Abstract
Purpose: To conduct a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis on marginal bone loss (MBL) in dental implants, enhancing the understanding and management of both bone-level and tissue-level implants. Methods: MEDLINE-PubMed and Scopus databases were searched for relevant English articles (up to April 2024), assessing the MBL as the primary outcome. The relevant data were extracted, and a meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the effect of implant neck design. Results: A total of 17 studies were included for qualitative analysis. Out of the 21 articles included, 15 studies established a statistically significant difference in MBL between the study groups; however, the differences were not found to be clinically relevant. Bone-level implants with platform-switched abutments in most of the cases showed better marginal bone stability compared to tissue-level implants or bone-level implants with matching abutments. Seven RCT studies were evaluated for the MBL between bone-level and tissue-level implants. The difference in MBL between bone-level implants and tissue-level implants was statistically significant, with a greater loss of bone in bone-level implants (Mean Difference: 0.11, 95% CI:0.02 to 0.19, p = 0.01 and I2 heterogeneity: 81%, p < 0.0001). Conclusions: This review underscores the need for standardized measurement techniques, consideration of patient-specific factors in clinical decision-making, and further long-term studies to optimize dental implant success and patient outcomes.
1. Introduction
Dental implants have emerged as a premier solution in dentistry over the past few decades, transforming clinical practice and significantly improving patients’ quality of life [1]. Dental implants have several advantages over other therapies: a high success rate and improvement in esthetics, chewing, eating, and speaking [2]. Dental-implant rehabilitation of edentulous patients is very widespread. Osteointegrated dental implants are being increasingly used to replace missing teeth in a variety of situations, ranging from a missing single tooth to complete edentulism [3]. Osseointegration was first introduced by Brånemark to describe the successful outcomes of dental implants after their placement in the jaw bone [4]. With the correct patient selection, planning, and maintenance, success rates exceed 90% over a ten-year period [5]. According to Albrektsson, the success criteria of dental implants showed a survival rate of 93.0% [6]. A previous study from Pjetursson’s 2004 and 2012 reviews (which define the concept of survival as ‘implant remains in situ at follow-up examination’) gave 10-year implant survival rates of 92.8% and 93.1%, respectively, from six prospective studies with a median of 81.5 implants per study [7,8]. A more recent cohort study by French et al. and a systematic review by Howe about the 10-year survival rate of implants presented a similar result, survival rates of 96.8% and 96.4%, respectively [9,10]. One of the earliest and most widely recognized success criteria for osseointegrated dental implants was the one proposed by Albrektsson et al. 1981 [4]. According to these criteria, a successful dental implant should display immobility: a proficient implant is securely affixed to the jawbone, demonstrating no signs of movement. Clinical mobility serves as an indicator of potential issues or a failure in the osseointegration process [5].
There are many related factors affecting implant failure. First, a group of factors are host-related; second, there are factors related to site-related implant placement; third, there are surgery-related factors; fourth, there are implant fixture-related factors; and, fifth, there are implant prosthesis-related factors. The age and gender of the patient, smoking habits, systemic disease, and oral hygiene are host-related factors. The position within the dental arch, quality, and quantity of bone are implant placement site-related factors. Initial stability, angulations, direction of implant, and the skillfulness of the operator come under surgery-related factors. Surface roughness, length, and diameter of the dental implant and the macrostructure and microstructure of an implant fixture are implant fixture-related factors. The type of prosthesis, retention method, and occlusal scheme are implant prosthesis-related factors. Albrektsson et al. concluded that factors such as the design and surface of implant, condition of implant placement site, surgery technique, and occlusal loading affect osteointegration [11].
