Forward Modeling Analysis in Advanced Exploration of Cross-Hole Grounded-Wire-Source Transient Electromagnetic Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
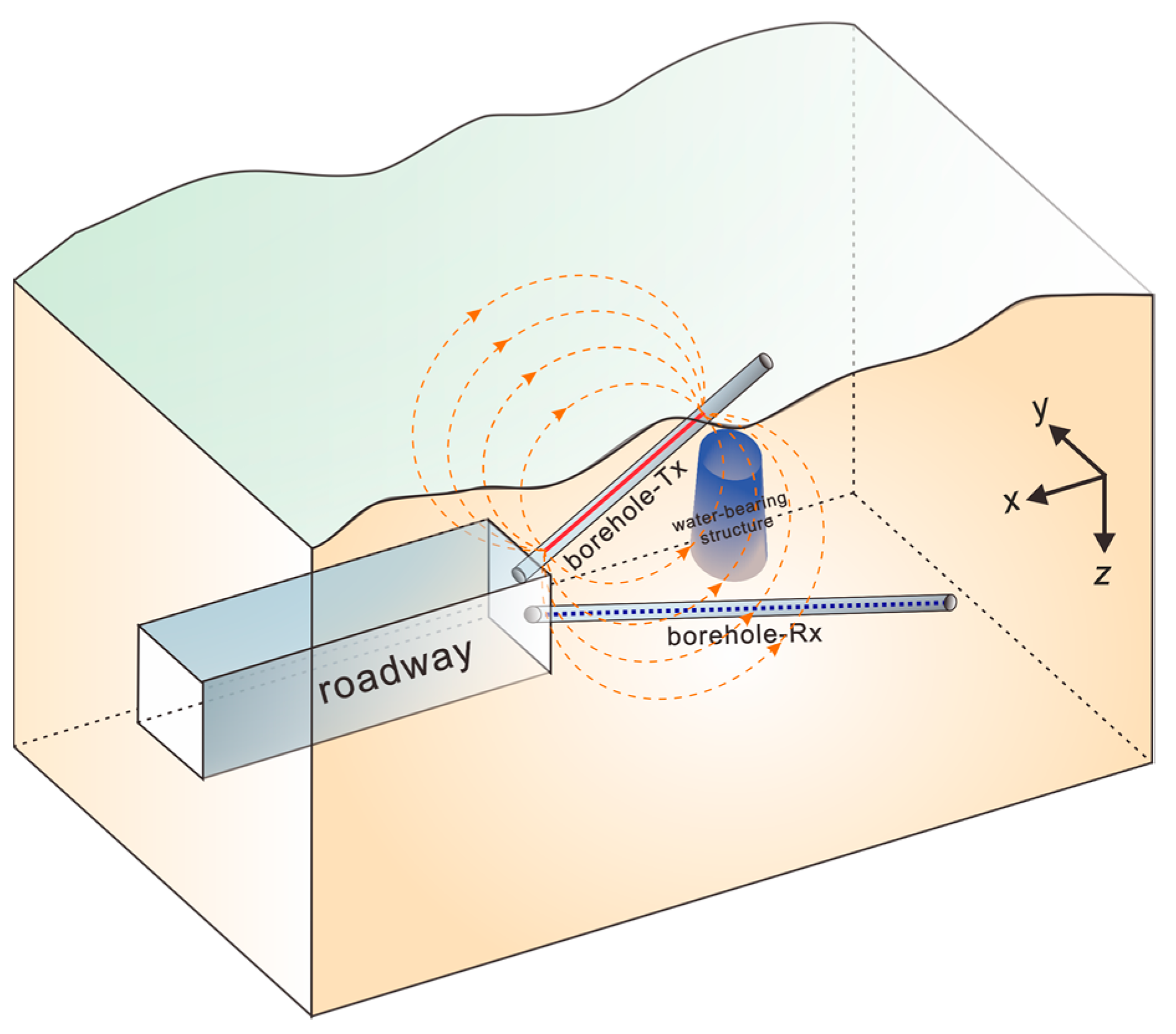
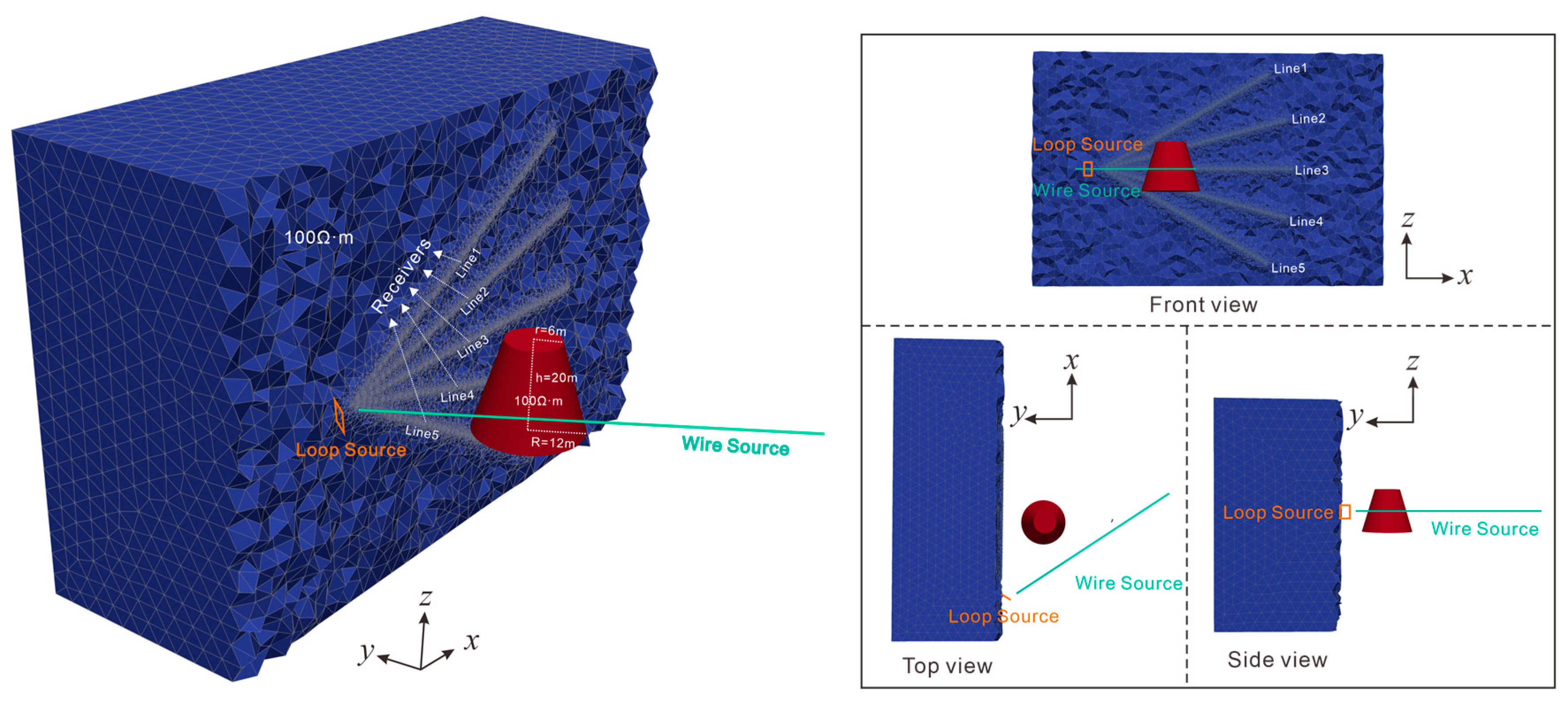
2. Cross-Hole Grounded-Wire-Source Transient Electromagnetic System
3. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Method Forward Modeling Theory
