Impacts of Cascade Reservoirs on Adjacent Climate and Land Use Change in the Upper Yellow River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
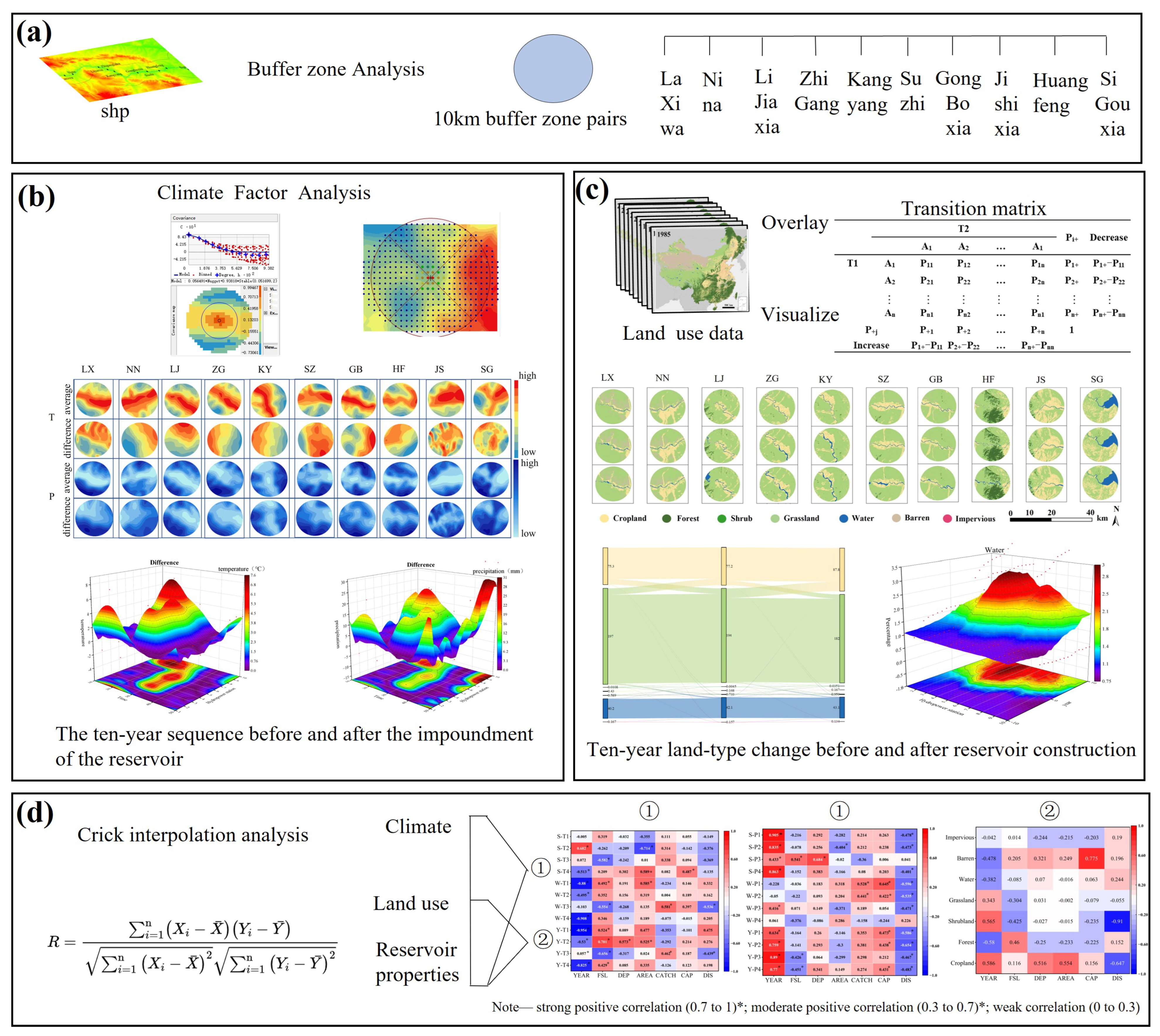
2.3. Methods of Analysis
2.3.1. Buffer Analysis
2.3.2. Land Use
2.3.3. Methods of Meteorological Analysis
- Linear regression: Taking the reservoir operation as the boundary, the climatic tendency rate method was used to calculate the variability in temperature and precipitation elements in the two periods of 10 a before and 10 an after the start of water storage in each reservoir. The change in climate propensity before and after impoundment can remove the influence of the general background of long-term changes in the elements, and together with whether or not the elements change suddenly during impoundment, it can reflect the influence of impoundment on the elements. The slope of the linear regression model was used to describe the trend of each meteorological variable (Figure 2b).
- Climate-type M-K mutation test to obtain the climate jumping points, tested at the significance level of 0.05: The Mann–Kendall mutation test is a nonparametric statistical test with the advantage that it is not only easy to compute but also identifies the moment of mutation onset and indicates the region of the mutation period.
