Exploring the Anti-Aging Mechanisms of Queen Bee Acid Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of Queen Bee Acid Structure and Regulatory Genes
2.2. Aging Genes Acquisition
2.3. Screening and Analysis of Common Target Genes
2.4. Constructing an Interaction Network Between Queen Bee Acid and Aging Genes
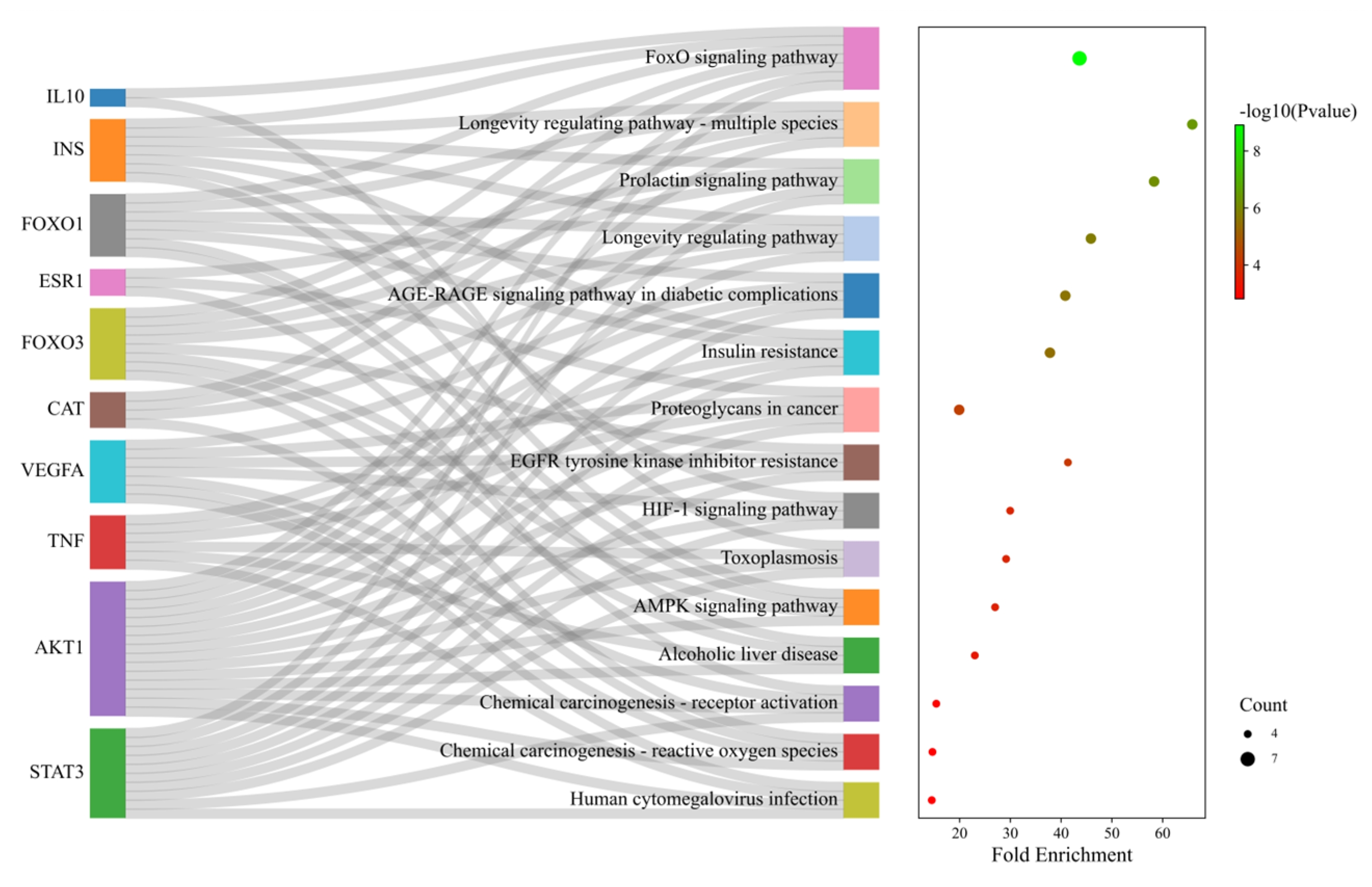
2.5. Enrichment Analysis of Core Target Genes
2.6. Molecular Docking
3. Results
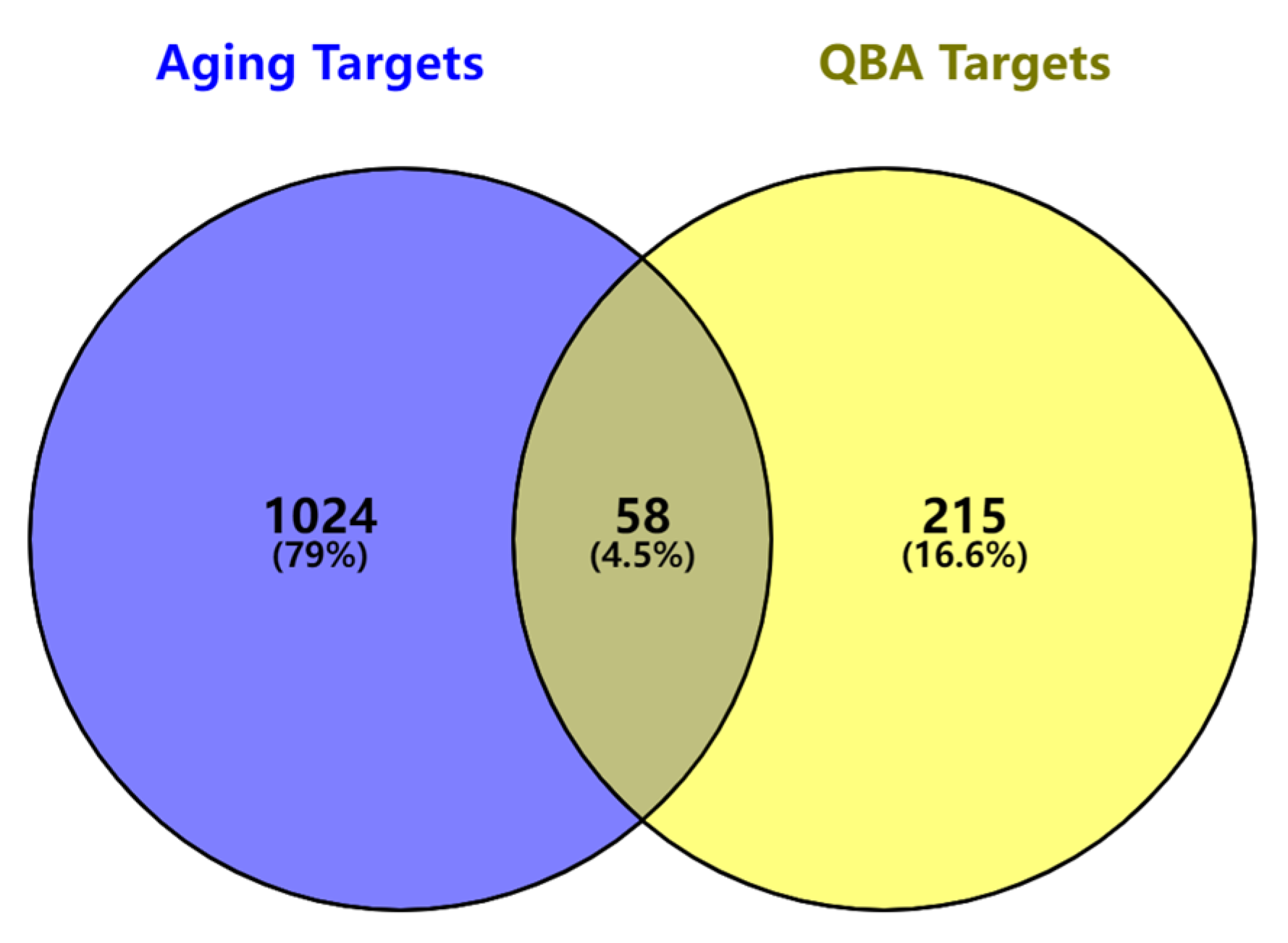
3.1. Aging Genes Regulated by Queen Bee Acid
3.2. Interactions Among Aging-Related Genes
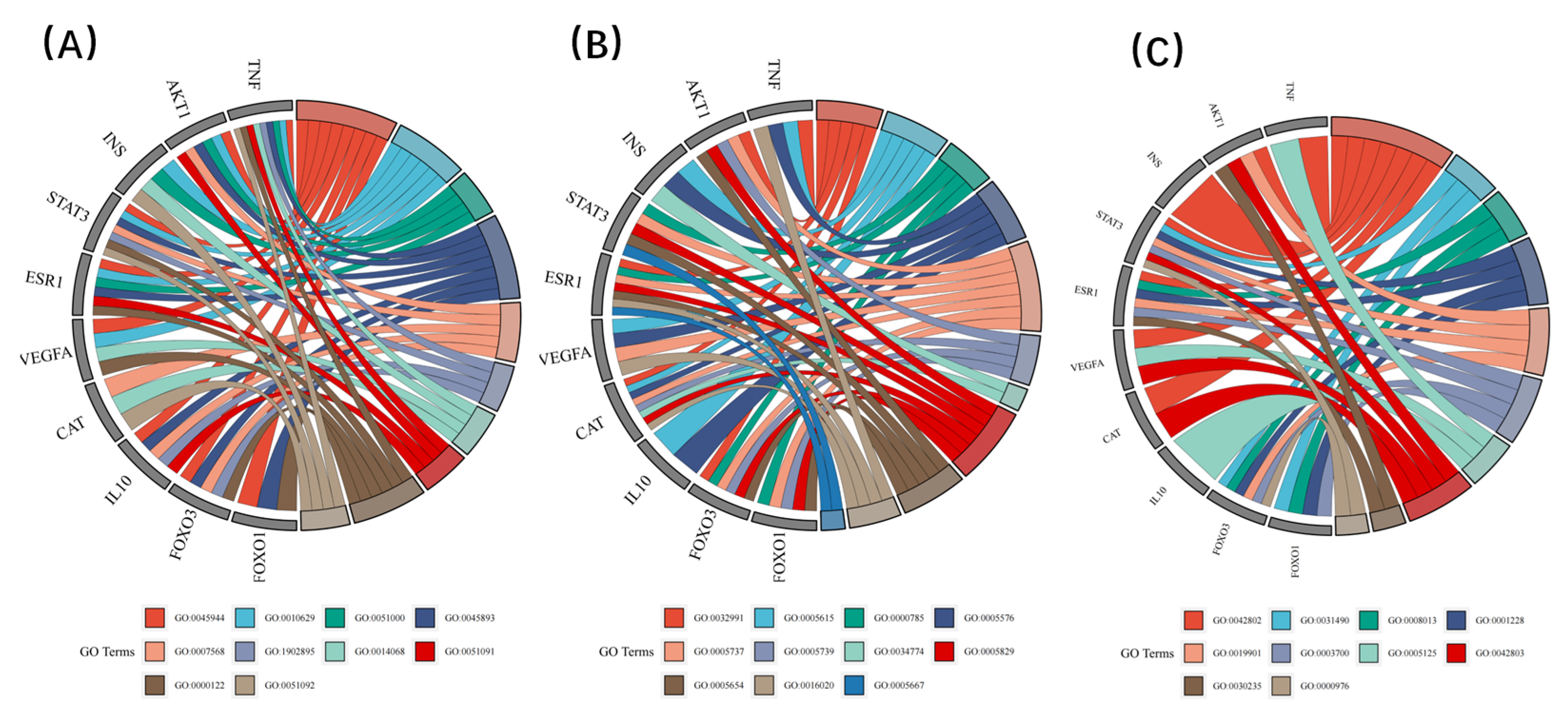
3.3. Functional Classification of Anti-Aging Genes
3.4. Molecular Docking Investigations on Queen Bee Acid Binding by Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martemucci, G.; Portincasa, P.; Di Ciaula, A.; Mariano, M.; Centonze, V.; D’Alessandro, A.G. Oxidative stress, aging, antioxidant supplementation and their impact on hu man health: An overview. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2022, 206, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Prather, E.R.; Stetskiv, M.; Garrison, D.E.; Meade, J.R.; Peace, T.I.; Zhou, T. Inflammaging and Oxidative Stress in Human Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Novel Treat ments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Liang, J.; Kirberger, M.; Chen, N. Irisin, an exercise-induced bioactive peptide beneficial for health promotion during aging process. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 80, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.K.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.H.; Pan, Y.H. Proteomic analysis of royal jel-lyfrom three strains of western honeybees (Apis mellifera). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8411–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureşan, C.I.; Buttstedt, A. pH-dependent stability of honey bee (Apis mellifera) major royal jelly proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, N.; Toda, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ikuta, T.; Tatefuji, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Shimizu, T. Royal Jelly Delays Motor Functional Impairment During Aging in Genetically Heter ogeneous Male Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.A.; Foster, A.B.; Lamb, D.C.; Hodgson, N. Identification of 10-hy-droxy-delta 2-decenoic acid in royal jelly. Nature 1959, 183, 996–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tu, X.; Tao, L.; Daddam, J.; Li, S.; Hu, F. Royal Jelly Fatty Acids: Chemical Composition, Extraction, Biological Activity, and Prospect. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 111, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunugi, N.; Mohammed, A. Royal Jelly and Its Components Promote Healthy Aging and Longevity: From Animal Models to Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Royal Jelly as an Intelligent Anti-Aging Agent—A Focus on Cognitive Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Antioxidants 2020, 29, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. Applications of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 6, 1646905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeneCards. Available online: http://www.genecards.org (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- DisGeNET. Available online: https://www.disgenet.org (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- OMIM. Available online: https://www.omim.org (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- STRING Database. Available online: https://string-db.org/cgi/input.pl (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- DAVID Database. Available online: https://david.ncifcrf.gov (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Bioinformatics Tool. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- RCSB Protein Data Bank. Available online: http://www.pdb.org/ (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Nogales, C.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; List, M.; Kiel, C.; Casas, A.I.; Schmidt, H.H. Network pharmacology: Curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davizon-Castillo, P.; McMahon, B.; Aguila, S.; Bark, D.; Ashworth, K.; Allawzi, A.; Campbell, R.A.; Montenont, E.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; et al. TNF-alpha driven inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction define the platelet hyperreactivity of aging. Blood 2019, 134, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasako, T.; Umehara, T.; Soeda, K.; Kaneko, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Tamura-Nakano, M.; Chiba, T.; Accili, D.; et al. Deletion of skeletal muscle Akt1/2 causes osteosarcopenia and reduces lifespan in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, J.; Chen, P.-J.; Xiao, W.-H. Mechanism of increased risk of insulin resistance in aging skeletal muscle. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardini, E.S.; Chen, G.G.; Fiacco, S.; Mernone, L.; Willi, J.; Turecki, G.; Ehlert, U. Differential ESR1 Promoter Methylation in the Peripheral Blood—Findings from the Women 40+ Healthy Aging Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Grob, S.; Avery, R.; Kimura, A.; Pieramici, D.; Lee, J.; Rabena, M.; Ortiz, S.; Quach, J.; Cao, G.; et al. Common variant in VEGFA and response to anti-VEGF therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Samini, F.; Farkhondeh, T. The Role of Saffron in Attenuating Age-related Oxidative Damage in Rat Hippocampus. Recent Patents on Food. Nutr. Agric. 