Research on Real-Time Control Strategy for HVAC Systems in University Libraries
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Overview of the Paper
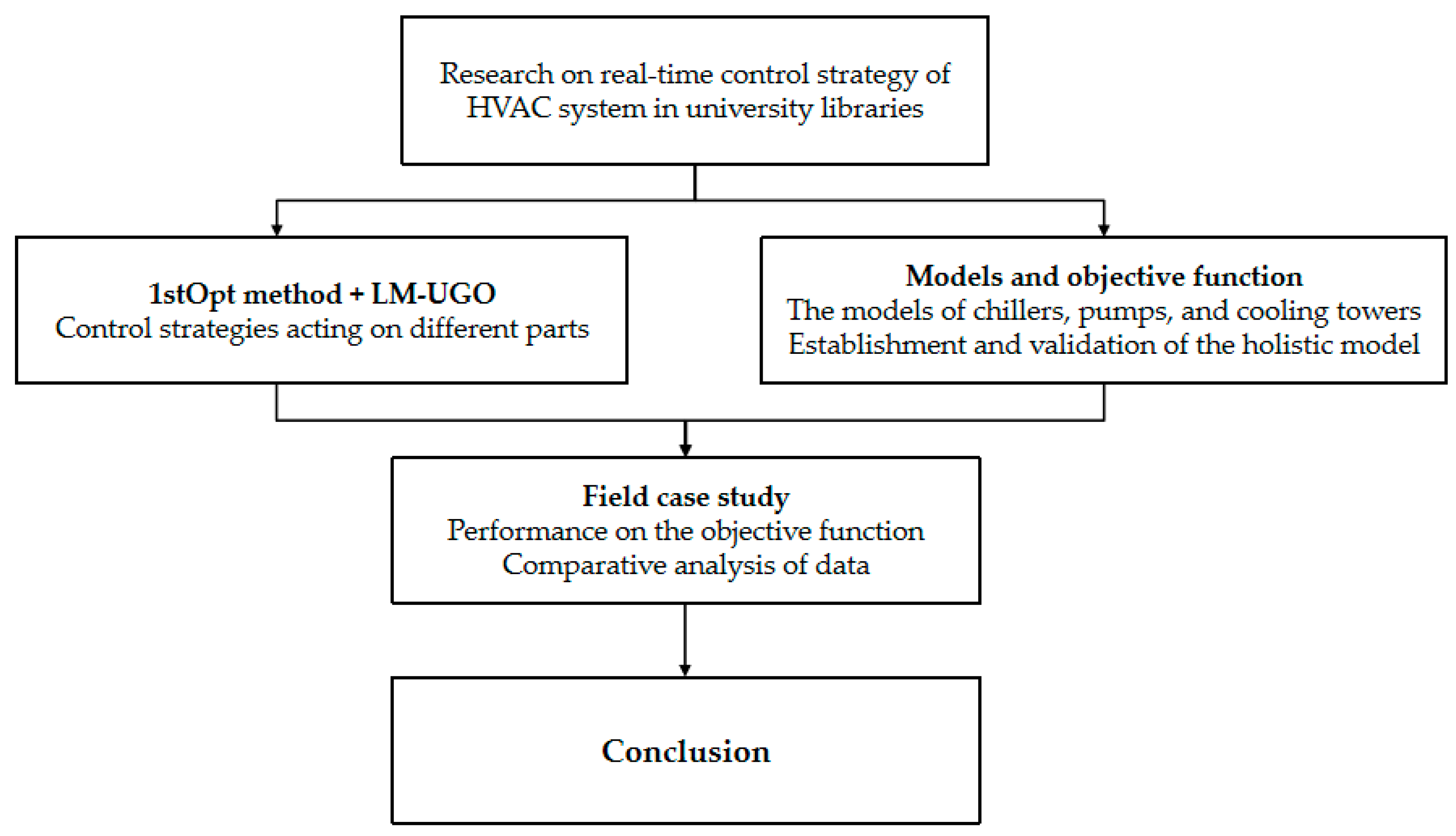
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Energy-Saving Strategies
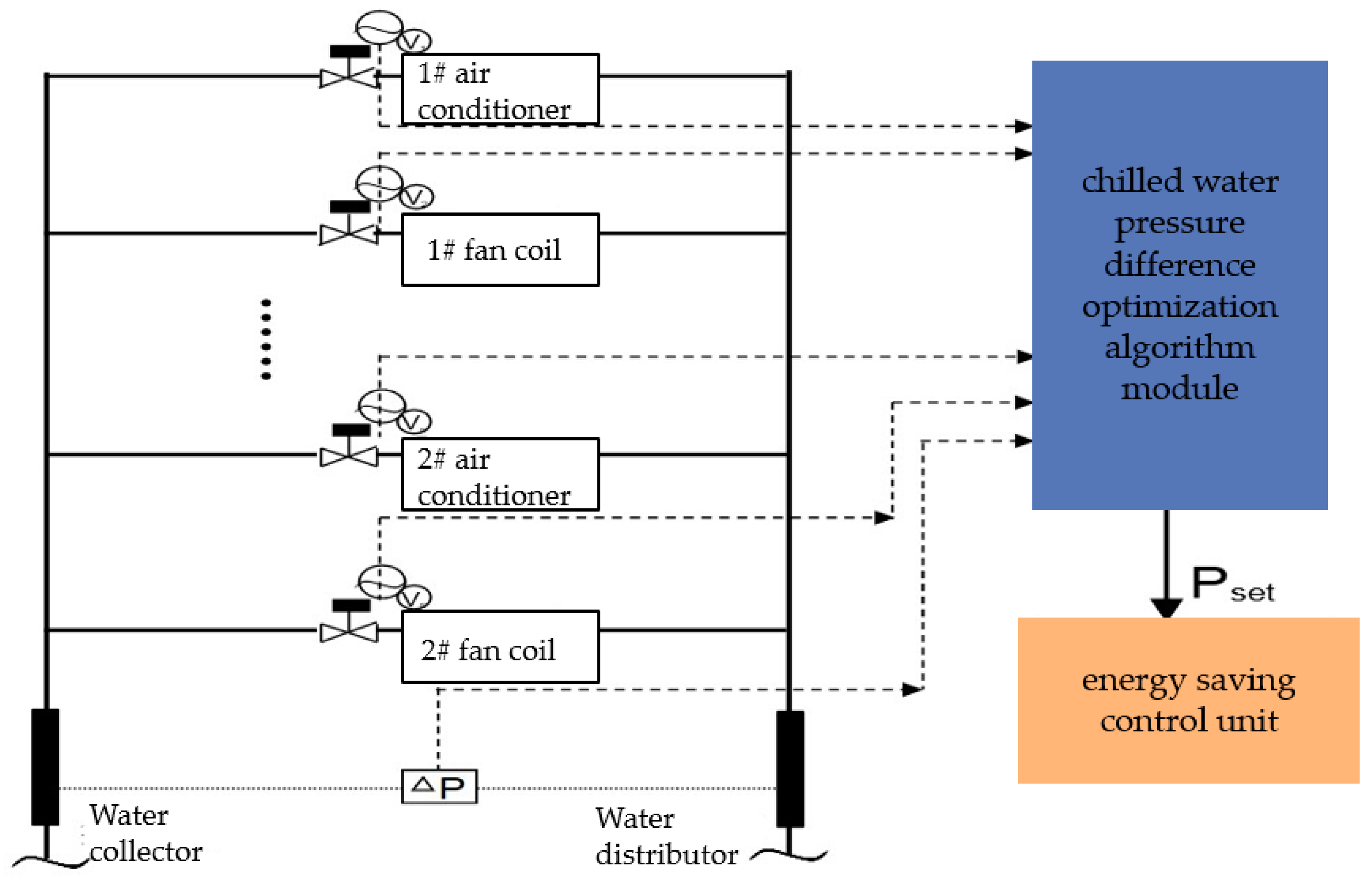
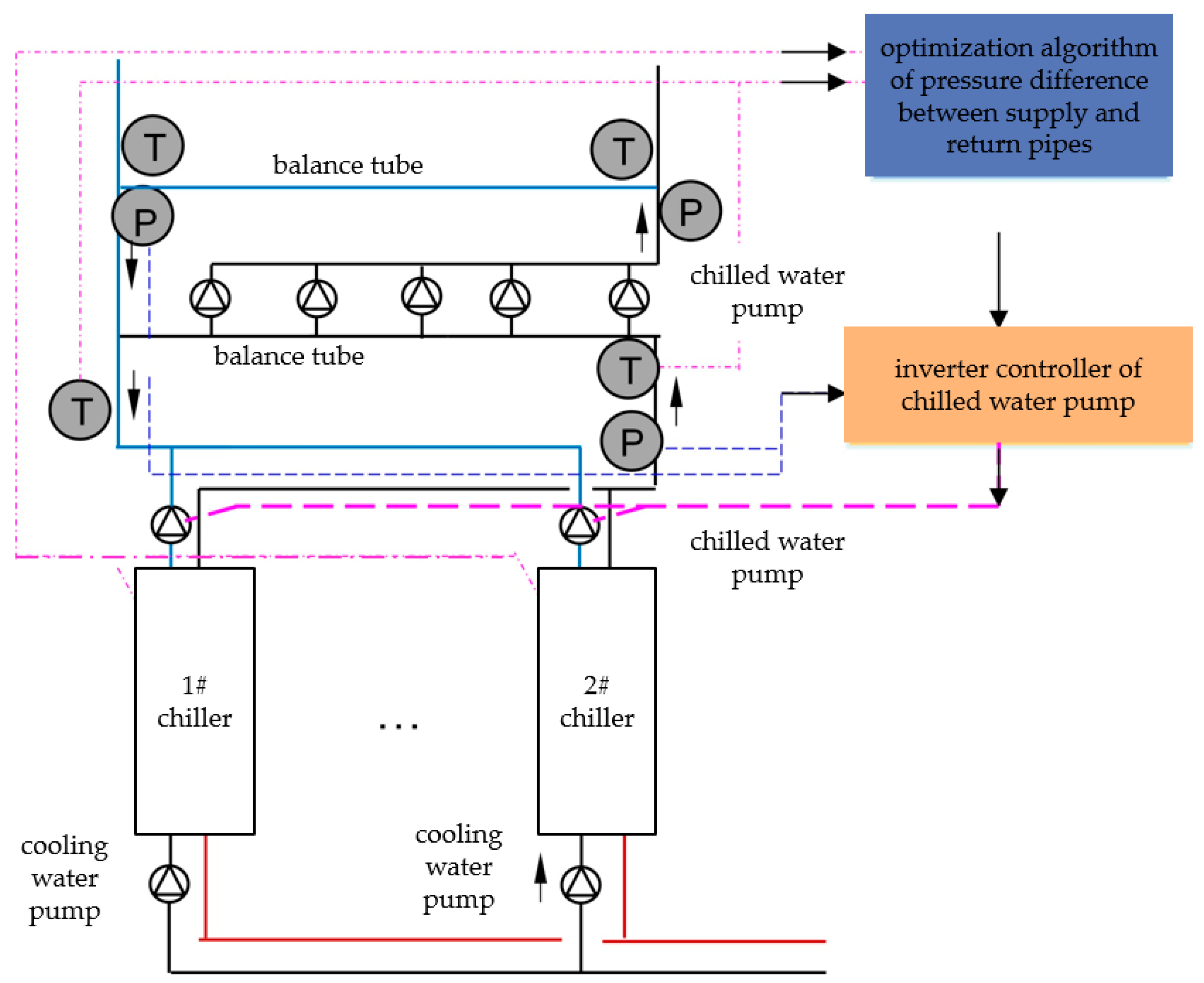
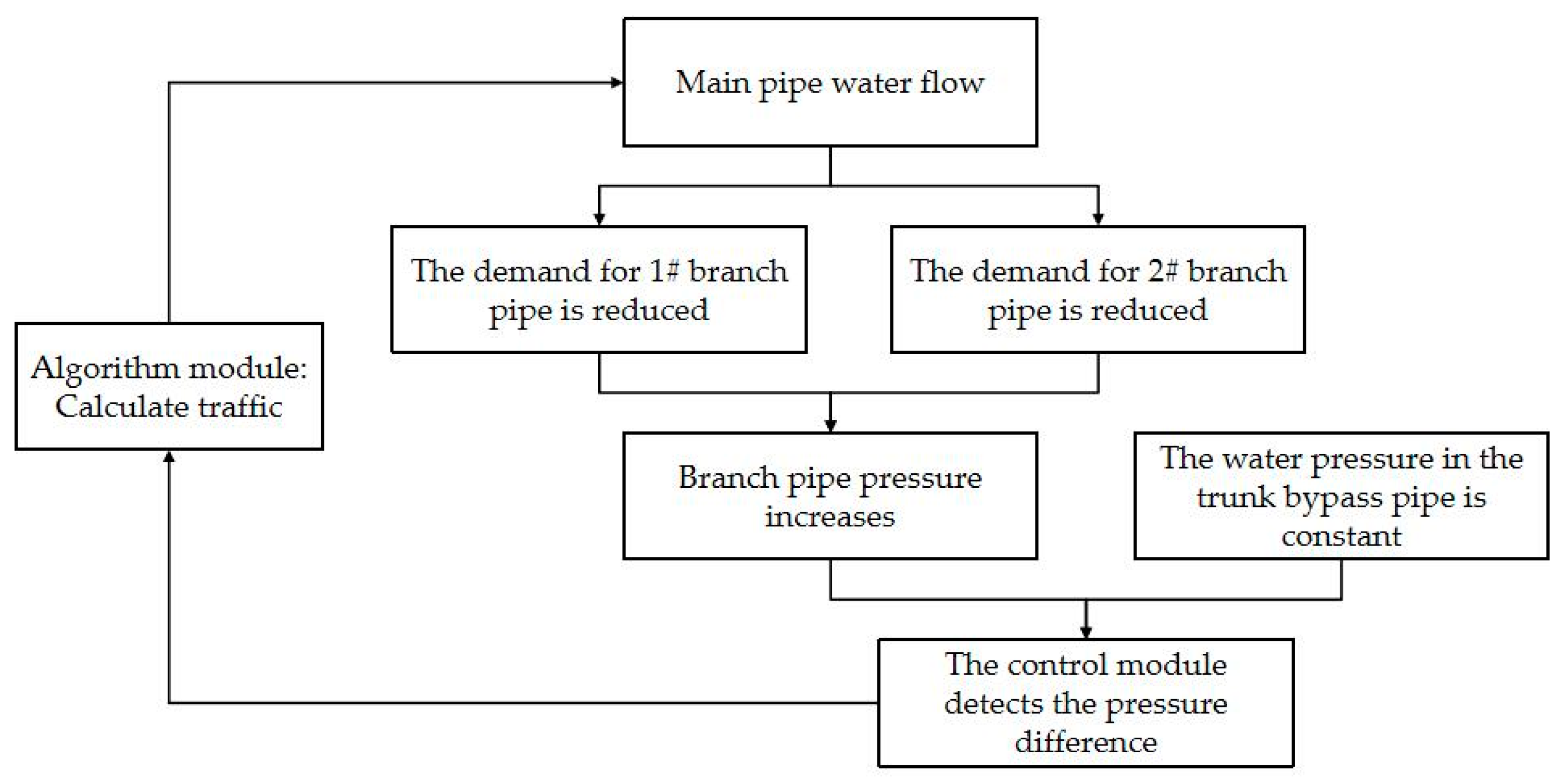
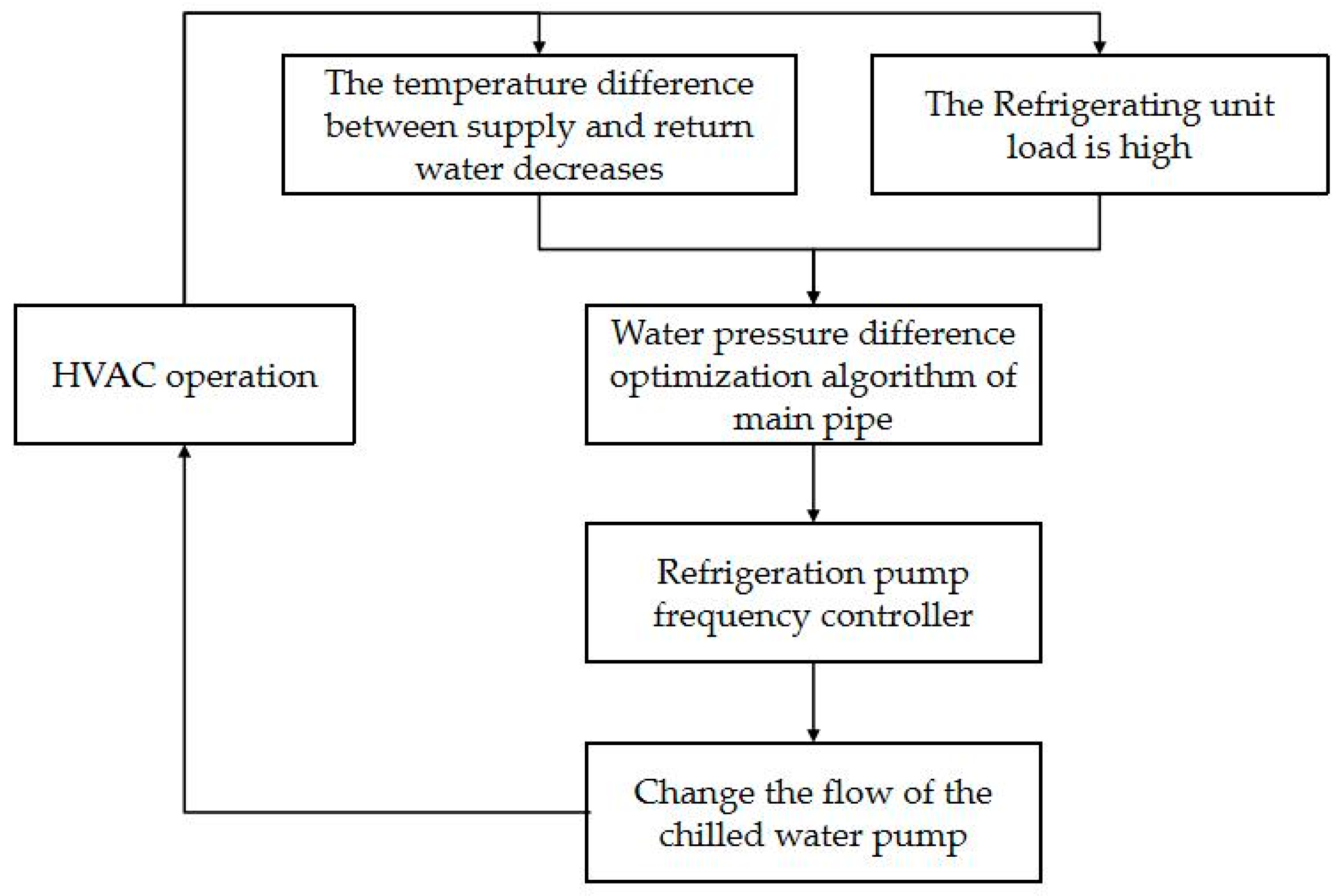
2.1.1. Optimization of Chilled Water Supply and Return Trunk Differential Pressure Setting Based on Weather Change
2.1.2. Optimization of Chilled Water Supply Temperature Setpoints Based on Climate Change
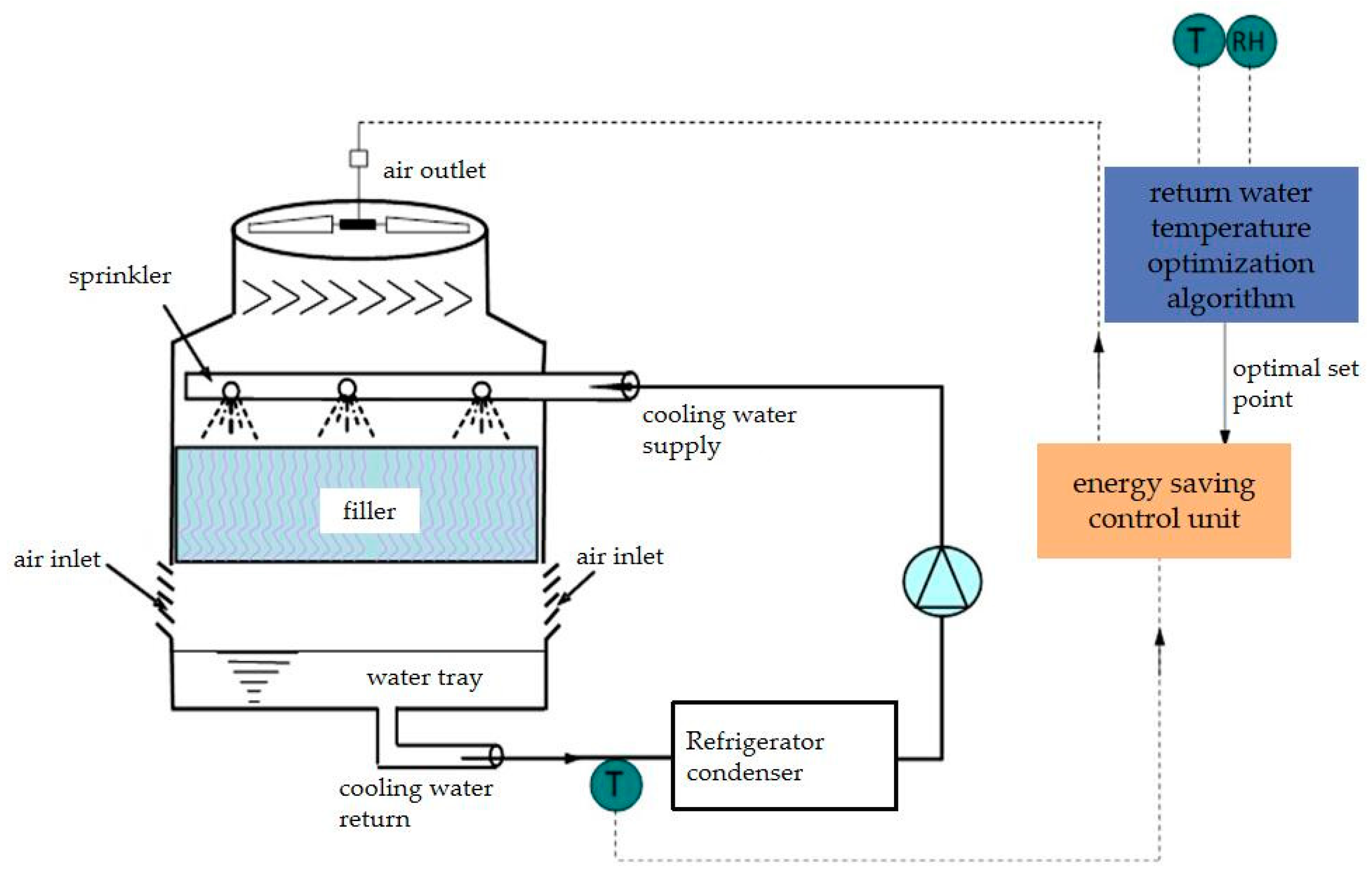
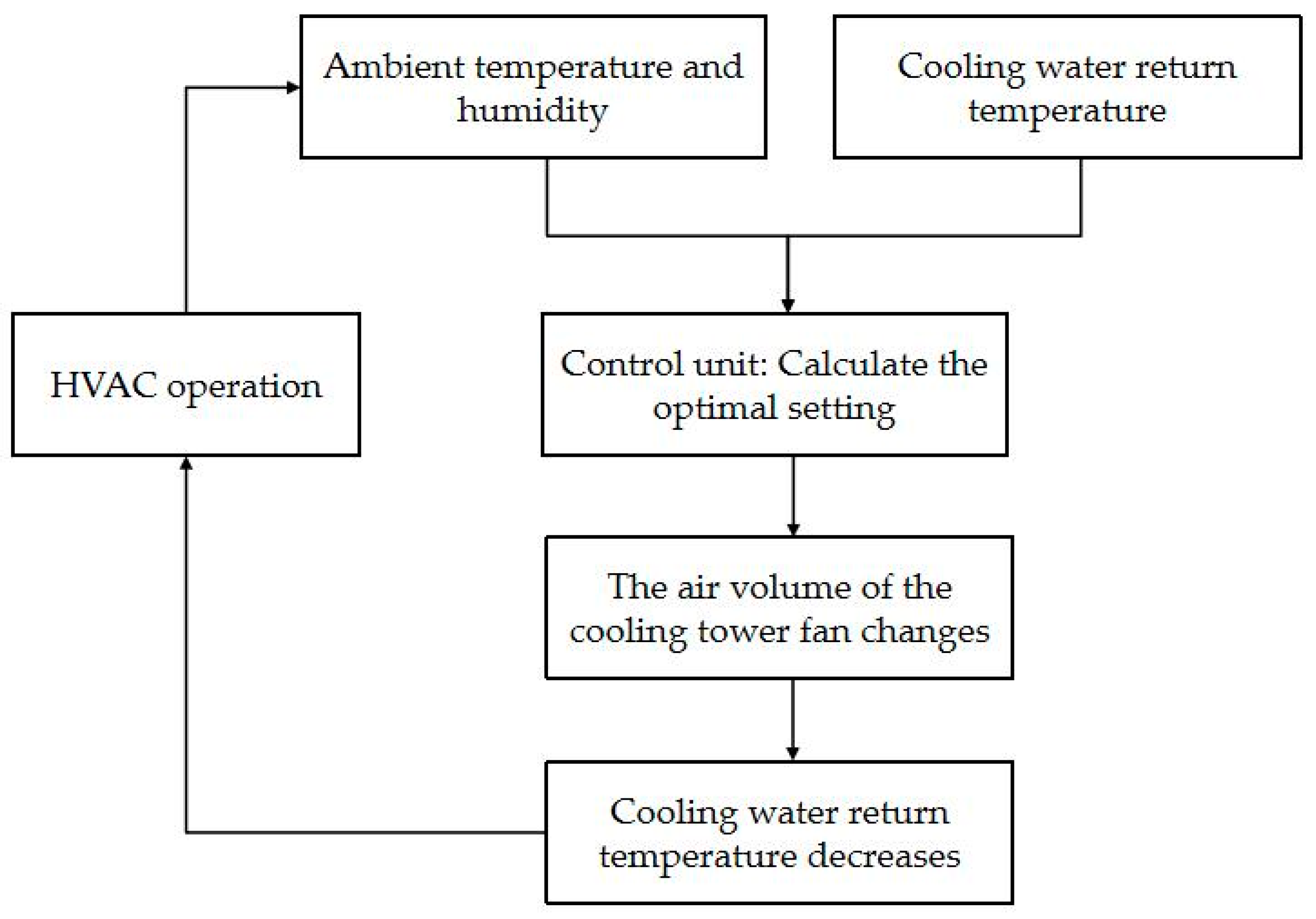
2.1.3. Climate Change-Based Optimization of Cooling Water Return Temperature Setpoints
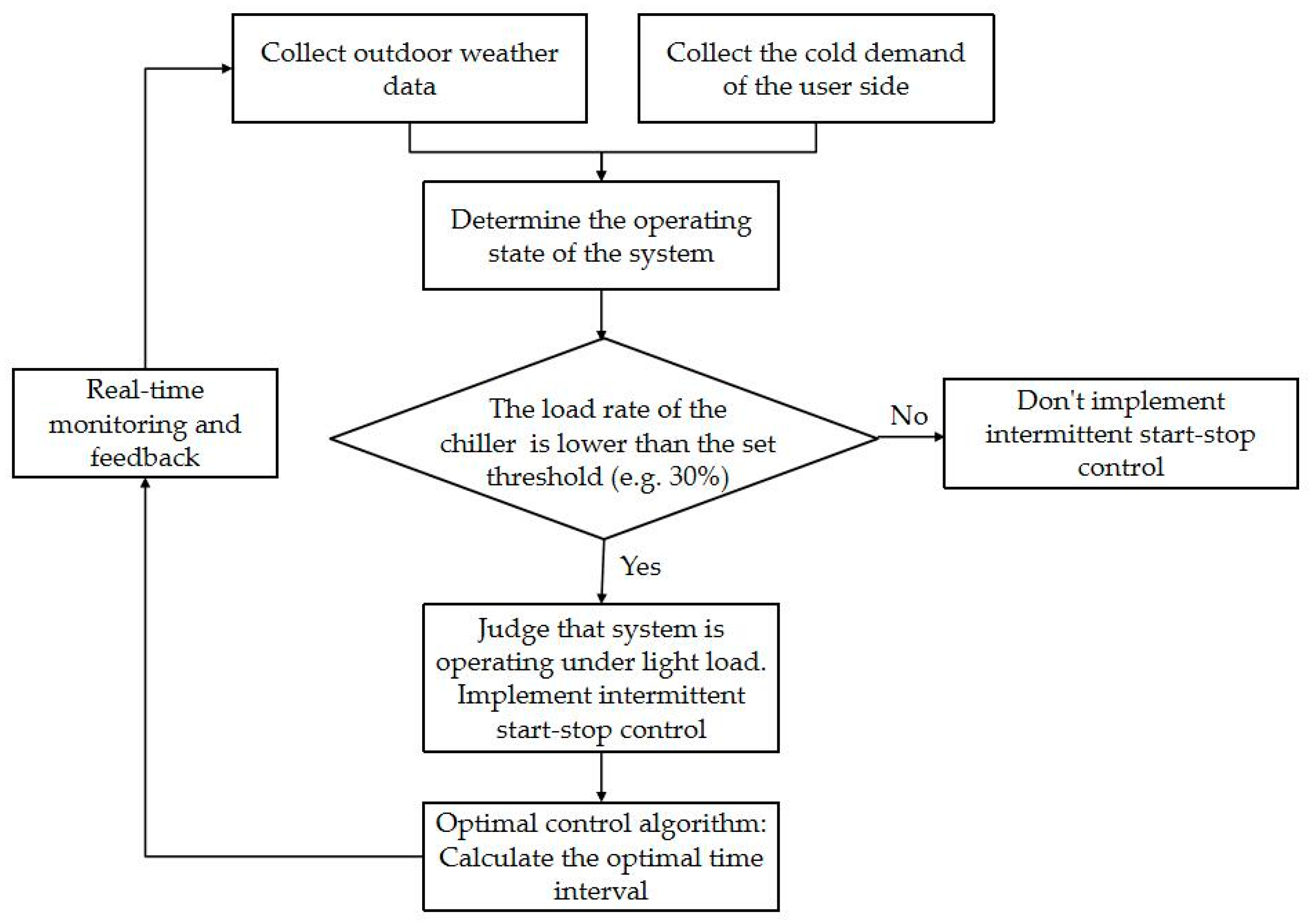
2.1.4. Optimal Control of Intermittent Operation of Small-Load Systems Based on Climate Characteristics
2.2. LM-UGO Algorithmic
2.2.1. 1stOpt
2.2.2. LM-UGO
2.2.3. Integration of Algorithm Module with HVAC System
2.3. Operation and Maintenance Platform System
3. Experimental Cases
3.1. Project Overview
3.2. Device Model and Objective Function
3.2.1. Chiller Model
3.2.2. Cooling/Chilled Water Pump Model
3.2.3. System Model and Boundary Conditions
3.2.4. Collection of Equipment Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Energy Consumption
4.2. Cost-Benefit Analysis
4.2.1. Cost Recovery
4.2.2. Long-Term Return on Investment
4.2.3. Policy Incentives
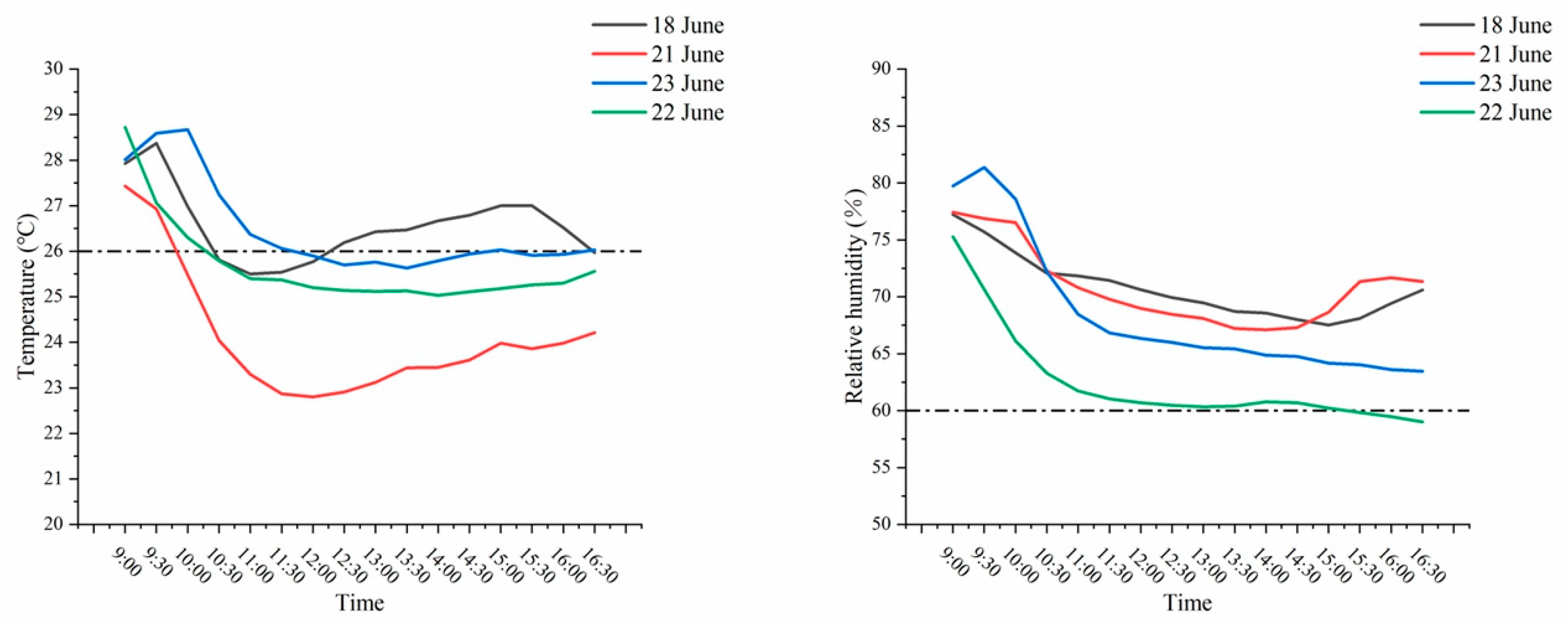
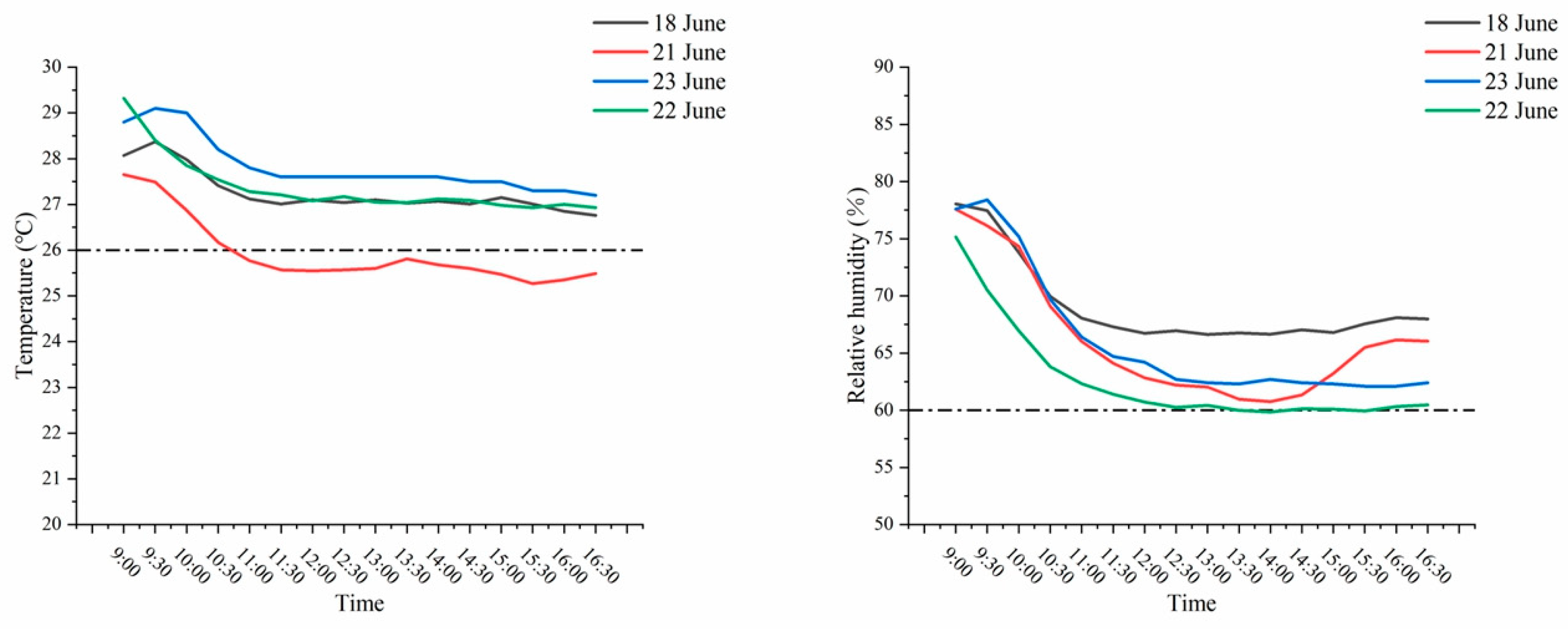
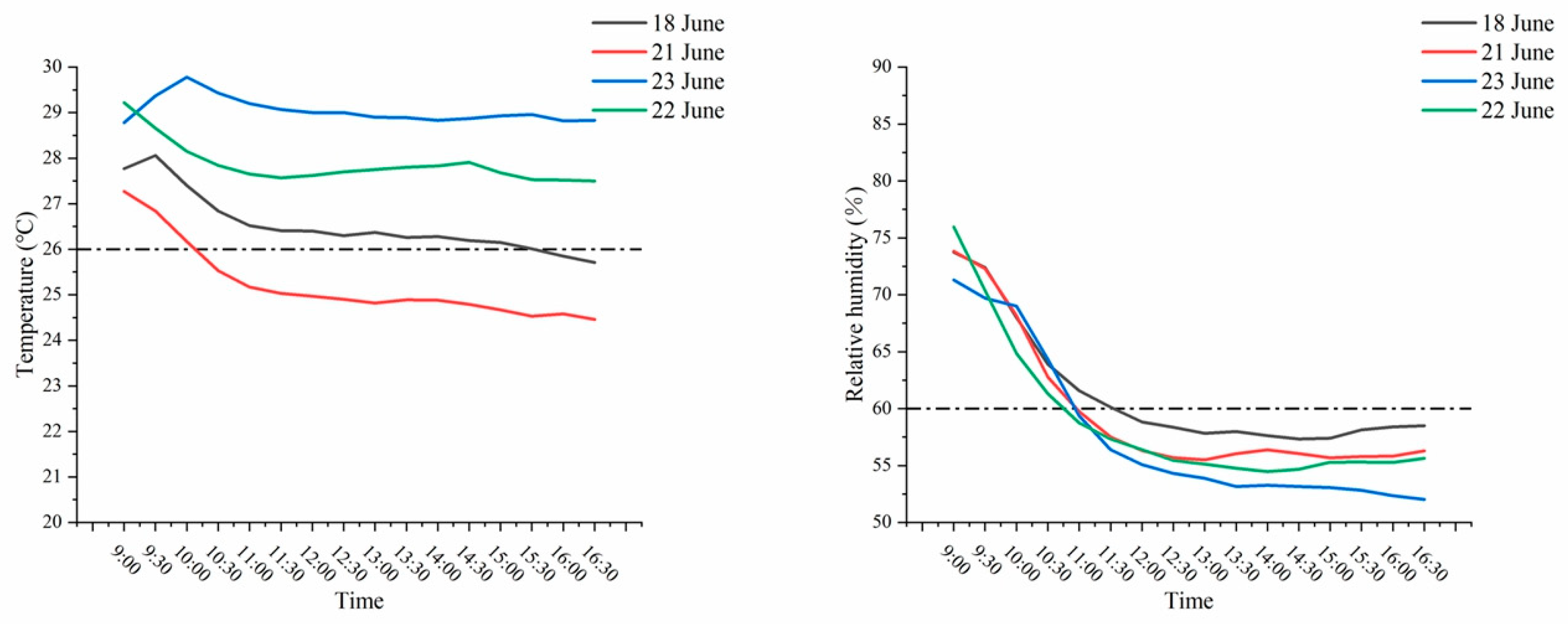
4.3. User Comfort
4.4. Limitations of the Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HVAC | Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning |
| LM | Levenberg–Marquardt |
| LM-UGO | Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm combined with universal global optimization algorithm |
| COP | Coefficient of performance |
| t | Temperature |
| to | Condensation temperature (°C) |
| tv | Evaporation temperature (°C) |
| z1 | Parameter |
| z2 | Parameter |
| r | Load rate of the chiller |
| tw,o,E | Outlet temperature of cooling water (°C) |
| tw,v,E | Outlet temperature of the chilled water (°C) |
