Impact of High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Quality and Functional Properties of Rehydrated Animal Blood Plasma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Sample and HHP Treatment
2.2. Color Measurement
2.3. Examination of Rheological Properties
2.4. Sodium Dodecyl-Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.5. In Vitro Digestion
2.6. Microbiological Analyses and Storage Experiment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Color
3.2. Rheological Properties
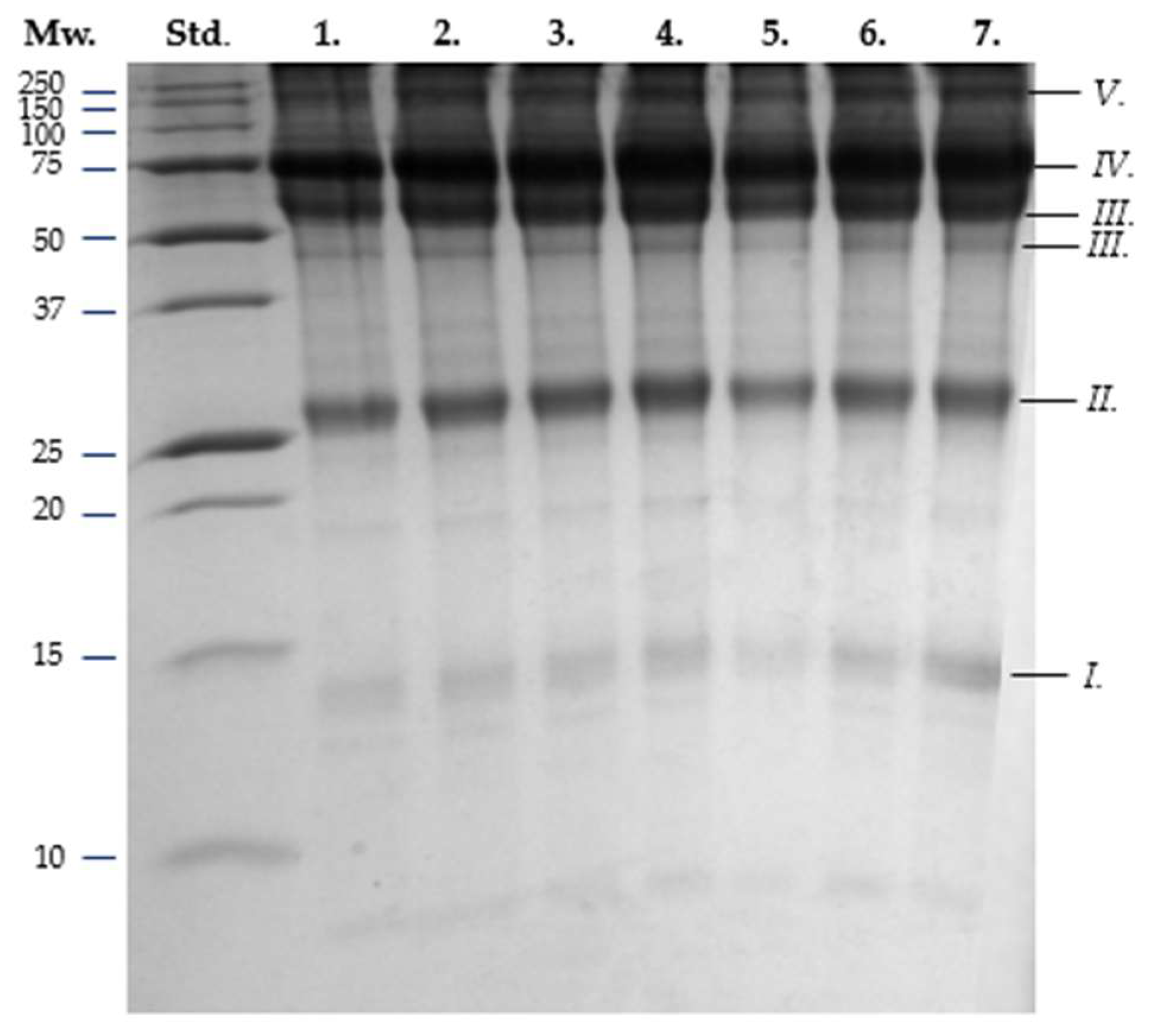
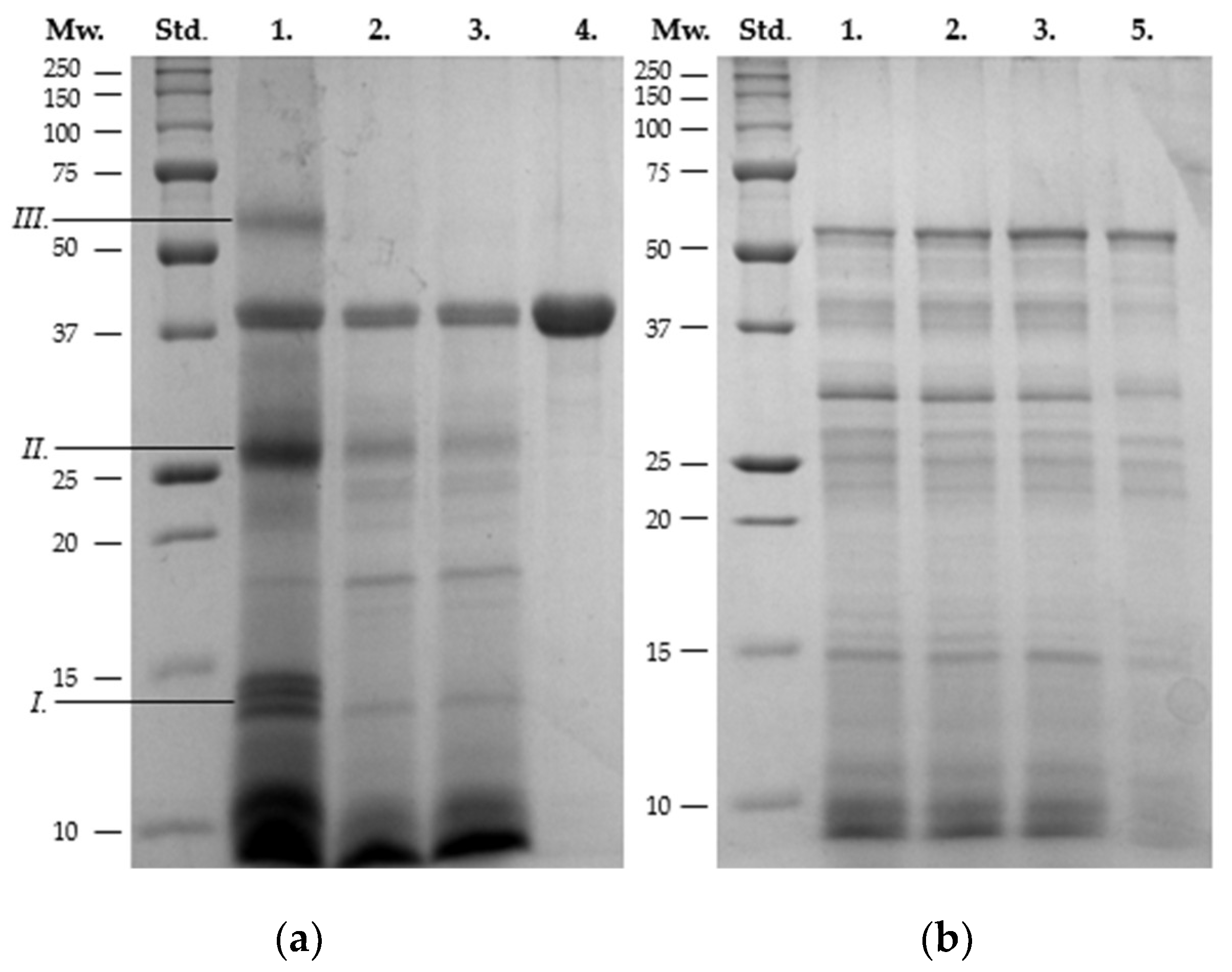
3.3. SDS-PAGE
3.4. Results of In Vitro Digestion
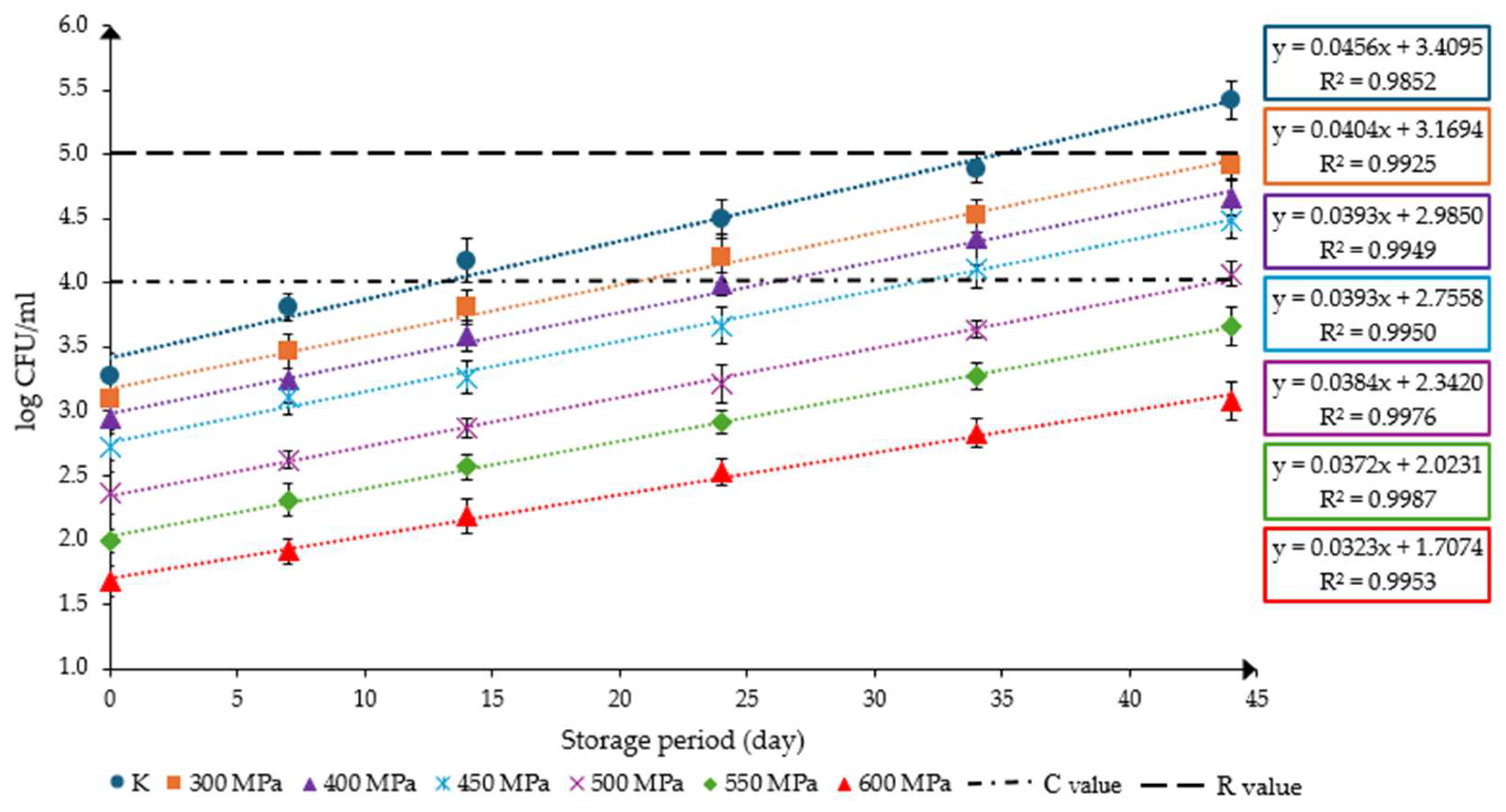
3.5. Microbiological Evaluation
4. Discussion and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The Future of Food and Agriculture—Drivers and Triggers for Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; ISBN 978-92-5-136639-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bahar, N.H.A.; Lo, M.; Sanjaya, M.; Van Vianen, J.; Alexander, P.; Ickowitz, A.; Sunderland, T. Meeting the Food Security Challenge for Nine Billion People in 2050: What Impact on Forests? Glob. Environ. Change 2020, 62, 102056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmaram, N.; Rosentrater, K.A. Overview of Some Recent Advances in Improving Water and Energy Efficiencies in Food Processing Factories. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.C.; Ojha, A.; Debnath, S.; Sharma, M.; Nayak, P.K.; Sridhar, K.; Inbaraj, B.S. Valorization of Food Waste as Animal Feed: A Step towards Sustainable Food Waste Management and Circular Bioeconomy. Animals 2023, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Castillo, E.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K.; Bengoechea, C.; Guerrero, A. Biorefinery Concept in the Meat Industry: From Slaughterhouse Biowastes to Superaborbent Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, S.H.; Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Ali, M.; Ahn, D.U.; Choi, Y.-S.; Nam, K.-C. Comparison of Functional Properties of Blood Plasma Collected from Black Goat and Hanwoo Cattle. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2023, 43, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazifa, T.H.; Saady, N.M.C.; Bazan, C.; Zendehboudi, S.; Aftab, A.; Albayati, T.M. Anaerobic Digestion of Blood from Slaughtered Livestock: A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiroque, R.G.S.; Santiago, H.P.C.; Espinoza, L.A.E.; Quispe, L.A.M.; Tirado, L.R.P.; Villegas, L.M.N.; Villegas, M.A.N. A Review of Slaughterhouse Blood and Its Compounds, Processing and Application in the Formulation of Novel Non-Meat Products. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 11, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, S. Dynamic Surface Tension Measurements as General Approach to the Analysis of Animal Blood Plasma and Serum. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 235, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bah, C.S.F.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.A. Composition and Biological Activities of Slaughterhouse Blood from Red Deer, Sheep, Pig and Cattle. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bułkowska, K.; Zielińska, M. Recovery of Biogas and Other Valuable Bioproducts from Livestock Blood Waste: A Review. Energies 2024, 17, 5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahru, U.J. Issues Related to Animal Blood into Food Products: A Review Paper. Food Res. 2021, 5, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.A.; Mullen, A.M.; O’Neill, E.E.; García, C.Á. Harnessing the Potential of Blood Proteins as Functional Ingredients: A Review of the State of the Art in Blood Processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Fadzlillah, N.A.; Sukri, S.J.M.; Adediran, O.A.; Rather, M.A.; Naik, B.; Kumar, V.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Ramli, M.A.; Jha, A.K.; et al. Slaughterhouse Blood: A State-of-the-Art Review on Transforming by-Products into Valuable Nutritional Resources and the Role of Circular Economy. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, B.O.; Falowo, A.B.; Chulayo, A.; Muchenje, V. The Potential of Animal By-Products in Food Systems: Production, Prospects and Challenges. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balda, F.P.; Aparicio, B.V.; Samson, C.T. Industrial High Pressure Processing of Foods: Review of Evolution and Emerging Trends. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2012, 2, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Serna-Hernandez, S.O.; Escobedo-Avellaneda, Z.; García-García, R.; Rostro-Alanis, M.d.J.; Welti-Chanes, J. High Hydrostatic Pressure Induced Changes in the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Milk and Dairy