Ecological Concrete-Based Modular System for Heavy Metal Removal in Riparian Transition Zones: Design, Optimization and Performance Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Ecological Concrete Preparation
2.2. Physical and Mechanical Properties Testing
2.3. Heavy Metal Solutions Preparation
2.4. Analytical Methods and Quality Control
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics of Ecological Concrete
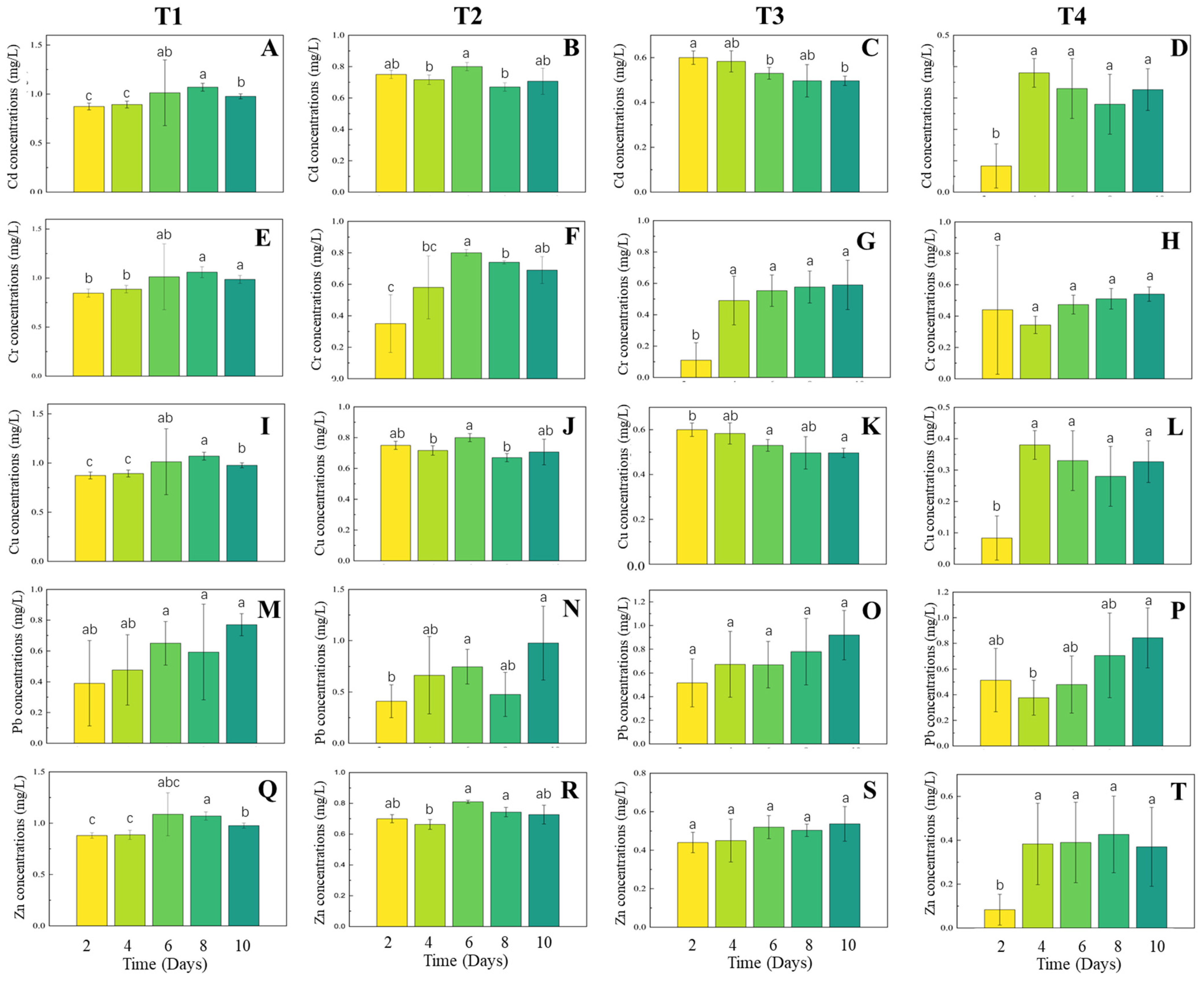
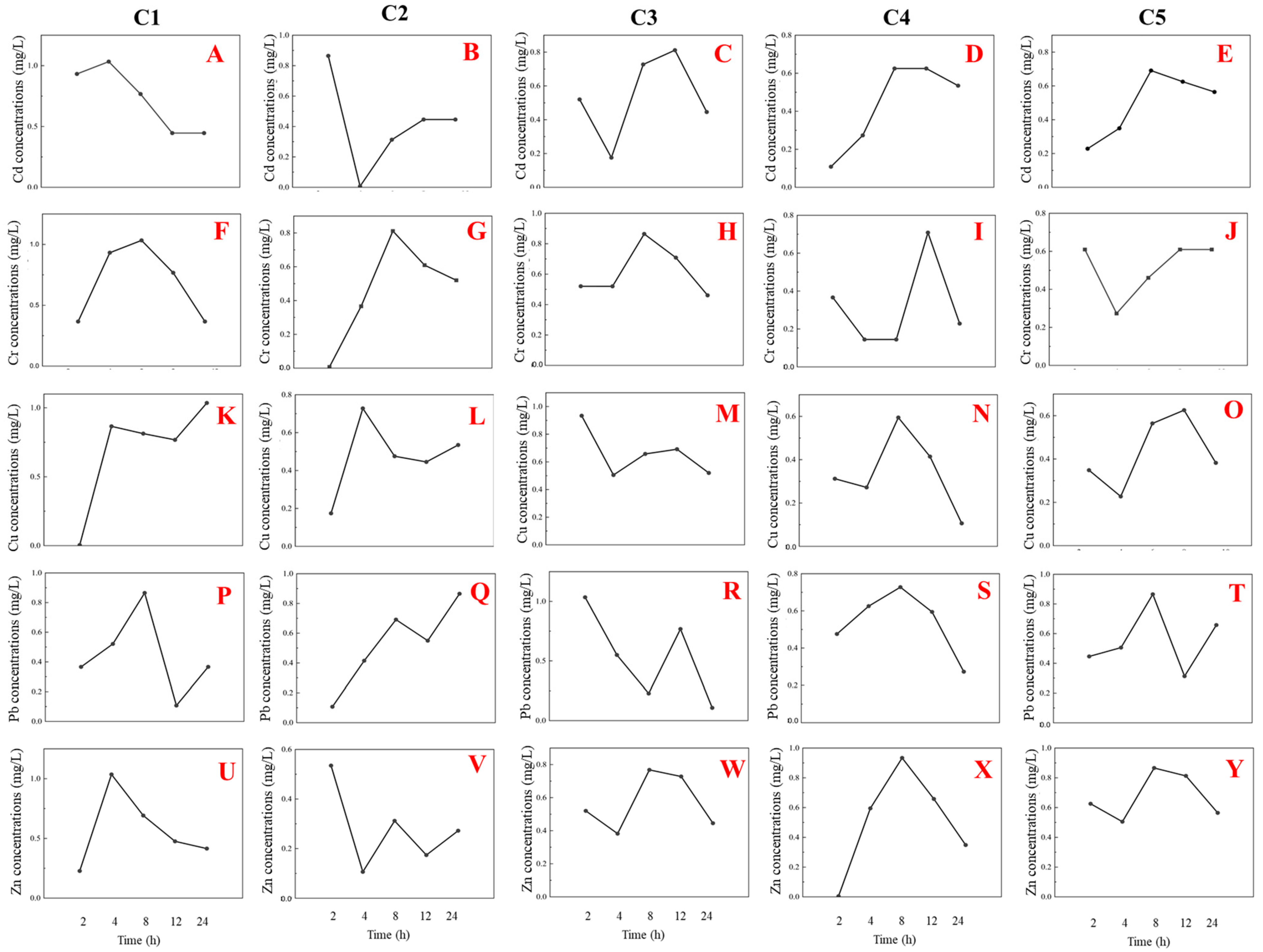
3.2. Heavy Metal Removal Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimization of Ecological Concrete Properties and Module Design
4.2. Metal Removal Mechanisms and Scale-Dependent Kinetics
4.3. Metal-Specific Removal Patterns
4.4. Environmental Implications and Practical Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.J.; Yang, H.W.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Liu, Y. Pollution, sources, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban areas around industrialization and urbanization-Northwest China. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. The Ministry of Environmental Protection in China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, M. Proper management of lead-contaminated agricultural lands against the exceedance of lead in agricultural produce: Derivation of local soil criteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Engdaw, F.; Hein, T.; Beneberu, G. Heavy metal distribution in surface water and sediment of Megech River, a Tributary of Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, K.; Taniwaki, R.H.; Macedo, D.R.; Leal, C.G.; Randhir, T.O. Biomonitoring for watershed protection from a multiscale land-use perspective. Diversity 2023, 15, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.; Zakeel, M.C.M.; Zavahir, J.S.; Marikar, F.M.M.T.; Jahan, I. Heavy metal accumulation in rice and aquatic plants used as human food: A general review. Toxics 2021, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauner, S.; Bauer, N.; Dirnaichner, A.; Van Dingenen, R.; Mutel, C.; Luderer, G. Coal-exit health and environmental damage reductions outweigh economic impacts. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 195–213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Z.; Dzakpasu, M.; Wang, X.C. Development and performance evaluation of a novel in-situ purification system for first flush rainwater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106335. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Mofijur, M.; Nuzhat, S.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Rafa, N.; Uddin, A.; Inayat, A.; Mahlia, T.; Ong, H.C.; Chia, W.Y.; et al. Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.E.; Escolero, O.; Wolf, L. Total urban water cycle models in semiarid environments—Quantitative scenario analysis at the area of San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 239–263. [Google Scholar]
- Abbassi, R.; Arzaghi, E.; Yazdi, M.; Aryai, V.; Garaniya, V.; Rahnamayiezekavat, P. Risk-based and predictive maintenance planning of engineering infrastructure: Existing quantitative techniques and future directions. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, D.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Xia, J. Ecological pervious concrete in revetment and restoration of coastal wetlands: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124590. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, W.; Ayub, T. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of recycled aggregate concrete exposed to accelerated and natural marine environment. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105867. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Huang, R.; Wu, J.; Chen, C.H. Influence of soaking and polymerization conditions on the properties of polymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 706–712. [Google Scholar]
- Yogafanny, E.; Triatmadja, R.; Nurrochmad, F.; Supraba, I. Permeability coefficient of pervious cement mortar measured by the constant head and falling head methods. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2023, 21, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Sheng, F.; Qing, H. Adsorption characteristics of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Hg(II) by four kinds of immobilized fungi residues. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Deng, G.; Wei, P. Influence of the porosity and pore size on the compressive and splitting strengths of cellular concrete with millimeter-size pores. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117508. [Google Scholar]