| tw,o,L | Inlet temperature of the cooling water (°C) |
| tw,v,L | Inlet temperature of the chilled water (°C) |
| Gw,o | Cooling water flow rate (kg/s) |
| Gw,v | Chilled water flow rate (kg/s) |
| UAo | Total heat-transfer coefficients (W/°C) of the condenser |
| UAv | Total heat-transfer coefficients (W/°C) of the evaporator |
| Qe | Cooling load (kW) |
| QL | Cooling load (kW) |
| Pchiller | Chiller power (kW) |
| Pp | Pump power (kW) |
| b0, b1, b2 | Parameter of pump |
| Gw | Water flow rate (m3/h) |
| tw | Water temperature |
| tm | Average water temperature |
| Psystem | Power of the whole system |
| Pchilledwaterpump | Chilled water pump power |
| Pcoolingwaterpump | Cooling water pump power |
| Tw,v,L | Parameter |
| hu | Humidity |
| ROI | Return on investment |
| Ii | Investment income |
| Ic | Investment cost |
References
- Zhang, X.; Lau, C.K.M.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Wanjiru, R.; Seetaram, N. Determinants of Carbon Emissions Cycles in the G7 Countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 201, 123261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Ren, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, X. Pathway to Sustainable Economic Growth: Linkage Among Energy Consumption, Carbon Emissions, Climate Change and Technological Innovation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2023, 50, 101253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, D.; Gu, J. Does Increasing Income Have a Positive Impact on Energy Consumption? New Evidence from China. Sustain. Futures 2024, 7, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Al Shraah, A.; Khudoykulov, K.; Albasher, G.; Ortiz, G.G.R. Role of Green Energy Usage in Reduction of Environmental Degradation: A Comparative Study of East Asian Countries. Energy Econ. 2023, 126, 106927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Cao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Sultan, M.; Attia, S. Coupling Effect of Radiative Cooling and Phase Change Material on Building Wall Thermal Performance. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Liu, Y. A Hierarchical HVAC Optimal Control Method for Reducing Energy Consumption and Improving Indoor Air Quality Incorporating Soft Actor-Critic and Hybrid Search Optimization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 302, 118118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guan, Y.; Oldfield, J.; Guan, D.; Shan, Y. China Carbon Emission Accounts 2020–2021. Appl. Energy 2024, 360, 122837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorizas, P.V.; Assimakopoulos, M.-N.; Santamouris, M. A Holistic Approach for the Assessment of the Indoor Environmental Quality, Student Productivity, and Energy Consumption in Primary Schools. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhorn-Kluttig, H.; Erhorn, H. School of the Future–Towards Zero Emission with High Performance Indoor Environment. Energy Procedia 2014, 48, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B.; Economou, V.; Lee, C.K.K.; Perks, T.; Smith, S.A.; Yip, Q. The Interaction Between Physical and Social-Psychological Factors in Indoor Environmental Health. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 85, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łokietek, T.; Jaszczak, S.; Nikończuk, P. Optimization of Control System for Modified Configuration of a Refrigeration Unit. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 159, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tian, P.; Wang, F. Energy Saving Control Method Research of Modular Water Chillers Group Operation and Pump Variable-Frequency Control Based on Dynamic Air Conditioning Load Requirements Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering, Changchun, China, 24–26 August 2010; IEEE: Changchun, China, 2010; p. 5610006. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzatto, L.R.; Nascimento, C.A.R.; Mendes, N. An Empirical Model of a Split-Type Inverter Air Conditioner for Building Energy Simulation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 236, 121714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Fu, P.; Wu, X. Study on Simplified Energy-Efficient Control Methods of HVAC Cooling Water System from the Global Online Optimization Perspective. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelvin Wijaya, T.; Sholahudin, M.I.; Idrus Alhamid, M.; Saito, K.; Nasruddin, N. Dynamic Optimization of Chilled Water Pump Operation to Reduce HVAC Energy Consumption. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 36, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Huang, D.; Huang, T.; Farid, U. Optimization of Buildings Energy Consumption by Designing Sliding Mode Control for Multizone VAV Air Conditioning Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Heo, Y.; Moon, J.W. An Intelligent HVAC Control Strategy for Supplying Comfortable and Energy-Efficient School Environment. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 55, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Gao, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; Lei, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, H. Load Rebound Suppression Strategy and Demand Response Potential of Thermal Storage HVAC Systems: An Experimental and Simulation Study. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigounis, A.-M.; Vallianos, C.; Athienitis, A. Model Predictive Control of Air-Based Building Integrated PV/T Systems for Optimal HVAC Integration. Renew. Energy 2023, 212, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, L.; Javed, S. Cost-Optimal Analysis of Energy Efficient Hvac Solution-Sets for Low-Energy Apartment Buildings. Energy Build. 2023, 295, 113332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, F.M.; Macii, A.; Patti, E.; Bottaccioli, L. An Online Reinforcement Learning Approach for HVAC Control. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroziak, A.; Chojecki, A. The PID Controller Optimisation Module Using Fuzzy Self-Tuning PSO for Air Handling Unit in Continuous Operation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bi, T.; Xu, L. A Module-Level Pipeline Based Gauss-Newton Online Ranging Method for High-Repetition-Frequency Full-Waveform LiDAR. Measurement 2024, 229, 114351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Pang, J.-S.; Mitchell, J.E. An Algorithm for Global Solution to Bi-Parametric Linear Complementarity Constrained Linear Programs. J. Glob. Optim. 2015, 62, 263–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Conde, A.; Ávila-Avendaño, C.; Quevedo-López, M.A.; García-Sánchez, F.J. Simplified EKV Model Parameter Extraction in Polysilicon MOSFETs. Solid-State Electron. 