Clinical Study on the Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Patients with Xerostomia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- ○
- Age ≥ 18 years with xerostomia of any etiology.
- ○
- Signed informed consent and commitment to attend the three intervention sessions.
- ○
- Patients with resection of major salivary glands.
- ○
- Decompensated systemic disease.
- ○
- Medical conditions such as pacemaker implants, active skin infections, vertigo, continuous headaches, hearing problems, neuralgia or pregnancy, motor problems or inability to follow instructions.
- Questionnaires:
- Visual Analog Scale for Xerostomia (VAS-X): It measures the intensity of xerostomia perceived by the patient [0–10].
- Xerostomia Inventory (XI): It assesses xerostomia with a scale of 11 items. The total score can vary between 11 and 55, representing the severity of the xerostomia. A score of 11 indicates a very slight or non-existent xerostomia, while a value of 55 indicates severe xerostomia; it is considered that scores of 14 or higher indicate intense xerostomia [20].
- Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14): It assesses the quality of life related to oral health. The total score varies from 0 to 70, where a higher score indicates a worse quality of life. It was given at the start and the end of the last session [21].
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López Jornet, P.; Hernandez, L.; Gomez García, F.; Galera Molero, F.; Pons-Fuster López, E.; Tvarijonaviciute, A. A Clinical Study on the Efficacy and Tolerability of a New Topical Gel and Toothpaste in Patients with Xerostomia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre-Donat, F.J.; Miralles-Jordá, L.; Martinez-Mihi, V. Tratamiento de la boca seca: Puesta al día. Med. Oral. 2004, 9, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López-López, J.; Jané Salas, E.; Chimenos Küstner, E. Pronóstico y tratamiento de la boca seca. Revisión sistemática [Prognosis and treatment of dry mouth. Systematic review]. Med. Clin. 2014, 142, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Sanaie, S.