Exhibiting minimal bone loss: According to Albrektsson, marginal bone loss (MBL) is defined as a loss in apical direction, of alveolar bone marginally adjacent to the dental implant, in relation to the marginal bone level initially detected after the implant was surgically placed, and it should be under 1.5 mm in the initial year post-loading and should not exceed 0.2 mm annually in subsequent years [4]. A recent study by French et al. 2024 evaluating marginal bone loss over 10 years reported losses of 2.0–2.5 mm [12]. One of the most debated topics within this realm pertains to the optimal placement of the implant—specifically, whether it should be positioned at, above, or below the bone crest. The controversy is driven by varying results in clinical outcomes, and the question remains: Which positioning best supports long-term implant success and patient satisfaction? [13]. Traditional crestal placement: Historically, implants were placed such that the implant collar was flush with the alveolar bone crest [1]. This crestal placement was thought to maximize the osseointegration surface and facilitate soft tissue management [14]. Sub-crestal placement: More recent advancements in implant design and understanding of peri-implant tissues have led some clinicians to place implants in a sub-crestal position. Here, the implant is positioned slightly below the crest of the bone [15]. Advocates believe that this promotes better esthetic outcomes, especially in the anterior region, by preserving the interdental papilla and soft tissue contour. Additionally, by positioning the implant–abutment junction below the bone, there might be enhanced protection against bacterial infiltration and peri-implantitis [16]. Supra-crestal placement: This less-common method involves positioning the implant above the alveolar bone crest. Proponents argue that this placement reduces crestal bone stress and allows better distribution of occlusal loads, potentially minimizing bone resorption [17]. Several factors can influence bone behavior, whether it pertains to growth or loss, during dental implant placement. These include the implant’s macro- and micro-design [18,19,20,21], the spacing between implants [22], the quality of the surrounding periodental tissue and bone [23], occlusal forces [24], the presence of microgaps that allow bacterial colonization between implant and abutment, and the position of the connection in relation to the bone crest [25,26,27,28,29]. Bone-level dental implants after 10-year follow-up had success rates of 99.4% in healthy patients without systemic disease and 95.9% with systemic disease [30]. Tissue-level dental implants in 4-year follow-ups had a success rate of 100%, with a mean marginal bone loss of 0.99 mm [31]. According to a recent study by Chacun 2024 where 301 tissue-level dental implants were placed, a follow-up of 4.5 years had a survival rate of 98.8% [32]. A study comparing bone and tissue-level implants with a follow-up of 4 years had a success rate of 100% and a mean marginal bone loss of 1.03 mm and 0.95 mm with non-significant difference [33].
For many clinicians, the placement of bone-level/tissue-level implants remains a dilemma. The purpose of this systematic review is to bring some insight into this controversial dichotomy; the next question is raised: Is there any significant difference in marginal bone loss (MBL) around the neck of bone-level and tissue-level implants?
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review aimed to answer the following question: Is there any differences in the MBL between bone-level/tissue-level implants? This study follows the Preferred Report Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) check list [34].
2.1. PICO Question
Are there any differences in the marginal bone loss between bone-level/tissue-level implants?
Population: patients who received dental implants.
Intervention: situation related to the bone level of implant placement
Comparison: bone-level implants vs. tissue-level implants.
Outcomes: MBL at the neck of the dental implant.
To develop the PICO question, we have followed the principles indicated in the manual prepared by the “Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad” (2016, Spain. Accessible at https://portal.guiasalud.es/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/manual_gpc_completo.pdf, accessed on 30 December 2024).
2.2. Search Strategy
A search was performed to detect the difference between the effect of bone-level and tissue-level implants on MBL; the search was conducted in PubMed and Scopus. The last electronic search was performed from January 2014 to April 2024. In PubMed, the key words were (((((tissue level) OR (supra crestal)) AND (bone level)) OR (crestal)) AND (marginal bone loss)) AND (dental implant [MeSH Terms]). For Scopus, the key words were TITLE-ABS-KEY (tissue AND level) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (supra AND crestal) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (bone AND level) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (crestal) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (marginal AND bone AND loss) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (dental AND implant).
The results of the above searching processes were added together, and duplicates were removed. Two independent reviewers (A.E. and N.T.-V.) then screened the articles and removed those that were not related to the topic being reviewed by reading the title, abstract, or full text. When necessary, the reviewers reached a consensus by discussion. Review articles on the topic were searched as well.
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria were English studies that used radiographic methods to measure MBL around the neck of both bone-level and tissue-level implants. The original studies included those such as retrospective cohorts, prospective studies, and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), clinical studies that include more than 10 patients, and studies comparing dental implants in the maxilla and mandible, with follow-up time periods of at least 1 year.
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
The exclusion criteria were in vivo or in vitro studies which did not mention the tool used for bone loss measurement, case reports or case series with less than 10 patients, articles published in languages other than English, a follow-up of less than 1 year, or articles published before 2014.
2.5. Quality Assessment
The quality assessment was conducted independently by two reviewers (A.E. and M.B.-H.). In case of discrepancies, these were resolved by S.E.-M. and J.L.-L. Each reviewer evaluated the selected articles based on the criteria specified in the appropriate assessment tool. They then conferred to resolve any discrepancies in their evaluations through discussion. This approach was not only systematic but also introduced a layer of checks and balances, minimizing the potential for oversight or bias in the assessment process.
To assess any potential risk of bias, the authors critically appraised each study by the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale for cohort and case-control studies [35]. A “star system” was developed in which a study was judged in the following three domains: selection of case and controls, comparability of cases and controls, and ascertainment of exposure. The rating was as follows. Good quality: three or four stars in the selection domain, one or two stars in the comparability domain, and two or three stars in the outcome/exposure domain. Fair quality: two stars in the selection domain, and one or two stars in the comparability domain, and two or three stars in the outcome/exposure domain. Poor quality: no or one star in the selection domain, or no stars in the comparability domain, or no or one star in the outcome/exposure domain [36]. For the RCT, the Jadad scale had been used. This grades them from 0 (lowest quality) to 5 (highest). In this system, points are awarded as follows: One point if the trial is randomized and another if a satisfactory method of randomization is described in the paper. One point if the trial is double-blinded and a second point if a satisfactory description of how double-blinding was achieved is given. One point is given if the number of dropouts from the trial and their reason for dropping out are recorded [37].