3.1. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Method Algorithm
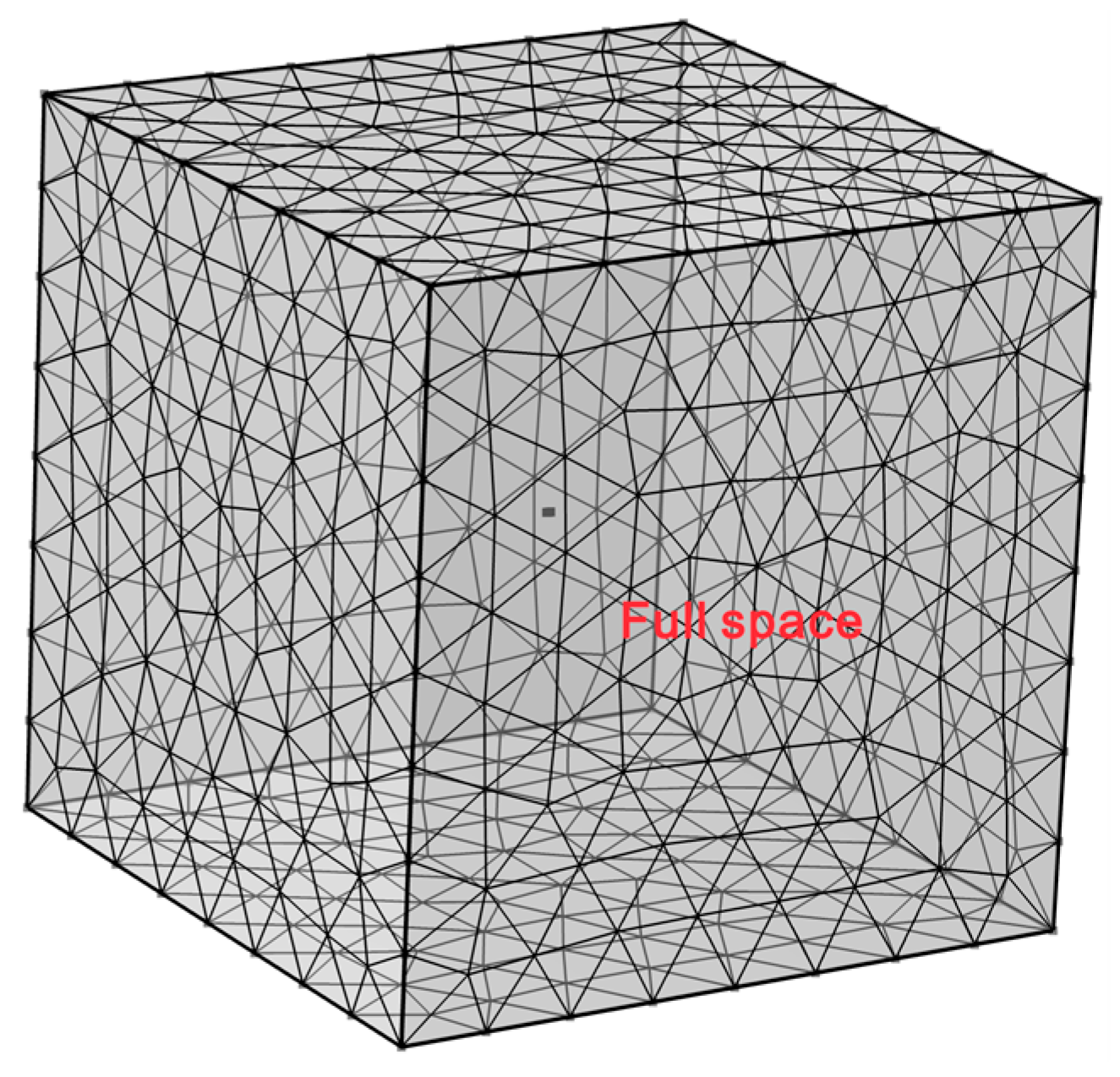
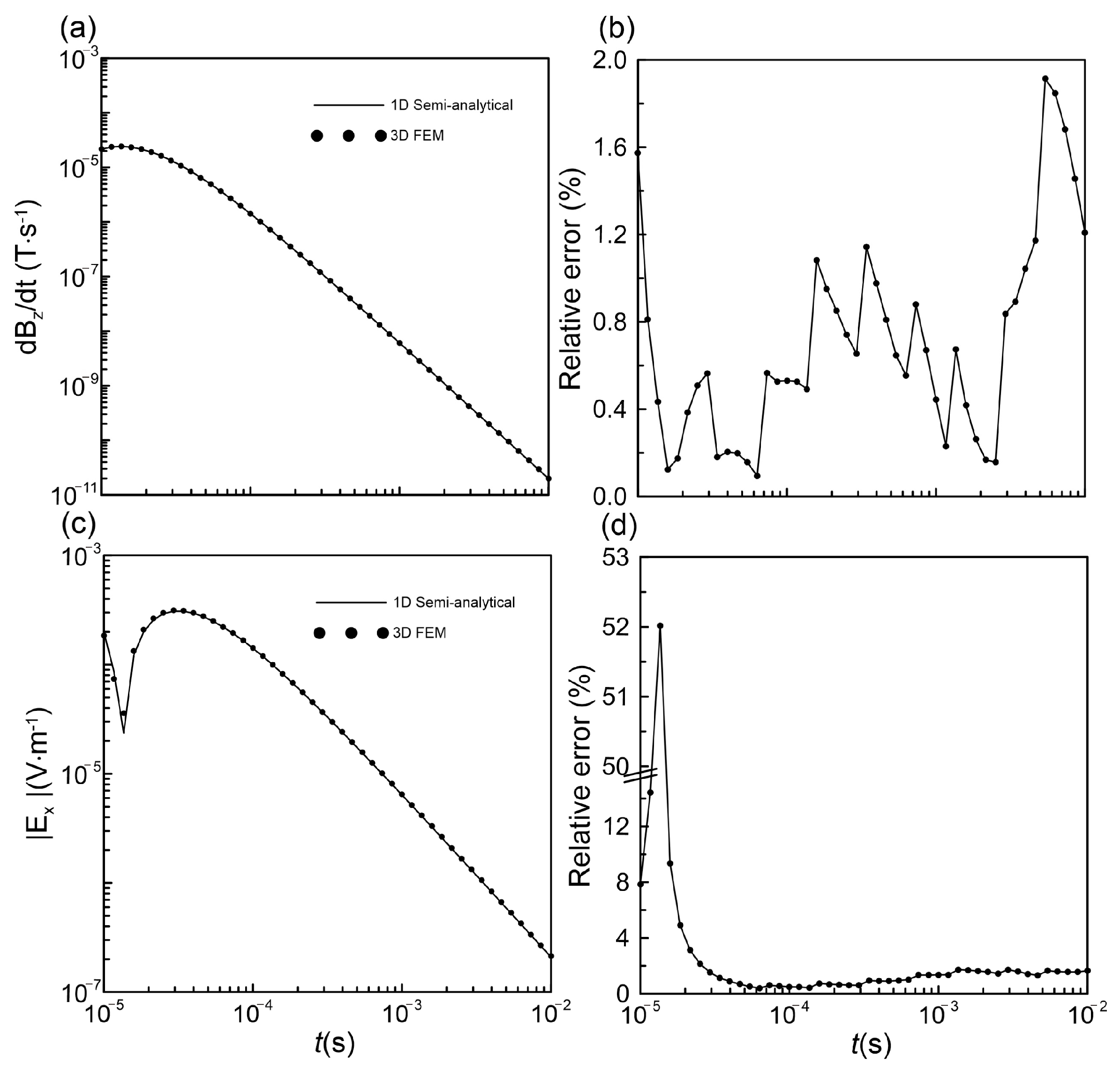
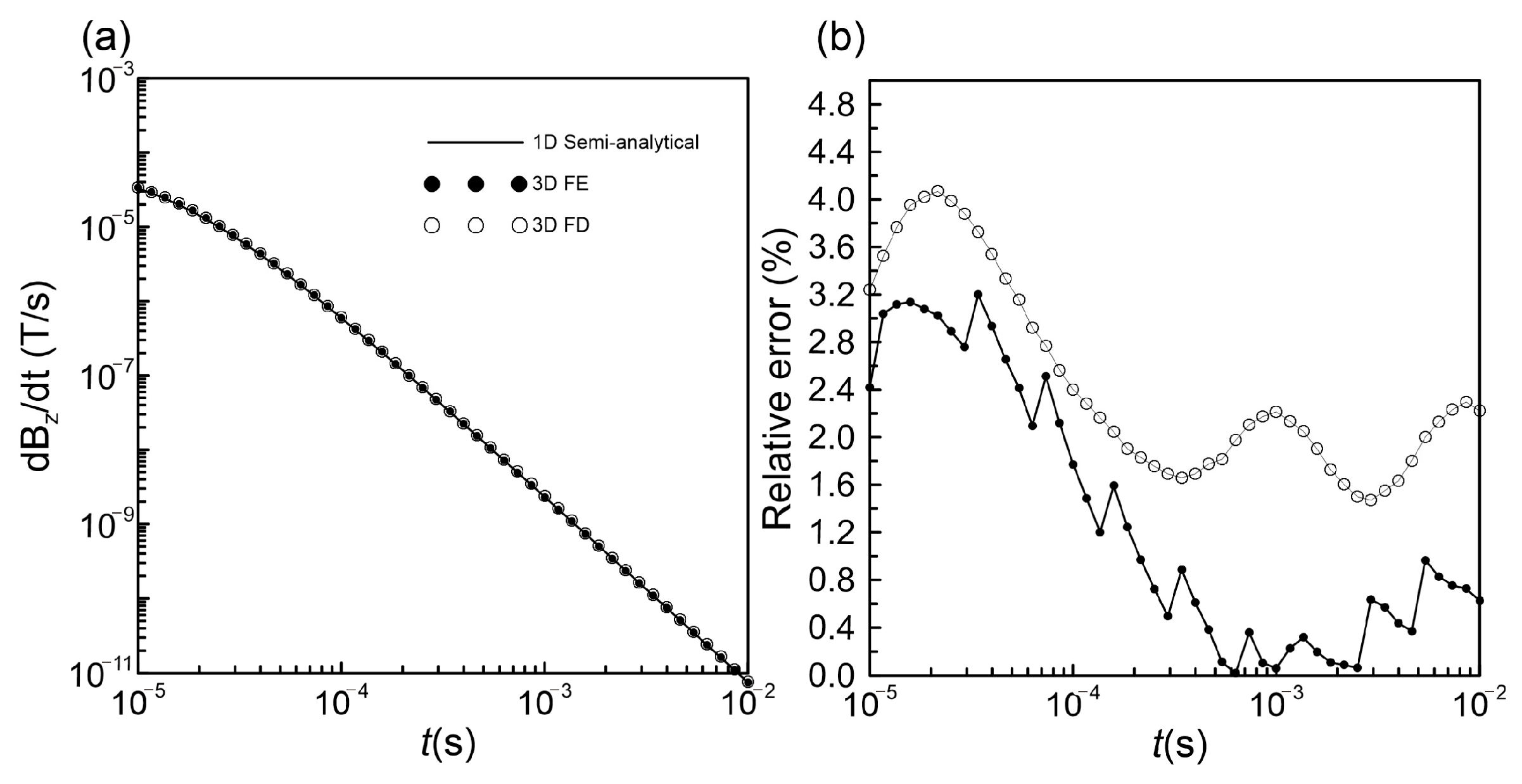
3.2. Validation Against Semi-Analytic Solution
4. Results and Analysis of Three-Dimensional Forward Modeling
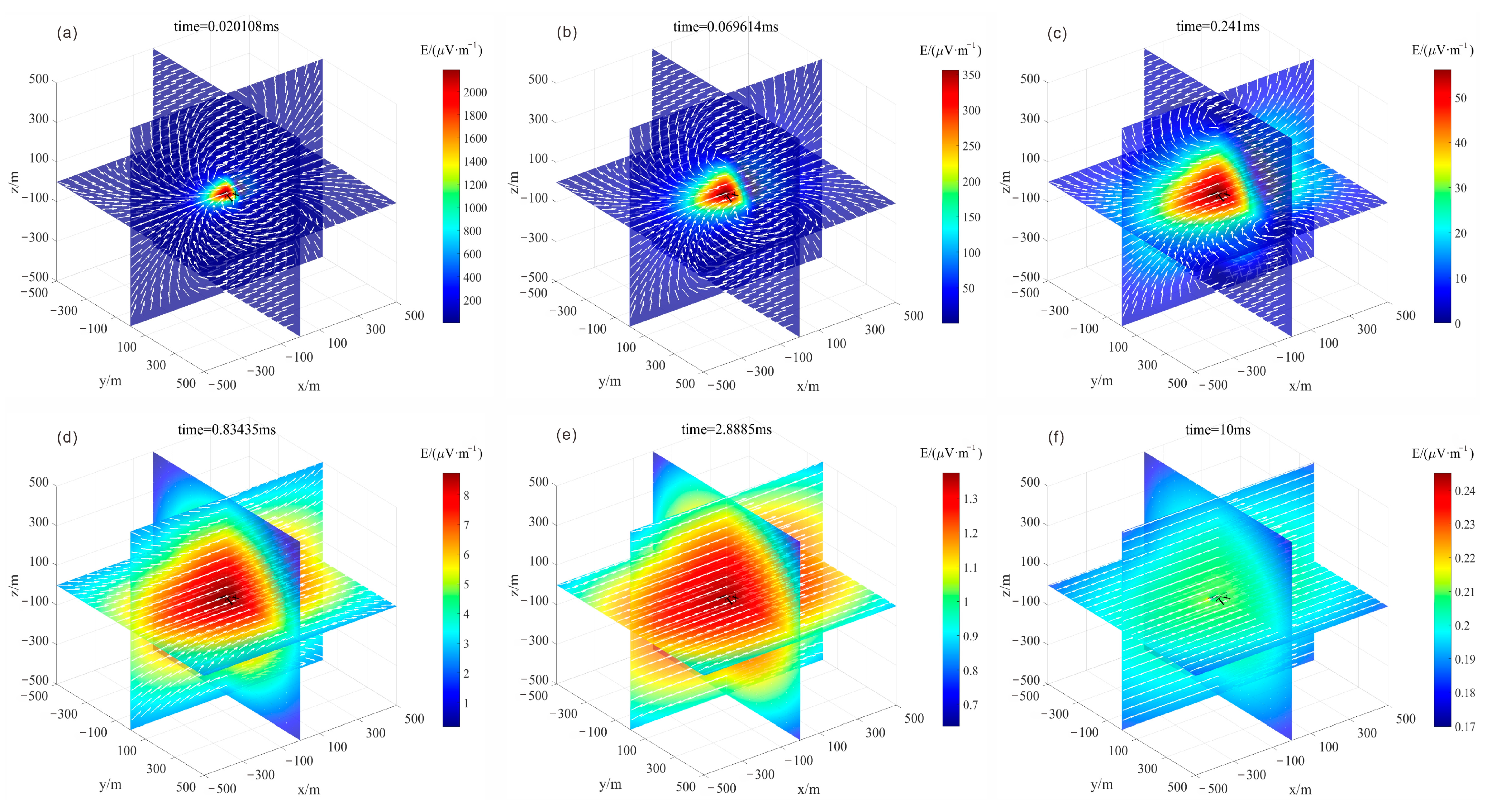
4.1. Full-Space Model
