Dynamic Alternations in Mother–Infant Dyad’s Gut Microbiota over the Period of Six Months
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Subject Recruitment
2.3. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Whole Genome Metagenomics Sequencing and Quality Control
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Data Availability
4. Results
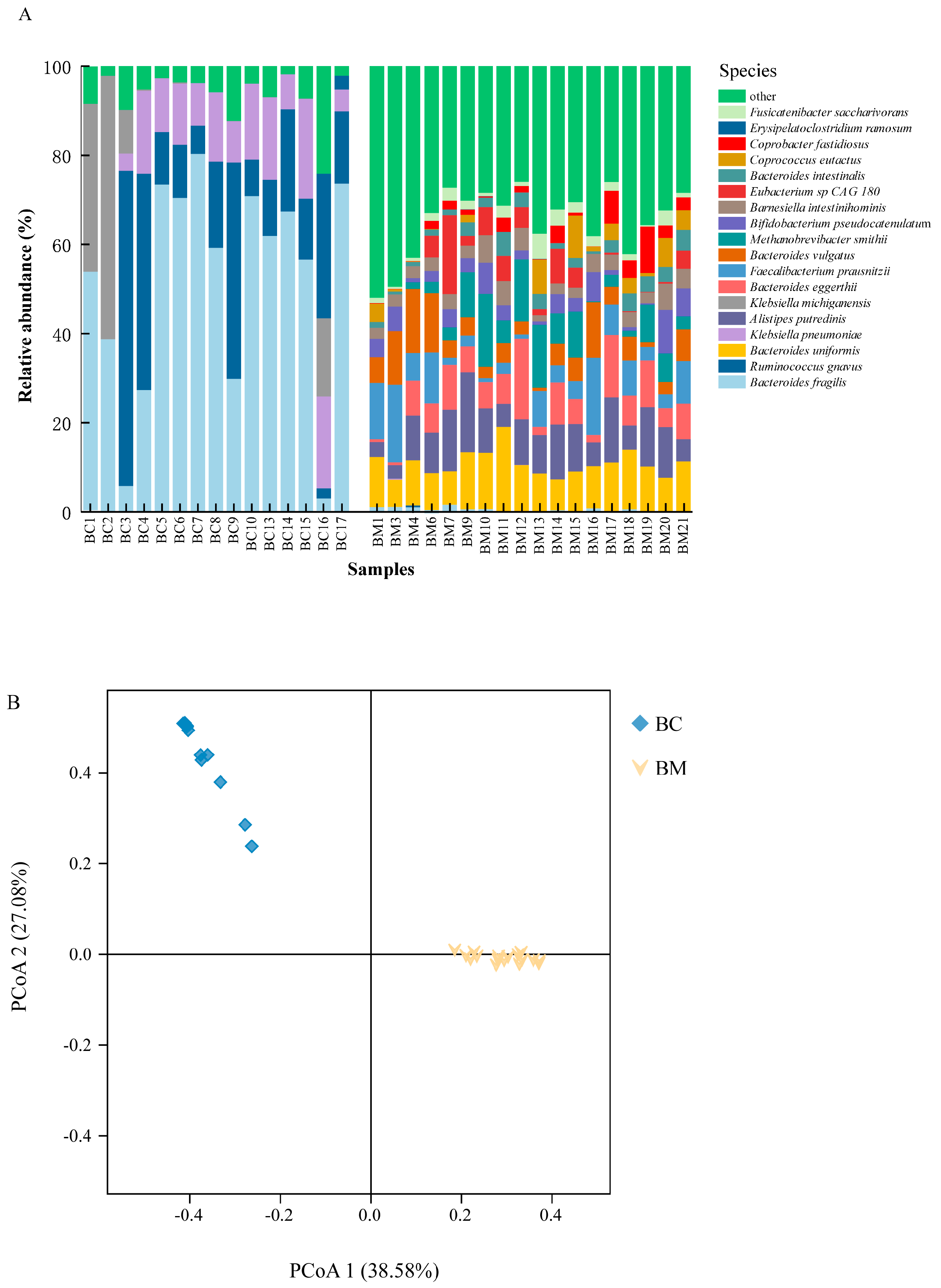
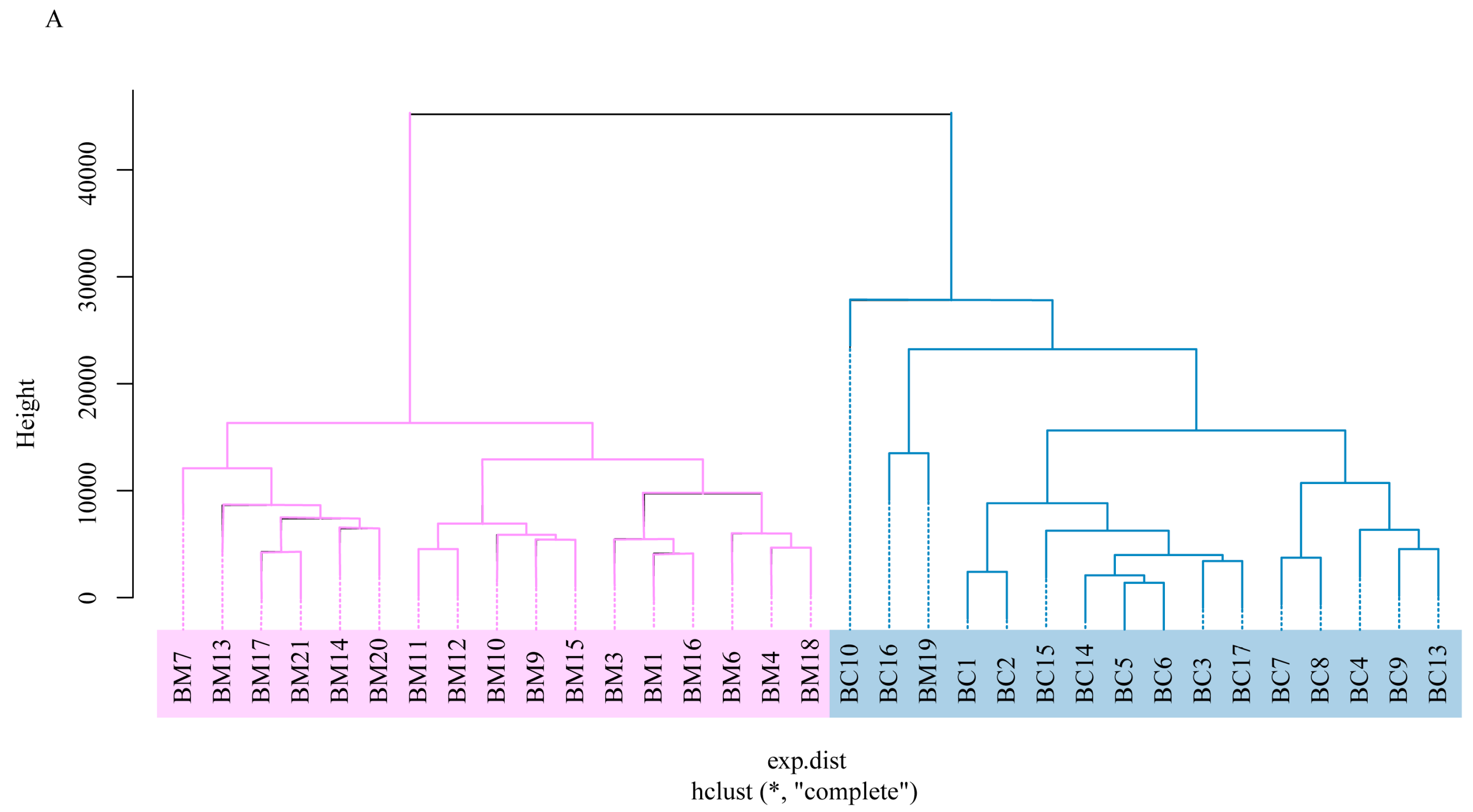
4.1. Microbial Dynamics of Mother’s and Infant’s Faecal Microbiomes
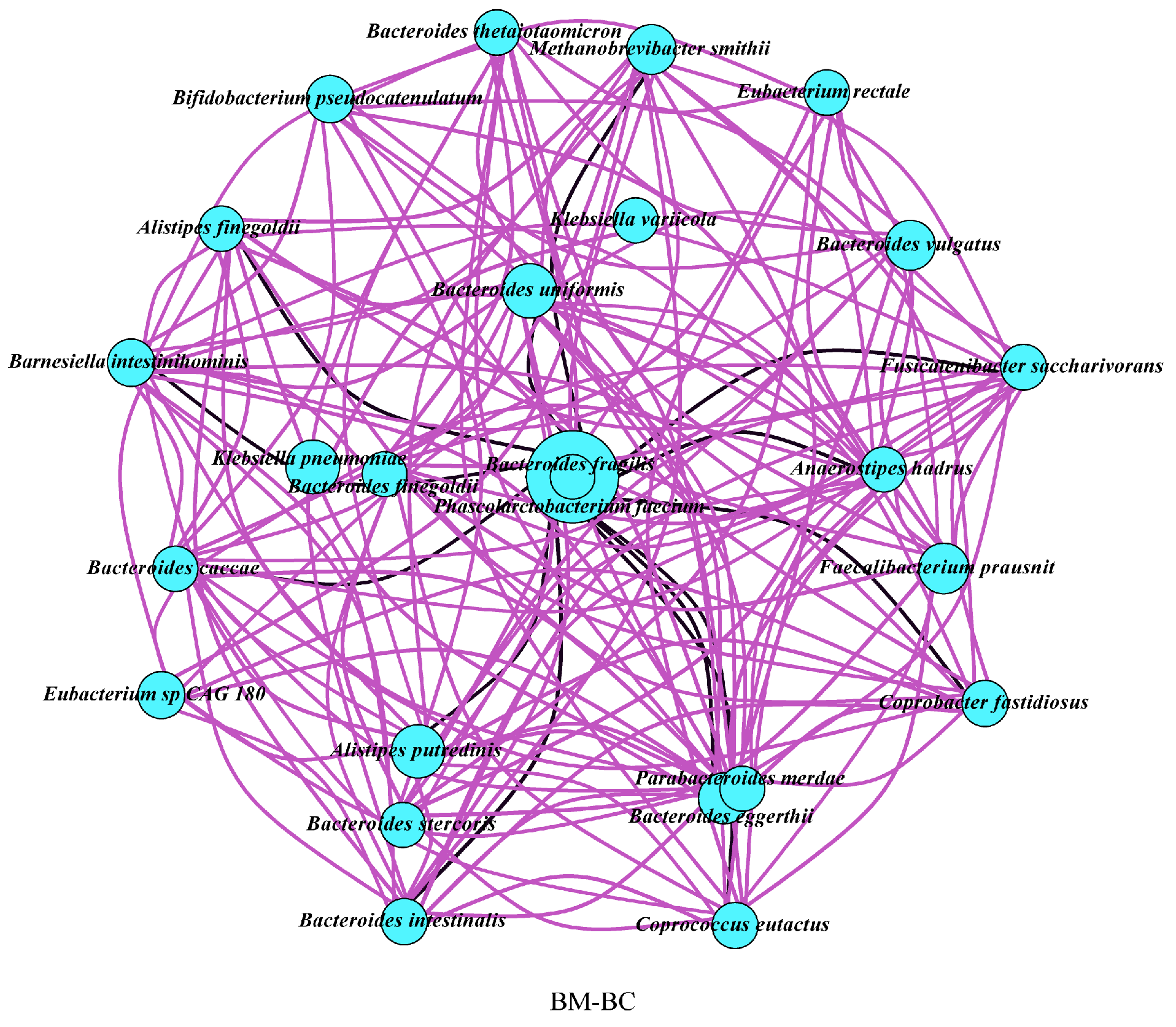
4.2. Correlation Network of Faecal Microbiota of Mother and Infant
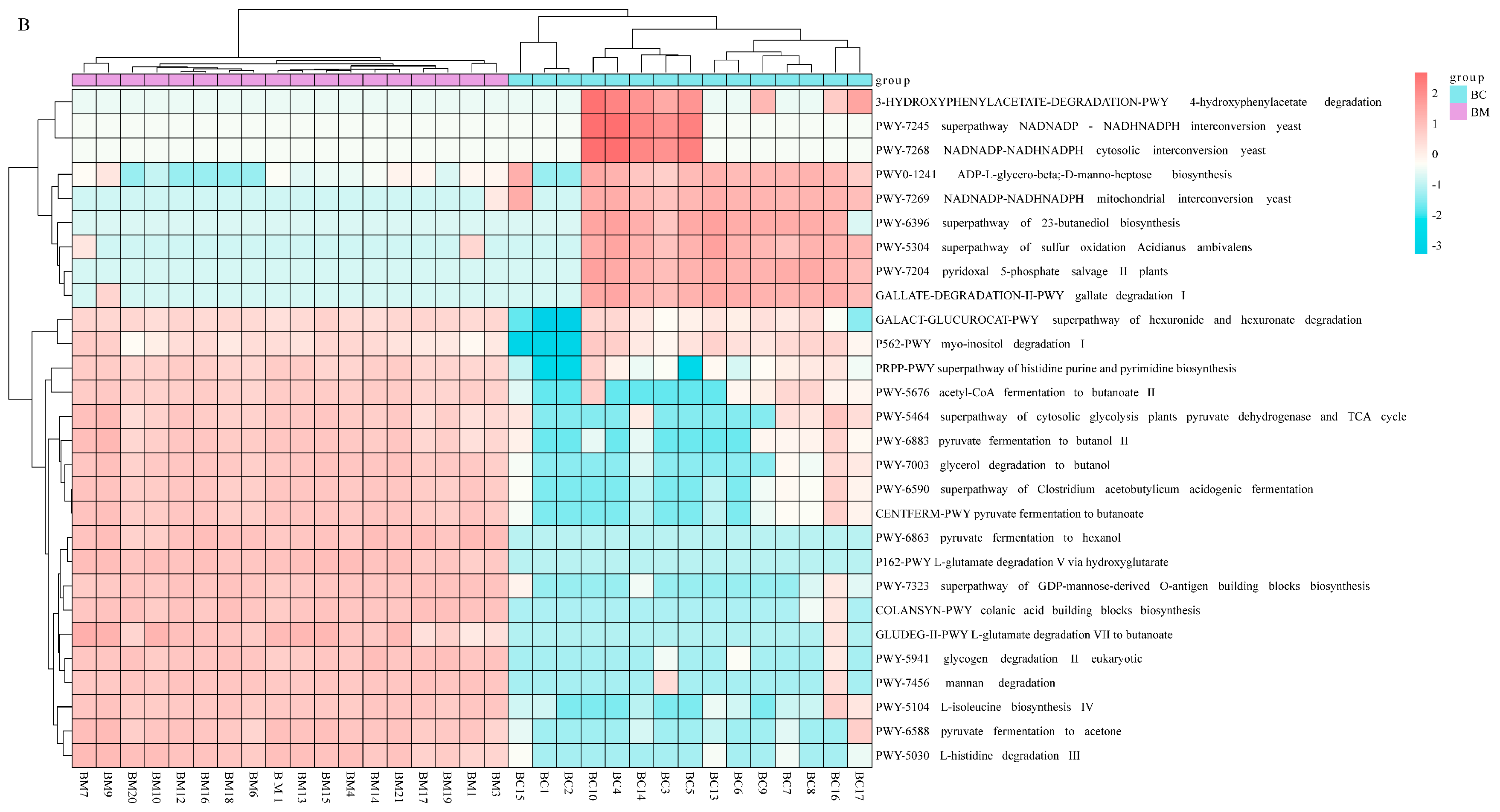
4.3. Metagenomic Potential of Mother’s and Infant’s Microbiota
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharp, C.; Foster, K.R. Host control and the evolution of cooperation in host microbiomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, J.; Hisamatsu, T. The impact of maternal exposure to antibiotics on the development of child gut microbiome. Immunol. Med. 2022, 45, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, K.; Finlay, B.B. Early-life interactions between the microbiota and immune system: Impact on immune system development and atopic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, J.; Marques, C.; Teixeira, D.; Durão, C.; Faria, A.; Brito, S. FEEDMI: A study protocol to determine the influence of infant-feeding on very-preterm-infant’s gut microbiota. Neonatology 2019, 116, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Nakayama, J. Development of the gut microbiota in infancy and its impact on health in later life. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quince, C.; Walker, A.W.; Simpson, J.T.; Loman, N.J.; Segata, N. Shotgun metagenomics, from sampling to analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Cai, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Xi, X.; Liang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Zhou, B.; et al. Unique features of ethnic Mongolian gut microbiome revealed by metagenomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousias, O.; Montesanto, F. Metagenomic profiling of host-associated bacteria from 8 datasets of the red alga Porphyra purpurea with MetaPhlAn3. Mar. Genom. 2021, 59, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.; Ward, D.V.; Pasolli, E.; Tolio, T.; Zolfo, M.; Asnicar, F.; Truong, D.T.; Tett, A.; Morrow, A.L.; Segata, N. Strain-level microbial epidemiology and population genomics from shotgun metagenomics. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W.J.B. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 26, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Simmons, B.A.; Singer, S.W. MaxBin 2.0: An automated binning algorithm to recover genomes from multiple metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, C.M.; Probst, A.J.; Sharrar, A.; Thomas, B.C.; Hess, M.; Tringe, S.G.; Banfield, J.F. Recovery of genomes from metagenomes via a dereplication, aggregation and scoring strategy. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olm, M.R.; Brown, C.T.; Brooks, B.; Banfield, J.F. DRep: A tool for fast and accurate genomic comparisons that enables improved genome recovery from metagenomes through de-replication. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcaire-Jones, G.; Scanlon, R. The first thousand days of life. Issues Law. Med. 2022, 37, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Selma-Royo, M.; Tarrazó, M.; García-Mantrana, I.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C. Shaping microbiota during the first 1000 days of life. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1125, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sakandar, H.A.; Sun, Z.H.; Zhang, H.P. Recent advances of intestinal microbiota transmission from mother to infant. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleya, S.; Sánchez, B.; Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Solís, G.; Fernández, N.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Ventura, M.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M. Intestinal microbiota development in preterm neonates and effect of perinatal antibiotics. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morreale, C.; Giaroni, C.; Baj, A.; Folgori, L.; Barcellini, L.; Dhami, A. Effects of perinatal antibiotic exposure and neonatal gut microbiota. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, M.B.; Konya, T.; Maughan, H.; Guttman, D.S.; Field, C.J.; Chari, R.S.; Sears, M.R.; Becker, A.B.; Scott, J.A.