Degradation and Ecotoxicity Mitigation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by Aeration-Assisted Cold Plasma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
2.2. Sample Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Statistical Analyses and Regressions
2.4. Acute Toxicity Test
2.5. Calculation of Electrical Energy per Order (EE/O)
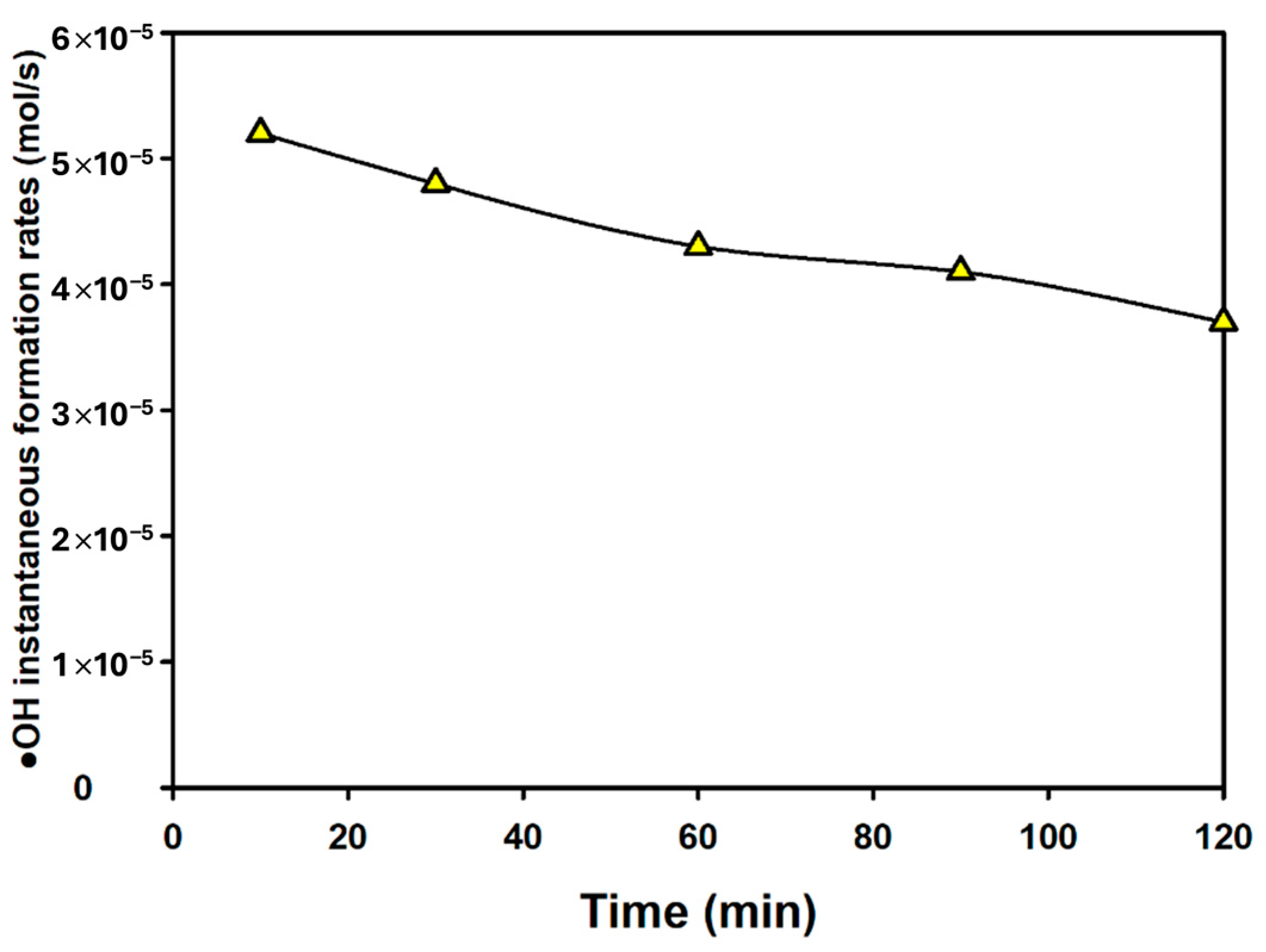
2.6. Quantification of Hydroxyl Radical
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PFOS Removal by CP
3.2. Degradation Kinetics of PFOS
3.3. Detection of Sulfate in the Suspension
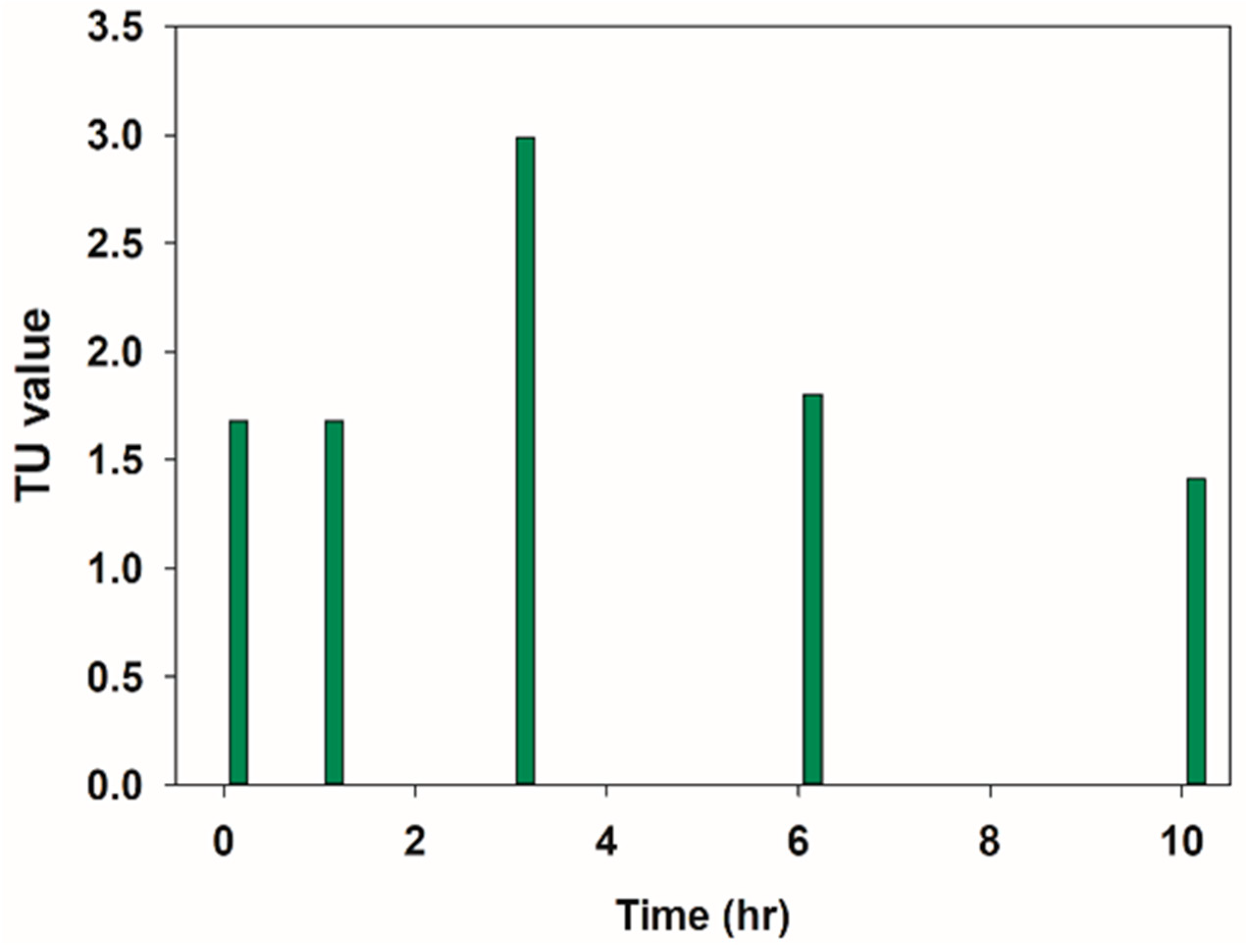
3.4. Evaluation of the Acute Toxicity of the PFOS
3.5. Comparison of Energy Cost of CP Versus Other AOPs
3.6. Comparison of Hydroxyl Radical Formation Rates of Various AOPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Duan, J.; Tian, S.; Ji, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, D. Short-Chain per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Aquatic Systems: Occurrence, Impacts and Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Ruan, T.; Jiang, G. Occurrence and Degradation Potential of Fluoroalkylsilane Substances as Precursors of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Daniels, K.D.; Wu, S.; Ziska, A.D.; Snyder, S.A. Magnetic Ion-Exchange (MIEX) Resin for Perfluorinated Alkylsubstance (PFAS) Removal in Groundwater: Roles of Atomic Charges for Adsorption. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jiang, J.-J.; Rodenburg, L.A.; Cai, M.; Wu, Z.; Ke, H.; Chitsaz, M. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Sediments from the Bering Sea to the Western Arctic: Source and Pathway Analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Grandjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; et al. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-M.; Chen, D.; Han, F.-J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F. A Short Review on Human Exposure to and Tissue Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Bao, K.; Chen, N.; Meng, B. Multicompartment Occurrence and Partitioning of Alternative and Legacy Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in an Impacted River in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, J.; Xia, Y.; Tong, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D. Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Using Carbon-Modified Bismuth Phosphate Composite: Effectiveness, Material Synergy and Roles of Carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 124991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L. Health Risks of Dietary Exposure to Perfluorinated Compounds. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Stroski, K.M.; Killeen, G.; Smitherman, C.; Simcik, M.F.; Brooks, B.W. 8:8 Perfluoroalkyl Phosphinic Acid Affects Neurobehavioral Development, Thyroid Disruption, and DNA Methylation in Developing Zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunada, Z.