2022, 195, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, C.; Chicco, F.; Pezzotta, A. Nanoscale MOSFET Modeling: Part 1: The Simplified EKV Model for the Design of Low-Power Analog Circuits. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2017, 9, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zheng, M.; Chen, W.; Bi, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Salt-Dissolved Regularity of the Self-Ice-Melting Pavement Under Rainfall. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niri, T.D.; Heydari, M.; Hosseini, M.M. Two Nonmonotone Trust Region Algorithms Based on an Improved Newton Method. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 64, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, C.; Liu, F.; Duan, Z.; Zhao, H. A Trust-Region-like Algorithm for Expensive Multi-Objective Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 148, 110892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.; Que, Y. Hierarchical Recursive Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm for Radial Basis Function Autoregressive Models. Inf. Sci. 2023, 647, 119506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Gai, M. Football Team Training Algorithm: A Novel Sport-Inspired Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithm for Global Optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 245, 123088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, A.S.; Scheinberg, K.; Vicente, L.N. Convergence of Trust-Region Methods Based on Probabilistic Models. SIAM J. Optim. 2013, 24, 1238–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Duan, Z.S.; Huang, L. Global Convergence of a Class of Discrete-Time Interconnected Pendulum-Like Systems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2007, 133, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 31349-2014; Technical Requirements of Measurement and Verification of Energy Savings-Central Air-Conditioning System. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB 50189-2015; Design Standard for Energy Efficiency of Public Buildings. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB 55016-2021; General Code for Building Environment. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2021.

