Optimization of Sensor Targeting Configuration for Intelligent Tire Force Estimation Based on Global Sensitivity Analysis and RBF Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Global Sensitivity Analysis Method
2.1. Variance-Based Global Sensitivity Index
2.2. Efficient Solution Method for Global Sensitivity Indices
3. The Finite Element Model of the Tire Established in ABAQUS
3.1. Establishment of the Tire Finite Element Model
3.2. Validation of the Tire Finite Element Model
4. Tire Force-Sensitive Response Areas and Variables
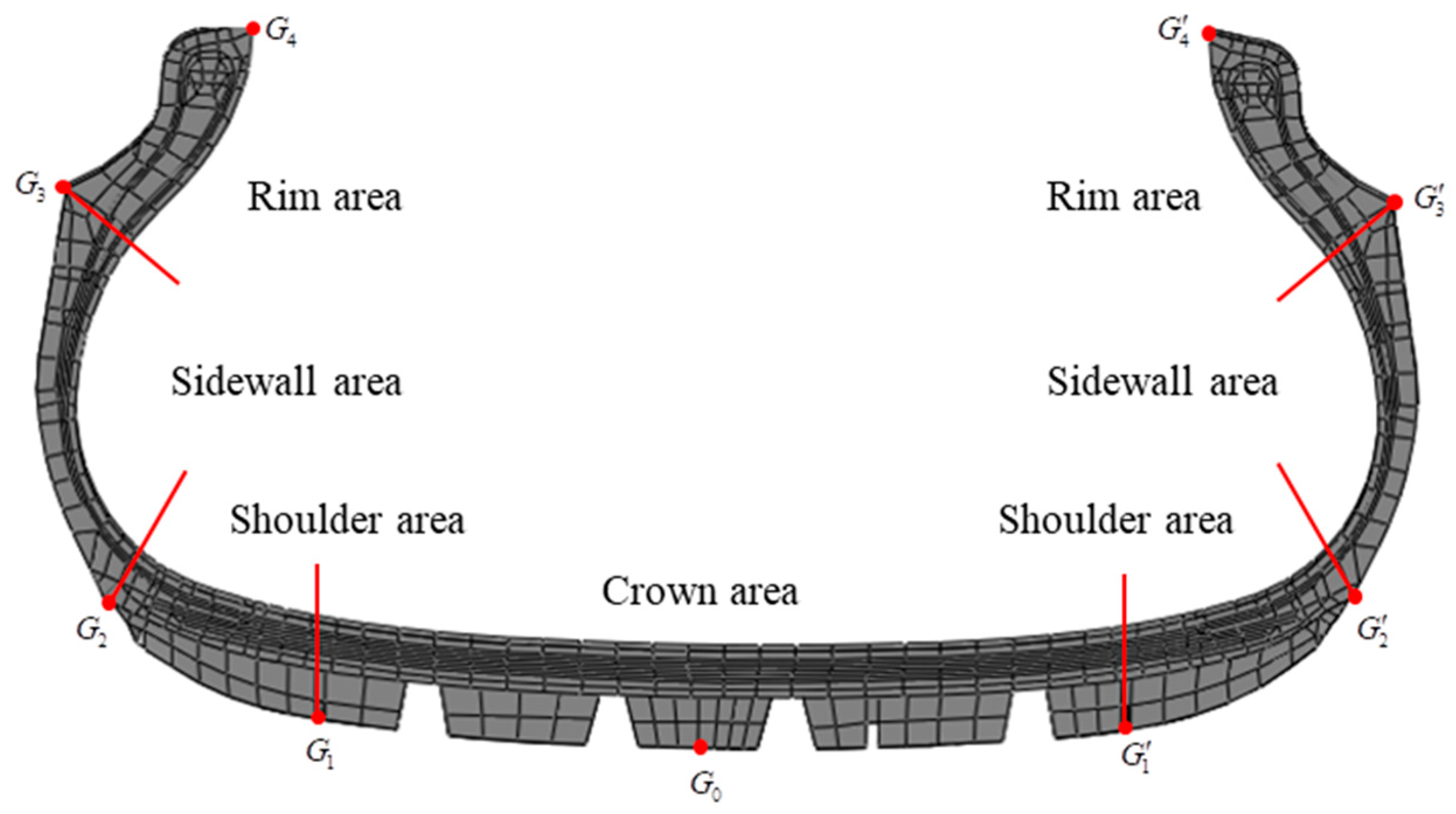
4.1. Division of the Tire Inner Liner Area
4.2. Global Sensitivity Analysis of Tire Forces
5. Intelligent Tire Force Estimation Method
5.1. Analysis of the Characteristics of Longitudinal Force-Sensitive Response Signal Curves
5.1.1. Circumferential Displacement Response Signal in the Crown Area
5.1.2. Radial Acceleration Response Signal in the Sidewall Area
5.2. Analysis of the Characteristics of Lateral Force-Sensitive Response Signal Curves
5.2.1. Lateral Acceleration Response Signal in the Right Sidewall Area
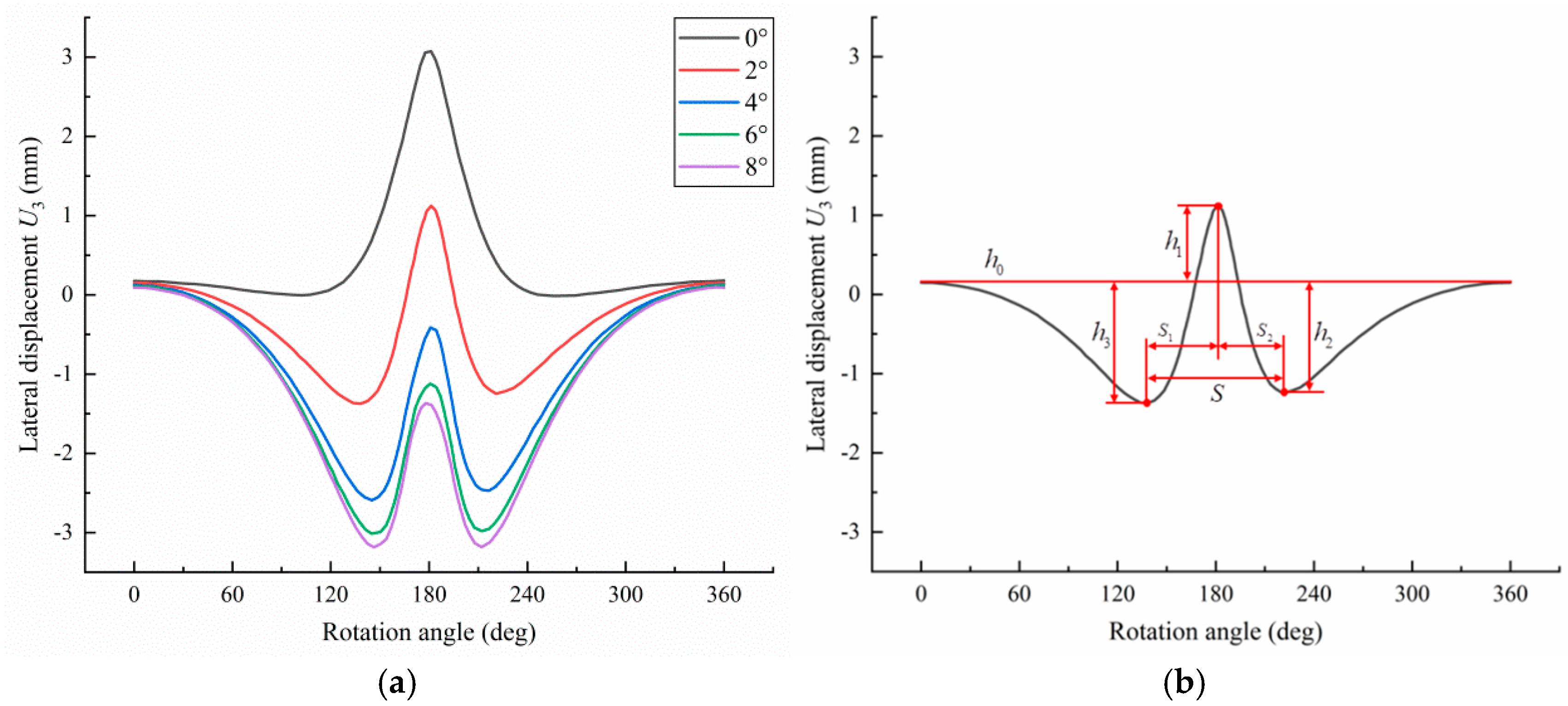
5.2.2. Lateral Displacement Response Signal in the Left Sidewall Area
5.3. RBF Neural Network
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Taheri, S. Intelligent tires-A review of tire characterization literature. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2017, 9, 114–135. [Google Scholar]
- Tuononen, A.J. Optical Position Detection to Measure Tyre Carcass Deflections and Implementation for Vehicle State Estimation. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Hiraoka, N.; Todoroki, A.; Mizutani, Y. Analysis of applied load estimation using strain for intelligent tires. J. Solid Mech. Mater. Eng. 2010, 4, 1496–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Cheli, F.; Leo, E.; Melzi, S.; Sabbioni, E. On the impact of smart tyres on existing ABS/EBD control systems. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2010, 48, 255–270. [Google Scholar]
