Magnesium Dross and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Utilisation for Phosphate Elimination from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
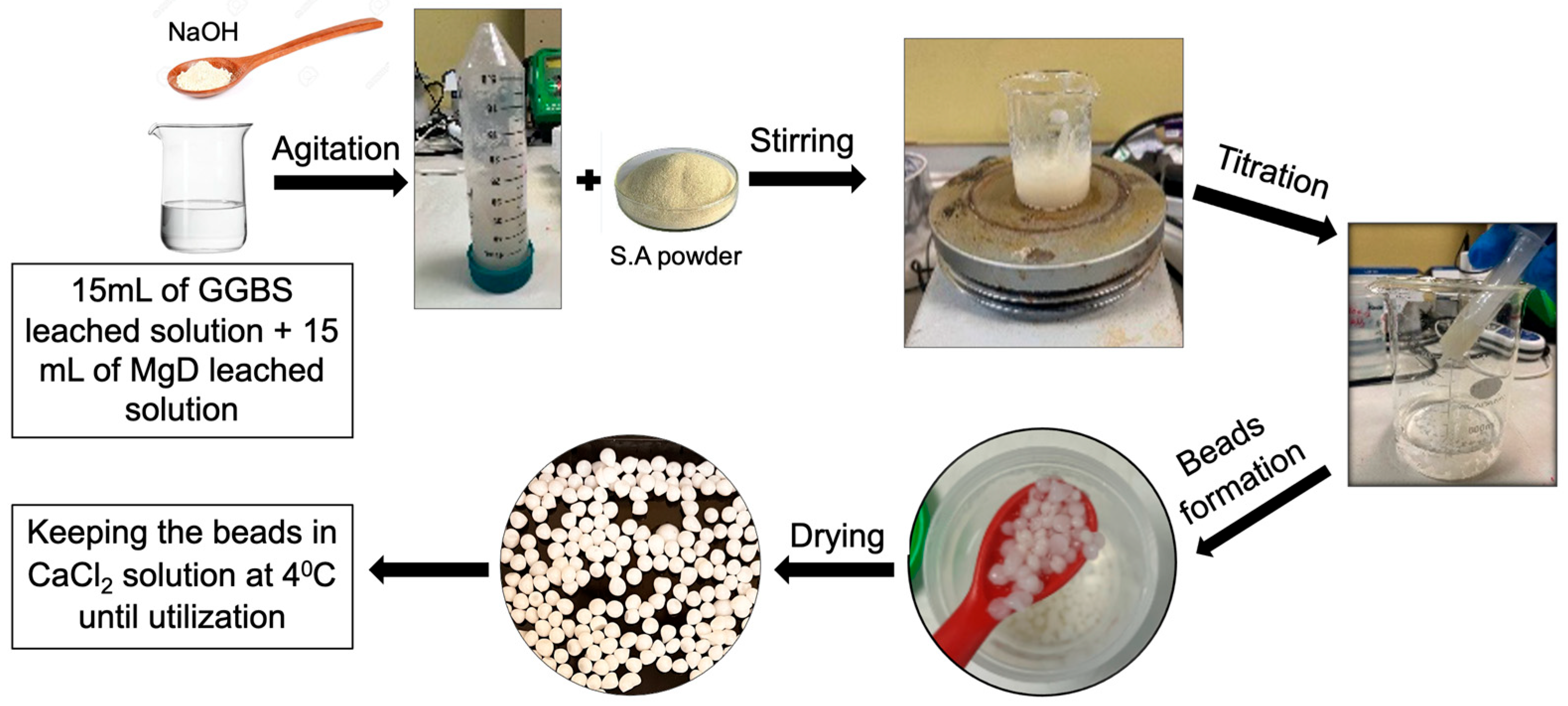
2.2. Preparation of the Adsorbent
2.2.1. Extraction Process
2.2.2. Immobilisation of Ions on Sodium Alginate and Bead Formation
2.3. Batch Adsorption Methodology
2.4. Adsorbent Characterisation Methods
2.5. Isotherms and Kinetic Models
2.5.1. Equilibrium Isotherm Models
2.5.2. Adsorption Kinetics Models
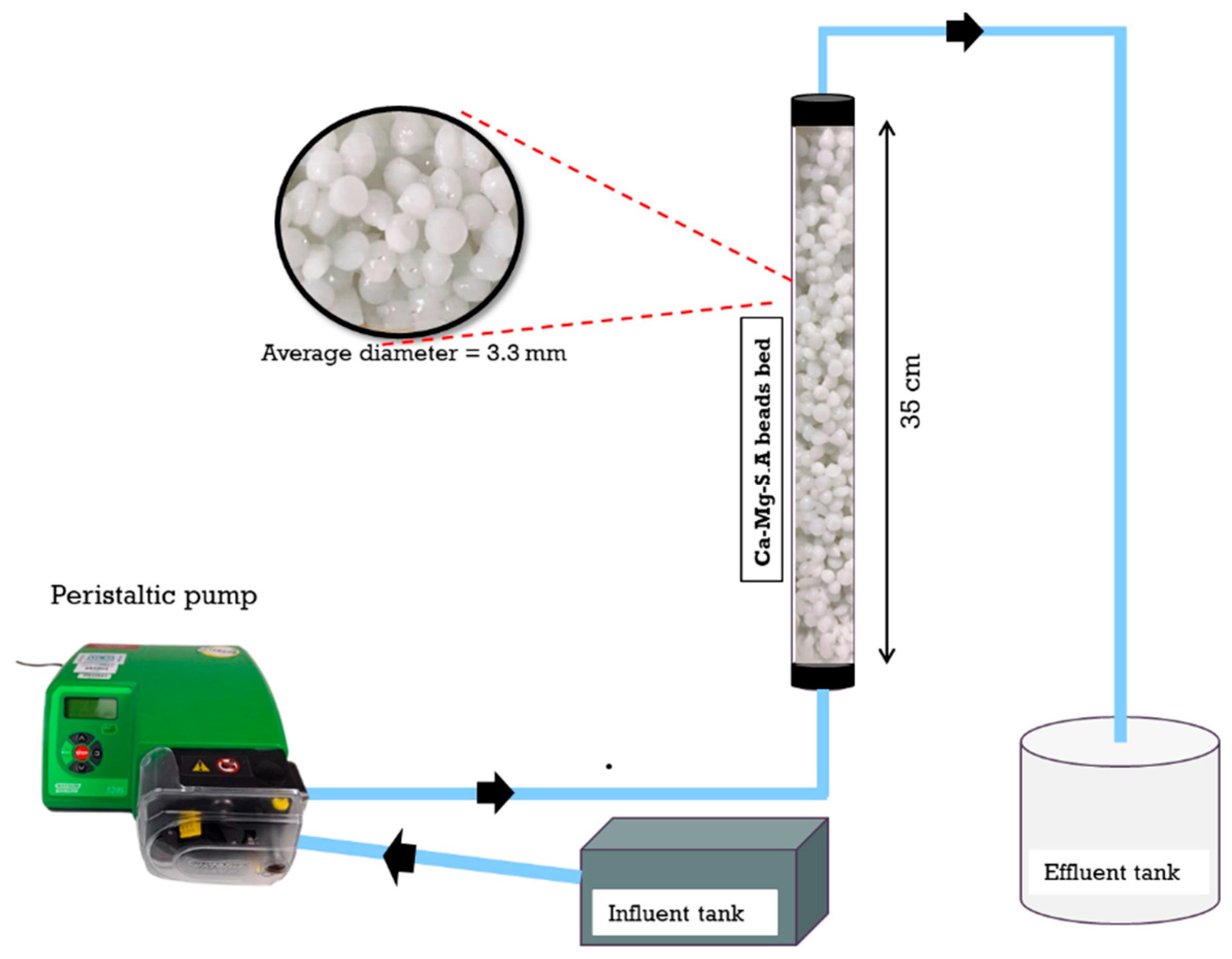
2.6. Column Experiments (Continuous Flow)
2.7. Biodegradability of the Adsorbent
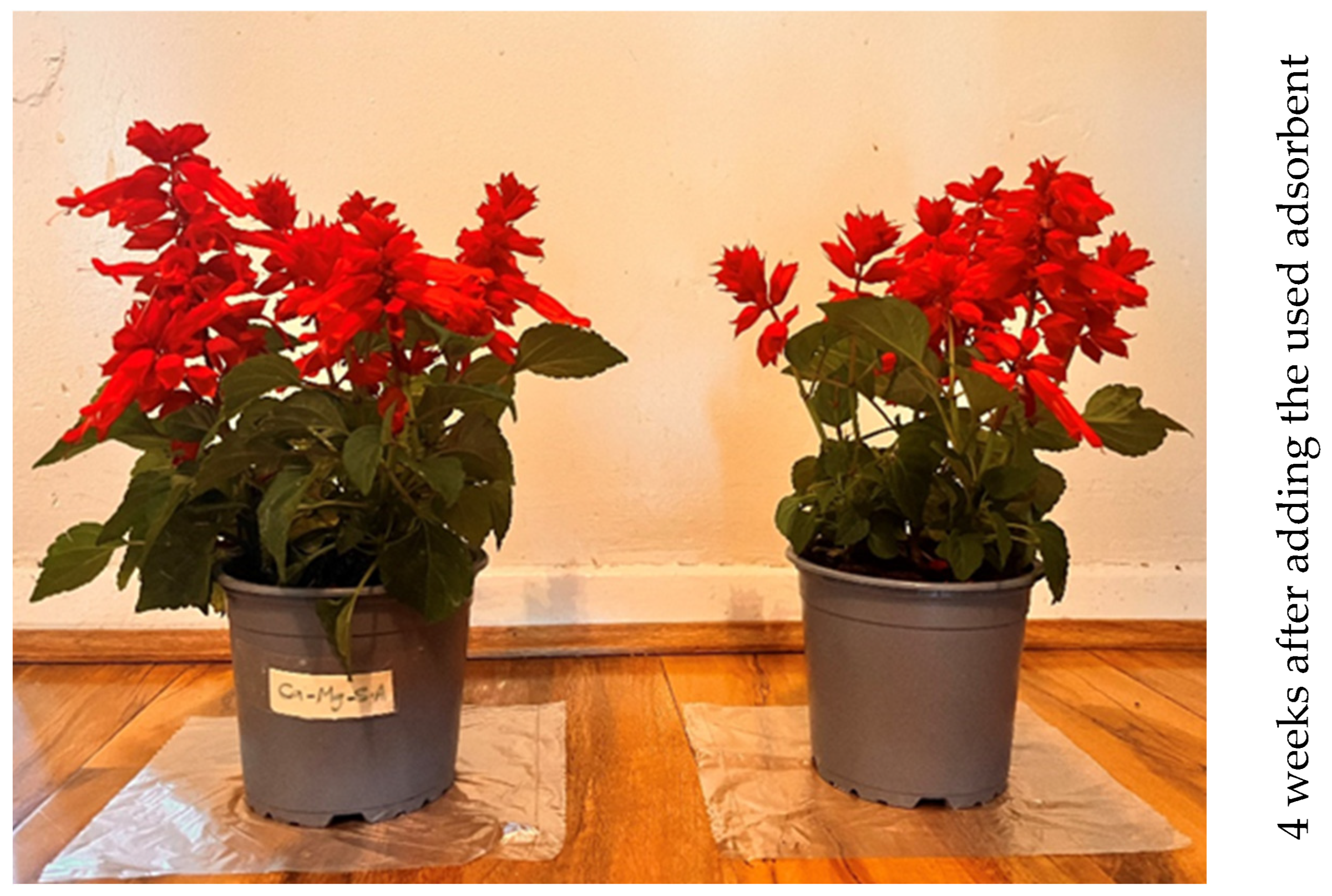
2.8. Recycling the Adsorbent as a Fertiliser
3. Results
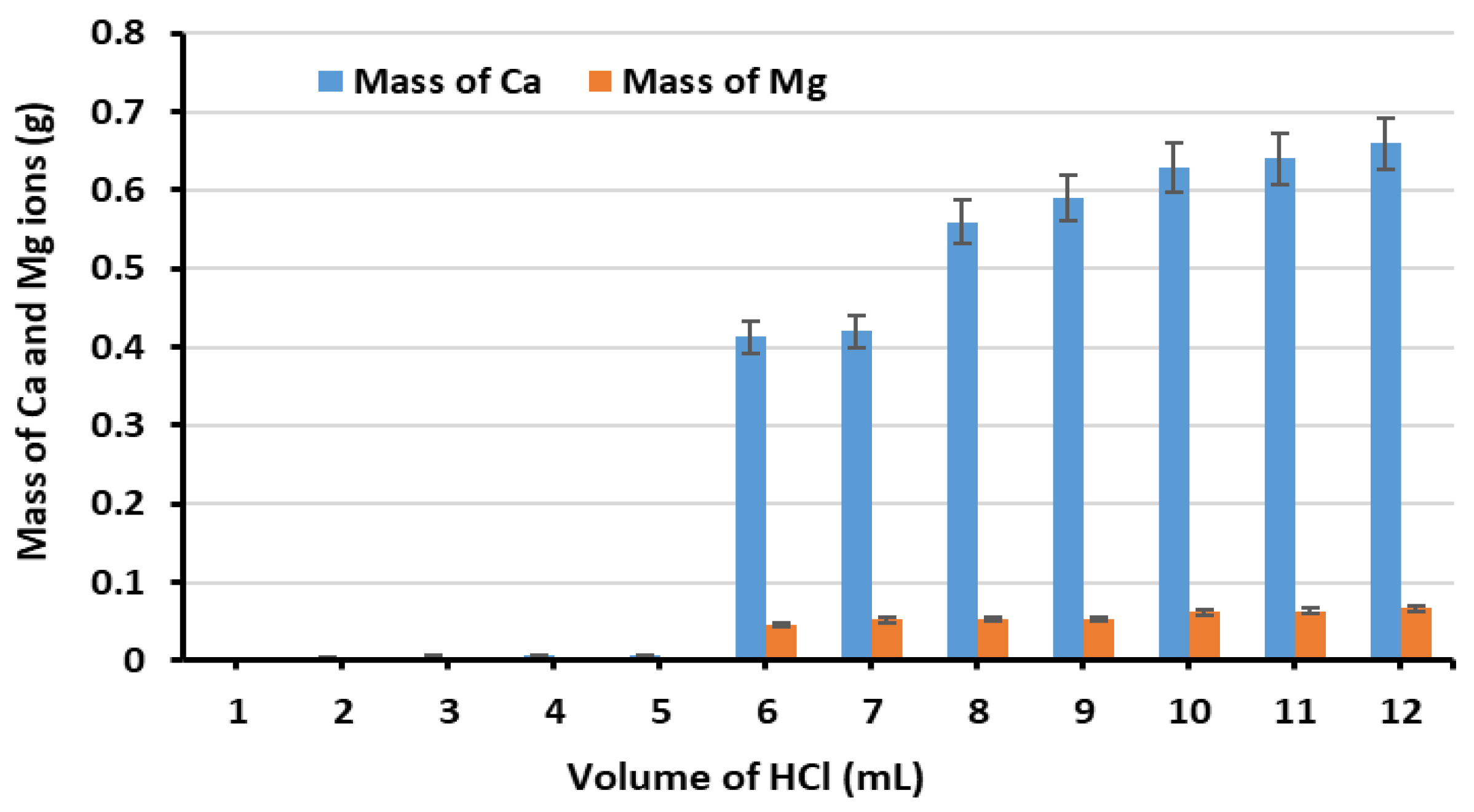
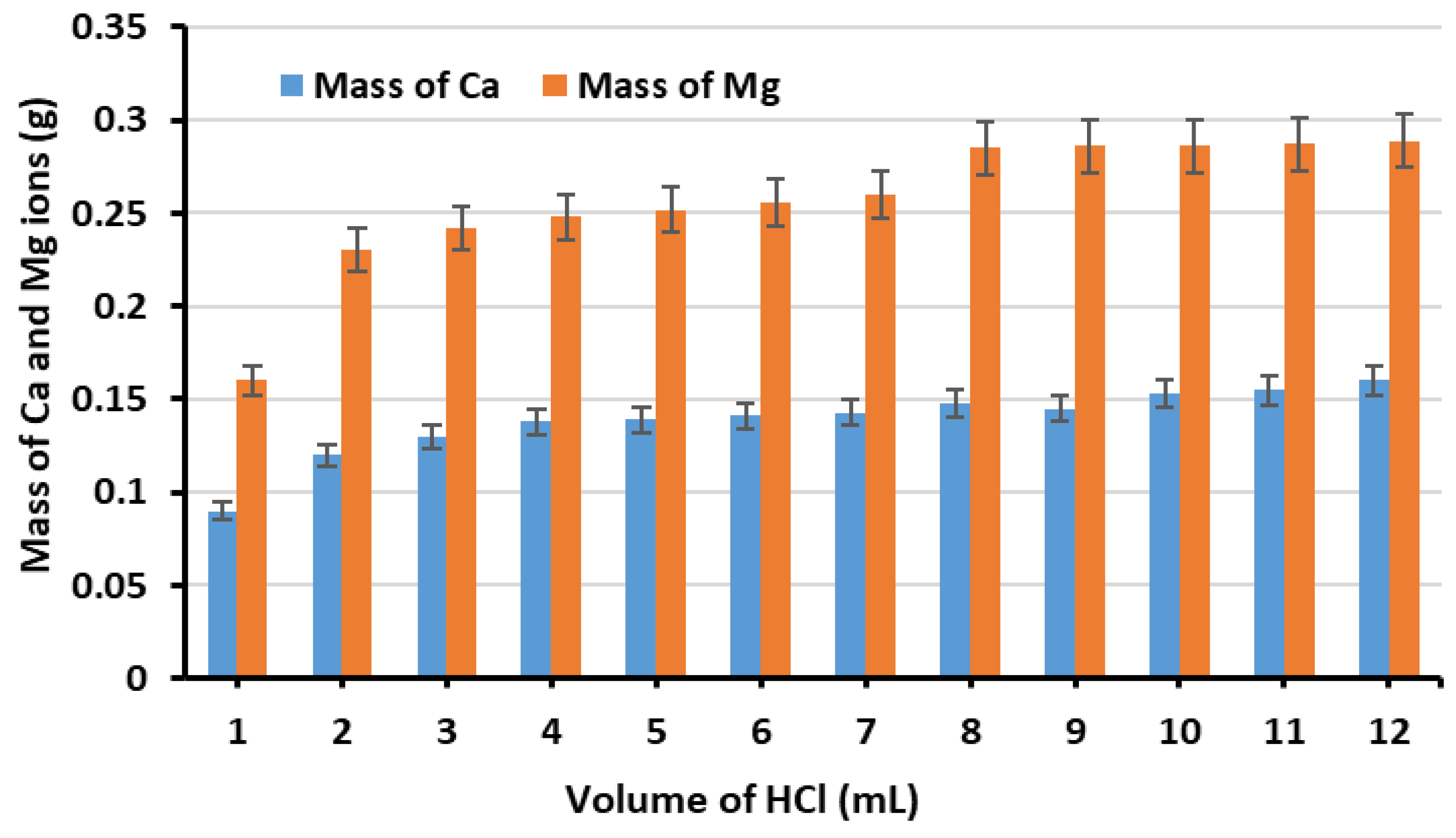
3.1. Ion Extraction Process
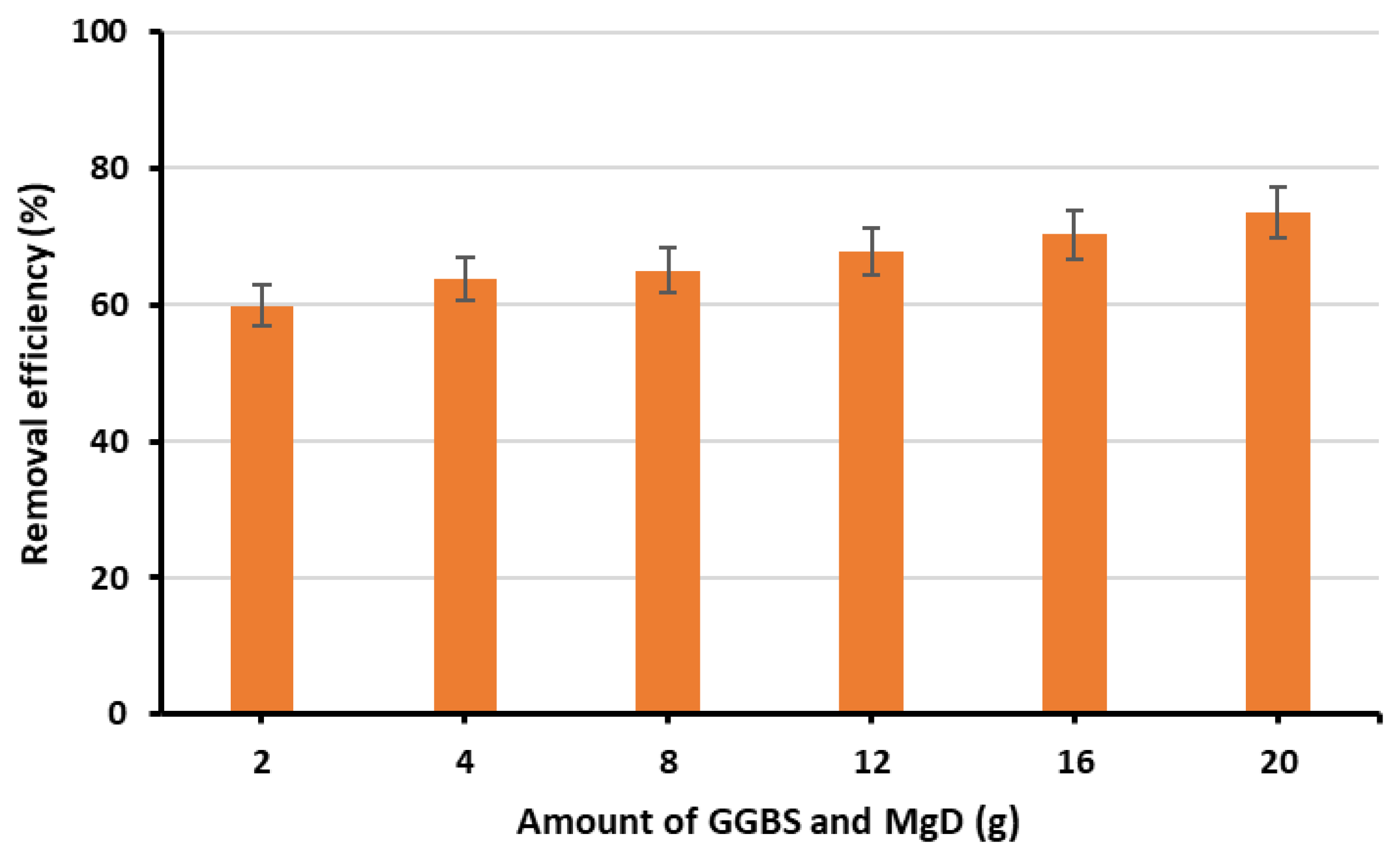
3.2. Optimisation of GGBS and MgD Loading Percentage
3.3. Batch Adsorption Performance
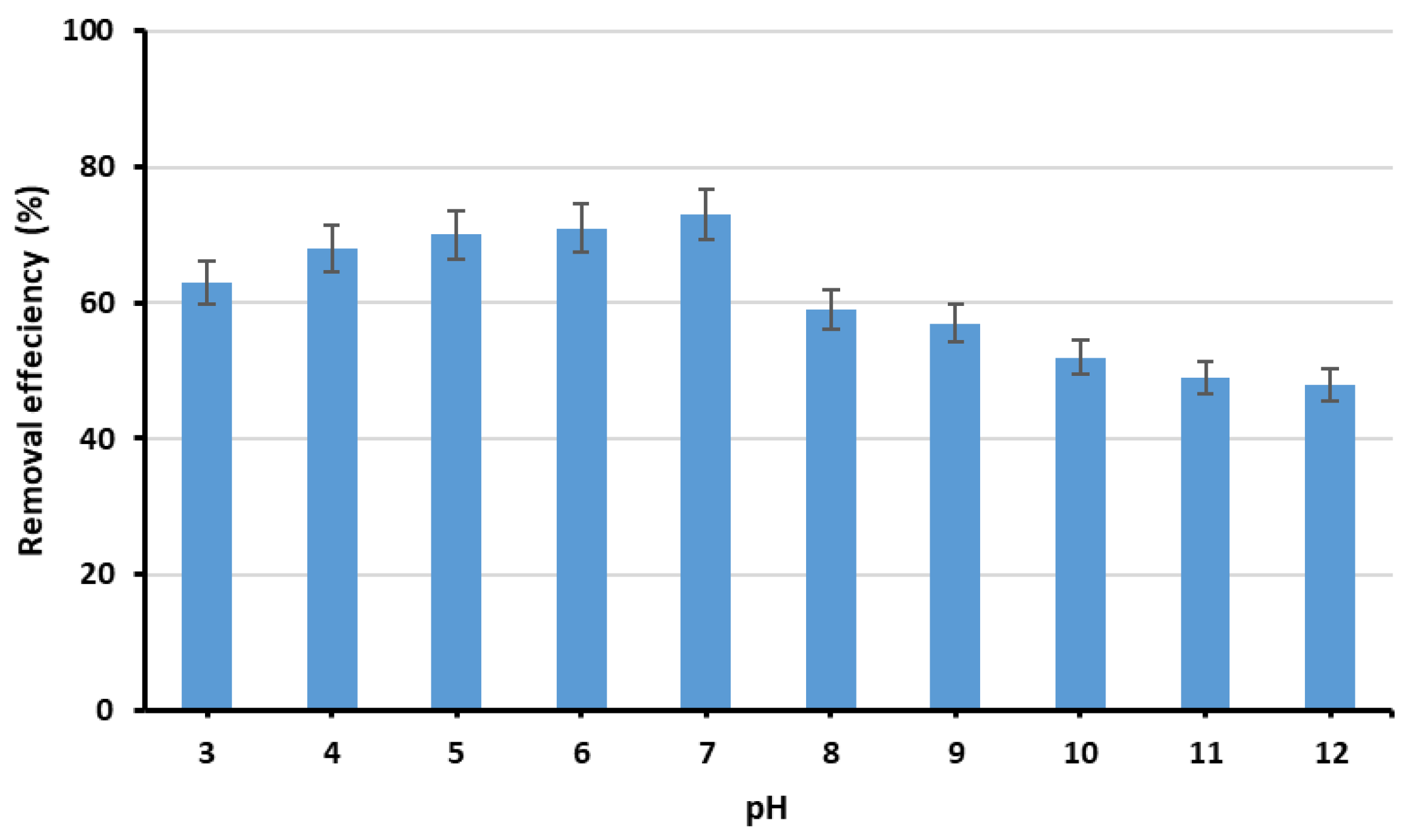
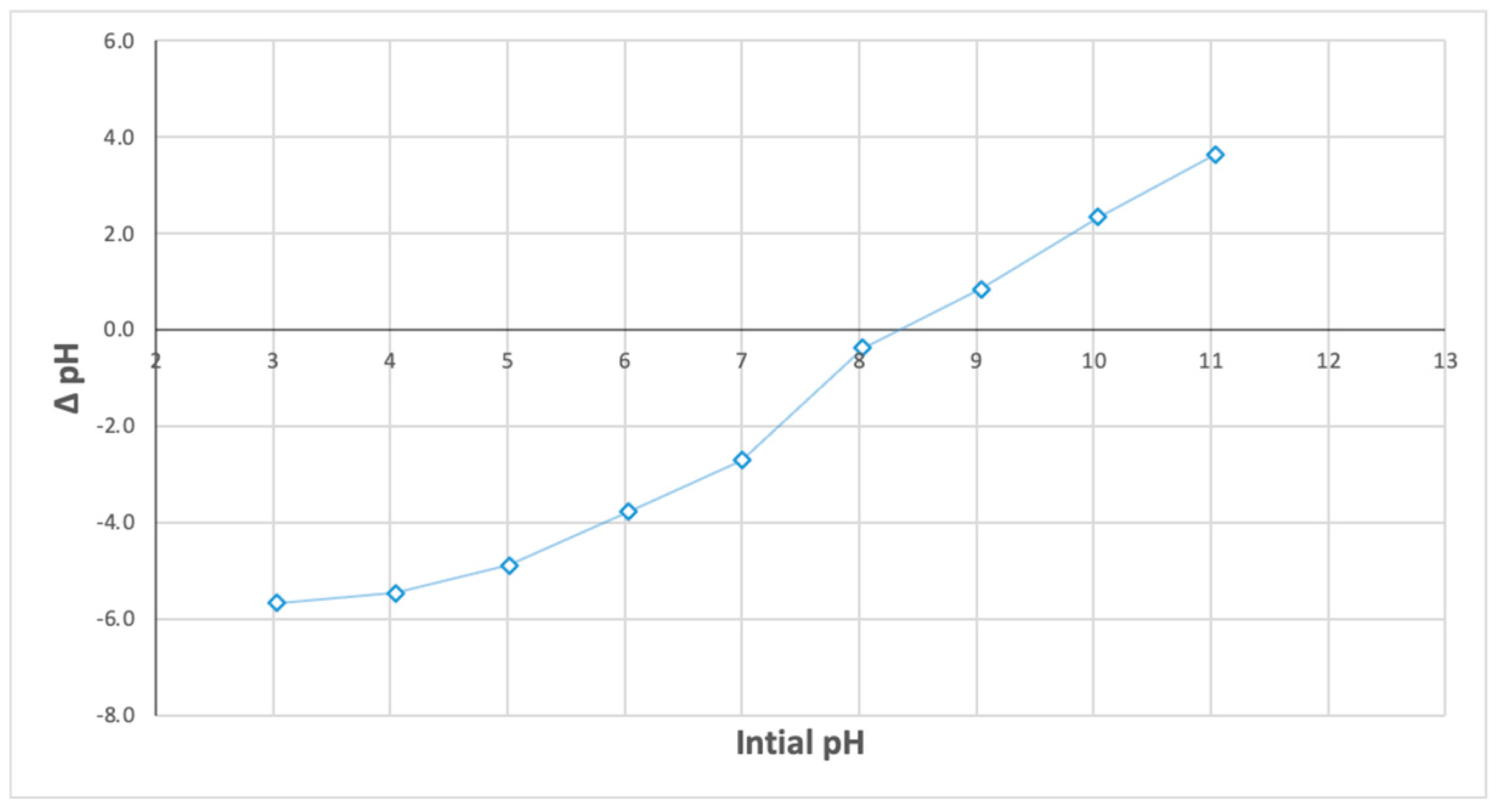
3.3.1. Effect of the Initial pH
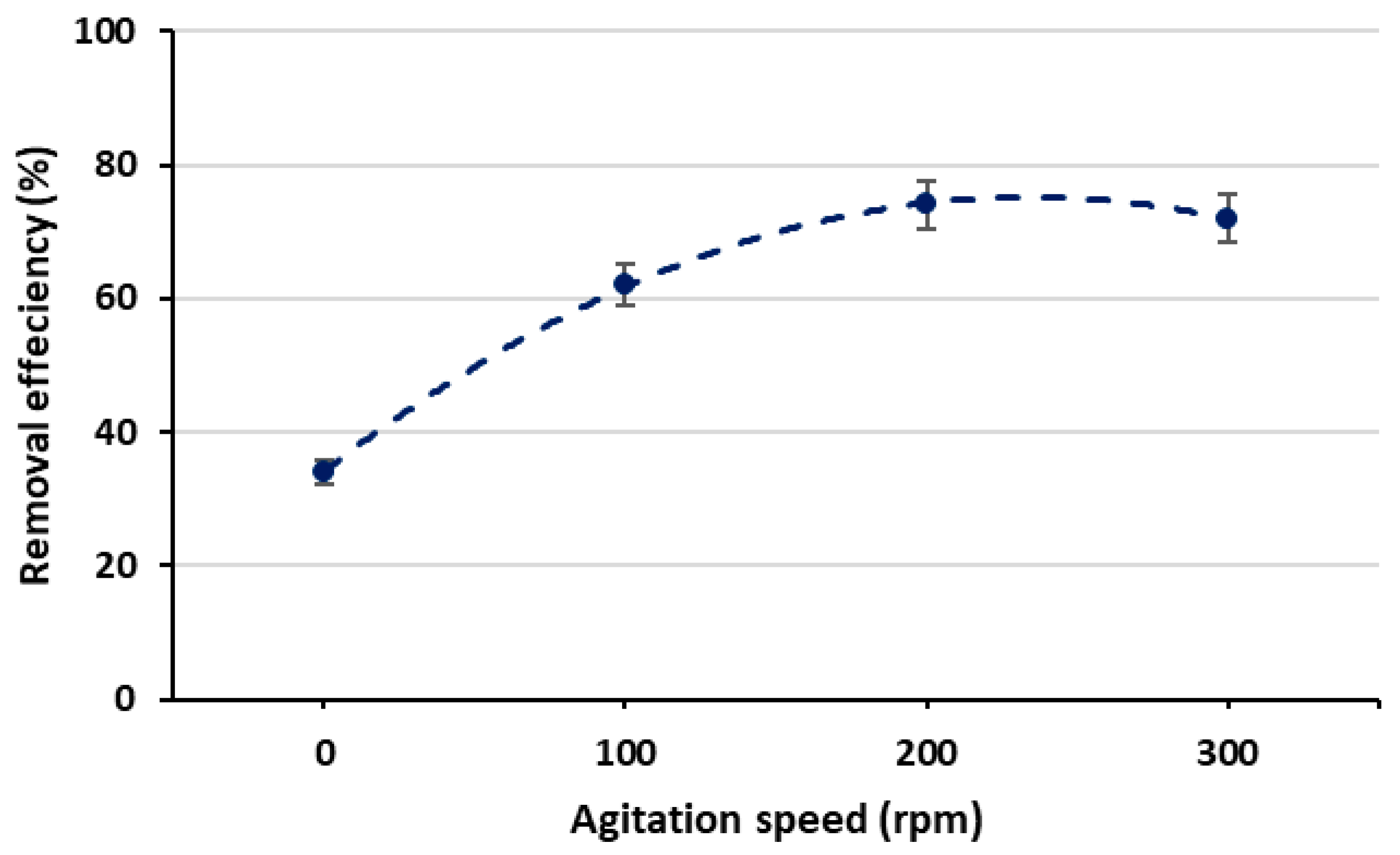
3.3.2. Effect of Agitation Speed
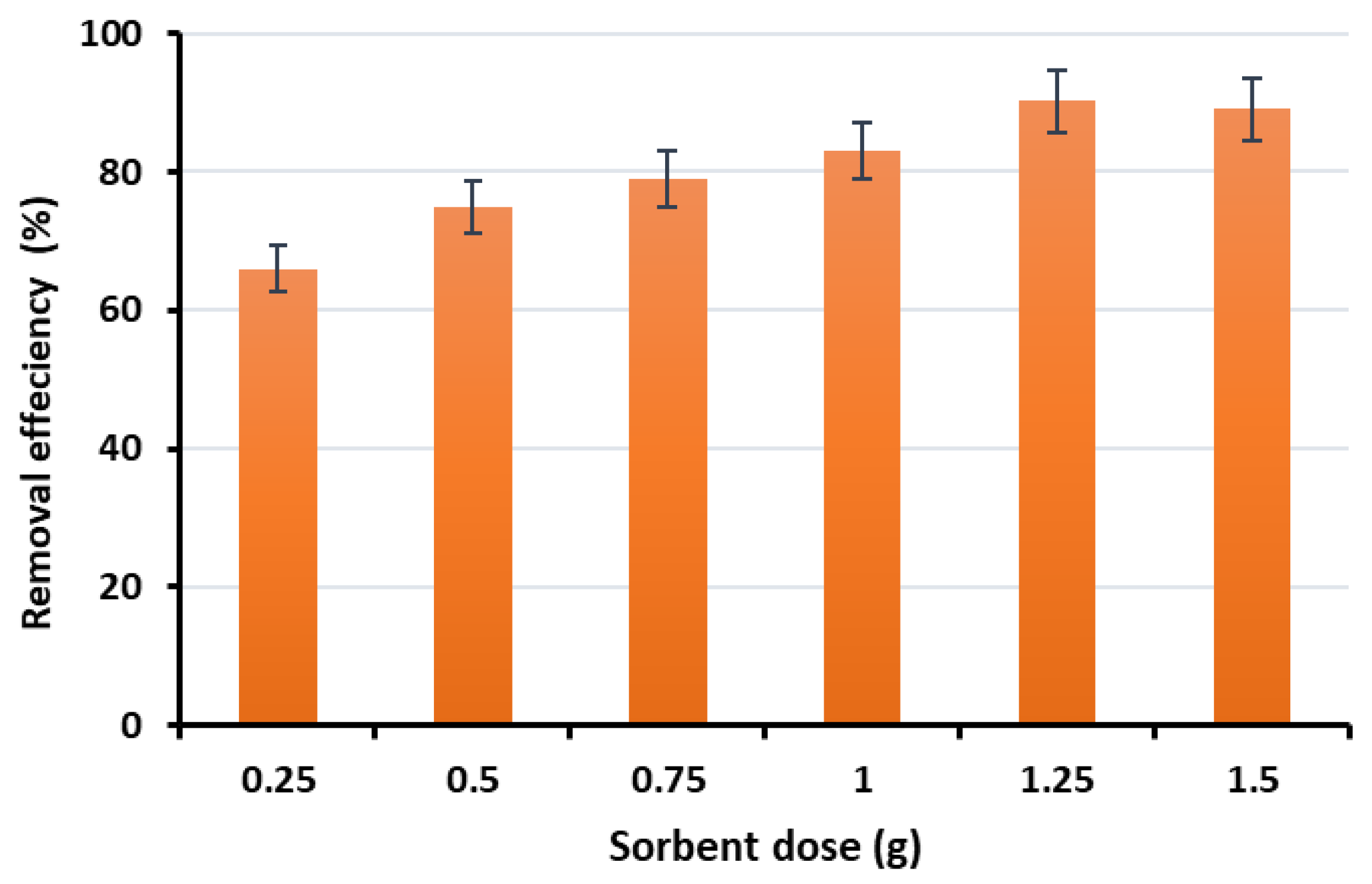
3.3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
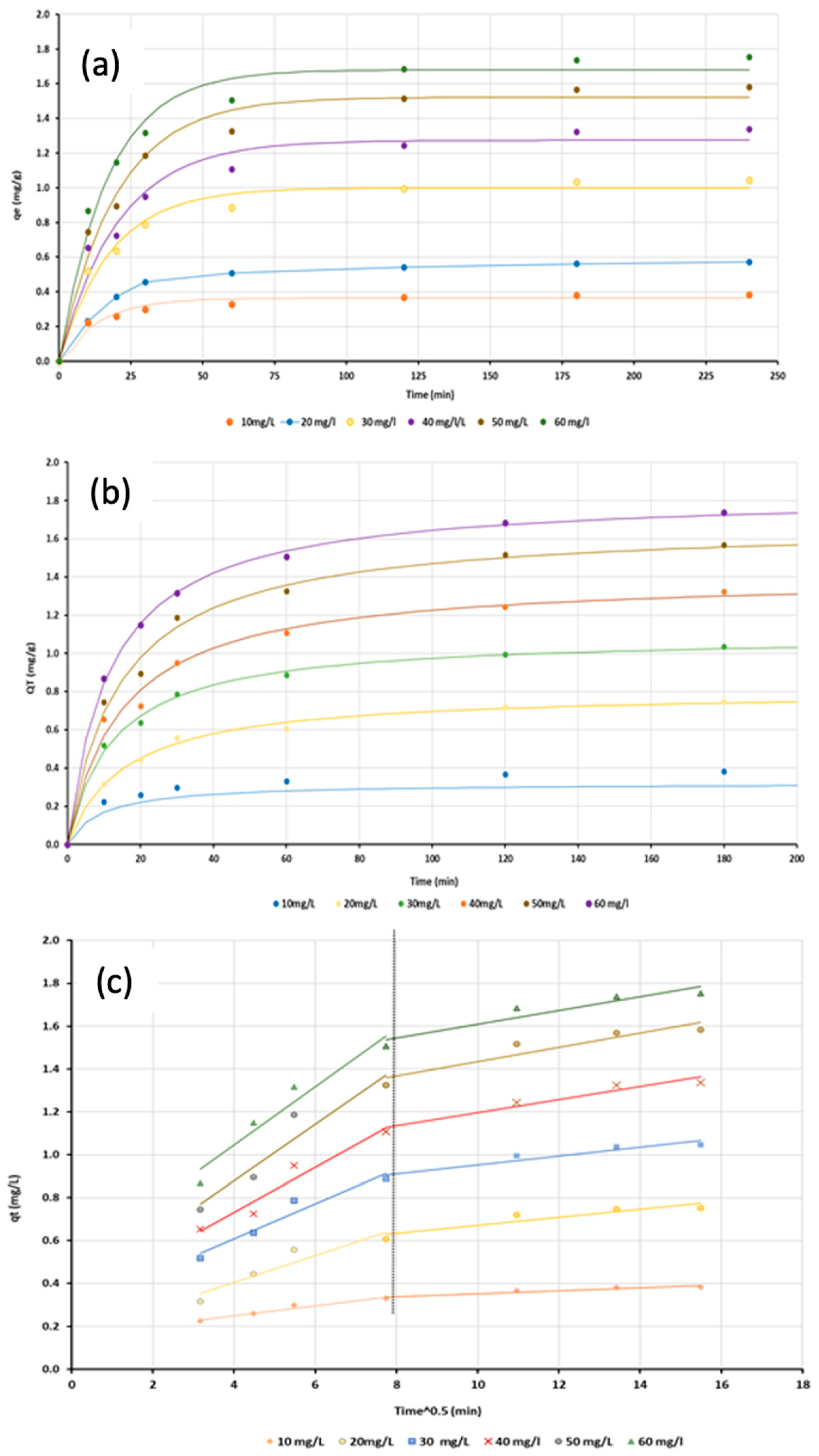
3.3.4. Effect of Contact Time
3.4. Characterisation of the Adsorbent
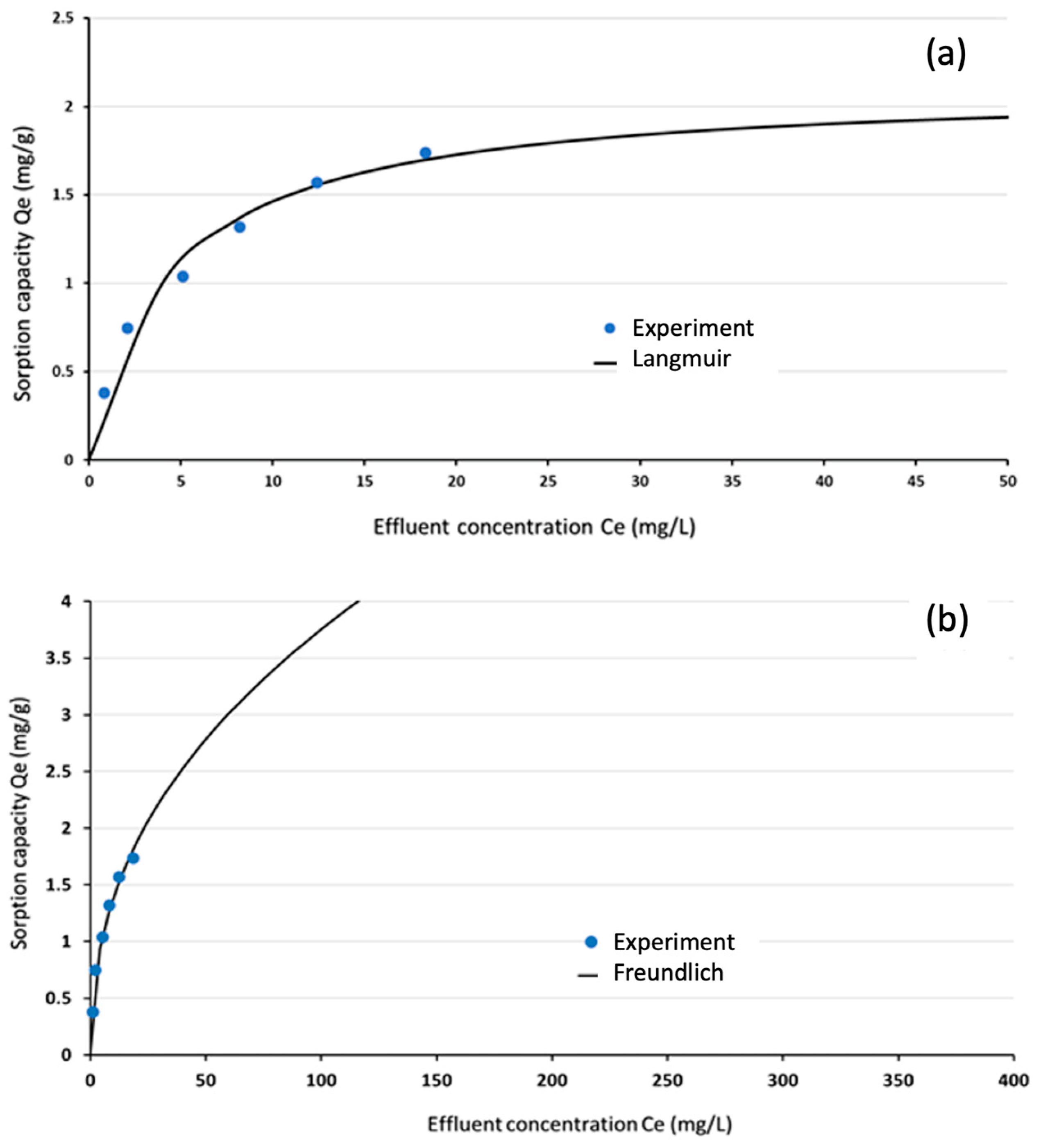
3.5. Equilibrium Isotherm Analysis
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
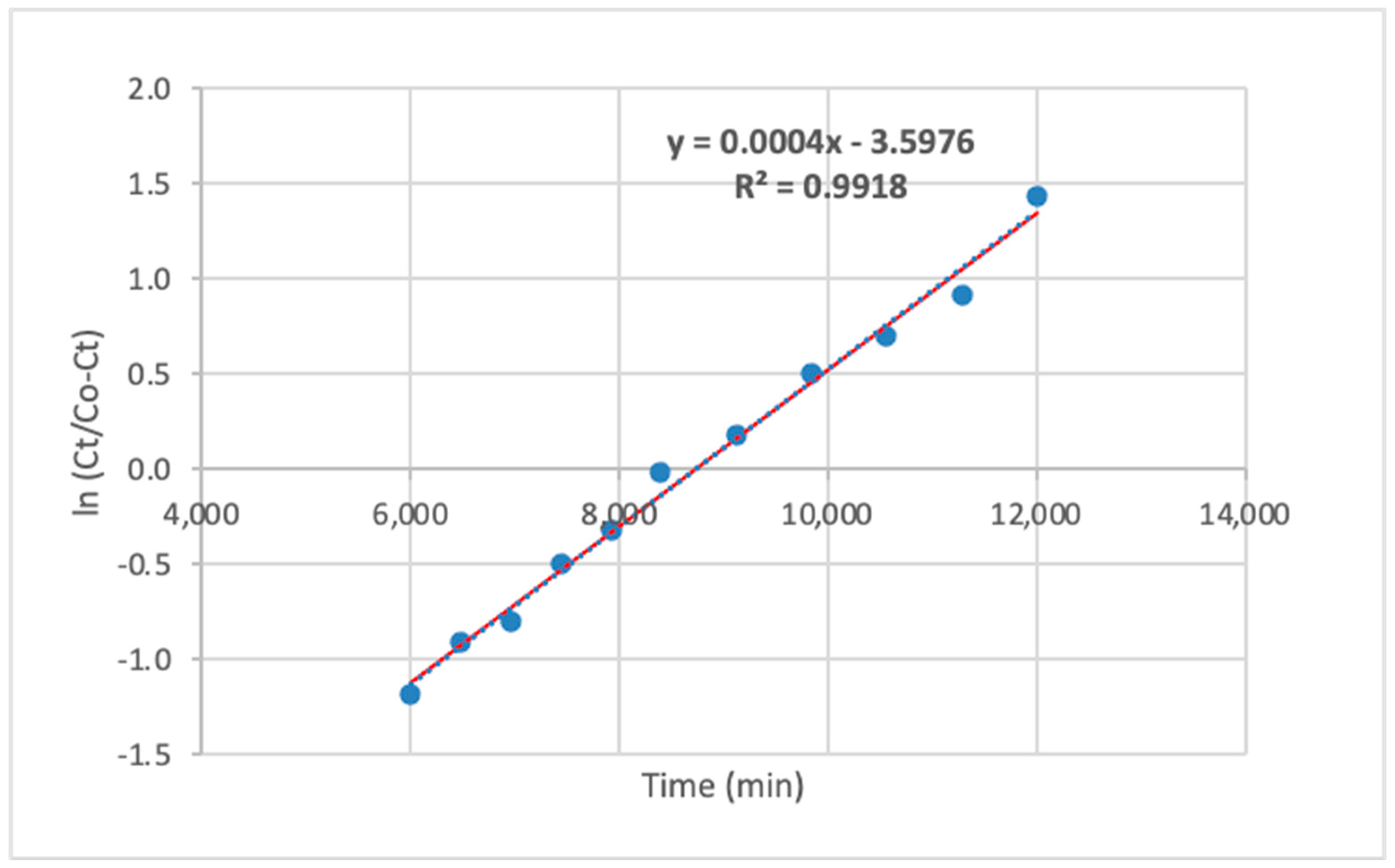
3.7. Mechanisms of Adsorption
3.8. Column Experiments
3.9. Biodegradability of Adsorbent
3.10. Recycling the Adsorbent as a Soil Fertiliser
