Cementitious Grouts in Ground Support Systems: A PRISMA-Guided Bibliometric and Mechanistic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
- (1)
- Targeted database query (Scopus)
- (2)
- Eligibility Criteria
- Inclusion: English-language journal articles (2006–2025) presenting primary data or validated modelling on cementitious-grout rheology, mechanics, or microstructure in ground-reinforcement applications.
- Exclusion: Conference papers, reviews, editorials, or studies focusing on polymeric, geopolymeric, or 3D-printing binders, as well as non-grout concretes or asphaltic materials. No automation tools were used beyond Scopus filters.
- (3)
- Quality Assessment
- (4)
- Bibliometric mapping (VOSviewer)
- (5)
- Evidence synthesis and interpretation
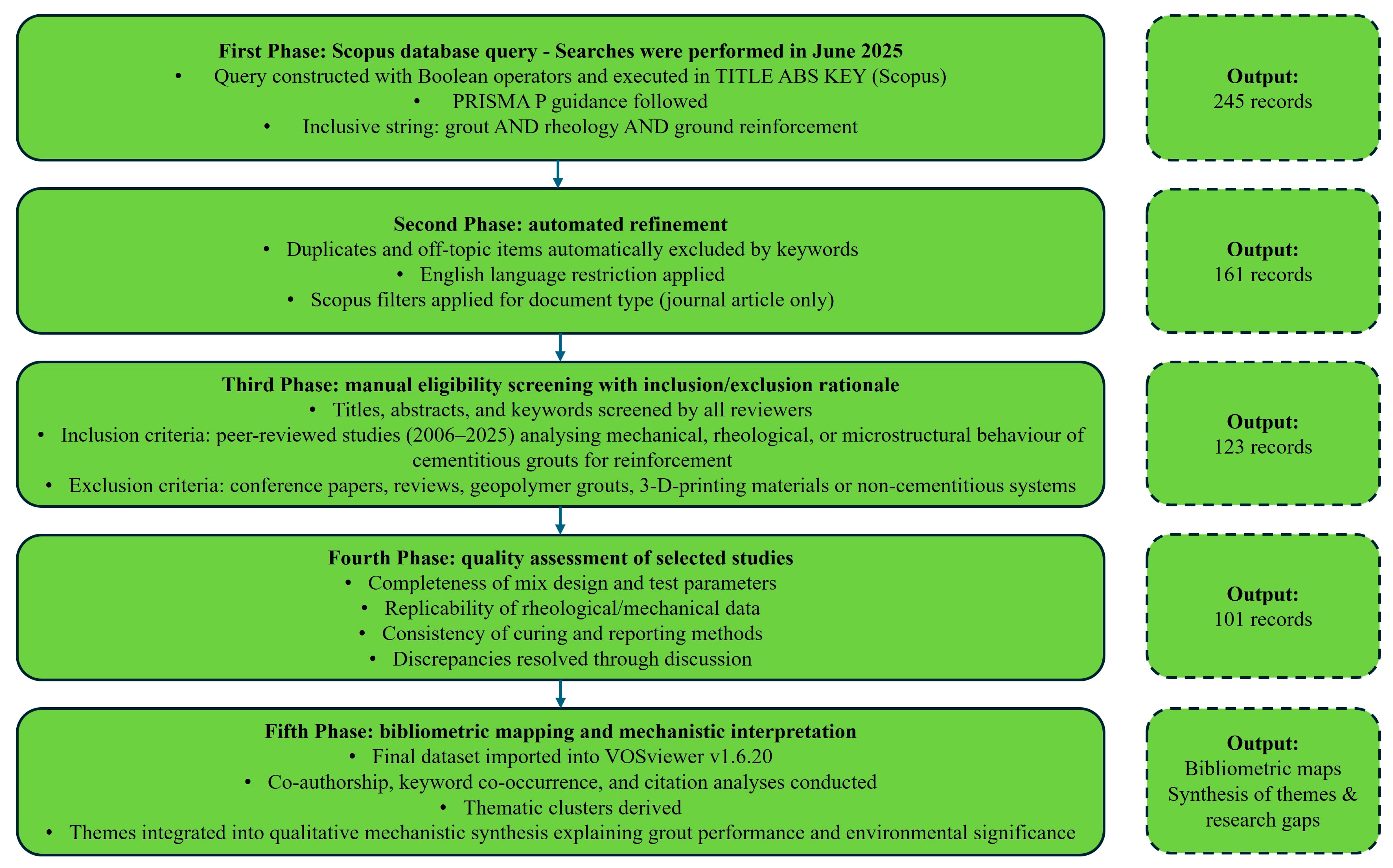
- Phase 1: Initial search
- Phase 2: Refining the search
- Phase 3: Manual selection
- Phase 4: Bibliometric analysis
3. Analysis and Results
3.1. Descriptive Results
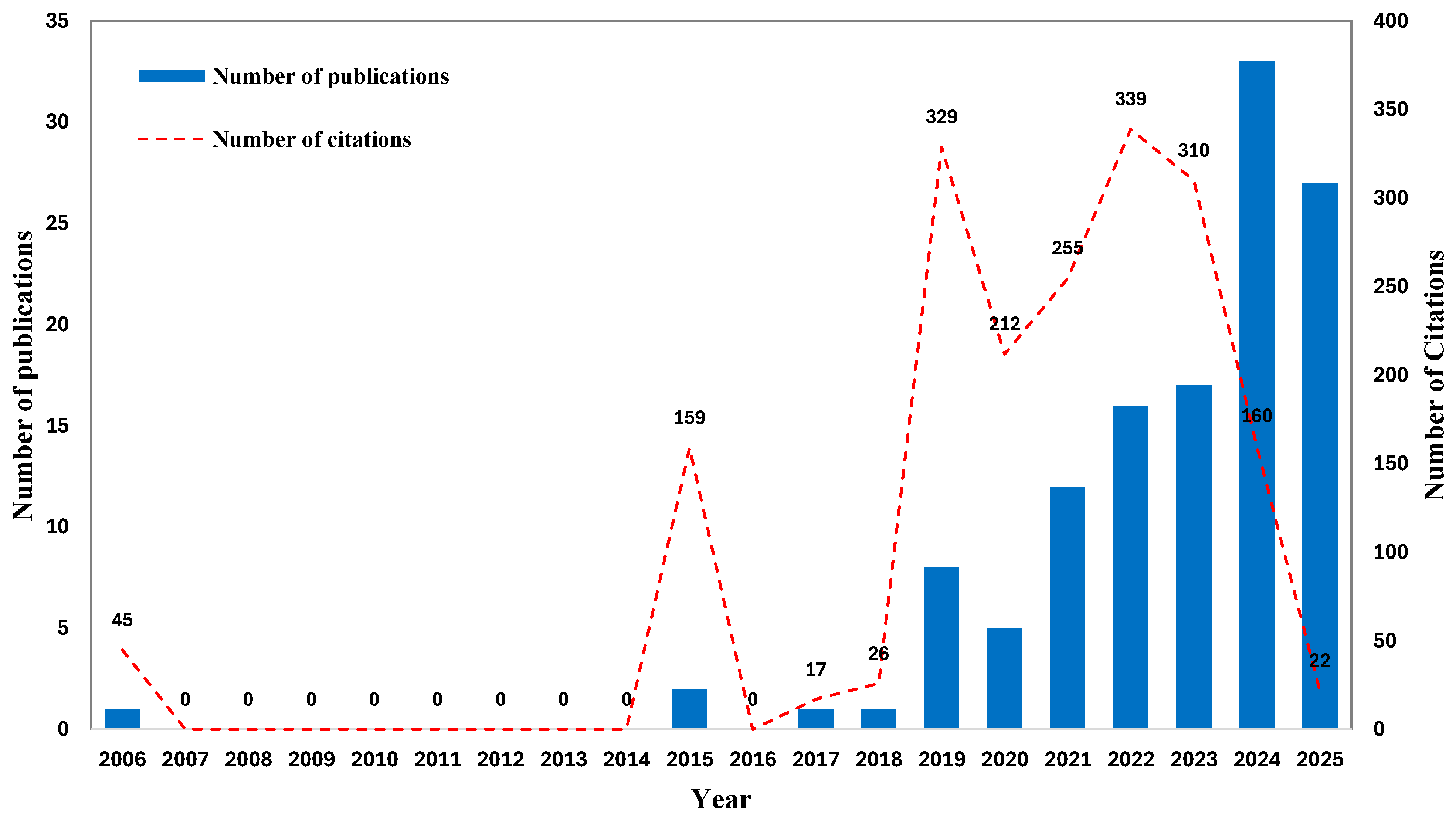
3.1.1. The Trend of Research on the Characteristics of Cementitious Grouts
3.1.2. Journal Outlets Leading Research on Characteristics of Cementitious Grouts
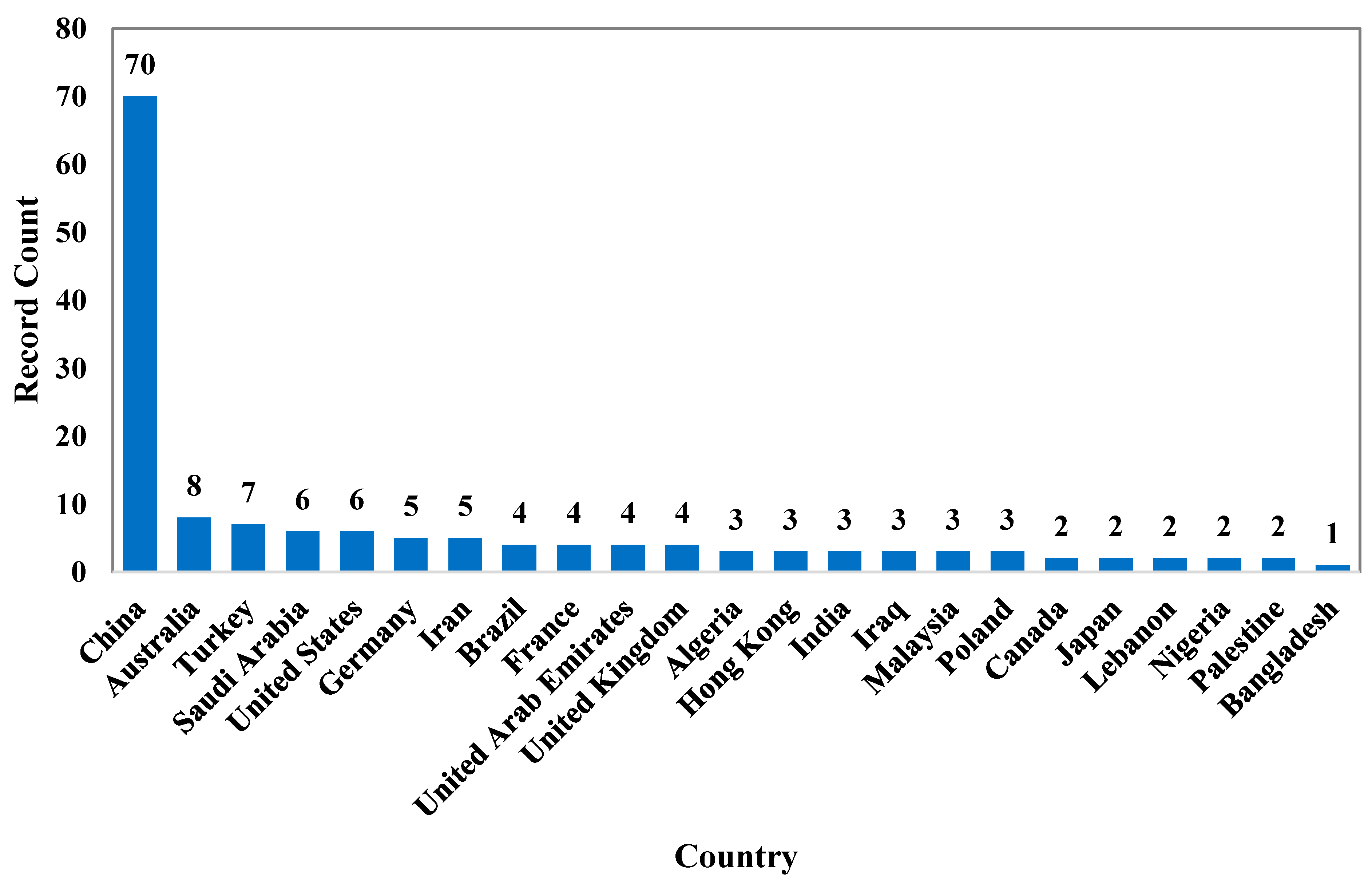
3.1.3. Institutions Leading Research on Characteristics of Cementitious Grouts
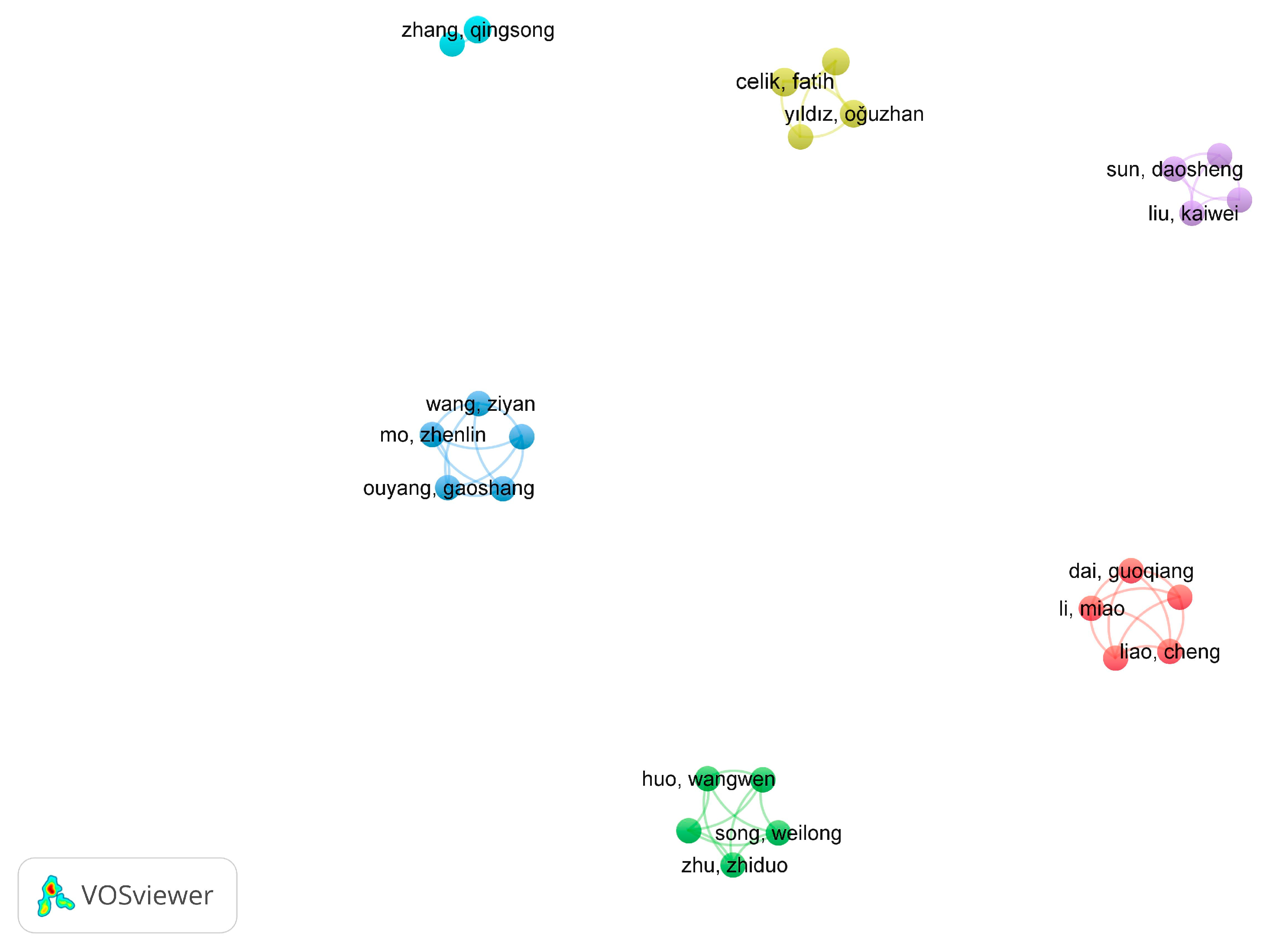
3.1.4. Researchers Leading Research on Characteristics of Cementitious Grouts
3.1.5. Articles Leading Research on Characteristics of Cementitious Grouts
| ID | Author(s) | Main Topic | Journal | Citations | Method | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Celik, Canakci [20] | An investigation of rheological properties of cementitious grout mixed with rice husk ash (RHA) | Construction and Building Materials | 159 | Laboratory experimental investigation | Increasing RHA (5–30%) raised Marsh cone time, plate cohesion, plastic/apparent viscosity and yield stress, while reducing mini-slump; at high RHA and w/b > 1.00, mixtures exhibited shear-thickening and pseudoplastic behaviour. |
| 2 | Song et al. [21] | Efficient use of steel slag in alkali-activated fly ash-steel slag-ground granulated blast furnace slag ternary blends | Construction and Building Materials | 102 | Laboratory experimental investigation | SS–GGBS slightly prolonged setting yet improved initial flow/viscosity control; increased compressive strength at early and later ages; reduced brittleness with an optimal 40% SS–GGBS for flexural strength; microstructure showed more amorphous gels, pore refinement, and lower total porosity, explaining strength gains. |
| 3 | Golewski [22] | Combined Effect of Coal Fly Ash (CFA) and Nanosilica (nS) on the Strength Parameters and Microstructural Properties of Eco-Friendly Concrete | Energies | 99 | Laboratory experimental investigation | Combined nS (5%) and CFA (0, 15 and 25%) synergistically improved microstructure (pore/crack filling) and mechanical properties; optimal 5% nS + 15% CFA raised 28-day compressive and splitting tensile strengths by 37.68% and 36.21% versus control; supports lower-carbon blended cements up to 30% replacement. |
| 4 | Nafees et al. [27] | Modelling of Mechanical Properties of Silica Fume-Based Green Concrete Using Machine Learning Techniques | Polymers | 91 | Machine learning modelling | Built ML models (DT, SVM; ensembles) on 283 tests using six mix inputs; DT outperformed SVM; ensembles improved accuracy (11% for DT; 1.5% for SVM); cement and water were the most influential variables; cross-validation confirmed generalisable performance. |
| 5 | Li et al. [25] | Investigation and practical application of a new cementitious anti-washout grouting material | Construction and Building Materials | 88 | Laboratory experimental and field investigation | CIS (cement + water glass + xanthan gum) showed short set time, high early strength, high viscosity and retention, and non-toxicity; outperformed conventional cement–water-glass grout; XRD/MIP/IR/SEM evidenced denser microstructure; grouting-parameter design method proposed from setting-time/viscosity evolution; field application effectively controlled water inrush. |