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Gut microbiota of healthy Canadian infants: Profiles by mode of delivery and infant diet at 4 months. CMAJ 2013, 185, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catlett, J.L.; Carr, S.; Cashman, M.; Smith, M.D.; Walter, M.; Sakkaff, Z.; Kelley, C.; Pierobon, M.; Cohen, M.B.; Buan, N.R. Metabolic synergy between human symbionts Bacteroides and Methanobrevibacter. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0106722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melsaether, C.; Høtoft, D.; Wellejus, A.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Damholt, A. Seeding the infant gut in early life-effects of maternal and infant seeding with probiotics on strain transfer, microbiota, and gastrointestinal symptoms in healthy breastfed infants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Gonzálvez, E.M.; Peña-Gil, N.; Rubio-del-Campo, A.; Coll-Marqués, J.M.; Gozalbo-Rovira, R.; Monedero, V.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Yebra, M.J. Infant gut microbial metagenome mining of α-l-Fucosidases with activity on fucosylated human milk oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0177522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, M.; Nicolaidou, V.; Papaneophytou, C. Special issue: The impact of early life nutrition on gut maturation and later life gut health. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegar, B.; Wibowo, Y.; Basrowi, R.W.; Ranuh, R.G.; Sudarmo, S.M.; Munasir, Z.; Atthiyah, A.F.; Widodo, A.D.; Supriatmo Kadim, M.; Suryawan, A. The role of two human milk oligosaccharides, 2’-fucosyllactose and Lacto-N-neotetraose, in infant nutrition. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yan, F.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Yue, Y.; Guan, J.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Distinct gut microbiota and metabolite profiles induced by different feeding methods in healthy Chinese infants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, S.K. Fasting intervention and its clinical effects on the human host and microbiome. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 293, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Wilson, I.D. Opinion: Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Du, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Tao, F. Potential therapeutic effects of short-chain fatty acids on chronic pain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Dynamic Alternations in Mother–Infant Dyad’s Gut Microbiota over the Period of Six Months. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063239
Yang L, Sun Z, Zhang H. Dynamic Alternations in Mother–Infant Dyad’s Gut Microbiota over the Period of Six Months. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063239
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lan, Zhihong Sun, and Heping Zhang. 2025. "Dynamic Alternations in Mother–Infant Dyad’s Gut Microbiota over the Period of Six Months" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063239
APA StyleYang, L., Sun, Z., & Zhang, H. (2025). Dynamic Alternations in Mother–Infant Dyad’s Gut Microbiota over the Period of Six Months. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063239




