Waste-Free Glucose to Erythritol Conversion—Innovations with Yarrowia lipolytica Wratislavia K1 UV15
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
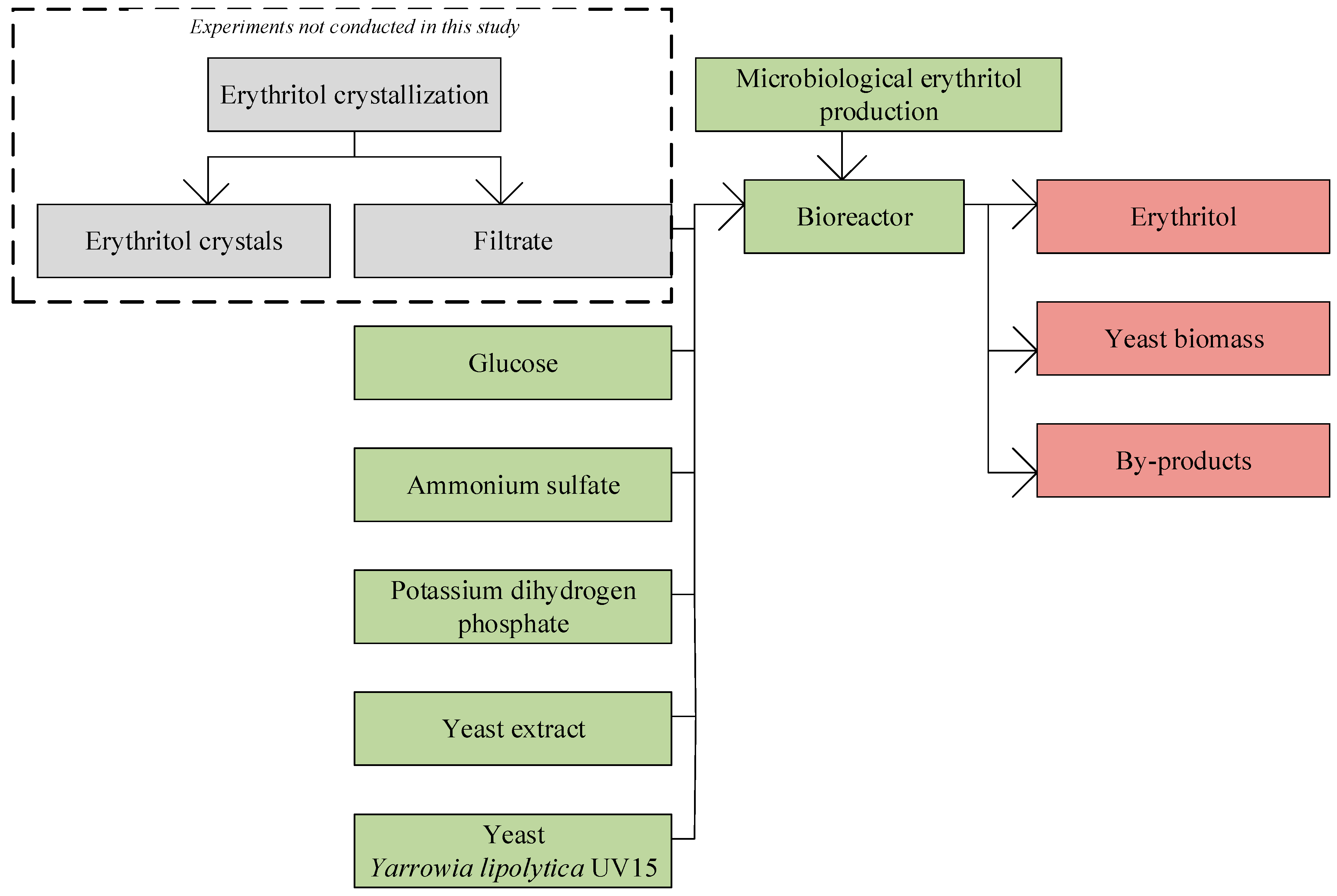
2.1. Microorganism
2.2. Media
2.3. Culture Conditions
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Calculation of Fermentation Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of (NH4)2SO4 Concentration for Efficient Erythritol Biosynthesis by Y. lipolytica Using Glucose and Post-Crystallization Filtrate

3.2. Impact of Yeast Extract Reduction on Erythritol Production and Purity in Y. lipolytica
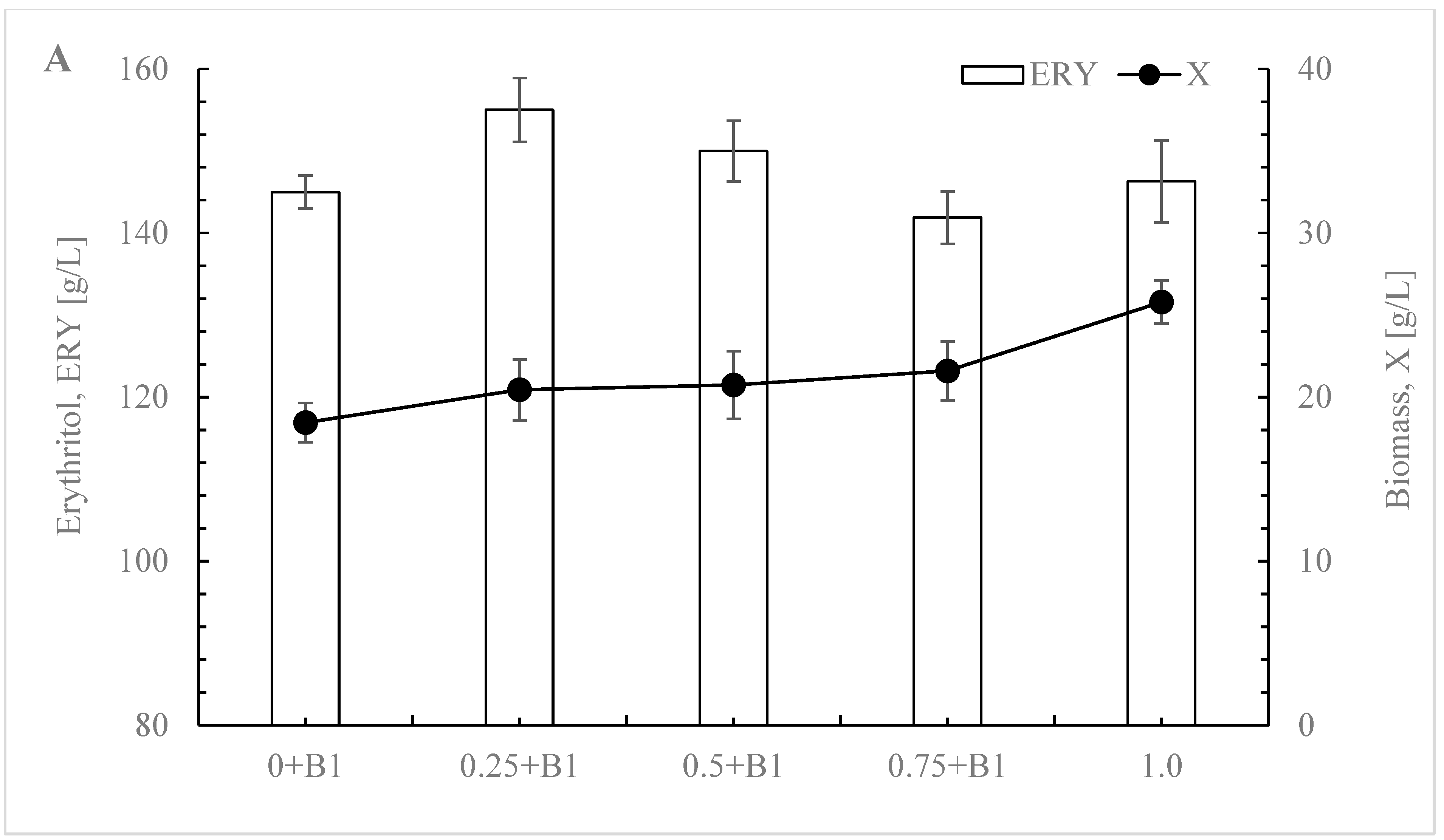
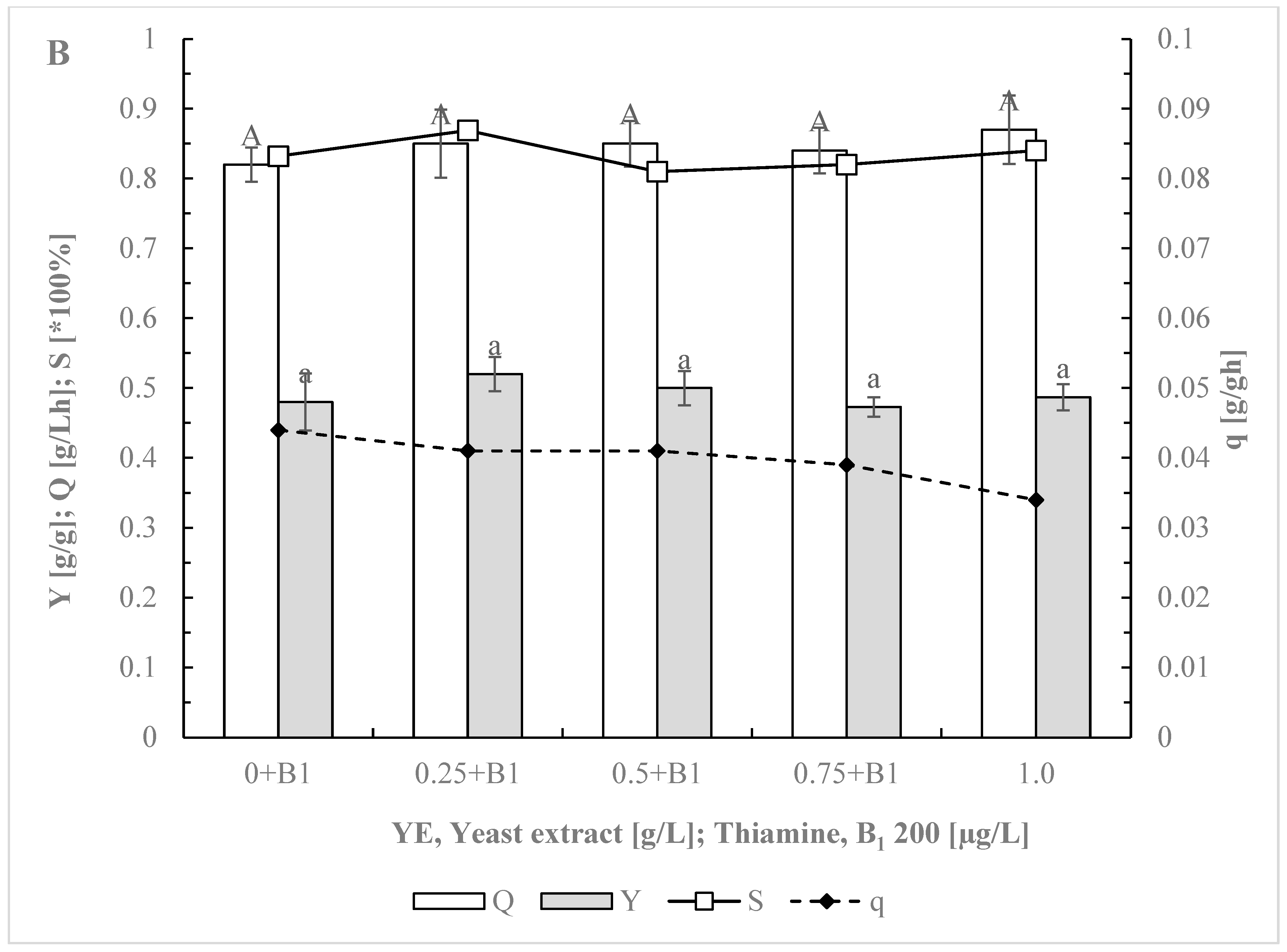
3.3. Optimizing Initial Glucose Concentration for Enhanced Selectivity in Erythritol Production
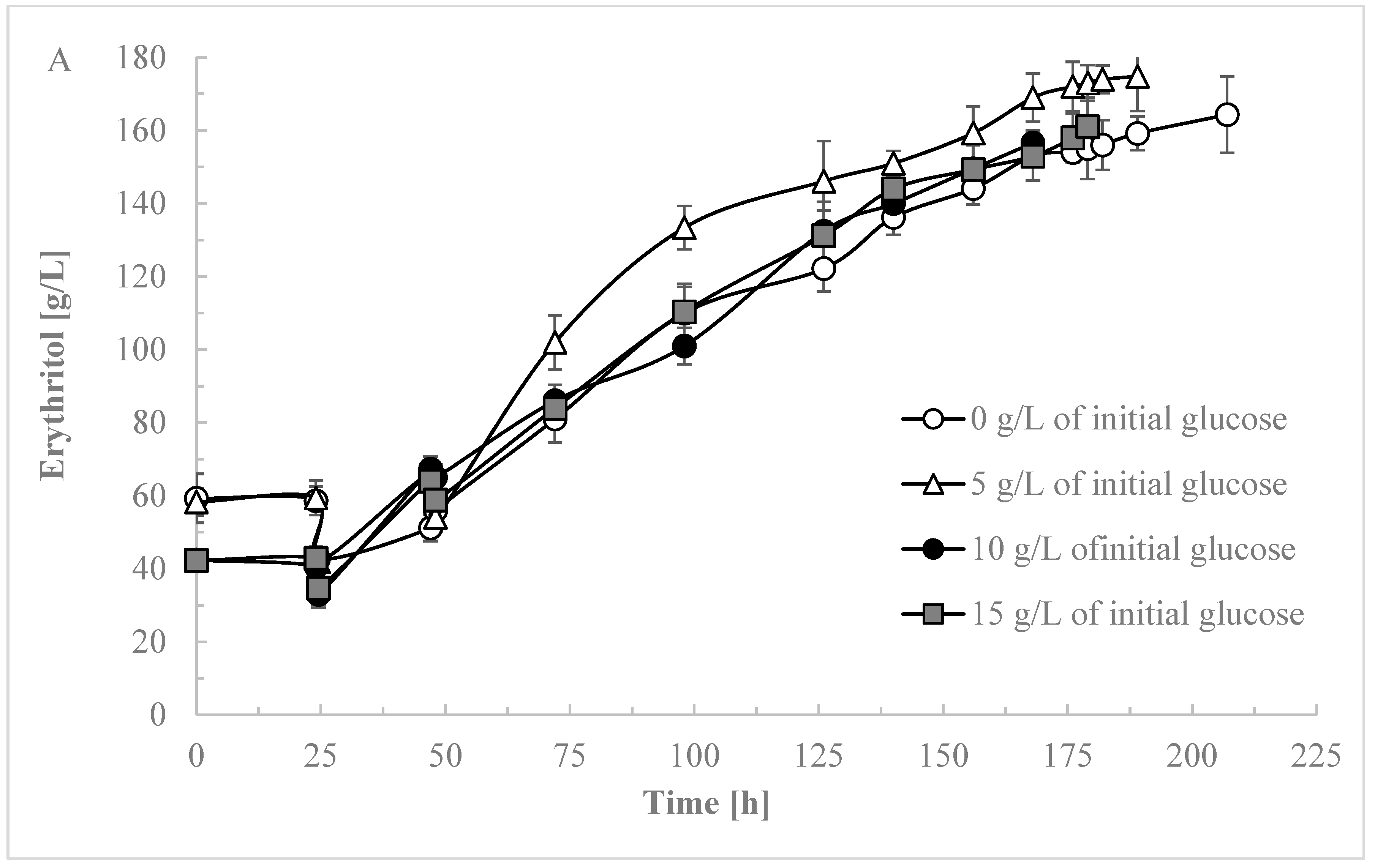

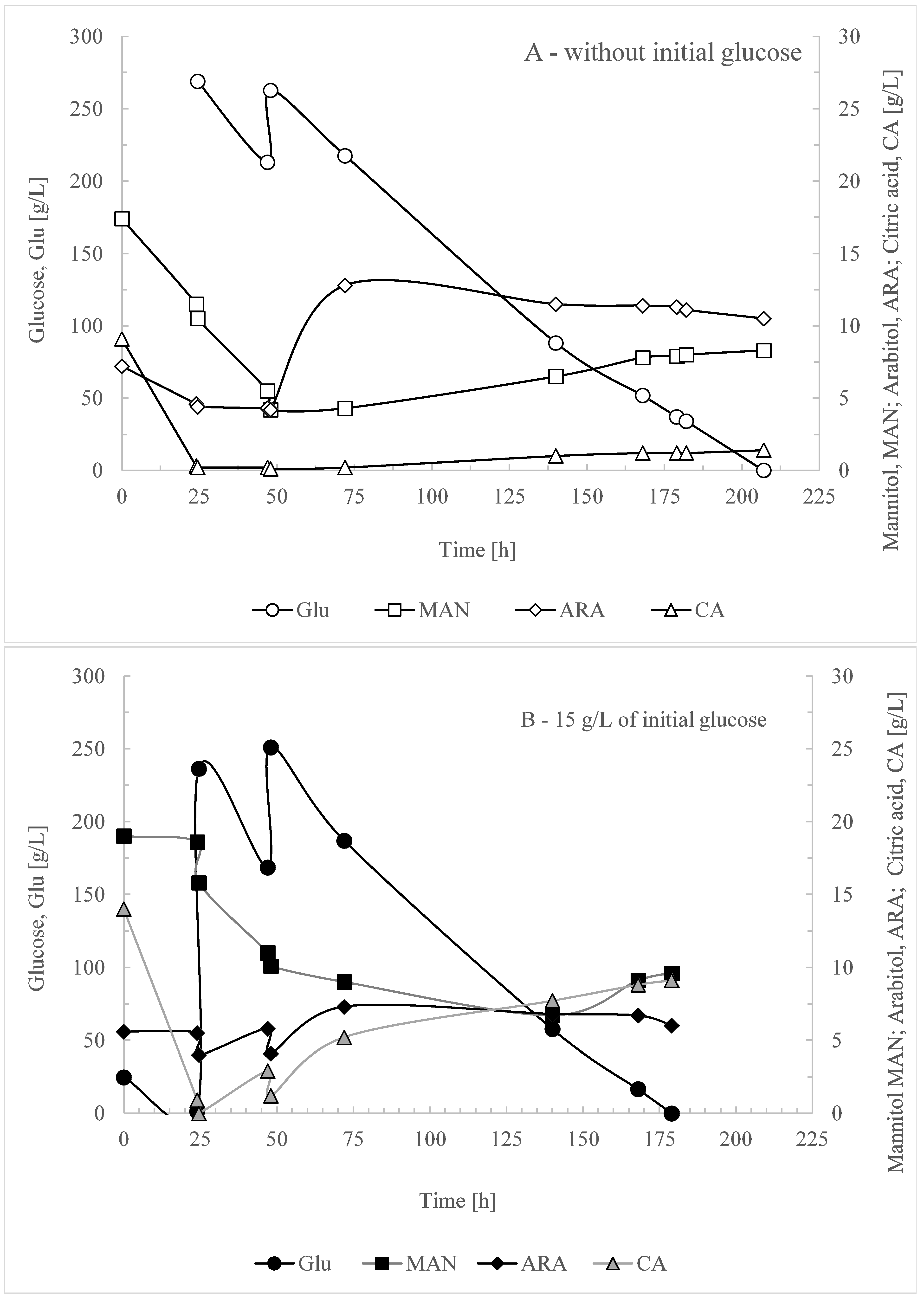
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jackson, E.B. Use of glucose syrups in the food industry. In Handbook of Starch Hydrolysis Products and Their Derivatives; Kearsley, M.W., Dziedzic, S.Z., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sarris, D.; Papanikolaou, S. Biotechnological production of ethanol: Biochemistry, processes and technologies. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamerou, E.E.; Parsons, S.; McManus, M.C.; Chuck, J.C. Using techno-economic modelling to determine the minimum cost possible for a microbial palm oil substitute. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, X.; Han, M.