Products: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csurka, T.; Szücs, F.; Csehi, B.; Friedrich, L.F.; Pásztor-Huszár, K. Analysis of Several Techno-Functional and Sensory Attributes upon Egg Allergen Ingredient Substitution by Blood Plasma Powder in Sponge Cake. Prog. Agric. Eng. Sci. 2021, 17, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csurka, T.; Szücs, F.; Csehi, B.; Friedrich, L.F.; Pásztor-Huszár, K. Substitution of Milk Allergen Ingredient by Blood Plasma Powder in Custard with Different Sweeteners. Prog. Agric. Eng. Sci. 2021, 17, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.D.M.; Silvestre, M.P.C. Functional Properties of Bovine Blood Plasma Intended for Use as a Functional Ingredient in Human Food. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aganovic, K.; Hertel, C.; Vogel, R.F.; Johne, R.; Schlüter, O.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Jäger, H.; Holzhauser, T.; Bergmair, J.; Roth, A.; et al. Aspects of High Hydrostatic Pressure Food Processing: Perspectives on Technology and Food Safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3225–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkacz, K.; Modzelewska-Kapituła, M.; Więk, A.; Nogalski, Z. The Applicability of Total Color Difference ΔE for Determining the Blooming Time in Longissimus Lumborum and Semimembranosus Muscles from Holstein-Friesian Bulls at Different Ageing Times. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnon, E.; Cayeux, E. Precise Method to Estimate the Herschel-Bulkley Parameters from Pipe Rheometer Measurements. Fluids 2021, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, A.L.B.; Sivieri, K.; Oliveira, M.N. Relation between Quality and Rheological Properties of Lactic Beverages. J. Food Eng. 2001, 49, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A Standardised Static in Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, M.L. The Estimation of Pepsin, Trypsin, Papain, and Cathepsin with Hemoglobin. J. Gen. Physiol. 1938, 22, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, B.C.W. A Modified Spectrophotometric Determination of Chymotrypsin, Trypsin, and Thrombin. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Rossi, G.; Pathak, N.; Durek, J.; Mahajan, P.; Schlüter, O.K. Microbial Growth and Physicochemical Quality Changes During Modified Atmosphere Storage of High Hydrostatic Pressure Processed Tenebrio Molitor Paste. Food Bioprocess Technol 2024, 17, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badpa, A.; Ahmad, S. Effect of Whey Protein Products on Microbiological Characteristics of Buffalo Meat Emulsion. Iran. Food Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2015, 11, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćkiw, E.; Kowalska, J.; Korsak, D.; Stasiak, M.; Antoszewska, A.; Ławrynowicz-Paciorek, M.; Postupolski, J. Thermal Resistance of Selected Strains of Salmonella Spp. Isolated from Eggs and Sesame Seeds. LWT 2024, 198, 115907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathare, P.; Opara, U.; Al Said, F. Colour Measurement and Analysis in Fresh and Processed Foods: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csehi, B.; Salamon, B.; Csurka, T.; Szerdahelyi, E.; Friedrich, L.; Pásztor-Huszár, K. Physicochemical and Microbiological Changes of Bovine Blood Due to High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatment. Acta Aliment. 2021, 50, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzinger, K.; Kovács-Bányász, B.; Horváth-Mezőfi, Z.; Pósa, E.; Csehi, B.; Hitka, G.; Alpár, B.; Nyulas-Zeke, I.C. The Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatment on the Quality Characteristics and the Protein Structure of Vacuum-Packed Fresh Pork and Wild Boar Meats. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsarskaia, O.; Bühl, L.; Beck, C.; Grimaldo, M.; Schweins, R.; Zhang, F.; Seydel, T.; Schreiber, F.; Roosen-Runge, F. Evolution of the Structure and Dynamics of Bovine Serum Albumin Induced by Thermal Denaturation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 18507–18517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parés, D.; Ledward, D.A. Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Porcine Blood Plasma as Influenced by High-Pressure Processing. Food Chem. 2001, 74, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Németh, C.; Palotás, P.; Surányi, J.; Zeke, I.; Csehi, B.; Castillo, L.A.; Friedrich, L.; Balla, C. HHP Treatment of Liquid Egg at 200-350 MPa. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 950, 042008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, C.; Xu, Z.; Xu, D.; Luan, S. Shear Thickening Behaviour of Polyborosiloxane. Polymer 2024, 308, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, K.S.; Bayomy, H.M.; Alamri, E.S.; Ozaybi, N.A.; Korma, S.A.; Lv, J.; Ragab, E.S. Impact of High-Pressure Treatments on Physicochemical and Structural Changes of Reconstituted Micellar Casein Concentrates from Bovine and Caprine Milk: A Comparative Study. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnad, D.; Emadzadeh, B.; Ghorani, B.; Assadpour, E.; Yang, N.; Jafari, S.M. The Influence of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Different Properties of Legume Proteins with an Emphasis on Soy Proteins; a Comprehensive Review. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarté, R. Meat-Derived Protein Ingredients. In Ingredients in Meat Products: Properties, Functionality and Applications; Tarté, R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 145–171. ISBN 978-0-387-71327-4. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Ucak, İ.; Jain, S.; Elsheikh, W.; Ali Redha, A.; Kurt, A.; Toker, O.S. Impact of Drying on Techno-Functional and Nutritional Properties of Food Proteins and Carbohydrates—A Comprehensive Review. Dry. Technol. 2024, 42, 592–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mocking-Bode, H.C.M.; van den Hoek, I.A.F.; Theunissen, M.; Voudouris, P.; Meinders, M.B.J.; Sagis, L.M.C. The Impact of Heating and Freeze or Spray Drying on the Interface and Foam Stabilising Properties of Pea Protein Extracts: Explained by Aggregation and Protein Composition. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gan, C.; Li, Y.; Kang, L.; Yi, J. Fabrication of Bovine Serum Albumin Nanofibrils: Physicochemical Characteristics, Emulsifying and Foaming Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Powers, J.R. Effects of High Pressure on Food Proteins. In High Pressure Processing of Food: Principles, Technology and Applications; Balasubramaniam, V.M., Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V., Lelieveld, H.L.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 353–389. ISBN 978-1-4939-3234-4. [Google Scholar]
- Braspaiboon, S.; Laokuldilok, T. High Hydrostatic Pressure: Influences on Allergenicity, Bioactivities, and Structural and Functional Properties of Proteins from Diverse Food Sources. Foods 2024, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepero-Betancourt, Y.; Opazo-Navarrete, M.; Janssen, A.E.M.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Pérez-Won, M. Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure (HHP) on Protein Structure and Digestibility of Red Abalone (Haliotis rufescens) Muscle. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 60, 102282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoy, I. A Review on the Food Digestion in the Digestive Tract and the Used in Vitro Models. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariëns, R.M.C.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; van de Berg-Somhorst, D.B.P.M.; El Bachrioui, K.; Boudewijn, A.; van den Dool, R.T.M.; de Jong, G.A.H.; Wichers, H.J.; Mes, J.J. Comparing Nutritional and Digestibility Aspects of Sustainable Proteins Using the INFOGEST Digestion Protocol. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierska, K.; Biel, W. Comparative Analysis of Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma and Hydrolyzed Porcine Protein as Animal-Blood-Derived Protein Ingredients for Pet Nutrition. Molecules 2023, 28, 7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Saborido, N.; Ródenas, J.; Polo, J. Effects of Spray-Dried Animal Plasma on Food Intake and Apparent Nutrient Digestibility by Cats When Added to a Wet Pet Food Recipe. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 216, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4/1998. (XI. 11.) rendelet, E. 4/1998. (XI. 11.) EüM Rendelet Az Élelmiszerekben Előforduló Mikrobiológiai Szennyeződések Megengedhető Mértékéről—Hatályos Jogszabályok Gyűjteménye. Available online: https://net.jogtar.hu/jogszabaly?docid=99800004.eum (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Patil, U.; Palamae, S.; Nazeer, R.A.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Combined Hurdle Effects of Pulsed Electric Field and Ultraviolet-C Irradiation on Microbial Load Reduction and Composition of Hemeproteins from Asian Seabass Gills. Food Control 2024, 164, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şayin Sert, T.; Coşkun, F. The Effects of High Pressure Processing on Total Mesophilic Aerobic Bacteria Number and Color Properties of Frozen and Unfrozen Beef Mince. Selcuk J. Agric. Food Sci. 2024, 3, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pares, D.; Saguer, E.; Toldra, M.; Carretero, C. High Hydrostatic Pressure as a Method to Reduce Microbial Contamination of Porcine Blood Plasma. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2001, 7, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picart-Palmade, L.; Cunault, C.; Chevalier-Lucia, D.; Belleville, M.