Automatic Baseline Correction of 1D Signals Using a Parameter-Free Deep Convolutional Autoencoder Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
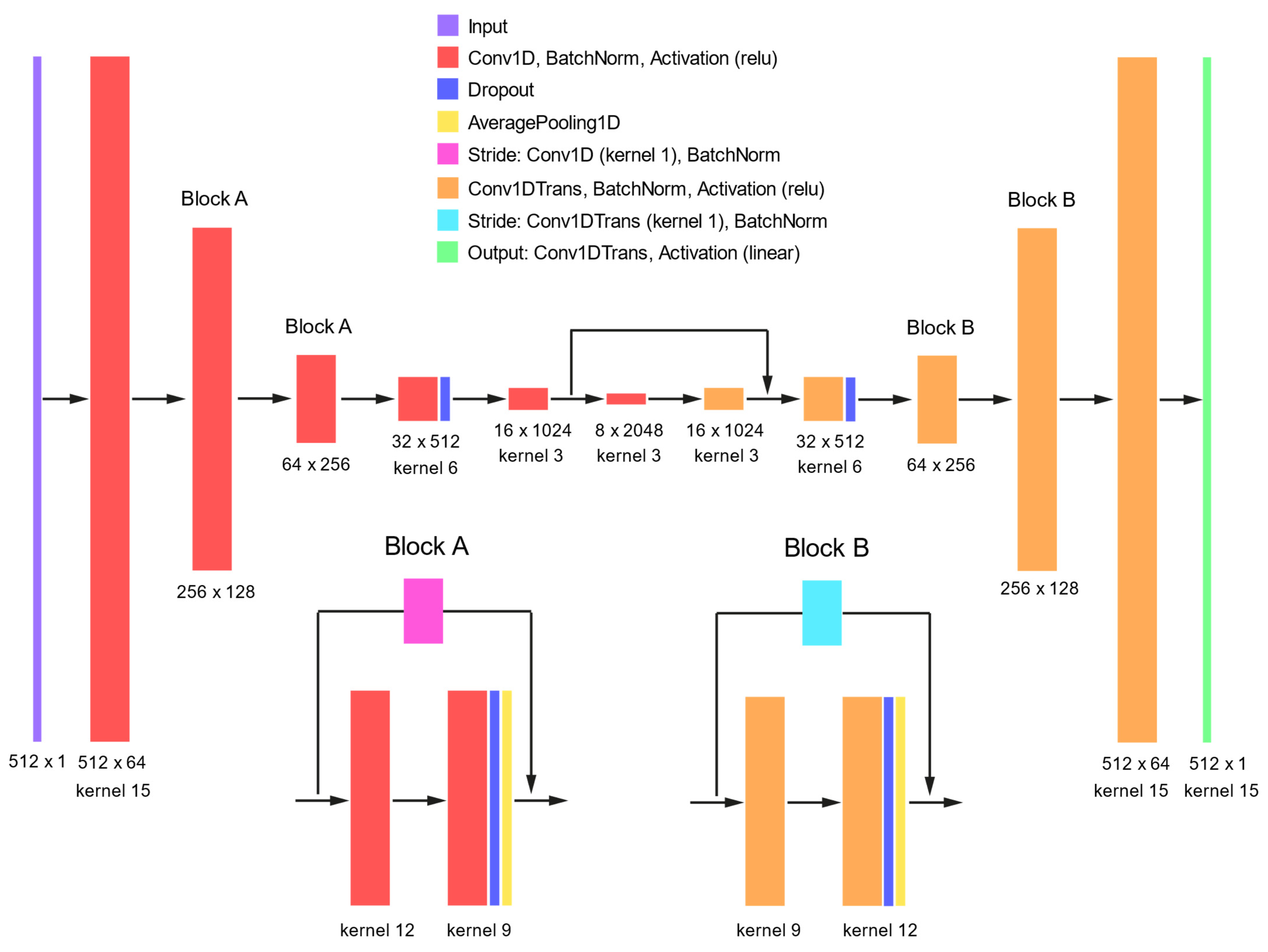
2.1. Convolutional Autoencoder Model
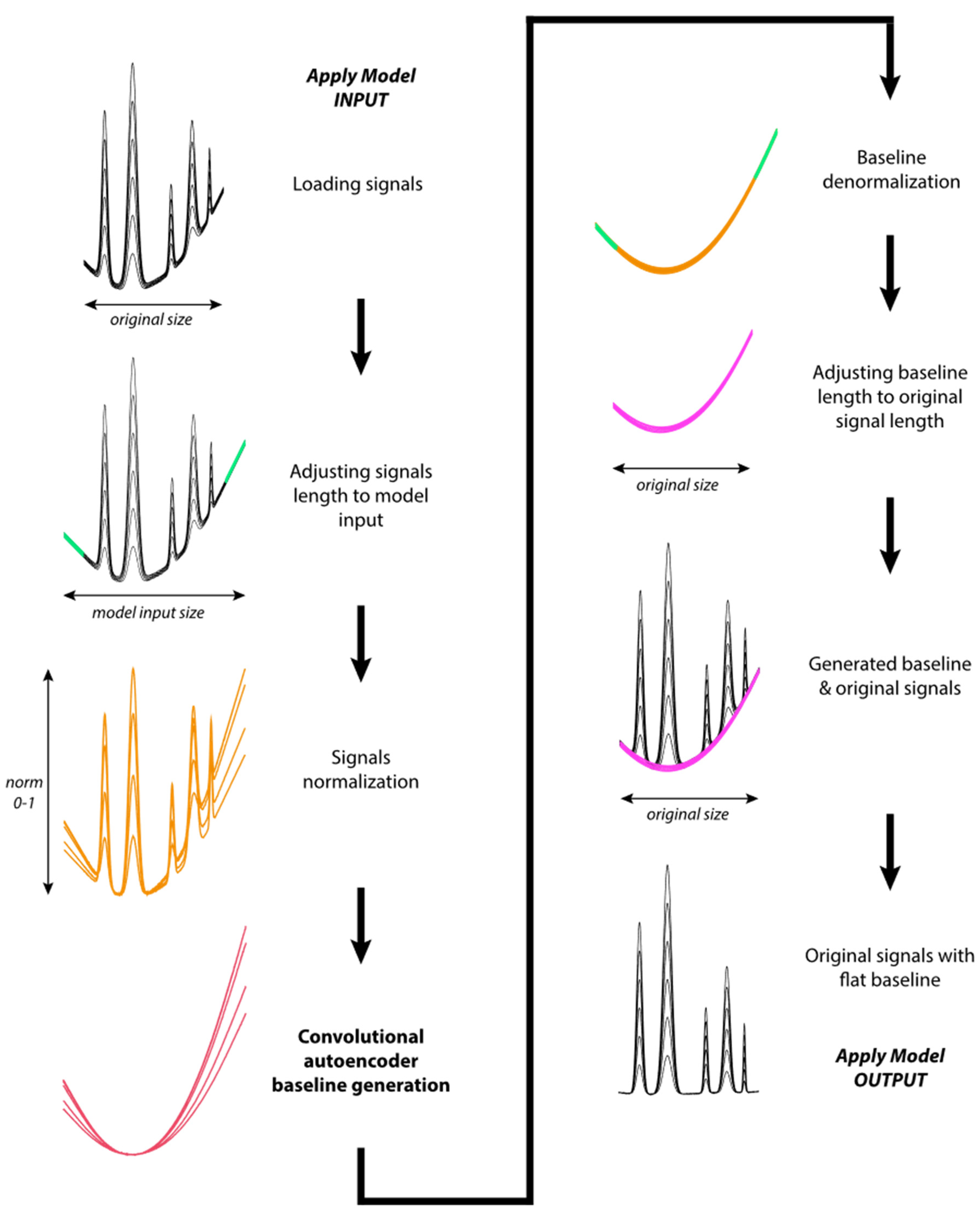
2.2. Apply Model Algorithm
3. Model Preparation
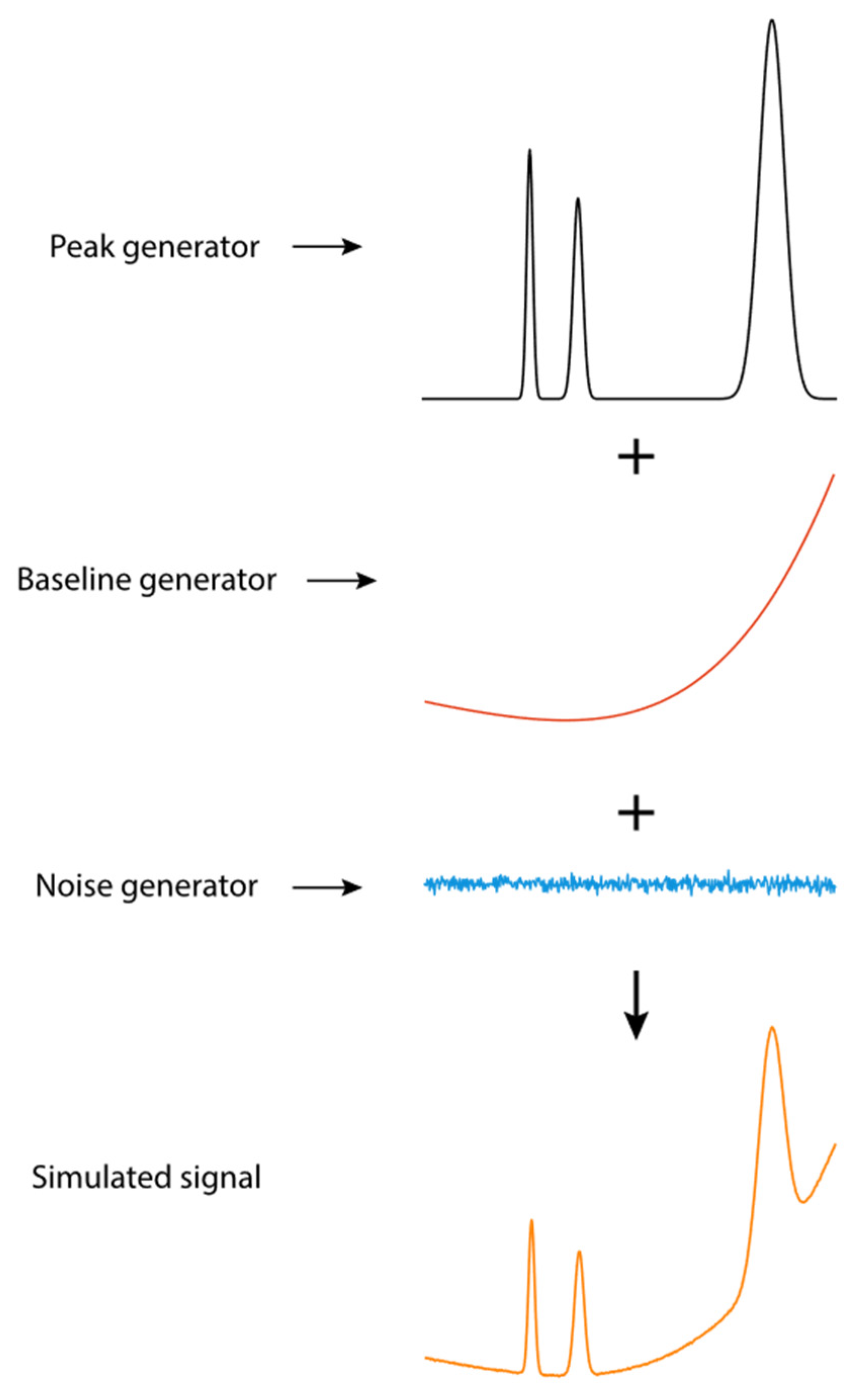
3.1. Generation of Simulated Signals for Model Training
3.2. Model Training Details
3.3. Experimental Signals
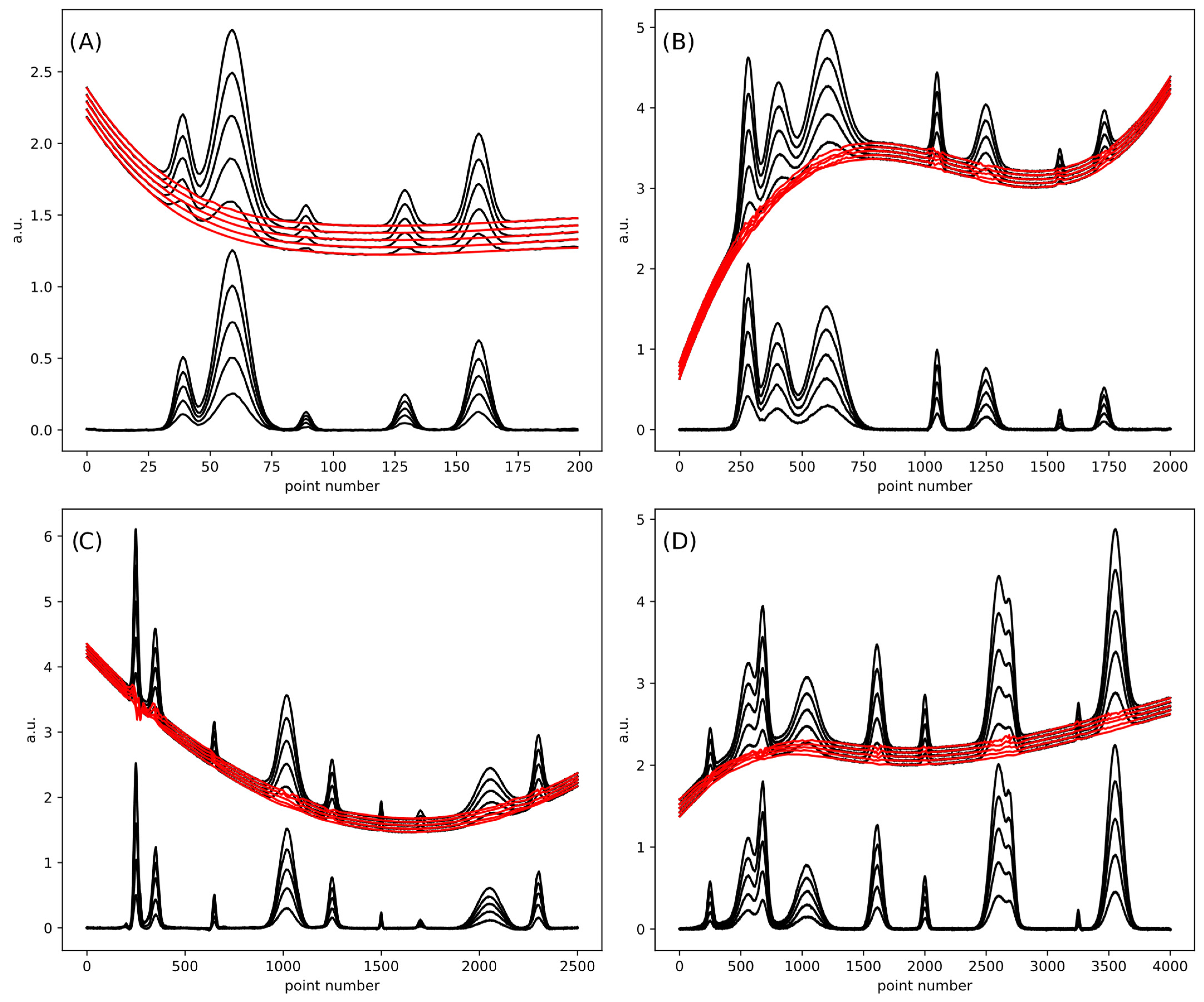
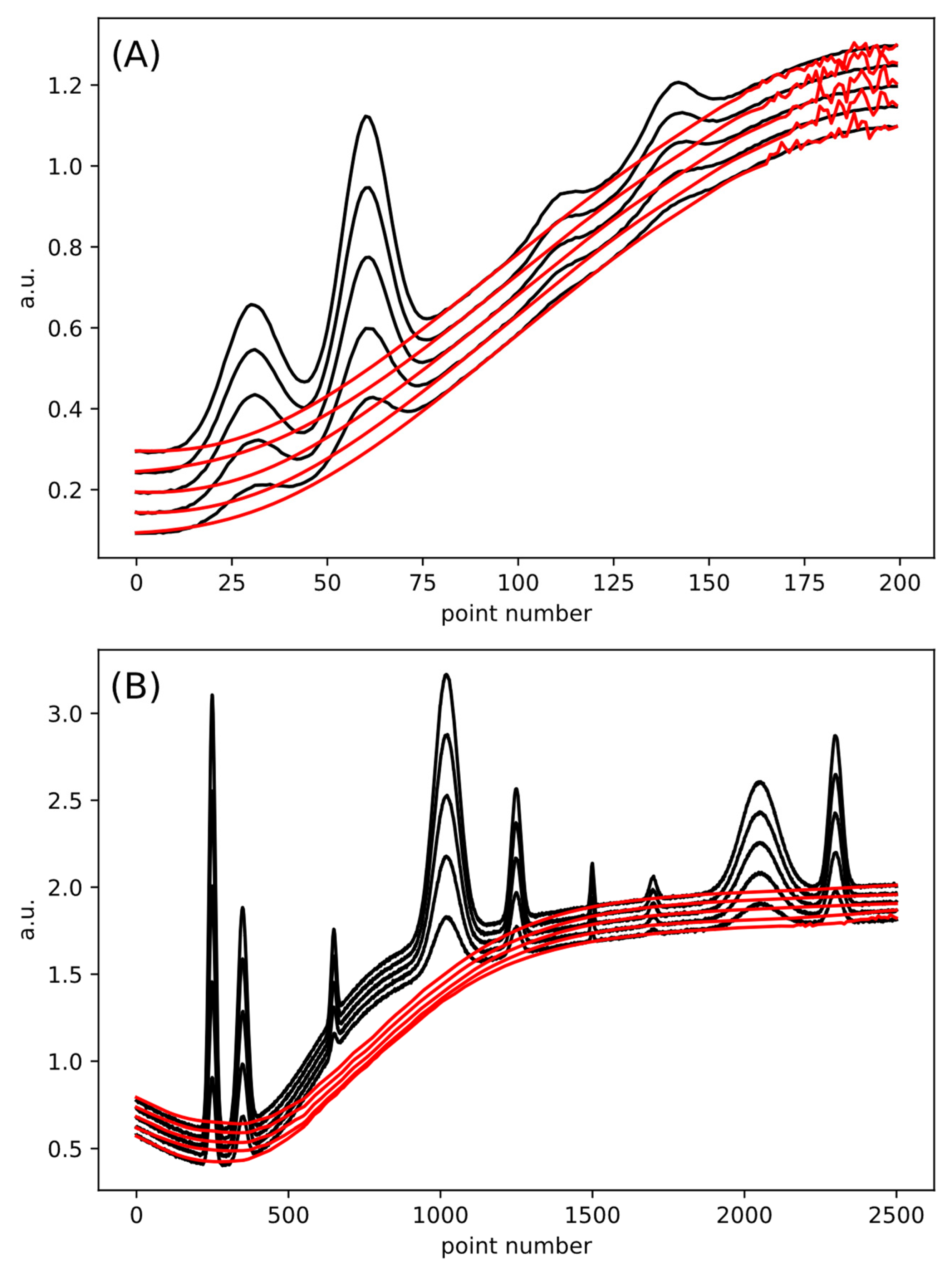
4. Results and Discussion
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallo, C.; Capozzi, V.; Lasalvia, M.; Perna, G. An algorithm for estimation of background signal of Raman spectra from biological cell samples using polynomial functions of different degrees. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 83, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Ruan, G.; Mo, J. Baseline correction by improved iterative polynomial fitting with automatic threshold. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2006, 82, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, Ł.; Ciepiela, F.; Jakubowska, M. Automatic baseline correction in voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Fang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, W.; Zhang, H.; Wei, D.; Fu, W.; Pei, D. Investigation of a genetic algorithm based cubic spline smoothing for baseline correction of Raman spectra. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 152, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Yu, Z.H. Baseline correction using morphological and iterative local extremum (MILE). Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 240, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, W. Automatic background correction method for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2023, 208, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.M.; He, P. Two-stage iteratively reweighted smoothing splines for baseline correction. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2022, 227, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, D.; Gui, W. Baseline correction for Raman spectra using penalized spline smoothing based on vector transformation. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3525–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, Ł.; Ciepiela, F.; Jakubowska, M.; Kubiak, W.W. Baseline correction in standard addition voltammetry by discrete wavelet transform and splines. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckstuhl, A.F.; Jacobson, M.P.; Field, R.W.; Dodd, J.A. Baseline subtraction using robust local regression estimation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2001, 68, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y. A robust baseline elimination method based on community information. Digit. Signal Process. 2015, 40, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, F.; Drescher, M. Background removal from rapid-scan EPR spectra of nitroxide-based spin labels by minimizing non-quadratic cost functions. J. Magn. Reson. Open 2023, 16–17, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazet, V.; Carteret, C.; Brie, D.; Idier, J.; Humbert, B. Background removal from spectra by designing and minimising a non-quadratic cost function. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2005, 76, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, J.; Pan, T.; Chang, C.; So, H.C. Sparse Bayesian learning approach for baseline correction. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 204, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, P.H.C. A perfect smoother. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3631–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilers, P.H.C.; Boelens, H.F.M. Baseline Correction with Asymmetric Least Squares Smoothing, Leiden University Medical Centre, The Netherlands. Available online: https://prod-dcd-datasets-public-files-eu-west-1.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/dd7c1919-302c-4ba0-8f88-8aa61e86bb9d (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Peng, J.; Peng, S.; Jiang, A.; Wei, J.; Li, C.; Tan, J. Asymmetric least squares for multiple spectra baseline correction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 683, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.-J.; Park, A.; Ahn, Y.-J.; Choo, J. Baseline correction using asymmetrically reweighted penalized least squares smoothing. Analyst 2015, 140, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, R. An improved PD-AsLS method for baseline estimation in EDXRF analysis. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Chen, S.; Liang, Y.Z. Baseline correction using adaptive iteratively reweighted penalized least squares. Analyst 2010, 135, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tang, X.; Tong, A.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, J. Baseline correction for infrared spectra using adaptive smoothness parameter penalized least squares method. Spectrosc. Lett. 2020, 53, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, X.; Zaho, Y. Beyond Traditional AirPLS: Improved Baseline Removal in SERS with Parameter-Focused Optimization and Prediction. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 16211–16218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tian, Y.; Zha, G.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C.; Sun, W.; Li, C.M.; Wei, L.; et al. Microstrip isoelectric focusing with deep learning for simultaneous screening of diabetes, anemia, and thalassemia. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1312, 342696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuyun, W.; Lin, F.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, H.; Fan, M.; Xu, L.; Kong, K.V.; Chen, Y.; Lin, D.; et al. Laser tweezer Raman spectroscopy combined with deep neural networks for identification of liver cancer cells. Talanta 2023, 264, 124753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, S.; Ciepiela, F.; Baś, B.; Jakubowska, M. Deep learning assisted distinguishing of honey seasonal changes using quadruple voltammetric electrodes. Talanta 2022, 241, 123213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Yan, C.; Min, H.; An, Y.; Liu, S. Interpretable deep learning-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for brand classification of iron ores. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1166, 338574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Kikuchi, J. Application of a Deep Neural Network to Metabolomics Studies and Its Performance in Determining Important Variables. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Xia, C.; Bai, Q.; Jin, L.; Shen, Y. An in silico scheme for optimizing the enzymatic acquisition of natural biologically active peptides based on machine learning and virtual digestion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1298, 342419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Zhao, W.; Yu, Q.; Qian, X.; Zhou, J.; Huo, X.; Tang, F. SR-Unet: A Super-Resolution Algorithm for Ion Trap Mass Spectrometers Based on the Deep Neural Network. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 17407–17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, T.; Xu, J.; Luo, X.; Ying, Y. DeepSpectra: An end-to-end deep learning approach for quantitative spectral analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Ryu, J.; Joo, H.; Jung, H.T.; Kim, J. Finding Hidden Signals in Chemical Sensors Using Deep Learning. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6529–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Luo, J.; Zeng, Q.