Abstract
In recent years, significant progress has been made in arbitrary motion style transfer. However, many existing methods primarily focus on end-to-end processes and overlook the differences and similarities among generated motions, thus failing to fully leverage style information. To address this limitation, we employ contrastive learning to bring generated motions closer to input motions and further away from others. This enables the model to construct better motion representations and optimize the quality of motion stylization. Additionally, existing methods often struggle to recognize different styles. To address this, we employ contrastive learning on random temporal motion clips of the same motion, allowing the model to compare details between the same and different styles at a finer temporal scale. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed method generates robust feature representations, resulting in a stronger stylization of generated motions and a more accurate preservation of content.
1. Introduction
The virtual industry is experiencing rapid growth, leading to an increased demand for customized human motion. However, the process of customizing specific human motions can be expensive. In many cases, a significant portion of the motion content is repetitive. Therefore, if we can stylize these repetitive motions to meet customization requirements, it would result in substantial cost savings and expedite the creation of virtual assets. Consequently, research on motion style transfer has gained significant importance.
Data-driven methods have emerged as a promising approach for motion style transfer due to their convenience, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in data-driven end-to-end methods (e.g., [1,2,3,4,5,6]). Despite the excellence of these methods, they primarily rely on a direct end-to-end approach to enhance the model’s ability to preserve style and content. They do not thoroughly explore the differences and similarities between various motions, which limits their ability to construct better representations of style and content. Furthermore, accurately preserving information from the input motions continues to be a challenge in these approaches.
In terms of the differences and similarities between the generated motion and other motions, contrastive learning offers a powerful framework for description. Contrastive learning discriminates each instance as a separate category, which aligns well with arbitrary motion transfer, treating each motion as an individual style or content category. Additionally, the instance similarities learned through contrastive learning aid in distinguishing between different motion styles and content. Our contrastive learning framework is based on the premise that the generated motion should be closer to the input style motion in terms of style, and closer to the input content motion in terms of content, while far away from other input motions and generated motions. By employing this, we can effectively capture and model the differences and similarities between different motions.
To enhance the model’s ability to recognize different styles, we employ contrastive learning between two random temporal motion clips of the same motion, as shown in Figure 1. By comparing and linking each small clip of the input motion individually, the model can explicitly learn the differences and similarities in style from various temporal clips of the same motion. Consequently, our framework is capable of accurately preserving the style of the input motion during the transfer process.
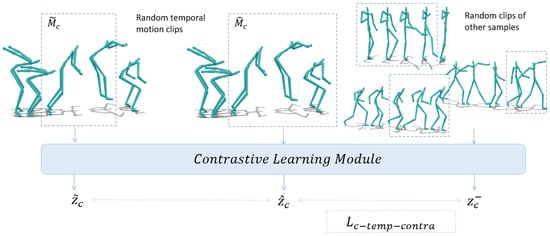
Figure 1.
Contrastive learning on random temporal motion clips. The clips are sampled from the same motion with random window size.
In this study, we make the following contributions:
- We propose a novel framework that incorporates contrastive learning for arbitrary motion style transfer, leveraging the differences and similarities between various motions.
- We introduce a dedicated module for contrastive learning on random temporal motion clips. This module enhances the style encoder’s ability to fully represent style motions.
- We conducted extensive experiments on the impact of contrastive learning and temporal contrastive learning on arbitrary motion style transfer, analyzing their ability to preserve style and content in the style transfer task.
2. Related Work
2.1. Arbitrary Image Style Transfer
Arbitrary image style transfer refers to the process of reproducing the structural content of one image using the style information from another image, without the need for paired data. The original approach, proposed by Gatys et al. [7], utilized a Gram matrix to compute mutual information from latent features. However, its optimization-based nature incurred significant computational overhead. To address this, Johnson et al. [8] introduced fast feed-forward neural networks as a more efficient solution. Additionally, Huang and Belongie [9] proposed a concise and effective style transfer method by aligning statistical information from style and content features, incorporating adaptive instance normalization (AdaIN). However, this method relied on paired data for supervised training, limiting its applicability to arbitrary image style transfer. In the absence of paired data, Zhu et al. [10] proposed a technique for style transfer between different image domains, leveraging cycle consistency loss to preserve image information from the source domain. Recently, Kwon et al. [11] proposed a method for aesthetic perception through frequency decomposition of images, enhancing the model’s ability to perceive aesthetic information in any given image.
