Colour Classification Analysis Based on MFCC Acoustic Feature Sets and Machine Learning Algorithms in Sound–Colour Synaesthesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
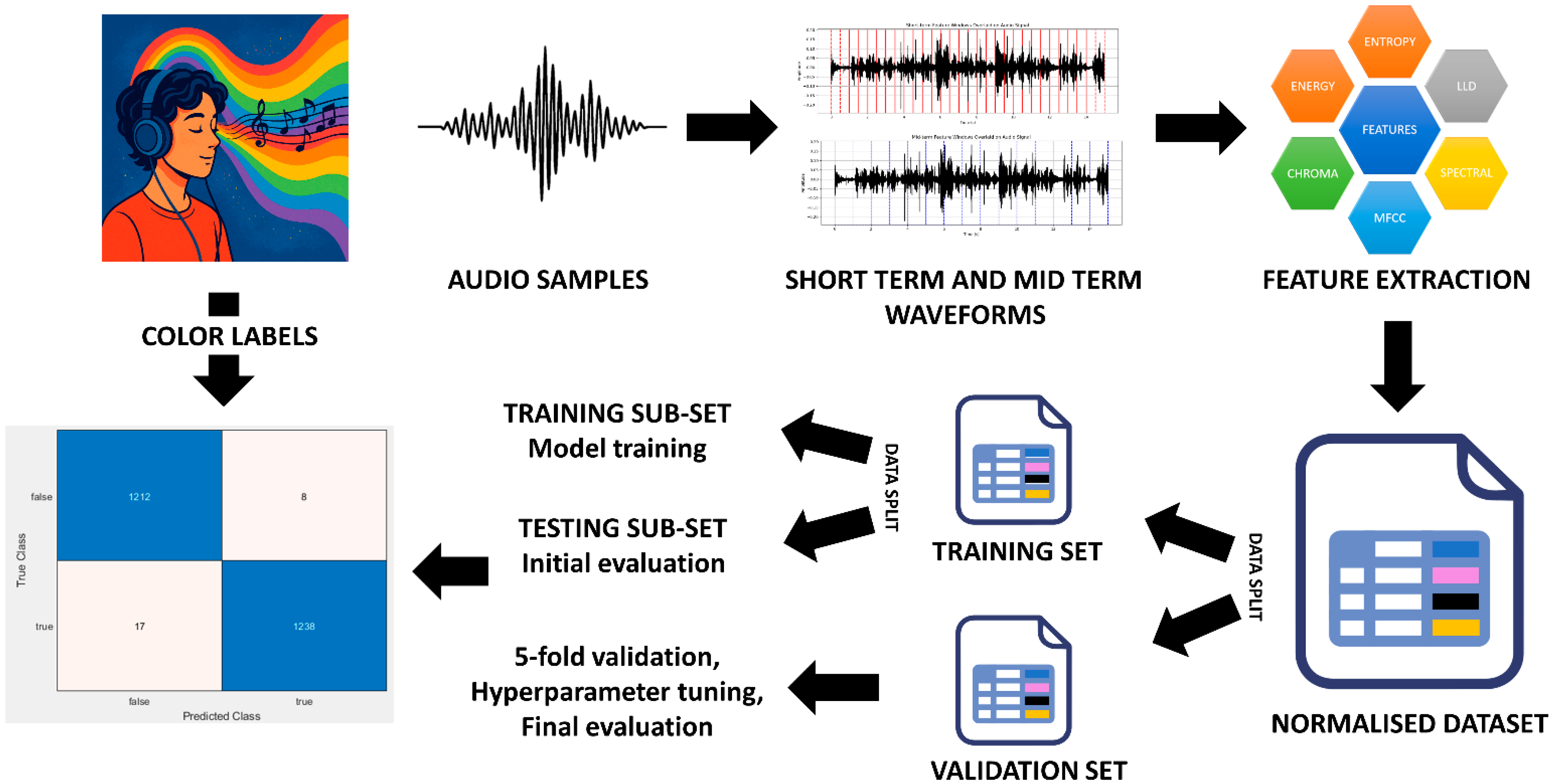
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
- Low-level audio descriptors (LLDs);
- Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs);
- Chroma features (Chroma).
