Impact of Mesh Resolution and Temperature Effects in Jet Ejector CFD Calculations
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Jet Ejector
2.2. Software and Modeling Approach
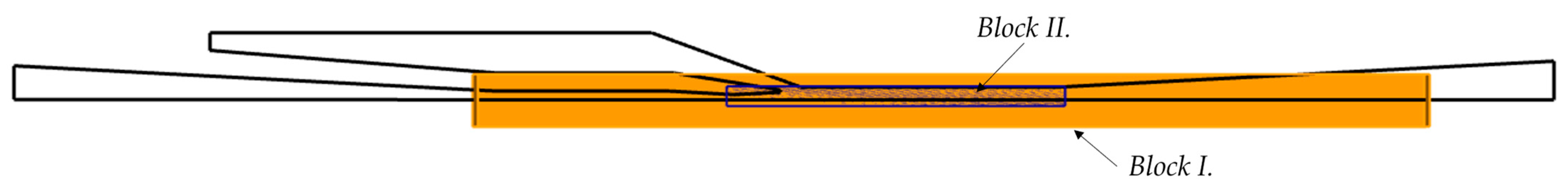
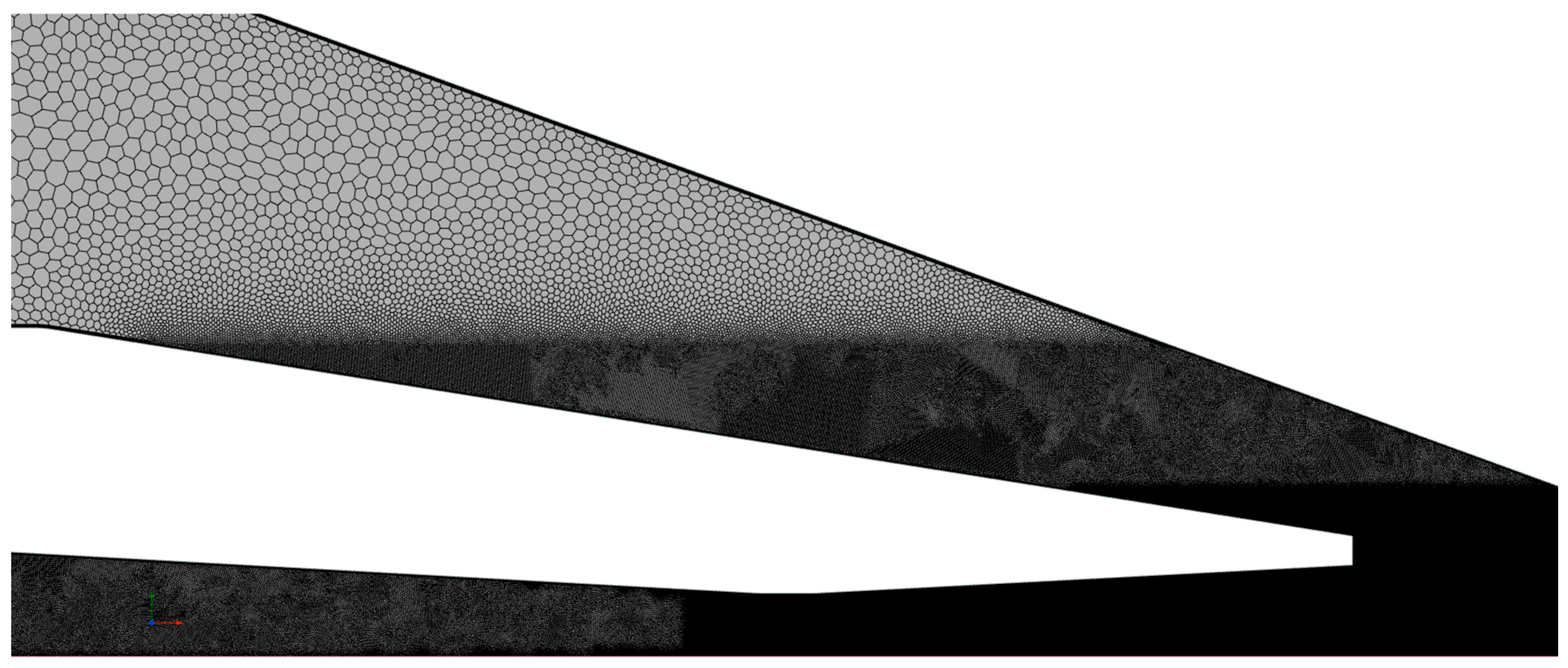
2.3. Mesh
2.4. Governing Equations
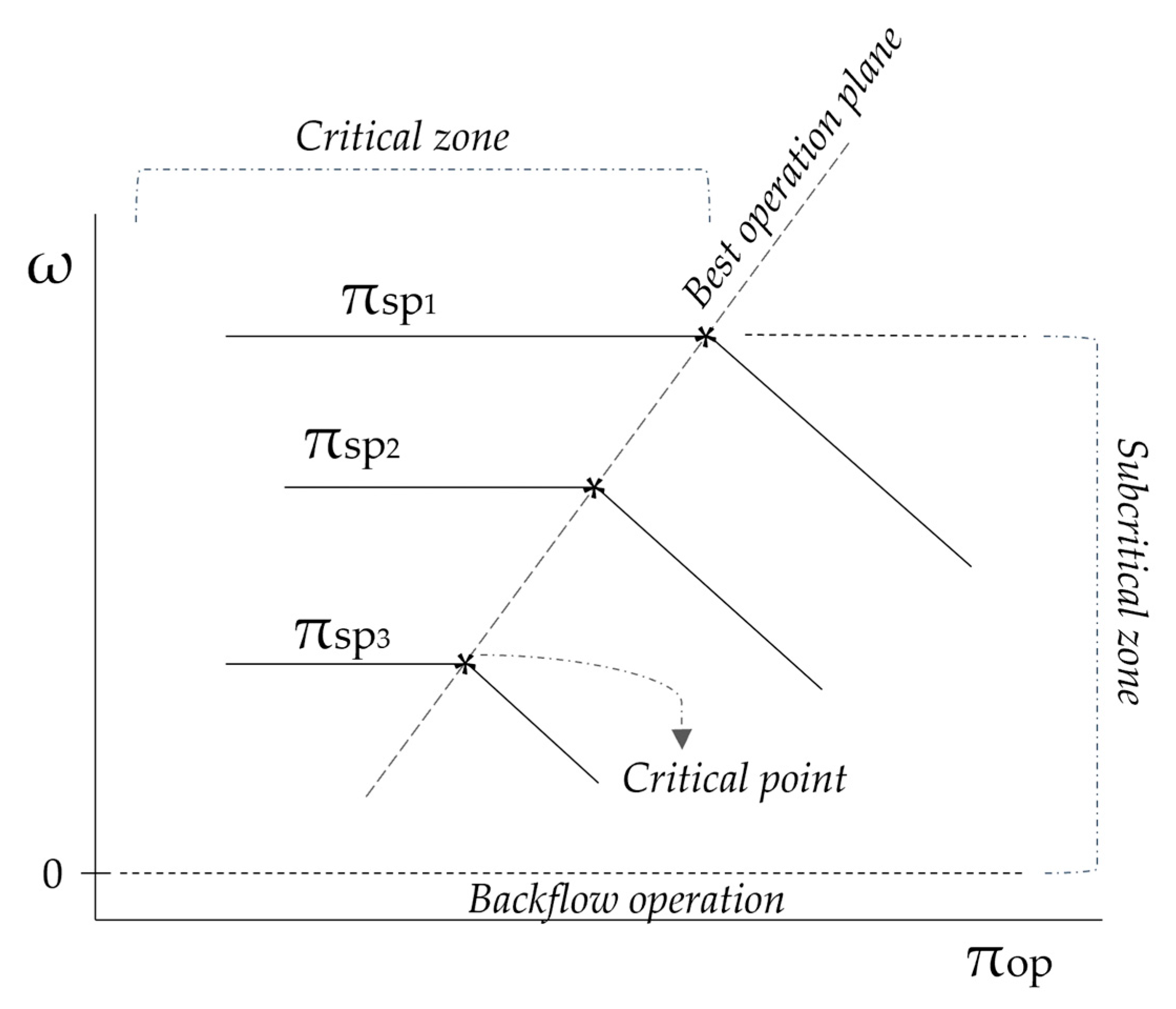
2.5. Simulation Campaign
3. Results
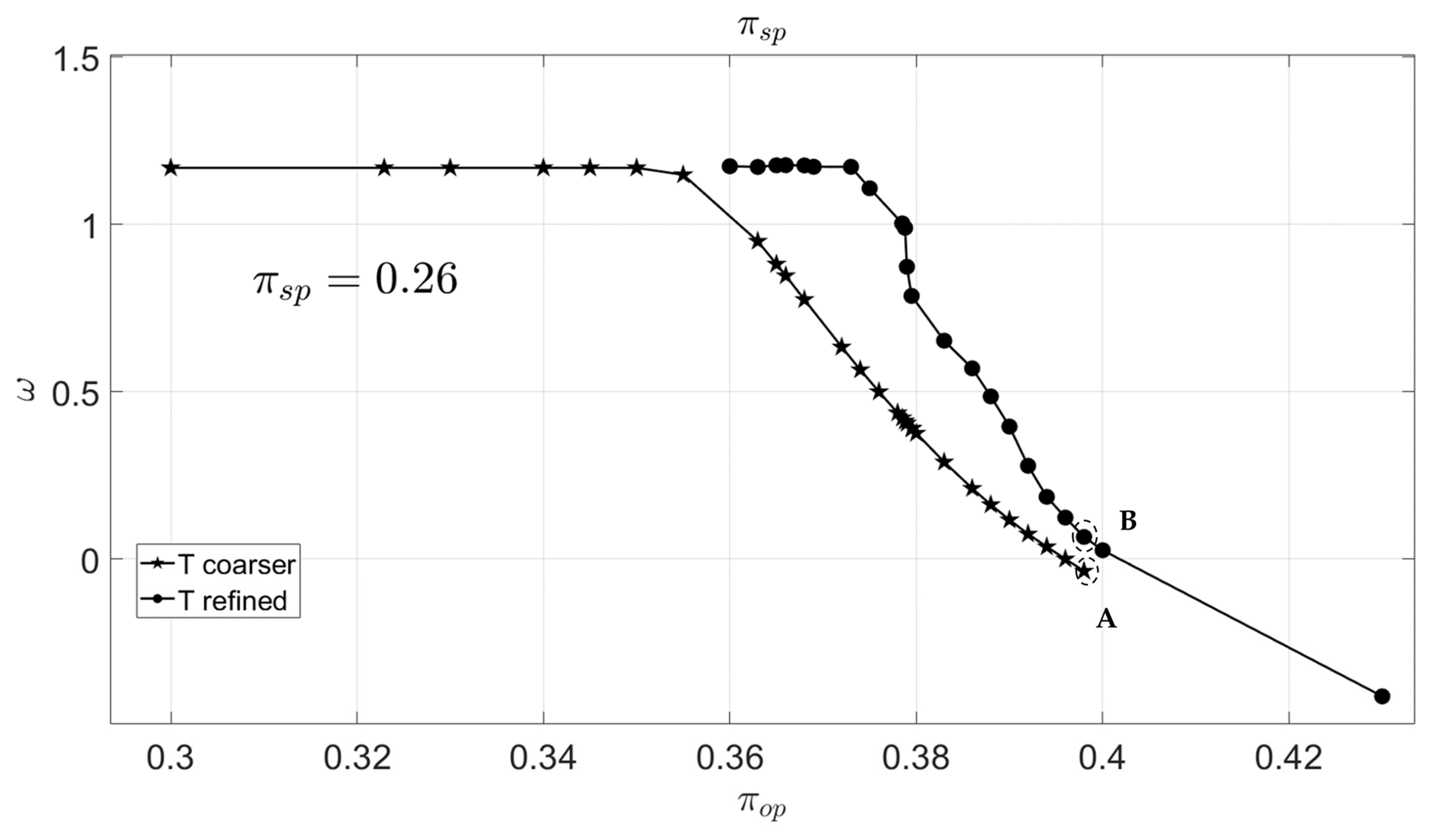
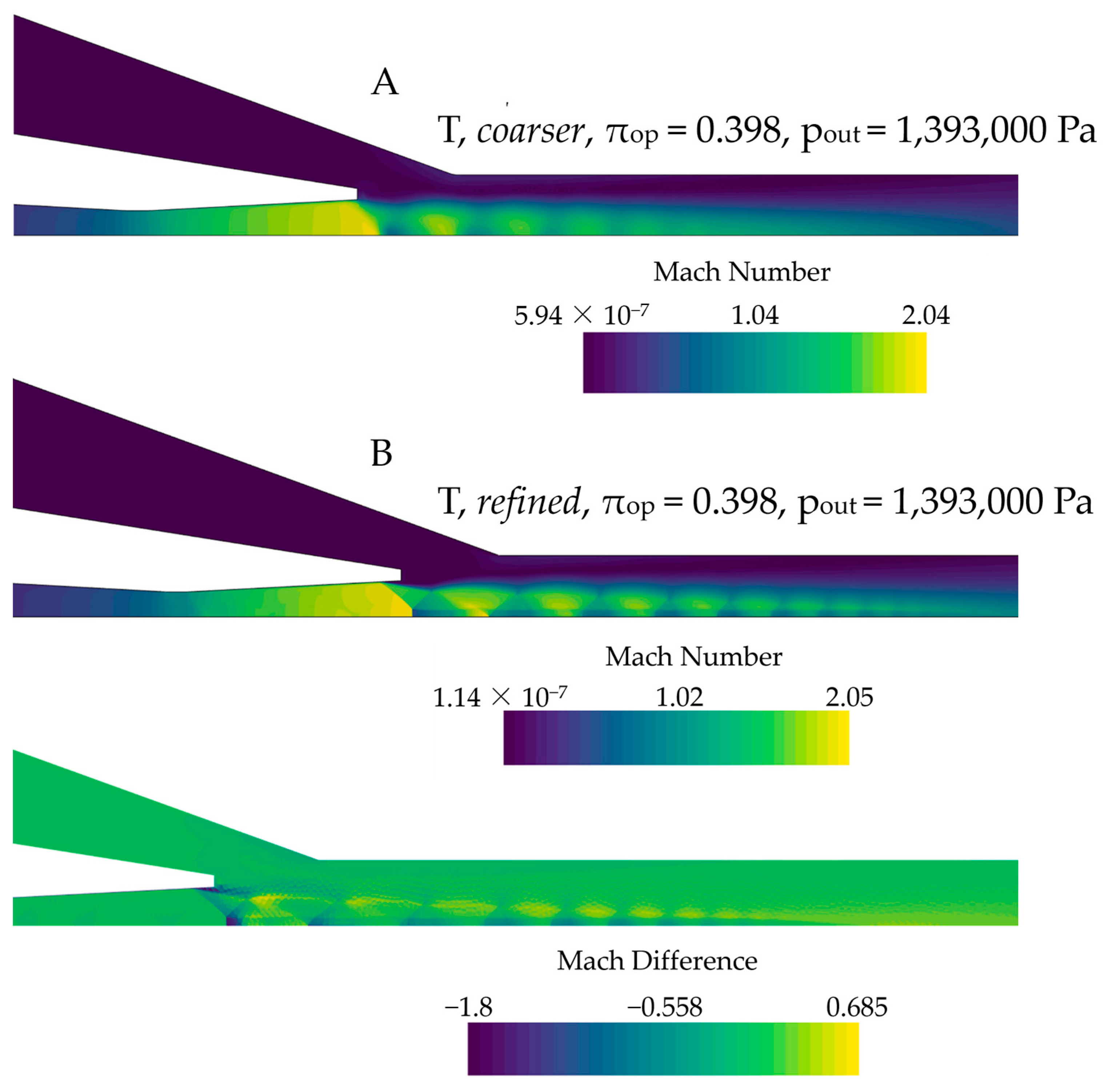
3.1. Analysis of Different Meshes—Coarser and Refined Meshes
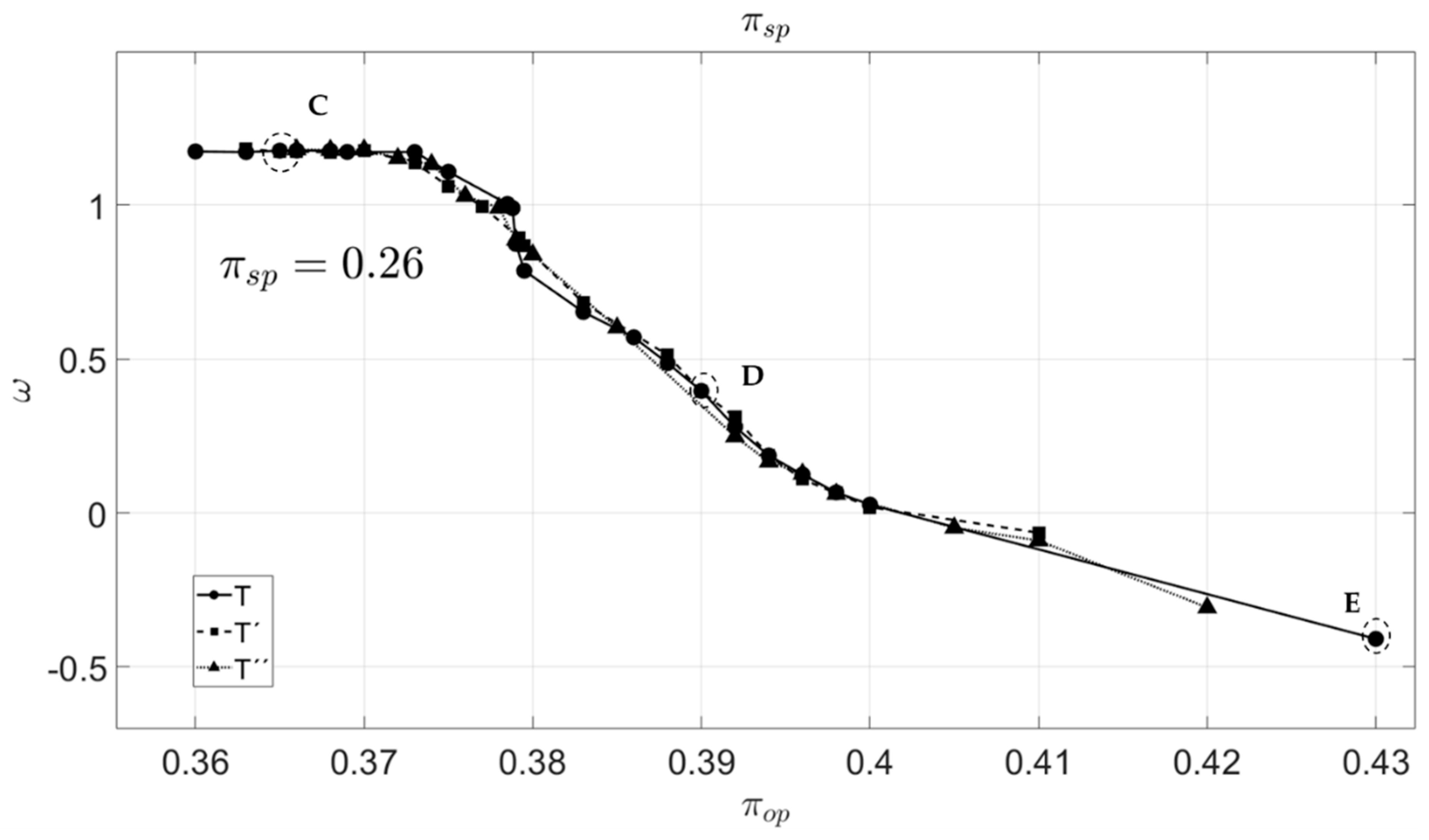
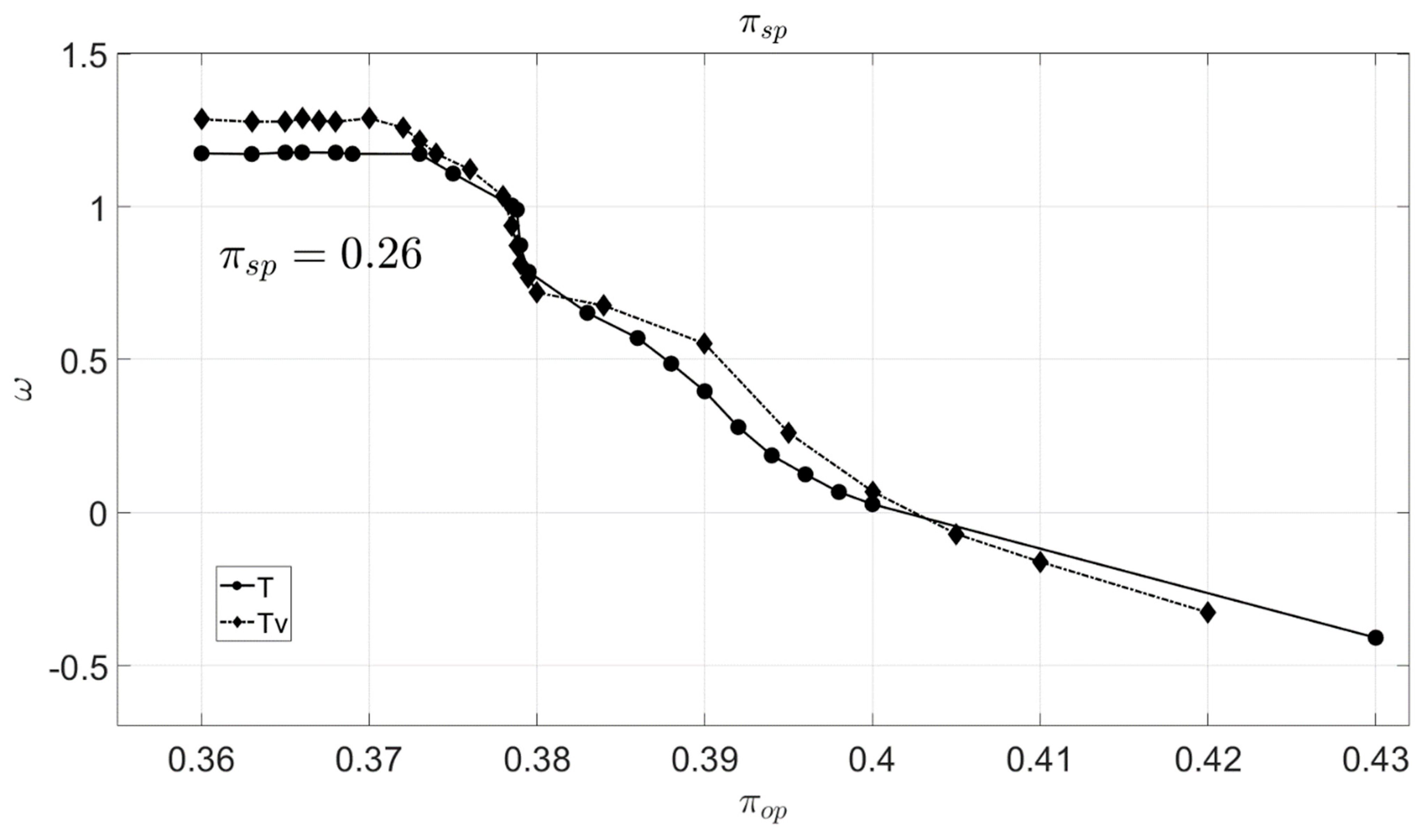
3.2. Analysis for Temperature Changes Using Refined Mesh
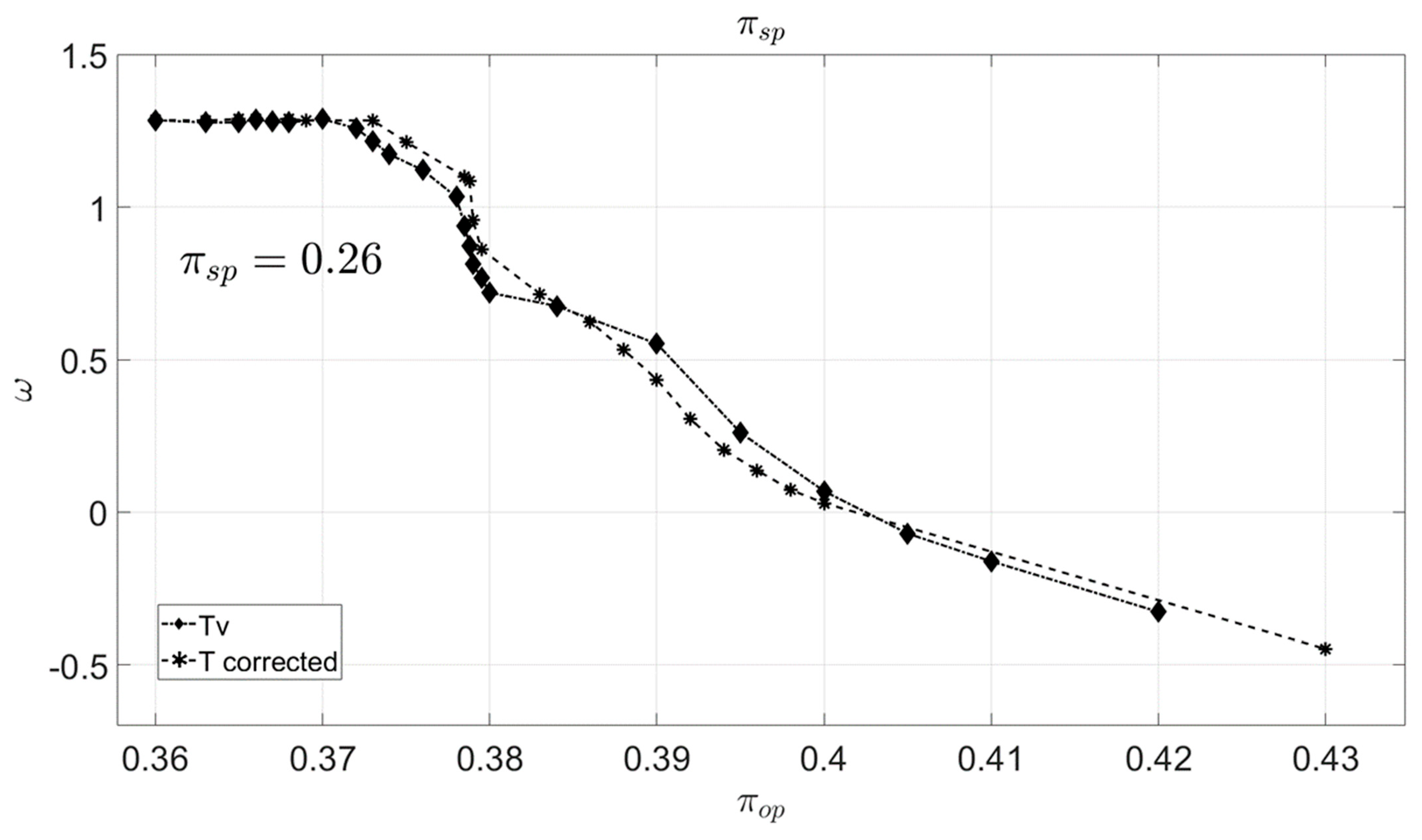
3.3. The Analysis for the Primary Temperature Variations Using the Refined Mesh
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elbel, S.; Hrnjak, P. Experimental validation of a prototype ejector designed to reduce throttling losses encountered in transcritical R744 system operation. Int. J. Refrig. 2008, 31, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Marasigan, A.R.; Matsukawa, T.; Kurashina, A. Experimental investigation on the effect of mixing length on the performance of two-phase ejector for CO2 refrigeration cycle with and without heat exchanger. Int. J. Refrig. 