2.2. Contrastive Learning
Contrastive learning has been widely applied in various domains, including image classification [12,13,14,15,16], image style transfer [17,18], text generation [19,20], and action recognition [21,22]. Extensive research has demonstrated the effectiveness and generalization of contrastive learning in machine learning tasks and data. In the context of image style transfer, Chen et al. [23] first introduced contrastive learning for style transfer by treating the generated images and images with the same style or content as positive pairs in the contrastive learning process. Zhang et al. [24] extended the application of contrastive learning to visual features, thereby leveraging richer style information. Recently, Zhang et al. [25] proposed an adaptive temperature adjustment mechanism for contrastive learning, which makes the comparison of contrastive learning samples in style transfer more accurate.
2.3. Motion Style Transfer
In earlier research, various data-driven methods have been proposed to learn representations of motion styles. Hsu et al. [26] introduced a linear time-invariant system to capture style differences between different motions, enabling style transfer for motions with similar content. Ikemoto et al. [27] employed a Gaussian process model based on kinematics and dynamics to manipulate input motions and achieve desired styles. Xia et al. [28] combined K-nearest neighbor search and a regression model to facilitate real-time style transfer between motion segments. Yummer and Mitra [1] focused on using spectral intensity features to express style variations between different motions and used them for style transfer and control.
Recent studies have explored deep learning methods for motion style transfer. Holden et al. [2,29] proposed an approach that manipulates the Gram matrix of feature variables in the latent space to achieve style transfer. Du et al. [30] introduced a conditional variational autoencoder that directly learns the distribution of style motions with a few style examples. Aberman et al. [4] employed AdaIN to combine style features and content features of motions, enabling a more concise style transfer. Moreover, they utilize an asymmetry encoder architecture in their framework. Park et al. [5] incorporated spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks (ST-GCN) to learn the representation of motions, enhancing the network’s ability to extract in a local spatio domain. Tao et al. [31] adopted a novel recurrent module to enable online motion style transfer. Mason et al. [32] presented a style modeling system based on the local motion phases. Tang et al. [33] conducted a hierarchical structure to achieve real-time controllable motion transition. Jang et al. [6] proposed a system that enables independent style transfer for different body parts of characters and a loss function to implement arbitrary motion style transfer. Song et al. [34] proposed a multi-condition diffusion model that separates and reintegrates trajectories, content, and style from motion, enhancing style transfer performance while preserving the core content of motion.
Inspired by previous works, our framework incorporates contrastive learning into arbitrary motion style transfer. Unlike previous end-to-end methods, our approach focuses on constructing more comprehensive feature representations by considering the various differences between different motions. This leads to improved stylization and accurate preservation of content.
3. Methodology
Existing unsupervised motion style transfer methods encounter challenges such as the inability to accurately preserve the details of various content and motion styles, and the distinctions between different motion styles are not sufficiently pronounced. In order to address these challenges, we propose an innovative unsupervised training framework that integrates contrastive learning. The overview of our framework is illustrated in Figure 2. This framework consists of a style transfer module and a contrastive learning module. In the following, we provide a detailed description of each module.
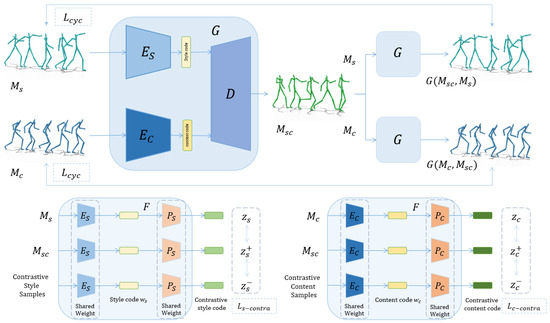
Figure 2.
Framework overview. Up: The content motion and style motion are separately encoded using a content encoder and a style encoder, then decoded into generated motion. This generated motion, along with the corresponding input motion, undergoes cycle generation within the generator. Down: Both the generated motion and the input motion are subjected to contrastive learning in a dedicated module, facilitating style and content contrastive learning.
