Gram-Scale Green-Emission Carbon Quantum Dots Produced from Wood via the Hydrothermal Synthesis Method for the Detection of Fe (III)
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Methods of N-CQDs
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Determination of Fluorescence Quantum Yield
2.5. Detection of the Concentration of Fe (III)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure and Morphology of N-CQDs
3.2. Surface Functional Characteristics and Elemental Analysis
3.3. Optical Properties of N-CQDs
3.4. Formation Mechanism of N-CQDs
3.5. Detection of the Concentration of Fe (III) by N-CQDs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CQDs | Carbon quantum dots |
| N-CQDs | Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| NL | Natural light |
| QY | Quantum yield |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| FL | Fluorescence |
| CIE | Coherent Infrared Energy |
References
- Ramanan, V.; Thiyagarajan, S.K.; Raji, K.; Suresh, R.; Sekar, R.; Ramamurthy, P. Outright green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from eutrophic algal blooms for in vitro imaging. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4724–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Teng, X.; Yan, M.; Bi, H.; Morais, P.C. Mitochondria-targeting nanoplatform with fluorescent carbon dots for long time imaging and magnetic field-enhanced cellular uptake. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10201–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bi, H.; Cesar Morais, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Hu, L. Room-temperature magnetism in carbon dots and enhanced ferromagnetism in carbon dots-polyaniline nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ni, G.; Tu, J.; Jin, X.; Peng, J. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive detection of Fe2+ and hydrogen peroxide. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, K.; Cui, J.; Hao, J. Facile synthesis of water-soluble rhodamine-based polymeric chemosensors via schiff base reaction for Fe3+ detection and living cell imaging. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 845627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Shanmughan, A.; Krishna, A.V.; Noushija, M.K.; Umadevi, D.; Shanmugaraju, S. Porous organic polymers-based fluorescent chemosensors for Fe (III) ions-a functional mimic of siderophores. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1361796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shu, H.; Niu, P.; Chen, P.; Jiang, H. Highly sensitive detection of trace tetracycline in water using a metal-organic framework-enabled sensor. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 1462107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.-L.; Moniotte, N.; Nivarlet, N.; Chen, L.-H.; Fu, Z.-Y.; Desmet, J.; Li, J. Fl–DFO molecules@ mesoporous silica materials: Highly sensitive and selective nanosensor for dosing with iron ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Hei, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, M.; Sha, T.; Wang, N.; Hassan, M.; Bo, X.; Zhou, M. Synthesis of a three-dimensional interconnected carbon nanorod aerogel from wax gourd for amperometric sensing. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Kuang, J.; Cao, W. Hydrothermal synthesis of carbon quantum dots using different precursors and their combination with TiO2 for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 11828–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of fluorescence carbon quantum dots with high product yield and quantum yield. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 085406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Xu, F.; Shi, X.; Feng, D.