3.11. Comparison with Previous Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saifuddin, M.; Bae, J.; Kim, K.S. Role of Fe, Na and Al in Fe-Zeolite-A for adsorption and desorption of phosphate from aqueous solution. Water Res. 2019, 158, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalou, I.; Papastergiadou, E.; Leonardos, I. Long term changes in the eutrophication process in a shallow Mediterranean lake ecosystem of W. Greece: Response after the reduction of external load. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Tanaka, M. Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: A review and synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 624–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Mckay, G.; Kochkodan, V.; Atieh, M.A.; Al-Ansari, T. A state of the art review on phosphate removal from water by biochars. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez Pasarín, M. Phosphate Adsorption onto Laterite and Laterite Waste from a Leaching Process. Master’s Thesis, Queen’s University Belfast, Belfast, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, K.S.; Ewadh, H.M.; Muhsin, A.A.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Kot, P.; Muradov, M.; Aljefery, M.; Al-Khaddar, R. Phosphate removal from water using bottom ash: Adsorption performance, coexisting anions and modelling studies. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzeyadi, A. An Experimental Investigation Into the Efficiency of Filter Materials for Phosphate Removal from Wastewater. Ph.D. Thesis, Liverpool John Moores University (United Kingdom), Liverpool, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al Tahmazi, T. Characteristics and Mechanisms of Phosphorus Removal by Dewatered Water Treatment Sludges and the Recovery. Ph.D. Thesis, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alwash, R. Treatment of Highly Polluted Water with Phosphate Using BAPPP-Nanoparticles. Master’s Thesis, University of Technology Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, K. Phosphate removal performance and mechanism of zirconium-doped magnetic gasification slag. Arab. J. Chem. 2025, 18, 106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Gao, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of magnesium-modified steel slag and its adsorption performance for simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 702, 135068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malektaj, H.; Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Mechanical properties of alginate hydrogels cross-linked with multivalent cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhao, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X. Efficient low-concentration phosphate removal from sub-healthy surface water by adsorbent prepared based on functional complementary strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.F.; Faisal, A.A. Calcium/iron-layered double hydroxides-sodium alginate for removal of tetracycline antibiotic from aqueous solution. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 63, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheju, M.; Miulescu, A. Sorption equilibrium of hexavalent chromium on granular activated carbon. Chem. Bull. Politech. Univ. 2007, 52, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Comparisons of porous and adsorption properties of carbons activated by steam and KOH. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, B.M.; Hua, G.; Ahiablame, L.M. Fixed bed column evaluation of phosphate adsorption and recovery from aqueous solutions using recycled steel byproducts. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, F.B.; Mayer, B.K. Fixed-bed column study of phosphate adsorption using immobilized phosphate-binding protein. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication of ceramsite adsorbent from industrial wastes for the removal of phosphorus from aqueous solutions. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8036961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Arim, A.L.; Lopes, D.V.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M.; Quina, M.J. Recovery of phosphate from aqueous solutions using calcined eggshell as an eco-friendly adsorbent. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, Y.; Srivastava, P.; Tripathy, B.C.; Dhal, N.K.; Martinez, F.; Kumar, N.; Yadav, A.K. Aluminium dross waste utilization for phosphate removal and recovery from aqueous environment: Operational feasibility development. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, Z.; Nasir, S.; Jamil, N.; Sheikh, A.; Akram, A. Adsorption studies of phosphate ions on alginate-calcium carbonate composite beads. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; He, Z.; Mahmood, Q.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Islam, E. Phosphate removal from solution using steel slag through magnetic separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, H. Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate by zeolite synthesized from fly ash as influenced by salt treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; Rudolph, V.; Haghseresht, F. Phosphate removal from wastewater using red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kwon, H.; Jeon, H.; Koopman, B. A new recycling material for removing phosphorus from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajima, T.; Haga, M.; Kuzawa, K.; Ishimoto, H.; Tamada, O.; Ito, K.; Nishiyama, T.; Downs, R.T.; Rakovan, J.F. Zeolite synthesis from paper sludge ash at low temperature (90 °C) with addition of diatomite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 132, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.A.; Viswanathan, N. Development of multivalent metal ions imprinted chitosan biocomposites for phosphate sorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Ding, X. Using recycled concrete as an adsorbent to remove phosphate from polluted water. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Mahmood, Q. Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous media by peat. Desalination 2010, 259, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, X.; Ye, X.; Niu, X.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M.; Zhou, S. Adsorption recovery of phosphate from waste streams by Ca/Mg-biochar synthesis from marble waste, calcium-rich sepiolite and bagasse. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhuo, G.; Xue, D.; Zhu, G.; Wang, C.-Y. Sustainable Phosphate Recovery Using Novel Ca–Mg Bimetallic Modified Biogas Residue-Based Biochar. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H.; Guo, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, W. Cost-effective and eco-friendly superadsorbent derived from natural calcium-rich clay for ultra-efficient phosphate removal in diverse waters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo-Velasco, L.; Hernández-Montoya, V.; Rangel-Vázquez, N.A.; Cervantes, F.J.; Montes-Morán, M.A.; del Rosario Moreno-Virgen, M. Screening of commercial sorbents for the removal of phosphates from water and modeling by molecular simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 262, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, S.M. Phosphate removal from aqueous solution using slag and fly ash. HBRC J. 2013, 9, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Preparation and controlled degradation of oxidized sodium alginate hydrogel. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-U.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, J.-A.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.-B. Immobilization of layered double hydroxide into polyvinyl alcohol/alginate hydrogel beads for phosphate removal. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 17, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hemmamı, H.; Amor, I.B.; Amor, A.B.; Zeghoud, S.; Ahmed, S.; Alhamad, A.A. Chitosan, its derivatives, sources, preparation methods, and applications: A review. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2024, 11, 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



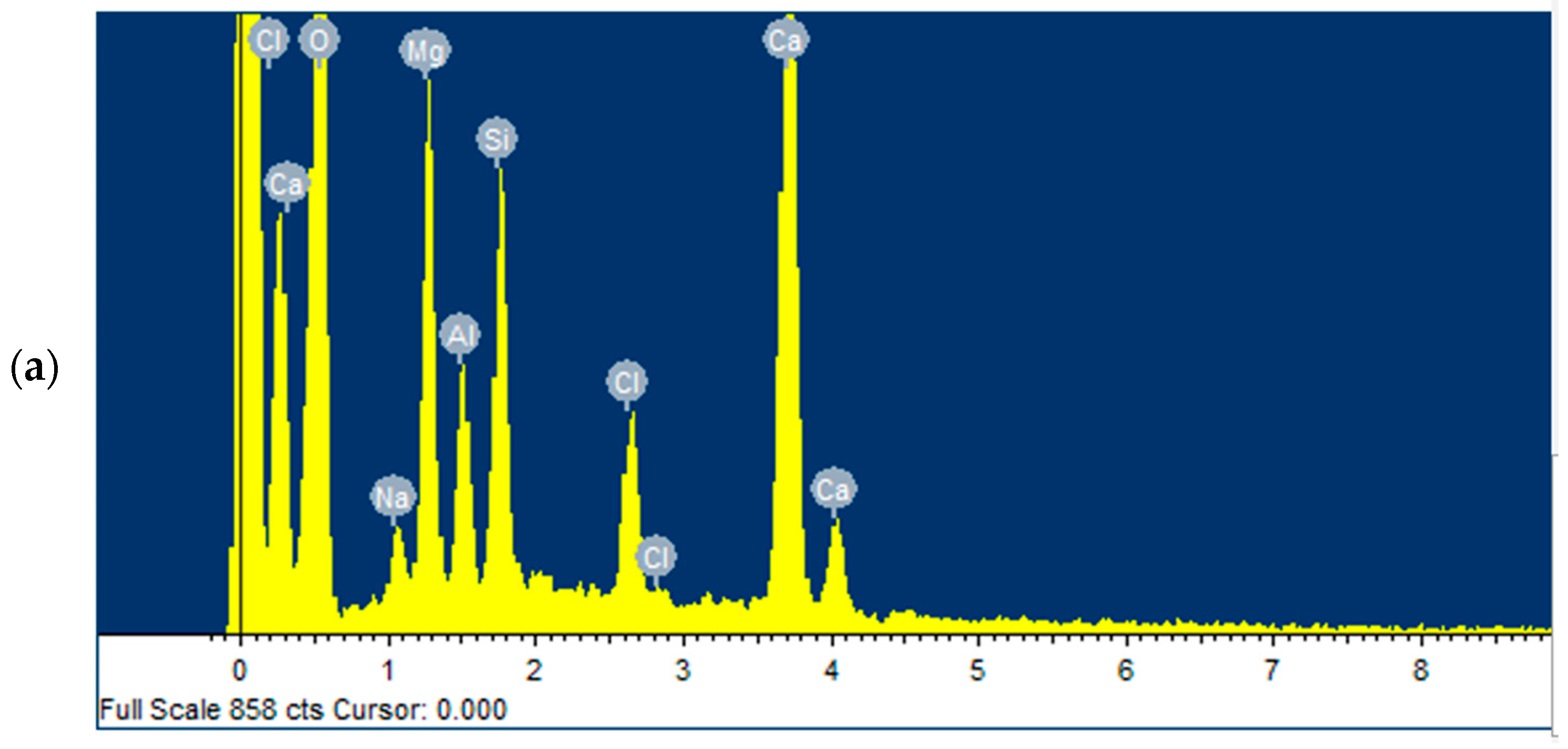
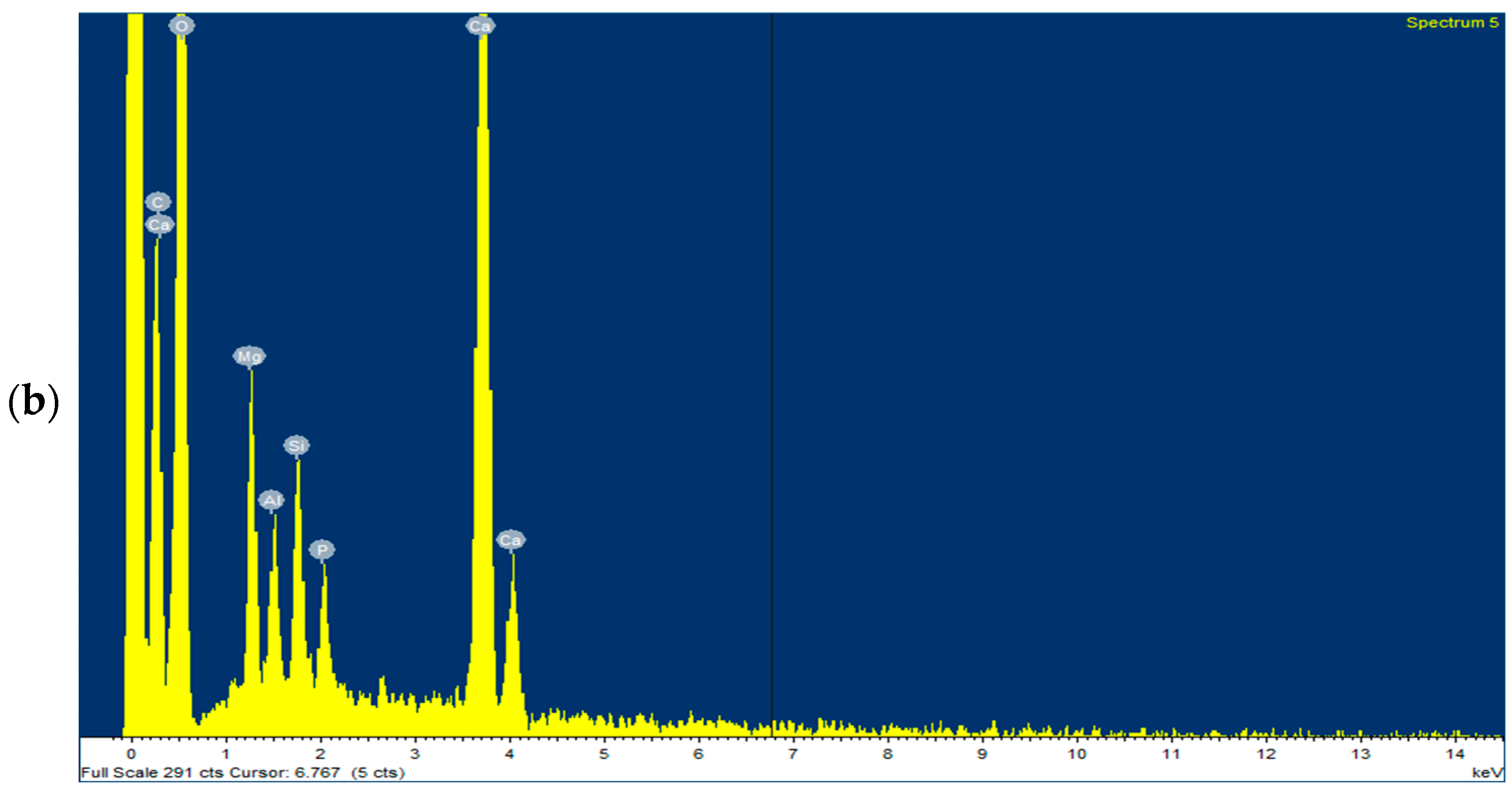

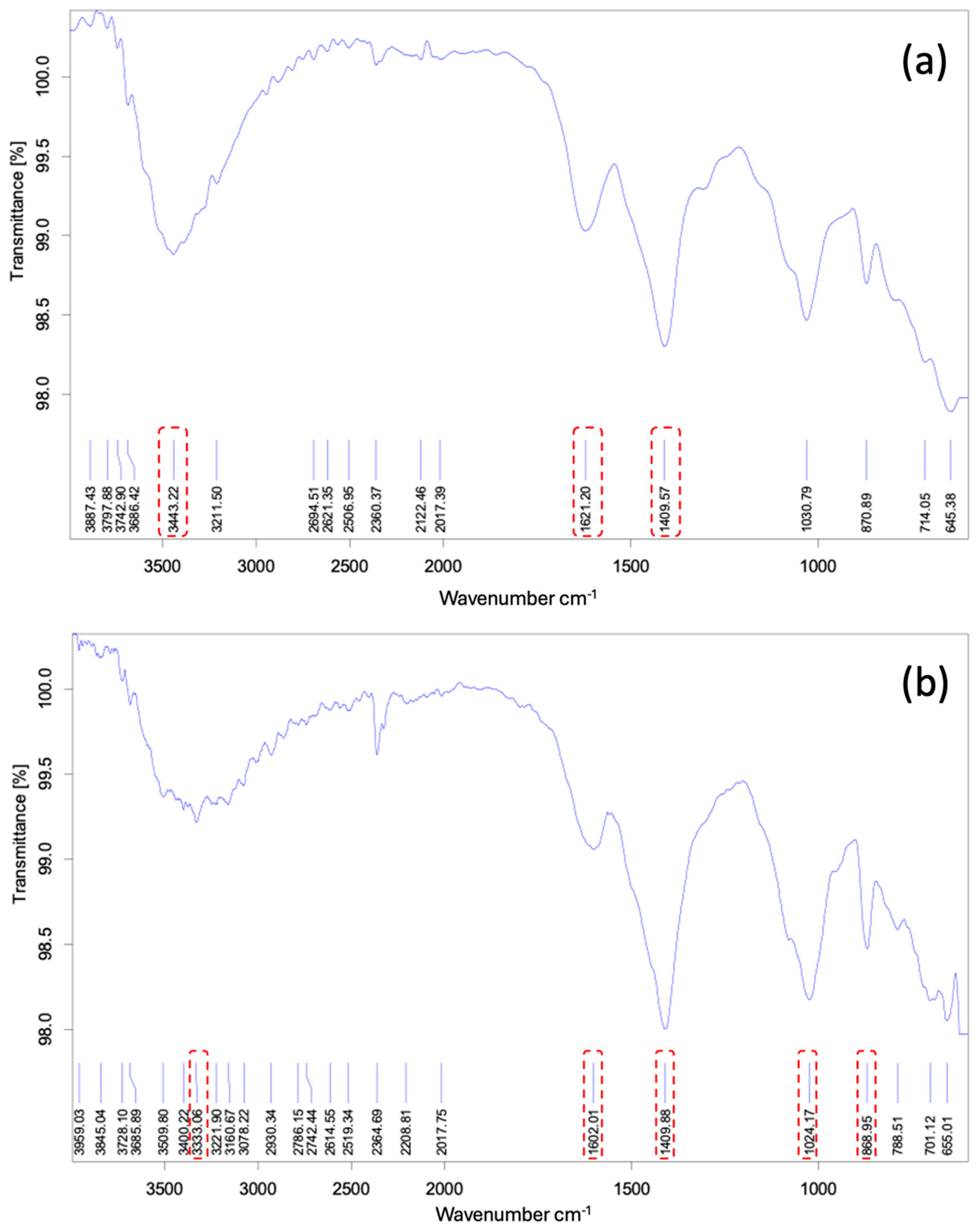




| Elements | Weights (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| GGBS | MgD | |
