Research on Active Control of X-Type Interconnected Hydropneumatic Suspensions for Heavy-Duty Special Vehicles via Extended State Observer-Model Predictive Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Dynamic Model of Hydropneumatic Suspension
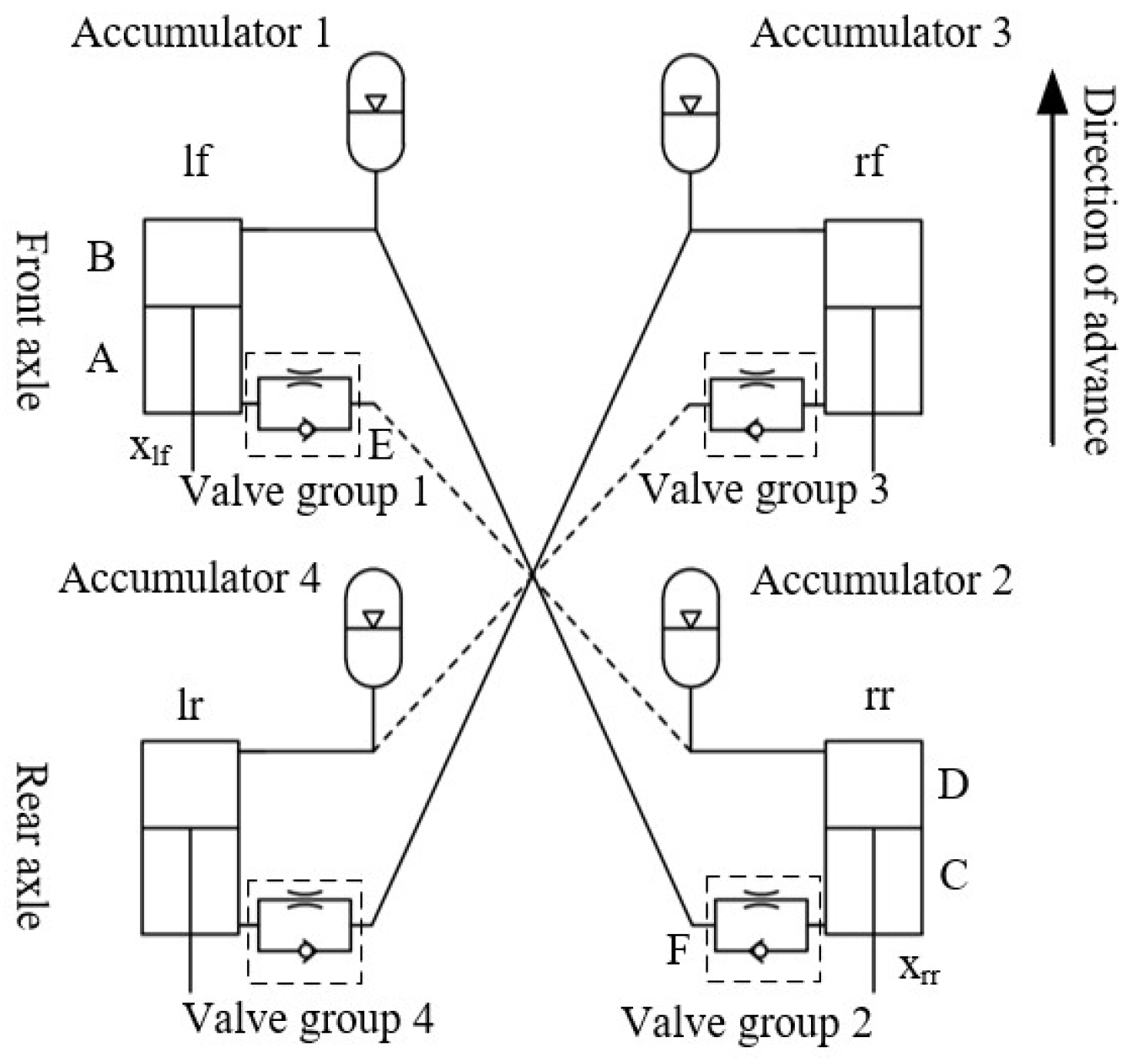
2.1.1. Active X-Type Interconnecting Hydropneumatic Suspension System
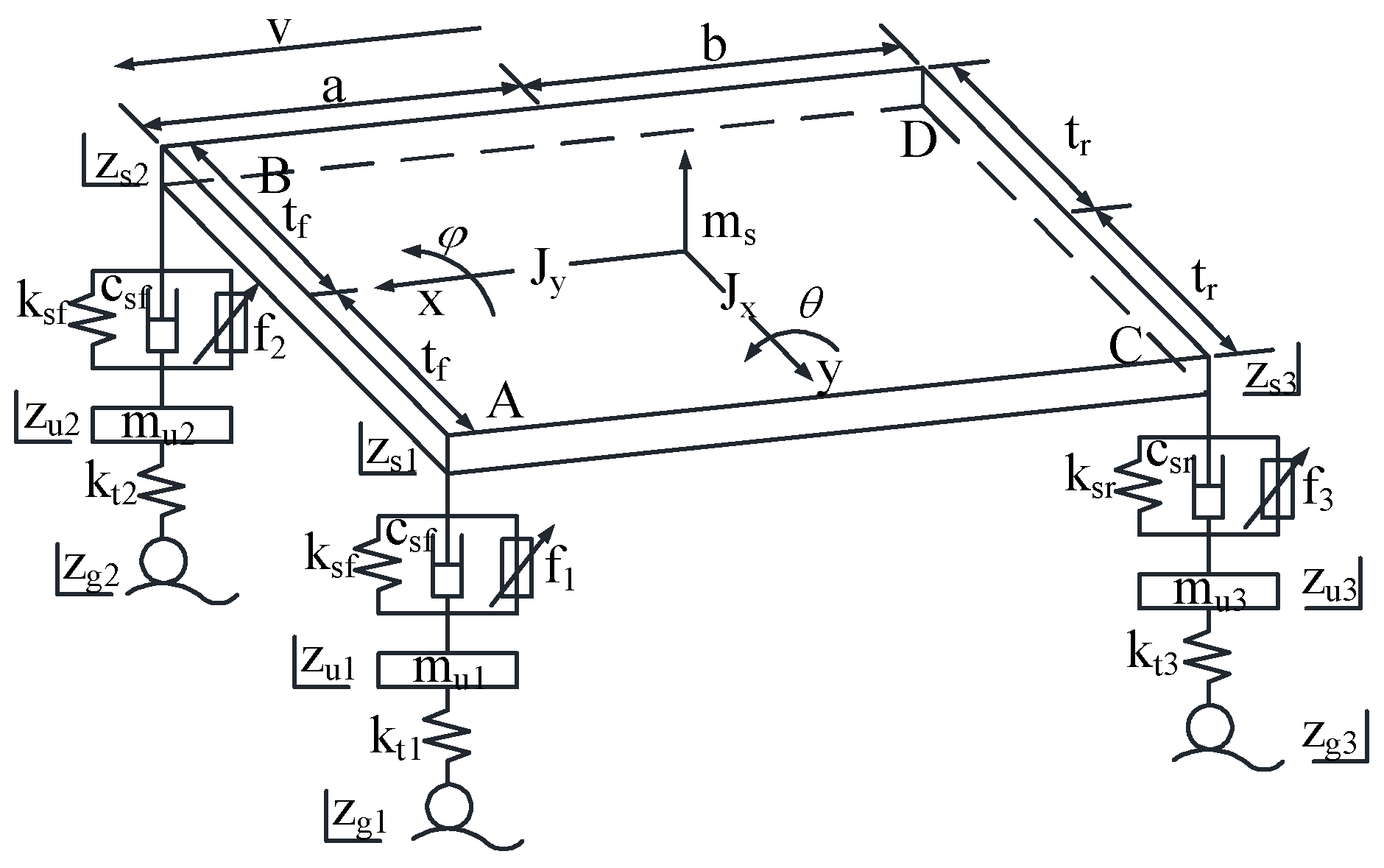
2.1.2. Seven-DOF Model
2.1.3. Linearization of a Seven-DOF Model
2.2. ESO-MPC Active Control Design
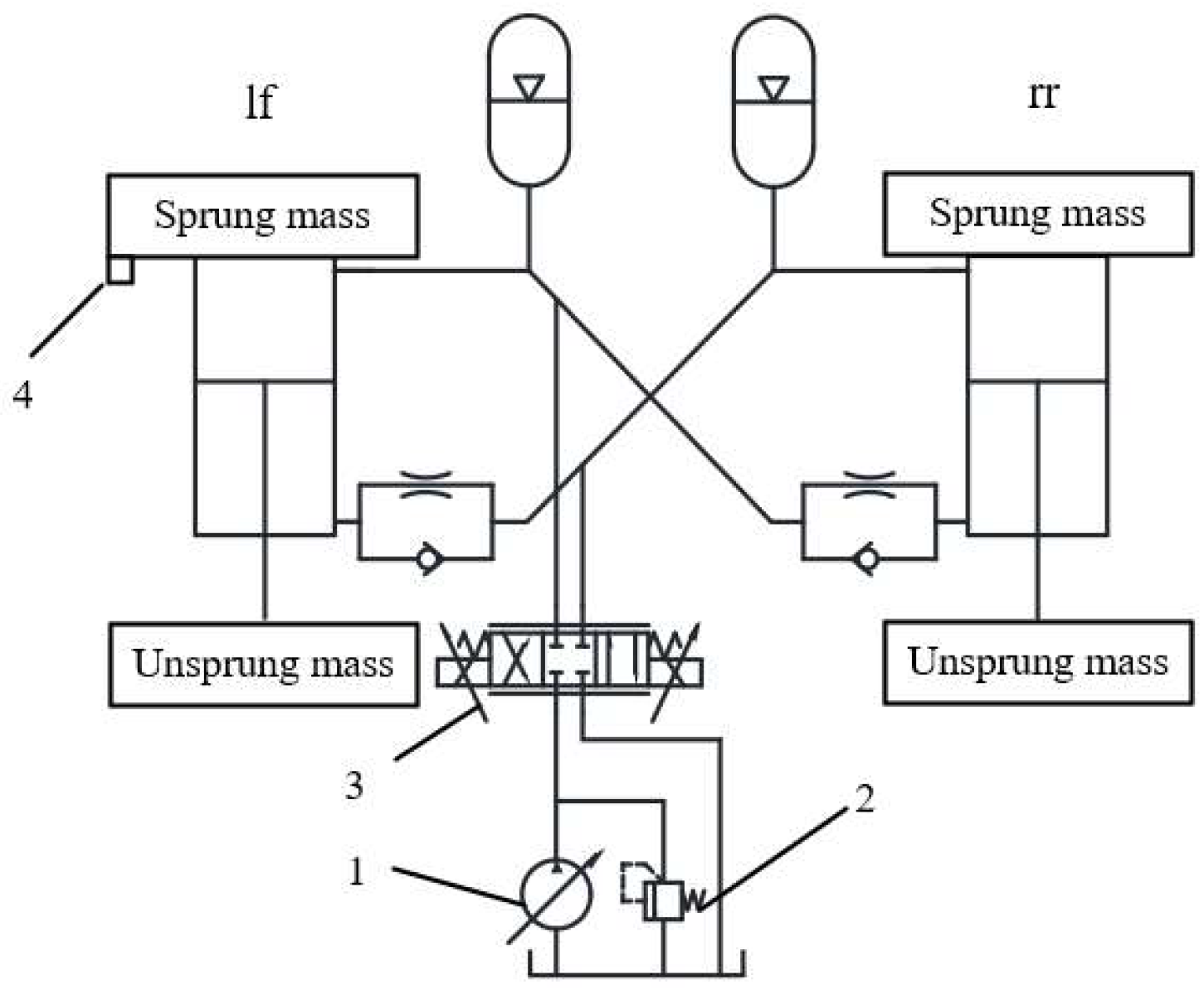
2.2.1. Active Control Architecture
2.2.2. ESO Design
2.2.3. MPC Active Control Design
2.3. Simulation Model
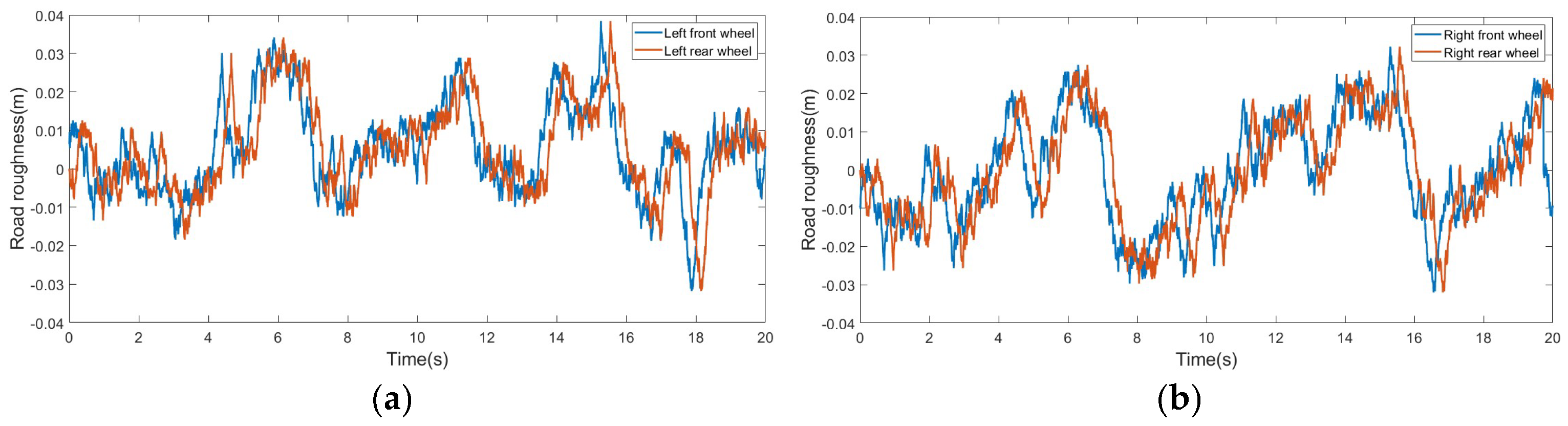
2.3.1. Pavement Modeling
2.3.2. Suspension Model
3. Results and Discussion
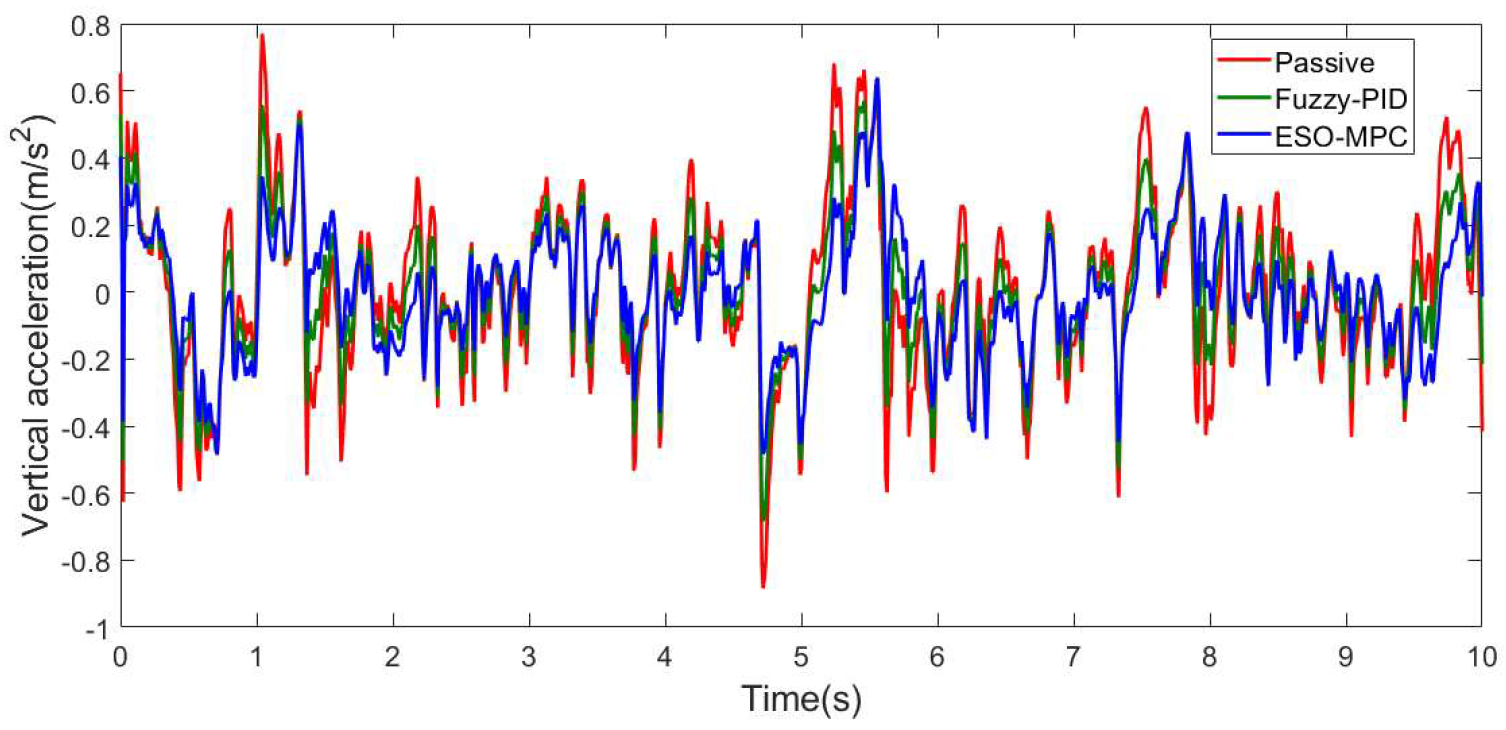
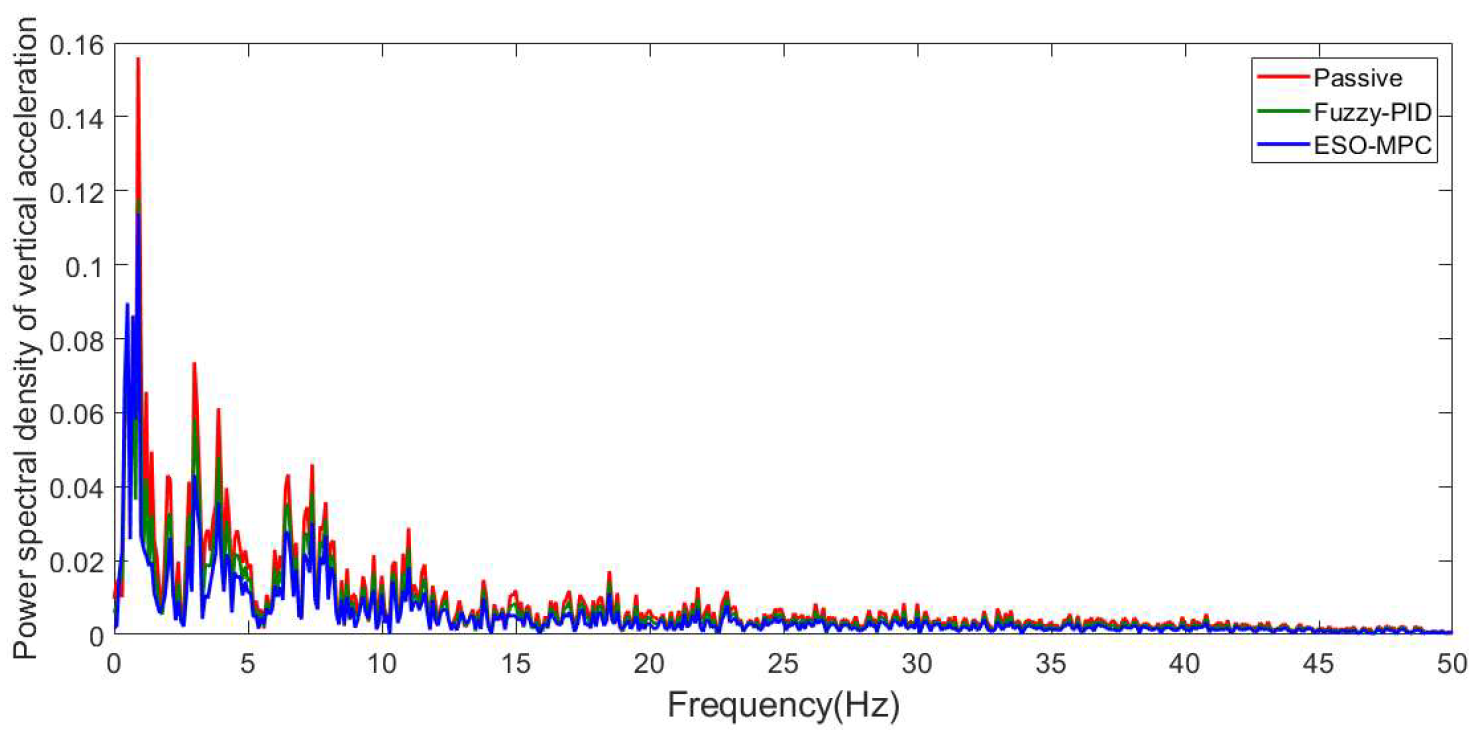
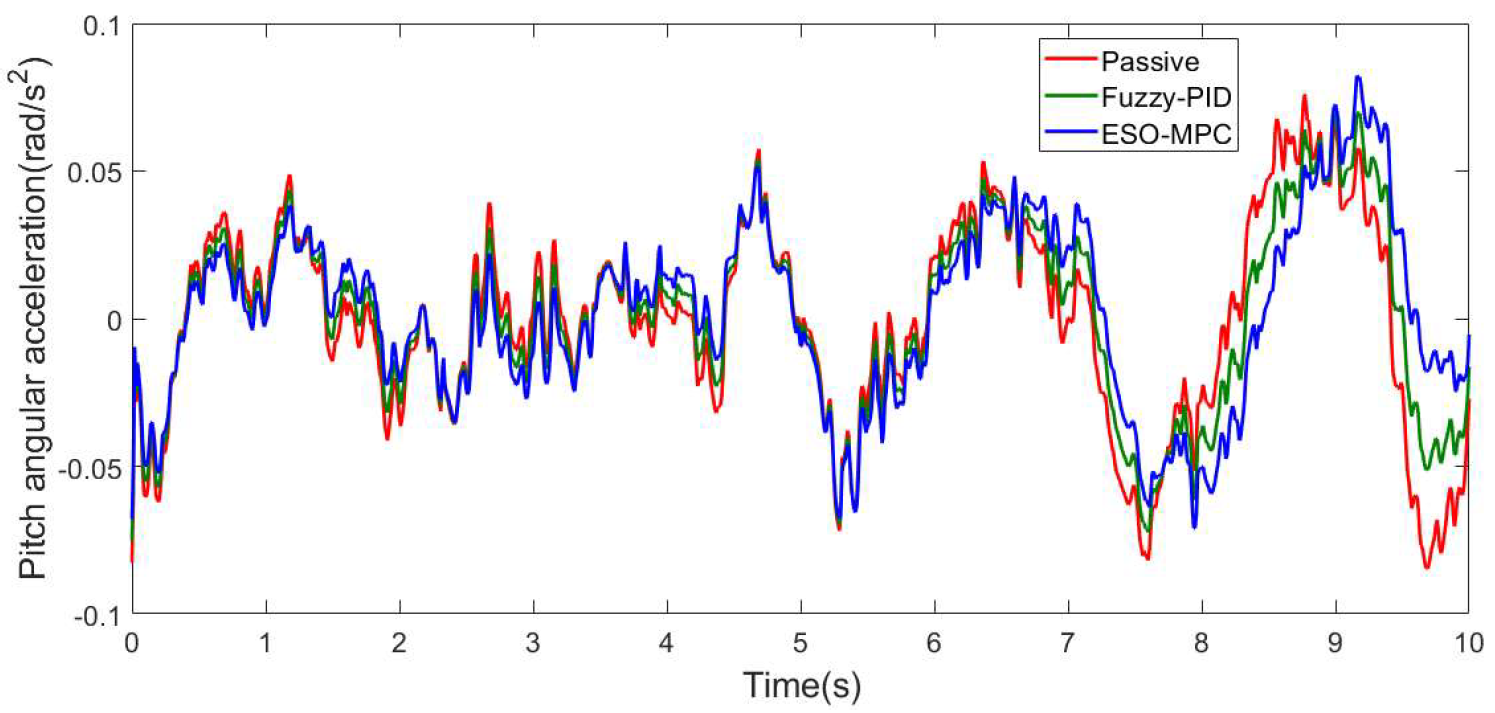
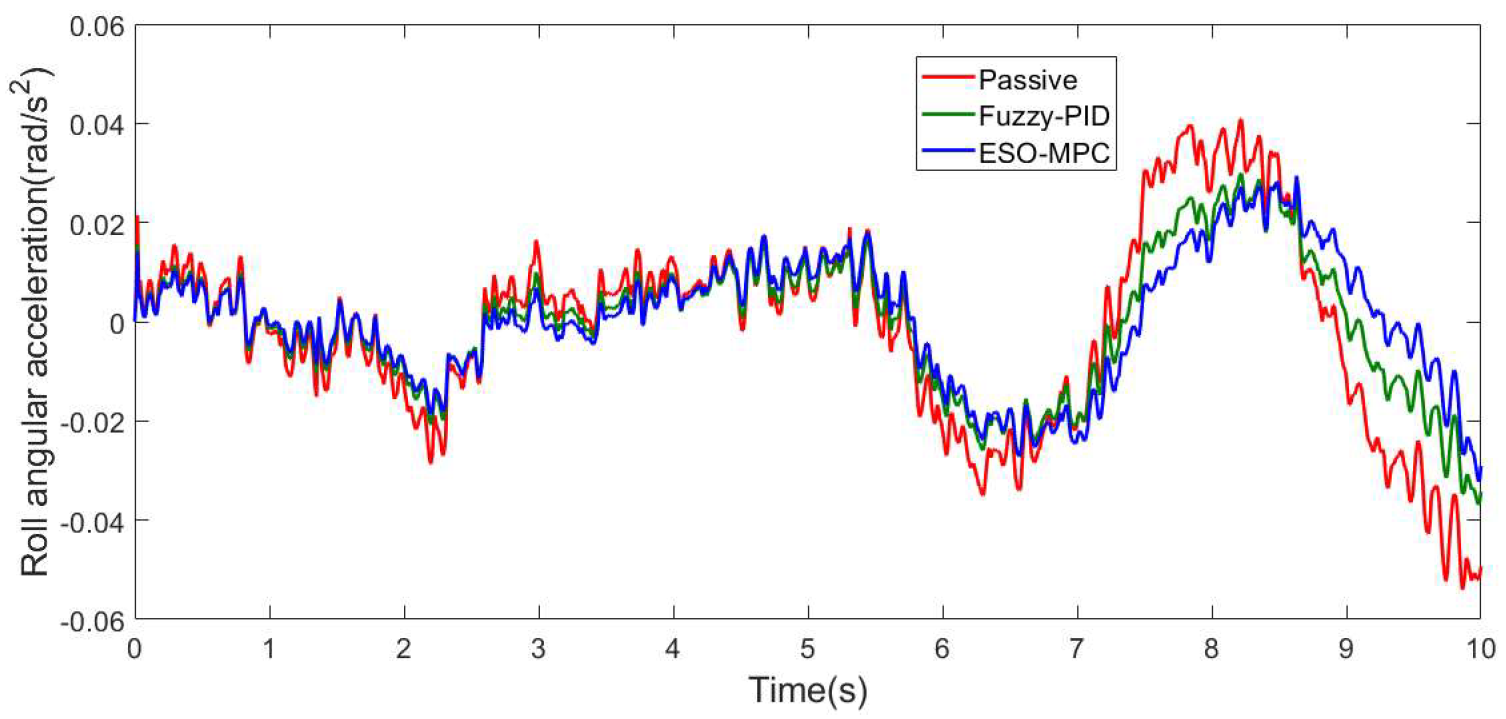
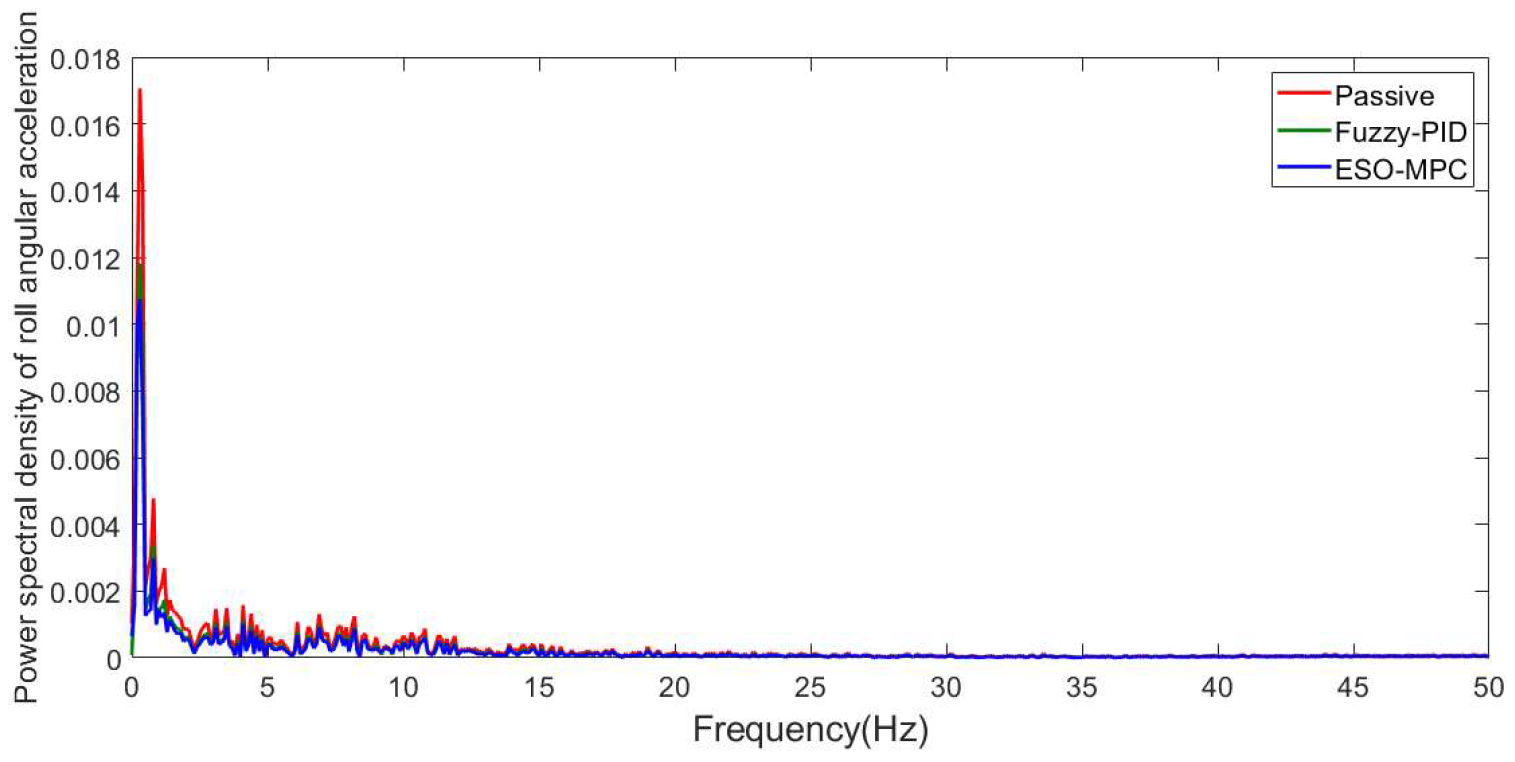
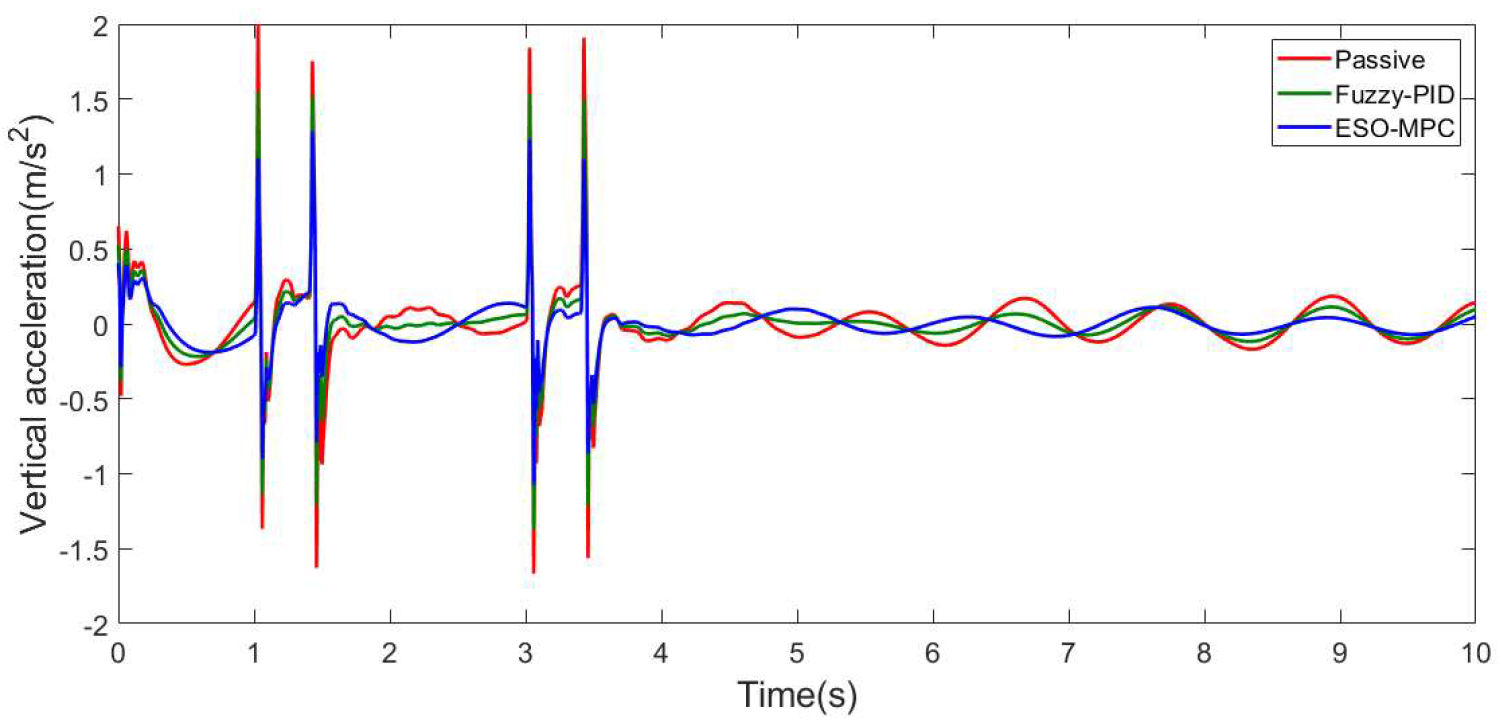