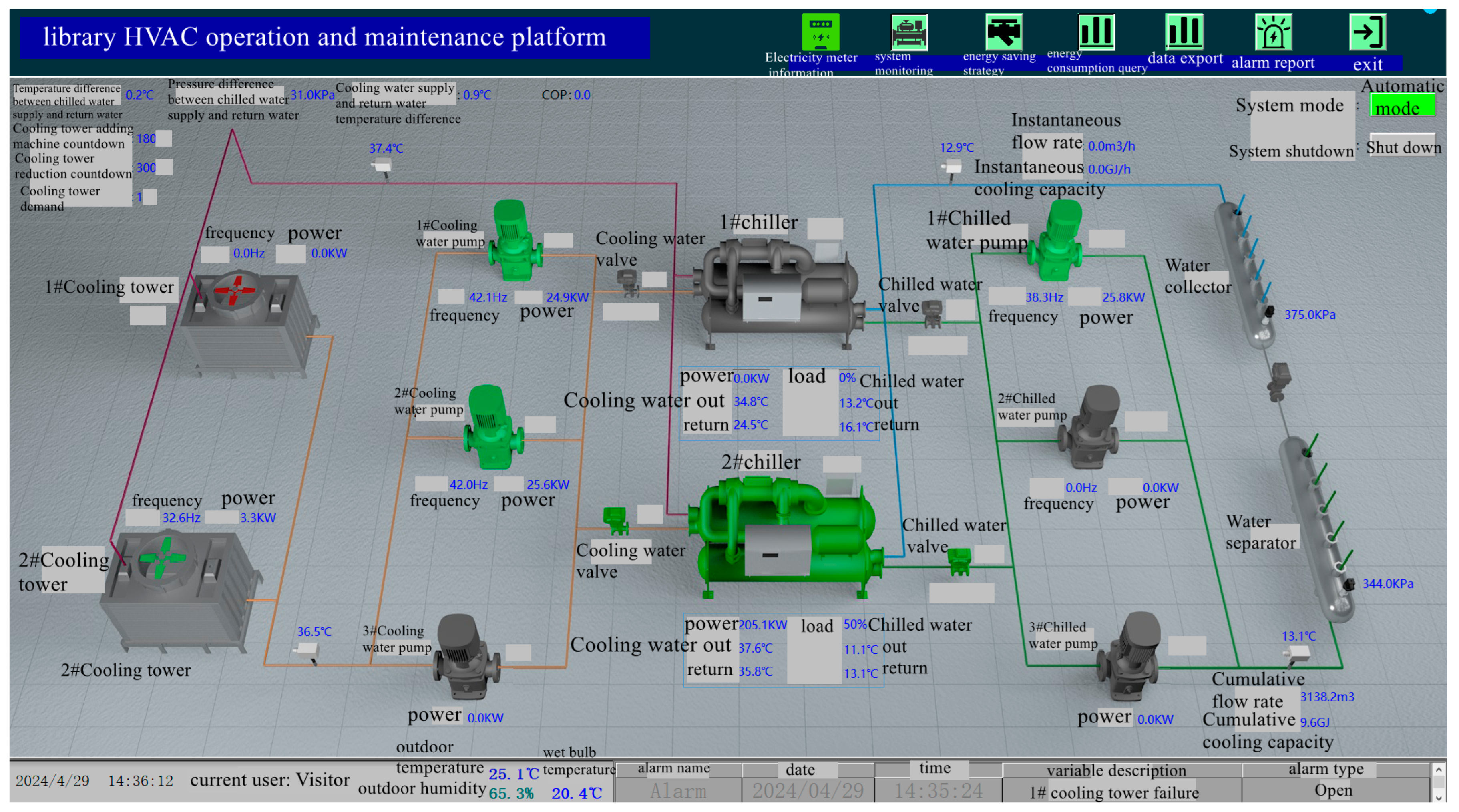
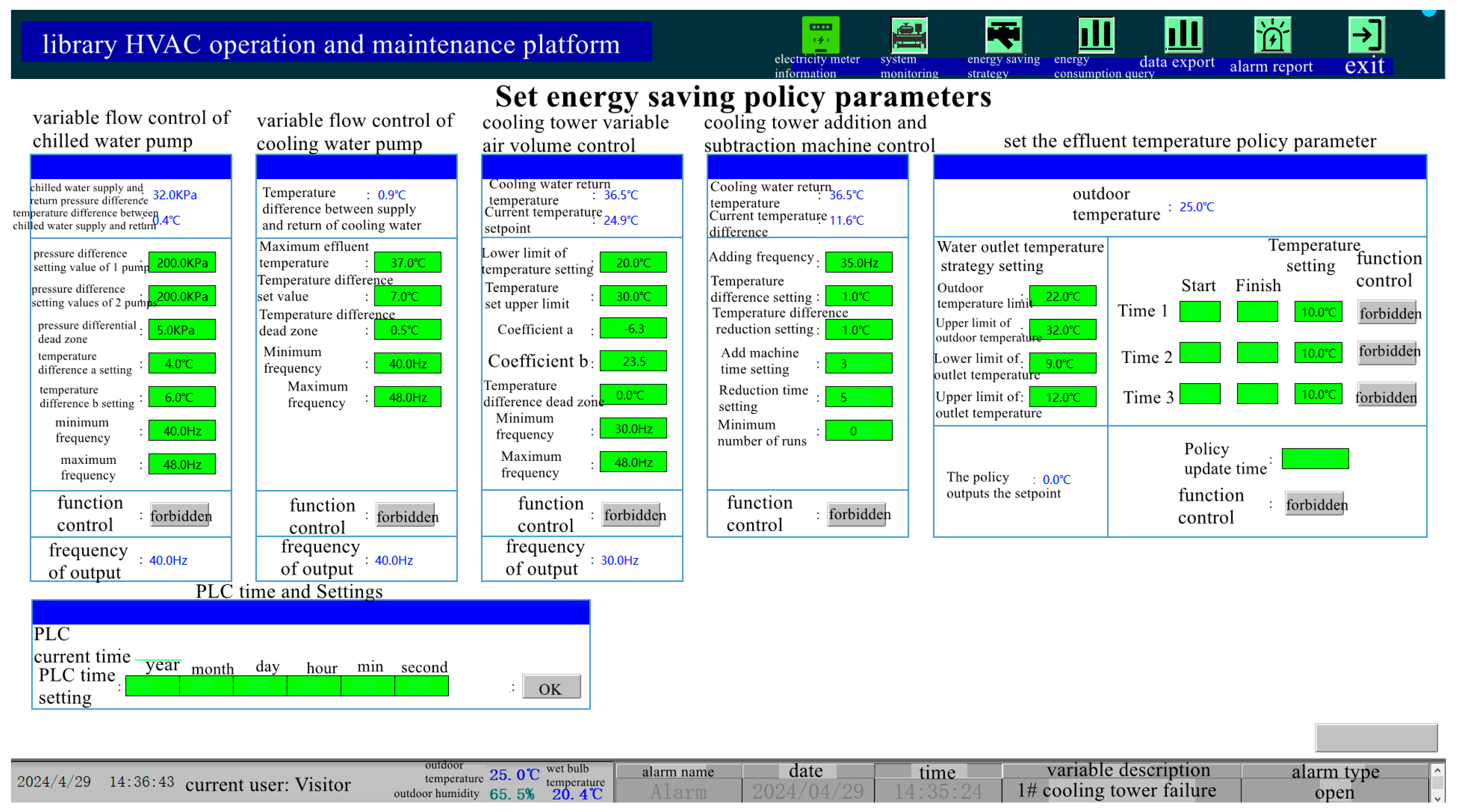
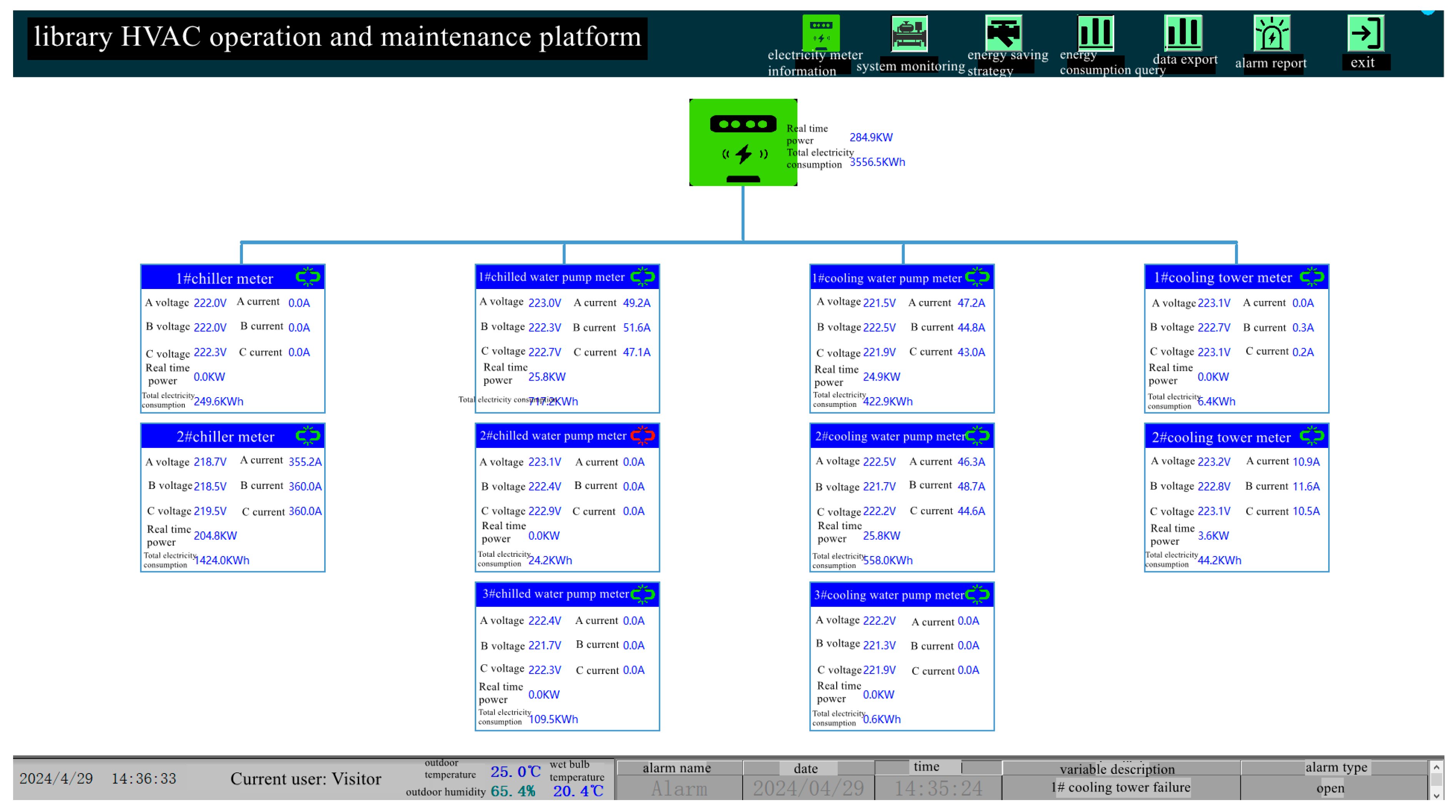
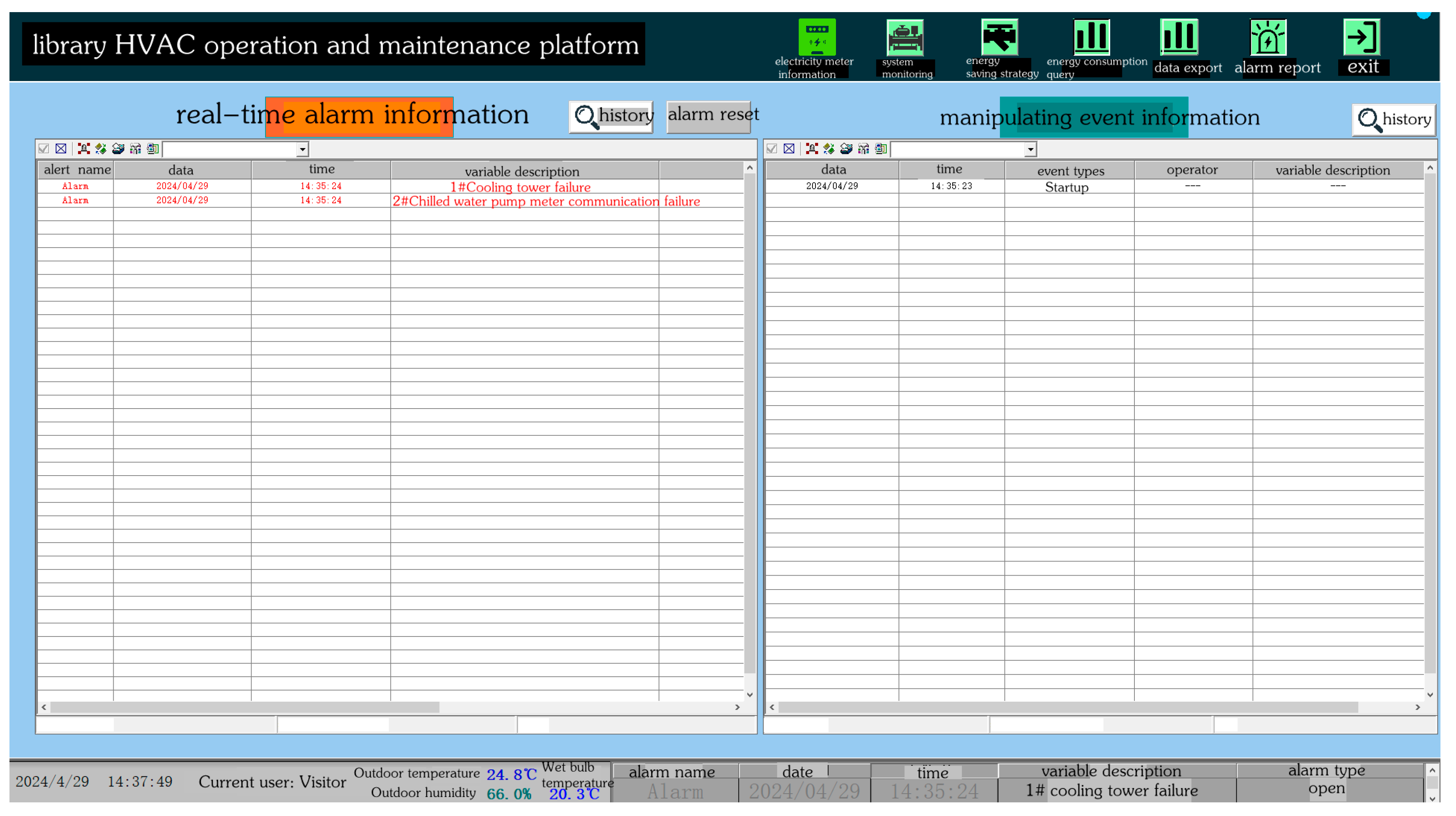






| Equipment Type | Parameters | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Chiller | Rated cooling capacity 2040 kW, rated power 361.7 kW | 2 |
| Chilled water pump | Rated flow 466 m3/h, rated power 55 kW | 3 |
| Cooling water pump | Rated flow 466 m3/h, rated power 45 kW | 3 |
| Cooling tower | Motor power: 11 kW Flow rate: 900 m3/h | 2 |
| Name | Brand | Type | Range and Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data collector | Qingdao Hantai | DAQ4090A | Basic DCV accuracy of 0.003%, scan rate up to 450 channels/second |
| Edge computing gateway | Beijing Hailin | HNE | Temperature measurement accuracy is ±1 °C. The measurement accuracy of voltage and current is ±1%. Measurement accuracy of pressure and flow rate is ±1% |
| Industrial intelligent gateway | Huachen Zhitong | HINET | Support Ethernet, serial port, CAN port, 10 port and other devices access and Ethernet, 2G/3G/4G full network access. Embedded a variety of industrial protocols, support more than 99% of PLC and most industrial equipment access. |
| Temperature sensor | TE Connectivity | 20011957 | Temperature measurement accuracy is ±1 °C. Measuring range is 0 to 50 °C. Temperature measurement accuracy is ±1 °C. Measuring range is 0 to 50 °C. |
| Humidity sensor | Amphenol | Telaire RH | Measurement range is 5 to 95% RH. Accuracy ±5% RH |
| Equipment Running Time | 9:00–17:00 | 9:00–17:00 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation Mode | Original Mode | Energy-Saving Mode | |
| Chiller | Number of enabled devices | 1 | Same as the day before |
| Effluent temperature setting | 7 °C | Automatic mode | |
| Chilled water pump | Number of enabled devices | 2 | Automatic mode |
| Operating frequency | 50 Hz | Automatic mode | |
| Cooling water pump | Number of enabled devices | 2 | Automatic mode |
| Operating frequency | 50 Hz | Automatic mode | |
| Cooling tower | Number of enabled devices | 2 | Automatic mode |
| Operating frequency | 50 Hz | Automatic mode | |
| Data | Mean Outdoor Temperature (°C) | Operation Mode | 1# Chiller (kWh) | 2# Chiller (kWh) | 1# Chilled Water Pump (kWh) | 2# Chilled Water Pump (kWh) | 3# Chilled Water Pump (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 June 2024 | 26.4 | Low-load mode | 1003.2 | 0 | 112.23 | 103.44 | 0 |
| 2 June 2024 | 27.7 | 0 | 820.8 | 95.67 | 88.29 | 0 | |
| 3 June 2024 | 28.3 | 1824 | 0 | 201.84 | 185.34 | 0 | |
| 4 June 2024 | 26.3 | 483.2 | 0 | 55.14 | 50.64 | 0 | |
| 5 June 2024 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0 | |