| CaO | 42 | 0.71 |
| SiO2 | 38 | 0.43 |
| Al2O3 | 6 | 1.77 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.82 | 0.42 |
| MgO | 4.99 | 64.3 |
| Na2O | 2.93 | NA |
| K2O | 1.6 | NA |
| TiO2 | 0.88 | NA |
| MnO | 0.38 | 0.27 |
| PbO | NA | 0.0056 |
| NA: not detectable | ||
| Model | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 2.11 mg/g |
| b (L/mg) | 0.22 | |
| R2 | 0.986 | |
| SSE | 0.0197 | |
| Freundlich | Kf (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n | 0.51 |
| n | 2.31 | |
| R2 | 0.985 | |
| SSE | 0.0189 |
| Materials | Qmax (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ca-Mg-SA beads | 2.11 | Current study |
| Steel furnace slag | 1.43 | [26] |
| Na-natural zeolite | 2.19 | [27] |
| Red mud | 0.58 | [28] |
| Oyster shell | 0.16 | [29] |
| Paper sludge ash | 2.1 | [30] |
| Chitosan + bentonite | 13.44 | [31] |
| Concrete waste + sea water | 2.39 | [32] |
| Peat | 8.9 | [33] |
| Kinetic Model | Parameter | C0 (mg/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | K1 (min−1) | 0.072 | 0.097 | 0.050 | 0.049 | 0.050 | 0.047 |
| qe (mg/g) | 0.364 | 0.592 | 0.990 | 1.273 | 1.522 | 1.703 | |
| R2 | 0.967 | 0.987 | 0.970 | 0.968 | 0.979 | 0.990 | |
| SSE | 0.003 | 0.166 | 0.019 | 0.049 | 0.046 | 0.028 | |
| Pseudo-second order | qexp. (mg/g) | 0.383 | 0.753 | 1.045 | 1.338 | 1.583 | 1.754 |
| K2 (g/mg min) | 0.347 | 0.081 | 0.073 | 0.048 | 0.042 | 0.046 | |
| qe (mg/g) | 0.321 | 0.804 | 1.096 | 1.407 | 1.680 | 1.837 | |
| R2 | 0.994 | 0.996 | 0.996 | 0.989 | 0.993 | 0.999 | |
| SSE | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.002 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion | Portion 1 | ||||||