3.1. Architecture
Motion transfer module. The motion transfer module, denoted as G, includes a style encoder , a content encoder , and a decoder D. It takes as input a style motion sequence and a content motion sequence to generate the motion .
The motion sequence M consists of T frames, each frame containing quaternion rotations for J joints . In temporal dimension, a motion sequence .
Our encoder architecture is designed based on the asymmetry encoder framework proposed by Aberman et al. [4]. The content encoder comprises multiple residual blocks that are utilized to transform the motion sequence into a suitable manifold space. Moreover, in order to eliminate style information [35], instance normalization (IN) is applied to each residual block. On the other hand, the style encoder consists of same residual blocks without instance normalization, complemented by a three-layer MLP (multilayer perceptron). This MLP is employed to make style code directly modify the means and variances of the content code. Moreover, the style encoder produces fixed-size latent code which is independent on the temporal length of the clip.
The decoder utilizes an adaptive normalization layer (AdaIN) to combine the style code and content code, enabling the reconstruction of the original joint rotations based on the merged latent representation.
Contrastive learning module. The contrastive learning module F comprises separate encoders and the corresponding contrastive learning projector, which consists of a two-layer MLP. Once the style encoder transforms the motion sequence into style code , the projector further converts the style code into contrastive style code . As z is a K-dimensional vector, and . This process explicitly constructs a contrastive learning space, facilitating the differentiation of various style representations. Similarly, the content encoding undergoes a similar procedure, ensuring the creation of a contrastive learning space for the content representations.
In addition, we have introduced a random temporal sampler, similar as the augmentation technique discussed in [6]. This sampler randomly selects a segment of the motion sequence as input for the contrastive learning module, instead of using the entire source motion sequence, shown in Figure 1. The purpose of this sampler is to facilitate contrastive learning through random temporal clips.
3.2. Training
Our framework adopts an end-to-end encoder–decoder architecture. The training process involves the following details and loss computation.
Motion reconstruction loss. We compute the reconstruction motion by applying the generator function to the input content motion . We then compare and using the L1 loss, measuring the absolute difference between corresponding elements of the two sequences. We calculate the loss in both the input style motion and the content motion .
Cycle consistency loss. Cycle consistency loss ensures that the generated motion can be accurately translated back to the source motion. This mechanism enhances the generator’s ability to maintain consistency and coherence by enforcing the mapping to be bijective, enabling the generated motion to faithfully represent the original source motion [10].
Contrastive learning loss. We have incorporated two types of contrastive learning techniques into our model. The first approach focuses on establishing difference between the generated motion and other motions. Specifically, it associates the generated motion with the input motion, ensuring that both belong to the same category while differing from others [23]. This enables the model to learn the similarity between the positive pair, denoted as and , while enhancing the ability to distinguish other contrastive motion codes .
where · represents the dot product of two vectors. is a temperature hyper-parameter per. Additionally, we adopt a memory bank architecture inspired by He et al. [36], which acts as a dynamic queue storing embeddings of negative samples. This architecture allows the model to efficiently access diverse negative examples during training, enhancing the discriminative power of contrastive representations. Specifically, we maintain separate memory banks for style and content features, each with a fixed capacity of 512 entries updated via a first-in-first-out (FIFO) strategy.
The second contrastive learning technique involves the use of two different random temporal motion clips, denoted as and , from the same motion sequence. This pairing serves as a positive example, explicitly enhancing the model’s ability to compare stylistic details across multiple time scales.
where is the contrastive code of the corresponding temporal motion clip . is the contrastive code of the corresponding temporal motion clip . is the contrastive code of other temporal motion clips.
Position loss. Apart from the reconstruction loss and cycle loss for quaternion rotations, we also incorporate the joint positions to regularize our encoder. This additional regularization enhances the model’s ability to generate faithful motion by providing extra information, effectively preventing strange rotation distortions.
where is a forward kinematic operator providing joint positions. Finally, the total loss of our framework is
where we mostly use = 1, = 1, = 0.3, = 2.