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, D. High-yield synthesis of strong photoluminescent N-doped carbon nanodots derived from hydrosoluble chitosan for mercury ion sensing via smartphone APP. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinaya, K.; Rajkishore, S.; Lakshmanan, A.; Anandham, R.; Dhananchezhiyan, P.; Praghadeesh, M. Synthesis and characterization of carbon dots from coconut shell by optimizing the hydrothermal carbonization process. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2021, 13, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Shanmugam, M.; Perumal, S.; Somanathan, T.; Lee, Y.R. Sustainable synthesis of carbon quantum dots from banana peel waste using hydrothermal process for in vivo bioimaging. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 126, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.N.; Jha, S.; Kailasa, S.K. One-pot green synthesis of carbon dots by using Saccharum officinarum juice for fluorescent imaging of bacteria (Escherichia coli) and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 38, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.A.A.; Lease, J.; Yoshito, A. Lignocellulosic biomass-derived carbon quantum dots (CQDs): A novel approach utilizing organosolv lignin from Moso bamboo waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Q.; Sun, R. Oxidized nanocellulose facilitates preparing photoluminescent nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots for Fe3+ ions detection and bioimaging. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, R.-C.; Zhong, L.; Peng, X. Facile and high-yield synthesis of carbon quantum dots from biomass-derived carbons at mild condition. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7833–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.L.; Li, S.J.; Yuan, N.N.; Chen, Y.; Lei, B.F.; Hu, C.F.; Liu, Y.L. Rapid hydrothermal method for the preparation of carbon quantum dots in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Rapid and high yield synthesis of carbon dots with chelating ability derived from acrylamide/chitosan for selective detection of ferrous ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellasamy, G.; Arumugasamy, S.K.; Govindaraju, S.; Yun, K. Green synthesized carbon quantum dots from maple tree leaves for biosensing of Cesium and electrocatalytic oxidation of glycerol. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Guo, S.; Qin, Q.; Liao, Y.; Li, M.; Du, F. Box–Behnken Design Optimizing Sugarcane Bagasse-Based Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Preparation and Application in Ferric Ion Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, F.; Coaquira, J.; Villegas-Lelovsky, L.; Da Silva, S.; Cesar, D.; Nagamine, L.; Cohen, R.; Menéndez-Proupin, E.; Morais, P. Evolution of the doping regimes in the Al-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by a polymer precursor method. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 095301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Ehrat, F.; Wang, Y.; Milowska, K.Z.; Reckmeier, C.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Carbon dots: A unique fluorescent cocktail of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6030–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R. Wood-cellulose photoluminescence material based on carbon quantum dot for light conversion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 290, 119429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, H.-A.S.