2.6. Data Extraction
Data extraction was performed by A.E., checked by J.L.-L. and S.E.-M. and recorded in an Excel table. Each study provided the following information: first author’s name, publication year, study design, method of bone loss measurements, follow-up duration, implant brand, implant placement protocol (one-stage vs. two-stage), implant connection type, presence of platform switching, and number of samples in each group (bone-level and tissue-level implants), as well as the mean and standard deviation of MBL and survival rate in each group.
2.7. Data Synthesis
For dichotomous outcomes, the summary measures considered were relative risks (RRs). Absolute frequencies and percentages were registered when available.
Pooled analyses were performed using a fixed-effects model. The heterogeneity of the studies was assessed by the I2 statistics. Heterogeneity among studies was considered statistically significant for a p-value < 0.05 and was interpreted as recommended by the Cochrane Handbook: 0–40% was considered unimportant, 30–60% as moderate heterogeneity, 50–90% as substantial heterogeneity, and 75–100% as considerable heterogeneity. The Review Manager 5.4 program was used as a tool to analyze the data, previously recorded in an Excel table. Forest plots were performed to graphically represent the difference between bone-level and tissue-level implants, with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
3. Results
As shown in Figure 1, a total of 273 articles were found by electronic and hand search. After eliminating the duplicated and the ineligible studies, 31 studies were elected by title and abstract. Twenty-one articles were reviewed. This review investigated the studies which were primarily concerned with comparing the effect of bone-level or tissue-level design on MBL around implants. According to the inclusion/exclusion criteria, 17 articles with a total of 1.895 implants were included [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Eight studies compared bone and tissue level [35,39,45,46,47,48,49,50]; seven articles studied bone-level implants [38,40,41,44,45,46,47], while two articles studied tissue-level implants [42,48]. It is noteworthy to mention that five articles, when read in full text, did not strictly compare bone-level with tissue-level implants, but we included them because they provided data of interest for this review [44,45,46,47,48] (Figure 1, Table 1).
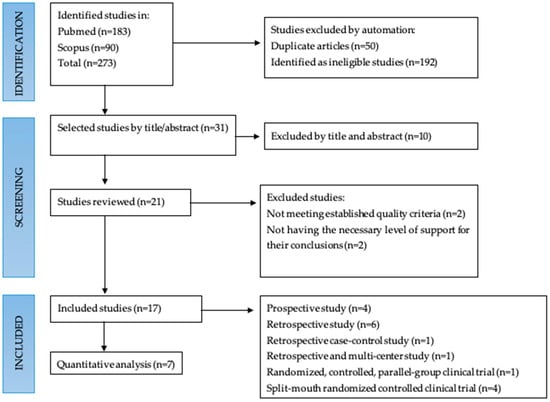
Figure 1.
Flow chart.

Table 1.
Most relevant data from the studies analyzed.
Patient (P), Implant (I), Month (m), Female (F), Male (M), Implants were inserted with a full-thickness periosteal flap elevation approach or flapless in post-extractive sites (Technique A), Implant was placed post extraction with GBR (Technique B), Post extraction of 6-months healing (Technique C), Survival rate (SVR), Success rate (SCR), Marginal bone loss (MBL), Peri-implant bone loss (PIL), Crestal bone loss (CBL), None reported (NR), Bone level (BL), Tissue Level (TL) Bone level inserted 0.75–1 mm above the crest (SC), 0.75–1 mm above the alveolar crest (SC), High bone loser (HBL), Narrow-diameter implants (NDIs), Regular-diameter implants (RDIs), Peri-implant probing depth (PD), Note Mentioned (N.m), Soft tissue level (STL), Bone level (BL), Maxilla (MAX), Mandible (MAN), Bleeding on probing (BOP), Pink esthetic score (PES), White esthetic score (WES), Periapical X-ray (Px), Panoramic X-ray (Pan), Intraoral Radiographs (Int), Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT)
Eight studies compared the MBL around dental implants placed at bone level and tissue level [39,43,49,50,51,52,53,54], with a total of 684 implants. Bone-level implants in these studies had mean MBLs (of 0.12 ± 1.47 mm, 0.97 ± 0.64 mm, infra crestal 0.09 ± 0.16, crestal 0.90 ± 1.09, 0.17 ± 0.017 mm, 0.93 ± 0.37 mm, 0.83 ± 0.58 mm, 1.324 ± 0.64 mm, 0.18 ± 0.46 mm) over a total of 341 implants. The average mean of each study was 0.795 mm, 0.805 mm, 0.125 mm, 0.995 mm, 0.17 mm, 0.65 mm, 0.705 mm, 0.982 mm, and 0.32 mm. Tissue-level implants in these studies had mean MBLs (of 0.04 ± 1.3 mm, 1.18 ± 0.89 mm, 0.22 ± 0.35 mm, 0.04 ± 0.08 mm, 0.28 ± 0.21 mm, 0.38 ± 0.46 mm, 1.194 ± 0.30 mm, 0.14 ± 0.35 mm) over a total of 338 implants. The average mean of each study was 0.67 mm, 1.035 mm, 0.285 mm, 0.06 mm, 0.245 mm, 0.42 mm, 0.747 mm, and 0.245 mm. The analysis results show that both bone-level and tissue-level implants have significantly near the same MBLs. While another study by López et al. [40] compared implants placed at the crestal level with a cylindrical and tapered Shiner XT, resulting in a 100% survival rate with mean MBLs of 0.1–0.3 mm. Another study by Guadio et al. [38], which compared cylindrical and tapered implants without mentioning the level of placement, had a 100% survival rate and mean MBLs of 0.9 ± 0.7 mm.