4. Experiments
In this section, we present a series of experiments designed to evaluate the performance of our approach. We start by describing our dataset and the preparation steps undertaken for the experiments. Next, we conduct both qualitative and quantitative assessments to demonstrate the quality of our motion style transfer. We also employ interpolation methods to evaluate the generation quality of motion features. Finally, we provide a detailed analysis of various aspects of our approach.
4.1. Dataset
Our method was trained and evaluated using the dataset introduced by Xia et al. [28]. The dataset was partitioned into eight distinct styles and six different content categories for testing purposes, as the training phase does not require labels. Subsequently, we performed downsampling on the original motion sequences, reducing the frame rate from 120 to 30 fps. Finally, to facilitate training, we employed a window size of and a window step of 8 to sample the downsampled motion sequences. This process yielded a total of approximately 1500 clips. The training duration was around 8 h on a single NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti.
In addition, to handle the varying lengths of motion sequences in testing, we opted for the minimum length between the input content and style motion sequences. All experiments were performed using unseen examples that are not included in the training process.
4.2. Comparison
We compared our framework with several state-of-the-art motion style transfer methods [4,6]. All these methods were employed by utilizing publicly available code repositories and default configurations.
Qualitative evaluation. Figure 3 shows the qualitative results obtained from our method as well as the two compared methods. Our approach enhances the exaggeration level of the generated motions. In particular, during the transfer of walking motion, our method demonstrates a greater range of torso and limb movements, closely resembling the desired style. Further supplementary video material can be found at https://github.com/Ask-Yang/Arbitrary-Motion-Style-Transfer-via-Contrastive-Learning, accessed on 10 February 2025.
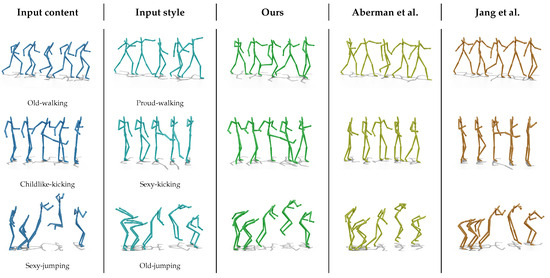
Figure 3.
Comparison between our method, Aberman et al. [4], and Jang et al. [6].
Additionally, our method strives to precisely preserve the content motion while reducing distortions. In the case of jumping motion, the method of Aberman et al. [4] yields wired knee joint angle, while the method of Jang et al. [6] prioritizes aligning the kicking motion with the input style rather than the content motion. In the case of jumping motions, only our method correctly captures the direction of the hand, while other results exhibit certain distortions.
This comparison suggests that our approach proves more effective in expressing the input motion style while retaining essential content information. This expressive ability can be attributed to the contrastive learning employed to capture the difference between the generated motion and other motions. By utilizing contrastive learning, our model not only learns to retain the features of the input motion but also captures significant differences between other motions [37]. For style transfer tasks, learning to distinguish the differences between various categories enhances the model’s understanding of different styles, allowing it to extract key information from the styles more effectively.
Furthermore, by incorporating temporal contrastive learning, the model can decompose the input motion and explicitly compare differences between motion clips at various time scales. This can be viewed from two angles. First, integrating different clips of the same motion allows the model to directly compare these clips and identify their similarities. This helps in extracting essential information for style transfer, which cannot be achieved through direct end-to-end methods. Second, by comparing these randomly selected temporal clips from others, the model’s understanding of styles can be enriched.
Quantitative evaluation. Firstly, we employed the quantitative evaluation approach outlined in Wen et al. [38], which quantifies Content Consistency (CC) as the Euclidean distance between generated and input content motions. In this context, both the input content motion and style motion share the same style (e.g., both are “Proud”), ensuring that the generated motion aligns structurally with the content motion while adopting the target style. Style Consistency (SC) follows a similar methodology, measuring the distance between generated and input style motions when the inputs share the same content. By utilizing these motion comparisons, this approach offers a standardized and reproducible evaluation protocol, effectively assessing the model’s ability to preserve both style and content.
Table 1 shows the result of CC and SC. Aberman et al. [4] shows the highest CC and SC. Jang et al. [6] gives a significant improvement in both of these metrics. Our method further reduces the CC and slightly improves the SC. This result suggests that our method is effectively retaining the content input and produces high-quality stylized motions.

Table 1.