| 6 | Wang, Liu [26] | Investigation on fundamental properties and chemical characterisation of water-soluble epoxy resin modified cement grout | Construction and Building Materials | 71 | Laboratory experimental investigation | Epoxy addition lowered bleeding and initially enhanced fluidity/retention; reduced particle size and induced electrostatic attraction (zeta potential) between phases; markedly increased UCS, splitting tensile strength and ultimate strain (reduced brittleness); boosted bonding; epoxy promoted hydration but excess epoxy formed films limiting further hydration; mechanism attributed to Ca2+–OH reactions forming a cross-linked network. |
| 7 | Afroughsabet et al. [23] | Investigation of the mechanical and durability properties of sustainable high-performance concrete based on calcium sulfoaluminate cement | Building Engineering | 65 | Laboratory experimental investigation | CSA substitution enhanced mechanical properties and reduced shrinkage; increased carbonation susceptibility and steel corrosion risk; binary/ternary CSA–OPC–GGBS mixes lowered strengths and durability vs. pure CSA; SEM indicated ettringite decomposition and formation of carbonated phases. |
| 8 | Aslani F, Gedeon [24] | Experimental investigation into the properties of self-compacting rubberised concrete incorporating polypropylene and steel fibres | Structural Concrete | 64 | Laboratory experimental investigation | Replacing 20% fine aggregate with crumb rubber and adding PP/steel fibres degraded fresh/rheological properties (steel > PP impact); PP fibres slightly reduced compressive strength and had limited effect on splitting tensile; steel fibres marginally increased compressive strength and improved splitting tensile with dosage. |
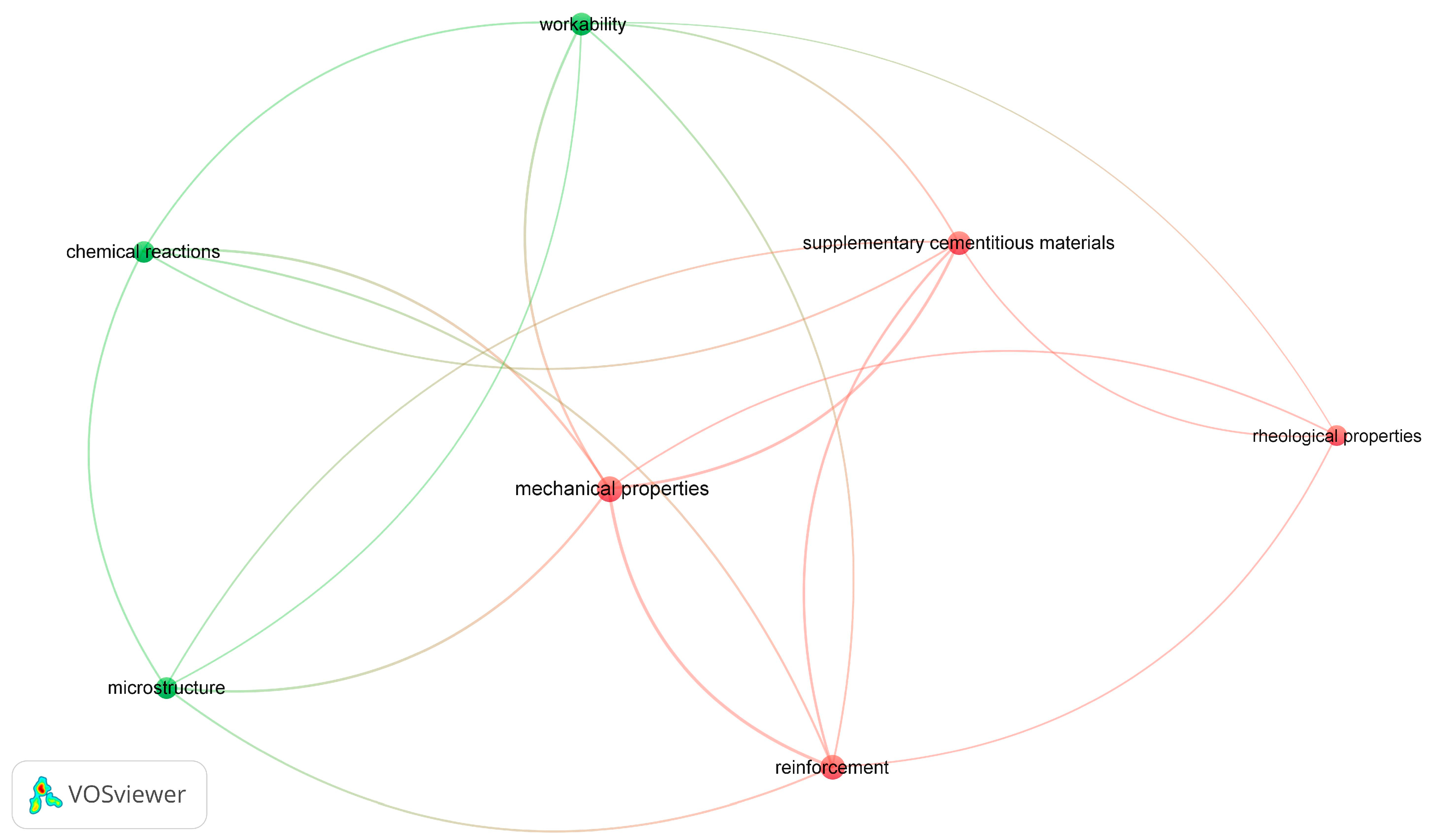
3.2. Research Hotspots on Characteristics of Cementitious Grouts
3.2.1. Reinforcement Mechanisms in Ground Support
3.2.2. Cementitious Grouts
3.2.3. Chemical Reactions and Pozzolanic Reactivity
3.2.4. Fresh and Hardened State Properties
3.2.5. Microstructural Development and Rheological Behaviour
4. Summary of Review Findings
4.1. Mechanistic Insights from Material Composition, Rheology, and Microstructure
4.2. Field-Scale Behaviour and Underground Boundary Conditions
4.3. Time-Dependent Mechanical Behaviour and Long-Term Degradation
4.4. Unresolved Issues and Research Needs
5. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FGRB | Fully grouted rock bolt |
| FGCB | Fully grouted cable bolt |
| OPC | Ordinary Portland cement |
| SCM | Supplementary cementitious material |
| GGBS | Ground granulated blast-furnace slag |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ITZ | Interfacial transition zone |
| W/G | Water-to-grout |
| UCS | Unconfined compressive strength |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| FA | Fly ash |
| RHA | Rice husk ash |
| SS | Steel slag |
| nS | nanosilica |
| CFA | Coal fly ash |
| CSA | Calcium sulfoaluminate |
| SVM | Support vector machines |
| FRP | Fibre-reinforced polymer |
| C-S-H | Calcium silicate hydrate |
| C-(A)-S-H | Calcium (alumino)silicate hydrate |
| w/b | Water-to-binder |
| SP | Superplasticiser |
| MIP | Mercury intrusion porosimetry |
| LCA | Life-cycle assessment |
| TBM | Tunnel boring machine |
| GFRP | Glass fibre reinforced polymer |
References
- Stillborg, E.B. Professional Users Handbook for Rock Bolting, 2nd ed.; Trans Tech: Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.C. Principles of Rockbolting Design. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Z. Mechanical Behavior Analysis of Fully Grouted Bolt under Axial Load. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezam, S.; Mirzaghorbanali, A.; Jodeiri Shokri, B.; Entezam, A.; Nourizadeh, H.; Craig, P.; McDougall, K.; Karunasena, W.; Aziz, N. Axial Load Transfer Mechanisms in Fully Grouted Fibreglass Rock Bolts: Experimental and Numerical Investigations. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezam, A.; Nourizadeh, H.; Burey, P.; McDougall, K.; Craig, P.; Jodeiri Shokri, B.; Entezam, S.; Aziz, N.; Mirzaghorbanali, A. Integrating Recycled Waste Materials in Cementitious Grouts: Evaluating Mechanical Integrity and Rheological Behaviour. Discov. Mater. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential Economically Viable Solutions for a Low-CO2 Cement-Based Materials Industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, M.; Cohen, M.D.; Olek, J. Sulfate Attack Research—Whither Now? Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Snellings, R.; Bernal, S.A. Supplementary Cementitious Materials: New Sources, Characterization, and Performance Insights. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fatoyinbo, I.O.; Sheng, R.; Wang, Q.; Mudassir Zia, S.M.; Cui, P.; Zhang, J.L. Advancing the Applicability of Recycled Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Bottom Ash as a Cement Substitute in Printable Concrete: Emphasis on Rheological and Microstructural Properties. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Rheology of Fresh Concrete: From Measurements to Predictions of Casting Processes. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2007, 40, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonebi, M.; Bassuoni, M.T.; Kwasny, J.; Amanuddin, A.K. Effect of Nanosilica on Rheology, Fresh Properties, and Strength of Cement-Based Grouts. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; De Schryver, R.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G. Thixotropic Structural Build-up of Cement-Based Materials: A State-of-the-Art Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 122, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, G.; Ulm, F.J. The Effect of Two Types of C-S-H on the Elasticity of Cement-Based Materials: Results from Nanoindentation and Micromechanical Modeling. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Muzenda, T.R.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Kawashima, S.; Sui, T.; Yong, H.; Xie, N.; Cheng, X. Mechanisms Dominating Thixotropy in Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3). Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Su, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ding, X. Strength Behavior and Microscopic Mechanisms of Geopolymer-Stabilized Waste Clays Considering Clay Mineralogy. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 530, 146877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Su, Y.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C. Modulation of Initial CaO/Al2O3 and SiO2/Al2O3 Ratios on the Properties of Slag/Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Stabilized Clay: Synergistic Effects and Stabilization Mechanism. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Miller, S.A.; John, V.M.; Provis, J.L.; Favier, A.; Horvath, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Environmental Impacts and Decarbonization Strategies in the Cement and Concrete Industries. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. CitNetExplorer: A New Software Tool for Analyzing and Visualizing Citation Networks. J. Inf. 2014, 8, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Estarli, M.; Barrera, E.S.A.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Grilo, A. Bibliometric Analysis and Review of Building Information Modelling Literature Published between 2005 and 2015. Autom. Constr. 2017, 80, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, S.M.; Mhaimeed, I.S.; Tayeh, B.A.; Najm, H.M.; Qaidi, S. Investigation of the Use of Textile Carbon Yarns as Sustainable Shear Reinforcement in Concrete Beams. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Adabre, M.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ameyaw, E.E. Artificial Intelligence in the AEC Industry: Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Research Activities. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, F.; Canakci, H. An Investigation of Rheological Properties of Cement-Based Grout Mixed with Rice Husk Ash (RHA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhu, Z.; Pu, S.; Wan, Y.; Huo, W.; Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Yao, K.; Hu, L. Efficient Use of Steel Slag in Alkali-Activated Fly Ash-Steel Slag-Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Ternary Blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golewski, G.L. Combined Effect of Coal Fly Ash (CFA) and Nanosilica (NS) on the Strength Parameters and Microstructural Properties of Eco-Friendly Concrete. Energies 2023, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroughsabet, V.; Biolzi, L.