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Bashir, M.J.K. An Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Environment: Source, Fate, Risk and Regulations. Water 2020, 12, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; Wolffe, T.A.M.; Kwiatkowski, C.F. PFAS Health Effects Database: Protocol for a Systematic Evidence Map. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.; Vanderzalm, J.; Kumar, A.; Cheng, K.Y.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Simpson, S. Risks of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) for Sustainable Water Recycling via Aquifers. Water 2019, 11, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Oyang, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Li, J. Metabolic Regulations in Lettuce Root under Combined Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Hydroponic Media. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-M.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liang-Ying, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Global Distribution of Perfluorochemicals (PFCs) in Potential Human Exposure Source–A Review. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Mair, D.C.; Church, T.R.; Ellefson, M.E.; Reagen, W.K.; Boyd, T.M.; Herron, R.M.; Medhdizadehkashi, Z.; Nobiletti, J.B.; Rios, J.A.; et al. Decline in Perfluorooctanesulfonate and Other Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals in American Red Cross Adult Blood Donors, 2000−2006. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4989–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shane, H.L.; Baur, R.; Lukomska, E.; Weatherly, L.; Anderson, S.E. Immunotoxicity and Allergenic Potential Induced by Topical Application of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in a Murine Model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultes, L.; Vestergren, R.; Volkova, K.; Westberg, E.; Jacobson, T.; Benskin, J.P. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Fluorine Mass Balance in Cosmetic Products from the Swedish Market: Implications for Environmental Emissions and Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2018, 20, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Wei, S.; Dai, J. Analysis of Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Progress and Current Issues. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, S.; Berry, J.; Newman, B. Ion Exchange Resin for PFAS Removal and Pilot Test Comparison to GAC. Remediat. J. 2017, 27, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, B.C.; Speth, T.F.; Wahman, D.G.; Smith, S.J.; Abulikemu, G.; Kleiner, E.J.; Pressman, J.G. Occurrence of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Source Water and Their Treatment in Drinking Water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 2359–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodowa, A.E.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Chiang, S.-Y.D.; Pohlmann, D.; Varley, C.; Bodour, A.; Field, J.A. Pilot Scale Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Precursors from AFFF-Impacted Groundwater by Granular Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, J.; McDonough, J.; Ross, I.; Houtz, E. Understanding and Managing the Potential By-Products of PFAS Destruction. Groundw. Monit. Rem 2020, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Alam, M.M.; Zhou, J.L.; Xu, B.; Johir, M.A.H.; Karmakar, A.