KOSLM: A Kalman-Optimal Hybrid State-Space Memory Network for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
- State-space reformulation of LSTM: We formalize LSTM networks as input- and state-dependent SSMs, where each gate dynamically parameterizes the state-transition and input matrices. This framework provides a principled explanation of LSTM’s long-term memory behavior.
- Kalman-optimal selective gating: Inspired by the Kalman filter and selective SSMs, we introduce a Kalman-optimal selective mechanism in which the state-transition and input matrices are linearly modulated by a Kalman gain learned from the innovation term, establishing a feedback pathway that minimizes state estimation uncertainty.
- Applications to real-world forecasting: KOSLM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across LTSF benchmarks in energy, finance, traffic, healthcare, and meteorology, achieving 14.3–38.9% lower mean squared error (MSE) and a maximum reduction in mean absolute error (MAE) of 25.2%; it also delivers up to 2.5× faster inference than Mamba-2. In real-world Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) tracking under noisy and irregular sampling, KOSLM demonstrates strong robustness and generalization.
2. Background and Theory
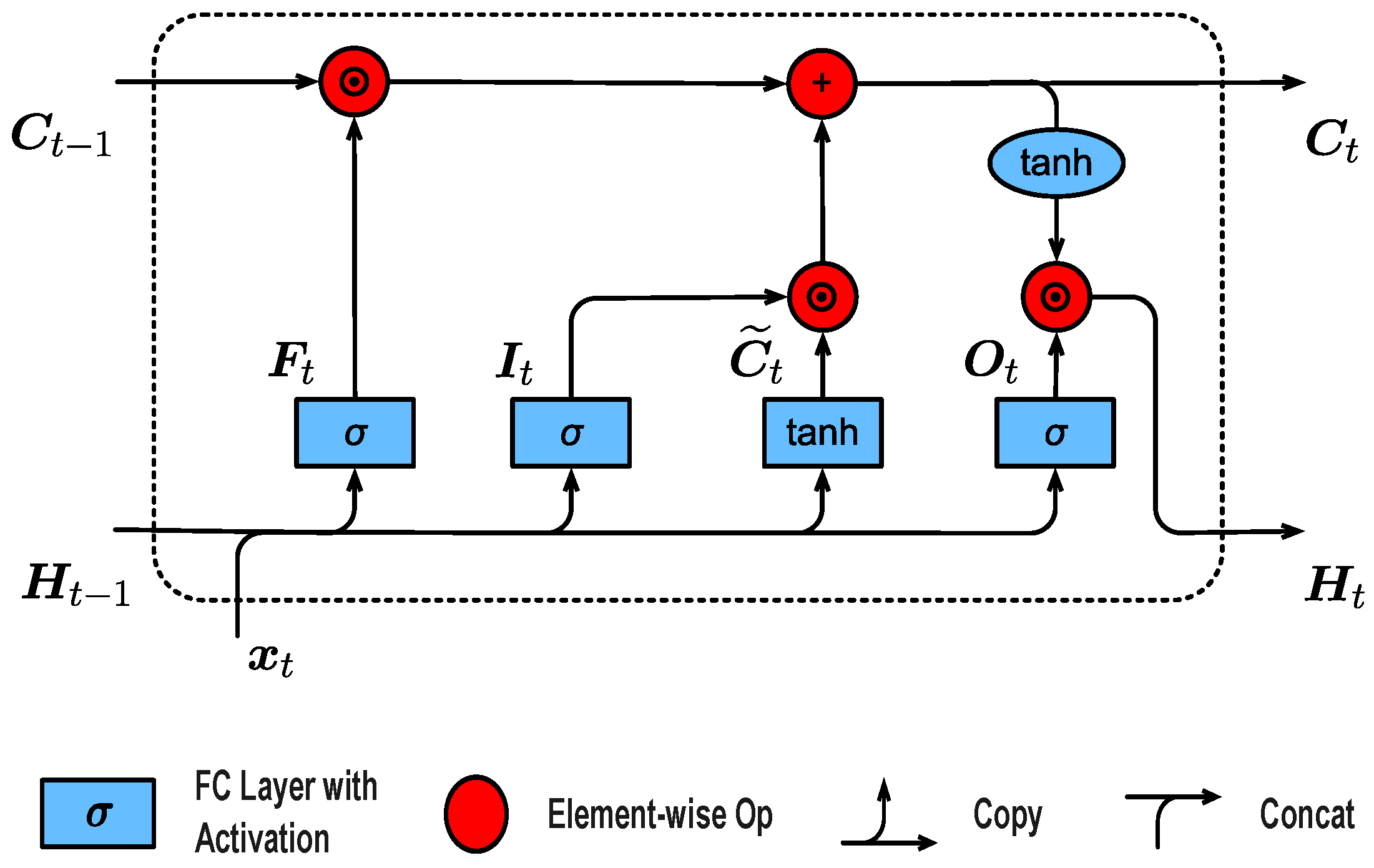
2.1. LSTM Networks
2.2. State Space Models
2.2.1. Selective State Space Models
2.2.2. Kalman Filter
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Reformulating LSTM as a State-Space Model
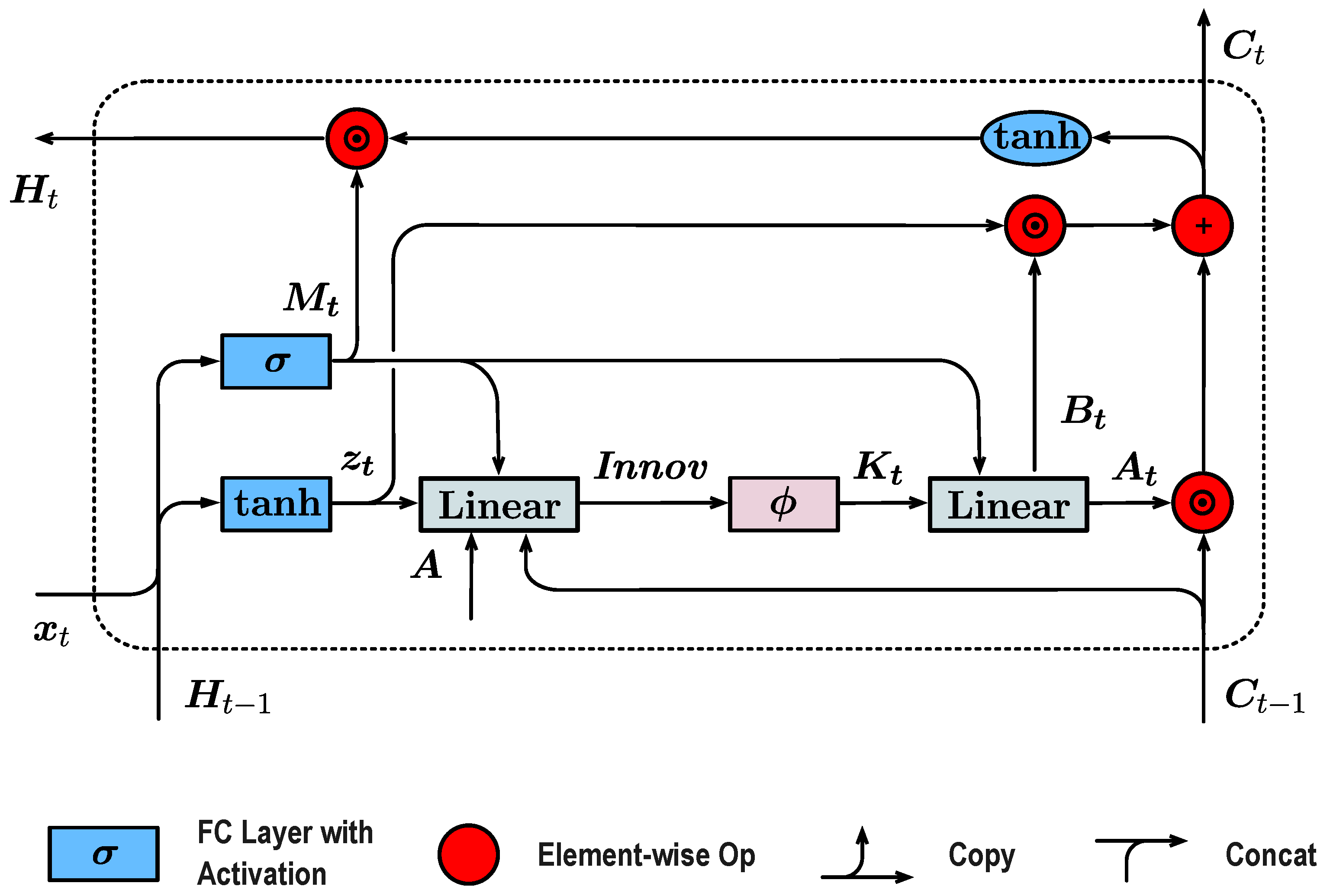
3.2. Kalman-Optimal Selectivity via Innovation-Driven Gain
3.3. Structural Overview of KOSLM
- Compute and via the candidate gate and output gate ;
- Compute the innovation: ;
- Estimate the Kalman gain: ;
- Update state transition matrices: , ;
- Propagate the hidden state: ;
- Compute the output hidden representation: .