2.3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Basic Reservoir Attributes and Climate Factors
3. Results
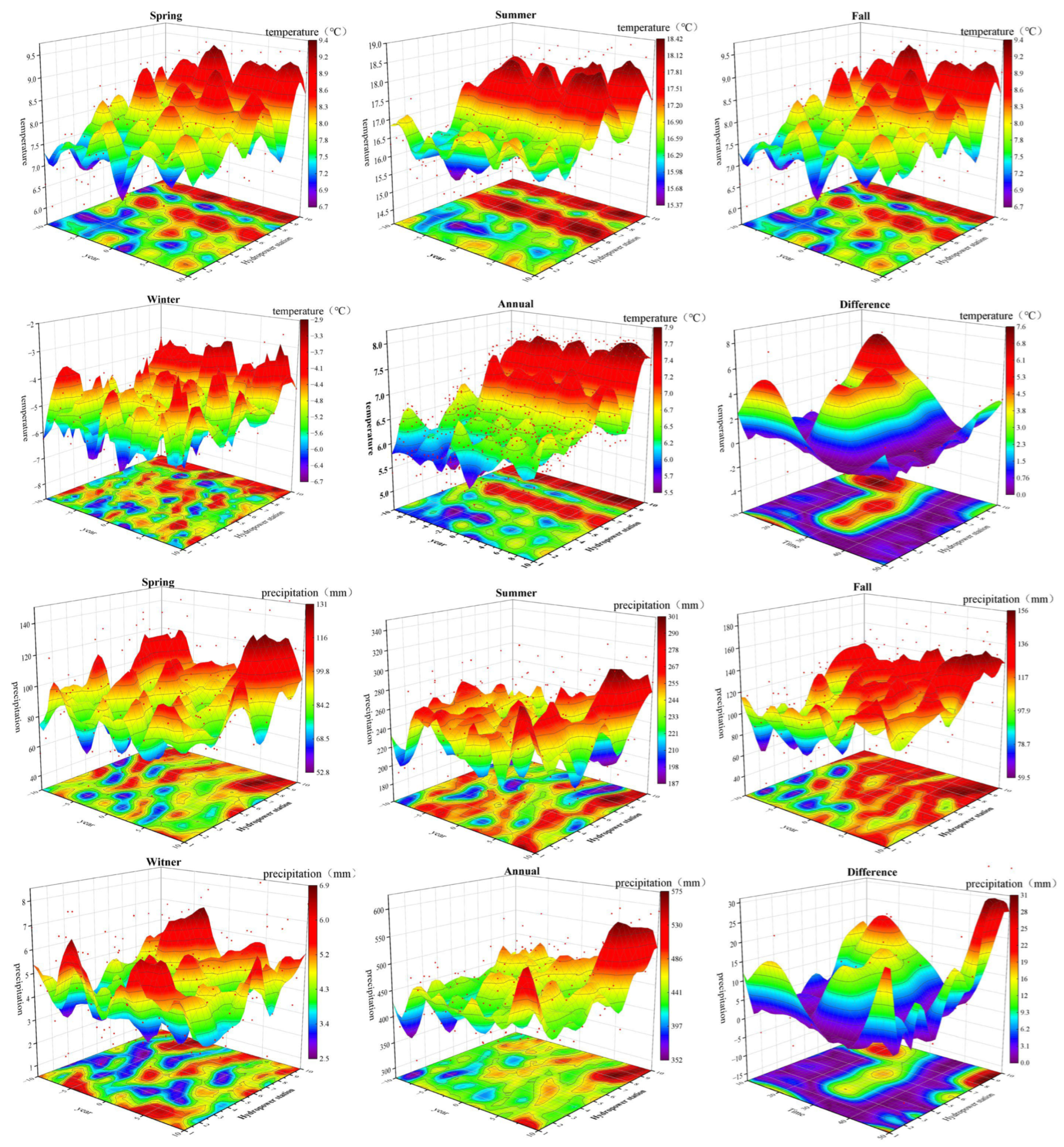
3.1. Localized Climate Change
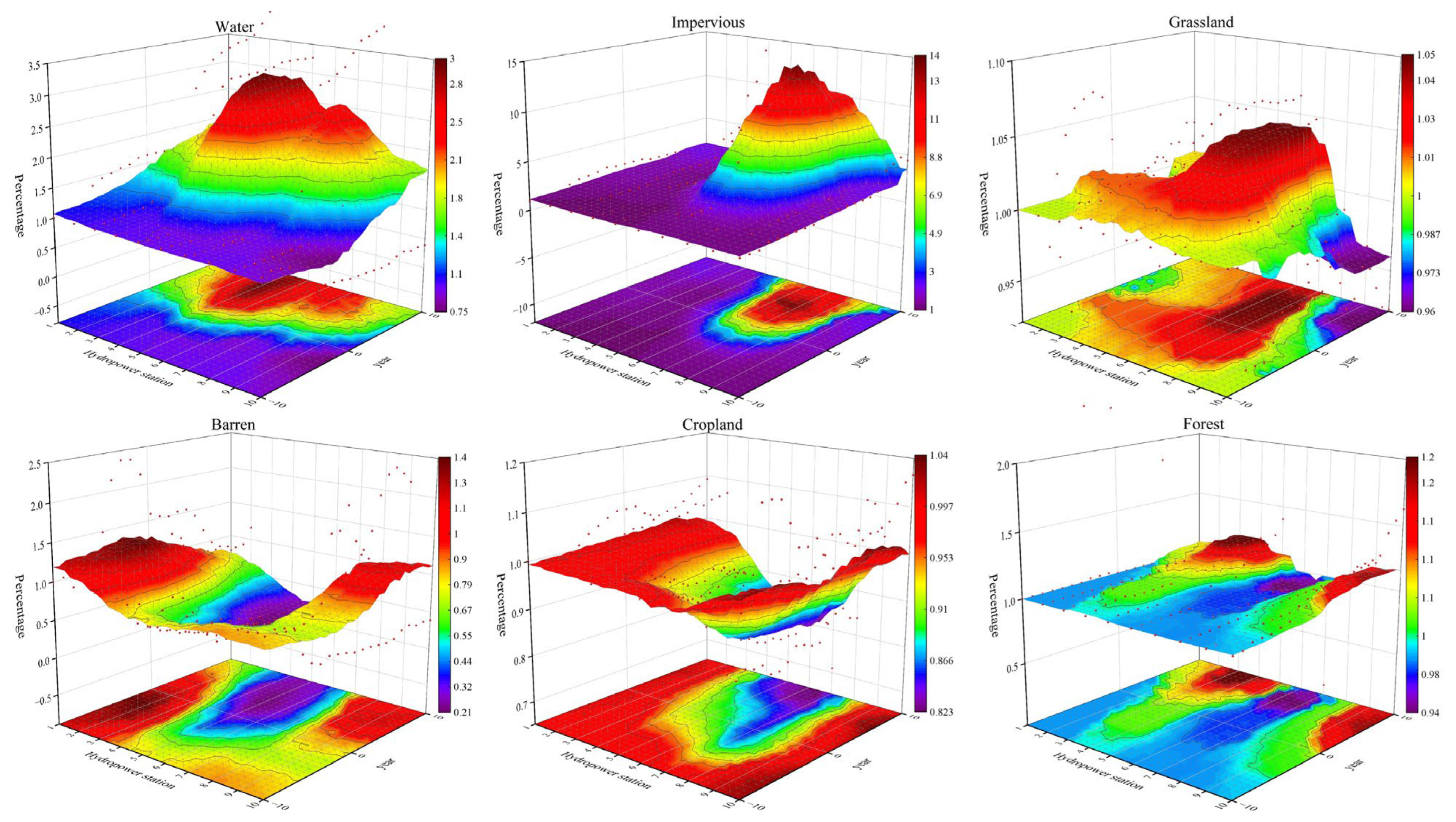
3.2. Land Use Change
3.3. Correlation Between Reservoir Properties, Climate, and Land Use Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Reservoir Construction on Climate Change
4.2. Impact of Reservoir Construction on Land Use
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Climate change around the reservoirs was significant. Following reservoir construction, both temperature and precipitation exhibited an upward trend, especially in spring and fall. For example, the spring temperature at the LJ reservoir increased by 0.51 °C per decade, while annual precipitation at the JS reservoir rose by 41.26 mm per decade. Precipitation changes showed regional variation, with areas such as ZG, KY, GB, and SZ experiencing a gradual decline in precipitation. However, summer precipitation generally increased, and winter precipitation remained relatively stable.