2011, 34, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Oliveira, A.; Diaconu, B. Influence of geometrical factors on steam ejector performance- a numerical assessment. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, R.; Ersoy, H.K. Performance characteristics of the ejector refrigeration system based on the constant area ejector f low model. Energy Conv. Manag. 2005, 46, 3117–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefroy, J.; Boukhanouf, R.; Riffat, S. Design, testing and mathematical modelling of a small-scale CHP and cooling system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogdakis, E.D.; Alexis, G.K. Design and parametric investigation of an ejector in an air-conditioning system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2000, 20, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusly, E.; Aye, L.; Charters, W.W.S.; Ooi, A. CFD analysis of ejector in a combined ejector cooling system. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 2. Flow structure of a steam ejector influenced by operating pressures and geometries. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, J.H.; Neumann, E.P.; Lustwerk, F. An investigation of ejector design by analysis and experiment. J. Appl. Mech. 1950, 17, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosiewicz, Y.; Aidoun, Z.; Mercadier, Y. Numerical assessment of ejector operation for refrigeration applications based on CFD. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.B.; Bartosiewicz, Y.; Garimella, S. Visualization and Validation of Ejector Flow Field with Computational and First-Principles Analysis. J. Fluids Eng. 2015, 137, 051107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizungu, K.; Mani, A.; Groll, M. Performance comparison of vapour jet refrigeration system with environment friendly working fluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, X.; Dang, C.; Hihara, E. Ejector performance analysis under overall operating conditions considering adjustable nozzle structure. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 84, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Elbel, S. Development of ejector performance map for predicting fixed-geometry two-phase ejector performance for wide range of operating conditions. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 128, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, P. Experimental and analytical studies on the shock wave length in convergent and convergent–divergent nozzle ejectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Li, A.; Guo, L.; Yeoh, G.H.; Tu, J. Characterization