3.4. Theoretical Interpretation
3.5. Practical Advantages
- Robustness: The feedback structure mitigates error accumulation and improves performance under noise or distributional shifts.
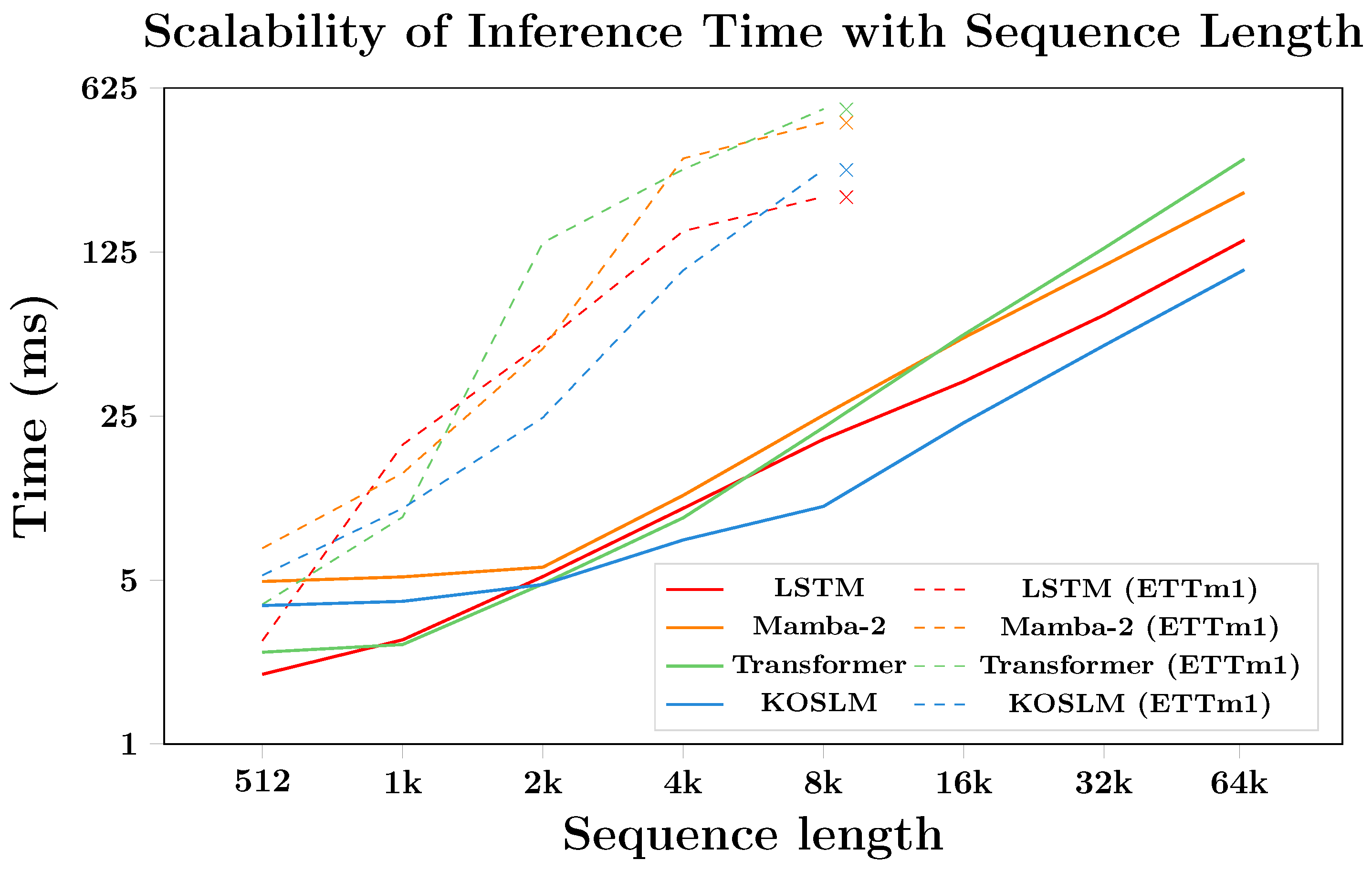
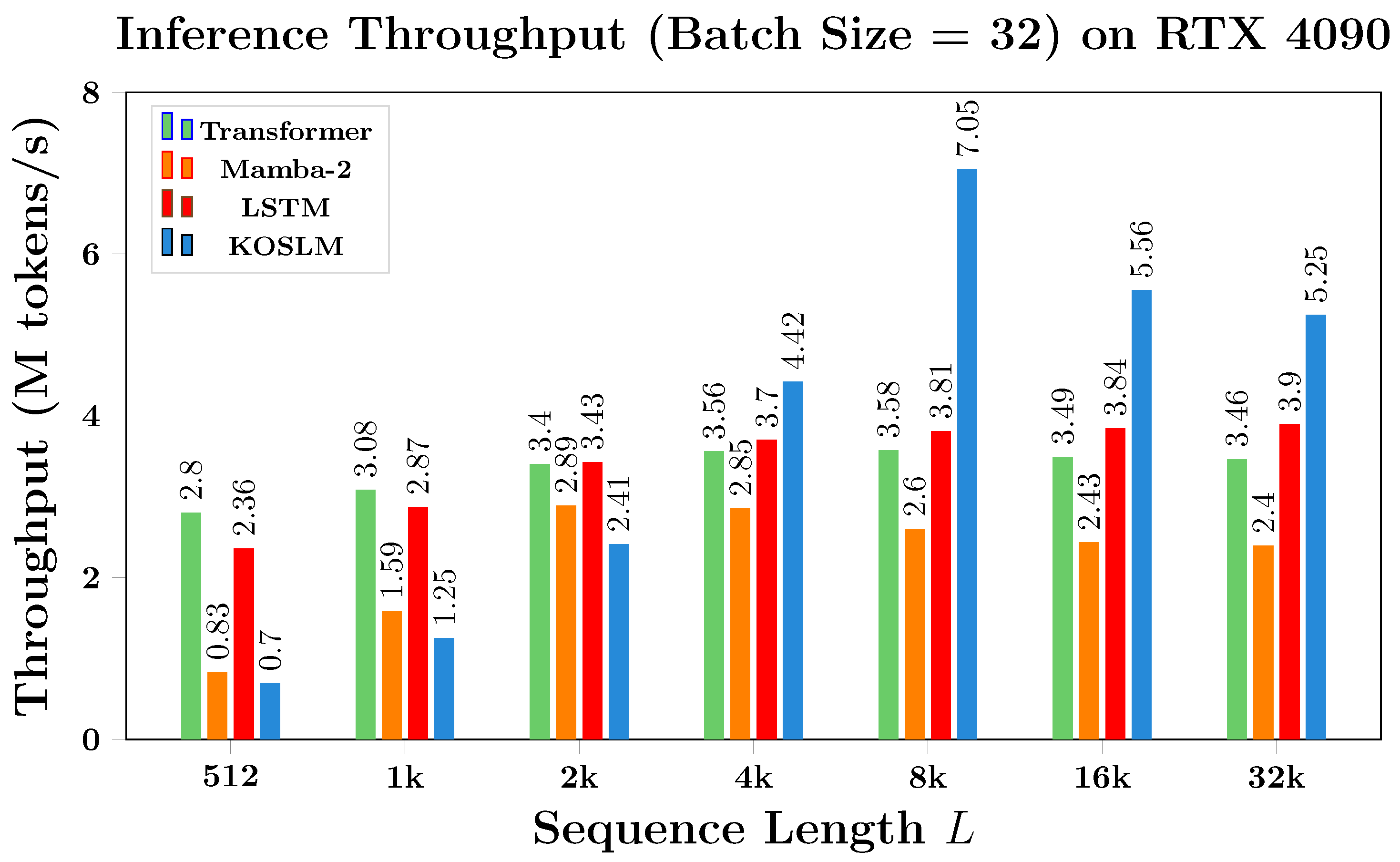
- Efficiency: With only 0.24 M parameters, KOSLM achieves up to 2.5× faster inference than Mamba-2, while maintaining competitive accuracy.