- (2)
- Reservoir construction induced substantial changes in land use types, particularly the conversion of grassland to water and cropland. Notably, the transformation of grassland into cropland constituted the largest portion of ecological change, accounting for approximately 93.2% of the total land use conversion, which included transitions between grassland, cropland, water, and impervious areas. Dynamic analysis revealed that water areas increased the most following reservoir construction, rising by over 200%, while cropland and grassland areas decreased correspondingly.
- (3)
- A significant correlation was found between reservoir attributes (e.g., water storage capacity and surface area) and both climate and land use changes. Specifically, a positive correlation was observed between water storage capacity and increased precipitation.
- (4)
- This study emphasizes the significant impacts of reservoir construction on local climate and ecological environments, providing valuable insights for future reservoir development and management. The findings can assist policymakers in understanding the long-term effects of reservoirs on local climates and ecosystems, offering a scientific foundation for the rational planning of water resource development, ecological protection, and land use. Furthermore, these results can serve as a reference for ecological and environmental assessments in similar regions, promoting sustainable regional development.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaofeng, J.; Yuan, L. Suggestions for strategic allocation of the Yellow River water resources under the new situation. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, S.; Wu, J.; Wan, F.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, X.; Shang, W.; Zhang, F. Study on the method and model of water balance allocation of the Yellow River with overall fairness and efficiency. Water Supply 2023, 23, 2711–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.Q.; Van Binh, D.; Tran, T.N.D.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T. Response of streamflow and sediment variability to cascade dam development and climate change in the Sai Gon Dong Nai River basin. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 7997–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Shi, B.; Fan, J.; Luo, X.; Tian, Q.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X. Streamflow decline in the Yellow River along with socioeconomic development: Past and future. Water 2020, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eekhout, J.P.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Pérez-Cutillas, P.; de Vente, J. The impact of reservoir construction and changes in land use and climate on ecosystem services in a large Mediterranean catchment. J. Hydrology 2020, 590, 125208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Peng, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, F. The mechanisms of a loess landslide triggered by diversion-based irrigation: A case study of the South Jingyang Platform, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4945–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Peng, J.; Nan, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, K.; Wei, B.; Wang, S. The shear behavior of the slip zone loess and landslide mechanism. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 257, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W. Continuous monitoring of the surface water area in the Yellow River basin during 1986–2019 using available Landsat imagery and the Google Earth Engine. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yang, D.; Gao, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G. Impacts of climate warming on the frozen ground and eco-hydrology in the Yellow River source region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Li, X.; Niu, Z.; Liang, X. A new complexity-based three-stage method to comprehensively quantify positive/negative contribution rates of climate change and human activities to changes in runoff in the upper Yellow River. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Lai, Z.; Ji, G. Using Budyko-type equations for separating the impacts of climate and vegetation change on runoff in the source area of the Yellow River. Water 2020, 12, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Lakshmi, V. Enhancing human resilience against climate change: Assessment of hydroclimatic extremes and sea level rise impacts on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, B.P.; Kelsey, T.R.; Vogl, A.L.; Wolny, S.A.; MacEwan, D.; Selmants, P.C.; Biswas, T.; Butterfield, H.S. Shaping land use change and ecosystem restoration in a water-stressed agricultural landscape to achieve multiple benefits. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, Z.; Decsi, B.; Ács, T.; Kardos, M.K.; Hidy, D.; Árvai, M.; Kalicz, P.; Kern, Z.; Pinke, Z. Supposed effects of wetland restoration on hydrological conditions and the provisioning ecosystem services—A model-based case study at a hungarian lowland catchment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehosmaa, K. Anthropogenic Impacts and Restoration of Boreal Spring Ecosystems; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Lyon, S.W.; Mao, J.; Dai, H.; Jarsjö, J. Impacts of multi-purpose reservoir construction, land-use change and climate change on runoff characteristics in the Poyang Lake basin, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 29, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranmer, A.W.; Weigel, D.; Marti, C.L.; Vidergar, D.; Benjankar, R.; Tonina, D.; Goodwin, P.; Imberger, J. Coupled reser-voir-river systems: Lessons from an integrated aquatic ecosystem assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, D.; Guo, S.; Xiong, L.; Liu, P.; Yin, J.; Tian, J.