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Hossen, J.; Hasan, A.T.M.K.; Moni, M.A. Advanced Treatment Technologies Efficacies and Mechanism of Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances Removal from Water. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 136, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xie, Z.; Dorian, B.; Gray, S.; Zhang, J. Comparative Study of PFAS Treatment by UV, UV/Ozone, and Fractionations with Air and Ozonated Air. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Sobhani, Z.; Niu, J.; Naidu, R. Removal of PFAS from Aqueous Solution Using PbO2 from Lead-Acid Battery. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Luo, K.; Yao, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, G. Photocatalytic Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Water: A Critical Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Q.; Wang, J.; Niu, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, Y. Electrochemical Oxidation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Substitute by Modified Boron Doped Diamond (BDD) Anodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James Wood, R.; Sidnell, T.; Ross, I.; McDonough, J.; Lee, J.; Bussemaker, M.J. Ultrasonic Degradation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Correlated with Sonochemical and Sonoluminescence Characterisation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 68, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.Y.; Doudrick, K.; Yu, S.; Kim, S.D. Decomposition of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Using a Hybrid Process with Electron Beam and Chemical Oxidants. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Recent Advances in the Electrochemical Oxidation Water Treatment: Spotlight on Byproduct Control. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Gao, P.; Deng, Y. Destruction of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) with Advanced Reduction Processes (ARPs): A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3752–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J.-C.; Nam, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-W. Degradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics and Their Intermediates Toxicity in an Aeration-Assisted Non-Thermal Plasma While Treating Strong Wastewater. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, H.-W. Prediction of Varying Microcystins during Non-Thermal Plasma Oxidation of Harvested Microalgal Biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Nam, G.-S.; Jang, J.-S.; Won, C.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Cold Plasma Treatment for Efficient Control over Algal Bloom Products in Surface Water. Water 2019, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, B.R.; Thagard, S.M. Analysis and Review of Chemical Reactions and Transport Processes in Pulsed Electrical Discharge Plasma Formed Directly in Liquid Water. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 2012, 32, 875–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, T.J. Electron and Ion Collisions with Water Vapour. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1993, 26, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Kushner, M.J.; Locke, B.R.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Graham, W.G.; Graves, D.B.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Maric, D.; Reid, J.P.; Ceriani, E.; et al. Plasma–Liquid Interactions: A Review and Roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Walker, K.L.; Han, H.S.; Kang, J.; Prinz, F.B.; Waymouth, R.M.; Nam, H.G.; Zare, R.N. Spontaneous Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide from Aqueous Microdroplets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19294–19298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Rabat, H.; Bauchire, J.M.; Chang, M.B. Measurement of Ozone Production in Non-Thermal Plasma Actuator Using Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 2014, 34, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemöller, M. Advanced Oxidation Process-Mediated Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Water: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Lee, J.-C.; Park, R.; Kim, H.-W. Integration of Submerged Microfiltration and Cold Plasma for High-Strength Livestock Excreta. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Understanding and Accounting for Method Variability in Whole Effluent Toxicity Applications under the NPDES Program; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- OECD. Daphnia Sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Lipps, W.C., Baxter, T.E., Braun-Howland, E.B., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; ISBN 0-87553-299-3. [Google Scholar]
- Behnajady, M.A.; Vahid, B.; Modirshahla, N.; Shokri, M. Evaluation of Electrical Energy per Order (EEO) with Kinetic Modeling on the Removal of Malachite Green by US/UV/H2O2 Process. Desalination 2009, 249, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Multari, N.; Nau-Hix, C.; Woodard, S.; Nickelsen, M.; Mededovic Thagard, S.; Holsen, T.M. Removal of Poly- and Per-Fluorinated Compounds from Ion Exchange Regenerant Still Bottom Samples in a Plasma Reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13973–13980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment—A Critical Review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, M.; Locke, B.R. Quantification of Hydroxyl Radicals Produced in Aqueous Phase Pulsed Electrical Discharge Reactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 5819–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, M.K.; Colina, R. The Reaction of OH Radicals with Dimethyl Sulfoxide. A Comparative Study of Fenton’s Reagent and the Radiolysis of Aqueous Dimethyl Sulfoxide Solutions. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ES 04605.2; Official Test Standards for Environmental Pollution. Ministry of Environment: Sejong-si, Republic of Korea, 2014; (Written in Korean).