- Versatility: The model generalizes across diverse domains, from energy demand forecasting to radar-based trajectory tracking.
4. Results
4.1. Main Experiments on Benchmark Datasets
4.1.1. Dataset Details
4.1.2. Implementation Details
4.1.3. Experimental Setup of Main Experiments
- LSTM-based: xLSTMTime [22];
4.1.4. Overall Performance
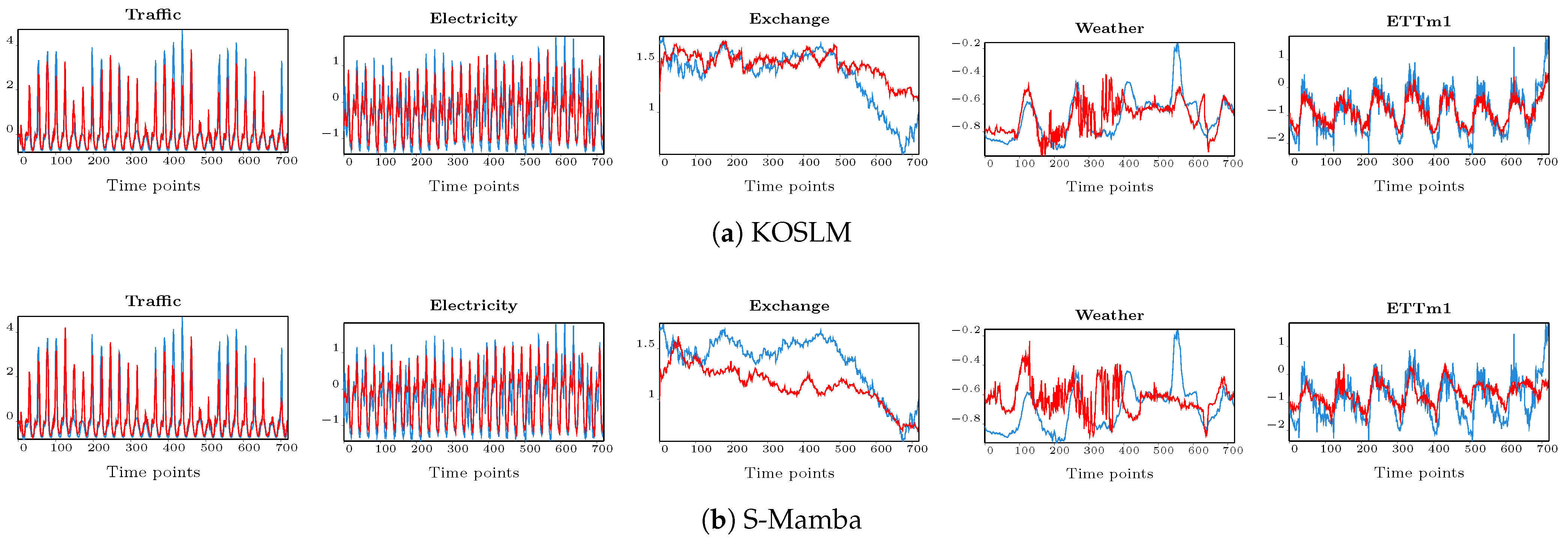
- Consistent superiority across domains: KOSLM outperforms all competing baselines, particularly under complex and noisy datasets. In terms of average MSE and MAE reductions, KOSLM achieves relative improvements of 31.96% and 18.77% on Traffic, 13.37% and 25.20% on Electricity, 5.47% and 20.27% on Exchange, 11.26% and 18.43% on Weather, and 22.04% and 23.09% on ILI. Moreover, on the four ETT benchmarks, KOSLM achieves MSE improvements of up to 27.46% and MAE improvements of up to 25.2%, demonstrating strong adaptability to varying periodic and nonstationary patterns. These consistent gains verify that the Kalman-inspired selective updating mechanism effectively filters noise and dynamically adjusts to regime shifts, ensuring stable forecasting accuracy over long horizons.
- Stable error distribution and reduced variance: The MSE–MAE gap of KOSLM remains narrower than that of other baselines, implying reduced large deviations and more concentrated prediction errors. This indicates more stable error behavior, which is crucial for long-horizon forecasting where cumulative drift often occurs. The innovation-driven Kalman gain estimation provides adaptive correction at each timestep, ensuring smooth and consistent prediction trajectories under uncertain dynamics.
- Strong scalability and generalization: KOSLM achieves leading performance not only on large-scale datasets (Traffic, Electricity) but also on small, noisy datasets (ILI), confirming robust generalization across different temporal resolutions and noise levels. Its consistent advantage over Transformer-based (e.g., iTransformer, FEDFormer, PatchTST), recurrent (e.g., xLSTMTime), and state-space models (e.g., S-Mamba, FiLM) demonstrates that the proposed Kalman-optimal selective mechanism provides an effective inductive bias for modeling long-term dependencies.
- Advantage over LSTM-based architectures: Compared with advanced LSTM-based models such as xLSTMTime, KOSLM achieves consistently better results across nearly all datasets and horizons. This verifies that replacing heuristic gates with Kalman-optimal selective gating enhances memory retention and update stability. While xLSTMTime alleviates gradient decay via hierarchical memory, KOSLM further refines state updates through innovation-driven gain estimation, thereby achieving a more principled and stable information flow.