| Kint (mg/g min0.5) | 0.023 | 0.063 | 0.081 | 0.105 | 0.131 | 0.1356826 | |
| C (mg/g) | 0.157 | 0.154 | 0.283 | 0.314 | 0.355 | 0.5024264 | |
| R2 | 0.953 | 0.881 | 0.941 | 0.942 | 0.916 | 0.9425405 | |
| Portion 2 | |||||||
| Kint (mg/g min0.5) | 0.007 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.031 | 0.033 | 0.032042 | |
| C (mg/g) | 0.283 | 0.483 | 0.745 | 0.888 | 1.102 | 1.288975 | |
| R2 | 0.878 | 0.856 | 0.906 | 0.942 | 0.876 | 0.8911297 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alwash, R.; Andredaki, M.; Carnacina, I.; Sadique, M.; Amoako-Attah, J. Magnesium Dross and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Utilisation for Phosphate Elimination from Water. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312844
Alwash R, Andredaki M, Carnacina I, Sadique M, Amoako-Attah J. Magnesium Dross and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Utilisation for Phosphate Elimination from Water. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312844
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlwash, Reham, Manolia Andredaki, Iacopo Carnacina, Monower Sadique, and Joseph Amoako-Attah. 2025. "Magnesium Dross and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Utilisation for Phosphate Elimination from Water" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312844
APA StyleAlwash, R., Andredaki, M., Carnacina, I., Sadique, M., & Amoako-Attah, J. (2025). Magnesium Dross and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Utilisation for Phosphate Elimination from Water. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312844









