Improving Mandarin ASR Performance Through Multimodality
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A new multimodal Chinese speech recognition neural network structure is proposed.
- Label denoising is introduced into pinyin-assisted Chinese speech recognition for the first time.
- Performance is improved by 4%.
2. Related Work
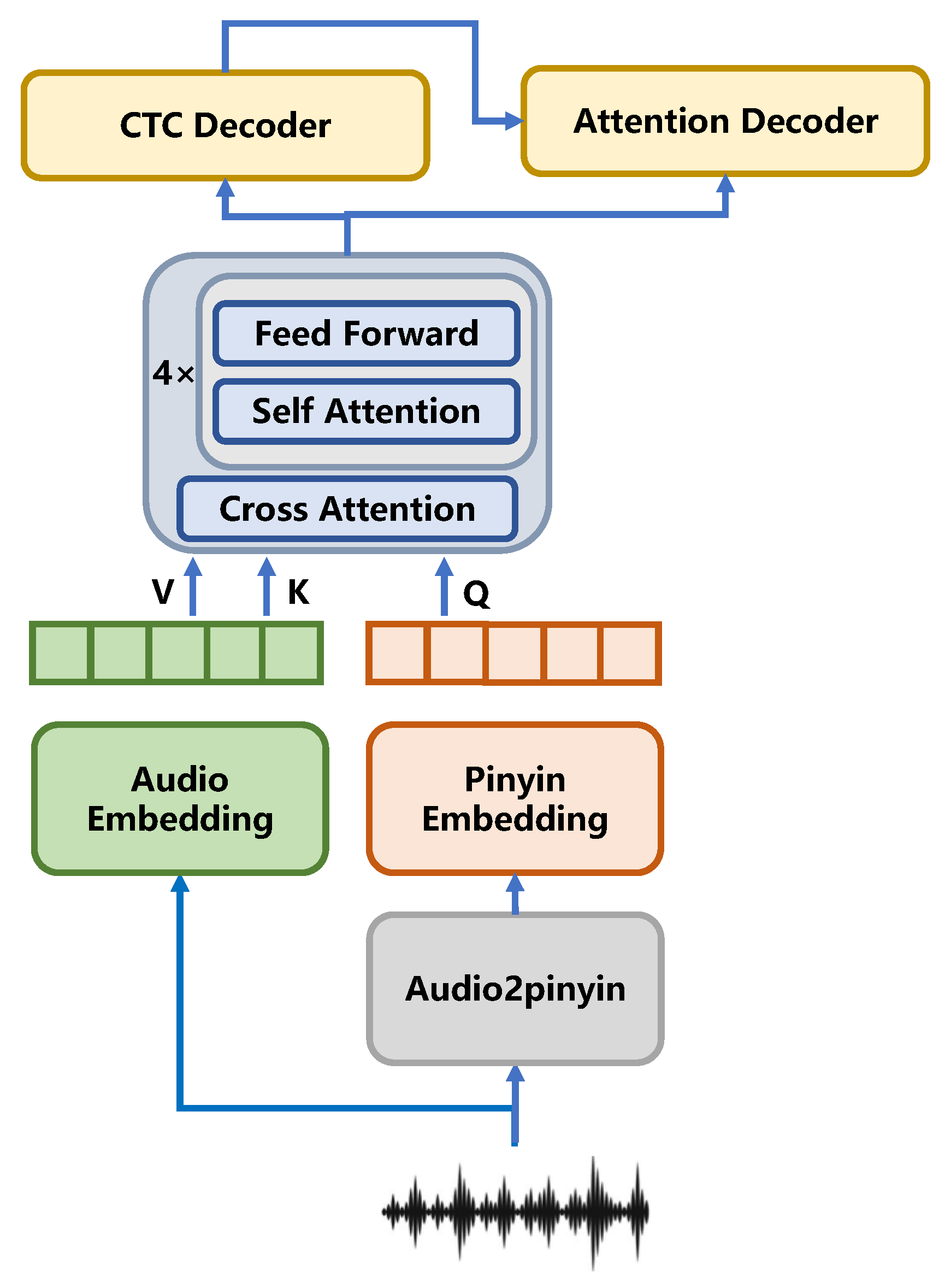
3. Method
3.1. Speech to Pinyin
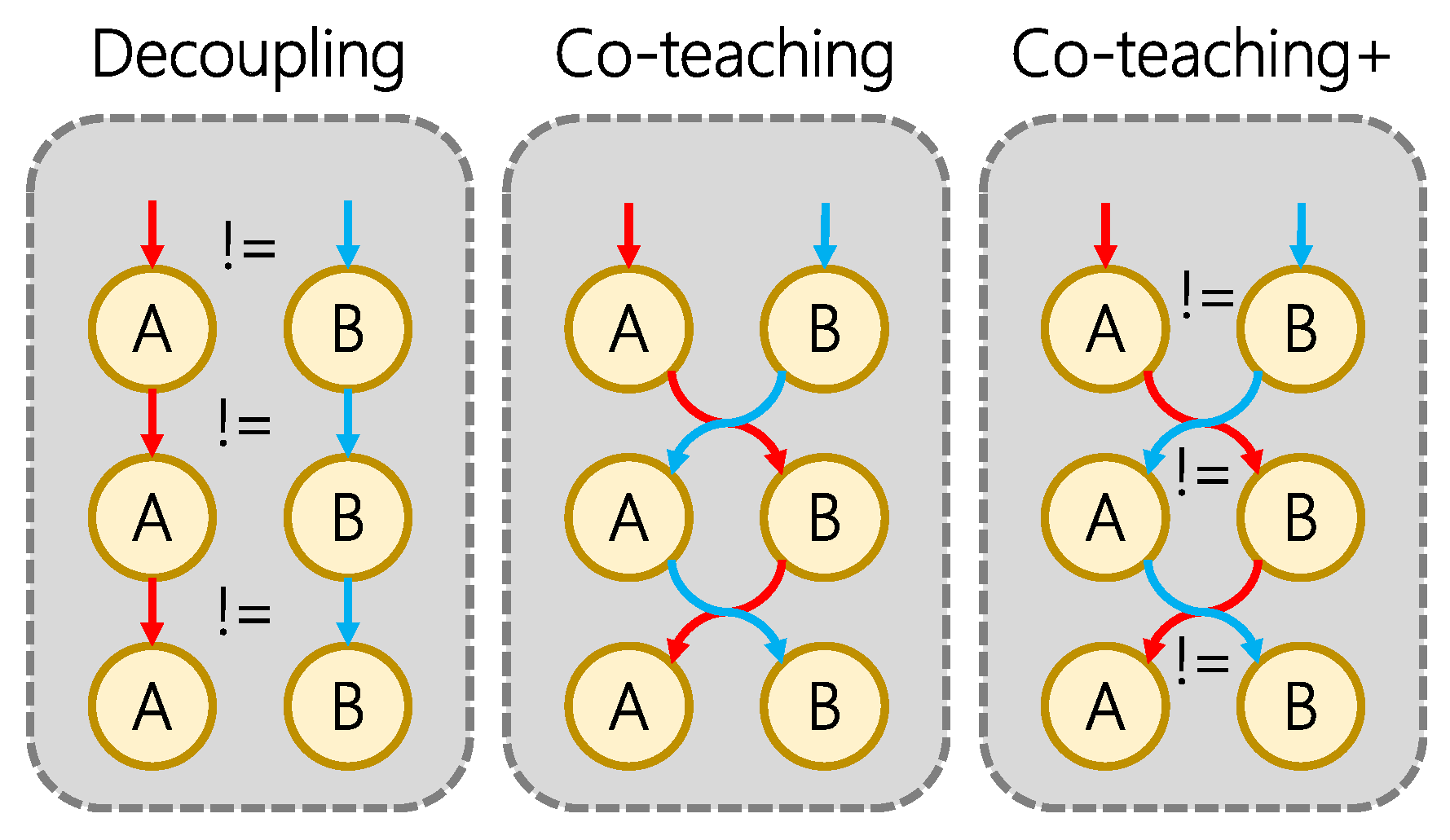
3.2. Label Denoising Module
3.3. Multimodal ASR Encoder
- The pinyin input serves as Q, and the speech input as K and V. It is required that the two different modality sequences have matching input dimensions.