4.2. Ablation Study
4.2.1. Structural Ablation
4.2.2. Capacity Ablation
4.3. Efficiency Benchmark
4.3.1. Runtime Scalability
4.3.2. Throughput Analysis
4.3.3. Memory Footprint
4.3.4. Model Size
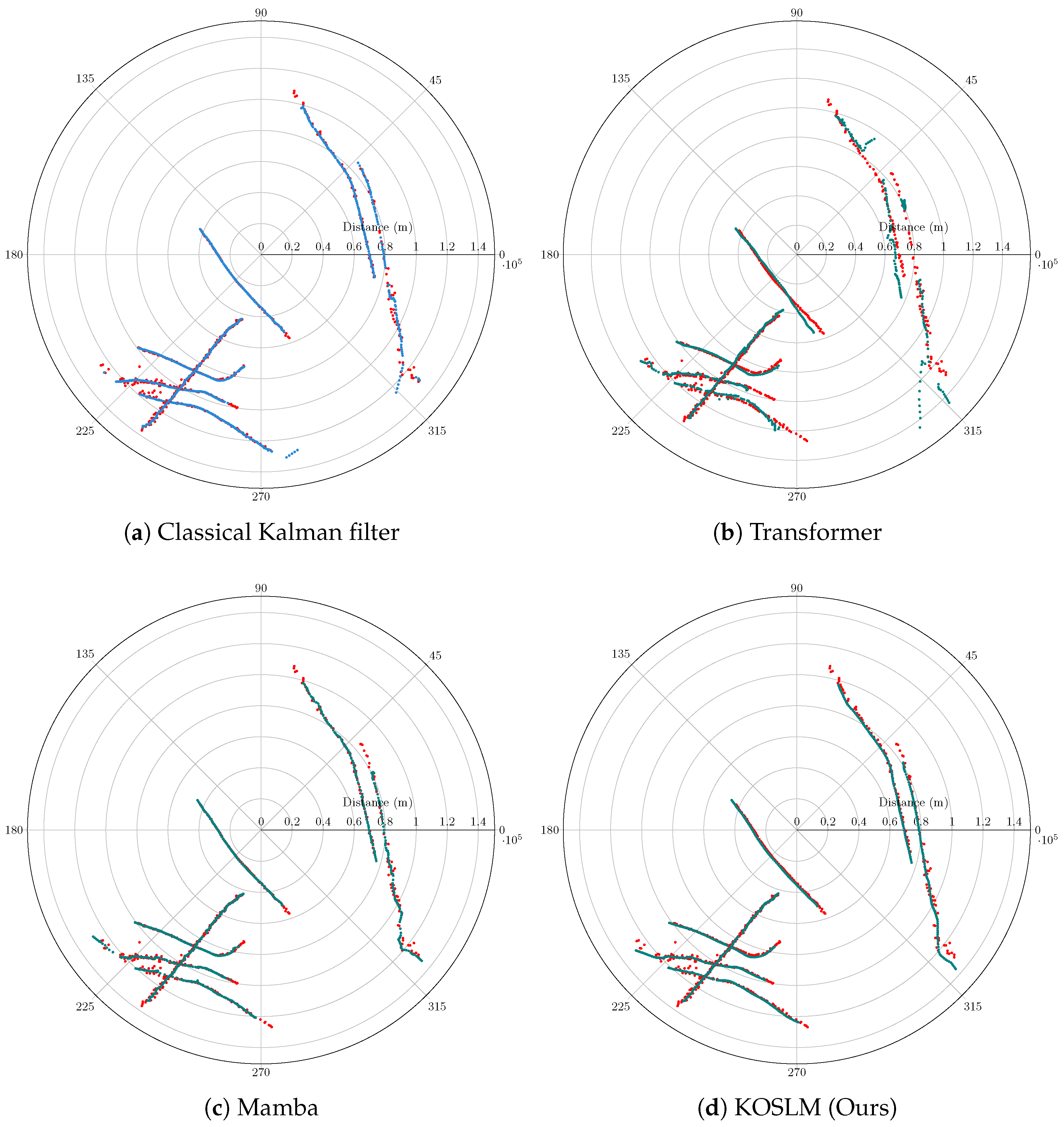
4.4. Real-World Application: Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) Target Trajectory Tracking
- High stochastic noise: Measurement noise leads to random fluctuations in the estimated positions;
- Irregular sampling: Aircraft maneuvers and radar scan intervals result in uneven temporal spacing;
- Correlated anomalies: Spurious echoes or missing detections introduce discontinuities in the trajectories.
4.4.1. Experimental Setup
4.4.2. Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Selective State Space Models
- Relation to Existing Concepts.
- Gating was originally introduced as a signal-control mechanism in recurrent neural networks (RNNs) such as LSTM [3] and GRU [33], where multiplicative gates regulate information updates across time steps. The concept has been generalized to other architectures, including gated convolutions and transformers [34,35], though often without an explicit interpretation in terms of temporal signal control.
- Hypernetworks [36] generate network parameters dynamically through auxiliary networks, enabling the model’s internal dynamics to adapt based on input signals.
- Data-dependent parameterization [37] represents a broader paradigm in which model parameters are directly conditioned on input data. Both gating and hypernetworks can be viewed as specific instances within this larger class.
- From Implicit to Explicit Selection.
- Semantic Clarification.
- Scope and Relevance.
Appendix B. Detailed Derivation
Appendix B.1. Kalman Gain as a Prototype for Dynamic Selectivity
Appendix B.2. LSTM-to-SSM Reconstruction
- The candidate cell state can be interpreted as a differentiable nonlinear mapping from the joint input :where the linear transformation fuses the external input and the hidden state into the observation space, with introducing nonlinearity to produce an intermediate representation . We treat this representation as the observation input at time t under the SSM (Here, the observation input denotes the externally observable signal that directly drives the state update process. It is written as in KF and as in SSMs, which are semantically equivalent).
- The interaction between the input gate and the candidate state establishes a structured pathway for injecting new information into the state dynamics, analogous to the excitation of state evolution by external inputs in SSMs.where serves as the input matrix, structurally equivalent to the input gate .
Appendix B.3. Kalman-Optimal Selective Mechanism
“One method of incorporating a selection mechanism into models is by letting their parameters that affect interactions along the sequence (e.g., the recurrent dynamics of an RNN or the convolution kernel of a CNN) be input-dependent.”
- Inspired by this, we design a selective mechanism based on Kalman-optimal state estimation within the SSM (Equation (3)). Unlike the input-dependent selection mechanism represented by S6, we make the key parameters (, ), which control how the model selectively propagates or forgets information along the sequence dimension, depend on the innovation term: the deviation between the observation input and the prior state prediction in the observation space, denoted as Innov in this paper. This method constructs a learnable selection path that integrates observational inputs and latent state feedback, with the optimization objective of minimizing the uncertainty in state estimation errors.
- Learnable Gain from Innovation.
- Optimal Selectivity via Gain.
Appendix B.4. Empirical Validation of Innovation-Driven Kalman Gain Learning
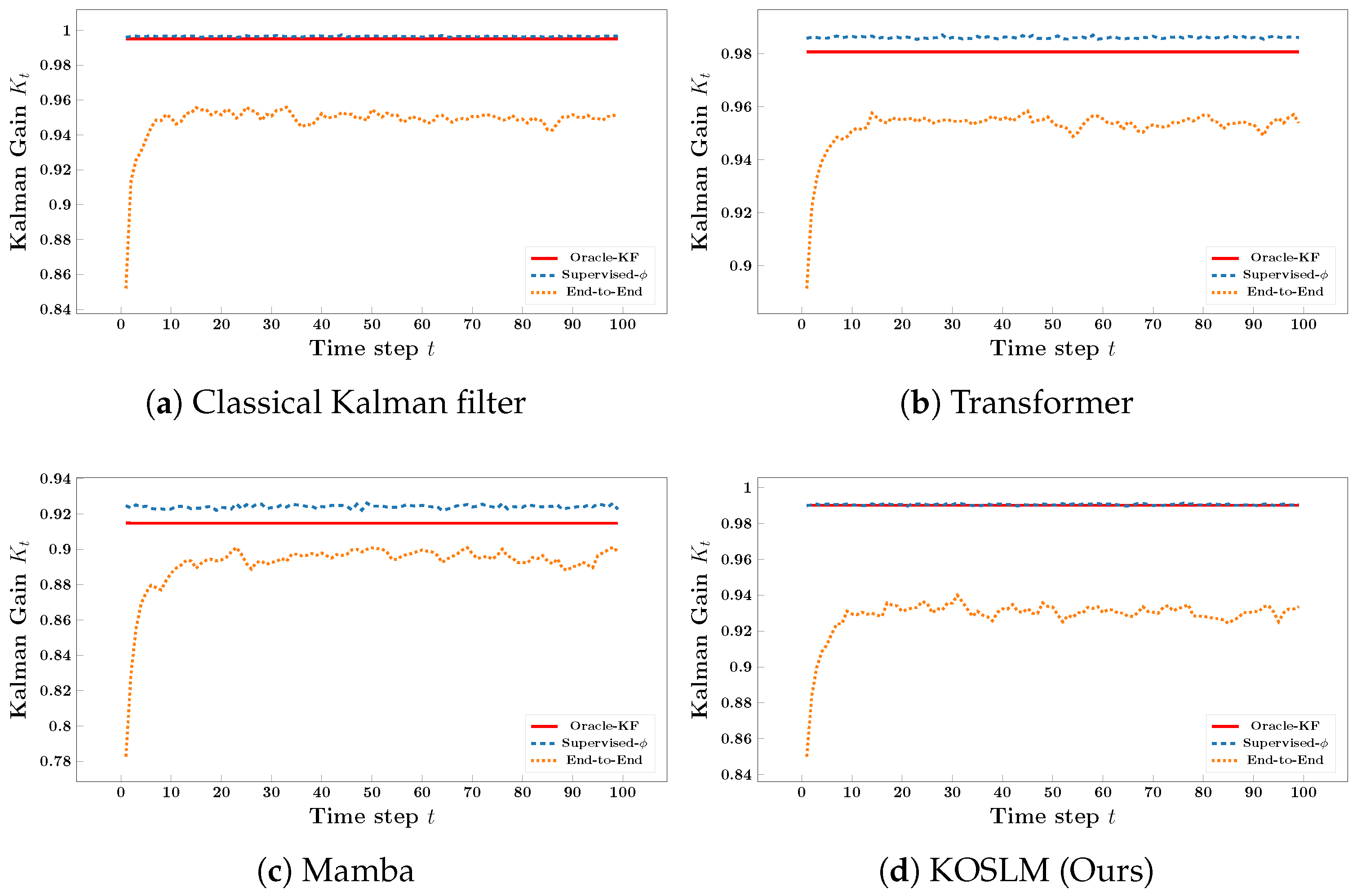
- Experimental Design.