- Bheel, N.; Mohammed, B.S.; Abdulkadir, I.; Liew, M.S.; Zawawi, N.A.W.A. Effects of graphene oxide on the properties of engineered cementitious composites: Multi-objective optimization technique using RSM. Buildings 2023, 13, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tan, K. Enhancing road performance of lead-contaminated soil through biochar-cement solidification: An experimental study. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119315. [Google Scholar]
- Das, K.P.; Chauhan, P.; Staudinger, U.; Satapathy, B.K. Exploring sustainable adsorbents to mitigate micro-/nano-plastic contamination: Perspectives on electrospun fibrous constructs, biochar, and aerogels. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 1217–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wu, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, S. Pore-scale transport dynamic behavior of microspheres and their mechanisms for enhanced oil recovery. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 2803–2815. [Google Scholar]
- Dhangar, K.; Kumar, M. Tricks and tracks in removal of emerging contaminants from the wastewater through hybrid treatment systems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, F.; Meng, Y.; Byrne, P.; Ghomshei, M.; Abbaspour, K.C. Modeling transport and fate of heavy metals at the watershed scale: State-of-the-art and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Maekawa, K. Lifetime assessment of structural concrete–multi-scale integrated hygro-thermal-chemo-electrical-mechanistic approach and statistical evaluation. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 18, 933–949. [Google Scholar]
- Vimonses, V.; Lei, S.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.; Saint, C. Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo Red adsorption by clay materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 354–364. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Burns, S.E. Modeling sorption and diffusion of organic sorbate in hexadecyltrimethylammonium-modified clay nanopores–a molecular dynamics simulation study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.; Iqbal, J.; Hableel, A.O.A.O.; Alzaabi, Z.N.K.B.; Nazzal, Y. Camel dung-derived biochar for the removal of Cu(II) and Cr(III) ions from aqueous solutions: Adsorption and kinetics studies. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 11500–11509. [Google Scholar]
- Salahshoori, I.; Nobre, M.A.; Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Malekshah, R.E.; Asghari, M.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Mohammadi, A.H. Navigating the molecular landscape of environmental science and heavy metal removal: A simulation-based approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 410, 125592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, X.; Geng, G. Influence of substrate moisture on the interfacial bonding between calcium silicate hydrate and epoxy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126252. [Google Scholar]
- Leybo, D.; Etim, U.J.; Monai, M.; Bare, S.R.; Zhong, Z.; Vogt, C. Metal–support interactions in metal oxide-supported atomic, cluster, and nanoparticle catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10450–10490. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, M.-Y.; Lee, T.-A.; Lin, Y.S.; Hsu, S.Y.; Wang, M.F.; Li, P.H.; Huang, P.H.; Lu, W.C.; Ho, J.H. On the removal efficiency of Cu ions in wastewater using calcined waste eggshells as natural adsorbents. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, B.A.; França, A.M.D.M.; Silva, L.T.V.D.; Gouveia, A.G.S.; Vidal, C.B.; Loiola, A.R.; Nascimento, R.F. Magnetic zeolite from fly ash as a cost-effective adsorbent for Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, and Cd2+ removal from aqueous media: A comprehensive study. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 3913–3935. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, P.; Fu, H.; Chen, J.; Ye, M.; Zhai, S.; Hu, F.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Y.; Fortin, C. A comparative study of the accumulation and detoxification of copper and zinc in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: The role of extracellular polymeric substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boguta, P.; Sokołowska, Z. Zn binding to fulvic acids: Assessing the impact of pH, metal concentrations, and chemical properties of fulvic acids on the mechanism and stability of formed soluble complexes. Molecules 2020, 25, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Fourmentin, M.