- For each position in Q, calculate its degree of association with all positions in K, obtain the similarity matrix, and normalize it to obtain the weight matrix.
- Use this normalized matrix to weight V, producing a new feature representation that integrates the new modality.
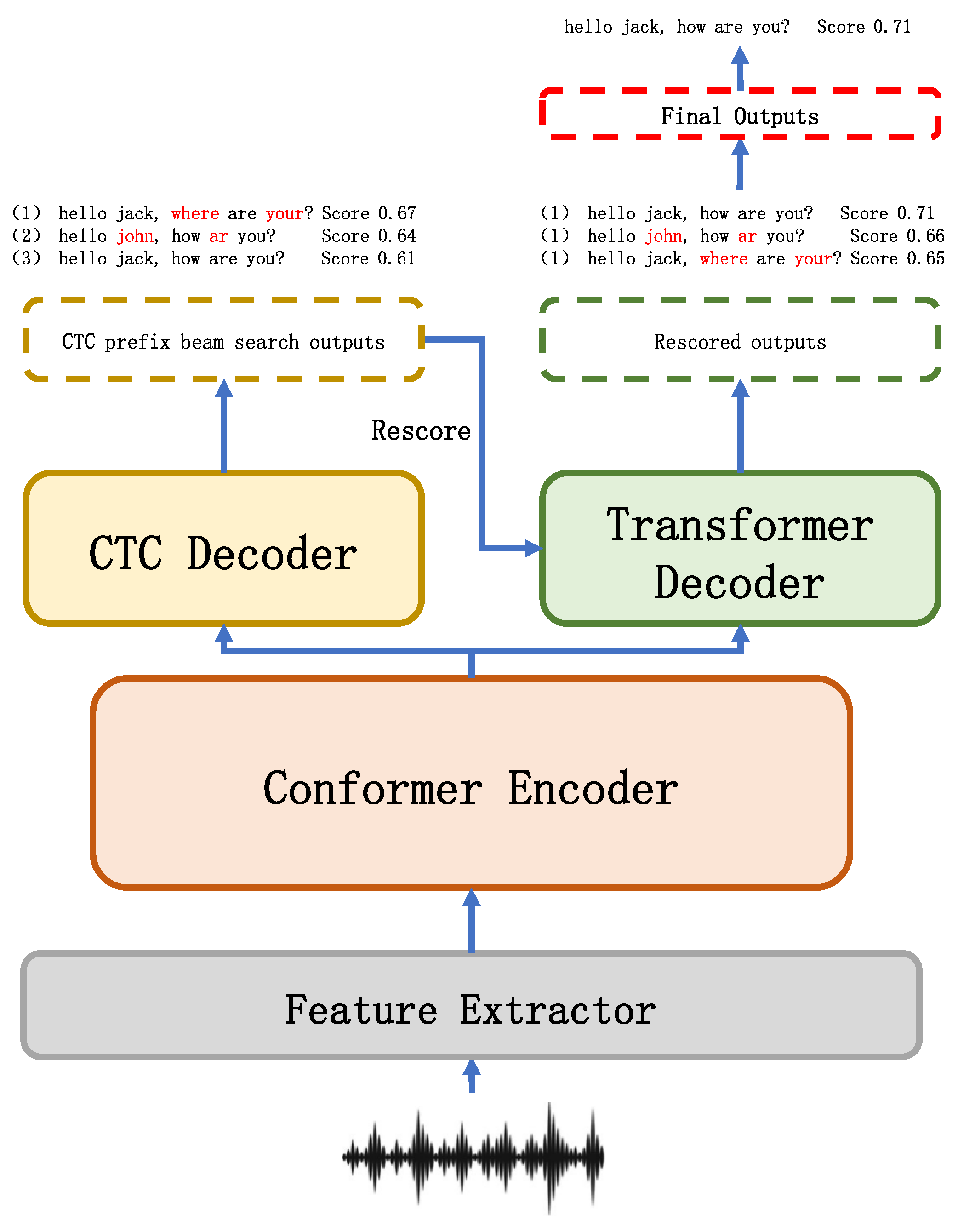
3.4. Decoder Module
4. Experiment
4.1. Experiment Setup
4.2. Results
4.3. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaur, P.; Singh, P.; Garg, V. Speech recognition system; challenges and techniques. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2012, 3, 3989–3992. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi, S.F.N.; Shukla, V.K.; Mishra, V.P.; Singh, B. Redefining home automation through voice recognition system. In Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security: Proceedings of IEMIS 2020, Volume 2; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Lei, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Investigation of modeling units for mandarin speech recognition using dfsmn-ctc-smbr. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 7085–7089. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Yu, F.; Yang, C.; Peng, Z.; Chen, X.; Xie, L.; Lei, X. WeNet: Production Oriented Streaming and Non-Streaming End-to-End Speech Recognition Toolkit. Interspeech 2021, 2021, 4054–4058. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, B. Speech-transformer: A no-recurrence sequence-to-sequence model for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5884–5888. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Long, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, Y. Boosting Character-based Mandarin ASR via Chinese Pinyin Representation. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2023, 26, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ng, D.; Fu, X.; Han, L.; Xi, W.; Wang, R.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, J. On the Effectiveness of Pinyin-Character Dual-Decoding for End-to-End Mandarin Chinese ASR. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.10792. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Andrews, J.F. Chinese Pinyin. Am. Ann. Deaf 2021, 166, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effendi, J.; Tjandra, A.; Sakti, S.; Nakamura, S. Listening while speaking and visualizing: Improving ASR through multimodal chain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), Singapore, 14–18 December 2019; pp. 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y. Design and Implementation of Smart Home Air Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer, Internet of Things and Control Engineering, Wuhan, China, 1–3 November 2024; pp. 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Mukherjee, P.; Verma, S.; Kavita; Kaur, M.; Singh, S.; Kobielnik, M.; Woźniak, M.; Shafi, J.; Ijaz, M.F. BBNSF: Blockchain-based novel secure framework using RP2-RSA and ASR-ANN technique for IoT enabled healthcare systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, P.; Qian, X. Speech-oriented sparse attention denoising for voice user interface toward industry 5.0. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, D.; Peng, Z.; Song, X.; Yao, Z.; Lv, H.; Xie, L.; Yang, C.; Pan, F.; Niu, J. Wenet 2.0: More productive end-to-end speech recognition toolkit. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.15455. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Ding, C.; Dong, L.; Dong, Q.; Du, Y.; Gao, K.; et al. Seed-ASR: Understanding Diverse Speech and Contexts with LLM-based Speech Recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.04675. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Toda, T. MF-AED-AEC: Speech Emotion Recognition by Leveraging Multimodal Fusion, ASR Error Detection, and ASR Error Correction. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 11066–11070. [Google Scholar]