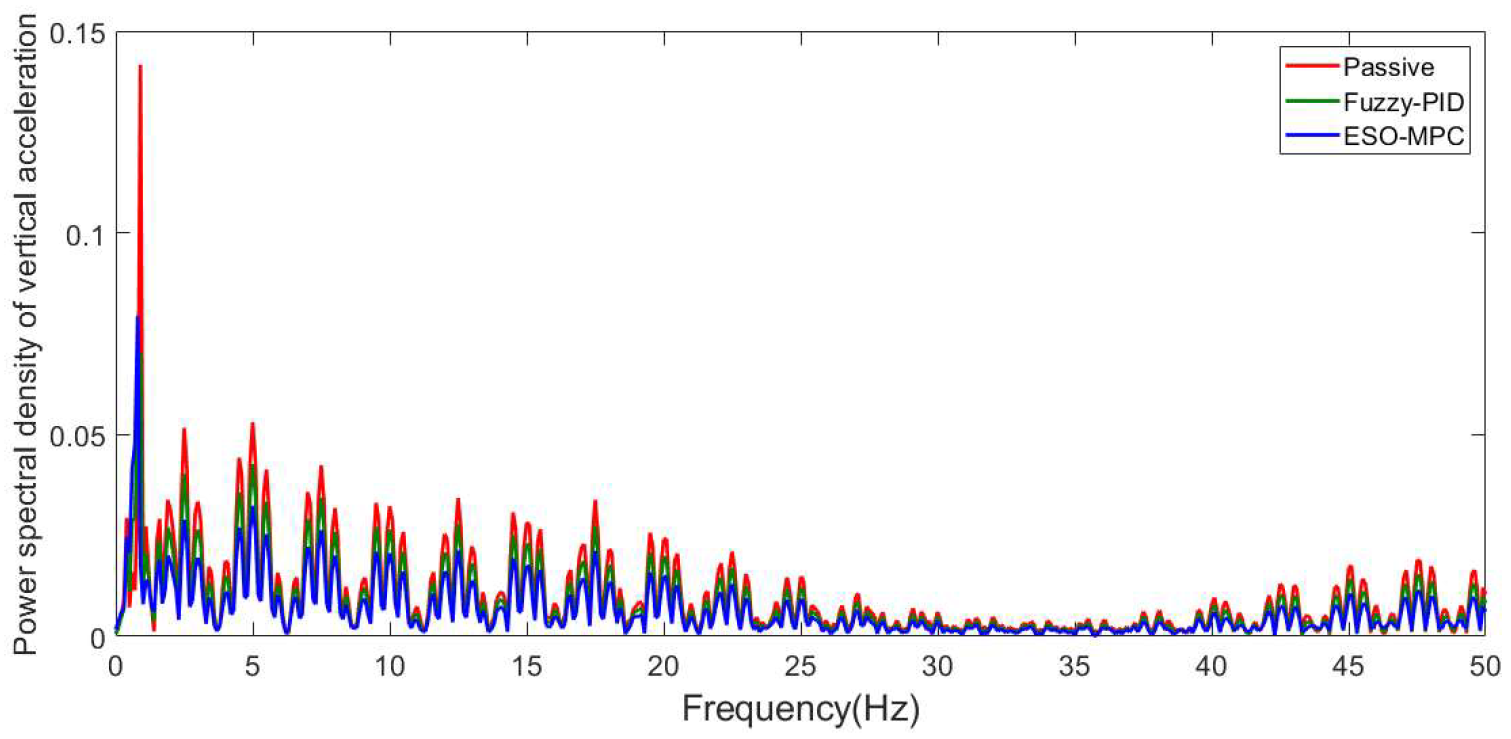
3.1. C-Class Random Pavement
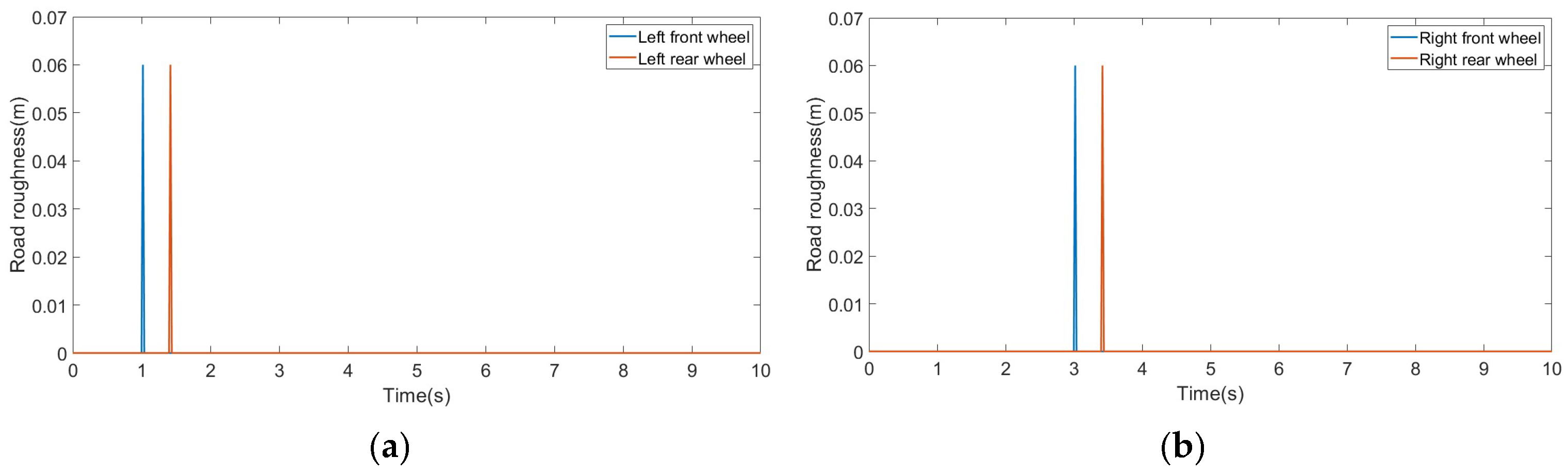
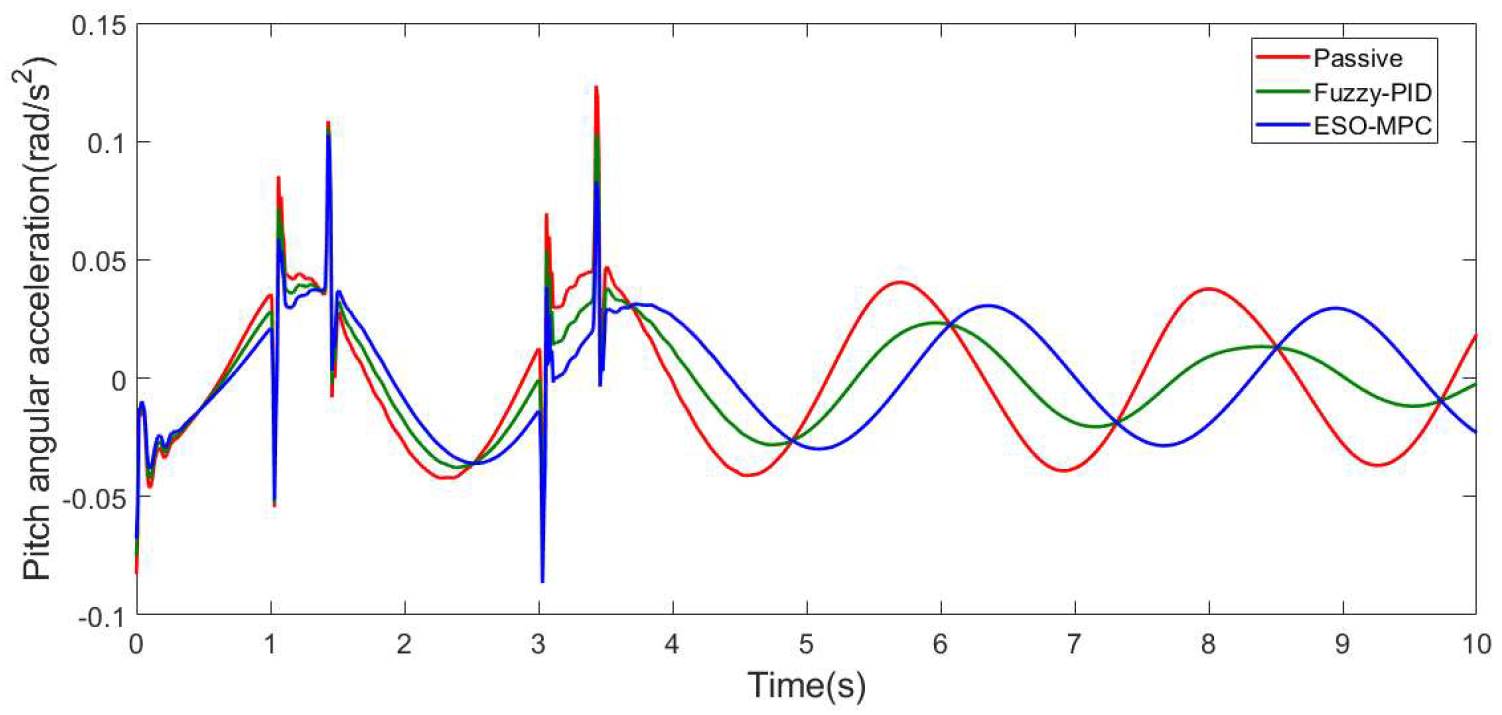
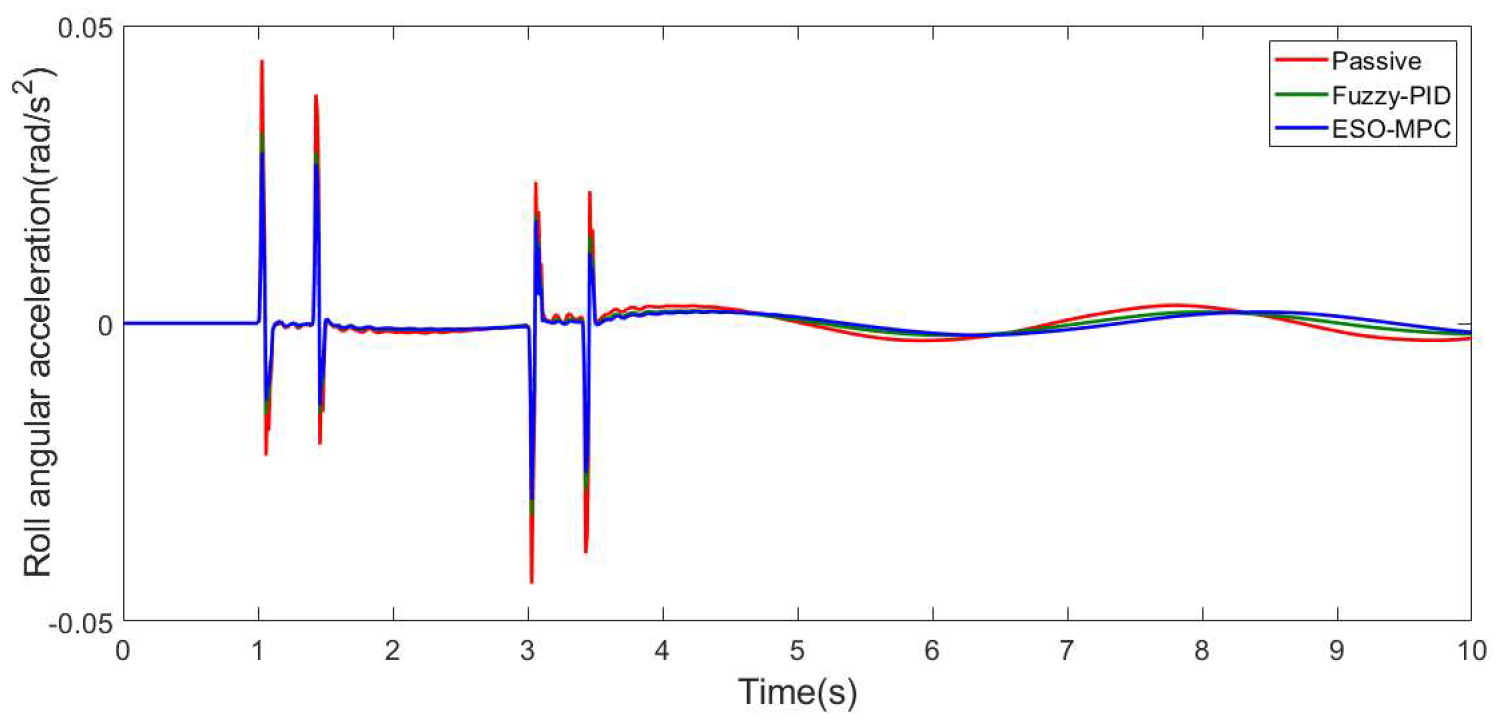
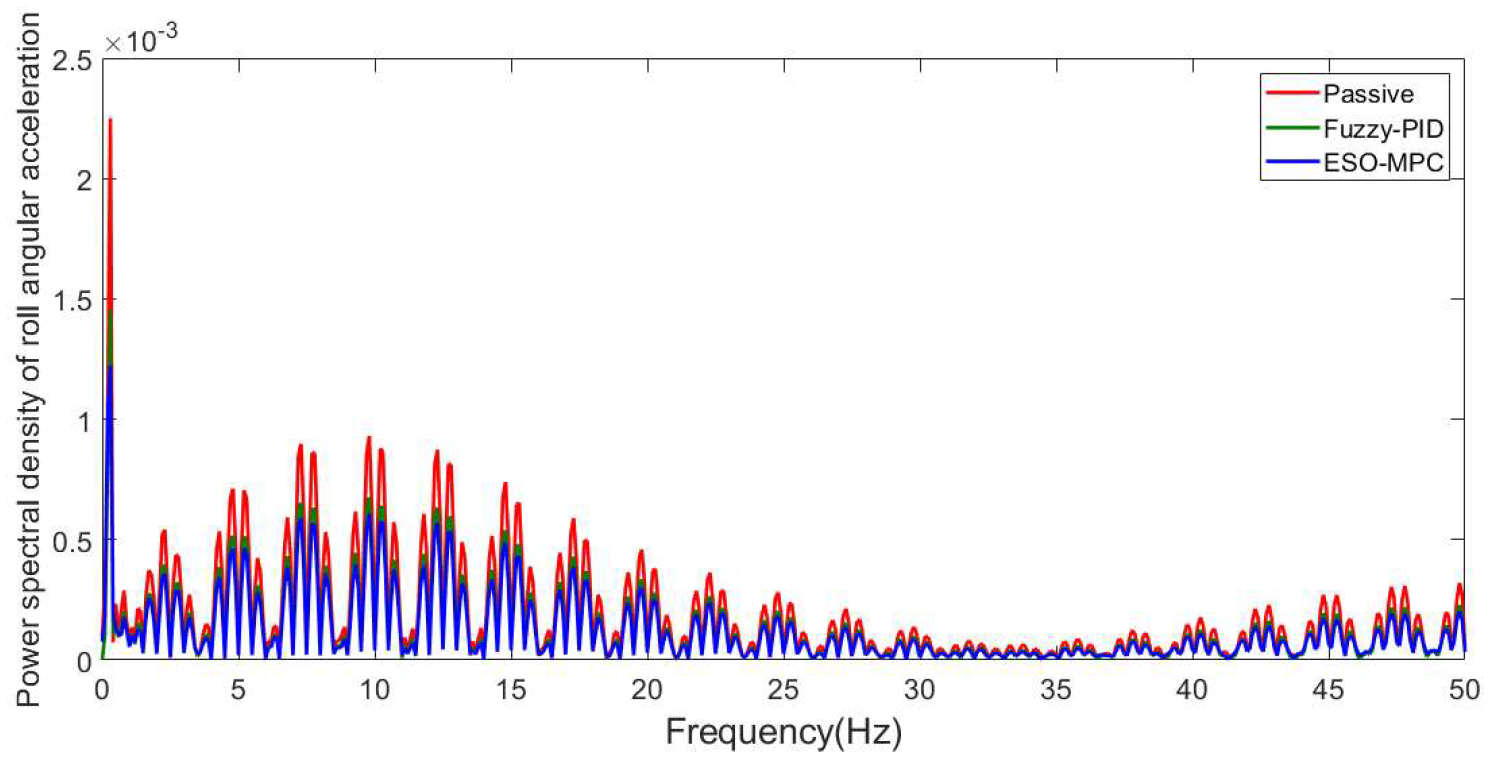
3.2. Convex Pavement
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Y.X.; Liu, T.H.; Yue, Z.S.; Cao, C.S.; Dou, B.; Zhao, H.H.; Yang, J.H. Study on Compound Control Method of Active Hydropneumatic Suspension of Mining Wide-body Vehicle. Mach. Tool Hydraul. 2023, 51, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Shi, Y. Research on the performance of a special vehicle active hydro-pneumatic suspension. Manuf. Autom. 2018, 40, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Nguyen, T.A.; Dang, N.D. A novel sliding mode control al-gorithm for an active suspension system considering with the hydraulic actuator. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2022, 19, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, P.; Wang, R.; Yang, L.; Thiyagarajan, J. Trajectory control for tire burst vehicle using thestandalone and roll interconnected active suspensions with safety-comfort controlstrategy. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 142, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokul, P.S.; Malar, M.K. A contemporary adaptive air suspension using LQR control for passenger vehicles. ISA Trans. 2019, 93, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Yuan, C. Fuzzy-PID Control on Semi-active Air Suspension. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2008, 39, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Caponetto, R.; Diamante, O.; Fargione, G.; Risitano, A.; Tringali, D. A soft computing approach to fuzzy sky-hook control of semiactive suspension. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Dynamic Characteristics and Control Method Investigation of Hydraulically Interconnected Suspension for Mining Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, H.; Chen, L. Microgrid Operation Controller Based on Active Disturbance Rejection Control Technology. High Volt. Technol. 2016, 42, 3336–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cairano, S.; Bemporad, A. Model Predictive Control Tuning by Controller Matching. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2010, 55, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, L.; Liu, A.; Zhang, W.A. Distribute Model Predictive Control for Large-scale Systems with Multi-Rate Sampling. In Proceedings of the 33th Chinese Control Conference, Nanjing, China, 28–30 July 2014; pp. 1401–1406. [Google Scholar]
- GK, V.S.; Fusic, J.; Ramesh, H. Advanced control strategies for Servo motors: Analysis of PID, FUZZY-PID and MPC with cuk converter integration. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Energy, Materials and Communication Engineering: International Conference on Energy, Materials and Communication Engineering (ICEMCE), Madurai, India, 14–15 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zinage, S.; Somayajula, A. A comparative study of