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Kamel, S. Microwave-assisted synthesis of amphoteric fluorescence carbon quantum dots and their chromium adsorption from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Jiang, X.; Pang, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots from bio-waste lignin for selective irons detection and cellular imaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Meng, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, N. Tribological and Grinding Properties of Spherical Diamond Grown on a Rough Discontinuous Surface. Coatings 2023, 13, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Song, X.; Chai, X.; Zhao, P.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Green production of fluorescent carbon quantum dots based on pine wood and its application in the detection of Fe3+. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, Z.; Afsharpour, M.; Tabar-Heydar, K. UV-assisted functionalization of carbon nanotube for synthesis of efficient desulfurization catalysts (NH2/COOH)-MWNT/MoO3. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 91, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.; Zhang, S.; Jaishi, M.; Adhikari, R.; Bi, J.; Fang, M.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luck, R.L.; Pati, R. New near-infrared fluorescent probes with single-photon anti-stokes-shift fluorescence for sensitive determination of pH variances in lysosomes with a double-checked capability. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaki, M.; Fallah, A.; Gülcan, H.O.; Gazi, M. A novel chitosan based fluorescence chemosensor for selective detection of Fe (III) ion in acetic aqueous medium. Mater. Technol. 2021, 36, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots based on quinoa straw and their application in alkali metal ions detection. BioResources 2024, 19, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, G.; Zou, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q. Visible–ultraviolet upconversion carbon quantum dots for enhancement of the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X. Nitrogen, sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots with large Stokes shift for real-time monitoring of pH in living cells. Talanta 2024, 269, 125479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Anjum, A.S.; Riaz, R.; Bibi, A.; Sun, K.C.; Jeong, S.H. Unraveling the surface states related Stokes shift dependent electrocatalytic activity of N-doped carbon quantum dots for photovoltaic applications. Carbon 2021, 181, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Gan, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Chu, P.K. Poly (ethylene glycol)/carbon quantum dot composite solid films exhibiting intense and tunable blue–red emission. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE (Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage); CIE 1931 Standard Book Information; Commission Internationale de l 'Eclairage Proceedings; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Jenzer, H.; Sadeghi-Reeves, L. Nutrigenomics-associated impacts of nutrients on genes and Enzymes with special consideration of Aromatase. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Qiao, X.; Shao, Q.; Hassan, M.; Ma, Z.; Yao, L. Synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and ammonia on lignin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, R.; Dhib, R.; Mehrvar, M. Photochemical degradation of aqueous artificial sweeteners by UV/H2O2 and their biodegradability studies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, J.M. Studies on the mechanism of alkaline peroxide delignification of agricultural residues. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1985, 27, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A facile and simple method for synthesis of graphene oxide quantum dots from black carbon. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, A.; Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Zhou, T.