of choking flow behaviors inside steam ejectors based on the ejector refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 113, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, Y.; Bouden, C.; Varga, S. A CFD analysis of the flow structure inside a steam ejector to identify the suitable experimental operating conditions for a solar-driven refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 39, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, J.; Gil, A.; Dolz, V.; Ponce-Mora, A. Numerical Optimization of an Ejector for Waste Heat Recovery Used to Cool Down the Intake Air in an Internal Combustion Engine. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2020, 12, 051024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L.; Tu, J. CFD simulation on the boundary layer separation in the steam ejector and its influence on the pumping performance. Energy 2019, 167, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianthong, K.; Sheehanam, W.; Behnia, M.; Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S. Investigation and improvement of ejector refrigeration system using computational fluid dynamics technique. Energy Conv. Manag. 2007, 48, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Wan, Y.; Chua, K.J. A double-choking theory as an explanation of the evolution laws of ejector performance with various operational and geometrical parameters. Energy Conv. Manag. 2020, 206, 112499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangtrakoon, N.; Aphornratana, S. Design of steam ejector in a refrigeration application based on thermodynamic performance analysis. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 31, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagan, J.; Smierciew, K.; Butrymowicz, D.; Karwacki, J. Comperative study of turbulence models in applications to gas ejectors. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 78, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, G.; Pinsker, R.; Stelzer, M.; Aggarwal, M.; Pertl, P.; Trattner, A. Ejector validation in proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A comparison of turbulence models in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) with experiment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 61, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, C.; Shen, S.; Mu, X.; Zhang, L. Turbulence model comperative study for complex phenomena in supersonic steam ejectors with double choking mode. Entropy 2022, 24, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzelli, F.; Little, A.B.; Garimella, S.; Bartosiewicz, Y. Computational and experimental analysis of supersonic jet ejector: Turbulence modelling and assessment of ·D effects. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow. 2015, 56, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, E.; Al-Mutairi, K.; Hussain, B.; El-Gizawy, A.S. Development of analytical model for predicting dual-phase ejector performance. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–17 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens Digital Industries Software. Siemens STAR-CCM+ User Guide, version 2021.1. In Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Overset Meshes; Siemens: Munich, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Macia, L.; Castilla, R.; Gámez, P.J. Simulation of ejector for vacuum generation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 659, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J.; Chong, D.; Yan, J. Numerical simulation study on the influence of primary nozzle deviation on the steam ejector performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Suárez, J.A.; Galeano Urueña, C.H.; Gómez Mejía, A. Adaptive Mesh Refinement Strategies for Cost-Effective Eddy-Resolving Transient Simulations of Spray Dryers. Chem. Eng. 2023, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehoon, K.; Sejin, K. Experimental Investigation of an Annular Injection Supersonic Ejector. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
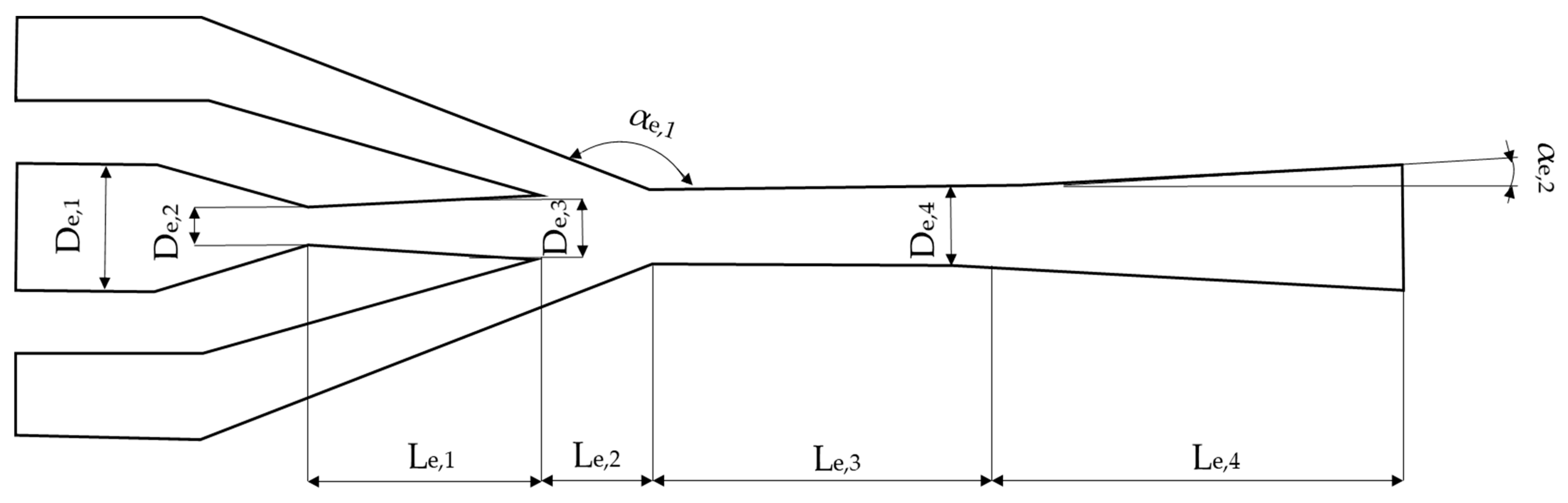


| De,1 [mm] | De,2 [mm] | De,3 [mm] | De,4 [mm] | Le,1 [mm] | Le,2 [mm] | Le,3 [mm] | Le,4 [mm] | αe,1 [°] | αe,2 [°] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15.194 | 2.252 | 3.1978 | 5.8862 | 11.01 | 4.4926 | 58.12 | 110.78 | 159.85 | 21.8 |
| primary inlet diameter | primary inlet throat diameter | throat diameter | mixing chamber diameter | primary inlet length | junction length | mixing chamber length | diffuser length | angle of secondary inlet entrance | angle of diffuser divergence |
| Symbol | Name | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. at primary inlet | 362.85 | K | |
| Temp. at secondary inlet | 273.15 | K | |
| Pressure at primary inlet | 30.6 | bar | |
| Pressure at a secondary inlet | 3.2 | bar | |
| Pressure at outlet | 10.7 | bar |
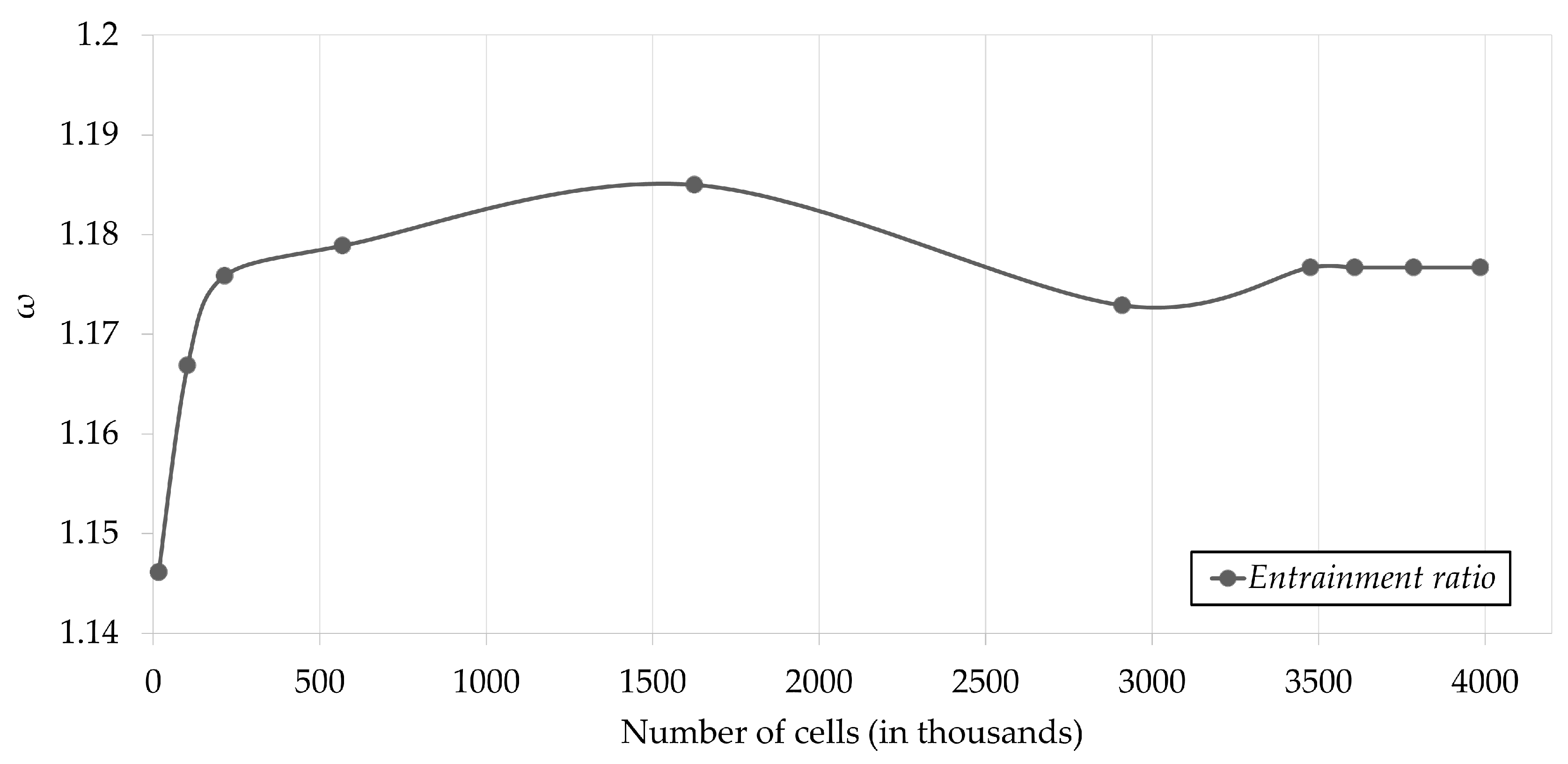
| Mesh Version Case Number | Entrainment Ratio | Number of Cells | Max. y+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.146127 | 16,274 | 500 |
| 2 | 1.146135 | 16,274 | 500 |
| 3 | 1.166865 | 103,191 | 160 |
| 4 | 1.175862 | 214,554 | 240 |