- Arat, M.A.; Singh, K.B.; Taheri, S. An intelligent tyre based adaptive vehicle stability controller. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2014, 65, 118–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pozuelo, D.; Olatunbosun, O.; Yunta, J.; Yang, X.; Diaz, V. A novel strain-based method to estimate tire conditions using fuzzy logic for intelligent tires. Sensors 2017, 17, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaan, J. Estimation of tyre forces using smart tyre sensors and artificial intelligence. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2018, 76, 110–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, Y.H.; Zhu, B.; Liu, S.L. Estimation algorithm for longitudinal and vertical forces of smart tire with accelerometer embedded. Automot. Eng. 2018, 40, 137–142, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Lin, B.Q.; Liang, G.Q. Tire vertical force estimation based on smart tire system. Tire Ind. 2019, 39, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Khaleghian, S.; Ghasemalizadeh, O.; Taheri, S.; Flintsch, G. A combination of intelligent tire and vehicle dynamic based algorithm to estimate the tire-road friction. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars Mech. Syst. 2019, 12, 81–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, S.W.; Wu, Z.Q.; Wei, S.; Wang, F. Vertical load measurement of automotive intelligent tire. Automot. Eng. 2020, 42, 1270–1276, 1283. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Han, T.; Ma, T. A strain-based method to estimate longitudinal force for intelligent tires by using a physics-based model. J. Mech. Eng. Stroj. Vestn. 2021, 67, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Askari, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Khajepour, A. Tire force estimation in intelligent tires using machine learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 3565–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, A.; Tsurita, T.; Kunii, M. System and Method for Determining Tire Force. U.S. Patent 7,249,498, 31 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, A. Pneumatic Tire with Specifically Arranged Strain Sensors. U.S. Patent 7,513,144, 7 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.N.; Lv, Z.Z.; Wang, W. A review of global sensitivity analysis for uncertainty structure. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2018, 48, 8–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sobol, I.M. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math. Comput. Simul. 