Cyber-Physical Security in Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Research Areas, Threats, and Countermeasures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
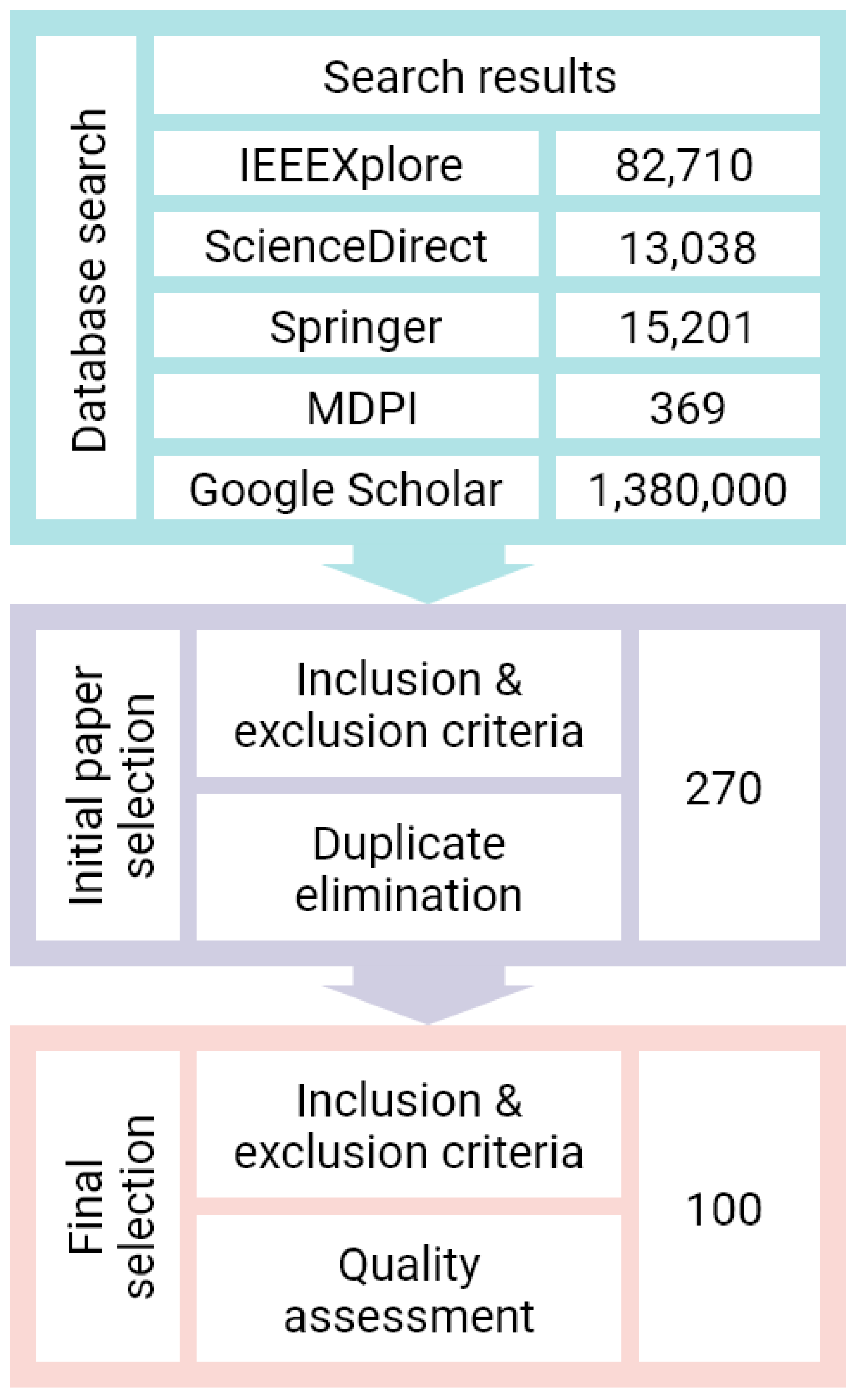
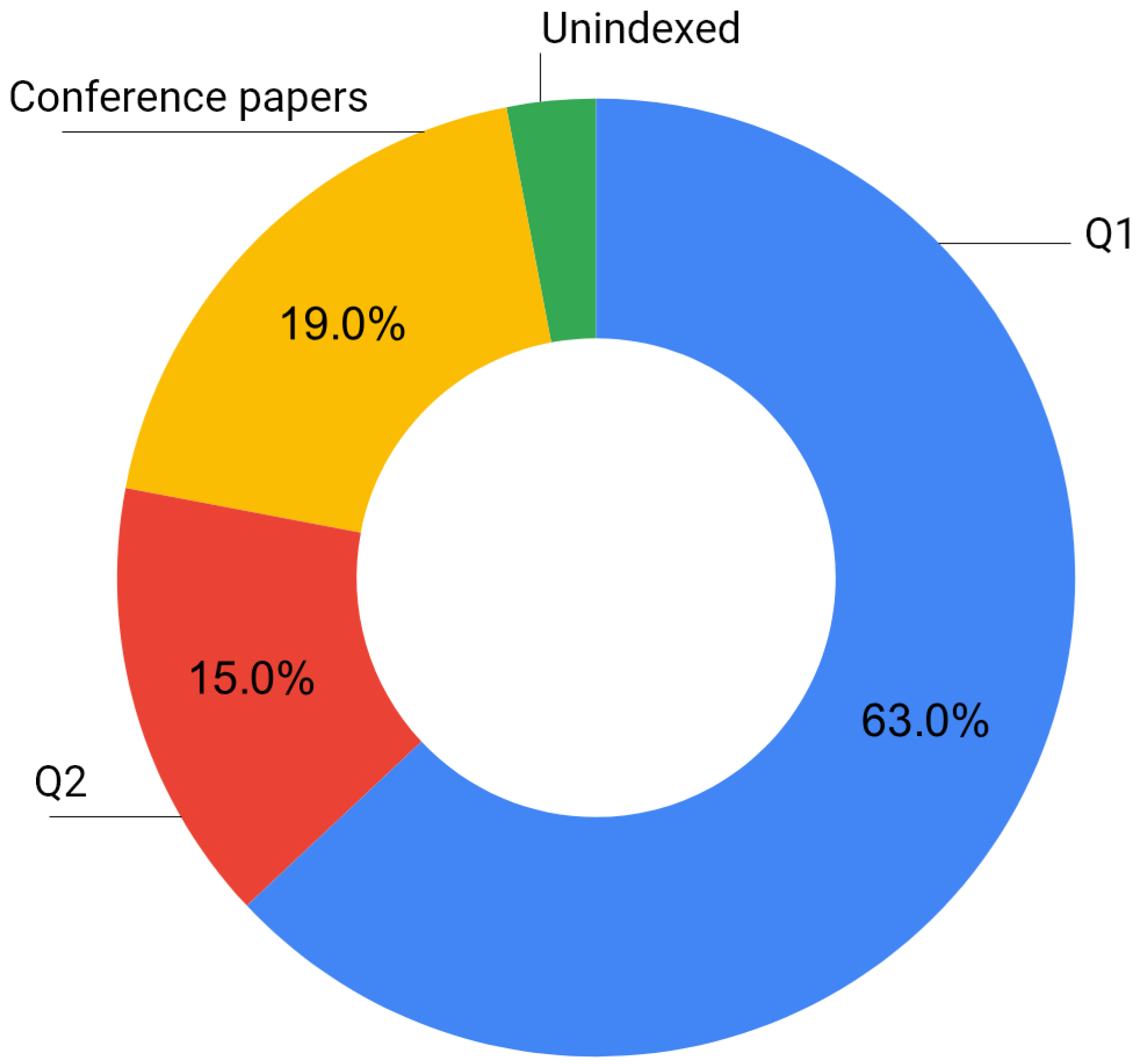
2.1. Paper Selection Criteria
- Q1:
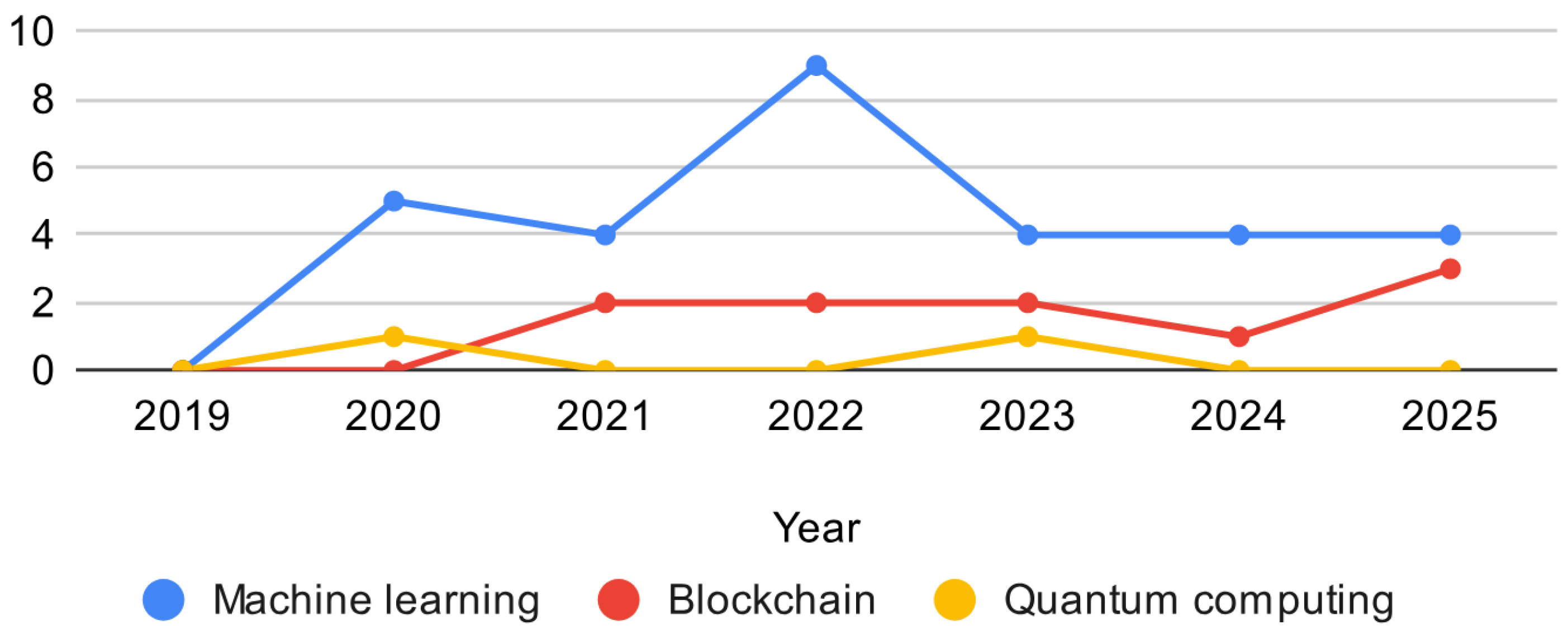
- How is the research focus on SG cyber-physical security evolving over the years in existing literature reviews?
- Q2:
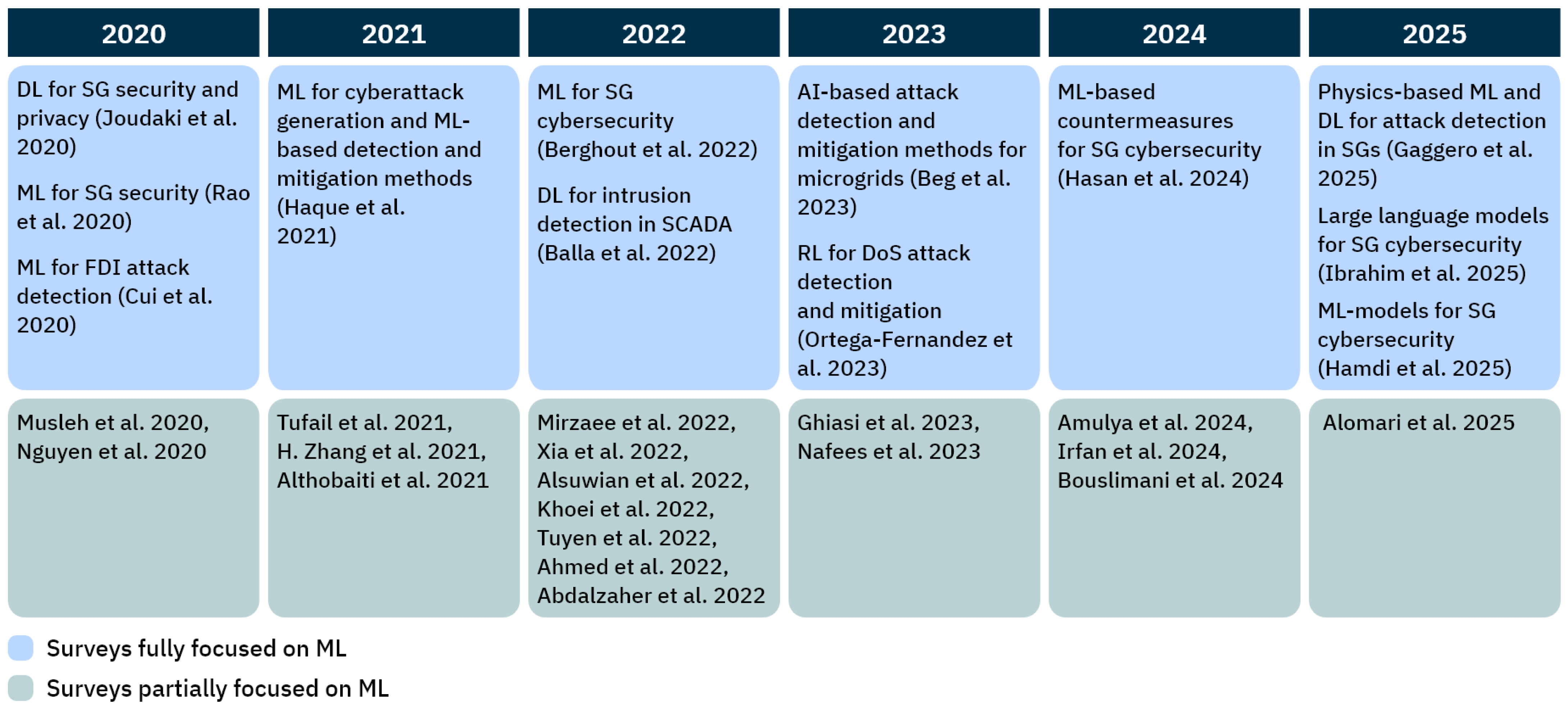
- How can we classify the existing reviews?