López et al. [40] compared cylindrical and conical implants, with a 100% survival rate on both implants but higher bone loss in the cylindrical 0.52 ± 0.21 mm than in the conical 0.48 ± 0.19 mm. Souza et al. [42] compared tissue-level implants of narrow diameter and regular diameter, showing higher survival for regular-diameter implants, with mean MBLs of 0.06 ± 0.09 mm, rather than in narrow-diameter implants, with mean MBLs 0.14 ± 0.16 mm. Bienz et al. [44], compared 18 tissue-level implants only, where 8 of them received soft tissue grafts, with a control of 12 years, and had no further significant peri-implantitis complication. Galindo-Moreno et al. [45], did not compare tissue-level with bone-level implants either but provided some interesting data; after the placement of 590 internal tapered conical connections, they observed >2 mm MBLs. Sui et al. [46], analyzed 6 mm length bone-level implants, with mean MBLs of 0.04 ± 0.14 mm. Pellicer-Chover et al. [47] analyzed dental implants inserted with high-speed drilling with irrigation and low-speed drilling without irrigation, having only high MBL in high-speed drilling (0.83 ± 0.73 mm) in comparison with low-speed drilling, 0.70 ± 0.62 mm. Prati et al. [48], placed 128 tissue-level only implants and had 2 implants’ failure and MBLs of 0.99 ± 0.68 mm.
3.1. Bias Analysis
The bias and quality analysis of the articles that specifically discuss the comparison between bone level and tissue level can be found in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Quality evaluation of the articles according to the Jadad scale [35].

Table 3.
Quality assessment for case-control and cohort studies based on Newcastle–Ottawa Scale [37].
3.2. Comparative Analysis
Regarding the quantitative analysis, seven studies [41,43,49,51,52,53,54] evaluated the MBL between bone-level and tissue-level implants. Forest plots were produced to represent it graphically (Figure 2). The difference in MBL between bone-level implants and tissue-level implants was statistically significant, with a greater loss of bone in bone-level implants (Mean Difference: 0.11, 95% CI:0.02 to 0.19, p = 0.01, and I2 heterogeneity: 81%, p < 0.0001). Figure 2.
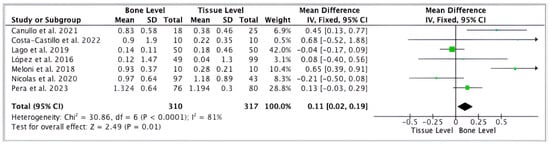
Figure 2.
Forest plot comparing MBL of tissue-level and bone-level implants [41,43,49,51,52,53,54].
Only one study analyzed soft-tissue thickness, concluding that, the less soft tissue, the greater the marginal bone loss, with a 12-year control of 0.88 mm [44].
4. Discussion
Bone-level and tissue-level implants have been widely and successfully used in dental practices. However, there is no consensus as to which one has better outcomes. This review studied the articles which were primarily concerned with comparing the effect of bone-level or tissue-level design with regards to the MBL around implants. In the realm of implant dentistry, diverse study designs ranging from retrospective cohorts to RCTs have been employed to evaluate MBL around dental implants [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. A comparison of these designs reveals nuanced differences in the reliability and interpretation of the results that must be meticulously dissected to appreciate the overarching narratives emerging from the data.