2001, 55, 221–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wei, P.; Tang, C.; Wang, P.; Yue, Z. Global sensitivity analysis for multivariate outputs based on multiple response Gaussian process model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 189, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Rosenthal, C.; Rabitz, H. High dimensional model representations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 7765–7777. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, W.; Lu, Z.; Tian, L. A modified variance-based importance measure and its solution by state dependent parameter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2013, 227, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, F.; Janon, A.; Klein, T.; Lagnoux, A. Sensitivity indices for multivariate outputs. C. R. Math. 2013, 351, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cabrejo, O.; Valocchi, A. Global sensitivity analysis for multivariate output using polynomial chaos expansion. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 126, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pandey, M.D. Structural reliability analysis based on the concepts of entropy, fractional moment and dimensional reduction method. Struct. Saf. 2013, 43, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Shen, F.; Zhou, H.C.; Yang, J. Evaluation of tyre pumping noise and design of low noise structure. J. Jilin Univ. Eng. Technol. Ed. 2017, 47, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, C.; Fu, J. Effect of friction model and tire maneuvering on tire-pavement contact stress. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23663-2009; Test Method of Automobile Tyre Longitudinal and Lateral Stiffness. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Xu, N.; Huang, Y.; Askari, H.; Tang, Z. Tire slip angle estimation based on the intelligent tire technology. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pandey, M.D. An effective approximation for variance-based global sensitivity analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 121, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, G.A.; Giveki, D.; Karami, M.; Rastegar, H. Radial basis function neural networks: A review. Comput. Rev. J. 2018, 1, 52–74. [Google Scholar]