- Q3:
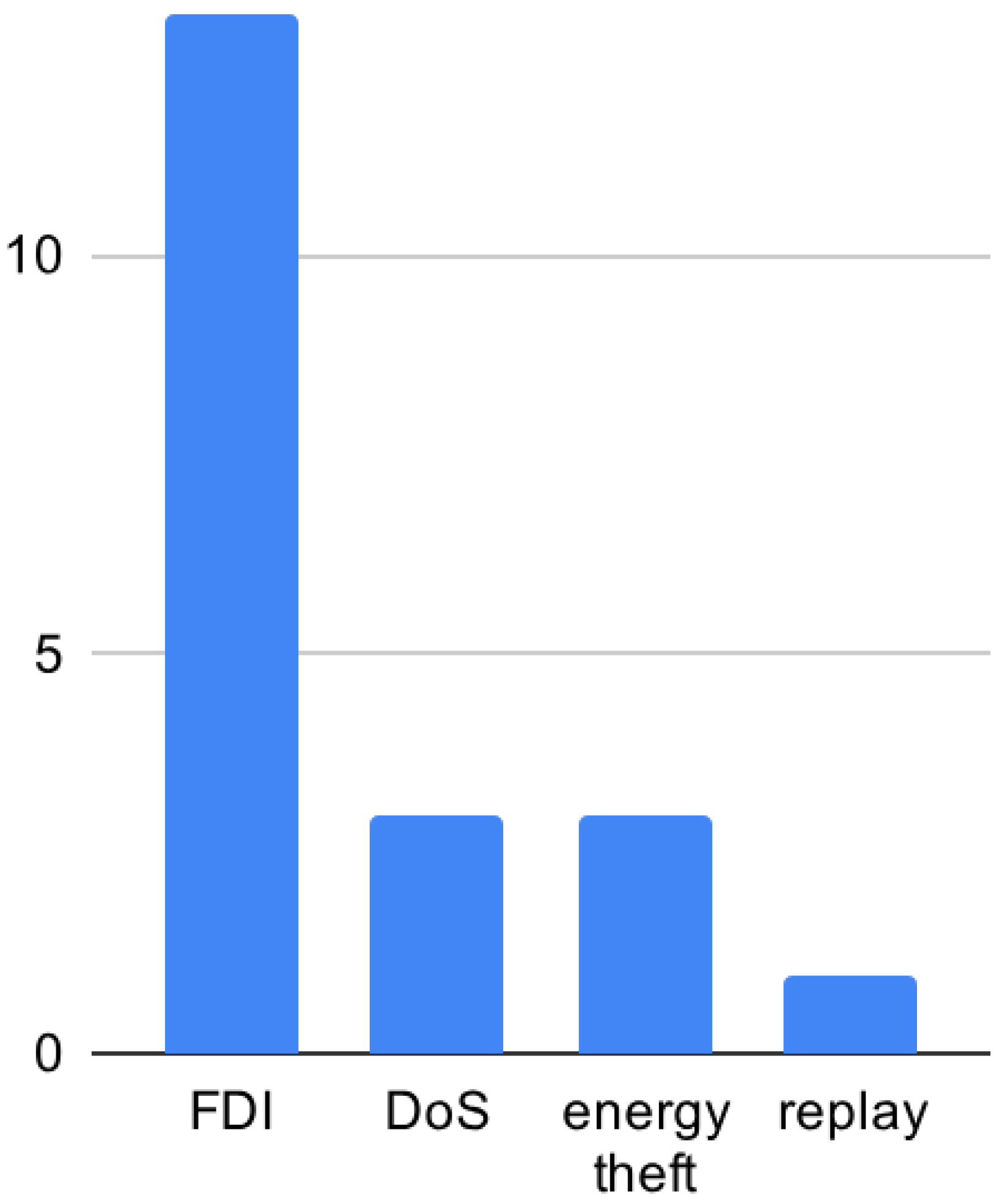
- Which cyberattacks on SGs have been the focus of researchers?
- Q4:
- What methods are used in securing grids against attacks?
- Q5:
- Which challenges are being faced by research on SG cybersecurity?
- I1:
- Works that review the cyber-physical security of SGs in general.
- I2:
- Works that review existing countermeasures for attacks on SGs.
- I3:
- Works that review attacks, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors on SGs.
- I4:
- Works that review the cyber-physical security of a particular component in the SG.
- I5:
- Works that review countermeasures against a particular attack on SGs.
- E1:
- Works that do not focus on electric grid cyber-physical security.
- E2:
- Works on the security and resilience of electric grids that focus on aspect other than cyber-physical security and attacks.
- E3:
- Works on the security of cyber-physical systems (CPSs) or industrial control systems (ICSs) in general.
- QA1:
- The survey must provide a comprehensive review of existing literature.
- QA2:
- The survey must introduce a novelty compared to previous works.
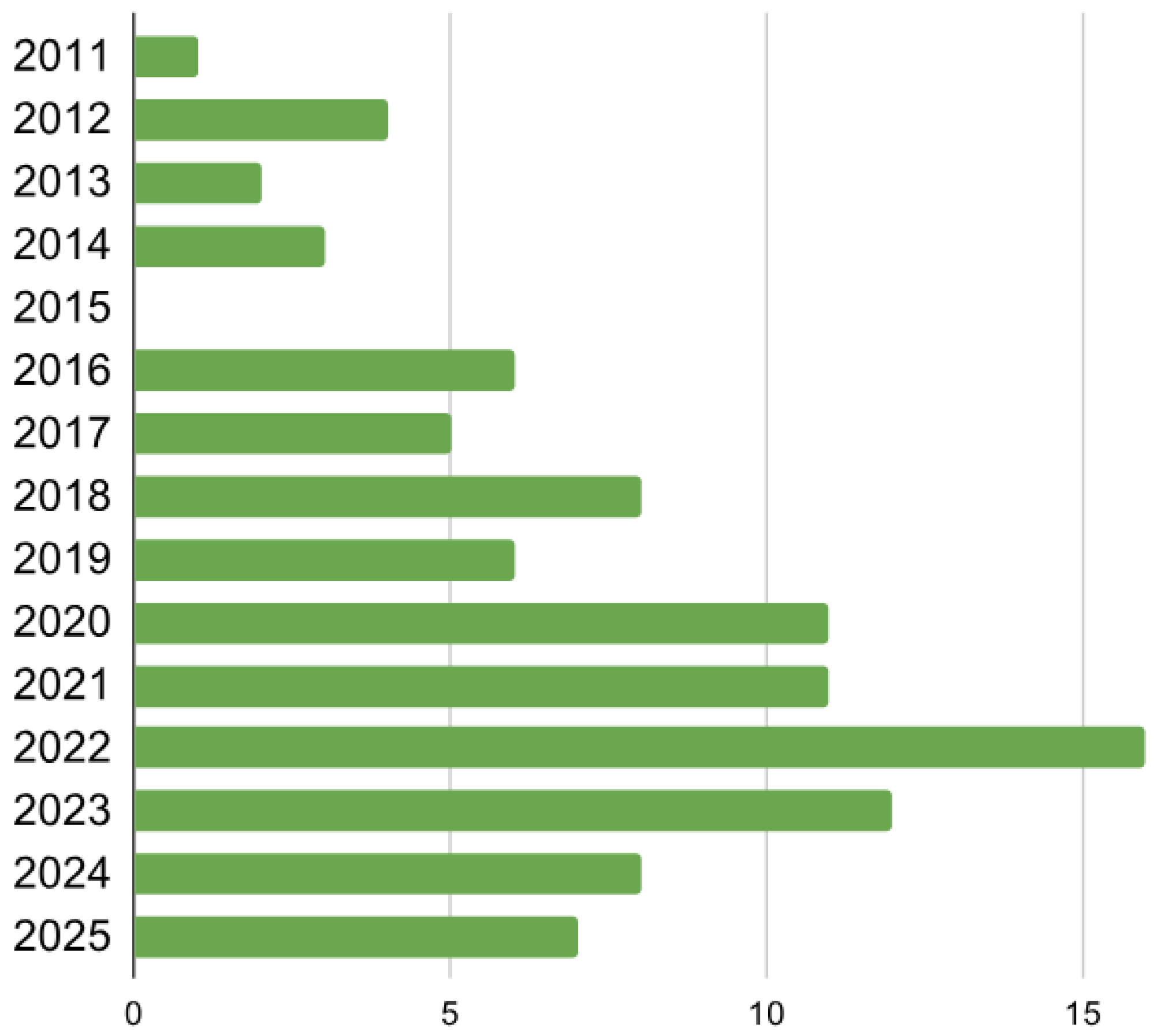
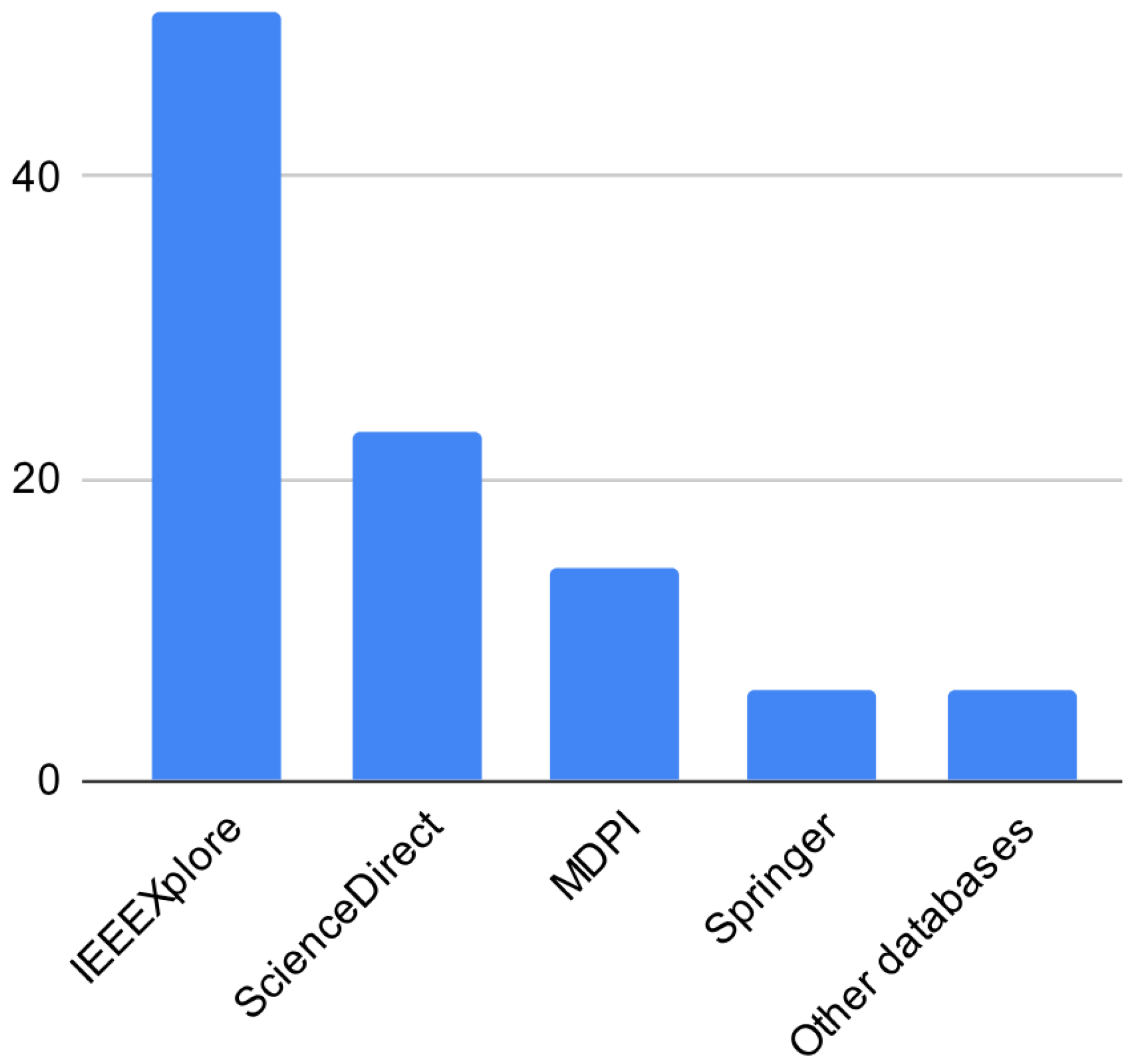
2.2. Search Process
3. Key Concepts and Definitions