2017, 8, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Dagdeviren, S.; Jung, D.Y.; Friedline, R.H.; Noh, H.L.; Kim, J.H.; Patel, P.R.; Tsitsilianos, N.; Inashima, K.; Tran, D.A.; Hu, X.; et al. IL-10 prevents aging-associated inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 2016, 31, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, B.J.; Willcox, D.C.; Donlon, T.A.; Willcox, B.J. FOXO3: A Major Gene for Human Longevity—A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2015, 61, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousteni, S. FoxO1: A molecule for all seasons. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.W.; Fan, X.; Maynard, J.C.; Wheatley, E.G.; Bieri, G.; Couthouis, J.; Burlingame, A.L.; Villeda, S.A. Age-related loss of neural stem cell O-GlcNAc promotes a glial fate switch through STAT3 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 202007439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, A.S.; Duffy, J.; Wang, M.C. Lipid metabolism and lipid signals in aging and longevity. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Lithgow, G.J.; Link, W. Long live FOXO: Unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and longevity. Aging Cell. 2015, 15, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Park, S.; Lakatta, E.G. RAGE signaling in inflammation and arterial aging. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzilai, N.; Ferrucci, L. Insulin resistance and aging: A cause or a protective response? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 67, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ouyang, S.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Gong, J.; Zheng, S.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, H. PharmMapper server: A web server for potential drug target identification using pharmacophore mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 609–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, M.; Othman, Y.; Xie, X.