- Oneață, D.; Cucu, H. Improving multimodal speech recognition by data augmentation and speech representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 4579–4588. [Google Scholar]
- Afouras, T.; Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. Asr is all you need: Cross-modal distillation for lip reading. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 2143–2147. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, R.W.; Clements, M.A. Reconstruction of speech from whispers. Med. Eng. Phys. 2002, 24, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, J.; Wang, R.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Ren, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Ko, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. SpeechT5: Unified-Modal Encoder-Decoder Pre-Training for Spoken Language Processing. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 5723–5738. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, M.P.; Anderson, A.J.; Lalor, E.C. Semantic context enhances the early auditory encoding of natural speech. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7564–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xi, W.; Gadyatskaya, O.; Song, Z.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y. FedFixer: Mitigating heterogeneous label noise in federated learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 12830–12838. [Google Scholar]
- Lukasik, M.; Bhojanapalli, S.; Menon, A.; Kumar, S. Does label smoothing mitigate label noise? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Online, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 6448–6458. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Madani, S.; Guan, J.; Alloulah, M.; Gupta, S.; Hassanieh, H. Bootstrapping autonomous driving radars with self-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15012–15023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Xiang, Z.; Qiao, C.; Fu, J.; Pu, T. Adaptive multi-modal cross-entropy loss for stereo matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5135–5144. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 42, 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, D.; Wu, X.; Tang, Y.; Lan, L. Continuous review and timely correction: Enhancing the resistance to noisy labels via self-not-true distillation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 5700–5704. [Google Scholar]
- Berthelot, D.; Carlini, N.; Goodfellow, I.; Papernot, N.; Oliver, A.; Raffel, C.A. Mixmatch: A holistic approach to semi-supervised learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Davis, J.; Rabin, Z.; Lewis, B.; Scherreik, M.; Ilin, R. Design choices for enhancing noisy student self-training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 1926–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Yao, Q.; Yu, X.; Niu, G.; Xu, M.; Hu, W.; Tsang, I.; Sugiyama, M. Co-teaching: Robust training of deep neural networks with extremely noisy labels. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Socher, R.; Hoi, S.C. Dividemix: Learning with noisy labels as semi-supervised learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07394. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Leung, T.; Li, L.J.; Li, F.F. Mentornet: Learning data-driven curriculum for very deep neural networks on corrupted labels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2304–2313. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X. THCHS-30: A Free Chinese Speech Corpus. arXiv e-Prints. 2015. arXiv–1512. Available online: http://index.cslt.org/mediawiki/images/f/fe/Thchs30.