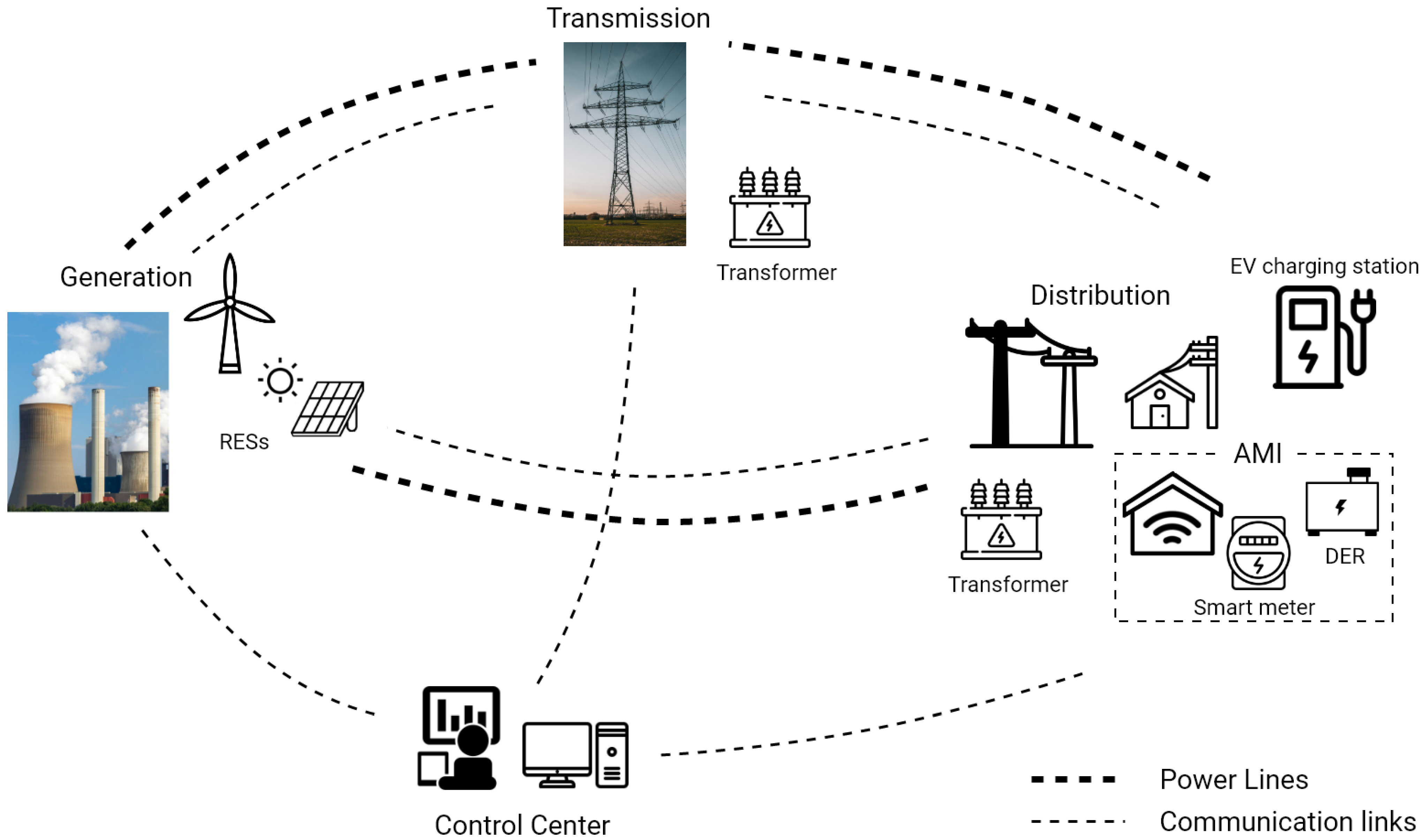
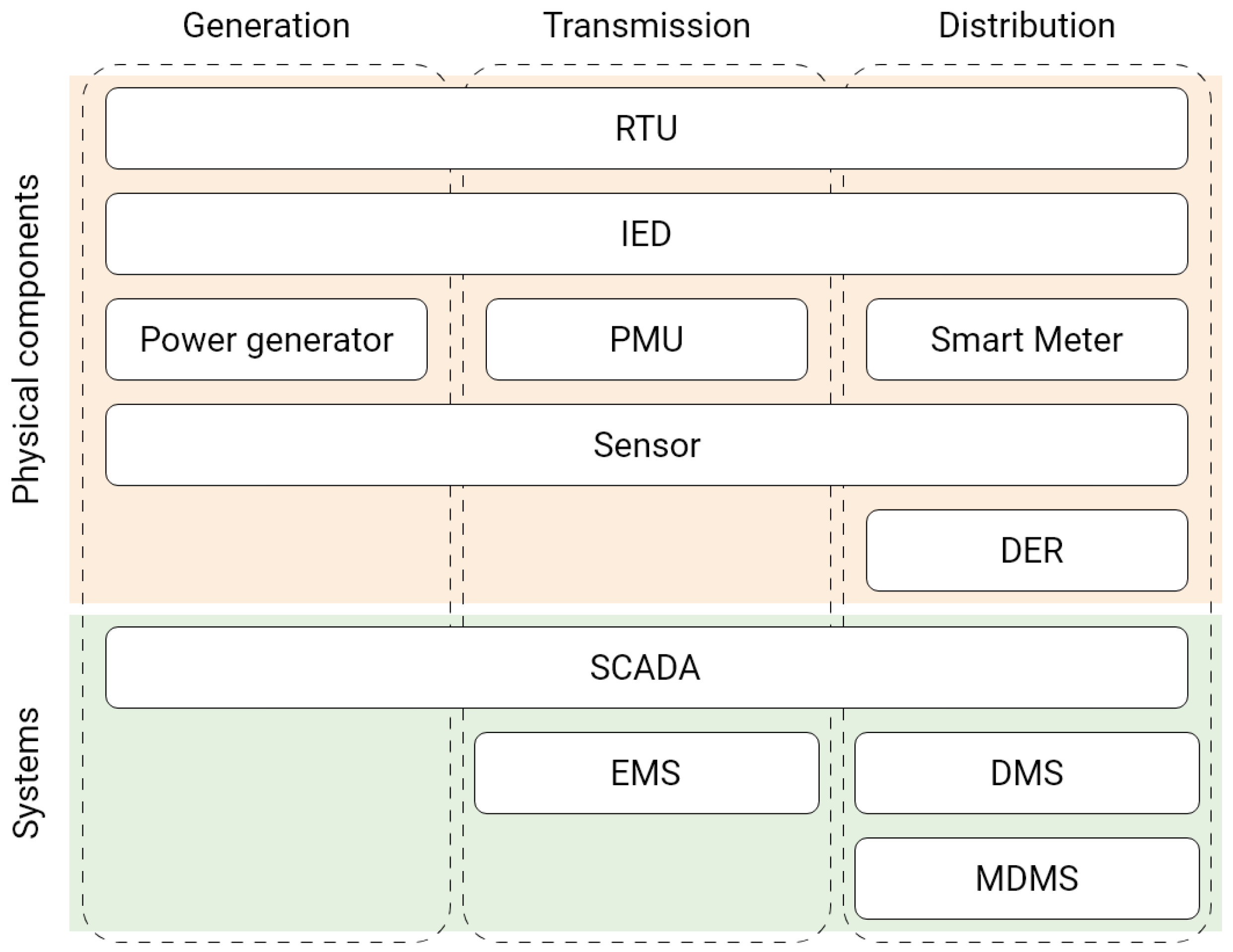
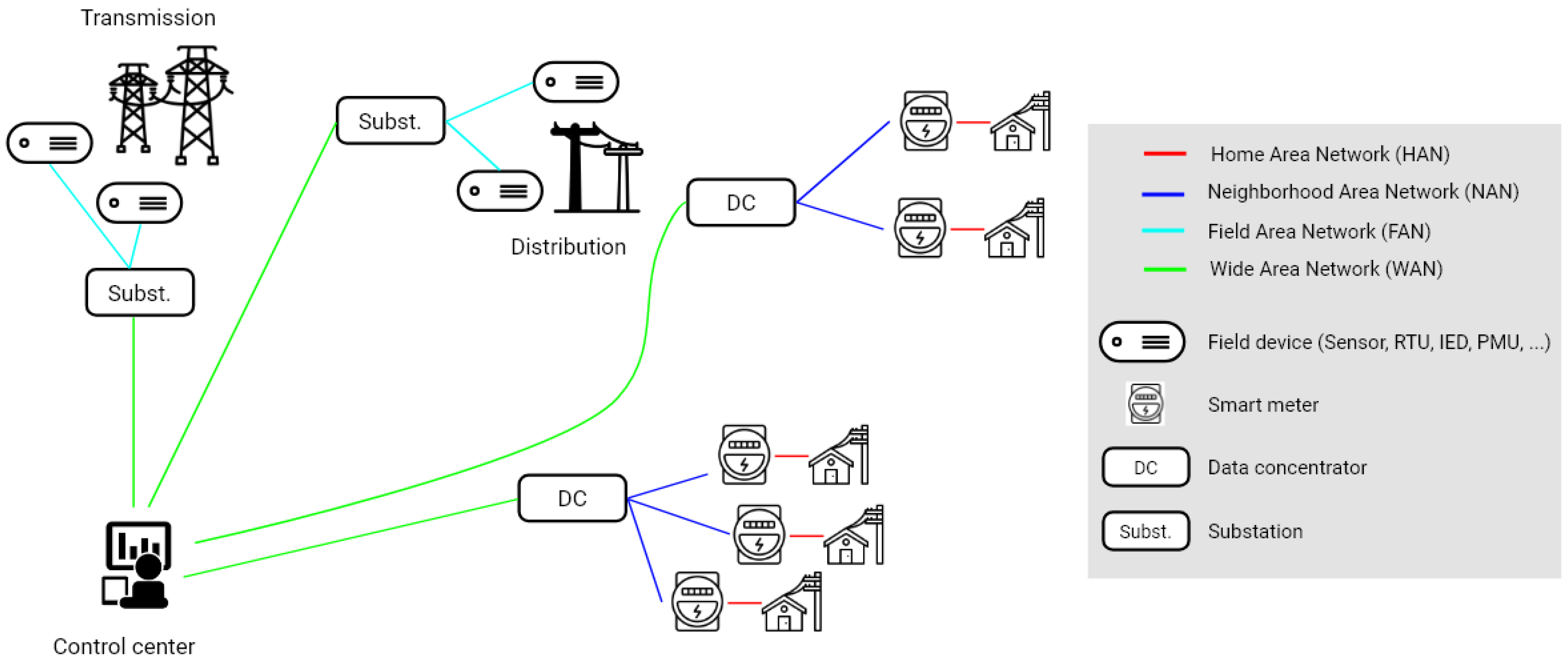
3.1. Architecture
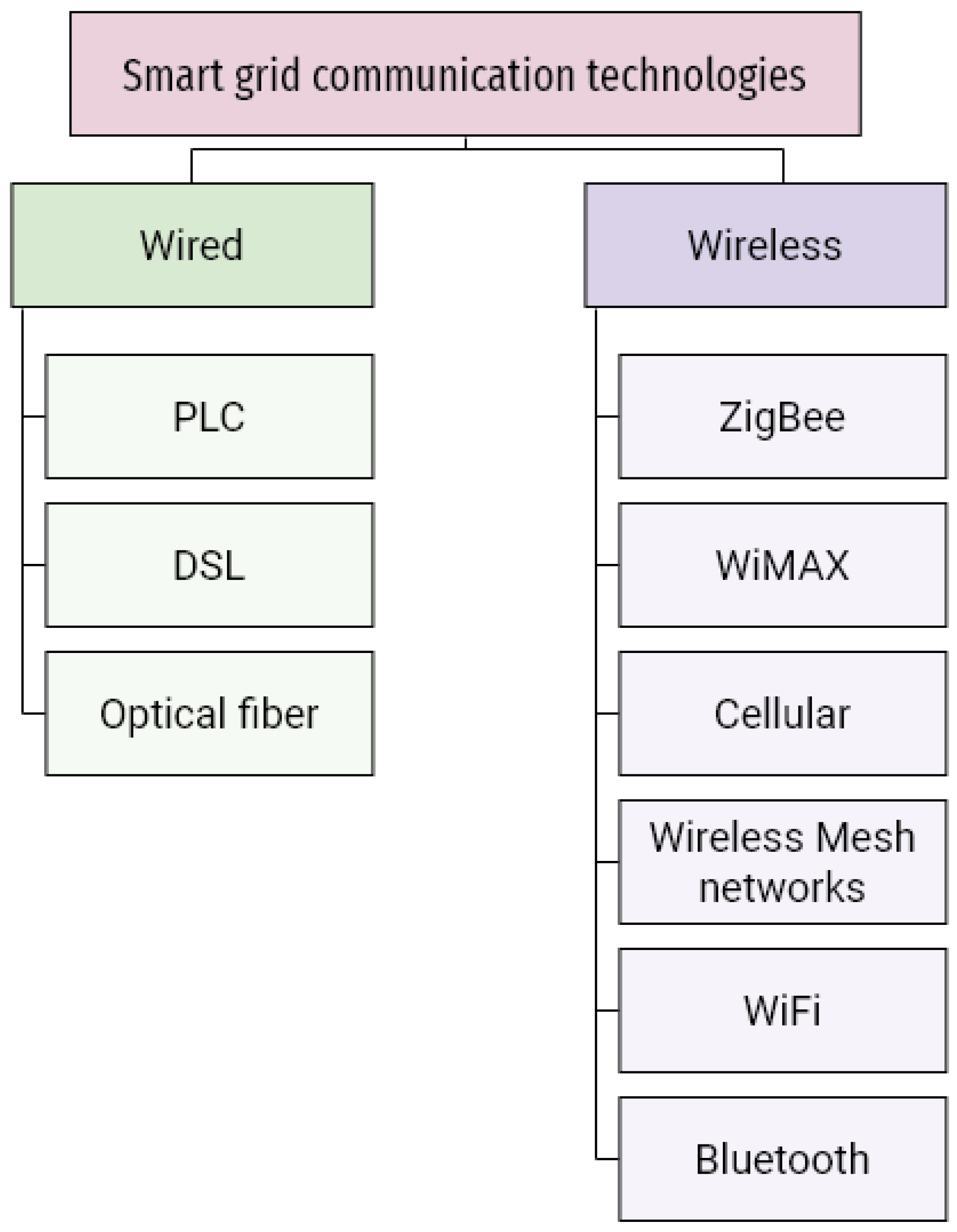
3.2. Smart Grid Communications
3.3. Standards and Protocols
- The ANSI C12 protocol suite was also defined for AMI applications [32];
- IEC 60870-6 provides a communication profile for SCADA that enables the exchange of telecontrol data between applications [31];
- DNP3 is mostly used for the communication between SCADA master stations, RTUs, and IEDs for substation automation [31];
- Modbus is also used for SCADA communications architecture [31];
- The North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection (NERC-CIP) defines a number of standards that aim to maintain a secure operation of bulk energy systems, which generally cover both generation and transmission [31,34]. The standard is applicable in multiple areas such as security control management, personnel training, and cybersecurity incident reporting [31,33];
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology Interagency Report 7628 (NISTIR 7628) provides a framework to guide organizations in developing effective cybersecurity strategies and assessing risks related to SGs [34].