- Yamamoto, T.; Noma, Y.; Sakai, S.; Shibata, Y. Photodegradation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by UV Irradiation in Water and Alkaline 2-Propanol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5660–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautmann, A.M.; Schell, H.; Schmidt, K.R.; Mangold, K.-M.; Tiehm, A. Electrochemical Degradation of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Groundwater. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Q.; Luo, M.; Guo, Q.; Yu, G.; Deng, S.; Xu, Z.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. Electrochemical Oxidation of Environmentally Persistent Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by a Novel Lead Dioxide Anode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Yu, S.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, T.-Y.; Kim, S.D. Profiling the Decomposition Products of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Irradiated Using an Electron Beam. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.J.; Joyce, T.; Hadaya, M.; Ebrahimi, F.; Dragiev, I.; Giardetti, N.; Yang, J.; Fridman, G.; Rabinovich, A.; Fridman, A.A.; et al. Rapid Degradation of PFAS in Aqueous Solutions by Reverse Vortex Flow Gliding Arc Plasma. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Fernando, S.; Baygi, S.F.; Multari, N.; Thagard, S.M.; Holsen, T.M. Breakdown Products from Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Degradation in a Plasma-Based Water Treatment Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, P.B.; Vitale, P.; Barreto, G.P.; Aparicio, F.; de los Ángeles Dublan, M.; Eyler, G.N. Treatment of Real Non-Biodegradable Wastewater: Feasibility Analysis of a Zero-Valent Iron/H2O2 Process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Liang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, C.; Du, J.; Wang, C. Energy-Saving Photo-Degradation of Three Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics under VUV/UV Irradiation: Kinetics, Mechanism, and Antibacterial Activity Reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Rodríguez, D.M.; Ávila-Torres, Y.; Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Data on Treatment of Nafcillin and Ampicillin Antibiotics in Water by Sonochemistry. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Di Mauro, A.; Cantarella, M.; Iaria, C.; Scalisi, E.M.; Brundo, M.V.; Gulino, A.; Spitaleri, L.; Nicotra, G.; Dattilo, S.; et al. Preferential Removal of Pesticides from Water by Molecular Imprinting on TiO2 Photocatalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M.; Bartosiewicz, I.; Bojanowska-Czajka, A.; Szreder, T.; Bobrowski, K.; Nałęcz-Jawecki, G.; Męczyńska-Wielgosz, S.; Nichipor, H. Application of Ionizing Radiation in Decomposition of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) in Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xing, L.; Zhou, Q.; Dong, W.; Hoffmann, M.R. UV/Nitrilotriacetic Acid Process as a Novel Strategy for Efficient Photoreductive Degradation of Perfluorooctanesulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sonochemical Degradation of Perfluorinated Surfactants: Power and Multiple Frequency Effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 92-4-004506-6. [Google Scholar]
- Arar, O.; Yavuz, E.; Yuksel, U.; Kabay, N. Separation of Low Concentration of Fluoride from Water by Electrodialysis (ED) in the Presence of Chloride and Sulfate Ions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Peña, G.C.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Martínez-Miranda, V. Competing Effects of Chloride, Nitrate, and Sulfate Ions on the Removal of Fluoride by a Modified Zeolitic Tuff. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, J.P. A Zirconium-Based Nanoparticle: Essential Factors for Sustainable Application in Treatment of Fluoride Containing Water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 416, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Xiang, P.; Mackey, H.R.; Chi, K.; Lu, H.; Chui, H.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Chen, G.-H. A Review of Biological Sulfate Conversions in Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2014, 65, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, N.; Trajkovska, S.; Oturan, M.A.; Couderchet, M.; Aaron, J.-J. Study of the Toxicity of Diuron and Its Metabolites Formed in Aqueous Medium during Application of the Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Process “Electro-Fenton. ” Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzeribe, B.N.; Crimi, M.; Mededovic Thagard, S.; Holsen, T.M. Physico-Chemical Processes for the Treatment of per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 866–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Andaya, C.; Urtiaga, A.; McKenzie, E.R.; Higgins, C.P. Electrochemical Treatment of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) in Groundwater Impacted by Aqueous Film Forming Foams (AFFFs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, P.; Shao, T.; Zhao, S. Ferric Ion Mediated Photodecomposition of Aqueous Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) under UV Irradiation and Its Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Cheng, J.