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Ran, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Y. Pseudo Labeling Methods for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation: A Review and Future Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 35, 3054–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, W.; Fu, R.; Yang, K.; Yu, Z. RPSC: Robust pseudo-labeling for semantic clustering. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 14008–14016. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, P.; Tao, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, H.; Ma, J.; Guan, X. Memory disagreement: A pseudo-labeling measure from training dynamics for semi-supervised graph learning. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2024, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 434–445. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Han, B.; Yao, J.; Niu, G.; Tsang, I.; Sugiyama, M. How does disagreement help generalization against label corruption? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June2019; pp. 7164–7173. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, A.; Qin, J.; Chiu, C.C.; Parmar, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Conformer: Convolution-augmented transformer for speech recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.08100. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, H.; Du, J.; Na, X.; Wu, B.; Zheng, H. AIShell-1: An Open-Source Mandarin Speech Corpus and A Speech Recognition Baseline. In Proceedings of the Oriental COCOSDA 2017, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–3 November 2017. Submitted. [Google Scholar]

| Wenet | Accuracy | CER | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 94.76 | 5.34 | |
| noise label | 86.47 | 13.53 | −8.19 |
| Model | Accuracy | CER | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wenet | 94.76 | 5.34 | −1.23 |
| baseline | 91.62 | 8.38 | −4.25 |
| Prop-Model w/o denoise | 81.09 | 18.91 | −14.78 |
| Proposed Model | 95.87 | 4.13 |
| Multimodal | CTC | CER | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concat | Cross-Att | w/ | w/o | ||
| w/o denoise | ✔ | ✔ | 18.91 | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 20.67 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 16.71 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 17.24 | |||
| Decoupling | ✔ | ✔ | 7.57 | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 8.11 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 7.21 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 7.68 | |||
| Co-teaching | ✔ | ✔ | 6.18 | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 6.37 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 5.17 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 6.09 | |||
| Co-teaching+ | ✔ | ✔ | 4.96 | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 5.23 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 4.13 | |||
| ✔ | ✔ | 4.83 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, R.; Yang, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhao, J. Improving Mandarin ASR Performance Through Multimodality. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12224. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212224
Jiang R, Yang Z, Fu X, Zhao J. Improving Mandarin ASR Performance Through Multimodality. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12224. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212224
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Rui, Zhao Yang, Xiao Fu, and Jizhong Zhao. 2025. "Improving Mandarin ASR Performance Through Multimodality" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12224. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212224
APA StyleJiang, R., Yang, Z., Fu, X., & Zhao, J. (2025). Improving Mandarin ASR Performance Through Multimodality. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12224. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212224






