and Flow Induced Vibrations: A Review. Procedia Eng. 2016, 144, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, S.; Hayatdavoodi, M.; Esfahani, J.A. Vortex shedding suppression and wake control: A review. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 126, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics; Dover Publication: Mineola, NY, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.T.; Srnsky, R.A. Laboratory Investigation of Atmospheric Effects on Vortex Wakes; Technical Report 497; Flow Research Inc.: Belleville, ON, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hallock, J.; Holzäpfel, F. A Review of Recent Wake Vortex Research for Increasing Airport Capacity. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2018, 98, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzäpfel, F.; Strauss, L.; Schwarz, C. Assessment of Dynamic Pairwise Wake Vortex Separations for Approach and Landing at Vienna Airport. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.; Vidille, M.; Bimbato, A.; Alcântara Pereira, L. Lagrangian Vortices with Corrected Core-Spreading Method and Large Eddy Simulation (LES). In Proceedings of the 27th ABCM International Congress of Mechanical Engineering, Florianópolis, SC, Brazil, 4–8 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.; Hesse, H.; Wang, P. LES validation on near-field wingtip vortex evolution with wind tunnel characterization at low Reynolds number. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 157, 109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, M.; Metais, O. New Trends in Large-Eddy Simulations of Turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1996, 28, 45–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, J.P.; Lesieur, M. Parameterization of Small Scales of Three Dimensional Isotropic Turbulence Utilizing Spectral Closures. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogami, Y. General Circulation Experiments with the Primitive Equations 1. The basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, A. Vortex methods for flow simulation. J. Comput. Phys. 1980, 37, 289–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimbato, A.; Alcântara Pereira, L.; Hirata, M. Development of a new Lagrangian vortex method for evaluating effects of surfaces roughness. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2019, 74, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, R.D. Applied Fluid Dynamics Handbook; Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.S.; Hanratty, T.J. Velocity gradients at the wall for flow around a cylinder at Reynolds numbers from 5 × 103 to 105. J. Fluid Mech. 1969, 35, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greengard, L.; Rokhlin, V. A fast algorithm for particle simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1987, 73, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, T.R.; Wolf, W.R.; Bimbato, A.M. Fast multipole method applied to Lagrangian simulations of vortical flows. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 51, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.; Magalhaes, E.; Azevedo, A.; dos Santos Paes, L.E.; Oliveira, A. An Implementation of LASER Beam Welding Simulation on Graphics Processing Unit Using CUDA. Computation 2024, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
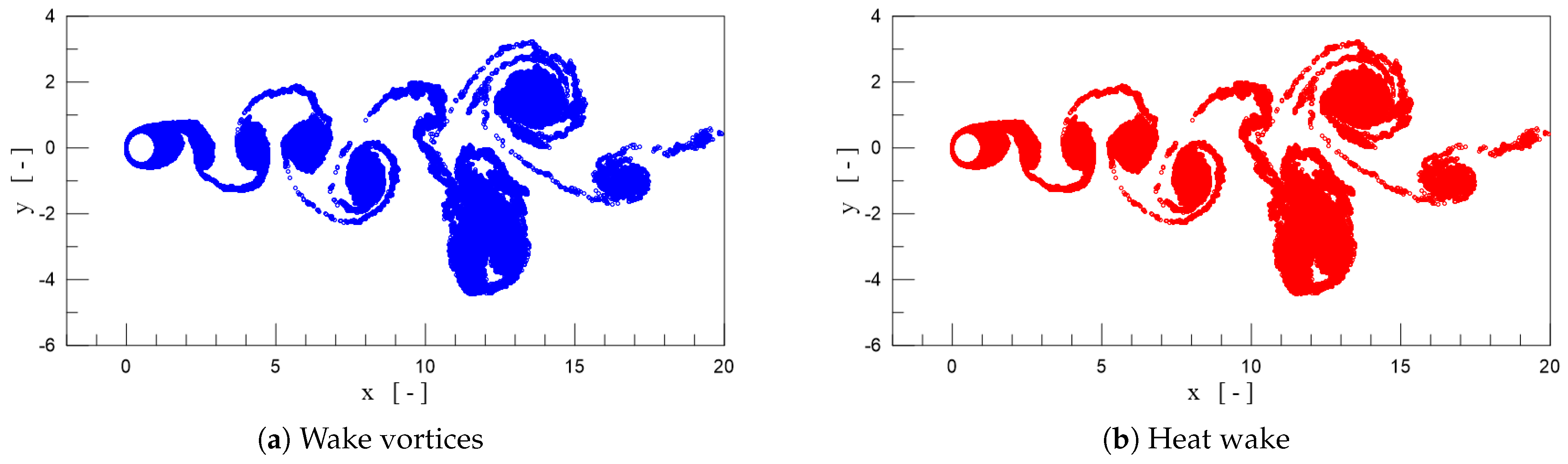
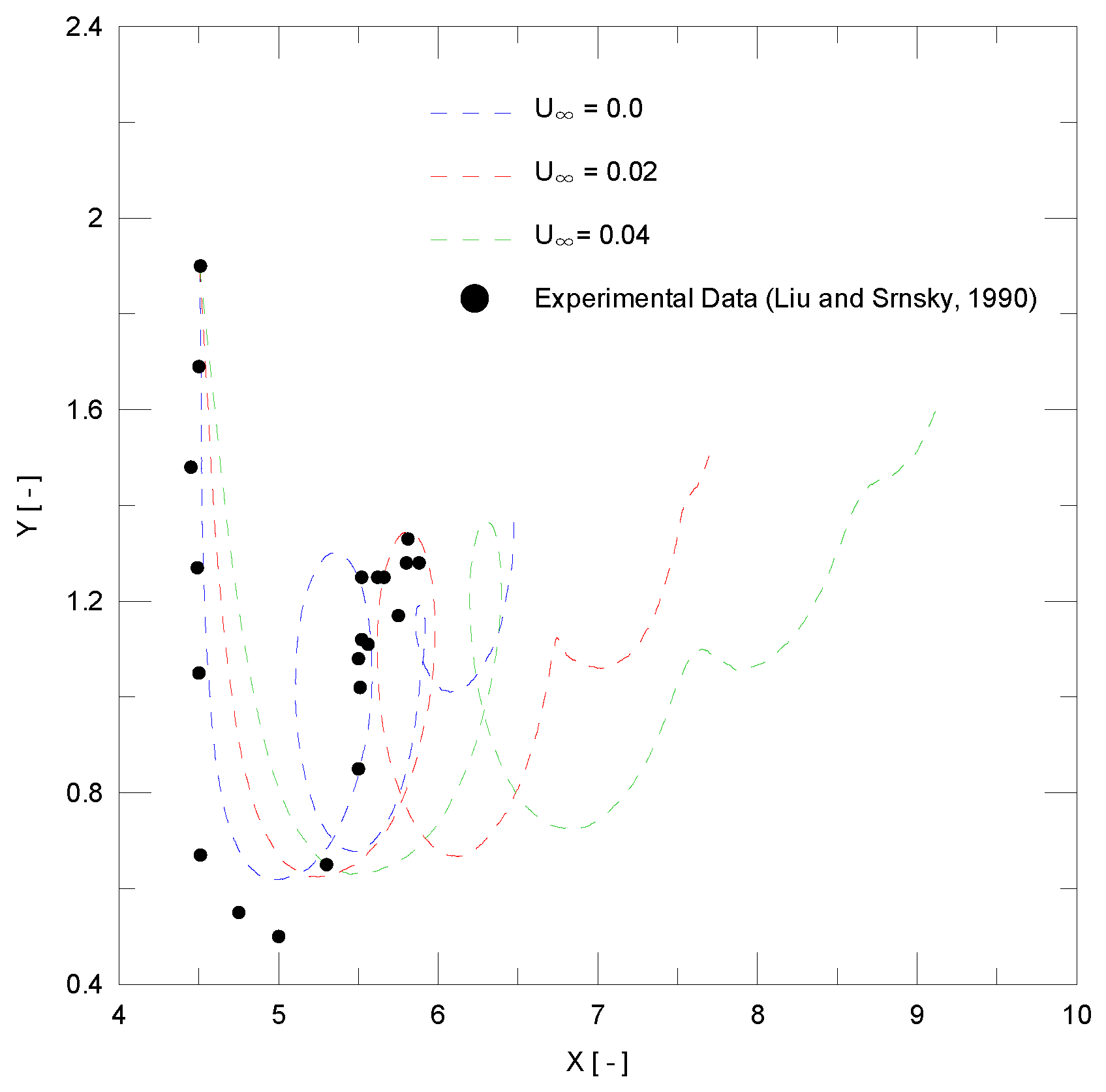
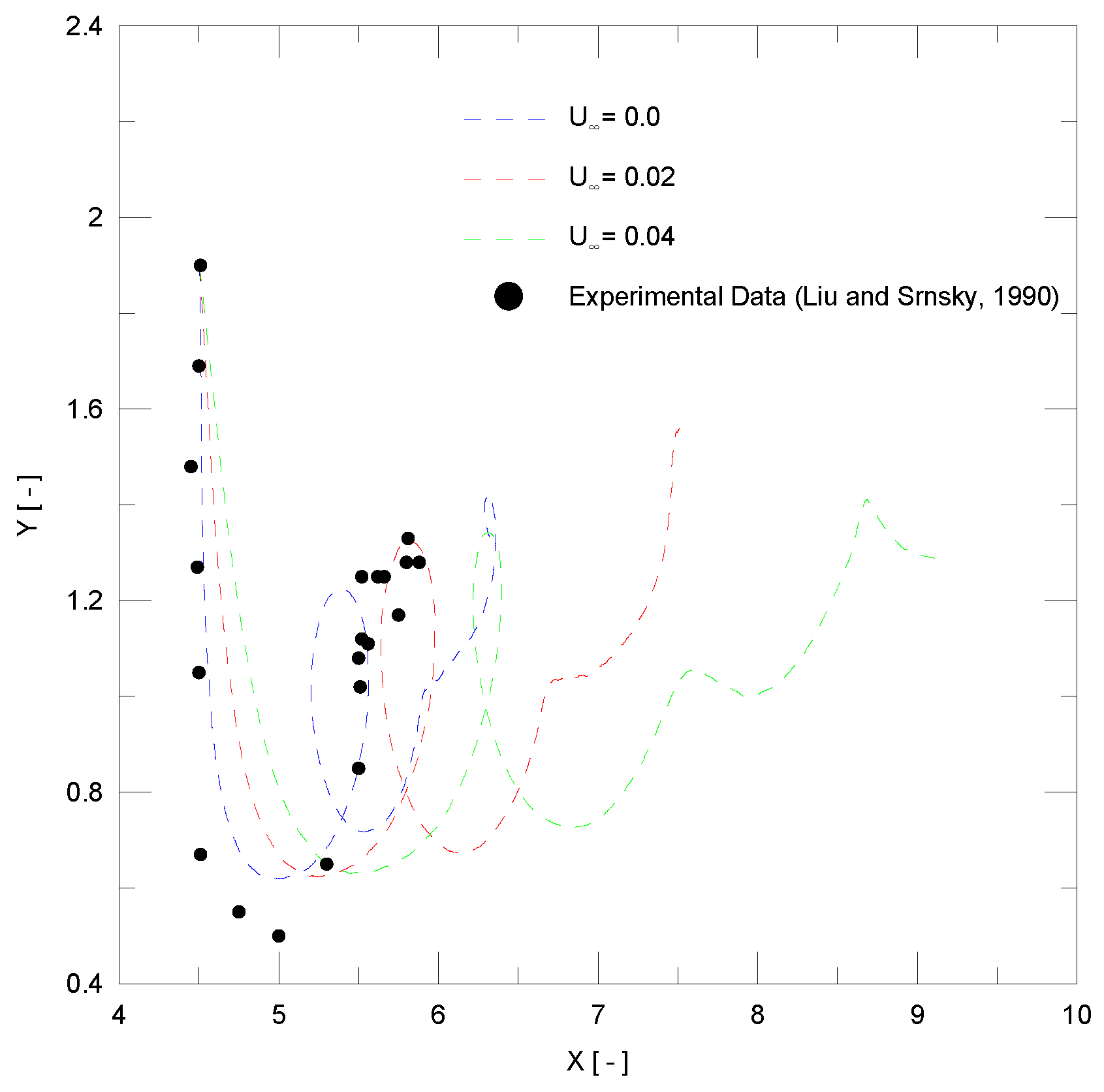
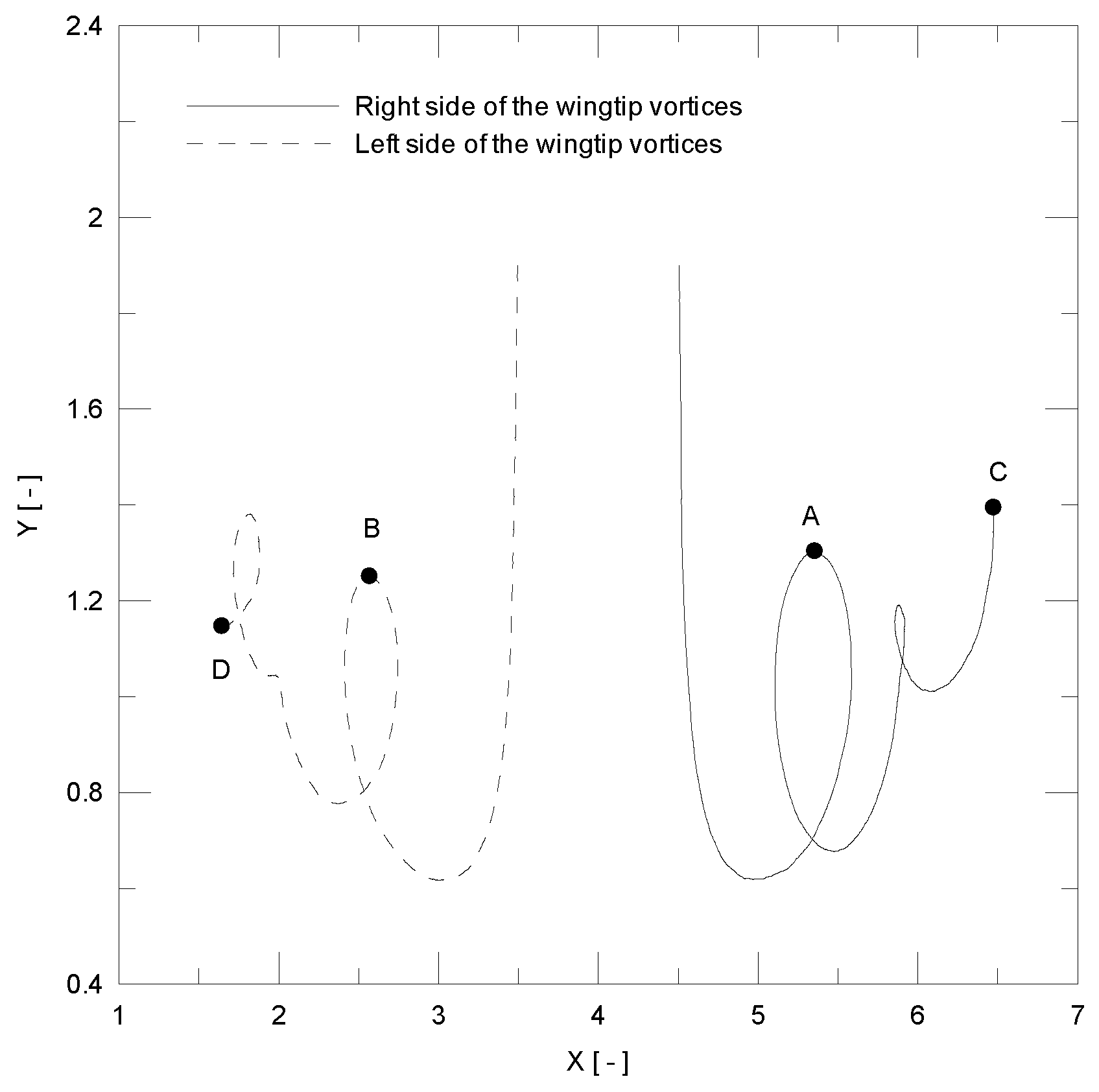
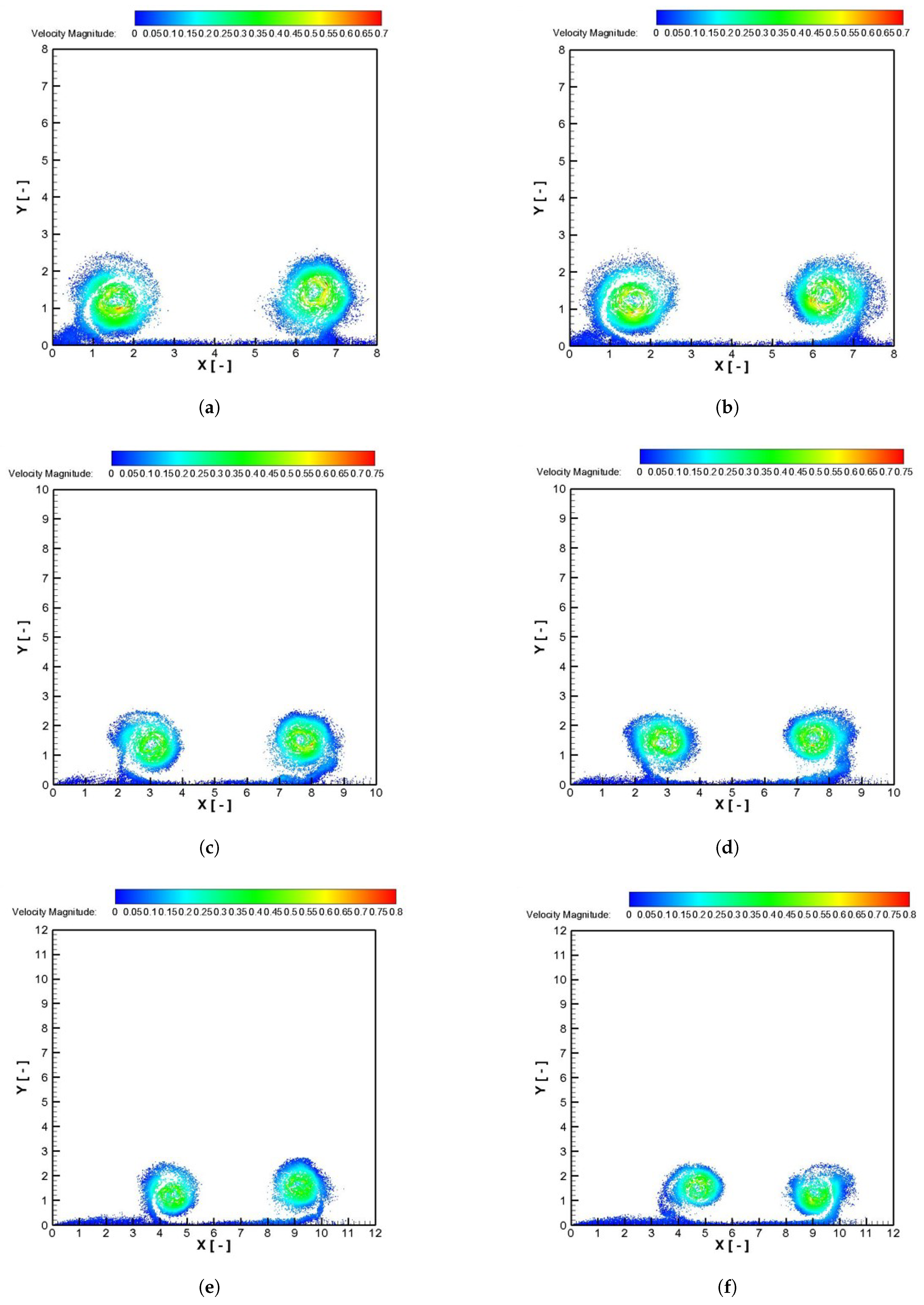
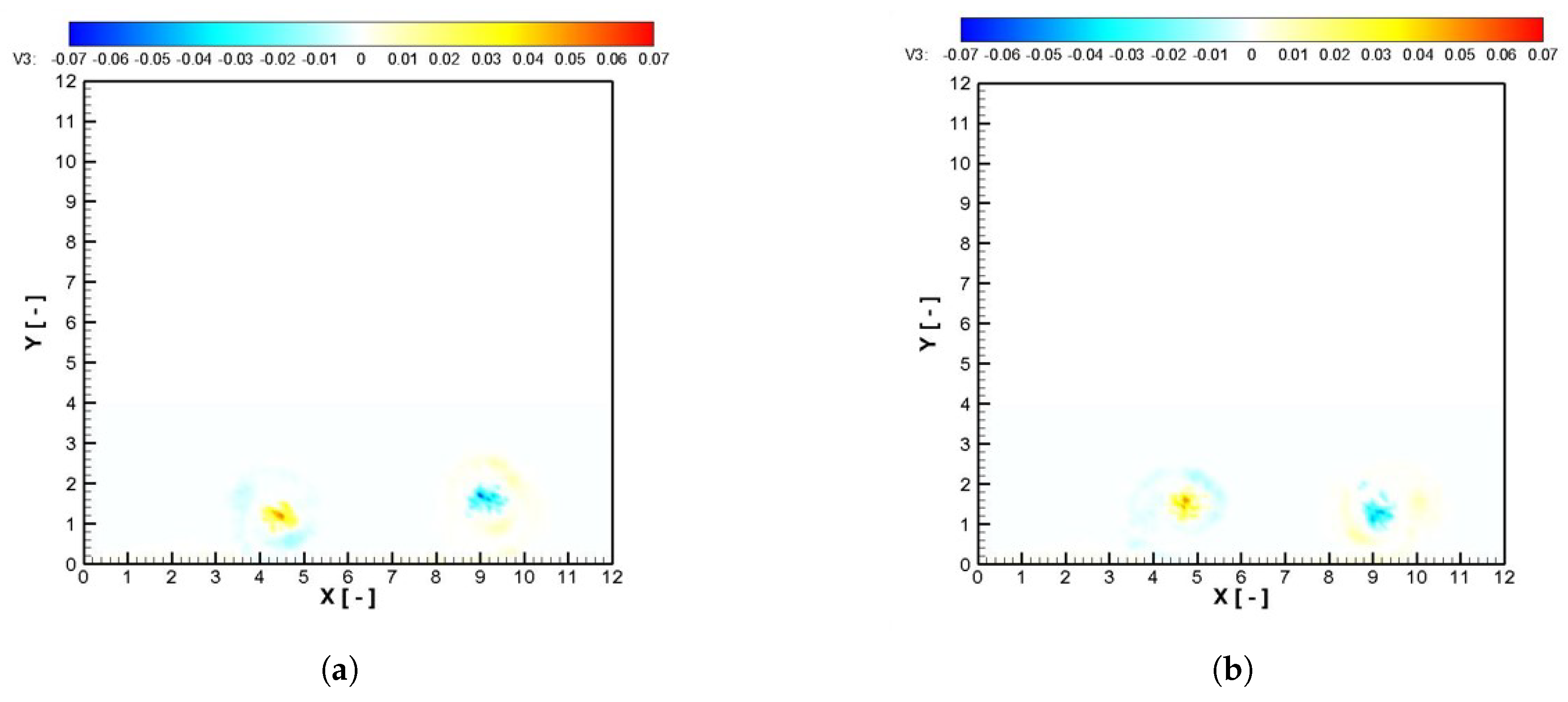
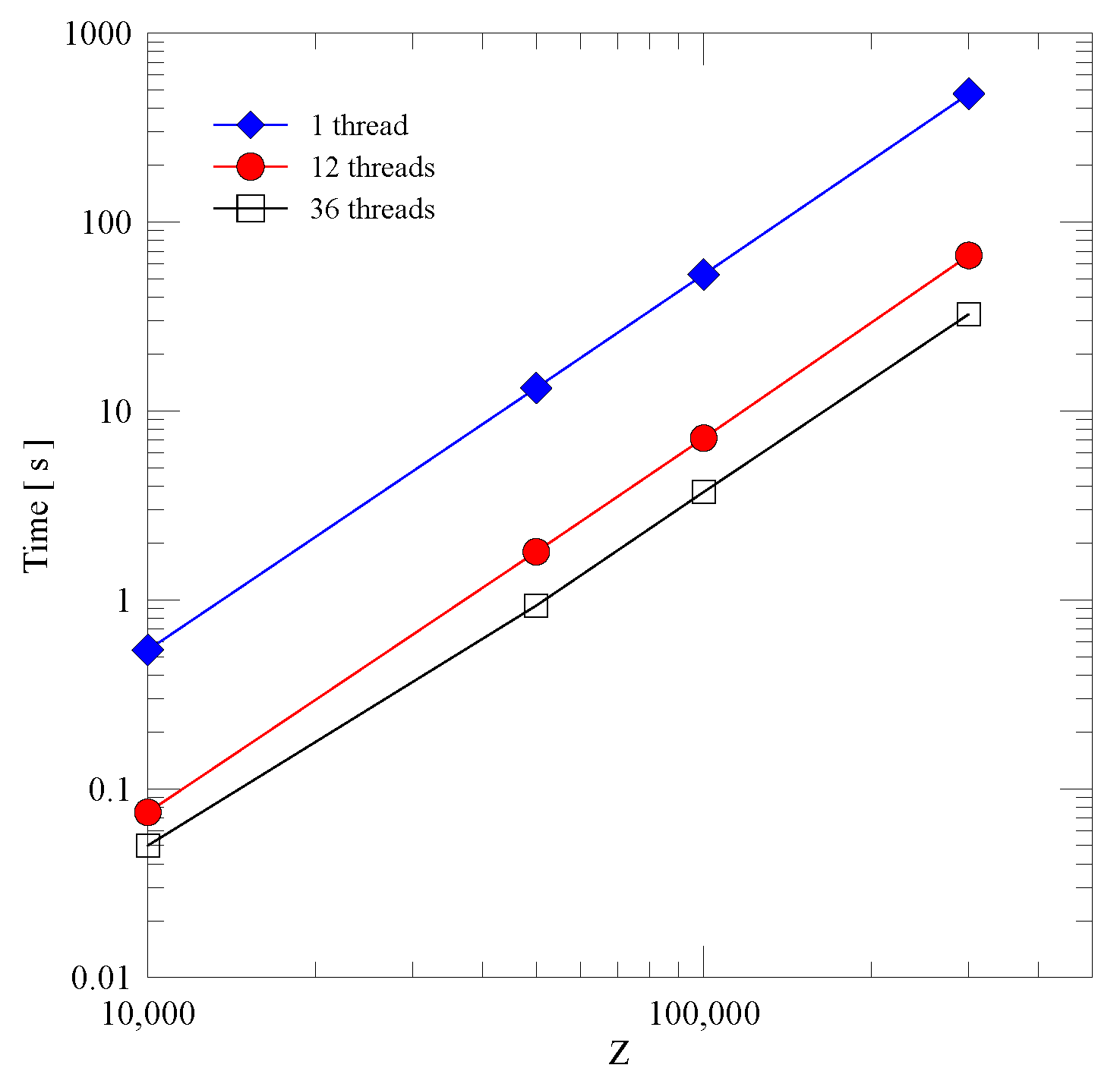