Retrospective cohort studies, such as those by Lopez et al. [38,39], provide the advantage of long-term follow-up data, which is invaluable for assessing the longevity and success of implants. However, retrospective analyses are susceptible to inherent biases such as selection and recall bias, potentially skewing the results. Prospective studies, exemplified by the work of Andreasi Bassi et al. [40] and Sui et al. [46], offer a more controlled environment for data collection and can reduce these biases, thereby enhancing the reliability of the outcomes reported. RCTs are the gold standard in clinical research due to their ability to minimize bias through randomization. Souza et al. [42] employed a split-mouth RCT design, offering a robust comparative analysis within the same patient, thus controlling for patient-related variables. As seen in the multi-center study by Sui et al. [46], increasing the sample of the study allows the detection of smaller differences in outcomes and provides a more precise estimate of the treatment effect. Conversely, smaller sample sizes may not adequately empower the study, leading to a potential Type II error, where a true effect may go undetected [41]. Studies with a heterogeneous population, such as the one by Nicolas et al. [43], which included non-compliant patients with a range of oral hygiene practices, may reflect a more realistic clinical scenario but complicate the direct comparison of outcomes between studies. In the discussion of implant dentistry research, it is crucial to acknowledge the influence of study design and sample size on the interpretation of results. The retrospective study by Lopez et al. [41], for instance, while providing a high survival rate (SVR) and success rate (SCR), may be influenced by the biases inherent to its design. In contrast, the prospective design by Andreasi Bassi et al. [40], with a 100% SVR but lower SCR due to mean MBL, offers a different perspective on implant success.
Implants come in various shapes and sizes and with different surface characteristics, each designed to optimize osseointegration and clinical success. The retrospective study by Lopez et al. [38] showcased the use of transmucosal implants with a conical connection, while Lopez et al. [39] compared bone-level and soft tissue-level cylindrical implants, each with unique micro-threaded and transmucosal neck designs. These design variations are critical to understanding the biomechanical integration of the implant with the surrounding bone and the potential for MBL. For instance, the conical plus octagonal connection system assessed by López et al. [41] was designed to enhance the implant–abutment interface, which could theoretically reduce micro-movements and contribute to the implant’s longevity. The sandblasted and acid-etched surfaces used in the implants studied by Lopez et al. [38] and Andreasi Bassi et al. [40] were designed to increase the surface area for bone contact, thereby potentially reducing the likelihood of bone loss. The placement technique also plays a crucial role in implant success. Flapless surgery, as reported by Prati et al. [48], tends to minimize surgical trauma and preserve blood supply, which can be beneficial for bone preservation. In contrast, the full-thickness periosteal flap elevation technique used by Lopez et al. [38] provides excellent access and visibility but may lead to greater disruption of the periosteal blood supply, which is essential for bone healing and regeneration. The use of regular-diameter implants (RDIs) showed a 100% success rate, while narrow-diameter implants (NDIs) showed 95% success rate in the posterior jaws, as investigated by Souza et al. [42]; this addresses the challenge of limited bone availability while still maintaining adequate support for occlusal forces. Studies with extended follow-ups, such as the 12-year retrospective analysis by Bienz et al. [44], offer valuable insights into the behavior of soft tissue contours and marginal bone over time. In contrast, shorter follow-up periods, like the one-year assessment reported by Costa Castillo et al. [49], may not capture the full spectrum of bone remodeling that occurs post-implantation. Despite the use of similar surface treatments, the study by Lopez et al. [39] reported a mean peri-implant bone loss of 0.12 ± 1.47 mm for bone-level implants and 0.04 ± 1.3 mm for soft tissue-level implants, whereas Souza et al. [40] observed a mean bone loss of −0.58 ± 0.39 mm for NDIs and −0.53 ± 0.46 mm for RDIs over a three-year period. These discrepancies highlight the multifactorial nature of bone loss, influenced by not only the implant’s physical characteristics but also by the surgical technique and patient factors. As we can see, the relationship between implant characteristics and MBL is multifaceted and influenced by a variety of factors. The collective evidence from the studies [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] underscores the need for careful consideration of implant design, surface treatment, and placement techniques in the pursuit of optimizing clinical outcomes. It also points to the necessity of individualizing implant selection based on patient-specific anatomical and functional requirements to maximize the potential for implant success and longevity. The standardization of measuring MBL is critical to compare results across studies. While most studies utilize radiographic assessments, the precision and angles of radiographs can vary, potentially affecting the measurement of bone levels [38,39,41]. Moreover, the timing of these measurements can influence the perceived rate of bone loss. For instance, studies with longer follow-up periods, such as that by Nicolas et al. [43], which considered a 10-year timeframe, offer insights into the long-term stability of peri-implant bone. In contrast, shorter-term studies may not capture the complete trajectory of bone remodeling [45]. When comparing quantitative results, the studies present a range of MBL figures, from the minimal loss reported by Lopez et al. [39] to the more significant loss in the study by Andreasi Bassi et al. [40]. These discrepancies can be attributed to differences in implant design, surgical techniques, and patient management. For example, the implementation of platform switching, as reported by Prati et al. [48], is known to influence peri-implant bone levels favorably. Such design modifications can mitigate stress concentration at the bone–implant interface and slow the progression of bone loss. Prati et al. [48] reported a mean preimplant bone loss of 0.04 mm in infra-crestal implants, 0.26 mm in crestal implants, and 0.19 mm in supra-crestal implants, while Costa-Castillo et al. [49] reported lower MBL in the sub-crestal group than in the crestal group (0.04 ± 0.08 vs. 0.17 ± 0.17 mm, p = 0.004). Covariates play a pivotal role in the interpretation of data and the understanding of bone loss around dental implants. Patient-related factors such as age, hygiene practices, and systemic health conditions can significantly influence the healing and maintenance of peri-implant tissues [43]. Studies that account for these variables offer a more nuanced interpretation of implant success and provide more individualized patient care guidelines. For instance, the influence of smoking and periodontal disease history on bone stability around implants has been documented, with conflicting reports on their impact on bone loss [43,45]. The interaction between these covariates and the type of implant and study design can complicate the interpretation of results. For example, while Souza et al. [42] found no significant difference in bone loss between narrow- and regular-diameter implants, the patient’s oral hygiene and compliance, which were not explicitly discussed in the study, could have a substantial impact on these outcomes. Similarly, the retrospective nature of studies such as those by Lopez et al. [38] and Costa Castillo et al. [49] can introduce recall bias and selective reporting, which might confound the results.