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Jabbari Beyrami, S.; Jabbari Beyrami, H.; Fattahi, S.; Jahanshahlou, F.; Zarei, M.; Rahimi Mamaghani, A.; Kuchaki Rafsanjani, M. Cancer treatment-related xerostomia: Basics, therapeutics, and future perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łysik, D.; Niemirowicz-Laskowska, K.; Bucki, R.; Tokajuk, G.; Mystkowska, J. Artificial Saliva: Challenges and Future Perspectives for the Treatment of Xerostomia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Montoya, J.A.; Silvestre, F.J.; Barrios, R.; Silvestre-Rangil, J. Treatment of xerostomia and hyposalivation in the elderly: A systematic review. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal 2016, 21, e355–e366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamdi, S.; Matangkasombut, O.; Lam-Ubol, A. Non-pharmacologic interventions for management of radiation-induced dry mouth: A systematic review. Oral. Dis. 2024, 30, 2876–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freni, F.; Gazia, F.; Stagno d’Alcontres, F.; Galletti, B.; Galletti, F. Use of botulinum toxin in Frey’s syndrome. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sivaramakrishnan, G.; Sridharan, K. Electrical nerve stimulation for xerostomia: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, F.; Saavedra, F.; Andrews, B.; FitzGerald, J.; Winter, S.C. Trans-cutaneous electrical nerve stimulation to treat dry mouth (xerostomia) following radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. A systematic review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 63, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, S.; Bryan, G.; McMillan, R.; Birchenough, S.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for the management of dry mouth: Non-pharmacological interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013, 2013, CD009603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Melo, J.L.M.A.; Coelho, C.P.E.S.; Nunes, F.P.E.S.; Heller, D.; Grisi, D.C.; Guimarães, M.D.C.M.; Dame-Teixeira, N. A scoping review on hyposalivation associated with systemic conditions: The role of physical stimulation in the treatment approaches. BMC Oral. Health 2023, 23, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, H.; Pal-Singh, M.; Mathur, H.; Astekar, S.; Gulati, P.; Lakhani, S. Evaluation of the effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) on whole salivary flow rate. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2015, 7, e13–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konidena, A.; Sharma, D.; Puri, G.; Dixit, A.; Jatti, D.; Gupta, R. Effect of TENS on stimulation of saliva in postmenopausal women with or without oral dryness—An interventional study. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 6 (Suppl. S1), S44–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyasnoor, S.; Kamath, S.; Khader, N.F.A. Effectiveness of Electrostimulation on Whole Salivary Flow Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Perm. J. 2017, 21, 15–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Su, Y.C.; Chin, C.C. The effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on increasing salivary flow rate in hemodialysis patients. Oral. Dis. 2019, 25, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrez, S.; Patil, N.; Sareen, M.; Meena, M.; Tyagi, N.; Kaswan, S. Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation (TENS) on Whole Salivary Flow Rate: A Descriptive Observational Study. J. Dent. 2022, 23 (Suppl. S1), 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jornet, P.; Camacho-Alonso, F.; Bermejo-Fenoll, A. A simple test for salivary gland hypofunction using Oral Schirmer’s test. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2006, 35, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoppmeier, C.M.; Janson, M.; Höfer, K.; Graf, I.; Wicht, M.J.; Barbe, A.G. Use of the modified Schirmer test to measure salivary gland hypofunction/hyposalivation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2024, 132, e12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.; Fariña, M.P.; Pérez, C.; Fernández, M.; Forman, K.; Carrasco, M. Translation and validation of a Spanish version of the xerostomia inventory. Gerodontology 2016, 33, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; López, J.F.; Vicente, M.P.; Galindo, M.P.; Albaladejo, A.; Bravo, M. Comparative validity of the OIDP and OHIP-14 in describing the impact of oral health on quality of life in a cross-sectional study performed in Spanish adults. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal 2011, 16, e816–e821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Talal, N.; Quinn, J.H.; Daniels, T.E. The clinical effects of electrostimulation on salivary function of Sjogren’s syndrome patients. Rheumatol. Int. 1992, 12, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.K.W.; Deshmukh, S.; Wyatt, G.; Sagar, S.; Singh, A.K.; Sultanem, K.; Nguyen-Tân, P.F.; Yom, S.S.; Cardinale, J.; Yao, M.; et al. Acupuncture-like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation versus pilocarpine in treating radiation-induced xerostomia: Results of RTOG 0537 phase 3 study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.K.W.; Jones, G.W.; Sagar, S.M.; Babjak, A.F.; Whelan, T. Phase I-II study in the use of acupuncture-like transcutaneous nerve stimulation in the treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia in head-and-neck cancer patients treated with radical radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, A.; Asha, M.L.; Babu, S.; Chakraborty, S. Prospective phase II study of the efficacy of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in post-radiation patients. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshman, A.R.; Subhas Babu, G.; Rao, S. Evaluation of effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on salivary flow rate in radiation-induced xerostomia patients: A pilot study. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2015, 11, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paim, E.D.; Zanella, V.G.; Martins, V.B.; Macagnan, F.E.; Berbert, M.C.B. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on the salivary flow of patients with hyposalivation induced by radiotherapy in the head and neck region—A randomized clinical trial. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2019, 46, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas, S.K.; Shashikant, M.C.; Ali, I.M. Evaluation of the effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on whole saliva flow: A clinical study. J. Indian. Acad. Oral. Med. Radiol. 