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Mapelli, F.; Fenyvesi, É.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; et al. Removal of emerging contaminants from wastewater using advanced treatments: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1333–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.E.; Bin Halmi, M.I.; Bin Abd Samad, M.Y.; Uddin, M.K.; Mahmud, K.; Abd Shukor, M.Y.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Shamsuzzaman, S.M. Design, operation, and optimization of constructed wetlands for removal of pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
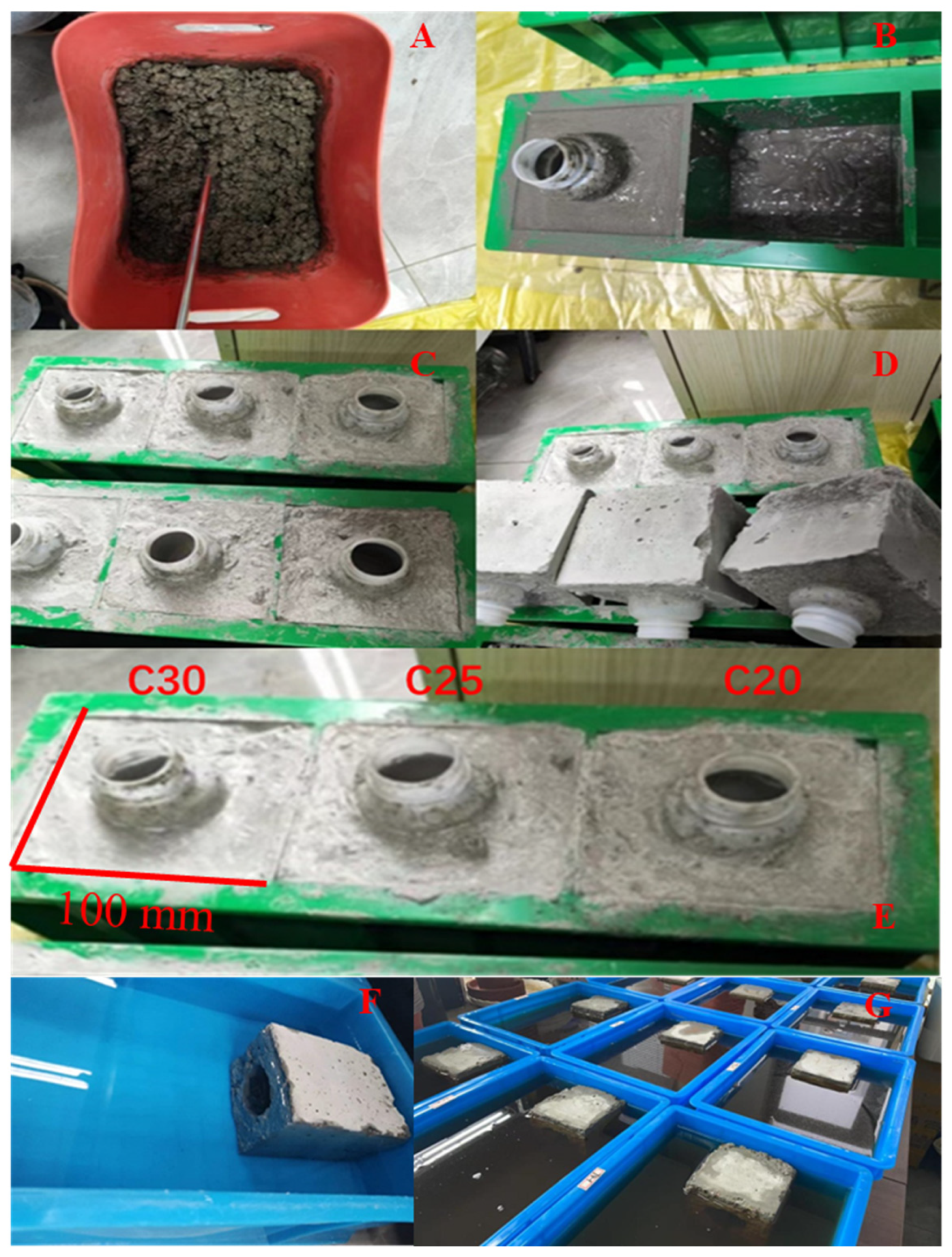
| Property Type | Parameter | C20 | C25 | C30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mix Proportions (kg m−3) | Cement | 358 | 378 | 398 |
| Reinforcing Agent | 10 | 12 | 15 | |
| Aggregate | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | |
| Water | 130 | 137 | 145 | |
| Performance Parameters | Strength Grade | C20 | C25 | C30 |
| 28-day Compressive Strength | 15–25 MPa | 20–30 MPa | 25–35 MPa | |
| Porosity | >18% | >15% | >12% | |
| Permeability Coefficient | >2 × 10−4 cm s−1 | >1 × 10−4 cm s−1 | >5 × 10−5 cm s−1 |
| Time Period | Parameter | Module-Scale | Kinetic Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4 h | Removal Rate (mg g−1 h−1) | 0.18–0.25 | 0.28–0.42 |
| Total Removal (%) | 25–35 | 45–65 | |
| 4–24 h | Removal Rate (mg g−1 h−1) | 0.10–0.15 | 0.12–0.18 |
| Total Removal (%) | 45–60 | 65–85 | |
| >24 h | Removal Rate (mg g−1 h−1) | 0.05–0.08 | 0.03–0.05 |
| Total Removal (%) | 75–85 | 80–95 |
| Metal | Initial Concentration (mg L−1) | Removal Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Module-Scale | Kinetic Studies | ||
| Cd | 0.25 | 85.4 | 92.3 |
| 2.5 | 84.2 | 89.7 | |
| 12.5 | 83.2 | 85.6 | |
| Pb | 0.05 | 92.1 | 95.6 |
| 0.5 | 89.8 | 93.2 | |
| 2.5 | 85.4 | 90.1 | |
| Cr | 2.50 | 78.5 | 84.2 |
| 25.0 | 80.2 | 82.8 | |
| 125.0 | 79.8 | 81.5 | |