3.4. Cyber-Physical Attacks on Smart Grids
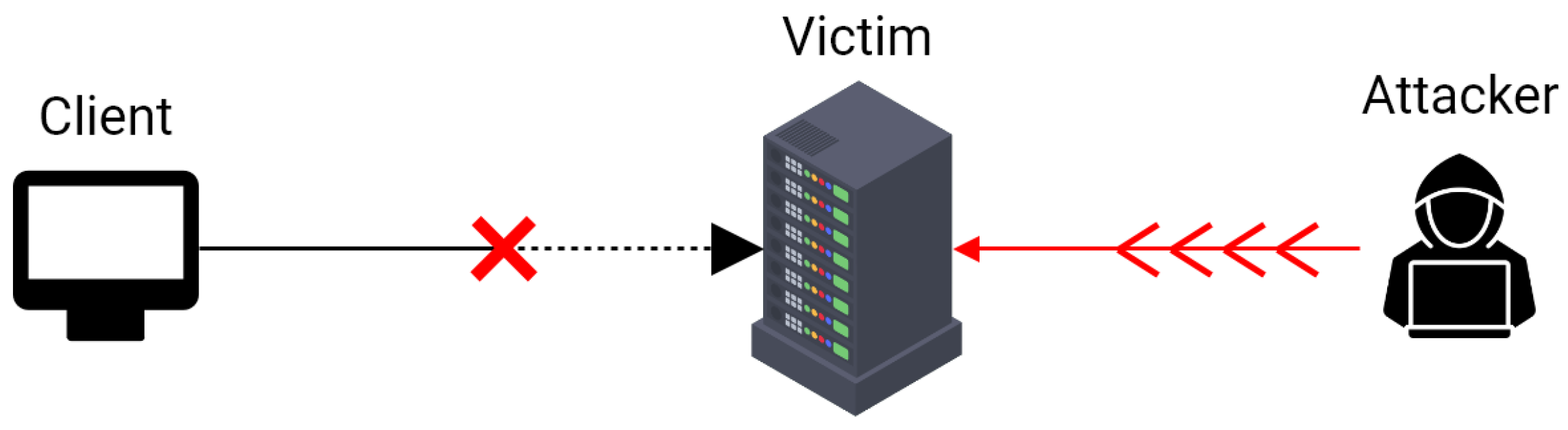
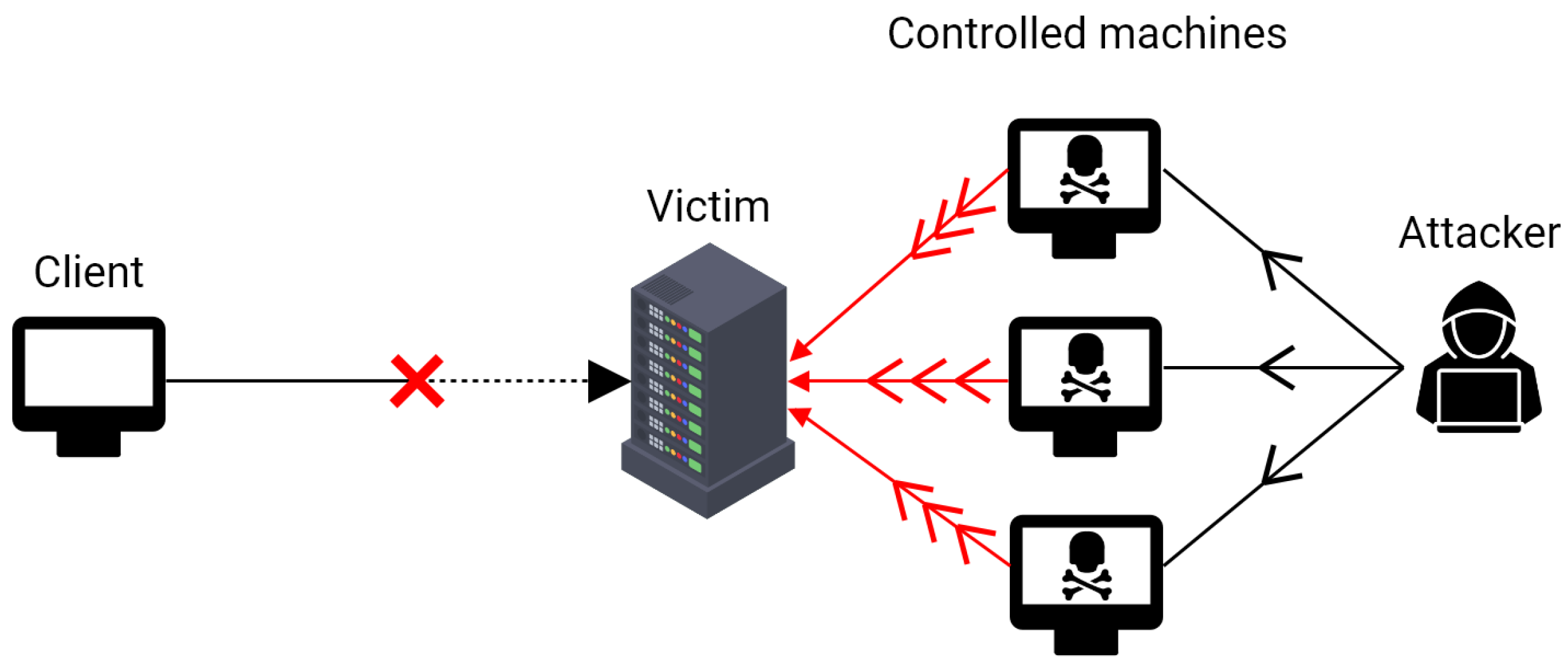
3.4.1. Denial-of-Service
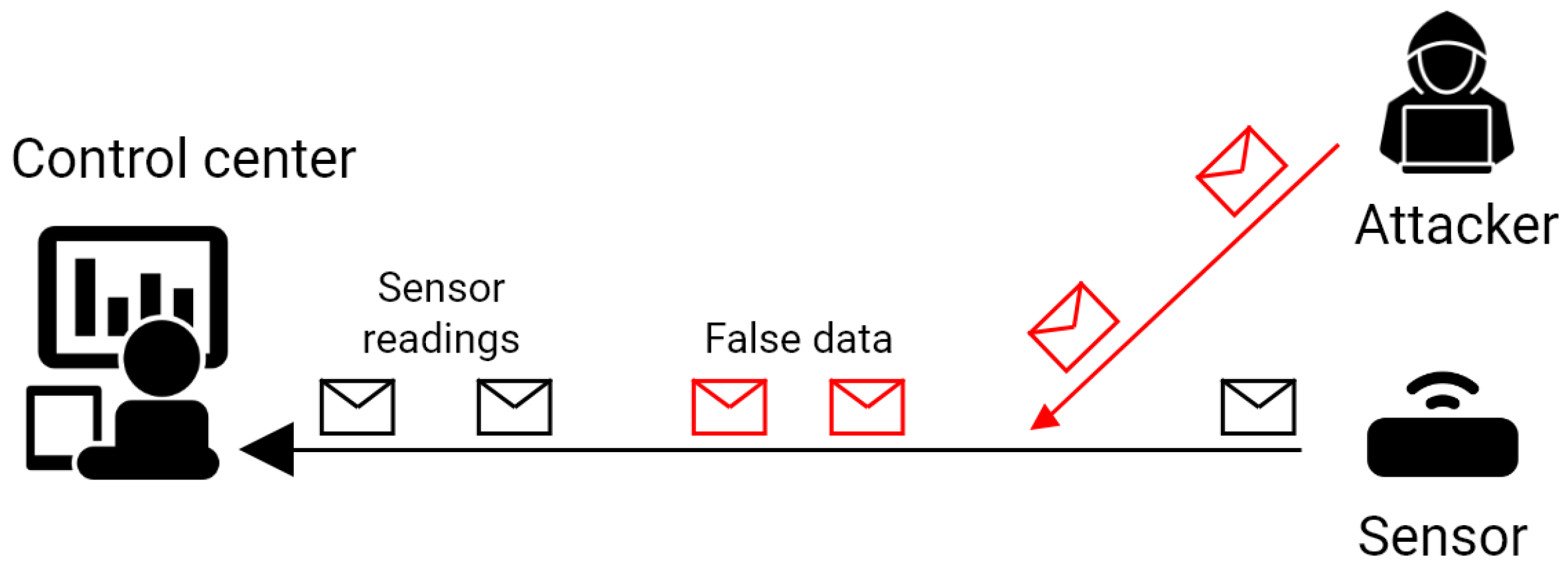
3.4.2. False Data Injection
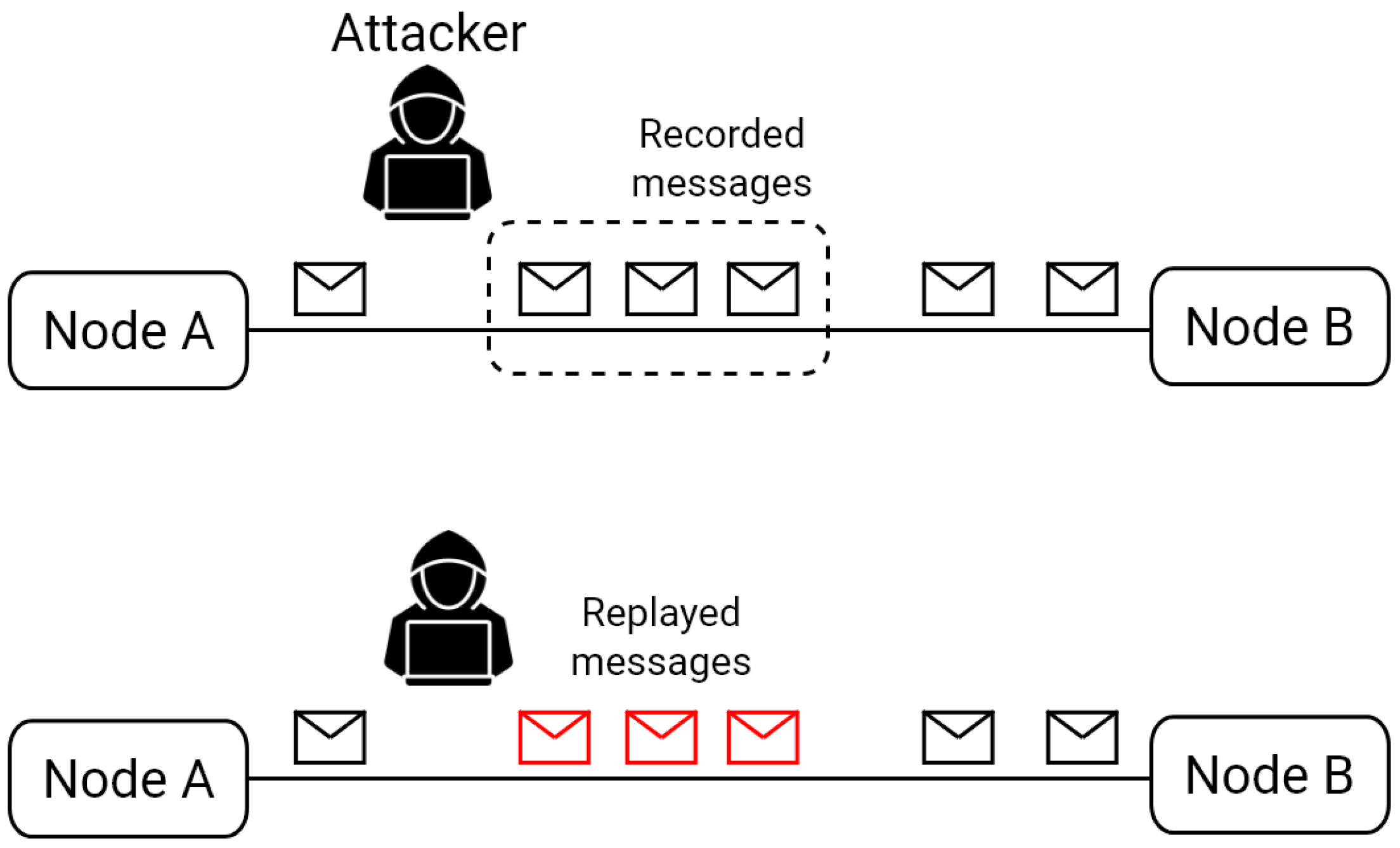
3.4.3. Replay Attack
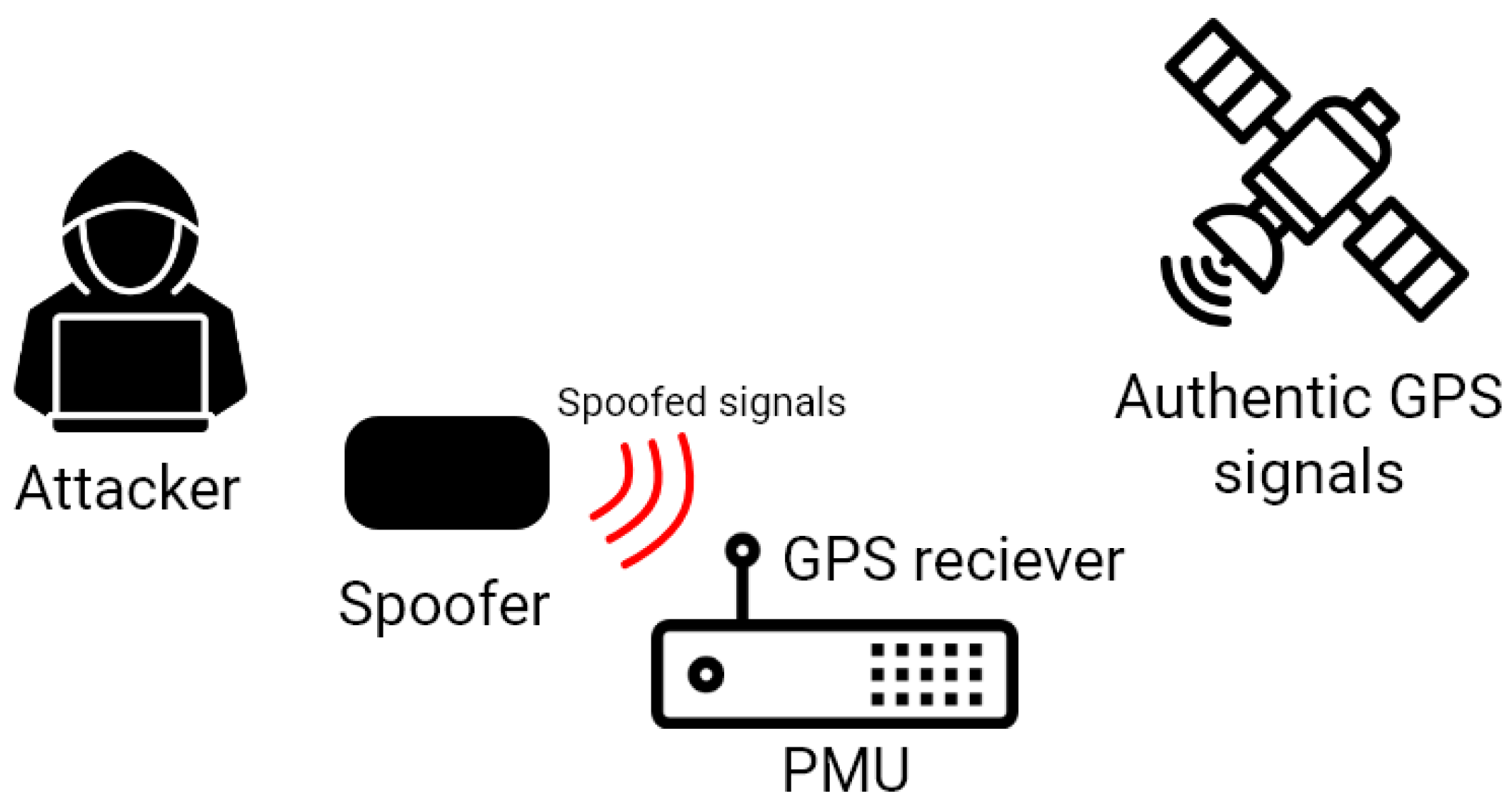
3.4.4. GPS Spoofing
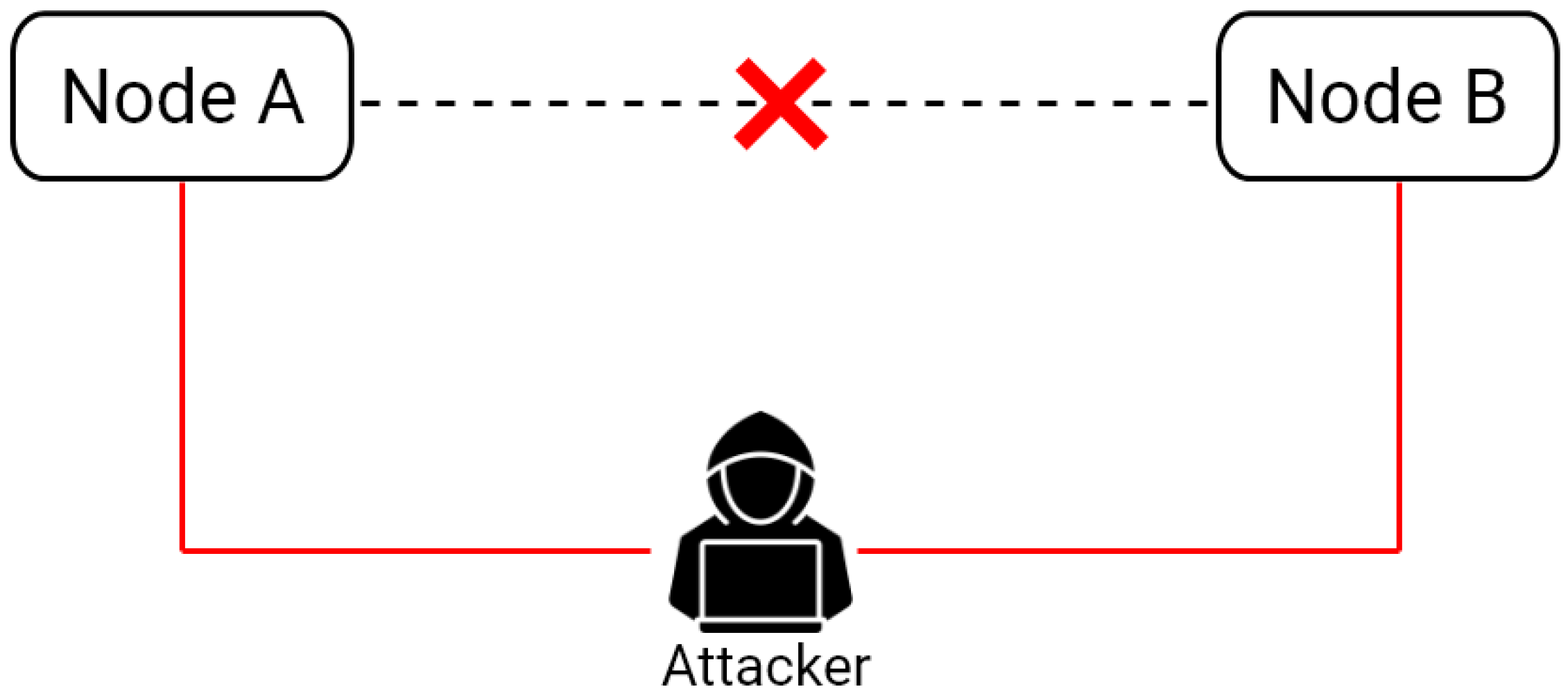
3.4.5. Man-in-the-Middle
3.5. Cyber-Physical Testbeds for Cybersecurity Testing
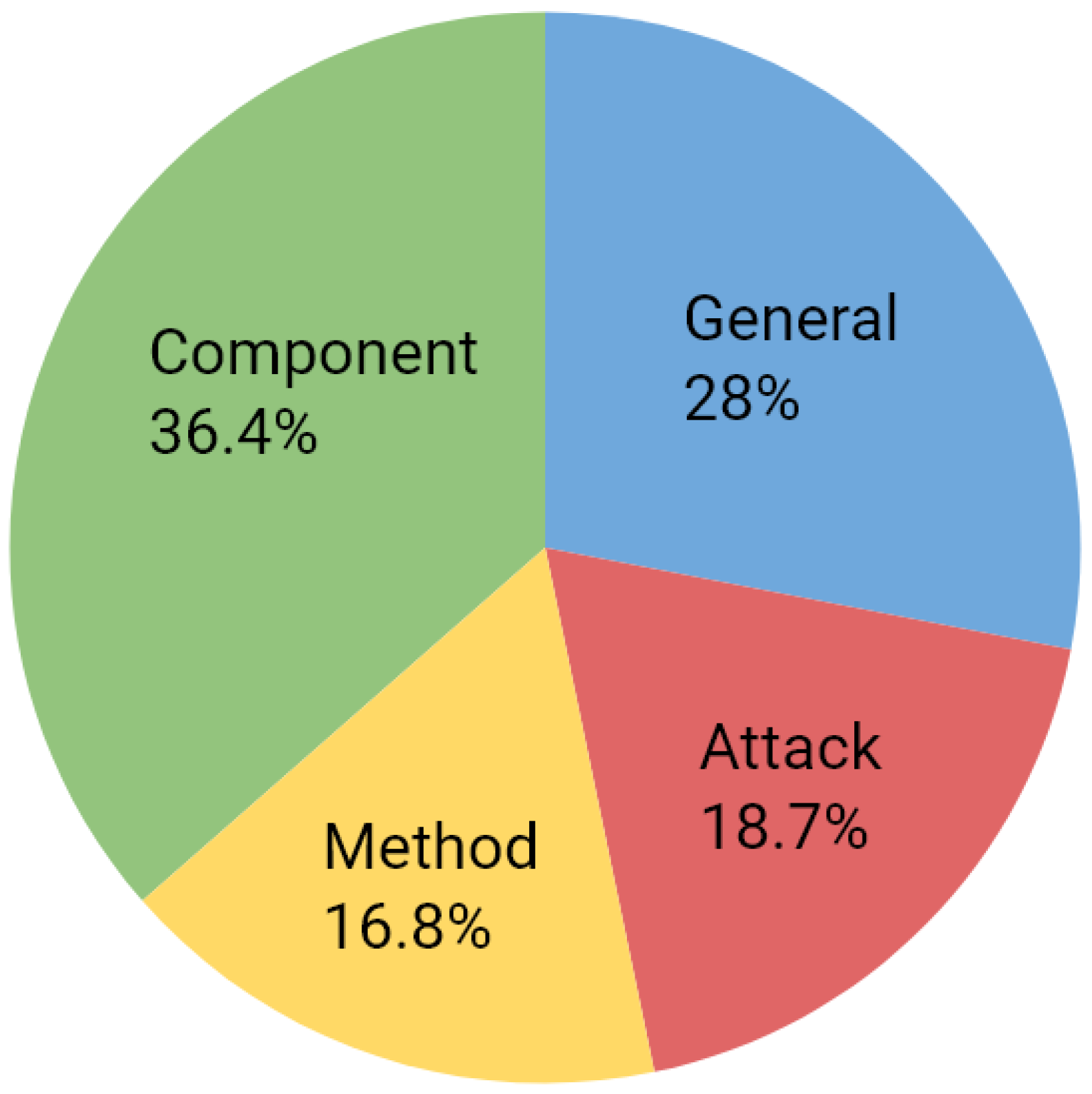
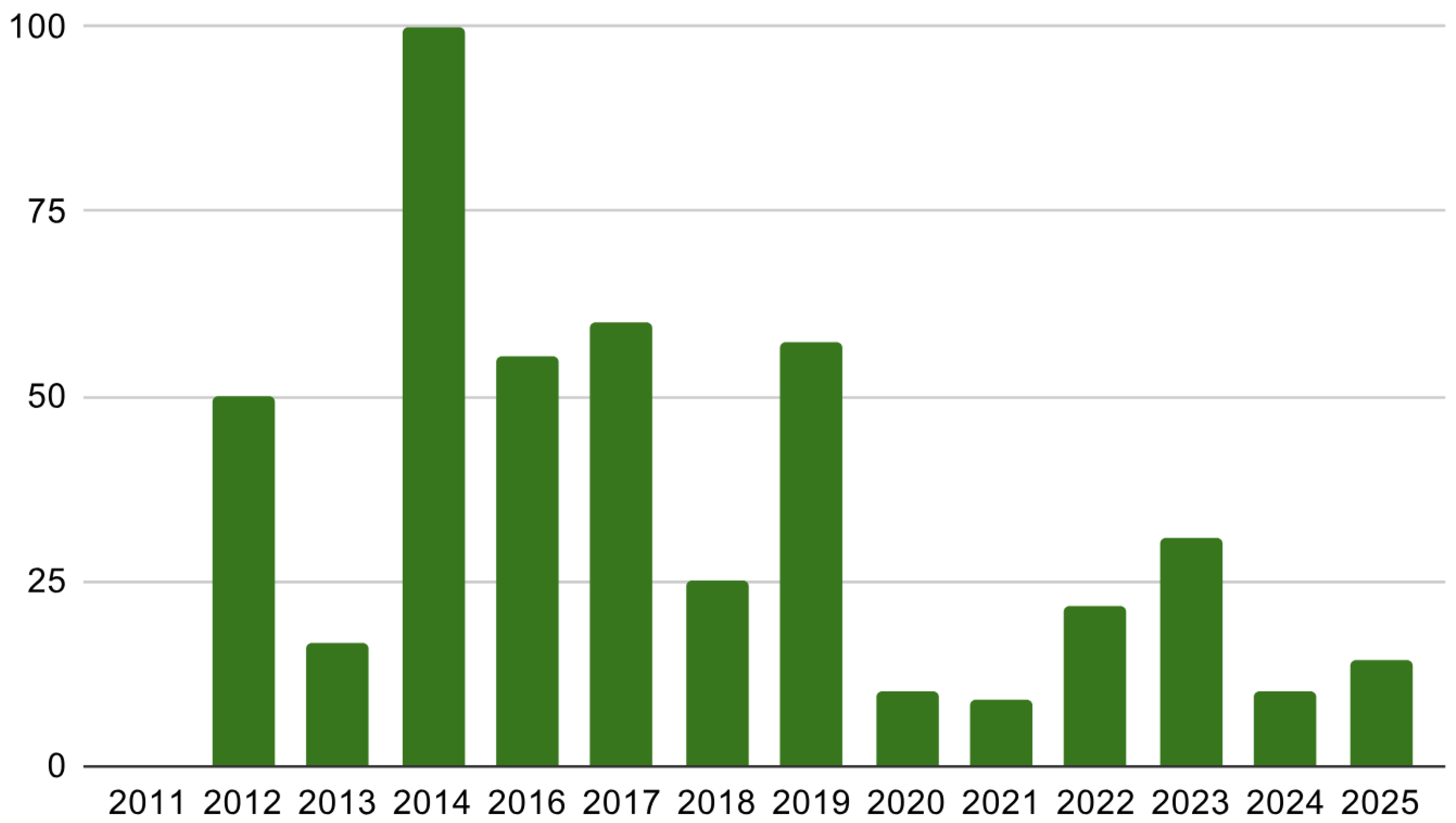
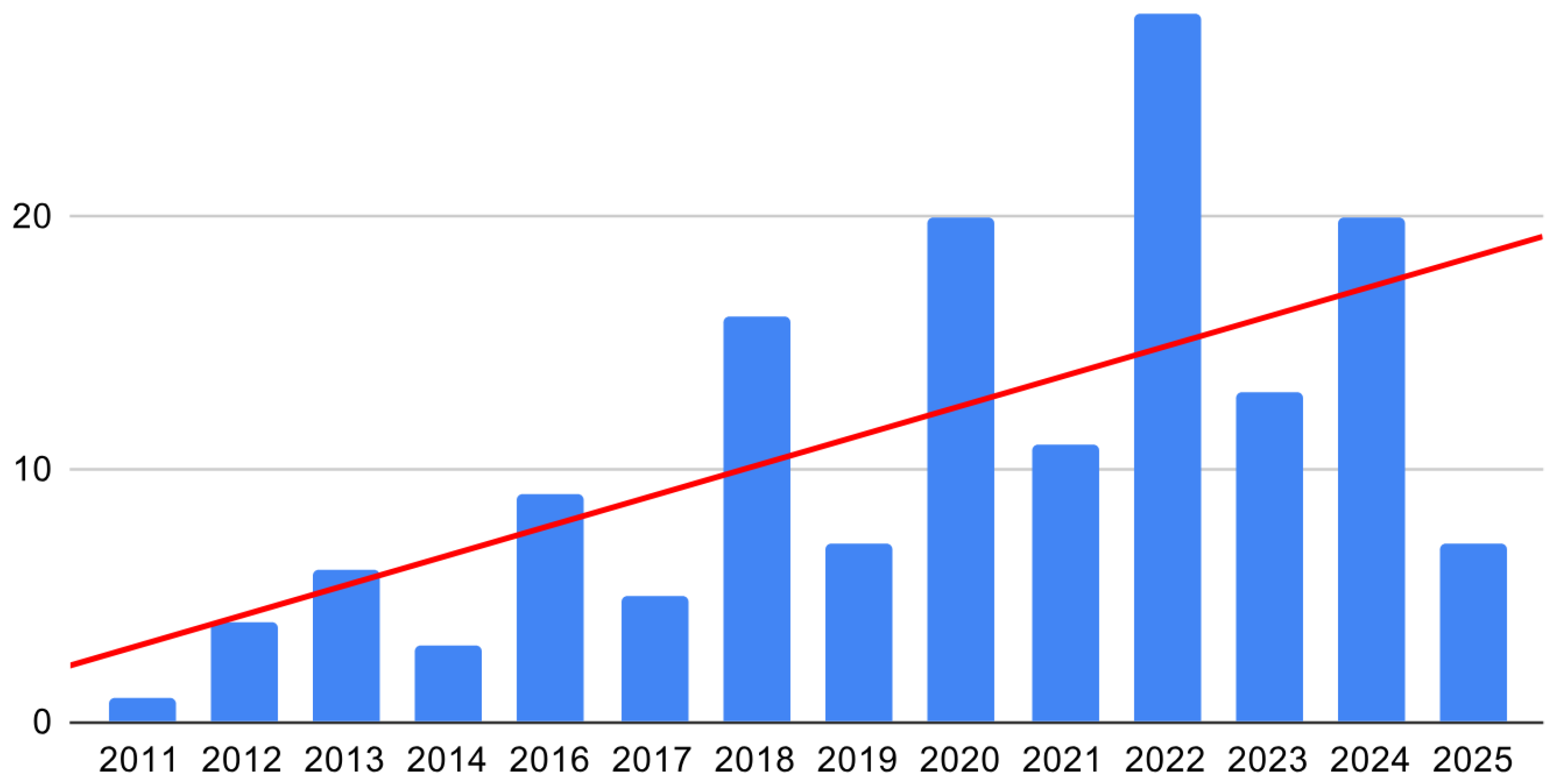
4. Synthesis of Existing Surveys: A Deep Dive into SG Cybersecurity Literature
4.1. Focused Analysis of General Surveys in SG Cybersecurity
4.2. Focused Analysis of Attack-Specific Surveys in SG Cybersecurity
4.3. Focused Analysis of Method-Specific Surveys in SG Cybersecurity
4.4. Focused Analysis of Component-Specific Surveys in SG Cybersecurity
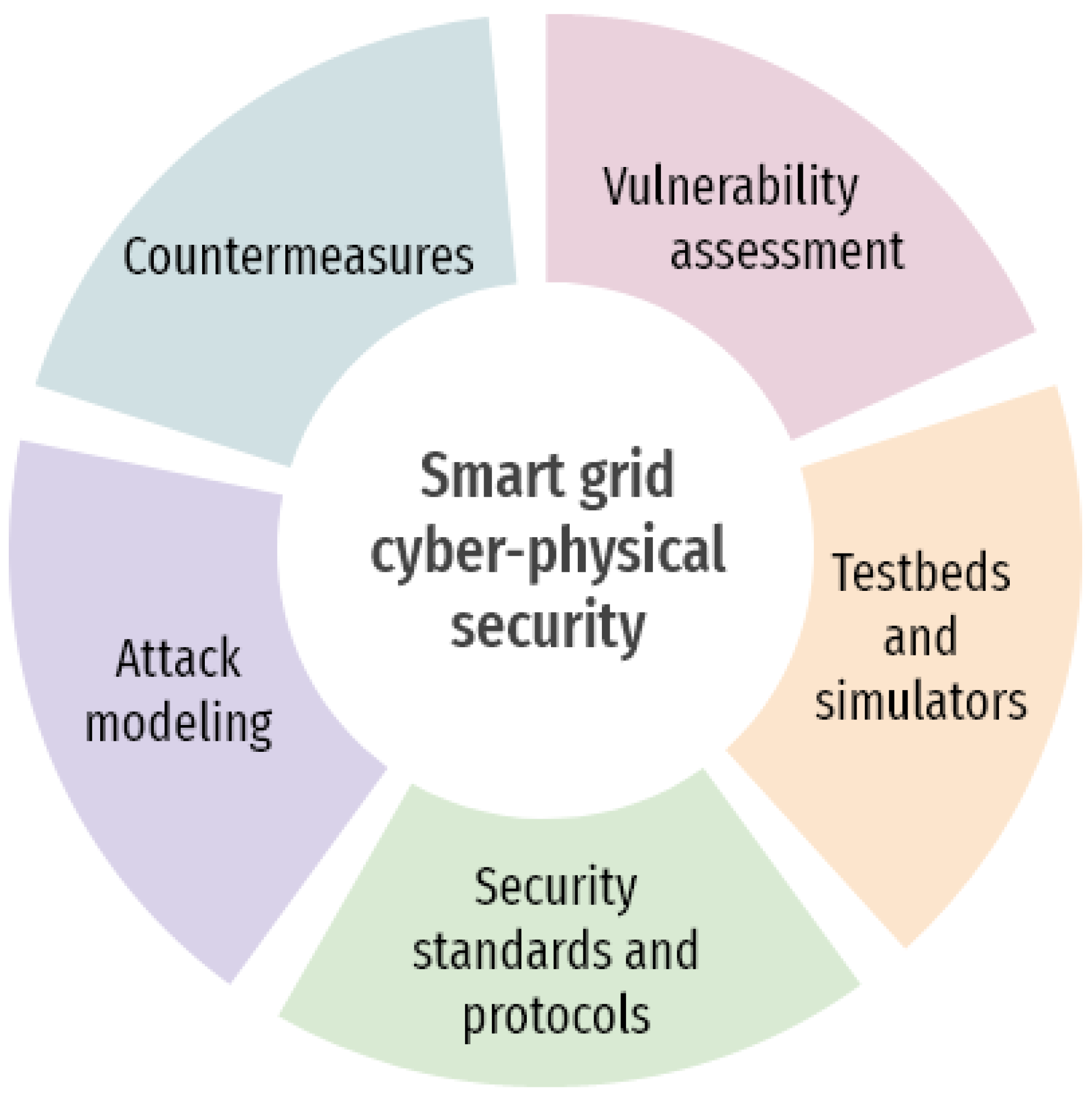
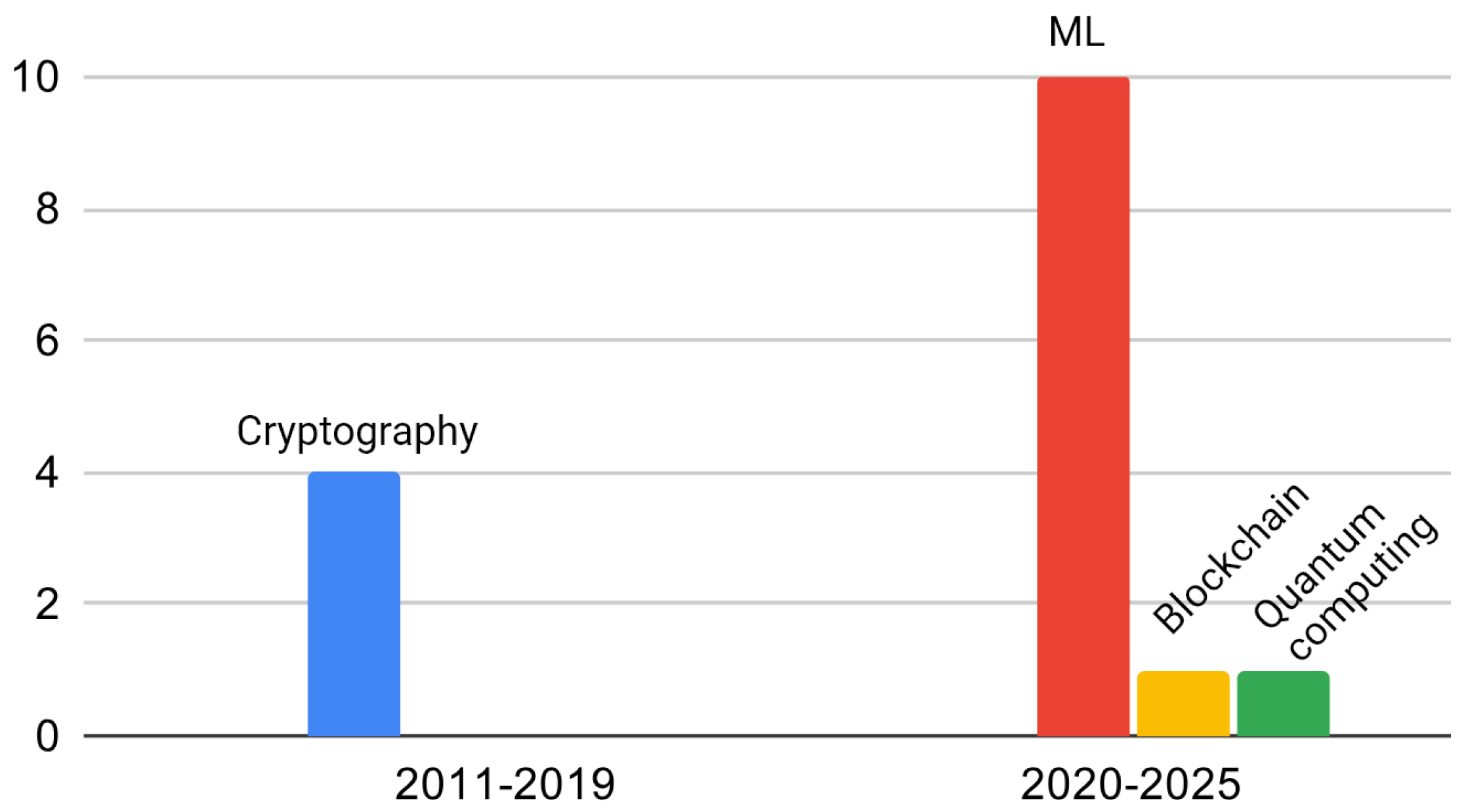
5. Overview of Key Research Aspects in Smart Grid Cybersecurity
5.1. Taxonomies
5.2. Discussion
6. Emerging Research Challenges and Future Directions in Smart Grid Cybersecurity
6.1. Smart Grid Cyber-Physical Structure
6.1.1. Current Research Challenges
6.1.2. Proposed Future Directions
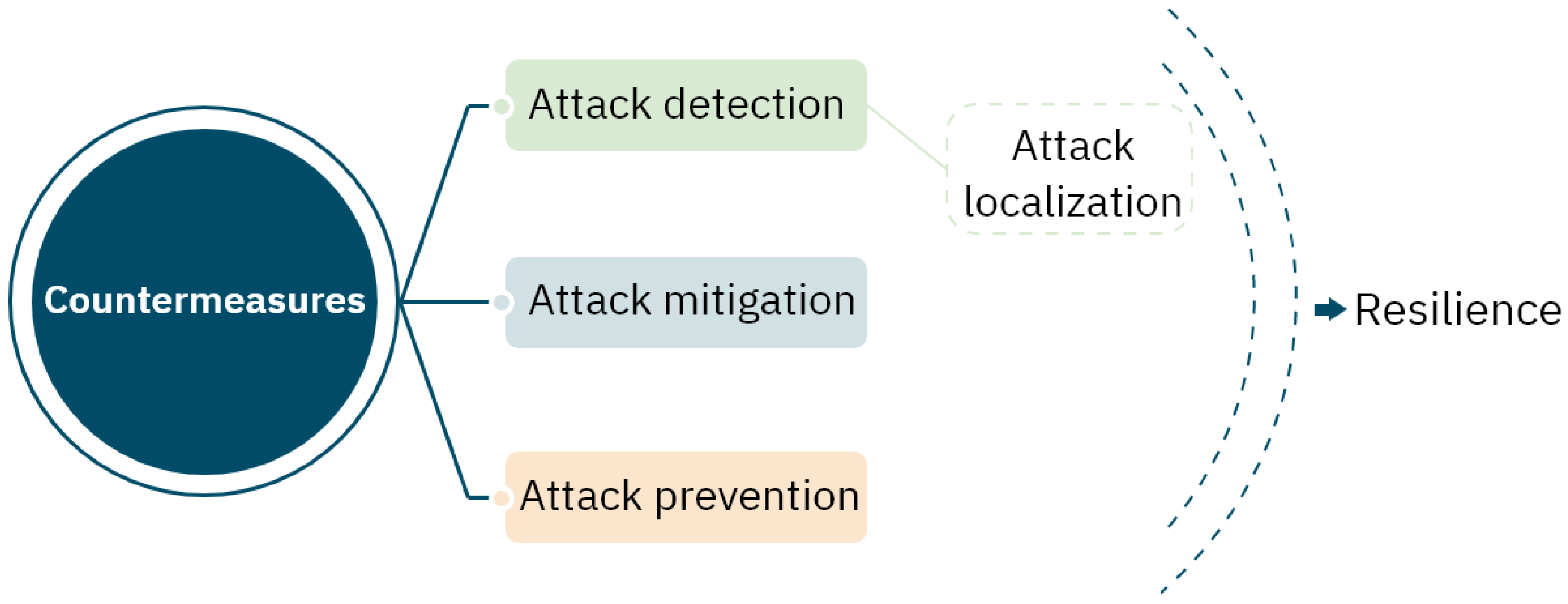
6.2. Advancements in Countermeasure Development
6.2.1. Current Research Challenges
6.2.2. Proposed Future Directions
6.3. Cyber-Physical Attacks
6.3.1. Current Research Challenges
6.3.2. Proposed Future Directions
7. Limitations and Outlook
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGC | automatic generation control |
| AMI | advanced metering infrastructure |
| BESS | battery energy storage system |
| CPS | cyber-physical system |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial-of-Service |
| DER | distributed energy resource |
| DG | distributed generation |
| DL | deep learning |
| DMS | distribution management system |
| DNP3 | Distributed Network Protocol 3 |
| DoS | Denial-of-Service |
| DSL | digital subscriber line |
| EMS | energy management system |
| ESS | energy storage system |
| EV | electric vehicle |
| FAN | field area network |
| FDI | False Data Injection |
| GOOSE | Generic Object Oriented Substation Event |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| HAN | home area network |
| ICS | industrial control system |
| IDS | intrusion detection system |
| IED | intelligent electronic device |
| IoT | Internet-of-Things |
| MDMS | meter data management system |
| MitM | Man-in-the-Middle |
| ML | machine learning |
| NAN | neighborhood area network |
| NS-3 | Network Simulator-3 |
| OSI | Open Systems Interconnection |
| PCC | point of common coupling |
| PKI | public key infrastructure |
| PLC | power line communication |
| PMU | phasor measurement unit |
| RES | renewable energy source |
| RL | reinforcement learning |
| RTDS | Real-Time Digital Simulator |
| RTU | remote terminal unit |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| SG | smart grid |
| V2G | vehicle-to-grid |
| WAMPAC | Wide-Area Monitoring, Protection, and Control |
| WAN | wide area network |
| WSN | wireless sensor network |
Appendix A
References
- Snyder, A.; Kranzler, D.; Simpson, R. Smart Meters and Advanced Metering Infrastructure. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 13; pp. 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musleh, A.S.; Chen, G.; Dong, Z.Y. A Survey on the Detection Algorithms for False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 2218–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, L.; Castro, S.R.; Lozano, J.; Koneru, K.; Zambon, E.; Huang, B.; Baldick, R.; Krotofil, M.; Rojas, A.; Cardenas, A.A. A Tale of Two Industroyers: It was the Season of Darkness. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2024; pp. 312–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersky ICS CERT. H2 2022–Brief Overview of Main Incidents in Industrial Cybersecurity. 2023. Available online: https://ics-cert.kaspersky.com/media/Kaspersky-ICS-CERT-H2-2022-brief-overview-of-main-incidents-En.pdf? (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Center for Strategic and International Studies. Significant Cyber Incidents Since 2006. 2023. Available online: https://csis-website-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/2023-04/230404_Significant_Cyber_Events.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Olorunlana, T.; Mohammed, H. Analysis of the Colonial Pipeline Cybersecurity Incident. Int. J. Sci. Archit. Technol. Environ. 2025, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, T.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, B. Current Status and Perspective of Vulnerability Assessment of Cyber-Physical Power Systems Based on Complex Network Theory. Energies 2023, 16, 6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B. Procedures for Performing Systematic Reviews; Technical Report TR/SE-0401; NICTA Technical Report 0400011T.1; Keele University: Keele, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; Technical Report EBSE-2007-01; EBSE: Durham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brandao, M.; Newton, C.W.; Wojszczyk, B. Overview of the Electric Utility Industry. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhani, A. Design of Smart Power Grid Renewable Energy Systems, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; p. 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlase, S. (Ed.) Smart Grid Technologies. In Smart Grids: Infrastructure, Technology, and Solutions, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; Chapter 3; pp. 61–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Sahin, D.; Kocak, T.; Ergut, S.; Buccella, C.; Cecati, C.; Hancke, G.P. Smart grid technologies: Communication technologies and standards. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2011, 7, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H.; Tipper, D. A Survey on Smart Grid Communication Infrastructures: Motivations, Requirements and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yan, J. Cyber-physical attacks and defences in the smart grid: A survey. IET Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2016, 1, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, H. The path of the smart grid. IEEE Pow Energy Mag. 2010, 8, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlase, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, X.; Giri, J.; Wilson, D.; Gray, G.R.; Huang, Z.H.; Sattinger, W.; Yang, B.; Zeng, B. Real-Time Grid Management. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 5; pp. 179–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, E. Substation Automation Systems: Design and Implementation; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoene, J.; Humayun, M. Advanced Protection and Control for the Smart Grid. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 6; pp. 253–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, M.; Allan, S.S.; Hettich, D.D. Communications Systems. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 4; pp. 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlase, S.; Behboodi, S.; Bradley, T.H.; Brandao, M.; Chassin, D.; Enslin, J.; McCarthy, C. Smart Energy Resources: Supply and Demand. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 3; pp. 67–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yu, W.; Griffith, D.; Golmie, N.; Moulema, P. Toward Integrating Distributed Energy Resources and Storage Devices in Smart Grid. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.F.; Elbouchikhi, E.; Benbouzid, M. Microgrids energy management systems: A critical review on methods, solutions, and prospects. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohassel, R.R.; Fung, A.; Mohammadi, F.; Raahemifar, K. A survey on Advanced Metering Infrastructure. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.E.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Etemadi, A.H.; Cañizares, C.A.; Iravani, R.; Kazerani, M.; Hajimiragha, A.H.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Saeedifard, M.; Palma-Behnke, R.; et al. Trends in Microgrid Control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizi, S.; Lotfi, H.; Khodaei, A.; Bahramirad, S. State of the Art in Research on Microgrids: A Review. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 890–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlase, S.; Ganji, M.; Shahidehpour, M.; Tian, W.; Burgess, P. Microgrids. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 19; pp. 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzlu, M.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Rahman, S. Communication network requirements for major smart grid applications in HAN, NAN and WAN. Comput. Netw. 2014, 67, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, E.; Kabalci, Y. Introduction to Smart Grid Architecture. In Smart Grids and Their Communication Systems; Kabalci, E., Kabalci, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std C37.118.2-2011 (Revision of IEEE Std C37.118-2005); IEEE Standard for Synchrophasor Data Transfer for Power Systems. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–53. [CrossRef]
- Cali, U.; Kuzlu, M.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Kempf, J.; Bai, L. Smart Grid Standards and Protocols. In Digitalization of Power Markets and Systems Using Energy Informatics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.V.; Appasani, B.; Ghazali, A.N.; Pattanayak, P.; Gurjar, D.S.; Kabalci, E.; Mohanta, D. Smart grid cyber-physical systems: Communication technologies, standards and challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2021, 27, 2595–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Habib, A.A.; Shukur, Z.; Ibrahim, F.; Islam, S.; Razzaque, M.A. Review on cyber-physical and cyber-security system in smart grid: Standards, protocols, constraints, and recommendations. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2023, 209, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J. Cybersecurity for the Smart Grid. In Smart Grids: Advanced Technologies and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Borlase, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 17; pp. 533–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.H.; Pan, S.; Adhikari, U. Cyber security recommendations for wide area monitoring, protection, and control systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katulić, F.; Sumina, D.; Erceg, I.; Groš, S. Enhancing Modbus/TCP-Based Industrial Automation and Control Systems Cybersecurity Using a Misuse-Based Intrusion Detection System. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Sorrento, Italy, 22–24 June 2022; pp. 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, I.; Igbe, O.; Celebi, O.; Saadawi, T.; Soryal, J. Smart Grid DNP3 Vulnerability Analysis and Experimentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing, New York, NY, USA, 3–5 November 2015; pp. 