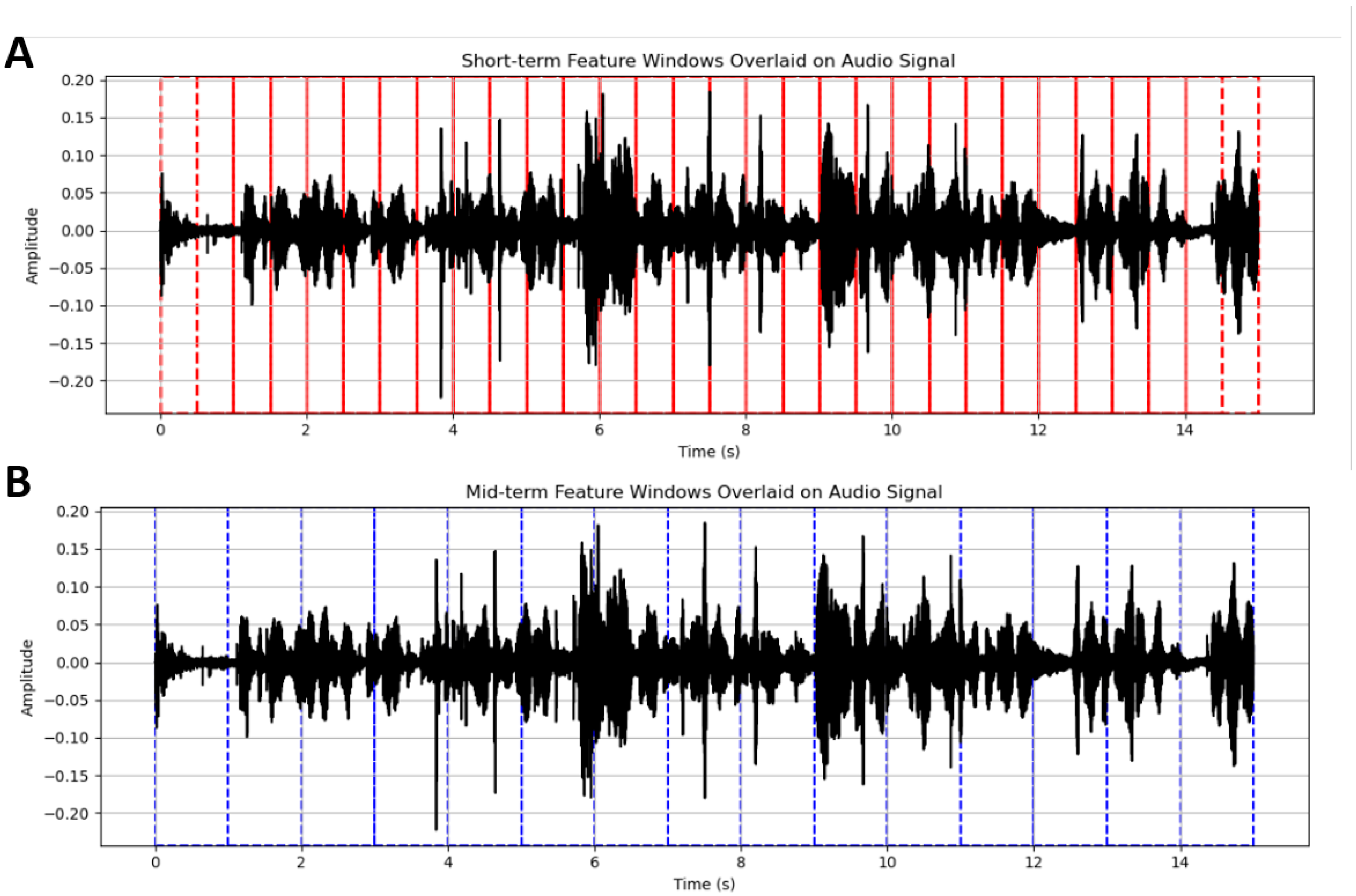
2.2. Audio Feature Extraction
2.3. Dataset Partitioning
2.4. Non-Binary Multi-Colour Classification
- Logistic Regression (LR);
- Support Vector Machine (SVM);
- Random Forest (RF);
- XGBoost (XGB) [57].