- (i)
- Oracle-KF: Standard Kalman filter using the known parameters to compute .
- (ii)
- Supervised-: A small MLP takes the innovation as input and predicts , trained by minimizing over all timesteps. During training, the predicted prior state is provided by the Oracle-KF to isolate the learning of the innovation-to-gain mapping. This tests whether the innovation term contains sufficient information to recover the oracle gain.
- (iii)
- End-to-End: The same MLP is trained to directly map from to without explicitly constructing the innovation term, serving as an ablation to assess the importance of innovation-driven modeling.
- Setup and Metrics.
- MSE of Gain: , measuring how well the learned gain matches the oracle trajectory.
- State Estimation RMSE: Root-mean-square error between estimated and true state trajectories, where the state estimates are produced by running a Kalman update step with the learned , verifying that accurate gain learning improves filtering quality.
- Results and Analysis.
| (Q, R) | Supervised- | End-to-End | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | RMSE | MSE | RMSE | |
| (5, 0.1) | 0.317 | 0.368 | ||
| (5, 0.5) | 0.684 | 0.694 | ||
| (10, 0.1) | 0.216 | 0.341 | ||
| (100, 0.5) | 0.310 | 0.747 | ||
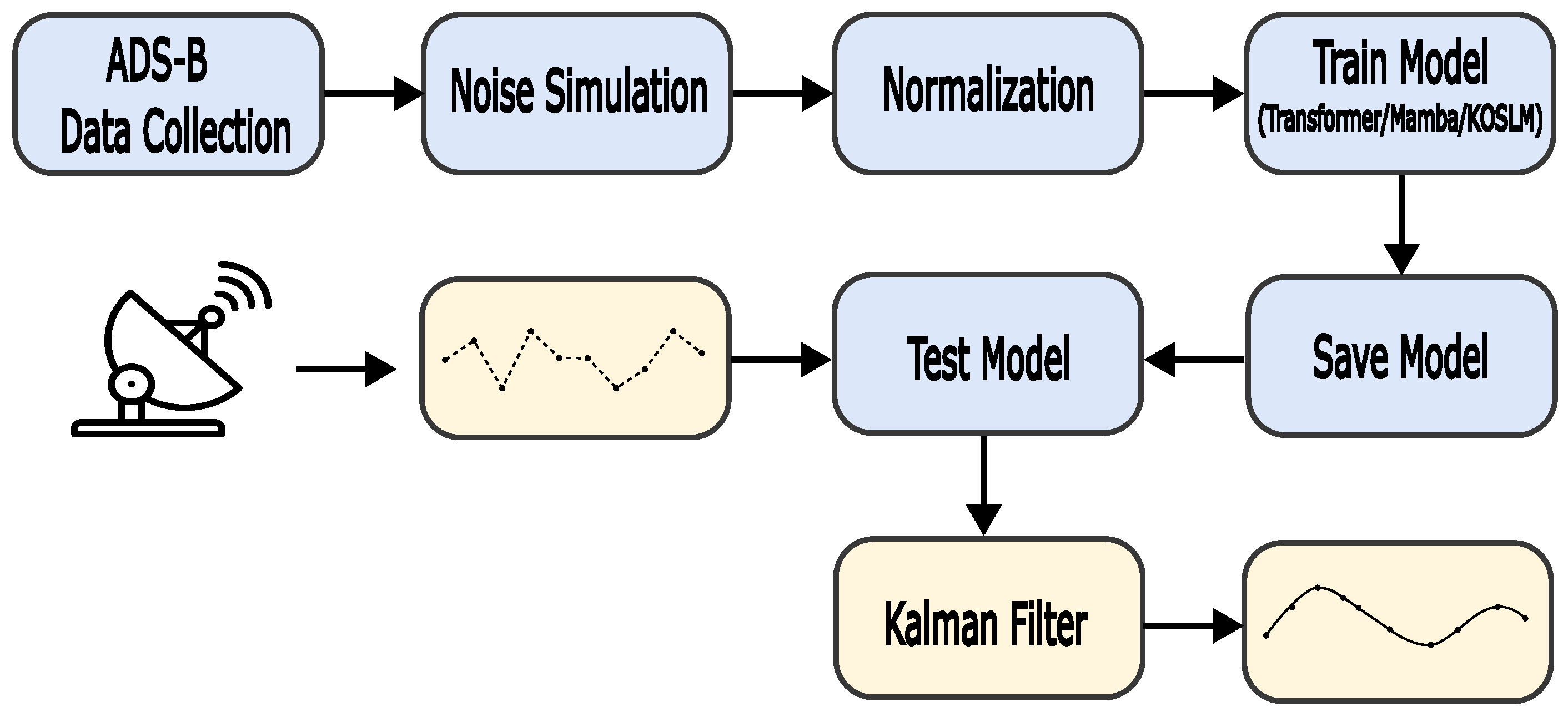
Appendix C. SSR Case Study: Data and Preprocessing Details
Appendix C.1. Data Acquisition
| Targets | Update Frequency | # Features | Total Samples | Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 503 | 5 s | 4 | 166,110 | 15 June 2025, 10:00–10:15 |
Appendix C.2. Normalization and Reverse Transformation
Appendix C.3. Field Data Collection
Appendix C.4. Processing Workflow
References
- Cheng, M.; Liu, Z.; Tao, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Pan, T.; Zhang, S.; He, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; et al. A comprehensive survey of time series forecasting: Concepts, challenges, and future directions. TechRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, C.; Banerjee, A.G. A distance correlation-based approach to characterize the effectiveness of recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting. Neurocomputing 2025, 629, 129641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, J.; Mathew, J. Enhancing continuous integration predictions: A hybrid LSTM-GRU deep learning framework with evolved DBSO algorithm. Computing 2025, 107, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascanu, R.; Mikolov, T.; Bengio, Y. On the Difficulty of Training Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’13), Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 1310–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Kuruoglu, E.E. Robustness enhancement in neural networks with alpha-stable training noise. Digit. Signal Process. 2025, 156, 104778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.G.; Shalit, U.; Sontag, D. Deep kalman filters. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.05121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revach, G.; Shlezinger, N.; Ni, X.; Escoriza, A.L.; Van Sloun, R.J.; Eldar, Y.C. KalmanNet: Neural network aided Kalman filtering for partially known dynamics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1532–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, Y.; Revach, G.; Dunik, J.; Shlezinger, N. Uncertainty quantification in deep learning based Kalman filters. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 13121–13125. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.; Gu, A. Transformers are ssms: Generalized models and efficient algorithms through structured state space duality. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.21060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, B.K.; Osheku, C.A.; Adetoro, L.M.; Funmilayo, A.A. Optimal Solution to Matrix Riccati Equation—For Kalman Filter Implementation. In MATLAB; Katsikis, V.N., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Gupta, A.; Ré, C. On the parameterization and initialization of diagonal state space models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 35971–35983. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Gulcehre, C.; Paine, T.; Hoffman, M.; Pascanu, R. Improving the gating mechanism of recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 3800–3809. [Google Scholar]
- Weather Dataset. 2024. Weather Data from the BGC Jena Climate Data Archive. Available online: https://www.hypermeteo.com/en/?gad_source=1&gad_campaignid=14712996685&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIvJ_HqOORkQMVSpCDBx3MFTosEAAYASAAEgLx7fD_BwE (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- ETT Datasets. 2024. Energy Transformer Temperature Dataset (ETT) for Long-Term Forecasting. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/documents/merged-ett-dataset-time-series-forecasting (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Electricity Dataset. 2024. Electricity Load Diagrams Dataset from UCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/documents/uci-dataset (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Exchange Rate Dataset. 2024. Daily Exchange Rate Dataset for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting, Provided with the ETT Benchmark Collection. Available online: https://github.com/juyongjiang/TimeSeriesDatasets (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Traffic Dataset. 2024. Traffic Flow Data from California Performance Measurement System (PeMS). Available online: https://www.smartmicro.com/traffic-sensor?utm_medium=advert&utm_source=google&utm_campaign=search-traffic&utm_content=ad&utm_term=traffic_sensor&gad_source=1&gad_campaignid=22435495111&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIlvLc8OORkQMVQJKDBx3FOSSQEAAYASAAEgITNPD_BwE (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Illness (ILI) Dataset. 