This systematic review presents some limitations. In the comparative analysis of MBL, the homogeneity of study groups is another factor that influences the reliability and comparability of results. Studies like that of Sui et al. [46] demonstrate high homogeneity by using multi-center data with standardized protocols, enhancing the comparability of their findings. Conversely, studies with heterogeneous groups, such as the case-control study by Bienz et al. [44], require careful interpretation, as the variability within the sample could mask or exaggerate the true effect of the implant characteristics on bone loss. Another limitation is the lack of data that allow us to classify the results in subgroups to identify the factors influencing bone loss. In future studies, it would be interesting to analyze bone loss according to the measurement method used to observe the differences.
5. Conclusions
Concluding this systematic review and meta-analysis, the analysis revealed that both bone-level and tissue-level implants are effective in managing marginal bone loss, yet they exhibit distinct characteristics and outcomes. For instance, bone-level implants demonstrated slightly higher rates of marginal bone loss in some cases, potentially due to their direct contact with the bone. In contrast, tissue-level implants, often featuring a transmucosal element, appeared to mitigate this loss more effectively in certain contexts. The nuanced differences in their performance can be attributed to variations in implant design, surface treatments, and placement techniques. The design and surface treatment of the implant play a significant role in how well bone is maintained around the implant site. For example, implants with rougher surfaces and platform-switching designs showed a tendency to reduce bone loss, possibly due to better stress distribution and osseointegration. This was reflected in a lower percentage of marginal bone loss compared to implants with smoother surfaces or traditional designs. There is a clear need for standardized measurement techniques for MBL to accurately compare the performance of different types of implants. Understanding their unique characteristics and how they interact with patient-specific factors is key to optimizing implant success. As dental implantology continues to evolve, a patient-centered approach that integrates the best available evidence with clinical expertise and patient preferences remains vital in providing effective, safe, and lasting dental treatment options.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.E. and J.L.-L.; methodology, A.E., S.E.-M. and J.L.-L.; software, A.E.; validation, all authors; formal analysis, A.E., S.E.-M. and J.L.-L.; investigation, A.E., N.T.-V. and M.B.-H.; resources, A.E. and M.B.-H.; data curation, A.E., R.A.-M. and S.E.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.E., X.R.-L. and M.B.-H.; writing—review and editing, A.E. and M.B.-H.; visualization, A.E. and J.L.-L.; supervision, J.L.-L., S.E.-M. and M.B.-H.; project administration, J.L.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Bihorizons Camblog-UB chair for their support in carrying out this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Alghamdi, H.S.; Jansen, J.A. The development and future of dental implants. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargozaie, N.; Moeintaghavi, A.; Shojaie, H. Comparing the Quality of Life of Patients Requesting Dental Implants Before an After Implant. Open Dent. J. 2017, 11, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brånemark, P.I. Osseointegration and its experimental background. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Brånemark, P.I.; Hansson, H.A.; Lindström, J. Osseointegrated titanium implants: Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydecke, G.; Locker, D.; Awad, M.A.; Lund, J.P.; Feine, J.S. Oral and general health-related quality of life with conventional and implant dentures. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2003, 31, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zarb, G.A.; Albrektsson, T. Osseointegration: A requiem for the periodontal ligament? Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1991, 11, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Belser, U.C.; Grütter, L.; Vailati, F.; Bornstein, M.M.; Weber, H.P.; Buser, D. Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single-tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: A cross-sectional, retrospective study in 45 patients with a 2- to 4-year follow-up using pink and white esthetic scores. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, D.; Ofec, R.; Levin, L. Long term clinical performance of 10 871 dental implants with up to 22 years of follow-up: A cohort study in 4247 patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, M.S.; Keys, W.; Richards, D. Long-term (10-year) dental implant survival: A systematic review and sensitivity meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2019, 84, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raikar, S.; Talukdar, P.; Kumari, S.; Panda, S.K.; Oommen, V.M.; Prasad, A. Factors Affecting the Survival Rate of Dental Implants: A Retrospective Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, D.; Clark-Perry, D.; Ofec, R.; Levin, L. Radiographic bone loss around dental implants: A large-cohort, long-term follow-up revealing prevalence and predictive factors. Quintessence Int. 2024, 55, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermann, J.S.; Cochran, D.L.; Nummikoski, P.V.; Buser, D. Crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A radiographic evaluation of unloaded non-submerged and submerged implants in the canine mandible. J. Periodontol. 