| Cu | 5.0 | 82.4 | 89.7 |
| 50.0 | 83.7 | 87.4 | |
| 250.0 | 82.9 | 85.2 | |
| Zn | 50.0 | 73.6 | 84.8 |
| 500.0 | 75.2 | 82.5 | |
| 2500.0 | 74.8 | 80.3 | |
| Ions | Concentration (mg·L−1) | k2 (g·mg−1·h−1) | qe (mg·g−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd2+ | 0.25 | 0.063 | 0.84 | 0.995 |
| 2.5 | 0.048 | 7.62 | 0.992 | |
| 12.5 | 0.032 | 35.78 | 0.987 | |
| Pb2+ | 0.05 | 0.095 | 0.18 | 0.997 |
| 0.5 | 0.078 | 1.74 | 0.995 | |
| 2.5 | 0.052 | 8.35 | 0.991 | |
| Cr3+ | 2.50 | 0.044 | 8.12 | 0.989 |
| 25.0 | 0.035 | 75.26 | 0.986 | |
| 125.0 | 0.021 | 348.42 | 0.982 | |
| Cu2+ | 5.0 | 0.057 | 16.38 | 0.994 |
| 50.0 | 0.039 | 154.52 | 0.988 | |
| 250.0 | 0.024 | 715.86 | 0.985 | |
| Zn2+ | 50.0 | 0.042 | 152.60 | 0.990 |
| 500.0 | 0.028 | 1360.45 | 0.986 | |
| 2500.0 | 0.016 | 5842.64 | 0.983 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Ke, D.; Moavia, H.; Ling, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Ecological Concrete-Based Modular System for Heavy Metal Removal in Riparian Transition Zones: Design, Optimization and Performance Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3721. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073721
Liu G, Ke D, Moavia H, Ling C, Zhang Y, Shen Y. Ecological Concrete-Based Modular System for Heavy Metal Removal in Riparian Transition Zones: Design, Optimization and Performance Evaluation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3721. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073721
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guangbing, Da Ke, Hasnain Moavia, Chen Ling, Yanhong Zhang, and Yu Shen. 2025. "Ecological Concrete-Based Modular System for Heavy Metal Removal in Riparian Transition Zones: Design, Optimization and Performance Evaluation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3721. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073721
APA StyleLiu, G., Ke, D., Moavia, H., Ling, C., Zhang, Y., & Shen, Y. (2025). Ecological Concrete-Based Modular System for Heavy Metal Removal in Riparian Transition Zones: Design, Optimization and Performance Evaluation. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3721. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073721