| 5 | 1.178889 | 568,805 | 8.5 |
| 6 | 1.185003 | 1,625,678 | 45 |
| 7 | 1.172905 | 2,910,279 | 55 |
| 8 | 1.176702 | 3,475,381 | 20 |
| 9 | 1.176702 | 3,608,526 | 20 |
| 10 | 1.176702 | 3,785,626 | 20 |
| 11 | 1.176702 | 3,985,944 | 20 |
| Default T Values | ζ’ = 1.1 [/] | ζ” = 1.2 [/] |
|---|---|---|
| = 380 K | = 418 K | = 456 K |
| = 313 K | = 344.3 K | = 375.6 K |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galindo, J.; Serrano, J.R.; Dolz, V.; Iljaszewicz, P. Impact of Mesh Resolution and Temperature Effects in Jet Ejector CFD Calculations. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073880
Galindo J, Serrano JR, Dolz V, Iljaszewicz P. Impact of Mesh Resolution and Temperature Effects in Jet Ejector CFD Calculations. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073880
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalindo, José, José Ramón Serrano, Vicente Dolz, and Paulina Iljaszewicz. 2025. "Impact of Mesh Resolution and Temperature Effects in Jet Ejector CFD Calculations" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073880
APA StyleGalindo, J., Serrano, J. R., Dolz, V., & Iljaszewicz, P. (2025). Impact of Mesh Resolution and Temperature Effects in Jet Ejector CFD Calculations. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073880