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J. Impacts of water resources allocation on water environmental capacity under climate change. Water 2021, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodnebrog, Ø.; Myhre, G.; Samset, B.H.; Alterskjær, K.; Andrews, T.; Boucher, O.; Faluvegi, G.; Fläschner, D.; Forster, P.M.; Watson-Parris, D.; et al. Water vapour adjustments and responses differ between climate drivers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12887–12899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.; Nadeau, D.F.; Thiboult, A.; Rousseau, A.N.; Tremblay, A.; Isabelle, P.E.; Anctil, F. Characteristic time scales of evaporation from a subarctic reservoir. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Lu, S.; Ye, L.; Qiu, D.; Meng, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; et al. The cooling effect of oasis reservoir-riparian forest systems in arid regions. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2024WR038301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderkelen, I.; van Lipzig, N.P.M.; Sacks, W.J.; Lawrence, D.M.; Clark, M.P.; Mizukami, N.; Pokhrel, Y.; Thiery, W. Simulating the impact of global reservoir expansion on the present-day climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, H. Impacts of dams and reservoirs on local climate change: A global perspective. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Haddad, O.B.; Loáiciga, H.A. Adaptive reservoir operation rules under climatic change. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Teng, M.; Wang, P. Land use/cover change in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China: Reconciling the land use conflicts between development and protection. Catena 2019, 175, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosmans, J.H.; van Beek, L.P.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Bierkens, M.F. Hydrological impacts of global land cover change and human water use. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5603–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, S.M.L.D.; Dayawansa, N.D.K.; Gunawardena, E.R.N. Land use changes resulting from construction of Deduru Oya reservoir and its impacts on livelihood. Trop. Agric. Res. 2017, 28, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlíček, M.; Uhrová, J. Changes in land use due to the construction of water reservoirs. Vodohospod. Tech.-Ekon. Inf. 2017, 59, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Verma, M.K.; Prasad, A.D.; Mehta, D.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Muttil, N.; Rathnayake, U. Simulating the hydrological processes under multiple land use/land cover and climate change scenarios in the Mahanadi reservoir complex, Chhattisgarh, India. Water 2023, 15, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Dias, V.; Pereira da Luz, M.; Medero, G.M.; Tarley Ferreira Nascimento, D. An overview of hydropower reservoirs in Brazil: Current situation, future per-spectives and impacts of climate change. Water 2018, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berga, L. The role of hydropower in climate change mitigation and adapta-tion: A review. Engineering 2016, 2, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingarro, M.; Cancela, J.P.; BurÓn-Ugarte, A.; García-Barros, E.; Munguira, M.L.; Romo, H.; Wilson, R.J. Butterfly communities track climatic variation over space but not time in the Iberian Peninsula. Insect Conserv. 