| 6 June 2024 | 25.6 | 560 | 0 | 61.5 | 56.34 | 0 | |
| 7 June 2024 | 27.3 | Energy-saving mode | 2443.2 | 0 | 273.21 | 249.57 | 0 |
| 8 June 2024 | 29.2 | 2035.2 | 0 | 217.2 | 199.11 | 0 | |
| 9 June 2024 | 26.5 | 0 | 1840 | 228.9 | 209.13 | 0 | |
| 10 June 2024 | 25.8 | 1856 | 0 | 216.51 | 197.61 | 0 | |
| 11 June 2024 | 28.6 | 0 | 2193.6 | 223.29 | 203.7 | 0 | |
| 12 June 2024 | 31.4 | 2438.4 | 0 | 228.48 | 208.59 | 0 | |
| 13 June 2024 | 32.5 | Energy-saving mode | 3209.6 | 0 | 272.1 | 248.28 | 0 |
| 14 June 2024 | 33 | 0 | 3422.4 | 265.5 | 242.13 | 0 | |
| 15 June 2024 | 33.9 | Original mode | 3870.4 | 16 | 524.88 | 482.67 | 0 |
| 16 June 2024 | 32.2 | Equipment failure period 1 | 0 | 2240 | 183 | 167.22 | 0 |
| 17 June 2024 | 30.4 | 627.2 | 0 | 52.83 | 48.39 | 0 | |
| 19 June 2024 | 29.6 | Energy-saving mode | 0 | 3020.8 | 278.79 | 254.46 | 0 |
| 19 June 2024 | 27.7 | 0 | 2694.4 | 250.62 | 228.78 | 0 | |
| 20 June 2024 | 27.6 | 2592 | 0 | 260.88 | 238.44 | 0 | |
| 21 June 2024 | 29.7 | Original mode | 3828.8 | 0 | 498.75 | 458.79 | 0 |
| 22 June 2024 | 27.4 | 3900.8 | 0 | 612.42 | 563.76 | 0 | |
| 23 June 2024 | 27.5 | Energy-saving mode | 2260.8 | 0 | 236.4 | 215.97 | 0 |
| 1# | 2# | 3# Cooling water pump (kWh) | 1# Cooling tower (kWh) | 2# Cooling tower (kWh) | Total (kWh) | 1# | 2# |
| Cooling water pump (kWh) | Cooling water pump (kWh) | Mean indoor temperature (°C) | Mean indoor temperature (°C) | ||||
| 104.37 | 111.96 | 0 | 22.81 | 20.17 | 1478.18 | 25.2 | 25.6 |
| 88.56 | 95.31 | 0 | 18.32 | 15.92 | 1222.87 | 25.3 | 25.8 |
| 187.56 | 200.94 | 0 | 37.48 | 33.41 | 2670.57 | 24.9 | 25.8 |
| 51.99 | 54.84 | 0 | 12.23 | 10.19 | 718.23 | 25.4 | 25.8 |
| 0.81 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 3.8 | 25.3 | 25.4 |
| 58.08 | 61.32 | 0 | 13.24 | 11.3 | 821.78 | 25.2 | 25.6 |
| 257.1 | 272.43 | 0 | 57.01 | 51.85 | 3604.37 | 24.5 | 25.4 |
| 206.43 | 216.87 | 0 | 52.45 | 47.36 | 2974.62 | 24.3 | 25.6 |
| 215.79 | 226.74 | 0 | 40.33 | 36.4 | 2797.29 | 23.9 | 25.4 |
| 205.32 | 214.68 | 0 | 47.45 | 42.96 | 2780.53 | 24 | 25.2 |
| 187.23 | 201.51 | 0 | 66.97 | 61.18 | 3137.48 | 24.3 | 25.4 |
| 197.55 | 202.53 | 0 | 76.57 | 70.09 | 3422.21 | 24.6 | 25.8 |
| 227.13 | 245.94 | 0 | 99.54 | 90.71 | 4393.3 | 24.5 | 26.1 |
| 221.52 | 239.43 | 0 | 100.5 | 91.86 | 4583.34 | 24.7 | 26.4 |
| 202.23 | 484.86 | 274.5 | 104.73 | 82.29 | 6042.56 | 25.1 | 26.6 |
| 0.81 | 108.69 | 421.5 | 67.71 | 61.17 | 3250.1 | 25.5 | 26.8 |
| 49.29 | 48.78 | 33.3 | 18.47 | 16.11 | 894.37 | 26.8 | 27.4 |
| 237.63 | 244.23 | 0 | 106.86 | 97.34 | 4240.11 | 25.8 | 27.2 |
| 215.28 | 221.19 | 0 | 94.19 | 86.16 | 3790.62 | 25.4 | 26.7 |
| 226.92 | 232.89 | 0 | 89.61 | 82.17 | 3722.91 | 25.1 | 26.3 |