2009, 21, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strietzel, F.P.; Martín-Granizo, R.; Fedele, S.; Lo Russo, L.; Mignogna, M.; Reichart, P.A.; Wolff, A. Electrostimulating device in the management of xerostomia. Oral. Dis. 2007, 13, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafaurie, G.; Fedele, S.; López, R.M.; Wolff, A.; Strietzel, F.; Porter, S.R.; Konttinen, Y.T. Biotechnological advances in neuro-electro-stimulation for the treatment of hyposalivation and xerostomia. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal 2009, 14, E76–E80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fedele, S.; Wolff, A.; Strietzel, F.; López, R.M.; Porter, S.R.; Konttinen, Y.T. Neuroelectrostimulation in treatment of hyposalivation and xerostomia in Sjögren’s syndrome: A salivary pacemaker. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
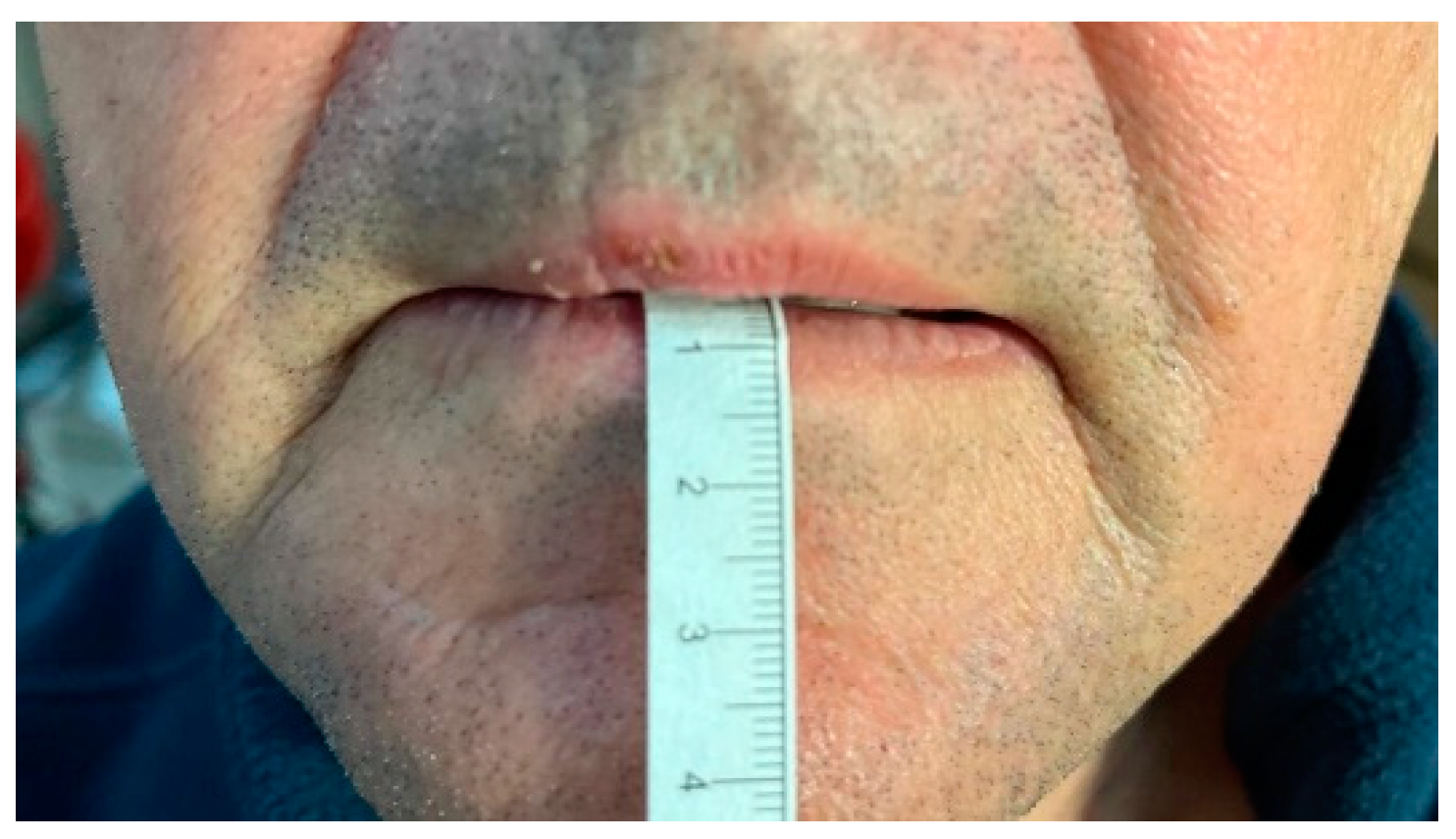


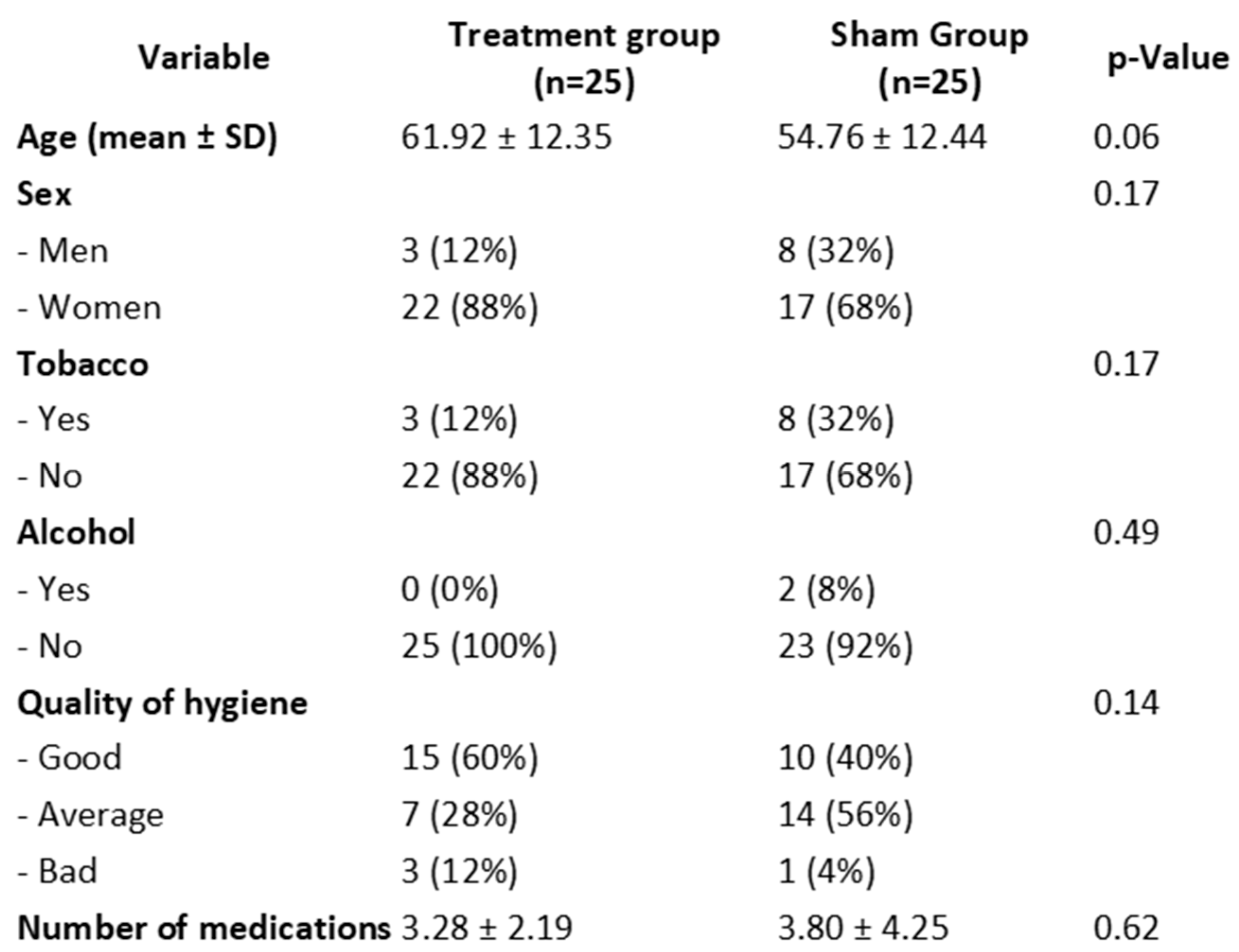
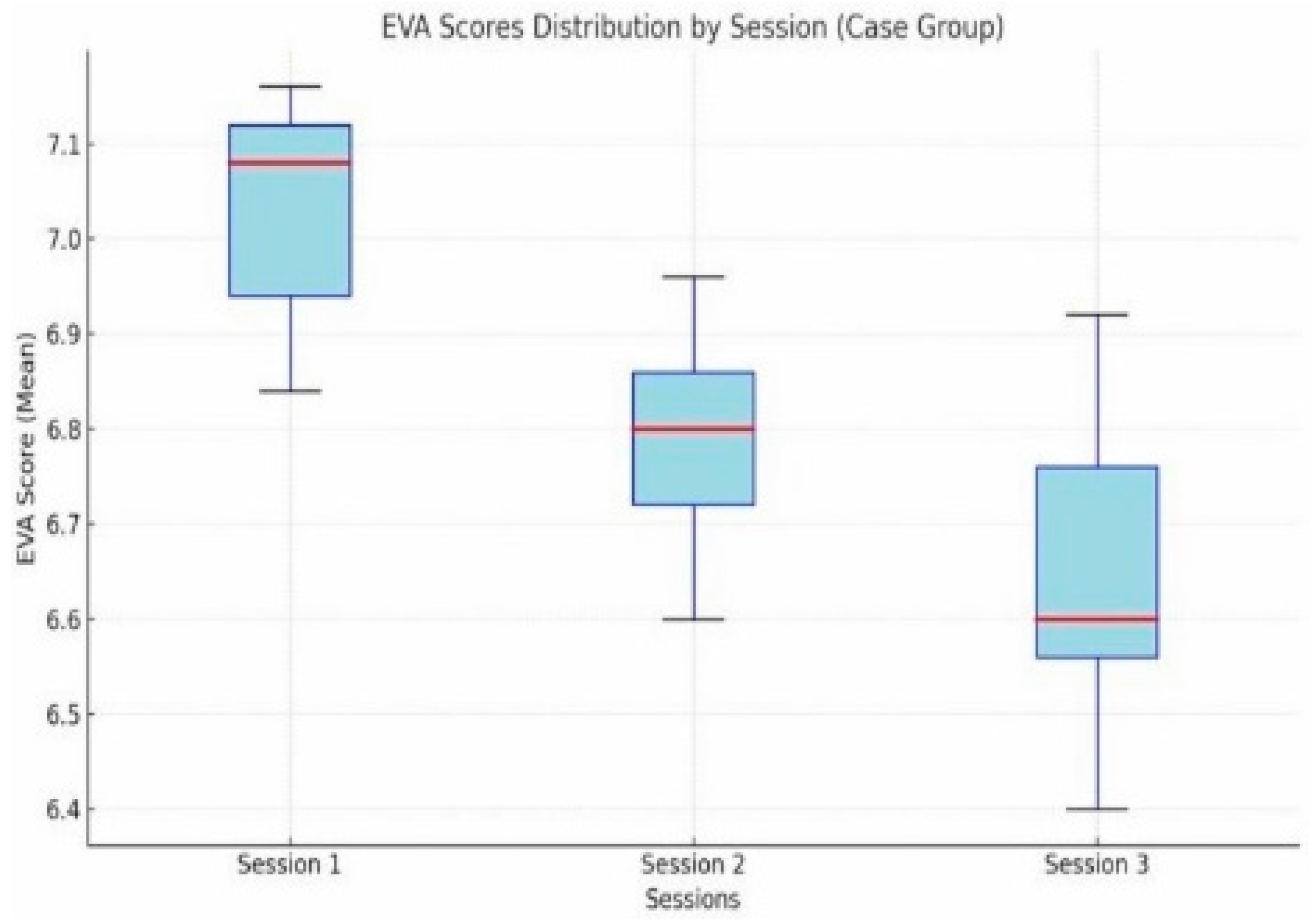
| Group | Test | Baseline (Mean ± SD) | Post-Session (Mean ± SD) | p-Value (Baseline vs. Post) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | VAS-X | 7.52 ± 1.92 points | 6.84 ± 1.84 points | <0.001 |
| Sialometry, mm | 21.00 ± 16.38 mm | 27.68 ± 29.44 mm | <0.001 | |
| Xerostomia Inventory (XI) | 36.88 ± 7.78 points | 35.60 ± 7.42 points | 0.01 | |
| Sham | VAS-X | 5.24 ± 2.13 points | 5.04 ± 2.15 points | 0.04 |
| Sialometry, mm | 29.56 ± 16.55 mm | 29.80 ± 16.51 mm | 0.68 | |
| Xerostomia Inventory (XI) | 28.74 ± 9.30 points | 28.74 ± 9.30 points | Not sig. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ros-Madrid, J.F.; Lopez-Jornet, P. Clinical Study on the Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Patients with Xerostomia. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052723
Ros-Madrid JF, Lopez-Jornet P. Clinical Study on the Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Patients with Xerostomia. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052723
Chicago/Turabian StyleRos-Madrid, Jose Fidel, and Pia Lopez-Jornet. 2025. "Clinical Study on the Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Patients with Xerostomia" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052723
APA StyleRos-Madrid, J. F., & Lopez-Jornet, P. (2025). Clinical Study on the Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Patients with Xerostomia. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052723