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Rong, Z.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in biosynthesis mechanisms and yield enhancement strategies of erythritol. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 13112–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.R.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, A.; Ying, H.; Qu, L.; Alam, M.A.; Xiong, W.; Xu, J.; Lv, Y. Recent advances in producing sugar alcohols and functional sugars by engineering Yarrowia lipolytica. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 648382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulou, P.; Papanikolaou, S. Biotechnological production of sugar-alcohols: Focus on Yarrowia lipolytica and edible/medicinal mushrooms. Process Biochem. 2023, 124, 113–131.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza-Serna, L.; Serna-Loaiza, S.; Masi, A.; Mach, R.L.; Mach-Aigner, A.R.; Friedl, A. From the culture broth to the erythritol crystals: An opportunity for circular economy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4467–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Dai, Z. Enhancing the thermotolerance and erythritol production of Yarrowia lipolytica by introducing heat-resistant devices. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1108653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, S.; Bilal, M.; Ge, X.; Zhang, C.; Fickers, P.; Cheng, H. Identification, characterization of two NADPH-dependent erythrose reductases in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica and improvement of erythritol productivity using metabolic engineering. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiao, B.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Cai, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y. Advances in efficient biosynthesis of erythritol by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2024, 40, 665–686. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chi, P.-H.; Zou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Bilal, M.; Fickers, P.; Cheng, H. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for thermoresistance and enhanced erythritol productivity. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Ji, L.; Chen, H. Concomitant production of erythritol and β-carotene by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11567–11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, X.; Song, Y.; Guo, B. Knock Down of Erythrulose Kinase (eyk1) Leads to the enhancement of erythritol production in Yarrowia lipolytica mutant strain YE4-2. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 16, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzechonek, D.A.; Dobrowolski, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Mirończuk, A.M. Recent advances in 315 biological production of erythritol. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 38, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhao, L.X.; Wei, L.J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Hua, Q. Metabolic engineering of erythritol production from glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2024, 29, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rywińska, A.; Tomaszewska-Hetman, L.; Juszczyk, P.; Rakicka-Pustułka, M.; Bogusz, A.; Rymowicz, W. Enhanced production of erythritol from glucose by the newly obtained UV mutant Yarrowia lipolytica K1UV15. Molecules 2024, 29, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rywińska, A.; Marcinkiewicz, M.; Cibis, E.; Rymowicz, W. Optimization of medium composition for erythritol production from glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica using response surface methodology. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 45, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finogenova, T.V.; Morgunov, I.G.; Kamzolova, S.V.; Chernyavskaya, O.G. Organic acid production by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica: A review of prospects. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2005, 41, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyavskaya, O.G.; Shishkanova, N.V.; Il’chenko, A.P.; Finogenova, T.V. Synthesis of α-ketoglutaric acid by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast grown on ethanol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tian, J.-T.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wei, L.-J.; Fickers, P.; Hua, Q. Improving an alternative glycerol catabolism pathway in Yarrowia lipolytica to enhance erythritol production. Yeast 2024, 41, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, S.G.; Bhatt, S.S.; Shah, A.R. Evaluation of corn steep liquor as a supplementary feed for Labeo rohita (Ham.) fingerlings. Aquac. Int. 2011, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahjudi, S.M.W.; Engel, D.; Büchs, R. Metabolic studies of Hansenula polymorpha using nine different corn steep liquors. BMC Biotechnol. 2025, 25, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.A.; Canettieri, E.V.; Bispo, J.A.C.; Giulietti, M.; de Almeida e Silva, J.B.; Converti, A. Strategies for xylitol purification and crystallization: A review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, T.; Cao, W.; Qiao, C. Effective decolorization of poly-γ-glutamic acid fermentation broth by integrated activated carbon adsorption and isoelectric point precipitation of glutamic acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Jiang, J.C.; Xu, J.M. Decolorization and chemical regeneration of granular activated carbon used in citric acid refining. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2009, 23, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rywińska, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Żarowska, B.; Skrzypiński, A. Comparison of citric acid production from glycerol and glucose by different strains of Yarrowia lipolytica. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lp. | Name | Composition (g/L) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inocula | glucose—40.0; peptone—2.0; yeast extract—3.0; distilled water up to 1.0 L | Inoculum preparation |