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Gastaldi, M.M. Investigation of the Mechanical and Durability Properties of Sustainable High Performance Concrete Based on Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F.; Gedeon, R. Experimental Investigation into the Properties of Self-Compacting Rubberised Concrete Incorporating Polypropylene and Steel Fibers. Struct. Concr. 2019, 20, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Investigation and Practical Application of a New Cementitious Anti-Washout Grouting Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. Investigation on Fundamental Properties and Chemical Characterization of Water-Soluble Epoxy Resin Modified Cement Grout. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafees, A.; Amin, M.N.; Khan, K.; Nazir, K.; Ali, M.; Javed, M.F.; Aslam, F.; Musarat, M.A.; Vatin, N.I. Modeling of Mechanical Properties of Silica Fume-Based Green Concrete Using Machine Learning Techniques. Polymers 2022, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.R.; Cecchin, D.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Valadão, I.; Alexandre, J.; da Silva, F.C.; Marvila, M.T.; Gunasekaran, M.; Filho, F.G.; Monteiro, S.N. Technological Characterization of Pet—Polyethylene Terephthalate—Added Soil-Cement Bricks. Materials 2021, 14, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.R.; Marvila, M.T.; Linhares, J.A.T.; Azevedo, A.R.G. de Evaluation of the Properties of Adobe Blocks with Clay and Manure. Buildings 2023, 13, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, C.R. Rock Reinforcement Systems. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1997, 34, 919–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.G.; Villaescusa, E.; Windsor, C.R. Ground Support Terminology and Classification: An Update. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2012, 30, 553–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodeiri Shokri, B.; Mirzaghorbanali, A.; Nourizadeh, H.; McDougall, K.; Karunasena, W.; Aziz, N.; Entezam, S.; Entezam, A. Axial Load Transfer Mechanism in Fully Grouted Rock Bolting System: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D. Theory and Technology of Rock Excavation for Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hyett, A.J.; Bawden, W.F.; Reichert, R.D. The Effect of Rock Mass Confinement on the Bond Strength of Fully Grouted Cable Bolts. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1992, 29, 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C. A New Energy-Absorbing Bolt for Rock Support in High Stress Rock Masses. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2010, 47, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourizadeh, H.; Mirzaghorbanali, A.; McDougall, K.; Jeewantha, L.H.J.; Craig, P.; Motallebiyan, A.; Shokri, B.J.; Rastegarmanesh, A.; Aziz, N. Characterization of Mechanical and Bonding Properties of Anchoring Resins under Elevated Temperature. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2023, 170, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Nie, W.; Date, K.; Iwano, K.; Okada, Y. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Interface Behaviour Between the Rock Bolt and Bond Material. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyett, A.J.; Moosavi, M.; Bawden, W.F. Load distribution along fully grouted bolts, with emphasis on cable bolt reinforcement. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1996, 20, 517–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, M.; Bawden, W.F. Shear Strength of Portland Cement Grout. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Aziz, N.; Ye, W.; Nemcik, J. Mechanical Properties of Grouts at Various Curing Times. In Proceedings of the 16th Coal Operators’ Conference, Mining Engineering, Wollongong, Australia, 10–12 February 2016; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Benmokrane, B.; Chennouf, A.; Mitri, H.S. Laboratory Evaluation of Cement-Based Grouts and Grouted Rock Anchors. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1995, 32, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachopoulos, N.; Cruz, D.; Tatone, B.S.A.; Lisjak, A.; Mahabadi, O.K.; Forbes, B.; Carrapatoso, C. The Performance of Axially Loaded, Fully Grouted Rock Bolts Based on Pull-Out Experiments Utilizing Fiber Optics Technology and Associated Numerical Modelling of Such Support Elements. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 1389–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Majoor, D.; Mirzaghorbanali, A. Strength Properties of Grout for Strata Reinforcement. In Procedia Engineering; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 191, pp. 1178–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Xu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, J.; Yan, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive Drive-Based Integration Technique for Predicting Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Fresh Gangue Backfill Slurry. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Han, Y.; Xia, L.; Fang, Z.; Lu, D.; Jia, Q.; Gao, Y. Study on the Flow Properties of Modified Magnesium-Coal-Based Solid Waste Carbon Sequestration Backfill Materials. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2025, 146, 104443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, J.; Yi, W.; Li, W.; Chen, L. Preparation and Performance Assessment of Multi-Solid Waste Synergistic Red Mud-Based Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 475, 141222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, J.; Ahmed, A. Performance of Ternary Corncob Ash and Anthill Soil Concrete in Sulfate Solutions. Eur. J. Eng. Res. Sci. 2017, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, G.; Ferraris, C.F.; Weiss, J. Rheological Properties of Cement Pastes: A Discussion of Structure Formation and Mechanical Property Development. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, P.; Mirzaghorbanali, A.; McDougall, K.; Aziz, N.; Jodeiri Shokri, B. Shear Behaviour of Fibreglass Rock Bolts for Various Pretension Loads. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 8083–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Nonat, A. Hydration of Cementitious Materials, Present and Future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollpracht, A.; Lothenbach, B.; Snellings, R.; Haufe, J. The Pore Solution of Blended Cements: A Review. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2016, 49, 3341–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balonis, M.; Lothenbach, B.; Le Saout, G.; Glasser, F.P. Impact of Chloride on the Mineralogy of Hydrated Portland Cement Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, Z. Investigations into the Cementation Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Coal-Derived Solid Waste-Cellulose Ether Composite Grout. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 491, 142742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, F.; Dong, Y.; Gu, S.; Fan, X.; Xiao, W. Study on Novel Alkali-Activated Cementitious Grout for Scour Control of Offshore Foundation. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2025, 42, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.S.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, H.S.; Chen, Z.T.; Li, Y.N.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.Z.; You, C.; Skoczylas, F. Injectability Analysis of Seawater-Mixed Magnesium Phosphate Cement Slurry Applied to a Sand Layer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avet, F.; Snellings, R.; Alujas Diaz, A.; Ben Haha, M.; Scrivener, K. Development of a New Rapid, Relevant and Reliable (R3) Test Method to Evaluate the Pozzolanic Reactivity of Calcined Kaolinitic Clays. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.J.; L’Hôpital, E.; Provis, J.L.; Lothenbach, B. Composition-Solubility-Structure Relationships in Calcium (Alkali) Aluminosilicate Hydrate (C-(N,K-)A-S-H). Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 13530–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Nonat, A. Calcium Silicate Hydrates: Solid and Liquid Phase Composition. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haha, M.B.; Lothenbach, B.; Le Saout, G.; Winnefeld, F. Influence of Slag Chemistry on the Hydration of Alkali-Activated Blast-Furnace Slag—Part I: Effect of MgO. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haha, M.B.; Lothenbach, B.; Le Saout, G.; Winnefeld, F. Influence of Slag Chemistry on the Hydration of Alkali-Activated Blast-Furnace Slag—Part II: Effect of Al2O3. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, D. Design and Evaluation of Alkali-Activated Slag-Calcined Coal Gangue Cement and the Shrinkage Control by Calcium Carbonate Whisker. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Suo, N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q. Influence of Glass Beads on Alkali-Activated Slag-Metakaolin-Based Novel Grouting Materials: Physical Properties, Leaching Kinetics and Microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 452, 138809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Calculations in Cementitious Systems. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2010, 43, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Winnefeld, F. Thermodynamic Modelling of the Hydration of Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Huang, K.; Shen, G.; Miao, Y.; Wu, J. The Effects of Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose and Metakaolin on the Properties of Self-Compacting Solidified Soil Based on Abandoned Slurry. Materials 2024, 17, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L. Alkali-Activated Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibong, G.A.; Sunday, E.U.; Akudike, J.C.; Okeke, O.C.; Amadi, C. A Review of the Principles and Methods of Soil Stabilization. Int. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2020, 6, 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall, G.H. Workability and Quality Control of Concrete, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Neville, A.M.; Brooks, J.J. Concrete Technology, 2nd ed.; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-273-73219-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Chu, Y.-S.; Seo, S.-K.; Kim, J.-H.J. The Non-Shrinkage Grout to Use Ground Fly Ash as Admixture. Ceram. Process. Res. 2018, 19, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Mikos, A.P.; Ng, C.W.W.; Faro, V.P. Sustainable Application of Fine Recycled-Concrete Aggregate in Soil-Nailing Grout. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Mamun, M.A.; Alyousef, R.; Amran, Y.H.M.; Aslani, F.; Alabduljabbar, H. Properties and Utilizations of Waste Tire Rubber in Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G. The Role of Cohesion in Cement Grouting of Rock. Comm. Int. Grands Barrages 1985, 58, 235–261. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, F.; Li, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Performance of Typical Cement Suspension-Sodium Silicate Double Slurry Grout. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, F.; Parron-Rubio, M.E.; Garcia-Manrique, J.M.; Rubio-Cintas, M.D. Study of the Suitability of Different Types of Slag and Its Influence on the Quality of Green Grouts Obtained by Partial Replacement of Cement. Materials 2019, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, O.; Zaimoglu, A.S.; Hinislioglu, S.; Altun, S. Taguchi Approach for Optimization of the Bleeding on Cement-Based Grouts. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2005, 20, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, K.; Xu, G.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Lü, Q. Sedimentation-Affected Engineering Performances and Microstructures of a Hybrid Portland-Sulfate Aluminate Cement Grout Cast in Long Tubes. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, T.S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Balasubramanian, K.; Bharatkumar, B.H.; Rama Mohan Rao, P. Investigations on the Cementitious Grouts Containing Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonebi, M.; Abdalqader, A.; Fayyad, T.; Perrot, A.; Bai, Y. Optimisation of Rheological Parameters, Induced Bleeding, Permeability and Mechanical Properties of Supersulfated Cement Grouts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bras, A.; Henriques, F.M.A. Natural Hydraulic Lime Based Grouts—The Selection of Grout Injection Parameters for Masonry Consolidation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, R.