2021, 14, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Noges, T.; Beklioğlu, M. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanny, J.; Cohen, S.; Assouline, S.; Lange, F.; Grava, A.; Berger, D.; Teltch, B.; Parlange, M.B. Evaporation from a small water reservoir: Direct measurements and estimates. J. Hydrol. 2008, 351, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degu, A.M.; Hossain, F.; Niyogi, D.; Pielke, R., Sr.; Shepherd, J.M.; Voisin, N.; Chronis, T. The influence of large dams on surrounding climate and precipitation patterns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L04405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Yang, J. Impacts of reservoir water level fluctuation on measuring seasonal seismic travel time changes in the Binchuan basin, Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, D.; Frei, C. Spatial analysis of precipitation in a high-mountain region: Exploring methods with multi-scale topographic predictors and circulation types. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4543–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Du, L.; Xiao, C.; Liu, L.; Tarroja, B. Climate change impacts on Three Gorges Reservoir impoundment and hydropower generation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 123922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Zheng, H.; Li, C.; Xiong, W. Response of runoff and suspended load to climate change and reservoir construction in the Lancang River. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 1966–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinhati, F.S.C.; Rodrigues, L.N.; de Souza, S.A. Modelling the impact of on-farm reservoirs on dry season water availability in an agricultural catchment area of the Brazilian savannah. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasanov, K. A comprehensive analysis of reservoir capacity loss: A case study of the Akhangaran Reservoir, Uzbekistan. Water Cycle 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.T.; Goethals, P.L. Opportunities and challenges for the sustainability of lakes and reservoirs in relation to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Water 2019, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, H.; Argaw, M.; Seifu, W. Impact of land use/land cover change on surface water hydrology in Akaki River catchment, Awash basin, Ethiopia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2024, 135, 103690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Yu, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, X. Impacts of land-use and land-cover changes on river runoff in Yellow River basin for period of 1956–2012. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Spatio-temporal evolution of land use transition and its eco-environmental effects: A case study of the Yellow River basin, China. Land 2020, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