-Q.; Feng, Z. Virus-CKB 2.0: Viral-Associated Disease-Specific Chemogenomics Knowledgebase. Acs Omega 2022, 7, 37476–37484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target Name | Degree | Betweenness | Closeness |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | 84 | 409.18216 | 0.7808219 |
| AKT1 | 84 | 417.0469 | 0.7808219 |
| INS | 80 | 461.00653 | 0.7702703 |
| STAT3 | 66 | 142.41878 | 0.686747 |
| ESR1 | 62 | 217.12914 | 0.6785714 |
| VEGFA | 62 | 125.693 | 0.67058825 |
| CAT | 46 | 72.715454 | 0.6195652 |
| IL10 | 44 | 55.924225 | 0.59375 |
| FOXO3 | 44 | 22.538624 | 0.60638297 |
| FOXO1 | 44 | 33.371983 | 0.60638297 |
| Name | PDB ID | Center | Size | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | |||
| TNF | 1TNR | 44.59 | 23.62 | 40.88 | 68 | 74 | 66 | −6 |
| AKT1 | 4EKL | 19.78 | −0.59 | 16.17 | 48 | 52 | 60 | −7 |
| INS | 1OS4 | 5.54 | 10.52 | 20.81 | 40 | 54 | 52 | −7.2 |
| STAT3 | 6NUQ | −2.03 | 18.68 | 25.84 | 78 | 116 | 94 | −6.3 |
| ESR1 | 7UJW | 0.56 | 30.07 | 49.67 | 78 | 76 | 94 | −6.8 |
| VEGFA | 6D3O | 25.03 | −38.14 | 4.83 | 44 | 68 | 42 | −5.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Huang, A. Exploring the Anti-Aging Mechanisms of Queen Bee Acid Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063192
Feng Y, Tian Y, Huang A. Exploring the Anti-Aging Mechanisms of Queen Bee Acid Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063192
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yinan, Yakai Tian, and Aixiang Huang. 2025. "Exploring the Anti-Aging Mechanisms of Queen Bee Acid Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063192
APA StyleFeng, Y., Tian, Y., & Huang, A. (2025). Exploring the Anti-Aging Mechanisms of Queen Bee Acid Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063192