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.; Cui, S.; Kang, J.; Yao, Z. Preparation and Properties Study of Cementitious Grouts Containing Crumb Rubber. Buildings 2021, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Kawashima, S.; Marchon, D.; Vasilic, K.; Wolfs, R. Recent Advances on Yield Stress and Elasticity of Fresh Cement-Based Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Fu, L.; Wu, B.; Xu, C.; Lim, C.W. Packing Fraction Effect on Dynamic Creep Deformation of Granular Materials. Acta Geotech. 2025, 20, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Fu, L.; Wu, B.; Xu, C.; Lim, C.W.; Ding, H. Particle Shape Effect on Creep and Fluidity of Granular Packing. J. Eng. Mech. 2025, 151, 04025067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, M.; Rossen, J.; Martirena, F.; Scrivener, K. Cement Substitution by a Combination of Metakaolin and Limestone. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lootens, D.; Jousset, P.; Martinie, L.; Roussel, N.; Flatt, R.J. Yield Stress during Setting of Cement Pastes from Penetration Tests. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Xue, Y.; Qiu, D.; Wang, P.; Lu, H. Multi-Channel Fusion Prediction of TBM Tunneling Thrust Based on Multimodal Decomposition and Reconstruction. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 167, 107061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Meng, C.; Qu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Niu, J.; Wang, L.; Song, N.; Yin, Z. Dual Effects of Caragana korshinskii Introduction on Herbaceous Vegetation in Chinese Desert Areas: Short-Term Degradation and Long-Term Recovery. Plant Soil 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ID | Journal | Number of Publications | Total Citations | Impact Factor | Publisher |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Construction and Building Materials | 28 | 771 | 8.0 | Elsevier—Amsterdam, Netherlands |
| 2 | Journal of Building Engineering | 8 | 145 | 7.4 | Elsevier |
| 3 | Case Studies in Construction Materials | 7 | 150 | 6.6 | Elsevier |
| 4 | Materials | 6 | 28 | 3.2 | MDPI—Basel, Switzerland |
| 5 | Buildings | 3 | 9 | 3.1 | MDPI |
| 6 | Advances in Cement Research | 2 | 10 | 1.3 | ICE Publishing—London, UK |
| 7 | Advances in Materials Science and Engineering | 2 | 3 | -- | John Wiley and Sons—Hoboken, NJ, USA |
| 8 | Applied Sciences (Switzerland) | 2 | 9 | 2.5 | MDPI |
| 9 | Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering | 2 | 17 | 2.9 | Springer—New York City, NY, USA |
| 10 | Journal of Sustainable Cement-Based Materials | 2 | 3 | 4.2 | Taylor and Francis—London, UK |
| ID | Institution | Number of Publications | Total Citations | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shandong University | 5 | 170 | China |
| 2 | Anhui Jianzhu University | 4 | 9 | China |
| 3 | University of Science and Technology Beijing | 4 | 47 | China |
| 4 | The University of Western Australia | 3 | 153 | Australia |
| 5 | Anhui University of Science and Technology | 3 | 64 | China |
| 6 | Gaziantep University | 3 | 200 | Turkey |
| 7 | Harbin Institute of Technology | 3 | 160 | China |
| 8 | Southeast University | 3 | 133 | China |
| 9 | China University of Mining and Technology | 3 | 14 | China |
| 10 | Nigde Omer Halisdemir University | 3 | 13 | Turkey |
| ID | Author | Institution | Number of Publications | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Celik, Fatih | Nigde Omer Halisdemir University, Turkey | 5 | 189 |
| 2 | Canakci, Hanifi | Gaziantep University, Turkey | 3 | 200 |
| 3 | Zhang, Qingsong | Shandong University, China | 3 | 127 |
| 4 | Cinar, Muhammet | Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Turkey | 3 | 47 |
| 5 | Wang, Kai | Henan University, China | 3 | 24 |
| 6 | Yıldız, Oguzhan | Nigde Omer Halisdemir University, Turkey | 3 | 13 |
| 7 | Colak, Andac Batur | Nigde Omer Halisdemir University, Turkey | 3 | 13 |