2024. Weekly Influenza-Like Illness (ILI) Dataset for Forecasting Tasks, Available Within the ETT Benchmark Suite. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Influenza-like-illness-ILI-data-from-the-FluID-database-Weekly-scaled-rates-of-ILI_fig1_337718309 (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Alharthi, M.; Mahmood, A. xlstmtime: Long-term time series forecasting with xlstm. AI 2024, 5, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.; Wen, Q.; Sun, L.; Yao, T.; Yin, W.; Jin, R. Film: Frequency improved legendre memory model for long-term time series forecasting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 12677–12690. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, F.; Feng, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y. Is mamba effective for time series forecasting? Neurocomputing 2025, 619, 129178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.; Wen, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, R. Fedformer: Frequency enhanced decomposed transformer for long-term series forecasting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 27268–27286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Long, M. itransformer: Inverted transformers are effective for time series forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.06625. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J. Crossformer: Transformer Utilizing Cross-Dimension Dependency for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Shen, Y.; Wu, Z. DLinear: A Linear Complexity Approach for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.13504. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Long time series of ocean wave prediction based on PatchTST model. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 301, 117572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Shi, X.; Hu, T.; Luo, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, J. Timemixer: Decomposable multiscale mixing for time series forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T. Flashattention-2: Faster attention with better parallelism and work partitioning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2307.08691. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Yanbo, Z. Study of ADS-B data evaluation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2011, 24, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, H.; Gupta, A.; Cutkosky, A.; Neyshabur, B. Long range language modeling via gated state spaces. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Dai, Z.; Liu, H.; Le, Q. Transformer quality in linear time. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2022; pp. 9099–9117. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, D.; Dai, A.; Le, Q.V. Hypernetworks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.09106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poli, M. Data-dependent neural networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13272. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Ré, C. Combining recurrent, convolutional, and continuous-time models with structured state space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 21984–21998. [Google Scholar]
- Funahashi, K.I.; Nakamura, Y. Approximation of dynamical systems by continuous time recurrent neural networks. Neural Netw. 1993, 6, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallec, C.; Ollivier, Y. Can recurrent neural networks warp time? arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.11188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahirovic, A.; Redzovic, A. Optimal Estimation for Continuous-Time Nonlinear Systems Using State-Dependent Riccati Equation (SDRE). arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.10442. [Google Scholar]
| Dataset | Variant | #Params | MSE ↓ | MAE ↓ | Δ MSE vs. SmallMLP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETTm1 | Linear | 0.183M | 0.480 ± 0.012 | 0.355 ± 0.008 | +46.3% |
| SmallMLP | 0.255M | 0.328 ± 0.010 | 0.282 ± 0.007 | — | |
| MediumMLP | 0.389M | 0.335 ± 0.011 | 0.284 ± 0.001 | +2.13% | |
| HighCap | 0.898M | 0.342 ± 0.015 | 0.288 ± 0.010 | +4.27% | |
| ETTh1 | Linear | 0.183M | 0.440 ± 0.010 | 0.330 ± 0.004 | +30.95% |
| SmallMLP | 0.255M | 0.336 ± 0.008 | 0.291 ± 0.006 | — | |
| MediumMLP | 0.389M | 0.341 ± 0.010 | 0.294 ± 0.002 | +1.49% | |
| HighCap | 0.898M | 0.355 ± 0.012 | 0.302 ± 0.008 | +5.65% | |
| Traffic | Linear | 0.183M | 0.290 ± 0.011 | 0.232 ± 0.006 | +9.02% |
| SmallMLP | 0.255M | 0.266 ± 0.010 | 0.212 ± 0.007 | — | |
| MediumMLP | 0.389M | 0.270 ± 0.012 | 0.216 ± 0.002 | +1.50% | |
| HighCap | 0.898M | 0.279 ± 0.014 | 0.222 ± 0.005 | +4.89% | |
| Exchange | Linear | 0.183M | 0.272 ± 0.010 | 0.305 ± 0.005 | +4.62% |
| SmallMLP | 0.255M | 0.260 ± 0.009 | 0.291 ± 0.009 | — | |
| MediumMLP | 0.389M | 0.264 ± 0.010 | 0.294 ± 0.007 | +1.54% | |
| HighCap | 0.898M | 0.285 ± 0.012 | 0.310 ± 0.009 | +9.62% |
| Aspect | KalmanNet | KOSLM (Ours) |
|---|---|---|
| Core idea | Strictly follows the classical KF architecture (Section 2.2.2); the neural network learns to correct the Kalman gain under partially known linear dynamics. | Reinterprets LSTM gating as a Kalman-optimal state estimation problem; state estimation does not strictly adhere to the KF equations, but directly learns from the innovation term. |
| System dynamics | Assumes fixed parameters ; suitable for systems with known or partially known dynamics. | Learns from data; A is a learnable parameter matrix; fully adaptive to nonlinear and nonstationary environments. |