different active heave compensation approaches. Ocean Syst. Eng. 2020, 10, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Integration of LQR and ESO for Enhanced Control Performance in Uncertain Systems. J. Control. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, L. A Novel ESO-based MPC Strategy for Industrial Motion Control Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 4567–4578. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, B.; Wen, G. A study on anti-roll control of half-car model active interconnected suspension with consideration of actuator dynamics. Vib. Shock 2017, 36, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, M. Integrated Vehicle Dynamics and Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, R. Research on Longitudinal Landing Track Control Technology of Carrier-based Aircraft. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC), Hefei, China, 22–24 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lin, F.; Pi, W. Decoupling control of active suspension and four-wheel steering based on Backstepping-ADRC with mechanical elastic wheel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2021, 236, 2356–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Mao, B.; Dong, Z.; Li, D. Optimal parameter identification of hydro-pneumatic suspension for mine cars. Int. J. Simul. Multidisci. Des. Optim. 2024, 15, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, J.; Smith, J. Modeling of Road Surface Profiles Using Filtered White Noise. J. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2020, 58, 456–470. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 5902-1986; Test Method for Automobile Ride Comfort by Random Input Running. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 1986.




| Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Sprung mass | 35,000 kg |
| Pitch moment of inertia | 2.14 × 106 kgm2 |
| Roll moment of inertia | 3.27 × 106 kgm2 |
| Front axle’s unsprung mass | 1350 kg |
| Rear axle’s unsprung mass | 1650 kg |