| 2. | Filtrate originating from erythritol crystallization | erythritol—224.0 ± 2.9, mannitol—82.6 ± 5.1, arabitol—42.8 ± 2.1, citric acid—60.2 ± 0.6 | Carbon source in the production medium |
| 4. | Production medium 1 | glucose 300.0 (25.0 g/L at the beginning of the process, 200.0 g/L and 75.0 g/L added after 24 h and 48 h), filtrate (130.0 mL), (NH4)2SO4—2.6, 3.1, 3.6, 4.1), MgSO4·7H2O—1; KH2PO4—0.22; yeast extract—1.0 | Selection of optimal nitrogen source concentration |
| 5. | Production medium 2 | glucose 300.0 (25.0 g/L at the beginning of the process, 200.0 g/L and 75.0 g/L added after 24 h and 48 h), filtrate (130.0 mL), (NH4)2SO4—3.1 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O—1.0; KH2PO4—0.22; yeast extract—0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0; thiamine 200 µg/L in medium with 0.0, 0.5, 0.75 of yeast extract | Selection of optimal yeast extract concentration |
| 6. | Production medium 3 | Glucose 300.0 (0.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 25.0 at the beginning of the process and 250.0 g/L and the rest to 300.0 g/L added after 24 h and 48 h), filtrate—250.0 mL, (NH4)2SO4—3.1 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O—1; KH2PO4—0.22; yeast extract—0.25. | Analyzing the potential for reducing the initial glucose concentration |
| Carbone [g/L] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Filtrate | Start Batch | End of Batch |