4.2. Single-Anomaly Model
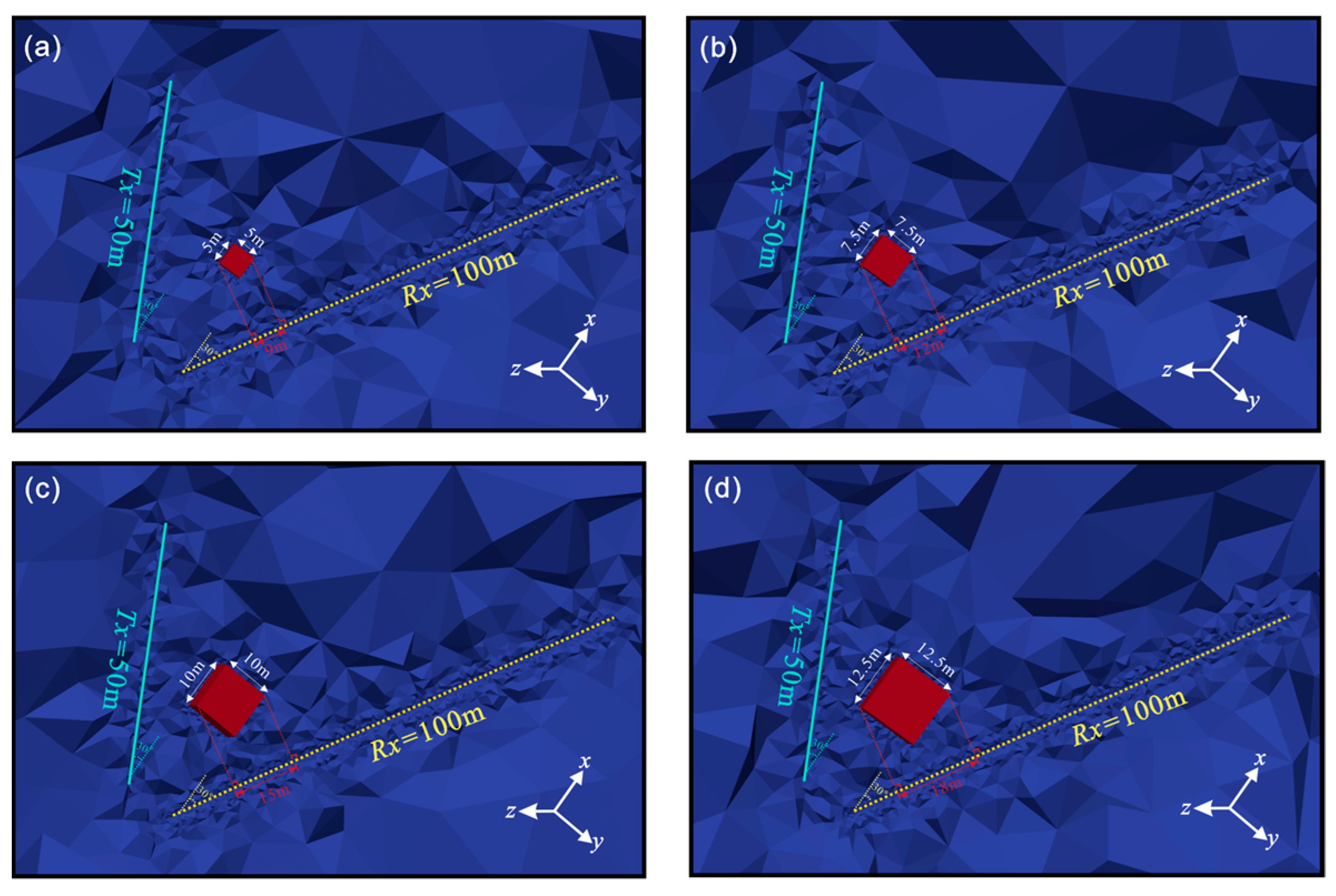
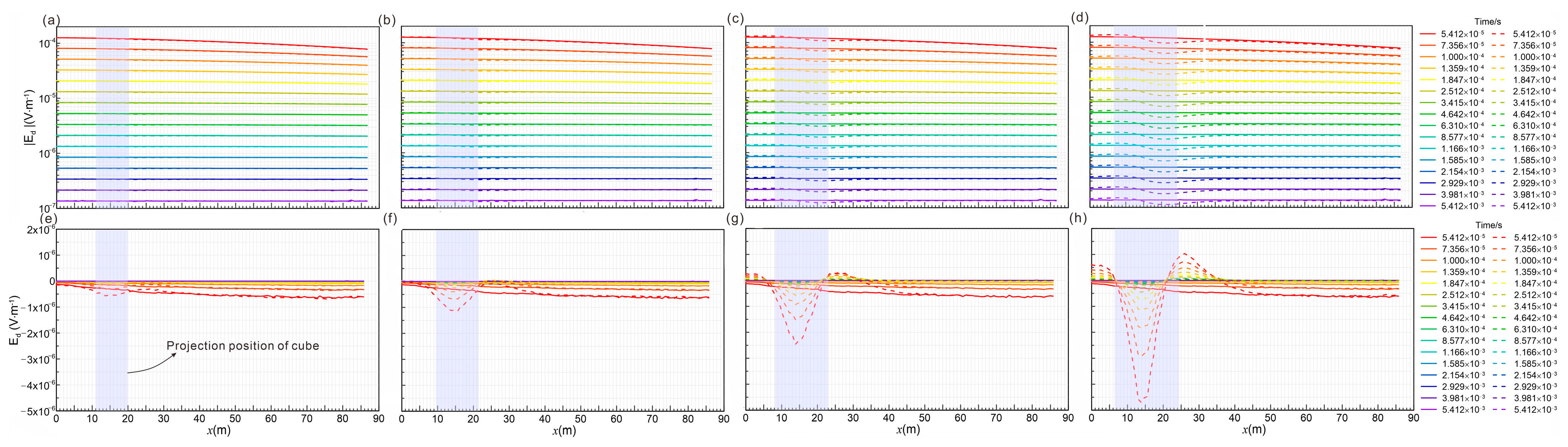
4.2.1. Individual Anomalies with Different Edge Lengths
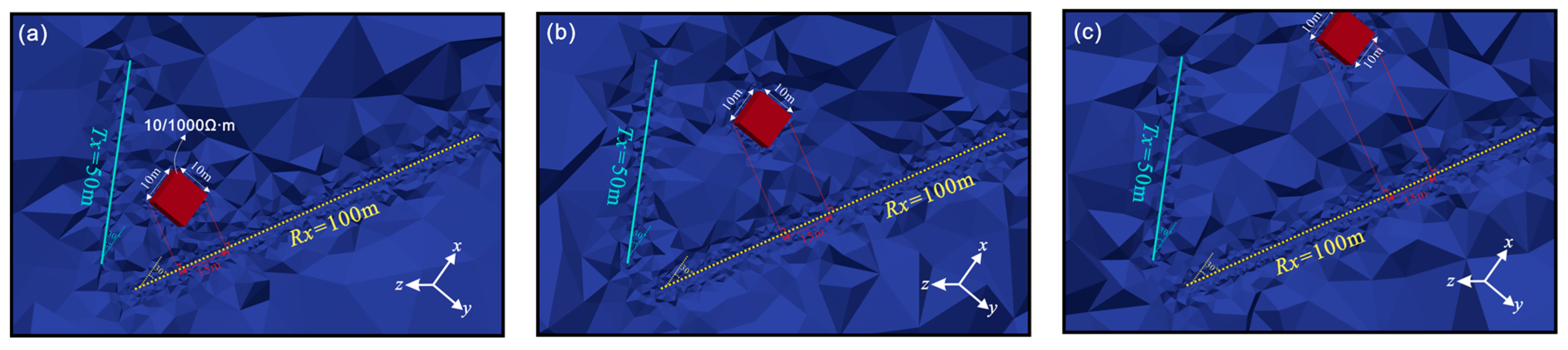
4.2.2. Individual Anomalies with Different Distances and Resistivities
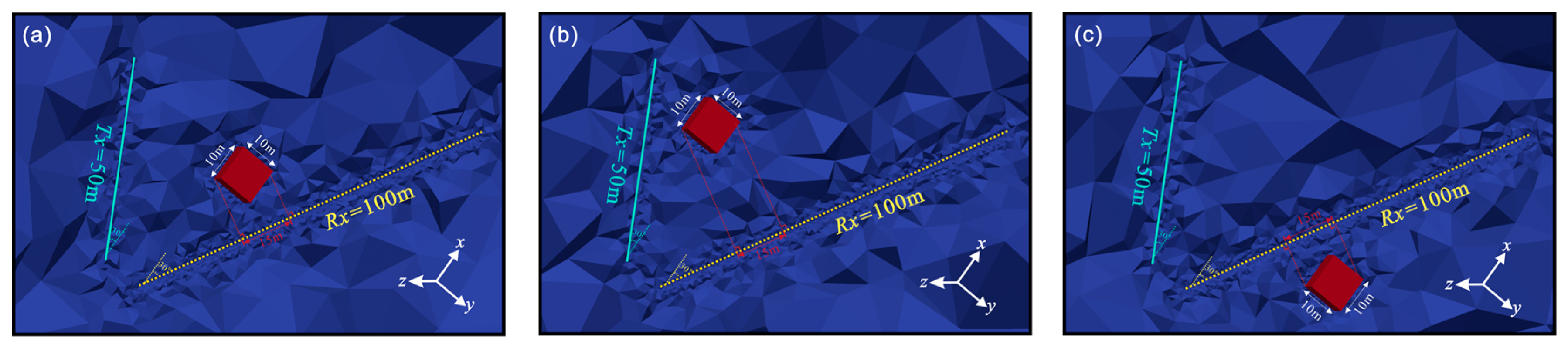
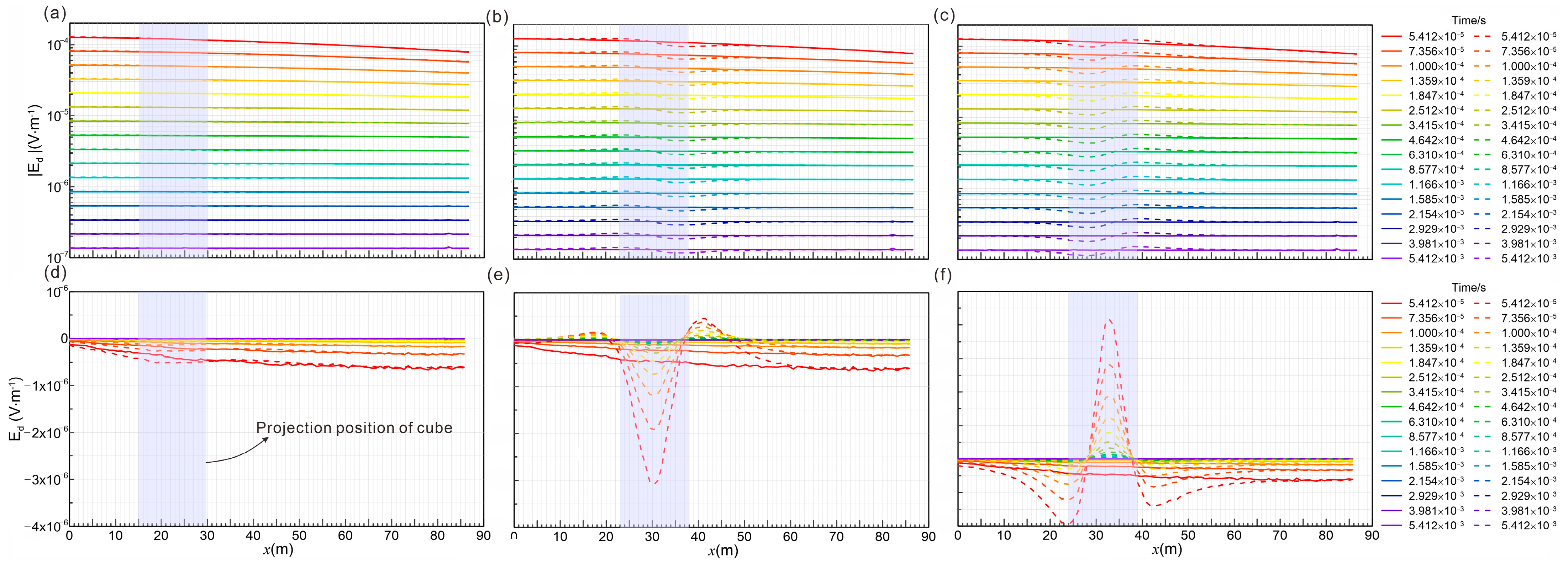
4.2.3. Individual Anomalies at Different Locations