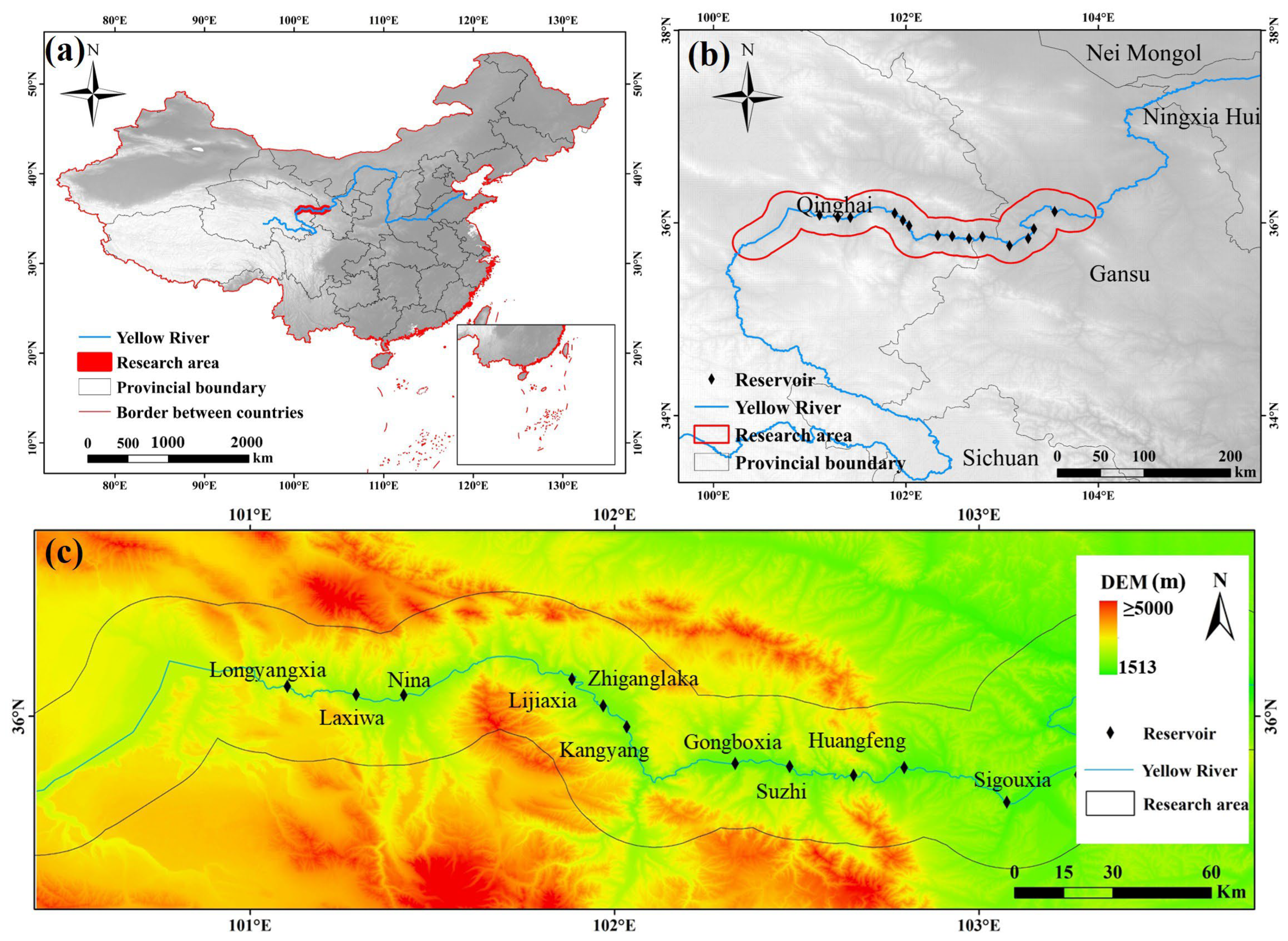

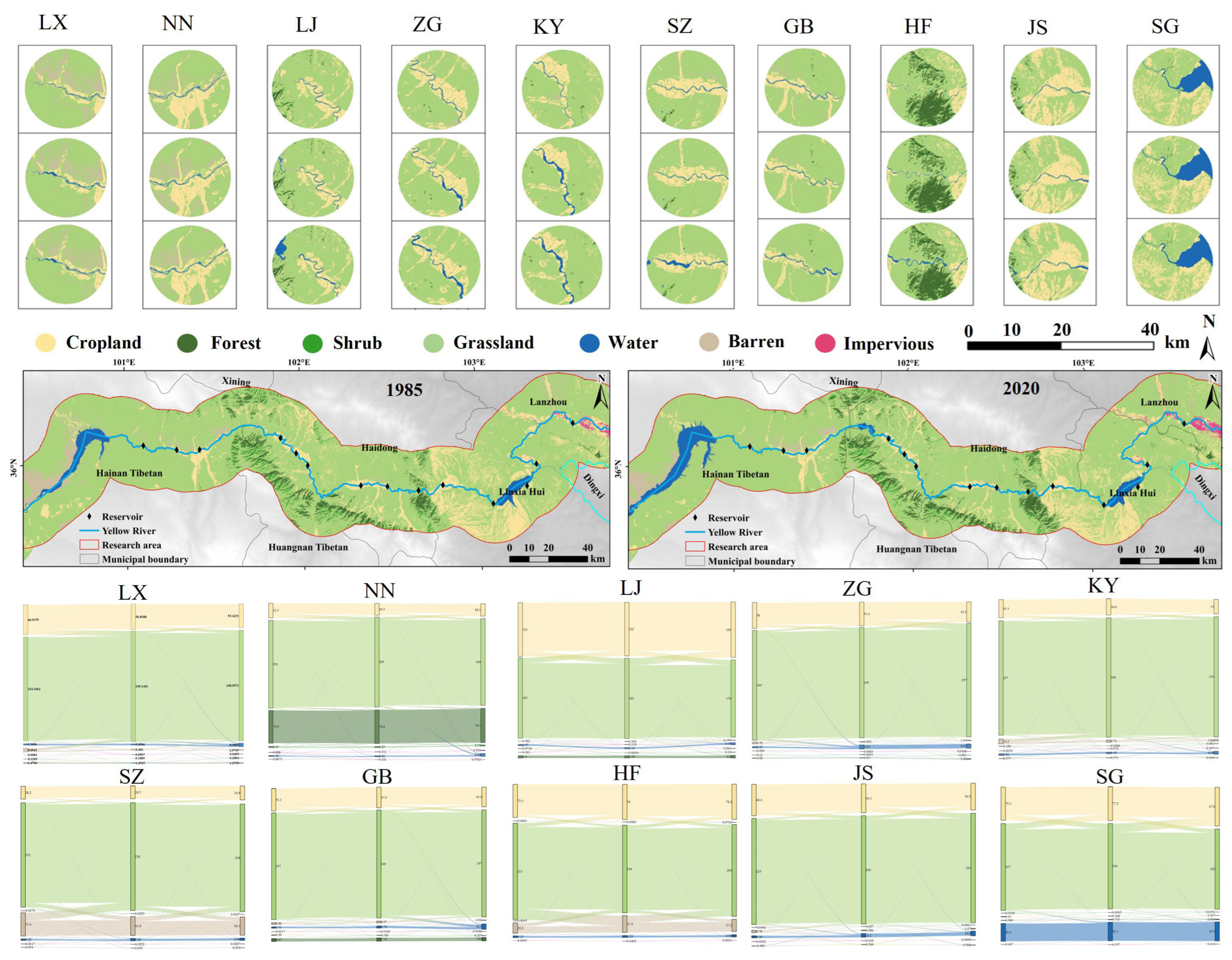
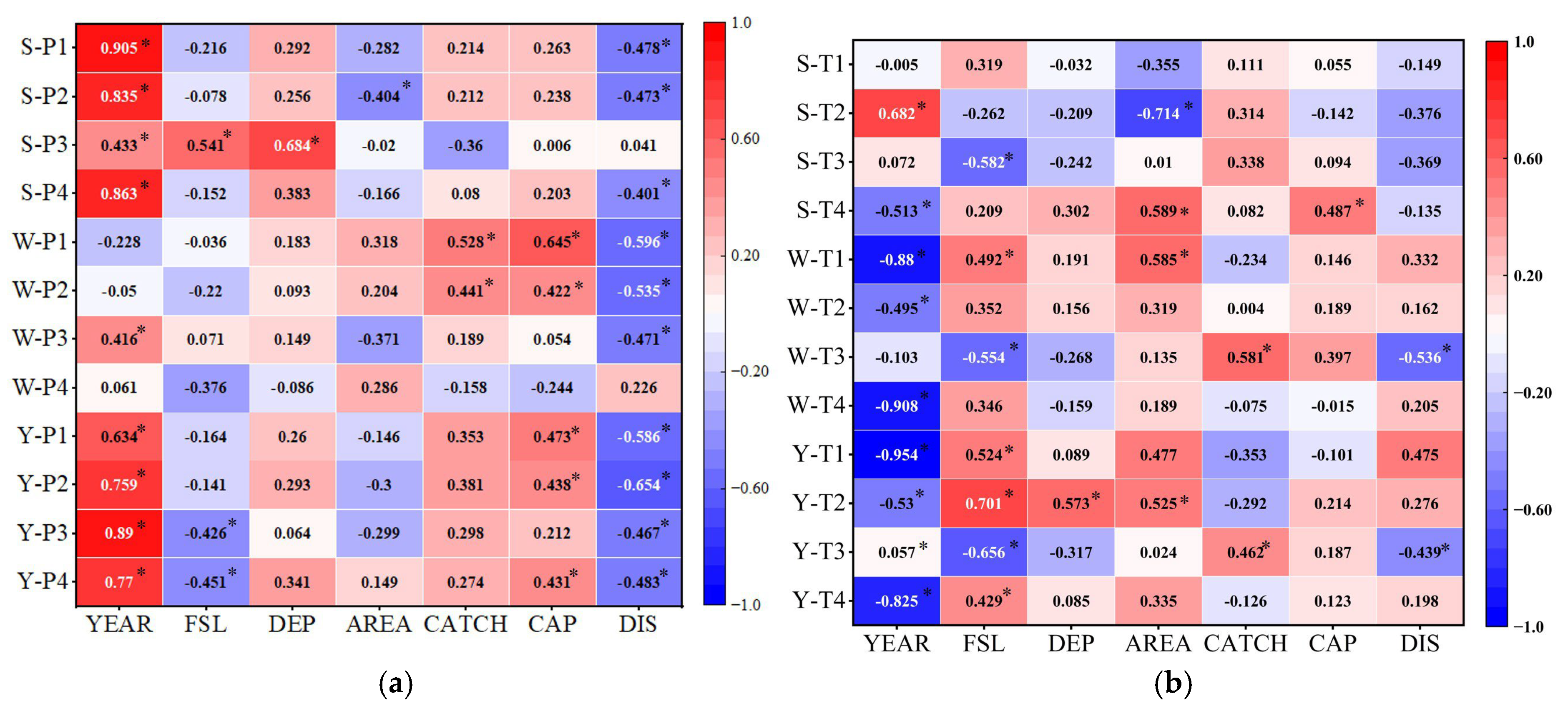
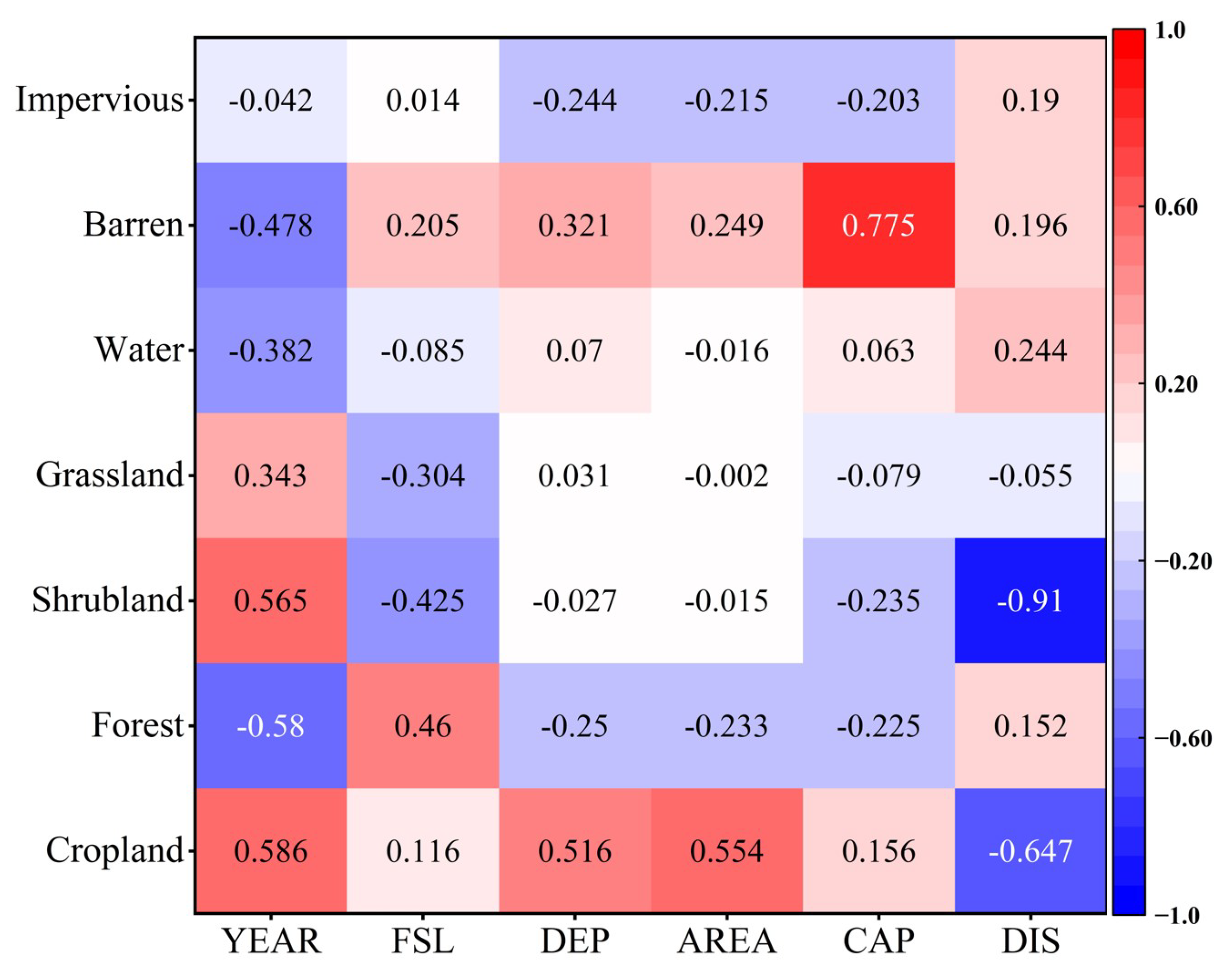
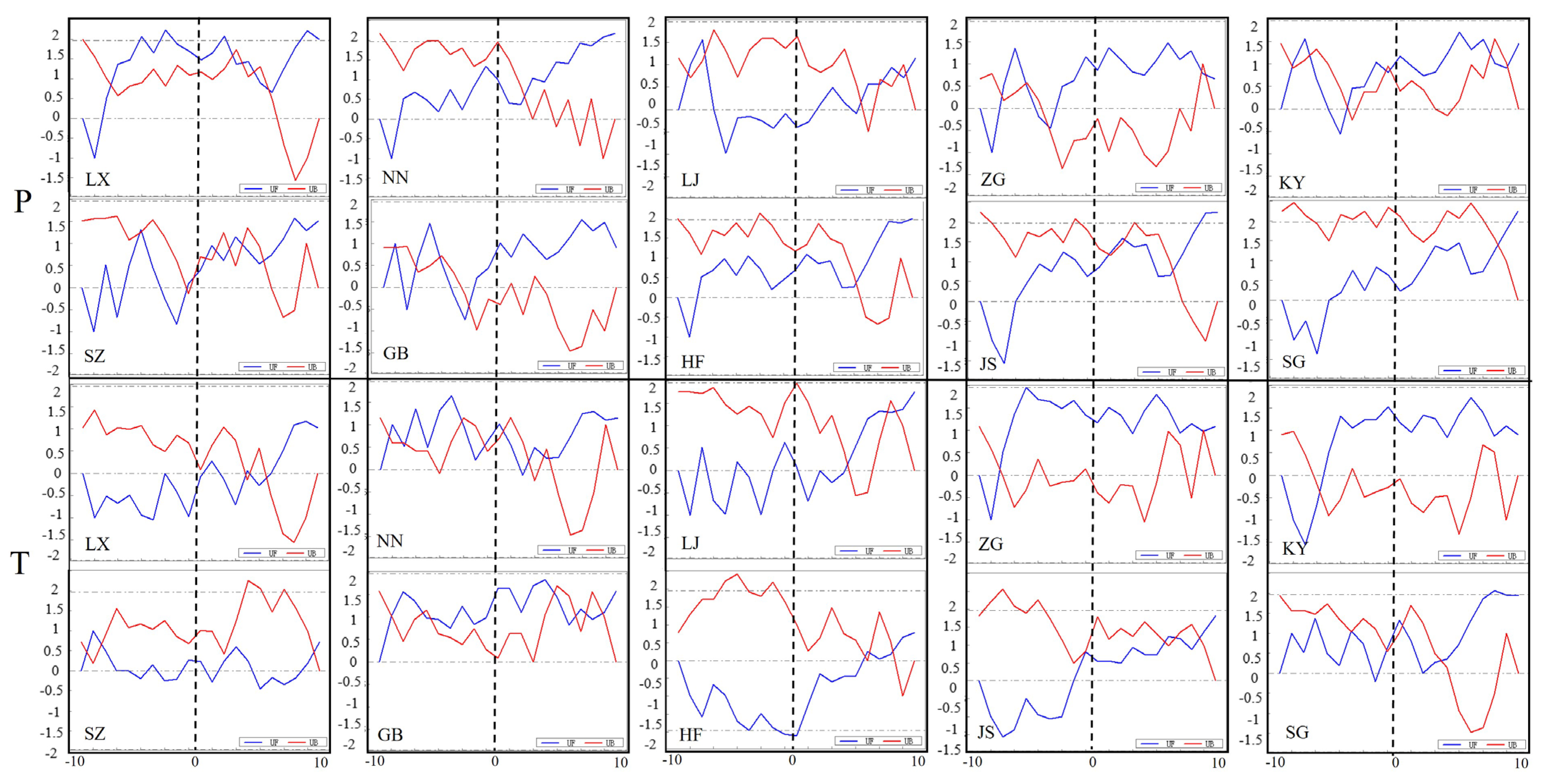
| Name of Reservoir | Year of Construction (YEAR) | Normal Storage Level (FSL) | Mean Depth (DEP) | Catchment Area CATCH | Storage Volume (CAP) | Long-Term Average Flow (DIS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | m | km2 | Billions of m3 | Billions of m3 | ||
| LX (Laxiwa) | 2010 | 2452 | 215 | 4.5 | 10.79 | 150 |
| NN (Nina) | 2000 | 2335.5 | 15.3 | 4.45 | 0.262 | 210 |
| LJ (Lijiaxia) | 2001 | 2180 | 128.3 | 6.78 | 16.5 | 210 |
| ZG (Zhigang) | 2006 | 2050 | 14 | 7.57 | 0.154 | 216 |
| KY (Kangyang) | 2007 | 2033 | 20.2 | 7.35 | 0.288 | 216 |
| GB (Gongbo) | 2004 | 2005 | 103 | 4.85 | 6.2 | 200 |
| SZ (Suzhi) | 2005 | 1900 | 18.6 | 4.5 | 0.455 | 221 |
| HF (Huang) | 2011 | 1880.5 | 17.2 | 3.61 | 0.59 | 221 |
| JS (Jishixia) | 2010 | 1856 | 69.7 | 3.6 | 2.635 | 180 |
| SG (Sigouxia) | 2009 | 1748 | 25.7 | 41.81 | 0.47 | 50 |
| Data Type | Data Description | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| DEM | 30 m × 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud |
| Land Use | China Land Cover Annual Data Set (CLCD) 1985–2022 | Landsat |
| Data | 1982–2022 1 km raster monthly mean temperature and precipitation dataset | National Tibetan Plateau Data |
| Temperature | ||
| Precipitation | Yellow River Hydrological Yearbook | |
| Reservoir Attributes | Attributes of each reservoir | Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center |
| Differences in Climatic Elements Across Reservoirs (10a After Impoundment—10a Before Impoundment) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate | Time | LX | NN | LJ | ZG | KY | GB | SZ | HF | JS | SG |
| Temperature (°C) | Spring | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| Summer | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.25 | |
| Fall | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.20 | −0.03 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.18 | |
| Winter | −0.17 | 0.49 | 0.24 | −0.01 | −0.14 | 0.01 | 0.21 | −0.28 | −0.13 | −0.04 | |
| Annual | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.12 | |
| Temperature slope (°C/a) | Spring | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.04 | 0.02 | −0.04 | −0.08 | −0.05 | 0.01 | −0.03 | −0.04 |
| Summer | −0.01 | −0.03 | 0.06 | −0.07 | 0.03 | −0.01 | −0.07 | 0.01 | −0.01 | 0.03 | |