| 444.93 | 458.55 | 0 | 86.94 | 71.35 | 5848.11 | 25.1 | 26.3 |
| 548.76 | 562.35 | 0 | 100.91 | 93.93 | 6382.93 | 23.2 | 25.7 |
| 204.3 | 209.94 | 0 | 62.76 | 57.22 | 3623.39 | 23.1 | 25.6 |
| Parameter | Mean Daily Outdoor Temperature | Mean Daily Indoor Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum allowable deviation for similar days | ±1 °C | ≤26 °C |
| Name | Data | Operation Mode | Mean Outdoor Temperature (°C) | 1# Mean Indoor Temperature (°C) | 2# Mean Indoor Temperature (°C) | Energy Consumption from 9 to 17 (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample1 | 18 June 2024 | Energy-saving mode | 29.6 | 25.8 | 27.2 | 3021 |
| 21 June 2024 | Original mode | 29.7 | 25.1 | 26.3 | 5190 | |
| Sample2 | 23 June 2024 | Energy-saving mode | 27.5 | 23.1 | 25.6 | 5244 |
| 22 June 2024 | Original mode | 27.4 | 23.2 | 25.7 | 3247 |
| Name | Data | Operation Mode | Daily Energy Consumption (kWh) | Energy Savings (kWh) | Energy-Saving Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 June 2024 | Energy-saving mode | 3021 | 2169 | 41.79% |
| 2 | 21 June 2024 | Original mode | 5190 | ||
| 3 | 23 June 2024 | Energy-saving mode | 3247 | 1997 | 38.08% |
| 4 | 22 June 2024 | Original mode | 5244 |
| Period Division | Electricity Price Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| First stage | 0:00–6:00, 12:00–14:00 | 0.48 | |
| Second stage | 6:00–12:00, 14:00–16:00 | 1 | |
| Third stage | 16:00–20:00, 22:00–24:00 (July and August) | 16:00–18:00, 20:00–24:00 (Other months) | 1.49 |
| Fourth stage | 20:00–22:00 (July and August) | 18:00–20:00 (Other months) | 1.8 |
| Period Division | Electricity Price (US Dollar) | |
|---|---|---|
| First stage | ≤1 kV | 0.1055 |
| Second stage | 1–35 kV | 0.1028 |
| Third stage | 35–110 kV | 0.1021 |
| Fourth stage | ≥110 kV | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Zou, W.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Zhu, L.; Shu, H. Research on Real-Time Control Strategy for HVAC Systems in University Libraries. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052855
Zou Y, Zou W, Chen H, Dong X, Zhu L, Shu H. Research on Real-Time Control Strategy for HVAC Systems in University Libraries. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052855
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yiquan, Wentao Zou, Han Chen, Xingyao Dong, Luxi Zhu, and Hong Shu. 2025. "Research on Real-Time Control Strategy for HVAC Systems in University Libraries" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052855
APA StyleZou, Y., Zou, W., Chen, H., Dong, X., Zhu, L., & Shu, H. (2025). Research on Real-Time Control Strategy for HVAC Systems in University Libraries. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052855