1997, 68, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantena, S.R.; Sivagami, G.; Gottumukkala, S.N. Evaluation of crestal bone loss and stability of immediate functional loading versus immediate non-functional loading of single-mandibular posterior implants: A pilot randomized controlled clinical trial. Dent. Res. J. 2014, 11, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, E.H.; Jeong, S.N. Profilometric, volumetric, and esthetic analysis of guided bone regeneration with L-shaped collagenated bone substitute and connective tissue graft in the maxillary esthetic zone: A case series with 1-year observational study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eekeren, P.; Tahmaseb, A.; Wismeijer, D. Crestal bone changes in macrogeometrically similar implants with the implant-abutment connection at the crestal bone level or 2.5 mm above: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Signoriello, A.; Marincola, M.; Liboni, P.; Bonfante, E.A.; Nocini, P.F. Survival rates of ultra-short (<6 mm) compared with short locking-taper implants supporting single crowns in posterior areas: A 5-year retrospective study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 904–919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Micarelli, C.; Lembo-Fazio, L.; Iannello, G.; Clementini, M. Microscopical and microbiologic characterization of customized titanium abutments after different cleaning procedures. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2014, 25, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Pérez, R.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Rizo-Gorrita, M.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Gutierrez, J.L. Benefits of residual aluminium oxide for sand blasting titanium dental implants: Osseointegration and bactericidal effects. Materials 2022, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; López-Jarana, P.; Lemos, B.F.; Gil, F.J.; Falcao, C.; Rios-Santos, J.V.; Rios-Carrasco, B. Relevant design aspects to improve the stability of titanium dental implants. Materials 2020, 13, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Silvente, A.I.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-García, I.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Gil, F.J.; Jimenez-Guerra, A. Influence of the Titanium implants surface treatment on the surface roughness and chemical composition. Materials 2020, 13, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ciurana, X.; Vela-Nebot, X.; Segalà-Torres, M.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Camba, J.; Méndez-Blando, V. The effect of interimplant distance on the height of the interimplant bone crest when using platform-switched implants. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2009, 29, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Linkevicius, T.; Apse, P.; Grybauskas, S.; Puisys, A. Th influence of soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants: A 1-year prospective controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2009, 24, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Naert, I.; Duyck, J.; Vandamme, K. Occlusal overload and bone/implant loss. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2012, 23, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosper, L.; Redaelli, S.; Pasi, M.; Zarone, F.; Radaelli, G.; Gherlone, E.F. A randomized prospective multicenter trial evaluating the platform-switching technique for the prevention of postrestorative crestal bone loss. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2009, 24, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Canullo, L.; Fedele, G.R.; Iannello, G.; Jepsen, S. Platform switching and marginal bone-level alterations: The results of a randomized-controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2010, 21, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E. Wound healing in immediately loaded implants. Periodontology 2000 2015, 68, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos, M.; Velasco, F.; Ginebra, M.P.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. Regenerating bone via multifunctional coatings: The blending of cell integration and bacterial inhibition properties on the Surface of biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 36449–36457. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos-Nogués, M.; Buxadera-Palomero, J.; Ginebra, M.P.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. All-in-One trifunctional strategy: A cell adhesive, bacteriostatic and bactericidal coating for titanium implants. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 169, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodnom-Ish, B.; Eo, M.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.M. A 10-year survival rate of tapered self-tapping bone-level implants from medically compromised Korean patients at a maxillofacial surgical unit. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 45, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, A.; Zamparini, F.; Romanos, G.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Prati, C. Tissue-Level Laser-Lok Implants Placed with a Flapless Technique: A 4-Year Clinical Study. Materials 2023, 16, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacun, D.; Laforest, L.; Langlois-Jacques, C.; Dard, M.; Gritsch, K.; Grosgogeat, B. A Multicenter Cohort Study on 301 Tissue-Level Implants: Cumulative Implant Survival Rate and Marginal Bone Level Change up to 4.5 Years. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2024, 39, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, M.; Dellepiane, E.; Deiana, T.; Fulcheri, E.; Pera, P.; Pesce, P. Comparison of Bone-Level and Tissue-Level Implants: A Pilot Study with a Histologic Analysis and a 4-Year Follow-up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2022, 42, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLOS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2013. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Jadad, A.R.; Moore, R.A.; Carroll, D.; Jenkinson, C.; Reynolds, D.J.; Gavaghan, D.J.; McQuay, H.J. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control Clin. Trials 1996, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.A.; Andreasi, B.M.; Confalone, L.; Gaudio, R.M.; Lombardo, L.; Lauritano, D. Clinical outcome of 215 transmucosal implants with a conical connection: A retrospective study after 5-year follow-up. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.A.; Andreasi Bassi, M.; Confalone, L.; Gaudio, R.M.; Lombardo, L.; Lauritano, D. Retrospective study on bone-level and soft-tissue-level cylindrical implants. Regul. Homeost Agents 2016, 30 (Suppl. S1), 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasi Bassi, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Confalone, L.; Gaudio, R.M.; Lombardo, L.; Lauritano, D. Clinical outcome of a two-piece implant system with an internal hexagonal connection: A prospective study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, M.A.; Andreasi, B.M.; Confalone, L.; Gaudio, R.M.; Lombardo, L.; Lauritano, D. The influence of “conical plus octagonal” internal connection on implant survival and success rate: A retrospective study of 66 fixtures. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.B.; Sukekava, F.; Tolentino, L.; César-Neto, J.B.; Garcez-Filho, J.; Araújo, M.G. Narrow- and regular-diameter implants in the posterior region of the jaws to support single crowns: A 3-year split-mouth randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Naaman, B.A.N.; Nohra, J.; Chaaya, B.M. Marginal bone stability around bone level versus tissue level implants in non-compliant patients with healthy or reduced periodontium: A 10-year retrospective study. Int. Arab. J. Dent. 2020, 11, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienz, S.P.; Ruales, C.E.; Hüsler, J.; Roccuzzo, A.; Jung, R.E.; Thoma, D.S. Soft tissue contour changes at implant sites with or without soft tissue grafting in the esthetic zone: A retrospective case–control study with a 12-year follow-up. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2023, 34, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; Catena, A.; Pérez-Sayáns, M.; Fernández-Barbero, J.E.; O’Valle, F.; Padial-Molina, M. Early marginal bone loss around dental implants to define success in implant dentistry: A retrospective study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, D.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y. A prospective, multicenter study of 6-mm short implants in posterior alveolar bone supporting splinted crowns: A 5-year follow-up study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer-Chover, H.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Aloy-Prosper, A.; Sanchis-Gonzalez, J.C.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.A.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M. Comparison of peri-implant bone loss between conventional drilling with irrigation versus low-speed drilling without irrigation. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2017, 22, e730–e736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prati, C.; Zamparini, F.; Pirani, C.; Montebugnoli, L.; Canullo, L.; Gandolfi, M.G. A multilevel analysis of platform-switching flapless implants placed at tissue level: 4-year prospective cohort study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2020, 35, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Castillo, M.; Martos, L.M.; Pitarch, M.R.; Selva, G.M.; Rodríguez, C.S.; Fons-Badal, C. Analysis of Peri-Implant Bone Loss with a Convergent Transmucosal Morphology: Retrospective Clinical Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, B. Clinical and radiographic results of crestal vs. subcrestal placement of implants in posterior areas: A split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meloni, S.M.; Baldoni, E.; Pisano, M.; Tullio, A.; De Riu, G.; Tallarico, M. 1-year results from a split-mouth randomised controlled pilot trial comparing implants with 0.75 mm of machined collar placed at bone level or supracrestally. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Menini, M.; Bagnasco, F.; Di Tullio, N.; Pesce, P. Tissue-level versus bone-level single implants in the anterior area rehabilitated with feather-edge crowns on conical implant abutments: An up to 5-year retrospective study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, F.; Carossa, M.; Bagnasco, F.; Crupi, A.; Ambrogio, G.; Isola, G.; Menini, M.; Pesce, P. Comparison between Bone-Level and Tissue-Level Implants in Immediate-Loading Full-Arch Rehabilitations: A Retrospective Multi-Center 1-Year Follow-Up Study. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, L.; Da Silva, L.; Martinez-Silva, I.; Rilo, B. Radiographic Assessment of Crestal Bone Loss in Tissue-Level Implants Restored by Platform Matching Compared with Bone-Level Implants Restored by Platform Switching: A Randomized, Controlled, Split-Mouth Trial with 3-Year Follow-Up. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).