| Fall | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.18 | −0.03 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Winter | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.34 | −0.16 | 0.01 | −0.15 | −0.19 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Annual | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.14 | −0.06 | 0.03 | −0.05 | −0.08 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | Spring | 5.81 | −5.15 | 3.08 | −3.71 | 0.65 | 2.99 | −0.67 | 5.56 | 8.68 | 14.12 |
| Summer | 23.39 | −6.01 | 0.18 | −0.35 | −0.51 | 0.47 | −1.29 | 21.72 | 22.69 | 12.40 | |
| Fall | 5.39 | 5.39 | 3.69 | 3.75 | 4.08 | 3.63 | 3.69 | 4.45 | 4.78 | 5.06 | |
| Winter | −0.20 | −0.38 | −0.28 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 0.34 | 0.34 | −0.01 | −0.06 | |
| Annual | 32.46 | −11.51 | 19.91 | 0.00 | 14.87 | 23.85 | 13.05 | 39.45 | 41.26 | 37.95 | |
| Precipitation slope (mm/a) | Spring | 0.22 | 3.18 | 1.76 | 0.80 | 6.61 | −3.79 | −4.02 | 3.76 | 0.00 | 1.69 |
| Summer | 0.40 | 0.05 | −1.43 | −0.73 | −5.38 | 6.89 | 1.79 | 0.84 | 3.68 | 5.23 | |
| Fall | 1.20 | −2.57 | 6.12 | −3.58 | −3.92 | −4.43 | −4.36 | −0.09 | 2.37 | 4.38 | |
| Winter | 0.09 | −0.10 | 0.11 | −0.27 | −0.22 | 0.12 | −0.22 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.17 | |
| Annual | 1.92 | 0.56 | 6.65 | −3.79 | −2.92 | −1.21 | −6.82 | 4.54 | 6.21 | 11.47 | |
| Land Use Change Dynamics | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | Forest | Shrubland | Grassland | Water | Barren | Impervious | Attitude | |
| Laxiwa | 8.60 | 0.00 | 4.55 | −0.08 | −0.09 | 0.19 | −0.33 | 7.15 |
| Nina | −0.28 | / | 0.00 | −0.53 | 6.44 | −0.45 | −1.22 | 6.33 |
| Lijiaxia | 0.77 | 0.08 | 0.00 | −0.72 | 3.50 | −15.82 | 7.43 | 6.71 |
| Zhigang | 1.00 | 4.20 | 3.64 | 0.47 | 0.31 | −0.16 | 0.00 | 8.68 |
| Kangyang | 0.70 | 1.02 | −1.16 | 0.90 | 0.01 | −0.27 | 1.02 | 9.67 |
| Gongboxia | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.06 | −0.01 | −19.65 | 0.72 | −0.18 | 12.54 |
| Suzhi | 0.88 | 91.57 | −2.04 | 0.15 | −7.00 | 0.32 | 0.13 | 10.01 |
| Huangfeng | −0.29 | 0.65 | −1.53 | −1.53 | 2.42 | −1.41 | −0.62 | 5.20 |
| Jishixia | −6.83 | 4.27 | −6.51 | −294.32 | 7.68 | 0.30 | −0.15 | 4.20 |
| Sigouxia | 5.53 | 1.28 | −11.66 | 3.28 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 1.67 | 10.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Ma, P.; Nan, Y.; Liu, K. Impacts of Cascade Reservoirs on Adjacent Climate and Land Use Change in the Upper Yellow River, China. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052816
Chen L, Ma P, Nan Y, Liu K. Impacts of Cascade Reservoirs on Adjacent Climate and Land Use Change in the Upper Yellow River, China. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052816
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lisen, Penghui Ma, Yalin Nan, and Kui Liu. 2025. "Impacts of Cascade Reservoirs on Adjacent Climate and Land Use Change in the Upper Yellow River, China" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052816
APA StyleChen, L., Ma, P., Nan, Y., & Liu, K. (2025). Impacts of Cascade Reservoirs on Adjacent Climate and Land Use Change in the Upper Yellow River, China. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052816