Comparison of Content Consistency (CC) and Style Consistency (SC) to evaluate the performance of our method against other approaches, including results from ablation studies. The symbol “↓” signifies that a lower value is better; the best-performing results are highlighted in bold. The label “(Limited)” denotes that a specific style and content category have been completely removed from the training dataset to assess the model’s generalization performance.
Additionally, we constructed a dataset that completely removes samples with the “childlike” style label and the “punching” content label for training the model, aimed at testing its generalization capability. As shown in Table 1, there is a slight increase in CC, while SC shows a significant increase. This indicates that the model can structurally analyze the content of the input motions and retain relevant details without a significant drop in performance due to unseen labels. However, the model’s ability to preserve style details demonstrates a noticeable degradation. We speculate that this may be partly due to the inherent difficulty in learning styles, combined with the limited variety of style data, which may not provide sufficient generalization capability. Additionally, our use of temporal contrastive learning may have slightly increased the model’s tendency to overfit to existing style.
Secondly, we utilized the spatio-temporal convolution-based recognition model proposed by Yan et al. [39] to train a baseline recognition model on the dataset used in this paper, aimed at monitoring the quality of generated motions. Content Recognition Accuracy (CRA) refers to the accuracy of the generated motions assessed by using a baseline recognition model as a classifier. It measures how effectively the generated motions align with their corresponding content labels. Style Recognition Accuracy (SRA), on the other hand, measures the accuracy of the generated motions in terms of their stylistic alignment. As shown in Table 2, our global style transfer contrastive learning group achieved the highest CRA. However, our final model exhibited the second highest SRA, with a noticeable gap compared to the model proposed by Jang et al. [6]. For content input, our model effectively retained content-related details. However, for style input, our model struggled to accurately generate the corresponding styles. We believe this can be attributed to two main factors: first, the inherent difficulty of learning styles, which requires a wide variety of styles to provide sufficient information; our training dataset (1.5k clips) is significantly smaller than the one used by Jang et al. [6] (120k clips). Second, we did not employ the skeleton-based graph convolution used by Jang et al. [6], which resulted in our model lacking an understanding of the spatial structure of the data. This understanding is crucial for recognition, as the baseline model also relies on spatio-temporal convolution. Overall, these factors contribute to the significant performance gap.

Table 2.
Content Recognition Accuracy (CRA) and Style Recognition Accuracy (SRA) for additional quantitative evaluation. The results from Jang et al. [6] are quoted directly from their original paper. The symbol ”↑”indicates that a higher value is preferable; the best-performing results are highlighted in bold.
4.3. Interpolation
In this experiment, we investigate content and style interpolation. For content interpolation, we utilize a content code that is a linear combination of two target contents, denoted as and . Specifically, we compute as follows:
where is a scalar value in the range [0, 1]. Figure 4 illustrates that, as increases, the direction of the kicking motion gradually aligns with the direction of the stylized motion. This indicates that the direction of the motion content transitions from that of “Childlike-kicking” to a direction closer to “sexy-kicking”.

Figure 4.
Content interpolation. Input content: Childlike-kicking. Input style: Sexy-kicking. represents reconstruction of input style motion.
Regarding style interpolation, we employ a style code that is a linear combination of two target styles, represented by and . Mathematically, is computed as follows:
where is a scalar value in the range [0, 1]. Figure 5 demonstrates that, as increases, there is a noticeable increase in torso and limb movements. This indicates a transition in the motion style from the subtle movements of “Old-walking” to the more pronounced movements of “Proud-walking”.
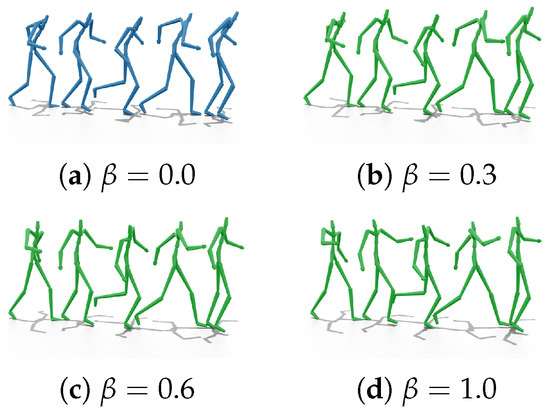
Figure 5.