| Form of gain | —learns a residual correction to the classical Kalman gain. | —directly learns the gain function from the innovation. |
| Gain network input | —uses both predicted state and innovation as inputs. | —relies solely on the innovation signal for gain computation (see Appendices Appendix B.3 and Appendix B.4, which prove its sufficiency). |
| Output role | Outputs a residual correction added to . | Outputs and integrates gain estimation into the state transition: , , forming a unified recurrent–estimation pathway. |
| System dependency | Requires partial knowledge of for baseline Kalman computation. | Fully data-driven; no analytical Kalman gain or explicit system parameters required. |
| Theoretical interpretation | Neural residual learning to compensate model mismatch. | Innovation-driven dynamic selectivity that enforces Kalman-optimal information update behavior. |
| Dataset | Frequency | # Features | Time Steps | Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETTh1 | 1 h | 7 | 17,420 | 2016–2017 |
| ETTh2 | 1 h | 7 | 17,420 | 2017–2018 |
| ETTm1 | 15 min | 7 | 69,680 | 2016–2017 |
| ETTm2 | 15 min | 7 | 69,680 | 2017–2018 |
| Exchange | 1 day | 8 | 7588 | 1990–2010 |
| Weather | 10 min | 21 | 52,696 | 2020 |
| Electricity | 1 h | 321 | 26,304 | 2012–2014 |
| ILI | 7 days | 7 | 966 | 2002–2020 |
| Traffic | 1 h | 862 | 17,544 | 2015–2016 |
| Models | KOSLM | xLSTMTime | FiLM | iTransformer | FEDFormer | S-Mamba | Crossformer | DLinear | PatchTST | TimeMixer | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | |
| Traffic | 96 | 0.290 | 0.230 | 0.358 | 0.242 | 0.416 | 0.294 | 0.395 | 0.268 | 0.587 | 0.366 | 0.382 | 0.261 | 0.522 | 0.290 | 0.650 | 0.396 | 0.462 | 0.295 | 0.462 | 0.285 |
| 192 | 0.260 | 0.210 | 0.378 | 0.253 | 0.408 | 0.288 | 0.417 | 0.276 | 0.604 | 0.373 | 0.396 | 0.267 | 0.530 | 0.293 | 0.598 | 0.370 | 0.466 | 0.296 | 0.473 | 0.296 | |
| 336 | 0.227 | 0.179 | 0.392 | 0.261 | 0.425 | 0.298 | 0.433 | 0.283 | 0.621 | 0.383 | 0.417 | 0.276 | 0.558 | 0.305 | 0.605 | 0.373 | 0.482 | 0.304 | 0.498 | 0.297 | |
| 720 | 0.290 | 0.232 | 0.434 | 0.287 | 0.520 | 0.353 | 0.467 | 0.302 | 0.626 | 0.382 | 0.460 | 0.300 | 0.589 | 0.328 | 0.645 | 0.394 | 0.514 | 0.322 | 0.506 | 0.313 | |
| +31.96% | Avg | 0.266 | 0.212 | 0.391 | 0.261 | 0.442 | 0.308 | 0.428 | 0.282 | 0.610 | 0.376 | 0.434 | 0.287 | 0.550 | 0.304 | 0.625 | 0.383 | 0.481 | 0.304 | 0.485 | 0.297 |
| Electricity | 96 | 0.136 | 0.184 | 0.128 | 0.221 | 0.154 | 0.267 | 0.148 | 0.240 | 0.193 | 0.308 | 0.139 | 0.235 | 0.219 | 0.314 | 0.197 | 0.282 | 0.181 | 0.270 | 0.153 | 0.247 |
| 192 | 0.131 | 0.184 | 0.150 | 0.243 | 0.164 | 0.258 | 0.162 | 0.253 | 0.201 | 0.315 | 0.159 | 0.255 | 0.231 | 0.322 | 0.196 | 0.285 | 0.188 | 0.274 | 0.166 | 0.256 | |
| 336 | 0.120 | 0.177 | 0.166 | 0.259 | 0.188 | 0.283 | 0.178 | 0.269 | 0.214 | 0.329 | 0.176 | 0.272 | 0.246 | 0.337 | 0.209 | 0.301 | 0.204 | 0.293 | 0.185 | 0.277 | |
| 720 | 0.158 | 0.205 | 0.185 | 0.276 | 0.236 | 0.332 | 0.225 | 0.317 | 0.246 | 0.355 | 0.204 | 0.298 | 0.280 | 0.363 | 0.245 | 0.333 | 0.246 | 0.324 | 0.225 | 0.310 | |
| +13.37% | Avg | 0.136 | 0.187 | 0.157 | 0.250 | 0.186 | 0.285 | 0.178 | 0.270 | 0.214 | 0.327 | 0.170 | 0.265 | 0.244 | 0.334 | 0.212 | 0.300 | 0.205 | 0.290 | 0.182 | 0.272 |
| Exchange | 96 | 0.135 | 0.212 | – | – | 0.086 | 0.204 | 0.086 | 0.206 | 0.148 | 0.278 | 0.086 | 0.207 | 0.256 | 0.367 | 0.088 | 0.218 | 0.088 | 0.205 | 0.095 | 0.207 |
| 192 | 0.279 | 0.292 | – | – | 0.188 | 0.292 | 0.177 | 0.299 | 0.271 | 0.315 | 0.182 | 0.304 | 0.470 | 0.509 | 0.176 | 0.315 | 0.176 | 0.299 | 0.151 | 0.293 | |
| 336 | 0.341 | 0.339 | – | – | 0.356 | 0.433 | 0.331 | 0.417 | 0.460 | 0.427 | 0.332 | 0.418 | 1.268 | 0.883 | 0.313 | 0.427 | 0.301 | 0.397 | 0.264 | 0.361 | |
| 720 | 0.282 | 0.322 | – | – | 0.727 | 0.669 | 0.847 | 0.691 | 1.195 | 0.695 | 0.867 | 0.703 | 1.767 | 1.068 | 0.839 | 0.695 | 0.901 | 0.714 | 0.586 | 0.602 | |
| +5.47% | Avg | 0.259 | 0.291 | – | – | 0.339 | 0.400 | 0.360 | 0.403 | 0.519 | 0.429 | 0.367 | 0.408 | 0.940 | 0.707 | 0.354 | 0.414 | 0.367 | 0.404 | 0.274 | 0.365 |
| Weather | 96 | 0.144 | 0.171 | 0.144 | 0.187 | 0.199 | 0.262 | 0.174 | 0.214 | 0.217 | 0.296 | 0.165 | 0.210 | 0.158 | 0.230 | 0.196 | 0.255 | 0.177 | 0.218 | 0.163 | 0.209 |
| 192 | 0.224 | 0.236 | 0.192 | 0.236 | 0.228 | 0.288 | 0.221 | 0.254 | 0.276 | 0.336 | 0.214 | 0.252 | 0.206 | 0.277 | 0.237 | 0.296 | 0.225 | 0.259 | 0.208 | 0.250 | |
| 336 | 0.249 | 0.248 | 0.237 | 0.272 | 0.267 | 0.323 | 0.278 | 0.296 | 0.339 | 0.380 | 0.274 | 0.297 | 0.272 | 0.335 | 0.283 | 0.335 | 0.278 | 0.297 | 0.251 | 0.287 | |
| 720 | 0.169 | 0.175 | 0.313 | 0.326 | 0.319 | 0.361 | 0.358 | 0.347 | 0.403 | 0.428 | 0.350 | 0.345 | 0.398 | 0.418 | 0.345 | 0.381 | 0.354 | 0.348 | 0.339 | 0.341 | |
| +11.26% | Avg | 0.197 | 0.208 | 0.222 | 0.255 | 0.253 | 0.309 | 0.258 | 0.278 | 0.309 | 0.360 | 0.251 | 0.276 | 0.259 | 0.315 | 0.265 | 0.317 | 0.259 | 0.281 | 0.240 | 0.271 |
| ILI | 24 | 1.160 | 0.507 | 1.514 | 0.694 | 1.970 | 0.875 | 3.154 | 1.235 | 3.228 | 1.260 | – | – | 3.041 | 1.186 | 2.215 | 1.081 | 1.319 | 0.754 | 1.453 | 0.827 |
| 36 | 1.262 | 0.561 | 1.519 | 0.722 | 1.982 | 0.859 | 2.544 | 1.083 | 2.679 | 1.150 | – | – | 3.406 | 1.232 | 1.963 | 0.963 | 1.579 | 0.870 | 1.627 | 0.903 | |
| 48 | 1.098 | 0.545 | 1.500 | 0.725 | 1.868 | 0.896 | 2.489 | 1.112 | 2.622 | 1.080 | – | – | 3.459 | 1.221 | 2.130 | 1.024 | 1.553 | 0.815 | 1.644 | 0.914 | |
| 60 | 1.118 | 0.583 | 1.418 | 0.715 | 2.057 | 0.929 | 2.675 | 1.034 | 2.857 | 1.078 | – | – | 3.640 | 1.305 | 2.368 | 1.096 | 1.470 | 0.788 | 1.633 | 0.908 | |