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Zhan, C.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Y. Improvement in signal-to-noise ratio of liquid-state NMR spectroscopy via a deep neural network DN-Unet. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantz, E.D.; Tiwari, S.; Watrous, J.D.; Cheng, S.; Jain, M. Deep Neural Networks for Classification of LC-MS Spectral Peaks. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12407–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Adversarial nets for baseline correction in spectra processing. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 213, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Guo, X.; Liu, M.; Kong, L.; Hui, M.; Dong, L.; Zhao, Y. Deep learning baseline correction method via multi-scale analysis and regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 235, 104779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, M.; Martinez-Calderon, M.; Xu, W.; Chamley, L.W.; Hisey, C.L.; Broderick, N.G.R. Cascaded Deep Convolutional Neural Networks as Improved Methods of Preprocessing Raman Spectroscopy Data. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12907–12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Son, Y.J.; Park, A.; Baek, S.J. Baseline correction using a deep-learning model combining ResNet and UNet. Analyst 2022, 147, 4285–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhao, P.; Fan, Q.; Jing, H.; Dang, R.; Sun, W.; Feng, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, Q. Deep Neural Network: As the Novel Pipelines in Multiple Preprocessing for Raman Spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 302, 123086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Dang, Y.; Han, J. Denoising and Baseline Correction Methods for Raman Spectroscopy Based on Convolutional Autoencoder: A Unified Solution. Sensors 2024, 24, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Woznicki, T.; Kusnierek, K. Estimating Baselines of Raman Spectra Based on Transformer and Manually Annotated Data. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 330, 125679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Fan, Q.; Dang, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Hu, B.; Gao, C.; Wang, Q. Interference Data Denoising and Baseline Correction via a Multi-Scale Deep Denoising Network and Multidimensional Gradient-Consistent Regularization. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 192, 113849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Son, J.Y.; Dong, C.; Baek, S.-J. Baseline Correction of Raman Spectral Data Using Triangular Deep Convolutional Networks. Analyst 2025, 150, 2653–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baś, B.; Jakubowska, M.; Reczyński, W.; Ciepiela, F.; Kubiak, W.W. Rapidly renewable silver and gold annular band electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 73, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, Ł.; Sordoń, W.; Jakubowska, M. Voltammetric Determination of Ternary Phenolic Antioxidants Mixtures with Peaks Separation by ICA. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, H42–H48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