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; McLaughlin, K.; Laverty, D.; Sezer, S. Analysis of IEEE C37.118 and IEC 61850-90-5 synchrophasor communication frameworks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Hahn, A.; Liu, C.C. Cyber security of a power grid: State-of-the-art. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 99, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseinović, A.; Mrdović, S.; Bicakci, K.; Uludag, S. A Survey of Denial-of-Service Attacks and Solutions in the Smart Grid. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 177447–177470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvene, C.; Shekari, T.; Formby, D.; Beyah, R. If I Knew Then What I Know Now: On Reevaluating DNP3 Security Using Power Substation Traffic. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Industrial Control System Security (ICSS) Workshop, San Juan, PR, USA, 10 December 2019; ICSS: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, H.T.; McLaughlin, K.; Gao, L.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, W.; Sezer, S. Cybersecurity test-bed for IEC 61850 based smart substations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–30 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.; Olson, R.; Howard, R. Cyber Security Essentials, 1st ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keromytis, A.D. Network Bandwidth Denial of Service (DoS). In Encyclopedia of Cryptography and Security, 2nd ed.; van Tilborg, H.C.A., Jajodia, S., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, Z.A.; Amoudi, A.R. An analysis of smart grid attacks and countermeasures. J. Commun. 2013, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capkun, S. Jamming Resistance. In Encyclopedia of Cryptography and Security, 2nd ed.; van Tilborg, H.C.A., Jajodia, S., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkovic, J.; Reiher, P. A taxonomy of DDoS attack and DDoS defense mechanisms. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2004, 34, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asri, S.; Pranggono, B. Impact of Distributed Denial-of-Service Attack on Advanced Metering Infrastructure. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2015, 83, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Shawon, M.H.; Khalid, H.M.; Muyeen, S.M. Denial-of-Service Attack on IEC 61850-Based Substation Automation System: A Crucial Cyber Threat Towards Smart Substation Pathways. Sensors 2021, 21, 6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Fernandez, I.; Liberati, F. A Review of Denial of Service Attack and Mitigation in the Smart Grid Using Reinforcement Learning. Energies 2023, 16, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kush, N.S.; Ahmed, E.; Branagan, M.; Foo, E. Poisoned GOOSE: Exploiting the GOOSE protocol. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Australasian Information Security Conference (AISC 2014), Auckland, New Zealand, 20–23 January 2014; Australian Computer Society: Darlinghurst, NSW, Australia, 2014; Volume 149, pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.; Zhu, H.; Lee, C.W.; Nicol, D.M.; Shin, I. The Not-So-Smart Grid: Preliminary work on identifying vulnerabilities in ANSI C12.22. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012; pp. 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.M.; Nabirasool, S.; Kiran, S.; Suhail Hussain, S.; Ustun, T.S. MPTCP based mitigation of Denial of Service (DoS) Attack in PMU Communication Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Chennai, India, 18–21 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtissam, K.; Abdelrahman, M.S.; Alrashide, A.; Mohammed, O.A. Assessment of Protection Schemes and their Security Under Denial of Service Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2022 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June–1 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlela, M.; Joos, G.; Kassouf, M. Impact of cyber-attacks on islanded microgrid operation. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Communications, Computation and Control for Resilient Smart Energy Systems, RSES ’16, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–30 June 2016; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Niknam, T.; Wang, Z.; Mehrandezh, M.; Dehghani, M.; Ghadimi, N. A comprehensive review of cyber-attacks and defense mechanisms for improving security in smart grid energy systems: Past, present and future. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 215, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ning, P.; Reiter, M.K. False data injection attacks against state estimation in electric power grids. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2011, 14, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Xiao, G.; Lu, R.; Liang, H.; Vasilakos, A.V. False Data Injection on State Estimation in Power Systems—Attacks, Impacts, and Defense: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhao, J.; Luo, F.; Weller, S.R.; Dong, Z.Y. A Review of False Data Injection Attacks Against Modern Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowu, T.O.; Dharmasena, S.; Jafari, H.; Sarwat, A. Investigation of False Data Injection Attacks on Smart Inverter Settings. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE CyberPELS (CyberPELS), Miami, FL, USA, 13 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.; Arani, M.F.M.; Jahromi, A.A.; Kundur, D. False Data Injection Attacks Against Synchronization Systems in Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 4471–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Morris, T.; Reaves, B.; Richey, D. On SCADA control system command and response injection and intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 eCrime Researchers Summit, Dallas, TX, USA, 18–20 October 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Weng, J.; Li, X.; Deng, R.H. Resonance Attacks on Load Frequency Control of Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 4490–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.A.; Tariq, M.; Behnamfar, M.; Sarwat, A.I. Analyzing Replay Attack Impact in DC Microgrid Consensus Control: Detection and Mitigation by Kalman-Filter-Based Observer. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 121368–121378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Sinopoli, B. Secure control against replay attacks. In Proceedings of the 2009 47th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, IL, USA, 30 September–2 October 2009; pp. 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, T.S.; Farooq, S.M.; Hussain, S.M.S. A Novel Approach for Mitigation of Replay and Masquerade Attacks in Smartgrids Using IEC 61850 Standard. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 156044–156053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Ding, W.; Zhou, J. Reinforcement Learning Solution for Cyber-Physical Systems Security Against Replay Attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 2583–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gong, S.; Dimitrovski, A.D.; Li, H. Time Synchronization Attack in Smart Grid: Impact and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, D.P.; Humphreys, T.E.; Fansler, A.A. Evaluation of the vulnerability of phasor measurement units to GPS spoofing attacks. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2012, 5, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlazlo, P.; Sahu, A.; Mao, Z.; Huang, H.; Goulart, A.; Davis, K.; Zonouz, S. Man-in-the-middle attacks and defence in a power system cyber-physical testbed. IET Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2021, 6, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Dragoni, N.; Lesyk, V. A Survey of Man In The Middle Attacks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 2027–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjidemetriou, L.; Tertytchny, G.; Karbouj, H.; Charalambous, C.; Michael, M.K.; Sazos, M.; Maniatakos, M. Demonstration of Man in the Middle Attack on a Feeder Power Factor Correction Unit. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT-Europe), The Hague, The Netherlands, 26–28 October 2020; pp. 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gou, X.; Huang, T.; Yang, S. Review on Testing of Cyber Physical Systems: Methods and Testbeds. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52179–52194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, M.; Mahmood, A.; Chowdhury, M.J.M. SCADA vulnerabilities and attacks: A review of the state-of-the-art and open issues. Comput. Secur. 2023, 125, 103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintuglu, M.H.; Mohammed, O.A.; Akkaya, K.; Uluagac, A.S. A Survey on Smart Grid Cyber-Physical System Testbeds. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 446–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Sahoo, S.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Blaabjerg, F.; Popovski, P. On the Assessment of Cyber Risks and Attack Surfaces in a Real-Time Co-Simulation Cybersecurity Testbed for Inverter-Based Microgrids. Energies 2021, 14, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffel, R.; Giesbrecht, J.; Maguire, T.; Wierckx, R.; McLaren, P. RTDS-a fully digital power system simulator operating in real time. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 1995 International Conference on Energy Management and Power Delivery EMPD ’95, Singapore, 21–23 November 1995; Volume 2, pp. 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kadavil, R.; Hooshyar, H. A Real-Time Cyber-Physical Simulation Testbed for Cybersecurity Assessment of Large-Scale Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 8329–8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ge, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Multifunctional cyber-physical system testbed based on a source-grid combined scheduling control simulation system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 3144–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, P.B.; Suryadevara, R. Hardware-based microgrid testbed to facilitate development of Distributed Energy Resource (DER) systems for sustainable growth. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 746, p. 012037. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Ye, T.; Zhou, B.; Xu, T.; Luo, H. A Testbed for Studying Security in Synchrophasor-Based State Estimation of Electric Power Transmission Grid. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Communication and Intelligent Technology, Paris, France, 27–29 September 2024; Dong, J., Zhang, L., Cheng, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Blazek, P.; Bohacik, A.; Fujdiak, R.; Jurak, V.; Ptacek, M. Smart Grids Transmission Network Testbed: Design, Deployment, and Beyond. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2025, 6, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Ni, Z.; Malla, N. Real-time cyber physical system testbed for power system security and control. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2017, 90, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Vellaithurai, C.; Biswas, S.S.; Gamage, T.T.; Srivastava, A.K. Analyzing the Cyber-Physical Impact of Cyber Events on the Power Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2444–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Hahn, A.; Govindarasu, M. Cyber–physical system security for the electric power grid. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, X.; Lu, R.; Shen, X.; Lin, X.; Zhu, H. Securing smart grid: Cyber attacks, countermeasures, and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.Z.; Das, R. Cyber-security on smart grid: Threats and potential solutions. Comput. Netw. 2020, 169, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Ding, F.; Utkarsh, K.; Liu, W.; O’Malley, M.J.; Barnett, J. On Vulnerability and Resilience of Cyber-Physical Power Systems: A Review. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Ernst, R.; Klaer, B.; Hacker, I.; Henze, M. Cybersecurity in Power Grids: Challenges and Opportunities. Sensors 2021, 21, 6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafees, M.N.; Saxena, N.; Cardenas, A.; Grijalva, S.; Burnap, P. Smart Grid Cyber-Physical Situational Awareness of Complex Operational Technology Attacks: A Review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, Z.E.; Kaabouch, N.; Ghazi, H.E.; Ghazi, H.E. Cyber-security in smart grid: Survey and challenges. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 67, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Sun, H.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.L. A Survey on Security Communication and Control for Smart Grids Under Malicious Cyber Attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 1554–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, H. Smart Grid Cyber-Physical Attack and Defense: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 29641–29659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Wang, S.; Alhazmi, M.; Nazemi, M.; Estebsari, A.; Dehghanian, P. Electric power grid resilience to cyber adversaries: State of the art. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87592–87608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrdad, S.; Mousavian, S.; Madraki, G.; Dvorkin, Y. Cyber-physical resilience of electrical power systems against malicious attacks: A review. Curr. Sustain. Energy Rep. 2018, 5, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, S.; Parvez, I.; Batool, S.; Sarwat, A. A Survey on Cybersecurity Challenges, Detection, and Mitigation Techniques for the Smart Grid. Energies 2021, 14, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuwian, T.; Shahid Butt, A.; Amin, A.A. Smart Grid Cyber Security Enhancement: Challenges and Solutions—A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyen, N.D.; Quan, N.S.; Linh, V.B.; Van Tuyen, V.; Fujita, G. A Comprehensive Review of Cybersecurity in Inverter-Based Smart Power System Amid the Boom of Renewable Energy. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 35846–35875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, S.; Ghafouri, M.; Au, M.; Kassouf, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Debbabi, M. Security of Wide-Area Monitoring, Protection, and Control (WAMPAC) Systems of the Smart Grid: A Survey on Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 1294–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, T.T.; Slimane, H.O.; Kaabouch, N. A comprehensive survey on the cyber-security of smart grids: Cyber-attacks, detection, countermeasure techniques, and future directions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.07738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji Mirzaee, P.; Shojafar, M.; Cruickshank, H.; Tafazolli, R. Smart Grid Security and Privacy: From Conventional to Machine Learning Issues (Threats and Countermeasures). IEEE Access 2022, 10, 52922–52954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achaal, B.; Adda, M.; Berger, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Awde, A. Study of smart grid cyber-security, examining architectures, communication networks, cyber-attacks, countermeasure techniques, and challenges. Cybersecurity 2024, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, U.; Zia, M.F.; Mahmood, S.; Berghout, T.; Benbouzid, M. Cybersecurity Enhancement of Smart Grid: Attacks, Methods, and Prospects. Electronics 2022, 11, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, M.A.; Al-Andoli, M.N.; Ghaleb, M.; Thabit, R.; Alkawsi, G.; Alsayaydeh, J.A.J.; Gaid, A.S.A. Security of Smart Grid: Cybersecurity Issues, Potential Cyberattacks, Major Incidents, and Future Directions. Energies 2025, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanlou, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Asma’ Mokhtar, U.; Mahmood Malik, K.; Islam, S.; Khan, S.; Attique Khan, M.; Asghar Khan, M. Cybersecurity Challenges in Smart Grid Systems: Current and Emerging Attacks, Opportunities, and Recommendations. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2025, 6, 1965–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathika, O.V.G.; Karthikeyan, A.; Rout, K.; Hatkar, S. Cybersecurity Deployment in Smart Grids: Critical Review, Applications, Protection, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 113618–113641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniuk, E.K.; Szczepaniuk, H. Cybersecurity of Smart Grids: Requirements, Threats, and Countermeasures. Energies 2025, 18, 5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaan, B.; Colicchio, B.; Ould Abdeslam, D. Microgrid Cyber-Security: Review and Challenges toward Resilience. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggero, G.B.; Girdinio, P.; Marchese, M. Advancements and Research Trends in Microgrids Cybersecurity. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafei, H.; Li, L.; Aguilera, R.P. A Comprehensive Review on Cyber-Attack Detection and Control of Microgrid Systems. In Power Systems Cybersecurity: Methods, Concepts, and Best Practices; Haes Alhelou, H., Hatziargyriou, N., Dong, Z.Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyna, R. Cybersecurity and privacy in standards for smart grids—A comprehensive survey. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2018, 56, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabatkhah, F.; Li, Y.W.; Liang, H.; Reza Ahrabi, R. Cyber-Security of Smart Microgrids: A Survey. Energies 2021, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, H.T.; Anwar, A.; Mahmood, A. Comprehensive survey and taxonomies of false data injection attacks in smart grids: Attack models, targets, and impacts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 163, 112423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Shi, Q.; Tomsovic, K.; Sun, J.; Ren, L. Profit-Oriented False Data Injection on Electricity Market: Reviews, Analyses, and Insights. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 5876–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnoo, M.A.; Anwar, A.; Hosseinzadeh, N.; Islam, S.N.; Mahmood, A.N.; Doss, R. False data injection threats in active distribution systems: A comprehensive survey. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 140, 344–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Sadighian, A.; Tanveer, A.; Al-Naimi, S.J.; Oligeri, G. A survey on detection and localisation of false data injection attacks in smart grids. IET Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2024, 9, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K. A Survey on the Effects of False Data Injection Attack on Energy Market. In Proceedings of the 2018 Clemson University Power Systems Conference (PSC), Charleston, SC, USA, 4–7 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Labeau, F. From Wired to Wireless: Challenges of False Data Injection Attacks Against Smart Grid Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical & Computer Engineering (CCECE), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–16 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Qu, Y.; Gao, L.; Xie, G.; Yu, S. Detecting false data attacks using machine learning techniques in smart grid: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 170, 102808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoufi, S.; Derhab, A.; Guerroumi, M. Survey of false data injection in smart power grid: Attacks, countermeasures and challenges. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 54, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.S.; Abianeh, A.J.; Ferdowsi, F.; Basulaiman, K.; Barati, M. Measurable Challenges in Smart Grid Cybersecurity Enhancement: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech), Denver, CO, USA, 7–9 April 2021; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouslimani, M.; Tayeb, F.B.S.; Amirat, Y.; Benbouzid, M. Replay Attacks on Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Review on Countermeasures. In Proceedings of the IECON 2024-50th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedramnia, K.; Rahmani, M. Survey of DoS Attacks on LTE Infrastructure Used in AMI System and Countermeasures. In Proceedings of the 2018 Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Sanandaj, Iran, 28–29 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althobaiti, A.; Jindal, A.; Marnerides, A.K.; Roedig, U. Energy Theft in Smart Grids: A Survey on Data-Driven Attack Strategies and Detection Methods. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 159291–159312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Khan, A.; Ahmed, M.; Tahir, M.; Jeon, G.; Fortino, G.; Piccialli, F. Energy Theft Detection in Smart Grids: Taxonomy, Comparative Analysis, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 578–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, W.; Cui, J. Detection Methods in Smart Meters for Electricity Thefts: A Survey. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 273–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghout, T.; Benbouzid, M.; Muyeen, S. Machine learning for cybersecurity in smart grids: A comprehensive review-based study on methods, solutions, and prospects. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2022, 38, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.U.; Sodhi, B.; Sodhi, R. Cyber Security Enhancement of Smart Grids Via Machine Learning - A Review. In Proceedings of the 2020 21st National Power Systems Conference (NPSC), Gandhinagar, India, 17–19 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.I.; Shahriar, M.H.; Dastgir, M.G.; Debnath, A.; Parvez, I.; Sarwat, A.; Rahman, M.A. A Survey of Machine Learning-Based Cyber-Physical Attack Generation, Detection, and Mitigation in Smart-Grid. In Proceedings of the 2020 52nd North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Tempe, AZ, USA, 11–13 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Abdulkadir, R.A.; Islam, S.