-P.; Marchesseau, S. Potentialities and Limits of Some Non-Thermal Technologies to Improve Sustainability of Food Processing. Front. Nutr. 2019, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldrà, M.; Dàvila, E.; Saguer, E.; Fort, N.; Salvador, P.; Parés, D.; Carretero, C. Functional and Quality Characteristics of the Red Blood Cell Fraction from Biopreserved Porcine Blood as Influenced by High Pressure Processing. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pressure Levels [MPa] | L* | a* | b* | ΔE* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 52.83 a ± 1.27 | 0.22 a ± 0.03 | 3.22 a ± 0.16 | 0 |
| 300 | 34.18 b ± 1.16 | 0.86 b ± 0.03 | 2.87 b ± 0.08 | 18.66 |
| 400 | 36.24 bc ± 0.88 | 0.81 bc ± 0.04 | 2.65 bc ± 0.14 | 16.60 |
| 450 | 38.50 cd ± 0.84 | 0.72 c ± 0.07 | 2.49 bc ± 0.06 | 14.35 |
| 500 | 38.24 cd ± 1.35 | 0.41 d ± 0.09 | 2.56 c ± 0.07 | 14.60 |
| 550 | 41.12 de ± 1.32 | 0.43 e ± 0.04 | 2.58 c ± 0.05 | 11.74 |
| 600 | 44.14 e ± 1.25 | −0.47 e ± 0.05 | 2.62 c ± 0.08 | 8.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barkó, A.; Pásztor-Huszár, K.; Mednyánszky, Z.; Hidas, K.I.; Csurka, T.; Horváth-Mezőfi, Z.; Varga-Tóth, A.; Jónás, G.; Dalmadi, I.; Visy, A. Impact of High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Quality and Functional Properties of Rehydrated Animal Blood Plasma. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063341
Barkó A, Pásztor-Huszár K, Mednyánszky Z, Hidas KI, Csurka T, Horváth-Mezőfi Z, Varga-Tóth A, Jónás G, Dalmadi I, Visy A. Impact of High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Quality and Functional Properties of Rehydrated Animal Blood Plasma. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063341
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarkó, Annamária, Klára Pásztor-Huszár, Zsuzsanna Mednyánszky, Karina Ilona Hidas, Tamás Csurka, Zsuzsanna Horváth-Mezőfi, Adrienn Varga-Tóth, Gábor Jónás, István Dalmadi, and Anna Visy. 2025. "Impact of High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Quality and Functional Properties of Rehydrated Animal Blood Plasma" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063341
APA StyleBarkó, A., Pásztor-Huszár, K., Mednyánszky, Z., Hidas, K. I., Csurka, T., Horváth-Mezőfi, Z., Varga-Tóth, A., Jónás, G., Dalmadi, I., & Visy, A. (2025). Impact of High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Quality and Functional Properties of Rehydrated Animal Blood Plasma. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063341