| Tire’s equivalent stiffness | 2 × 106 N/m |
| Wheelbase | 4 m |
| Distance from front wheels to center of mass | 2.2 m |
| Distance from rear wheels to center of mass | 1.8 m |
| Front wheel’s gauge | 1.6 m |
| Rear wheel’s gauge | 1.45 m |
| Index | Passivity | Fuzzy PID | Reduction | ESO-MPC | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical acceleration (m/s2) | 0.26502 | 0.25021 | 5.588% | 0.2154 | 18.725% |
| Pitch-angle acceleration (rad/s2) | 0.045875 | 0.042206 | 7.99% | 0.034537 | 24.716% |
| Roll-angle acceleration (rad/s2) | 0.040128 | 0.033891 | 15.542% | 0.029654 | 26.102% |
| Index | Passivity | Fuzzy PID | Reduction | ESO-MPC | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical acceleration (m/s2) | 0.23744 | 0.20410 | 14.041% | 0.15076 | 36.507% |
| Pitch-angle acceleration (rad/s2) | 0.029651 | 0.026508 | 10.599% | 0.023365 | 21.199% |
| Roll-angle acceleration (rad/s2) | 0.0044827 | 0.0041275 | 7.923% | 0.0036723 | 18.079% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Research on Active Control of X-Type Interconnected Hydropneumatic Suspensions for Heavy-Duty Special Vehicles via Extended State Observer-Model Predictive Control. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063041
Li G, Yan Y, Liu Y, Wang S. Research on Active Control of X-Type Interconnected Hydropneumatic Suspensions for Heavy-Duty Special Vehicles via Extended State Observer-Model Predictive Control. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Geqiang, Yuze Yan, Yuchang Liu, and Shuai Wang. 2025. "Research on Active Control of X-Type Interconnected Hydropneumatic Suspensions for Heavy-Duty Special Vehicles via Extended State Observer-Model Predictive Control" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063041
APA StyleLi, G., Yan, Y., Liu, Y., & Wang, S. (2025). Research on Active Control of X-Type Interconnected Hydropneumatic Suspensions for Heavy-Duty Special Vehicles via Extended State Observer-Model Predictive Control. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063041