| 8 | Golewski, Grzegorz Ludwik | Lublin University of Technology, Poland | 2 | 136 |
| 9 | Huo, Wangwen | Southeast University, China | 2 | 132 |
| 10 | Pu, Shaoyun | Southeast University, China | 2 | 132 |
| Property | Significance for Ground Support | Main Influencing Factors | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workability (flowability and cohesion) | Ensures grout can be pumped/injected without segregation | w/b ratio, SCM type, aggregate fineness, admixtures, temperature | Raw fly ash ↑ * flowability; ground fly ash minimal effect; recycled aggregate ↓ * flow but superplasticisers can restore; rubberised mixes markedly ↓ workability | Kim et al., 2018 [74] Mikos et al., 2021 [75] Siddika et al., 2019 [76] |
| Bleeding (stability) | Indicates risk of voids and weak encapsulation | w/b ratio, particle size distribution, SCM type, additives | Bleeding ↑ with w/b ratio; <5% is acceptable; slag and fly ash blends ↓ bleeding; silica fume most effective in minimising | Sha et al., 2019 [78] Perez-Garcia et al., 2019 [79] Tan et al., 2005 [80] |
| Consistency (plasticity) | Determines flow class (fluid, plastic, flowable) and ease of injection | w/b ratio, SCM replacement, superplasticiser (SP) dosage | Higher SCM replacement ↑ SP demand; adjusted water content can reduce SP use; yield stress/viscosity mapping supports design optimisation | Krishnamoorthy et al., 2002 [82] Sonebi et al., 2020 [83] |
| Injectability (penetrability) | Governs grout’s ability to fill voids and fractures effectively | Rheological parameters (yield stress, viscosity), particle size, stability | Injectability depends on rheology and fracture aperture; poor penetrability compromises encapsulation | Bras & Henriques, 2011 [84] |
| Compressive and flexural strength | Determines load transfer and structural capacity | w/b ratio, curing time, SCM content | UCS ↑ with lower w/b; strength gains continue up to 28 days; bar bolts stiffer than cables due to bond uniformity | Aziz et al., 2017 [47]; Mirzaghorbanali et al., 2016 [44]; Benmokrane et al., 1995 [45] |
| Shear strength | Critical for resisting slip at grout–steel and grout–rock interfaces | Confining pressure, grout composition | Direct shear tests confirm shear resistance ↑ with confinement | Moosavi & Bawden, 2003 [43] |
| Toughness and resilience | Enhances performance under impact or dynamic loading | Use of rubber aggregates, nano-additives | Rubber ↓ strength but ↑ toughness; nanosilica densifies microstructure and ↓ permeability | Yuan et al., 2021 [85] Sonebi et al., 2015 [11] |
| Top Contributing Journals | Co-Authorship Analysis: Leading Authors | Co-Authorship Analysis: Leading Institutions | Research Hot Spots | Frequency of Keywords Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Entezam, A.; Nourizadeh, H.; Burey, P.; McDougall, K.; Craig, P.; Jodeiri Shokri, B.; Entezam, S.; Aziz, N.; Mirzaghorbanali, A. Cementitious Grouts in Ground Support Systems: A PRISMA-Guided Bibliometric and Mechanistic Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12439. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312439
Entezam A, Nourizadeh H, Burey P, McDougall K, Craig P, Jodeiri Shokri B, Entezam S, Aziz N, Mirzaghorbanali A. Cementitious Grouts in Ground Support Systems: A PRISMA-Guided Bibliometric and Mechanistic Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12439. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312439
Chicago/Turabian StyleEntezam, Alireza, Hadi Nourizadeh, Paulomi (Polly) Burey, Kevin McDougall, Peter Craig, Behshad Jodeiri Shokri, Shima Entezam, Naj Aziz, and Ali Mirzaghorbanali. 2025. "Cementitious Grouts in Ground Support Systems: A PRISMA-Guided Bibliometric and Mechanistic Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12439. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312439
APA StyleEntezam, A., Nourizadeh, H., Burey, P., McDougall, K., Craig, P., Jodeiri Shokri, B., Entezam, S., Aziz, N., & Mirzaghorbanali, A. (2025). Cementitious Grouts in Ground Support Systems: A PRISMA-Guided Bibliometric and Mechanistic Review. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12439. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312439