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Sun, Y. One-pot green synthesis of biocompatible graphene quantum dots and their cell uptake studies. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, N.; Chinnathambi, S.; Kumar, M.; Etezadi, F.; Bakhori, N.M.; Zubir, Z.A.; Salleh, S.N.M.; Shueb, R.H.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thangavel, V. Development of biomass waste-based carbon quantum dots and their potential application as non-toxic bioimaging agents. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 28230–28249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.G.; Huš, M.; Baragau, I.A.; Bowen, J.; Heil, T.; Nicolaev, A.; Abramiuc, L.E.; Sapelkin, A.; Sajjad, M.T.; Kellici, S. Engineering Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Tailoring Optical and Chemical Properties through Selection of Nitrogen Precursors. Small 2024, 20, 2310587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, K.S.; Das, G.S.; Tripathi, K.M. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from biomass as a FRET-based sensing platform for the selective detection of H2O2 and aspartic acid. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxin, F.P.; Jackson, S.D.; Jarvis, M.C. Isolation of high quality lignin as a by-product from ammonia percolation pretreatment of poplar wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Malico, I.; Sousa, A.M. Solid biomass from forest trees to energy: A review. In Renewable Resources and Biorefineries; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Volume 2013, pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euring, D.; Bai, H.; Janz, D.; Polle, A. Nitrogen-driven stem elongation in poplar is linked with wood modification and gene clusters for stress, photosynthesis and cell wall formation. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, E.; Carnevale, M.; Vincenti, B.; Palma, A.; Guerriero, E.; Borello, D.; Gallucci, F. Evaluation of VOCs emitted from biomass combustion in a small CHP plant: Difference between dry and wet poplar woodchips. Molecules 2022, 27, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, H.; Chaima, M.; Wang, X.; Xiu, L.; Yang, L.; Huang, J. Fluorescent detection of organophosphorus pesticides using carbon dots derived from broccoli. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 8315–8324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Han, X.; Li, M.; Yuan, J.; Wei, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Zhao, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from hawthorn for the rapid determination of chlortetracycline in pork samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 255, 119736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandihalli, N. Microwave-driven synthesis and modification of nanocarbons and hybrids in liquid and solid phases. J. Energy Storage 2025, 111, 115315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Kalimuthu, R.; Kanagaraj, T.; Kulandaivelu, R.; Nagappan, R.; Pragasan, L.A.; Ponnusamy, V.K. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of multi-functional carbon quantum dots as efficient fluorescence sensor for ultra-trace level monitoring of ammonia in environmental water. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B. An efficient synthesis and photoelectric properties of green carbon quantum dots with high fluorescent quantum yield. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jo, S.; Chae, A.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, J.E.; Lim, D.; Park, S.Y.; In, I. Simple microwave-assisted synthesis of amphiphilic carbon quantum dots from A3/B2 polyamidation monomer set. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27883–27893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, D.; Liu, Q.; Luo, K.H.; Li, C. Mild acidolysis-assisted hydrothermal carbonization of lignin for simultaneous preparation of green and blue fluorescent carbon quantum dots. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9888–9898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martindale, B.C.; Hutton, G.A.; Caputo, C.A.; Reisner, E. Solar hydrogen production using carbon quantum dots and a molecular nickel catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6018–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jing, S.; Peng, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhuo, H.; Sun, R.; Zhong, L. Synthesizing green carbon dots with exceptionally high yield from biomass hydrothermal carbon. Cellulose 2020, 27, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X. Simultaneously enhancing up-conversion fluorescence and red-shifting down-conversion luminescence of carbon dots by a simple hydrothermal process. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6947–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Full-wood photoluminescent and photothermic materials for thermal energy storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.U.; Park, E.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.-W.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huh, Y.S.; Lee, J. Photoluminescent green carbon nanodots from food-waste-derived sources: Large-scale synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




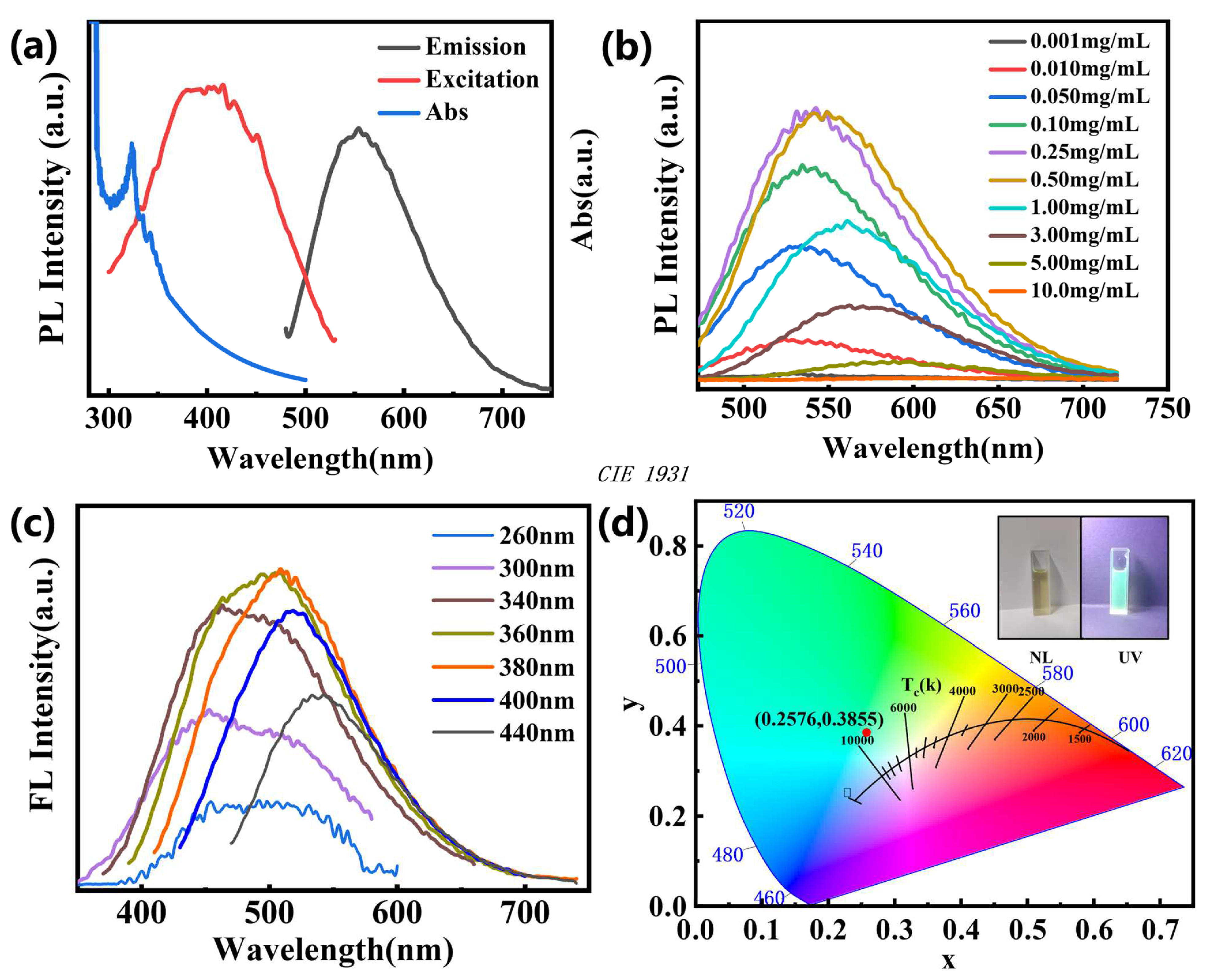
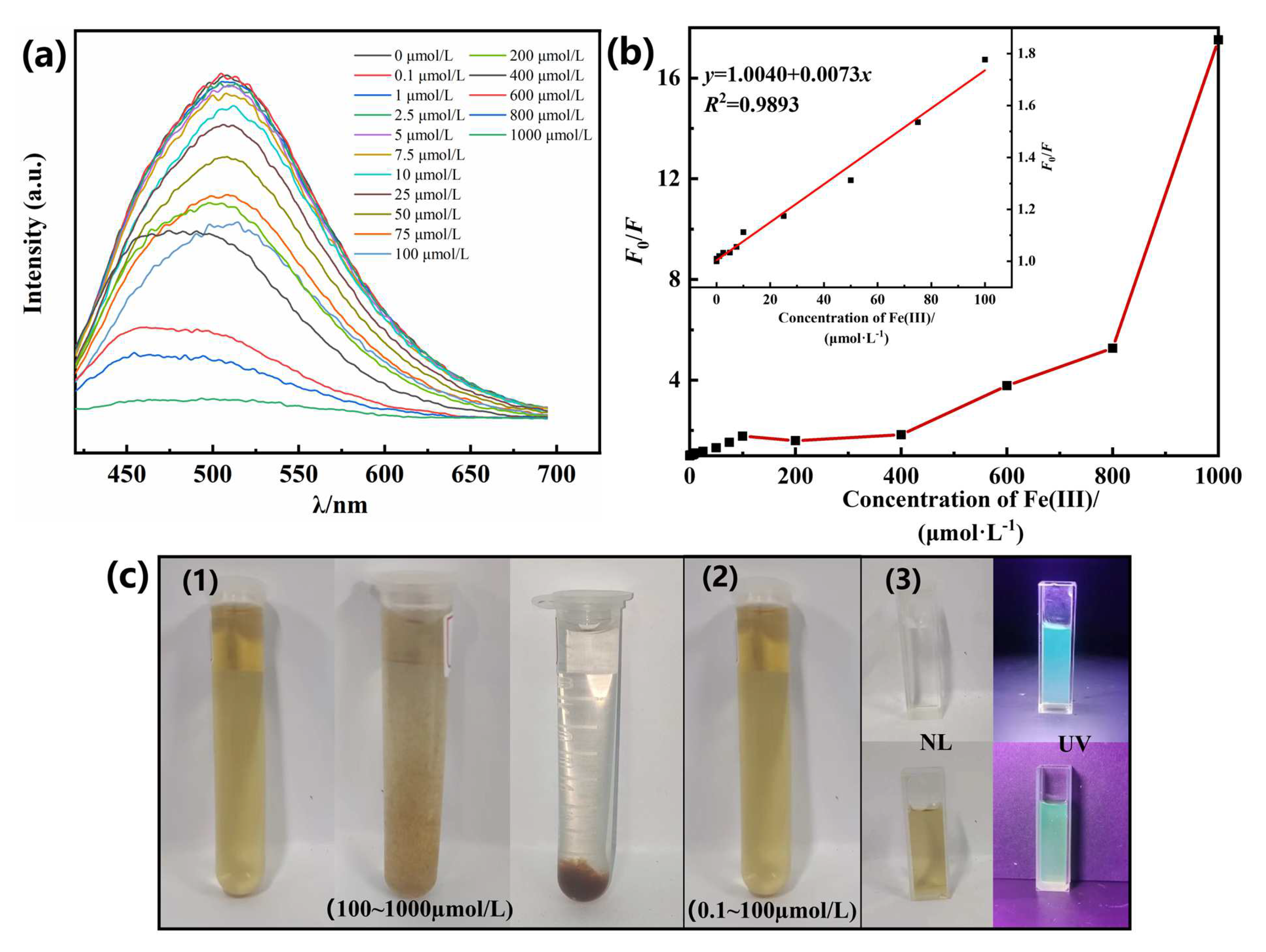
| Serial Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Mass Yield/% | 37.4 | 40.2 | 43 | 50.6 | 39 | 41.8 | 43 | 42 | 42.8 | 42 |
| Serial Number | Precursor | Synthesis Method | Mass Yield/% | LOD/μmol/L | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2,7-dihydroxynaphthalene | One-step hydrothermal | 70.9 | none | [59] |
| 2 | Citric acid and 4,7,10-trioxa-1,13-tridecanediamine | Microwave assisted | 66.4 | none | [60] |
| 3 | Lignin | Acid pretreatment/hydrothermal synthesis | 45.8 | none | [61] |
| 4 | Citric acid | Straightforward thermolysis | 45 | none | [62] |
| 5 | Glucose | Hydrothermal | 44.3 | 1.3–106.7 | [20] |
| 6 | Lignin, cellulose | Solvothermal carbonization | 42.5 | 0.085 | [63] |
| 7 | Ammonium citrate | Hydrothermal | 34 | none | [64] |
| 8 | Poplar leaf | Hydrothermal | 30 | none | [65] |
| 9 | Cellulose | Hydrothermal | 16.1 | 1.14 (Fe3+) | [19] |
| 10 | Durian pulp | Hydrothermal | 6.8 | 3.5 | [11] |
| 11 | Food waste, ethanol | Hydrothermal | 0.12 | none | [66] |
| 12 | Poplar wood | Hydrothermal | 42 | 4.1 (Fe3+) | This paper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, J. Gram-Scale Green-Emission Carbon Quantum Dots Produced from Wood via the Hydrothermal Synthesis Method for the Detection of Fe (III). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041958
Mu P, Han Y, Wang J. Gram-Scale Green-Emission Carbon Quantum Dots Produced from Wood via the Hydrothermal Synthesis Method for the Detection of Fe (III). Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(4):1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041958
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Pingxuan, Yu Han, and Jinxin Wang. 2025. "Gram-Scale Green-Emission Carbon Quantum Dots Produced from Wood via the Hydrothermal Synthesis Method for the Detection of Fe (III)" Applied Sciences 15, no. 4: 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041958
APA StyleMu, P., Han, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). Gram-Scale Green-Emission Carbon Quantum Dots Produced from Wood via the Hydrothermal Synthesis Method for the Detection of Fe (III). Applied Sciences, 15(4), 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041958