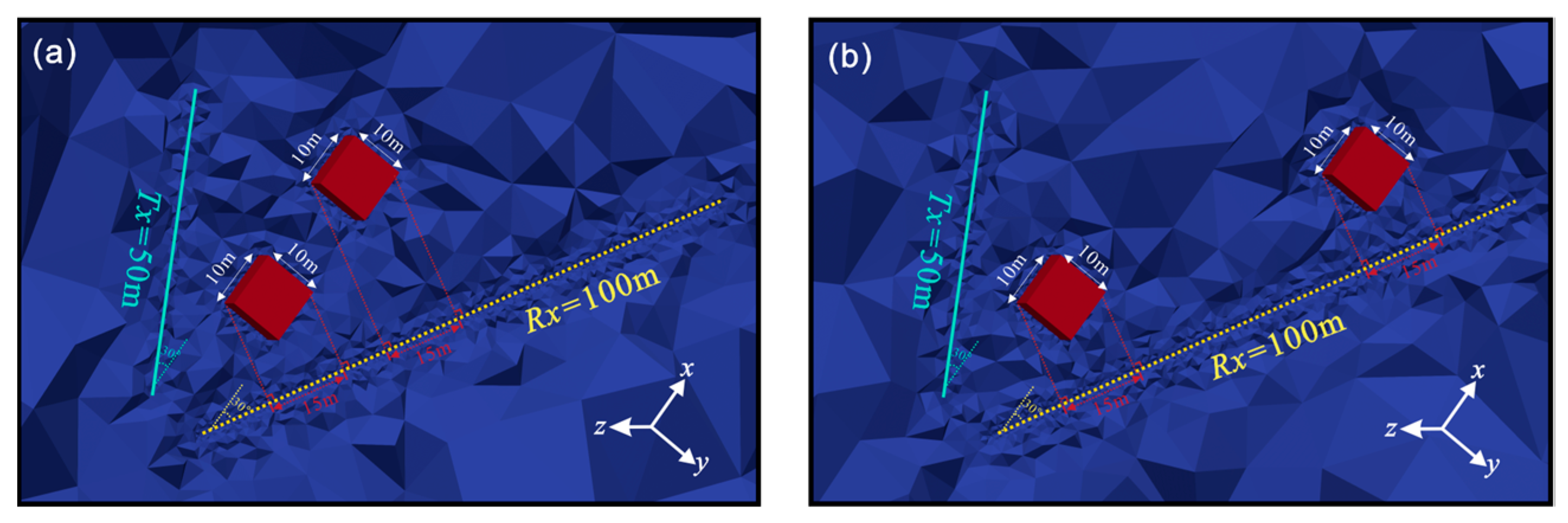
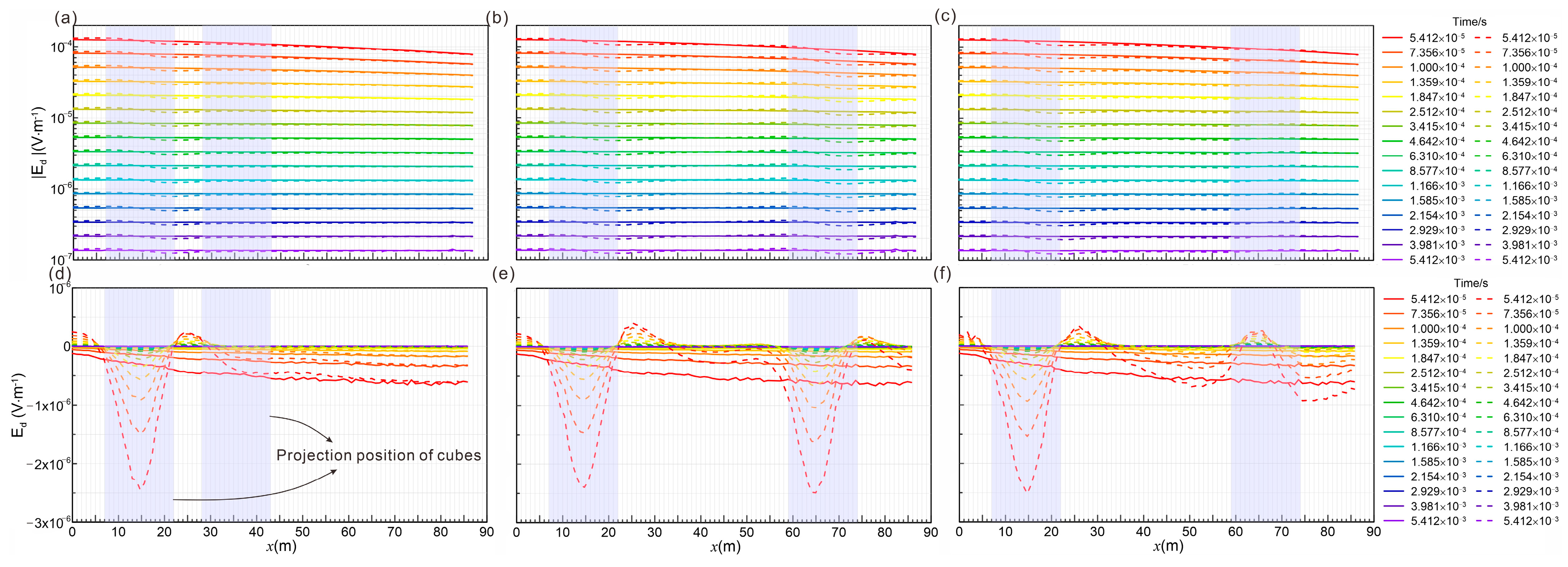
4.2.4. Two Anomalies’ Response and Localization
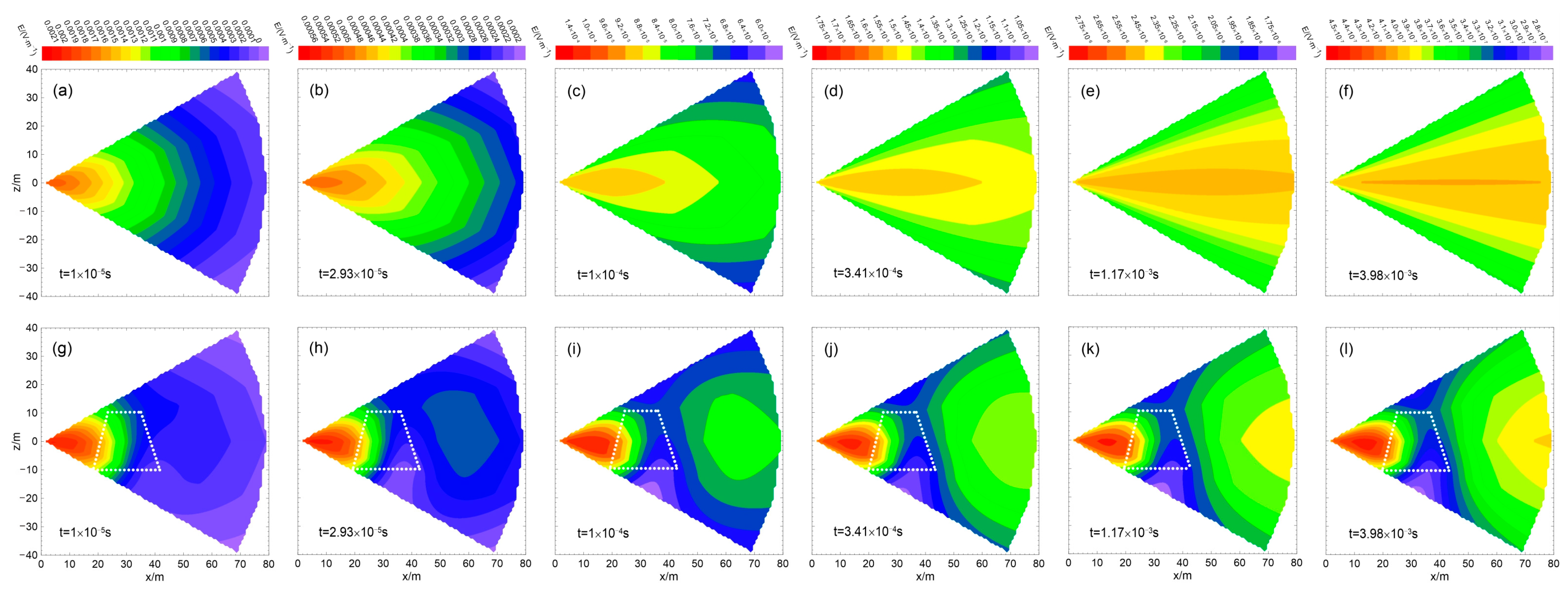
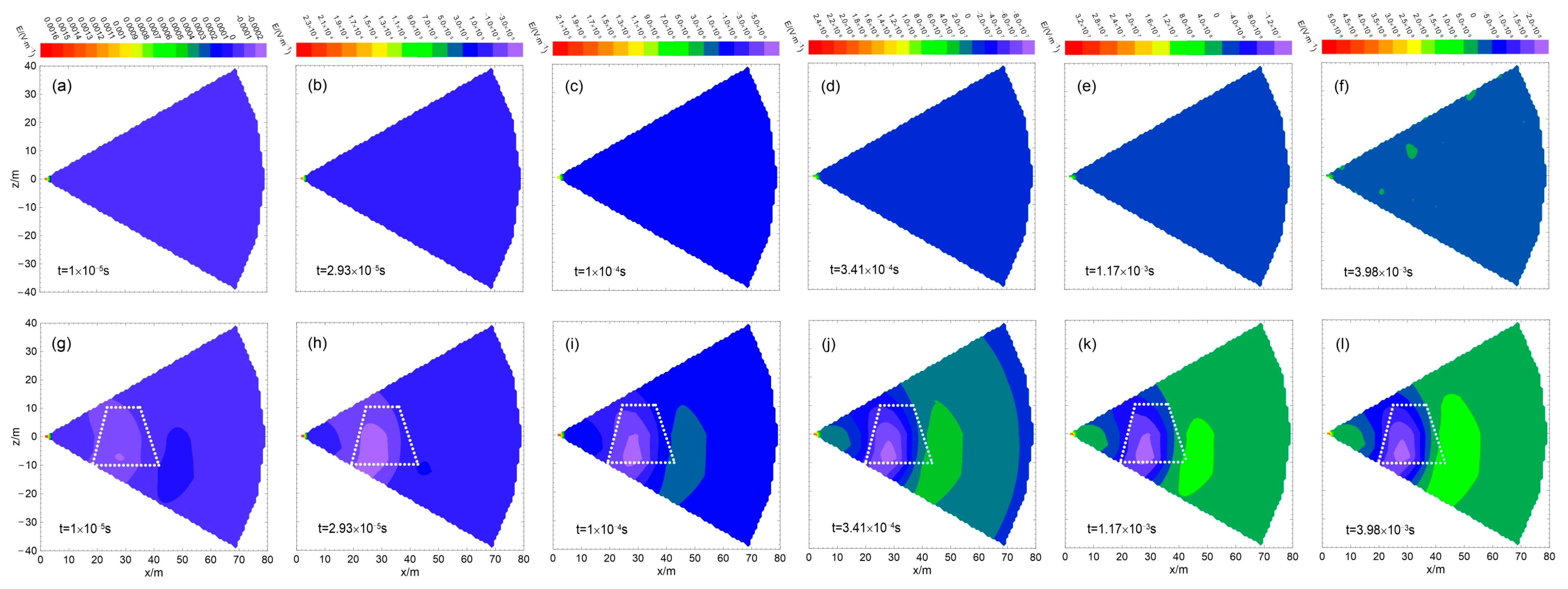
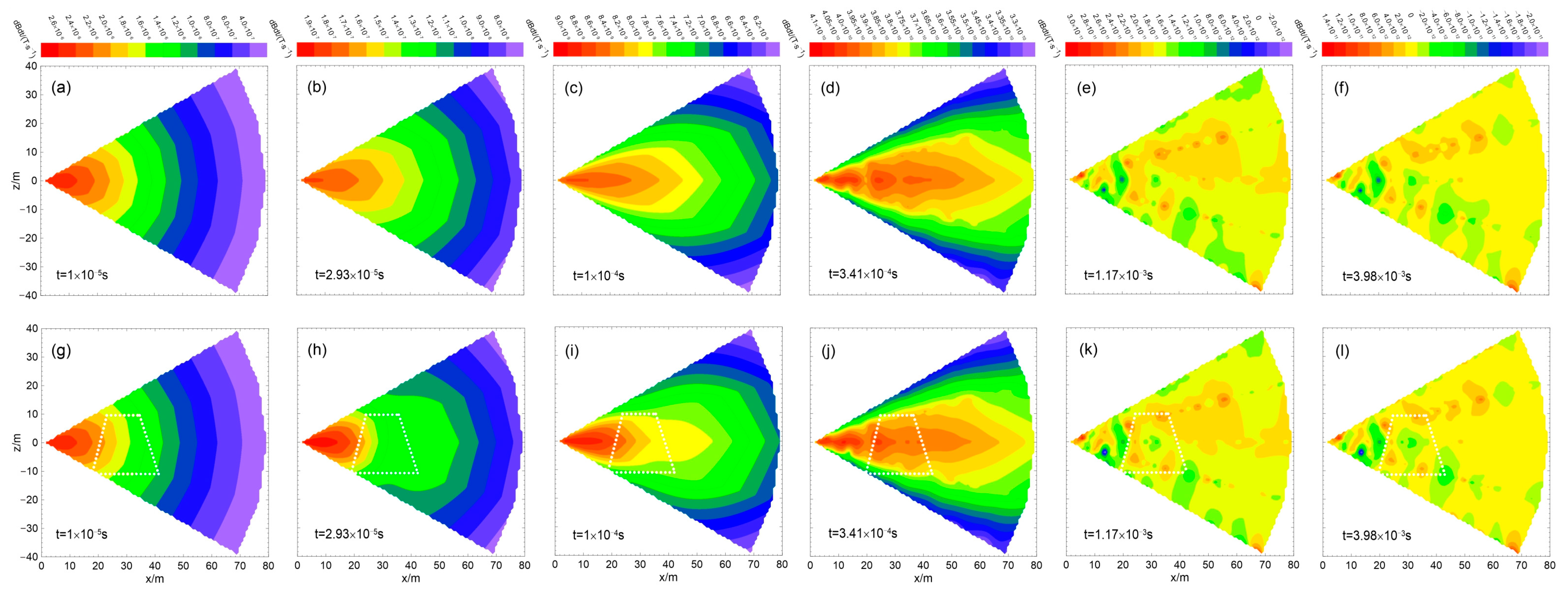
4.3. Detection of Water-Bearing Trap Columns by Cross-Hole EM with Multiple Grounded-Wire Source
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Larger volumes, lower resistivity values, and closer proximity of anomalous bodies result in larger response amplitudes, thereby improving detection effectiveness.
- (2)
- High-resistivity and low-resistivity anomalous bodies produce opposite anomalies (positive and negative, respectively) in the electric field. The system is more sensitive to low-resistivity anomalous bodies, making it particularly useful for detecting water-bearing targets in coal mines.
- (3)
- The position of the receivers has a greater impact on the final response strength than the source location. This suggests that the borehole-based arrangement proposed in this paper improves detectability.
- (4)
- The proposed setup can effectively determine key parameters, such as the anomalous body’s size, resistivity contrasts, and spatial position by analyzing changes in the electric field and first-order differential derivatives. This allows for the approximate localization of the anomaly’s boundary. Moreover, the cross-hole arrangement takes advantage of borehole spatial positioning, offering multi-directional information about the detected target.