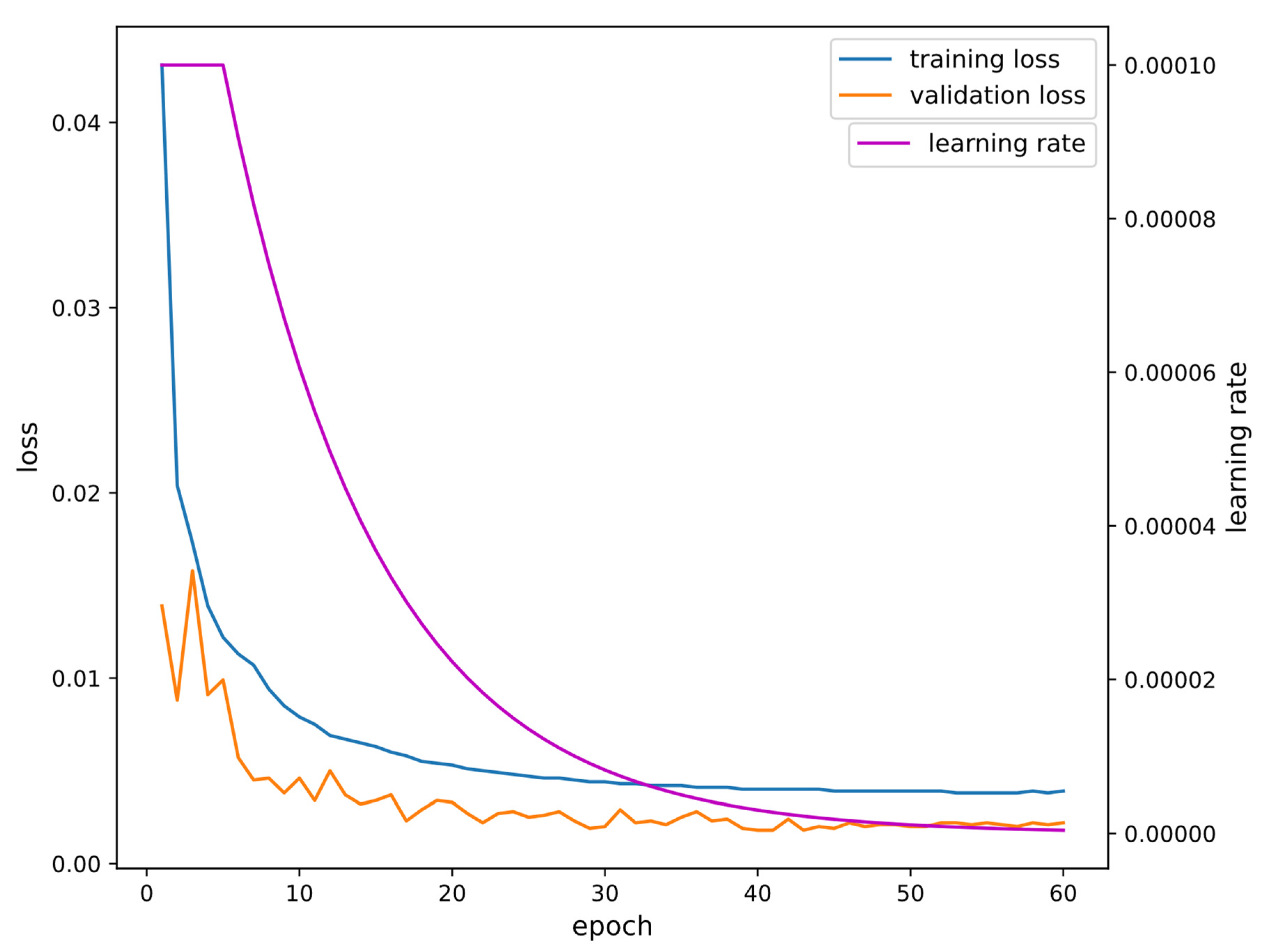


| Loss (MAE) | Metrics (RMSE) | |
|---|---|---|
| Train | 0.0039 | 0.0093 |
| Validate | 0.0022 | 0.0047 |
| Test | 0.0022 | 0.0051 |
| ConvAuto | ResUNet | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | |
| SimSet 1 | 0.0034 | 0.0045 | 0.0023 | 0.0030 |
| SimSet 2 | 0.0192 | 0.0230 | 0.0114 | 0.0198 |
| SimSet 3 | 0.0102 | 0.0120 | 0.0119 | 0.0224 |
| SimSet 4 | 0.0198 | 0.0263 | 1.6839 | 1.7957 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górski, Ł.; Jakubowska, M. Automatic Baseline Correction of 1D Signals Using a Parameter-Free Deep Convolutional Autoencoder Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212069
Górski Ł, Jakubowska M. Automatic Baseline Correction of 1D Signals Using a Parameter-Free Deep Convolutional Autoencoder Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212069
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórski, Łukasz, and Małgorzata Jakubowska. 2025. "Automatic Baseline Correction of 1D Signals Using a Parameter-Free Deep Convolutional Autoencoder Algorithm" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212069
APA StyleGórski, Ł., & Jakubowska, M. (2025). Automatic Baseline Correction of 1D Signals Using a Parameter-Free Deep Convolutional Autoencoder Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212069