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter (D) | 1.0 |
| Inlet flow velocity () | 1.0 |
| Reynolds number (Re) | 100,000 |
| Prandtl number (Pr) | 0.71 |
| Richardson number (Ri) | 0 and 0.168 |
| Test Case | Ri | St | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | 0.0 | 1.23 | −0.027 | 0.200 |
| (B) | 0.168 | 1.21 | −0.05 | 0.199 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Runway length (L) | 8.0 |
| Release height of the primary vortical structures (h) | 2.0 |
| Center-to-center spacing of the vortical structure pair (b) | 1.0 |
| Core radius of each primary vortical structure (r) | 0.1 |
| Number of flat panels (M) | 40 |
| Number of Lamb vortex elements of each primary vortical structure (N) | 50 |
| Time stepping () | 0.05 |
| Number of time steps (NSteps) | 1500 |
| Core radius of each Lamb vortex () | 0.001 |
| Core radius of each temperature particle () | 0.006 |
| Preheating time () | 1.5 |
| Test Case | Ri | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| (2) | 0.02 | 0.0 |
| (3) | 0.04 | 0.0 |
| (4) | 0.0 | 1.018 |
| (5) | 0.02 | 1.018 |
| (6) | 0.04 | 1.018 |
| Test Case | Points A–B | Points C–D |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | 2.7849 | 4.8974 |
| (2) | 2.7789 | 4.6310 |
| (3) | 2.8429 | 4.5377 |
| (4) | 2.7541 | 4.7548 |
| (5) | 2.7361 | 4.6138 |
| (6) | 2.8274 | 4.3671 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiaradia, T.R.; Carvalho, G.F.M.d.; Bimbato, A.M.; Alcântara Pereira, L.A. A Contribution to the Temperature Particles Method—Implementation of a Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) Model for the Temperature Field. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084122
Chiaradia TR, Carvalho GFMd, Bimbato AM, Alcântara Pereira LA. A Contribution to the Temperature Particles Method—Implementation of a Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) Model for the Temperature Field. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084122
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiaradia, Tiago Raimundo, Gabriel Ferraz Marcondes de Carvalho, Alex Mendonça Bimbato, and Luiz Antonio Alcântara Pereira. 2025. "A Contribution to the Temperature Particles Method—Implementation of a Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) Model for the Temperature Field" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084122
APA StyleChiaradia, T. R., Carvalho, G. F. M. d., Bimbato, A. M., & Alcântara Pereira, L. A. (2025). A Contribution to the Temperature Particles Method—Implementation of a Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) Model for the Temperature Field. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084122