Style interpolation. Input content: Old-walking. Input style: Proud-walking. represents reconstruction of input content motion.
These two interpolation experiments demonstrate that our framework establishes a flattened manifold in both content and style dimensions for motion style transfer.
4.4. Ablation Study
Cycle loss. Compared to the method proposed by Aberman et al. [4], our model shows a significant decrease in both CC and SC scores, as presented in Table 1. We attribute this improvement to the use of cycle loss, which enhances the model’s ability to retain both the content and style of the input motion during style transfer. Unlike the method of Aberman et al. [4], which directly uses reconstruction loss to enhance the model’s ability to retain the content of the motion, our approach employs cycle loss that leverages the cycle consistency in style transfer [10]. This allows style transfer to operate without relying on paired data, thereby deepening and broadening the model’s perception of the style transfer task. In Table 2, our model, which incorporates reconstruction loss and cyclic consistency loss, achieved a higher CRA than Jang et al. [6]. This improvement may be due to the fact that the 1D convolution is more suitable for smaller datasets like Xia et al. [28].
Contrastive loss. After incorporating contrastive learning for both generation motion and input motion, there is a noticeable decrease in the CC and SC scores. This indicates that the model effectively learns the differences between various motion styles through contrastive learning, enabling it to accurately identify and retain the content and stylistic details of the input motion in the generated motions. In Table 2, the model that incorporates contrastive learning shows an increase in CRA but a decrease in SRA. Considering the decline in CC, this suggests that the enhancement in content retention capability due to contrastive learning enables the model to generate content that more closely exhibits the characteristics of the corresponding content labels.
Temporal contrastive loss. In the experimental group that incorporated temporal contrastive learning, the SC score showed a significant decrease, while the CC score experienced a slight increase. We speculate that this is because the content features are closely related to temporal characteristics, whereas style features can be viewed as second-order statistics of the content features, which are less influenced by time. As a result, the more granular temporal contrastive learning may have caused the model to lose some overall control over the content, leading to a decrease in its ability to retain content. However, the impact on style was minimal, as style is not directly associated with the temporal dimension. Instead, this finer-grained contrastive learning allows the model to decompose the input motion into smaller clips, enabling it to explicitly learn the stylistic characteristics of each part. This approach creates a broader latent space for style features within the model. In Table 2, the model that incorporates temporal contrastive learning shows increases in both CRA and SRA. Considering the decline in SC, this indicates that the enhancement in style retention capability through temporal contrastive learning improves the generation of motions, allowing them to exhibit some characteristics corresponding to the style labels.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
In this work, we propose a novel framework that integrates two contrastive learning strategies into arbitrary motion style transfer. The contrastive learning on style and content enables us to bring generated motions closer to input motions and further away from others. This effectively captures the difference between each styles and content motions, enhancing the model’s ability to retain the input’s content and style. Additionally, the model is able to express the transferred style more distinctly, while retaining certain content details more accurately. Furthermore, contrastive learning on random temporal clips decomposes the input motion, enabling the model to better discern various details within the style and enhancing its ability to preserve the style. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our framework in arbitrary motion style transfer compared to state-of-the-art methods. However, a current limitation is the need for a more optimized method to effectively combine the two contrastive learning losses, as well as how to adapt to larger-scale datasets simultaneously. In the future, we plan to investigate the impact of contrastive learning on style transfer for different body parts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Y. and Z.L.; methodology, Z.Y.; software, Z.Y.; validation, Z.Y. and Z.W.; formal analysis, Z.Y.; investigation, Z.Y. and Z.L.; resources, Z.W.; data curation, Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. and Y.L.; visualization, Z.Y.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, Z.L.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province grant (2023AFB572) and Hubei Key Laboratory of Intelligent Geo-Information Processing (KLIGIP-2022-B10).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The article contains all original contributions of the study. For further inquiries, please contact the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yumer, M.E.; Mitra, N.J. Spectral style transfer for human motion between independent actions. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2016, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, D.; Saito, J.; Komura, T. A deep learning framework for character motion synthesis and editing. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2016, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, A.; Slock, D.T.; Meilhac, L. A Newton-type Forward Backward Greedy method for multi-snapshot compressed sensing. In Proceedings of the 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1178–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Aberman, K.; Weng, Y.; Lischinski, D.; Cohen-Or, D.; Chen, B. Unpaired motion style transfer from video to animation. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2020, 39, 64:1–64:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jang, D.K.; Lee, S.H. Diverse motion stylization for multiple style domains via spatial-temporal graph-based generative model. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2021, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.K.; Park, S.; Lee, S.H. Motion puzzle: Arbitrary motion style transfer by body part. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2022, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2414–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, Proceedings of the 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016, Proceedings, Part II 14; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1501–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.; Kim, S.; Lin, Y.; Yoo, S.; Cha, J. AesFA: An Aesthetic Feature-Aware Arbitrary Neural Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 13310–13319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Han, K.; Wei, X.S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Contrastive learning based hybrid networks for long-tailed image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 943–952. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Cao, P.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.; Feris, R.S.; Indyk, P.; Katabi, D. Targeted supervised contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6918–6928. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z. Emotion-oriented Cross-modal Prompting and Alignment for Human-centric Emotional Video Captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yin, G.; Wei, L.; Chen, Z. Noise-resistant multimodal transformer for emotion recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, S.; Liu, S.; Zhan, Y.; Tao, D.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Sample-Cohesive Pose-Aware Contrastive Facial Representation Learning. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Efros, A.A.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J.Y. Contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Proceedings of the 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020, Proceedings, Part IX 16; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 319–345. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Du, J.; Bai, X. CCPL: Contrastive coherence preserving loss for versatile style transfer. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Lan, T.; Wang, Y.; Yogatama, D.; Kong, L.; Collier, N. A contrastive framework for neural text generation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 21548–21561. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.B.; Hwang, S.J. Contrastive learning with adversarial perturbations for conditional text generation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.07280. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Chakraborty, O.; Varshney, A.; Panda, R.; Feris, R.; Saenko, K.; Das, A. Semi-supervised action recognition with temporal contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10389–10399. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, J.; Yue, H.; Xu, P.; Hu, R.; Chai, H. Spatio-temporal contrastive domain adaptation for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9787–9795. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Li, A.; Xing, W.; Lu, D. Artistic style transfer with internal-external learning and contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 26561–26573. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, F.; Dong, W.; Huang, H.; Ma, C.; Lee, T.Y.; Xu, C. Domain enhanced arbitrary image style transfer via contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference Proceedings, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–11 August 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, F.; Dong, W.; Huang, H.; Ma, C.; Lee, T.Y.; Xu, C. A unified arbitrary style transfer framework via adaptive contrastive learning. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, E.; Pulli, K.; Popović, J. Style translation for human motion. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1082–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto, L.; Arikan, O.; Forsyth, D. Generalizing motion edits with gaussian processes. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2009, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wang, C.; Chai, J.; Hodgins, J. Realtime style transfer for unlabeled heterogeneous human motion. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2015, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, D.; Habibie, I.; Kusajima, I.; Komura, T. Fast neural style transfer for motion data. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2017, 37, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Herrmann, E.; Sprenger, J.; Cheema, N.; Hosseini, S.; Fischer, K.; Slusallek, P. Stylistic Locomotion Modeling with Conditional Variational Autoencoder. In Proceedings of the Eurographics (Short Papers), Genoa, Italy, 6–10 May 2019; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Zhan, X.; Chen, Z.; van de Panne, M. Style-ERD: Responsive and coherent online motion style transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6593–6603. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, I.; Starke, S.; Komura, T. Real-time style modelling of human locomotion via feature-wise transformations and local motion phases. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2022, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, B.; Gong, X.; Yi, R.; Kou, Q.; Jin, X. Real-time controllable motion transition for characters. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2022, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jin, X.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Hao, A.; Hou, X.; Li, N.; Qin, H. Arbitrary Motion Style Transfer with Multi-condition Motion Latent Diffusion Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 821–830. [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.08022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, S.X.; Lin, D. Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3733–3742. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.H.; Yang, Z.; Fu, H.; Gao, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.J. Autoregressive stylized motion synthesis with generative flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13612–13621. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).