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Sonolytic Conversion of the Aqueous Perfluorinated Surfactants, Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) into Inorganic Products. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 4261–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.; Peng, J.-F.; Liu, J.-F.; Jiang, G.-B.; Zou, H. Determination of Hydroxyl Radicals in Advanced Oxidation Processes with Dimethyl Sulfoxide Trapping and Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 527, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-A.; Yang, B.; Park, C.; Choi, J.-W.; Van Genuchten, C.M.; Lee, S.-H. Oxidation of Microcystin-LR by the Fenton Process: Kinetics, Degradation Intermediates, Water Quality and Toxicity Assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Strategies of Antioxidant Defense. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 215, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhu, T.; Sun, Y.; Yan, X. The Roles of Various Plasma Species in the Plasma and Plasma-Catalytic Removal of Low-Concentration Formaldehyde in Air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.-J.; Li, J.; Li, J.-X.; Zhu, T.; Jin, Y.-Q. Formaldehyde Removal from Gas Streams by Means of NaNO2 Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.B.; Lee, C.C. Destruction of Formaldehyde with Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasmas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, D.G.; Kushner, M.J. Destruction Mechanisms for Formaldehyde in Atmospheric Pressure Low Temperature Plasmas. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Grzelczak, M.; Hou, Y.; Maeda, K.; Domen, K.; Fu, X.; Antonietti, M.; Wang, X. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Water by Polymeric Carbon Nitride Nanohybrids Made of Sustainable Elements. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, W.P.; Voelker, B.M. Rates of Hydroxyl Radical Generation and Organic Compound Oxidation in Mineral-Catalyzed Fenton-like Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Conditions | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Working volume | L | 3 |
| Total operating time | Hour | 10 |
| Air flow rate | L/min | 5 |
| Applied power for CP | kW | 0.15 |
| Parameter | Unit | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Test organism | species | Daphnia magna |
| Maintenance temperature | °C | 20 ± 2 |
| Light photoperiod | h | 16 |
| Dark photoperiod | h | 8 |
| Dilution ratio of PFOS solution | % | Control (0), 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100 |
| Number of Daphnia magna | EA | 20 |
| Test repetition | times | 4 |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier gas | Species | He (or N2) |
| Flow rate | mL/min | 0.5~4 |
| Column temp | °C | 40~310 |
| Injector temp | °C | 150~300 |
| Injection volume | μL | 2 |
| Process | Target Pollutant | Rate Constant (k, h−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fenton | Real textile effluent | 0.4 | [58] |
| VUV/UV | Levofloxacin | 5.4 | [59] |
| Ultrasound | Nafcillin | 3.3 | [60] |
| Photocatalytic oxidation (TiO2) | 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid | 0.04 | [61] |
| Electron beam | PFOS | 1.2 | [62] |
| Photochemical (UV/NTA) | PFOS | 0.3 | [63] |
| Ultrasonic | PFOS | 1.3 | [64] |
| Aeration-assisted CP | PFOS | 3.1 | This study |
| Process | Target Pollutant | Rate Constant (k, h−1) | EE/O (kWh/m3) | Energy Cost (USD/m3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical (Ti/RuO2/stainless steel) | PFOS | 0.3 | 935 | 84.5 | [72] |
| Enhanced-contact (EC) Plasma | PFOA + PFOS | 2.3 | 830 | 75.0 | [47] |
| Photochemical (UV/Fe3+) | PFOS | 0.1 | 576 | 52.0 | [73] |
| Oxidation (Nanocrystalline BDD) | PFOS | 0.4 | 500 | 45.2 | [74] |
| Ultrasound | PFOS | 1.6 | 273 | 24.7 | [75] |
| Aeration-assisted CP | PFOS | 3.1 | 117 | 10.6 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.; Nam, J.-Y.; Hong, Y.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Kim, H.-W. Degradation and Ecotoxicity Mitigation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by Aeration-Assisted Cold Plasma. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062936
Oh S, Nam J-Y, Hong Y, Lee T-H, Lee J-C, Kim H-W. Degradation and Ecotoxicity Mitigation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by Aeration-Assisted Cold Plasma. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062936
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Sengbin, Joo-Youn Nam, Youngpyo Hong, Tae-Hun Lee, Jae-Cheol Lee, and Hyun-Woo Kim. 2025. "Degradation and Ecotoxicity Mitigation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by Aeration-Assisted Cold Plasma" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062936
APA StyleOh, S., Nam, J.-Y., Hong, Y., Lee, T.-H., Lee, J.-C., & Kim, H.-W. (2025). Degradation and Ecotoxicity Mitigation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by Aeration-Assisted Cold Plasma. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062936