| Characteristic Parameter | Experimental Value (mm) | Simulation Value (mm) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact patch length | 147 | 148 | 0.68 |
| Contact patch width | 161 | 163.8 | 1.74 |
| Tire Stiffness | Experimental Value (N/mm) | Simulation Value (N/mm) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radial stiffness | 198.48 | 191.34 | 3.60 |
| Longitudinal stiffness | 132.99 | 122.22 | 8.10 |
| Lateral stiffness | 86.92 | 78.31 | 9.91 |
| Scheme Number | Input Variables | |
|---|---|---|
| Slip Ratio (SR) | Slip Angle (SA) | |
| 1 | 0.47% | 4.0° |
| 2 | 2.31% | 4.0° |
| 3 | 5.0% | 4.0° |
| 4 | 7.69% | 4.0° |
| 5 | 9.53% | 4.0° |
| 6 | 5.0% | 1.8° |
| 7 | 5.0% | 4.0° |
| 8 | 5.0% | 6.2° |
| 9 | 5.0% | 7.6° |
| Model Number | Sensor | Structure of the RBF Neural Network Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Quantity | Type of Input Vector | Size of Input Vector | |
| 1 | Right sidewall | 1 | , | 16 × 200 |
| 2 | Left and right sidewalls | 2 | , , | 23 × 200 |
| 3 | Crown and left/right sidewalls | 3 | , , , | 29 × 200 |
| Model Number | MRE | |
|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal Force (%) | Lateral Force (%) | |
| 1 | 9.59 | 8.73 |
| 2 | 5.83 | 3.69 |
| 3 | 1.42 | 1.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Optimization of Sensor Targeting Configuration for Intelligent Tire Force Estimation Based on Global Sensitivity Analysis and RBF Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073913
Zhang Y, Wang G, Zhou H, Zhang J, Li X, Wang X. Optimization of Sensor Targeting Configuration for Intelligent Tire Force Estimation Based on Global Sensitivity Analysis and RBF Neural Networks. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073913
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Guolin Wang, Haichao Zhou, Jintao Zhang, Xiangliang Li, and Xin Wang. 2025. "Optimization of Sensor Targeting Configuration for Intelligent Tire Force Estimation Based on Global Sensitivity Analysis and RBF Neural Networks" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073913
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, H., Zhang, J., Li, X., & Wang, X. (2025). Optimization of Sensor Targeting Configuration for Intelligent Tire Force Estimation Based on Global Sensitivity Analysis and RBF Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073913