| +22.04% | Avg | 1.160 | 0.549 | 1.488 | 0.714 | 1.969 | 0.890 | 2.715 | 1.116 | 2.847 | 1.170 | – | – | 3.387 | 1.236 | 2.169 | 1.041 | 1.480 | 0.807 | 1.589 | 0.888 |
| Models | KOSLM | xLSTMTime | FiLM | iTransformer | FEDFormer | S-Mamba | Crossformer | DLinear | PatchTST | TimeMixer | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | |
| ETTm1 | 96 | 0.204 | 0.221 | 0.286 | 0.335 | – | – | 0.334 | 0.368 | 0.379 | 0.419 | 0.333 | 0.368 | 0.404 | 0.426 | 0.345 | 0.372 | 0.329 | 0.367 | 0.320 | 0.357 |
| 192 | 0.233 | 0.237 | 0.329 | 0.361 | – | – | 0.377 | 0.391 | 0.426 | 0.441 | 0.376 | 0.390 | 0.450 | 0.451 | 0.380 | 0.389 | 0.367 | 0.385 | 0.361 | 0.381 | |
| 336 | 0.414 | 0.339 | 0.358 | 0.379 | – | – | 0.426 | 0.420 | 0.445 | 0.459 | 0.408 | 0.413 | 0.532 | 0.515 | 0.413 | 0.413 | 0.399 | 0.410 | 0.390 | 0.404 | |
| 720 | 0.481 | 0.368 | 0.416 | 0.411 | – | – | 0.491 | 0.459 | 0.543 | 0.490 | 0.475 | 0.448 | 0.666 | 0.589 | 0.474 | 0.453 | 0.454 | 0.439 | 0.458 | 0.441 | |
| +4.03% | Avg | 0.333 | 0.291 | 0.347 | 0.372 | – | – | 0.407 | 0.410 | 0.448 | 0.452 | 0.398 | 0.405 | 0.513 | 0.496 | 0.403 | 0.407 | 0.387 | 0.400 | 0.382 | 0.395 |
| ETTm2 | 96 | 0.100 | 0.232 | 0.164 | 0.250 | 0.165 | 0.256 | 0.180 | 0.264 | 0.203 | 0.287 | 0.179 | 0.263 | 0.287 | 0.366 | 0.193 | 0.292 | 0.175 | 0.259 | 0.175 | 0.258 |
| 192 | 0.132 | 0.274 | 0.218 | 0.288 | 0.222 | 0.296 | 0.250 | 0.309 | 0.269 | 0.328 | 0.250 | 0.309 | 0.414 | 0.492 | 0.284 | 0.362 | 0.241 | 0.302 | 0.237 | 0.299 | |
| 336 | 0.244 | 0.382 | 0.271 | 0.322 | 0.277 | 0.333 | 0.311 | 0.348 | 0.325 | 0.366 | 0.312 | 0.349 | 0.597 | 0.542 | 0.369 | 0.427 | 0.305 | 0.343 | 0.298 | 0.340 | |
| 720 | 0.268 | 0.408 | 0.361 | 0.380 | 0.371 | 0.389 | 0.412 | 0.407 | 0.421 | 0.415 | 0.411 | 0.406 | 1.730 | 1.042 | 0.554 | 0.522 | 0.402 | 0.400 | 0.275 | 0.323 | |
| +24.39% | Avg | 0.186 | 0.324 | 0.254 | 0.310 | 0.259 | 0.319 | 0.288 | 0.332 | 0.305 | 0.349 | 0.288 | 0.332 | 0.757 | 0.610 | 0.350 | 0.401 | 0.281 | 0.326 | 0.246 | 0.306 |
| ETTh1 | 96 | 0.298 | 0.277 | 0.368 | 0.395 | – | – | 0.386 | 0.405 | 0.376 | 0.419 | 0.386 | 0.405 | 0.423 | 0.448 | 0.386 | 0.400 | 0.414 | 0.419 | 0.375 | 0.400 |
| 192 | 0.337 | 0.306 | 0.401 | 0.416 | – | – | 0.441 | 0.436 | 0.420 | 0.448 | 0.443 | 0.437 | 0.471 | 0.474 | 0.437 | 0.432 | 0.460 | 0.445 | 0.479 | 0.421 | |
| 336 | 0.395 | 0.334 | 0.422 | 0.437 | – | – | 0.487 | 0.458 | 0.459 | 0.465 | 0.489 | 0.468 | 0.570 | 0.546 | 0.481 | 0.459 | 0.501 | 0.466 | 0.484 | 0.458 | |
| 720 | 0.471 | 0.364 | 0.441 | 0.465 | – | – | 0.503 | 0.491 | 0.506 | 0.507 | 0.502 | 0.489 | 0.653 | 0.621 | 0.519 | 0.516 | 0.500 | 0.488 | 0.498 | 0.482 | |
| +8.09% | Avg | 0.375 | 0.320 | 0.408 | 0.428 | – | – | 0.454 | 0.447 | 0.440 | 0.460 | 0.455 | 0.450 | 0.529 | 0.522 | 0.456 | 0.452 | 0.469 | 0.454 | 0.459 | 0.440 |
| ETTh2 | 96 | 0.194 | 0.338 | 0.273 | 0.333 | – | – | 0.297 | 0.349 | 0.358 | 0.397 | 0.296 | 0.348 | 0.745 | 0.584 | 0.333 | 0.387 | 0.302 | 0.348 | 0.289 | 0.341 |
| 192 | 0.238 | 0.384 | 0.340 | 0.378 | – | – | 0.380 | 0.400 | 0.429 | 0.439 | 0.376 | 0.396 | 0.877 | 0.656 | 0.477 | 0.476 | 0.388 | 0.400 | 0.372 | 0.392 | |
| 336 | 0.258 | 0.394 | 0.373 | 0.403 | – | – | 0.428 | 0.432 | 0.496 | 0.487 | 0.424 | 0.431 | 1.043 | 0.731 | 0.594 | 0.541 | 0.426 | 0.433 | 0.386 | 0.414 | |
| 720 | 0.314 | 0.432 | 0.398 | 0.430 | – | – | 0.427 | 0.445 | 0.463 | 0.474 | 0.426 | 0.444 | 1.104 | 0.763 | 0.831 | 0.657 | 0.431 | 0.446 | 0.412 | 0.434 | |
| +27.46% | Avg | 0.251 | 0.387 | 0.346 | 0.386 | – | – | 0.383 | 0.407 | 0.437 | 0.449 | 0.381 | 0.405 | 0.942 | 0.684 | 0.559 | 0.515 | 0.387 | 0.407 | 0.364 | 0.395 |
| Dataset | Model | MSE ↓ | MAE ↓ | Δ MSE vs. Full |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETTm1 | Full | 0.498 ± 0.011 | 0.416 ± 0.007 | — |
| No-Gain | 0.662 ± 0.017 | 0.553 ± 0.014 | +32.9% | |
| No-Innov | 0.583 ± 0.012 | 0.487 ± 0.008 | +17.1% | |
| ETTh1 | Full | 0.510 ± 0.012 | 0.378 ± 0.010 | — |
| No-Gain | 0.605 ± 0.022 | 0.448 ± 0.015 | +18.6% | |
| No-Innov | 0.554 ± 0.016 | 0.411 ± 0.010 | +8.6% | |
| Traffic | Full | 0.321 ± 0.008 | 0.195 ± 0.016 | — |
| No-Gain | 0.428 ± 0.011 | 0.260 ± 0.008 | +33.4% | |
| No-Innov | 0.375 ± 0.009 | 0.228 ± 0.007 | +16.9% | |
| Exchange | Full | 0.266 ± 0.014 | 0.341 ± 0.023 | — |
| No-Gain | 0.299 ± 0.018 | 0.383 ± 0.023 | +12.3% | |
| No-Innov | 0.294 ± 0.015 | 0.377 ± 0.019 | +10.6% |
| Batch Size | Transformer (GB) | Mamba-2 (GB) | LSTM (GB) | KOSLM (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.223 | 0.085 | 0.081 | 0.061 |
| 2 | 0.363 | 0.158 | 0.109 | 0.104 |
| 4 | 0.640 | 0.290 | 0.166 | 0.188 |
| 8 | 1.180 | 0.561 | 0.283 | 0.344 |
| 16 | 2.256 | 1.103 | 0.518 | 0.668 |
| 32 | 4.408 | 2.188 | 0.987 | 1.317 |
| 64 | 8.712 | 4.357 | 1.926 | 2.615 |
| 128 | 17.000 | 8.696 | 3.803 | 5.211 |
| Model | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|
| LSTM | 2.17 |
| Transformer | 5.33 |
| Mamba-2 | 0.21 |
| FiLM | 1.50 |
| KOSLM | 0.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y. KOSLM: A Kalman-Optimal Hybrid State-Space Memory Network for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312684
Tan X, Wang L, Wang M, Zhang Y. KOSLM: A Kalman-Optimal Hybrid State-Space Memory Network for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312684
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Xin, Lei Wang, Mingwei Wang, and Ying Zhang. 2025. "KOSLM: A Kalman-Optimal Hybrid State-Space Memory Network for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312684
APA StyleTan, X., Wang, L., Wang, M., & Zhang, Y. (2025). KOSLM: A Kalman-Optimal Hybrid State-Space Memory Network for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312684