- (5)
- In the collapse column model with multiple survey lines, both the electric field response and first-order differential results clearly delineate the boundary of the collapse column, demonstrating significantly improved detection accuracy over the traditional BRTEM method. Additionally, this configuration enables 2D/3D observations in roadway environments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, G.Q.; Li, X.; Di, Q.Y. The progress of TEM in theory and application. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Nabighian, M.N. Time-domain electromagnetic methods of exploration. Geophysics 1984, 49, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Present study situation review of borehole transient electromagnetic method. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.; Pan, D.; Yu, J. Review the applications of geophysical methods for mapping coal-mine voids. Prog. Geophys. 2018, 33, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Li, F.; Peng, S.; Sun, X. Research and development direction on advanced detection in mine roadway working face using geophysical methods. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.C. Exploration Prospecting for TEM in Mine; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Yue, J.; Liu, S. Mine transient electromagnetic observation system of small multi-turn coincident configuration. J. China Coal Soc. 2007, 32, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Xia, T.; Xue, Y.; Mao, D.; Qiu, D.; Zhu, J.; Wang, P. Small fixed-loop transient electromagnetic in tunnel forward geological prediction. Geophys. Prospect. 2020, 68, 1399–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Song, W.; Lei, K.; Zhu, Y. Application of surface-to-roadway TEMs for detecting deep aquifers in coal fields: An example from North China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2023, 219, 105242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Yue, J. Surface-to-underground transient electromagnetic detection of water-bearing goaves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5303–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, P. Development status and prospect of geological guarantee technology for precise coalmining. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Spies, B. Electrical and electromagnetic borehole measurements: A review. Surv. Geophys. 1996, 174, 517–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.H. Insights on electromagnetic scattering by steel casings in surface-to-borehole and borehole-to-surface methods. Lead. Edge 2022, 41, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Reyes, O.; Queralt, P.; Marcuello, A.; Ledo, J. Land CSEM simulations and experimental tests using metallic casing in geothermal exploration Vallès Basin (NE Spain) case study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Reyes, O.; Queralt, P.; Pias-Varas, P.; Ledo, J.; Rojas, O. Electromagnetic subsurface imaging in the presence of metallic structures: A review of numerical strategies. Surv. Geophys. 2024, 45, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.H. An approximate inversion scheme for surface-borehole electromagnetic in the presence of steel casing: 1D implementation. Geophysics 2021, 86, E111–E121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.H. Insights on electromagnetic field distribution due to a vertical electric dipole source inside an infinite steel casing. Geophysics 2024, 89, E47–E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heagy, L.J.; Oldenburg, D.W. Impacts of magnetic permeability on electromagnetic data collected in settings with steel-cased wells. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 234, 1092–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heagy, L.J.; Oldenburg, D.W. Modeling electromagnetics on cylindrical meshes with applications to steel-cased wells. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 125, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heagy, L.J.; Oldenburg, D.W. Electrical and electromagnetic responses over steel-cased wells. Lead. Edge 2022, 41, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yue, J.; Hu, W.; Li, F.; Liu, Z. The characteristics of the early signal in TEM affected by self-induction of multiturn coil. Comput. Tech. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2007, 29, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- West, R.C.; Ward, S.H. The borehole transient electromagnetic response of a three-dimensional fracture zone in a conductive half-space. Geophysics 1988, 53, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi, J.; Macklin, D. Discovery of the Eureka volcanogenic massive sulphide lens using downhole electromagnetics. Explor. Geophys. 2016, 47, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, D.; Torres-Verdín, C.; Zhang, Z. Sensitivity study of borehole-to-surface and crosswell electromagnetic measurements acquired with energized steel casing to water displacement in hydrocarbon-bearing layers. Geophysics 2008, 73, F261–F268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Z.; Xu, Y. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of surface-to-borehole electromagnetic method for monitoring reservoir. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 14, 559–569. [Google Scholar]
- Su, B.; Yu, J.; Królczyk, G.; Gardoni, P. Innovative Surface-Borehole Transient Electromagnetic Method for Sensing the Coal Seam Roof Grouting Effect. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Sun, H.; Cheng, M.; Guo, J. CO2 injection monitoring using transient electromagnetic in ground-borehole configuration. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2018, 23, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, N.H.; Pezzoli, M. On the effect of the metal casing in surface-borehole electromagnetic methods. Geophysics 2018, 83, E173–E187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, C.; Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Ren, X.; Hui, Z.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, B. Three-dimensional forward modeling for the SBTEM method using an unstructured finite-element method. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 18, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Mao, Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, H. Key Technologies for Surface-Borehole Transient Electromagnetic Systems and Applications. Minerals 2024, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Han, S.; Khan, M.Y.; Chen, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Xue, G. A surface-to-borehole TEM system based on grounded-wire sources: Synthetic modeling and data inversion. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 4207–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yin, C.; Su, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, B. Three-Dimensional Dual-Mesh Inversions for Sparse Surface-to-Borehole TEM Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivochieva, S.; Chouteau, M. Whole-space modeling of a layered earth in time-domain electromagnetic measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 50, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T. Experimental study on the exploration of coal mine goaf by dynamic source and fixed reception roadway-borehole TEM detection method. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 3229–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.; Li, P.; Qi, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, X.; Yan, B.; Zhao, R.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Fang, Z. Borehole transient electromagnetic stereo imaging method based on horizontal component anomaly feature clustering. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 197, 104537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, D.; Wang, C.; Fan, T.; Li, B. Application of roadway-borehole TEM in water-bearing and water conducting structure prospecting. Coal Geo. China 2019, 31, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Ding, H.; Sun, Y.; Yi, X. Borehole transient electromagnetic response calculation and experimental study in coal mine tunnels. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 045112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Qi, Z.; Cao, K. Seismic prediction of unfavorable geobodies in tunnels using the borehole-roadway transient electromagnetic method. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 48, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, J.; Wang, A. Numerical simulation of drillhole transient electromagnetic response in mine roadway whole space using integral equation method. Chinese J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 4182–4193. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hu, W.; Xue, G. 3D modeling of multi-radiation source semi-airborne transient electromagnetic response. Chinese J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 716–723. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, C.; Güttel, S.; Ren, X.; Yin, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Egbert, G. A block rational Krylov method for 3-D time-domain marine controlled-source electromagnetic modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, X.; Farquharson, C.; Hu, X. A finite-element time-domain forward solver for electromagnetic methods with complex-shaped loop sources. Geophysics 2018, 83, E117–E132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Qi, Y.; Liu, Y. 3D time-domain airborne EM forward modeling with topography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 134, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druskin, V.; Knizhnerman, L. Spectral approach to solving three dimensional Maxwell’s diffusion equations in the time and frequency domains. Radio Sci. 1994, 29, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Elements | DOFs | Time Channel | Relative Error (%) | Time (s) | Max Memory (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 270,270 | 316,559 | 1100 | 0.70 | 550 | 41 |
| Method | Elements | DOFs | Relative Error (%) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FE | 363,546 | 424,425 | 1.31 | 770 |
| SLDMEM | 71 × 71 × 71 | 357,911 | 2.44 | 694 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Dou, Z.; Gao, Z. Forward Modeling Analysis in Advanced Exploration of Cross-Hole Grounded-Wire-Source Transient Electromagnetic Method. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052672
Zhu J, Jiang Z, Li M, Dou Z, Gao Z. Forward Modeling Analysis in Advanced Exploration of Cross-Hole Grounded-Wire-Source Transient Electromagnetic Method. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052672
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiao, Zhihai Jiang, Maofei Li, Zhonghao Dou, and Zhaofeng Gao. 2025. "Forward Modeling Analysis in Advanced Exploration of Cross-Hole Grounded-Wire-Source Transient Electromagnetic Method" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052672
APA StyleZhu, J., Jiang, Z., Li, M., Dou, Z., & Gao, Z. (2025). Forward Modeling Analysis in Advanced Exploration of Cross-Hole Grounded-Wire-Source Transient Electromagnetic Method. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052672