| Glucose | 0.0 | 120.0 | 0.0 |
| Erythritol | 88.0 | 11.2 | 68.7 |
| Mannitol | 32.7 | 6.5 | 2.2 |
| Arabitol | 17.1 | 4.5 | 1.2 |
| Citric acid | 28.1 | 4.8 | 4.9 |
| Biomass | 0.0 | 0.0 | 10.0 |
| CO2 theoretically from glucose | - | - | 40.0 |
| SUM | 165.9 | 147.0 | 127.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rywińska, A.; Juszczyk, P.; Lazar, Z.; Tomaszewska-Hetman, L.; Kuźmińska-Bajor, M.; Rymowicz, W.; Rakicka-Pustułka, M. Waste-Free Glucose to Erythritol Conversion—Innovations with Yarrowia lipolytica Wratislavia K1 UV15. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063190
Rywińska A, Juszczyk P, Lazar Z, Tomaszewska-Hetman L, Kuźmińska-Bajor M, Rymowicz W, Rakicka-Pustułka M. Waste-Free Glucose to Erythritol Conversion—Innovations with Yarrowia lipolytica Wratislavia K1 UV15. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063190
Chicago/Turabian StyleRywińska, Anita, Piotr Juszczyk, Zbigniew Lazar, Ludwika Tomaszewska-Hetman, Marta Kuźmińska-Bajor, Waldemar Rymowicz, and Magdalena Rakicka-Pustułka. 2025. "Waste-Free Glucose to Erythritol Conversion—Innovations with Yarrowia lipolytica Wratislavia K1 UV15" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063190
APA StyleRywińska, A., Juszczyk, P., Lazar, Z., Tomaszewska-Hetman, L., Kuźmińska-Bajor, M., Rymowicz, W., & Rakicka-Pustułka, M. (2025). Waste-Free Glucose to Erythritol Conversion—Innovations with Yarrowia lipolytica Wratislavia K1 UV15. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063190