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Safie, N. A review on machine learning techniques for secured cyber-physical systems in smart grid networks. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 1268–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, O.A.; Khan, A.A.; Rehman, W.U.; Hassan, A. A Review of AI-Based Cyber-Attack Detection and Mitigation in Microgrids. Energies 2023, 16, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudaki, M.; Zadeh, P.T.; Olfati, H.R.; Deris, S. A Survey on Deep Learning Methods for Security and Privacy in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th International Conference on Protection and Automation of Power Systems (IPAPS), Shiraz, Iran, 30–31 December 2020; pp. 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, A.; Habaebi, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Mubarak, S. Applications of deep learning algorithms for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition intrusion detection system. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 9, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, N. Enhancing Cybersecurity in smart grid: A review of machine learning approaches. Telecommun. Syst. 2025, 88, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Kashef, R. Exploring the emerging role of large language models in smart grid cybersecurity: A survey of attacks, detection mechanisms, and mitigation strategies. Front. Energy Res. 2025, 13, 1531655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopstein, A.; Nguyen, C.; O’Fallon, C.; Hastings, N.; Wollman, D. NIST Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards, Release 4.0; Special Publication 1108r4; National Institute of Standards and Technology, Department of Commerce: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Gaggero, G.B.; Girdinio, P.; Marchese, M. Artificial Intelligence and Physics-Based Anomaly Detection in the Smart Grid: A Survey. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 23597–23606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, T. Adapting PKI for the smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Brussels, Belgium, 17–20 October 2011; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badra, M.; Zeadally, S. Key management solutions in the smart grid environment. In Proceedings of the 6th Joint IFIP Wireless and Mobile Networking Conference (WMNC), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 23–25 April 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Agarwal, A. Research issues related to cryptography algorithms and key generation for smart grid: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th India International Conference on Power Electronics (IICPE), Patiala, India, 17–19 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, A.; Conti, M. Key Management Systems for Smart Grid Advanced Metering Infrastructure: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2831–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Zamir, T.; Liang, H. Blockchain for Cybersecurity in Smart Grid: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wu, Q.; Liang, H. Blockchain-empowered security and privacy protection technologies for smart grid. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2023, 85, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.Y. A Review of Quantum Key Distribution Protocols in the Perspective of Smart Grid Communication Security. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.R.; Dán, G.; Miorandi, D.; Chlamtac, I. Smart Meter Data Privacy: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2820–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Lin, Y.; Bai, G.; Paverd, A.; Dong, J.S.; Martin, A. Smart Grid Metering Networks: A Survey on Security, Privacy and Open Research Issues. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2886–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalzaher, M.S.; Fouda, M.M.; Ibrahem, M.I. Data Privacy Preservation and Security in Smart Metering Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokry, M.; Awad, A.I.; Abd-Ellah, M.K.; Khalaf, A.A. Systematic survey of advanced metering infrastructure security: Vulnerabilities, attacks, countermeasures, and future vision. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 136, 358–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S. Privacy-preserving metering in smart grid for billing, operational metering, and incentive-based schemes: A survey. Comput. Secur. 2019, 84, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Lu, L.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Jin, X. A Survey on Intrusion Detection System for Advanced Metering Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2016 Sixth International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC), Harbin, China, 21–23 July 2016; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, M.; Mirafzal, B. On Self-Security of Grid-Interactive Smart Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Kansas Power and Energy Conference (KPEC), Manhattan, KS, USA, 19–20 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Lichtenwalner, M.E.; Johnson, T.J. A Review of Cybersecurity in Grid-Connected Power Electronics Converters: Vulnerabilities, Countermeasures, and Testbeds. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 113543–113559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevizan, R.D.; Obert, J.; De Angelis, V.; Nguyen, T.A.; Rao, V.S.; Chalamala, B.R. Cyberphysical Security of Grid Battery Energy Storage Systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59675–59722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamova, N.; Træhold, C.; Hashemi, S. Cyberattack detection methods for battery energy storage systems. J. Energy Storage 2023, 69, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekeraho, A.; Cotfas, D.T.; Cotfas, P.A.; Bălan, T.C.; Tuyishime, E.; Acheampong, R. Cybersecurity challenges in IoT-based smart renewable energy. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2024, 23, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosughi, A.; Tamimi, A.; King, A.B.; Majumder, S.; Srivastava, A.K. Cyber–physical vulnerability and resiliency analysis for DER integration: A review, challenges and research needs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Kemmeugne, A.; Kassouf, M.; Debbabi, M. Cybersecurity of distributed energy resource systems in the smart grid: A survey. Appl. Energy 2025, 383, 125364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdantseva, Y.; Burnap, P.; Blyth, A.; Eden, P.; Jones, K.; Soulsby, H.; Stoddart, K. A review of cyber security risk assessment methods for SCADA systems. Comput. Secur. 2016, 56, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsios, D.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Lagkas, T.; Sarigiannidis, A.G. A Survey on SCADA Systems: Secure Protocols, Incidents, Threats and Tactics. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1942–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Babaghayou, M.; Yazici, M.A. Cyber security for fog-based smart grid SCADA systems: Solutions and challenges. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 52, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, A.; Barenghi, A.; Pelosi, G.; Zonouz, S. Security challenges in building automation and SCADA. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology (ICCST), Rome, Italy, 13–16 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabus, J.E.U.; Bütün, İ.; Lagerström, R. Security Considerations for Remote Terminal Units. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Zooming Innovation in Consumer Technologies Conference (ZINC), Novi Sad, Serbia, 25–26 May 2022; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H.; Tipper, D. A Survey on Cyber Security for Smart Grid Communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 14, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia Le, T.; Chin, W.L.; Chen, H.H. Standardization and Security for Smart Grid Communications Based on Cognitive Radio Technologies—A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaya, L.; Sharma, P.; Bhagwatikar, G.; Kumar, A. Wireless Sensor Network Based Smart Grid Communications: Cyber Attacks, Intrusion Detection System and Topology Control. Electronics 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, C.; Zhong, X.; Deng, J.; Brooks, R.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K. A survey of electric power synchrophasor network cyber security. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Europe, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–15 October 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; De, D.; Song, W.Z.; Yang, J.; Das, S.K. Survey of Security Advances in Smart Grid: A Data Driven Approach. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carryl, C.; Ilyas, M.; Mahgoub, I.; Rathod, M. The PEV security challenges to the smart grid: Analysis of threats and mitigation strategies. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Connected Vehicles and Expo (ICCVE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–6 December 2013; pp. 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Xiao, Y. Privacy preservation for V2G networks in smart grid: A survey. Comput. Commun. 2016, 91-92, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.; Blesa, J.; Romero, E.; Villanueva, D. Security in cognitive wireless sensor networks. Challenges and open problems. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.P.A.; Fernandez, J.H.; Noura, H.N.; Chehab, A. Security of Power Line Communication systems: Issues, limitations and existing solutions. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 39, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Dener, M. Security with Wireless Sensor Networks in Smart Grids: A Review. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, D. Cyber-Attacks Related to Intelligent Electronic Devices and Their Countermeasures: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2018 53rd International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Glasgow, UK, 4–7 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalipi, F.; Yayilgan, S.Y. Security and Privacy Considerations for IoT Application on Smart Grids: Survey and Research Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 4th International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud Workshops (FiCloudW), Vienna, Austria, 22–24 August 2016; pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, K.; Oduol, V.; Langat, K. Cyber security challenges for IoT-based smart grid networks. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2019, 25, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.; Philippou, E.; Pitsillides, A. Survey in Smart Grid and Smart Home Security: Issues, Challenges and Countermeasures. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1933–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.; Cruz, T.; Lam, C.T.; Simões, P. Smart Substation Communications and Cybersecurity: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 2456–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulya, A.; Swarup, K.S.; Ramanathan, R. Cyber Security of Smart-Grid Frequency Control: A Review and Vulnerability Assessment Framework. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2024, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghavi, P.; Solanki, R.; Parmar, V.; Shah, K. Comprehensive Study of Cyber Security in AI Based Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing and Data Sciences, Kolkata, India, 27–28 April 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Lee, Y.; Hyun, S.H.; Koo, I. Feature Selection–Based Detection of Covert Cyber Deception Assaults in Smart Grid Communications Networks Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 27518–27529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.M.; Meskin, N.; Mehrjerdi, H. Covert Attack in Load Frequency Control of Power Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th IEEE International Energy Conference (ENERGYCon), Tunis, Tunisia, 28 September–1 October 2020; pp. 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, M. Myth or reality — Does the Aurora vulnerability pose a risk to my generator? In Proceedings of the 2011 64th Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers, College Station, TX, USA, 11–14 April 2011; pp. 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, K. Modeling Load Redistribution Attacks in Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, T.; Irfan, H.M.; Khan, S.; Haq, I.; Ullah, I.; Iqbal, M.; Hamam, H. Analysis of Cyber Security Attacks and Its Solutions for the Smart grid Using Machine Learning and Blockchain Methods. Future Internet 2023, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Liu, C.C.; Stefanov, A.; Basumallik, S.; Hussain, M.M.; Somda, B.; Rajkumar, V.S. Digital Twins Serving Cybersecurity: More Than a Model: Cybersecurity as a Future Benefit of Digital Twins 2. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2024, 22, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S. ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), Hong Kong, China, 1–6 June 2008; pp. 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Attack | Target | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Industroyer2 (malware) | Power plant, Ukraine | Operators discovered a second version of the Industroyer malware that was used in the 2015 attack. The malware targets circuit breakers with the aim of causing blackouts. | [3] |
| 2022 | Ransomware | DESFA (Natural gas distributer), Greece | System outage and data exposure. | [4] |
| 2022 | DoS | Gestore dei Servizi Energetici (Energy agency), Italy | Hackers compromised servers, blocked access to systems, and suspended access to the agency’s website for a week. | [5] |
| 2022 | DDoS | Energy provider, Lithuania | Hackers targeted Lithuania’s state-owned energy provider in a DDoS attack. | [5] |
| 2021 | Ransomware | Colonial pipeline (oil/fuel pipeline), US | The company shut down its pipeline system for a few days in response to the attack. Although the company paid the ransom, the data encrypted by the ransomware could not be restored. | [6] |
| Aspect | Traditional Power Grid | SG | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer | Simple consumer | Active participation | [12] |
| Generation | Centralized in power plants | DERs | [14] |
| Power Flow | Unidirectional (hierarchical) | Bidirectional | [15] |
| Control | Limited | Widespread | [16] |
| Standard | Purpose | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| AMI-SEC 7628 | Security requirements for AMI | [31,33] |
| ANSI C12.18 | Communication between smart meters | [13] |
| ANSI C12.19 | Data structures for meter communication | [1] |
| C37.118.2-2011 | Communication for PMU and phasor data concentrator | [20,30,31] |
| DNP3 | Automation system devices communications | [31] |
| IEC 60870-6 | Communication profile for SCADA | [31] |
| IEC 61850 | Communication for substation automation | [13,20,31,32] |
| IEC 62056 | Electricity metering data exchange | [1,32] |
| IEC 62351 | Cybersecurity of protocols | [31,32,33] |
| Modbus | Communication protocol | [31] |
| NERC-CIP | Security standards for bulk energy systems | [31,33,34] |
| NISTIR 7628 | Security framework for organizations | [34] |
| Ref. | Target | Year | Type | Power System | Communication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [82] | Transmission network | 2025 | Hybrid | Digital-twin city model, RTUs, IEDs, SCADA, Raspbery Pi | Real network |
| [81] | Synchrophasor network | 2024 | Hybrid | RTDS, PMUs, RTUs | - |
| [78] | Large-scale power systems | 2024 | Simulation | OPAL-RT, RTDS | EXata network emulator |
| [80] | Microgrid | 2021 | Hardware | Motor generators, RES emulators, inverters, transmission lines, electric loads | Wired and wireless communication networks (real network) |
| [76] | AC microgrid | 2021 | Simulation | OP5700, HYPERSIM, OPAL-RT | - |
| [79] | SG | 2017 | Simulation | RTDS, energy resource simulators | Wide area network emulator |
| [83] | SG | 2017 | Hybrid | OPAL-RT, IEDs | Serial communication (real network) |
| [84] | SG | 2015 | Hybrid | RTDS, PMUs | NS-3 |
| [42] | IEC 61850-based substation | 2015 | Hybrid | RTDS, IEDs, RTU | Ethernet switch, fiber-optic network |
| Classification Criteria | Refs. |
|---|---|
| CIA triad | [33,87,104,105,135] |
| Target | [86,93,98,102,105,106,135] |
| Layer | [2,56,87,100,105,134,135] |
| Ref. | Method | Role | Target | M vs. D | Attack | Att. Type | Att. Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [91] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ |
| [92] | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| [56] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - |
| [93] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [95] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - |
| [96] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [97] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| [98] | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - |
| [100] | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [101] | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - |
| [89] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [99] | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [90] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [103] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - |
| [2] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - |
| [116] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - |
| [120] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [122] | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [40] | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [123] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [124] | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| [125] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [126] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [146] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [147] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [148] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [153] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [160] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [74] | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [161] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [163] | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [173] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [175] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [176] | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [178] | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | - |
| [105] | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [157] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [106] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [107] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [134] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [135] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Research Challenge | Proposed Directions |
|---|---|
| Lack of research on the distribution grid. Predominance of the simplified DC model over the AC and hybrid models. | Adopting data-driven solutions (ML) for their model-independence nature, allowing their reproducibility and generalization over different models and components. |
| Interdependence between the cyber and physical layers. Coordinated and complex attacks. | Hardware-in-the-loop for a realistic representation of SG operation to identify complex attack scenarios and design robust countermeasures. |
| Literature focuses on countering a single attack (notably FDI). | Focusing on developing countermeasures against multiple attacks and for various attack stages. |
| ML-related issues, including data privacy and data imbalance. | Adapting and improving existing solutions for the context of SG cybersecurity, such as oversampling, federated learning, and learning over encrypted data. |
| Countermeasure testing for reproducibility in real-life conditions. Lack of SG cybersecurity datasets. | Digital twins for their ability to reproduce realistic SG operation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouslimani, M.; Benbouzid-Si Tayeb, F.; Amirat, Y.; Benbouzid, M. Cyber-Physical Security in Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Research Areas, Threats, and Countermeasures. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12367. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312367
Bouslimani M, Benbouzid-Si Tayeb F, Amirat Y, Benbouzid M. Cyber-Physical Security in Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Research Areas, Threats, and Countermeasures. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12367. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312367
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouslimani, Mariem, Fatima Benbouzid-Si Tayeb, Yassine Amirat, and Mohamed Benbouzid. 2025. "Cyber-Physical Security in Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Research Areas, Threats, and Countermeasures" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12367. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312367
APA StyleBouslimani, M., Benbouzid-Si Tayeb, F., Amirat, Y., & Benbouzid, M. (2025). Cyber-Physical Security in Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Research Areas, Threats, and Countermeasures. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12367. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312367