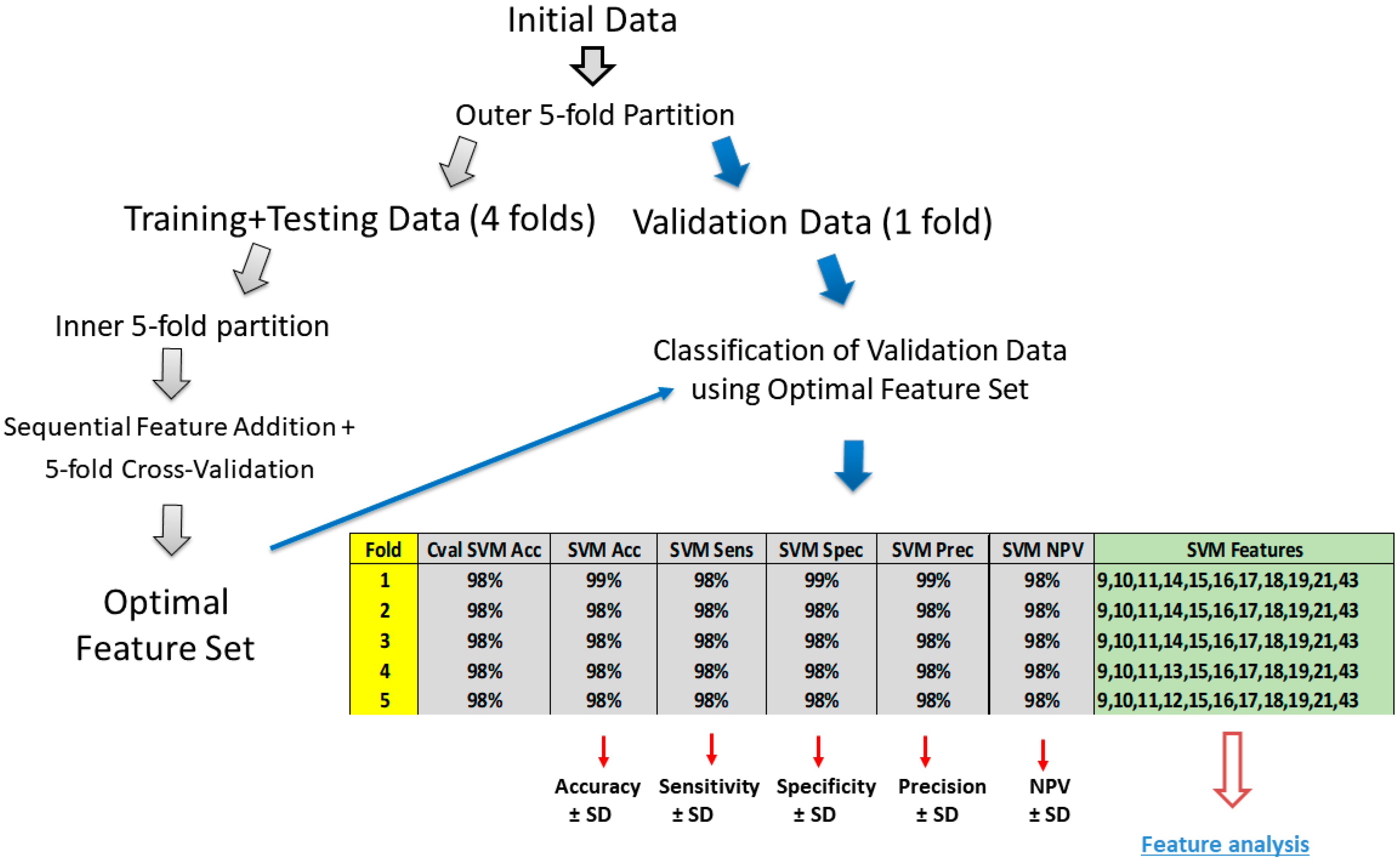
2.5. Binary Classification for Synaesthesia-Related Feature Determination
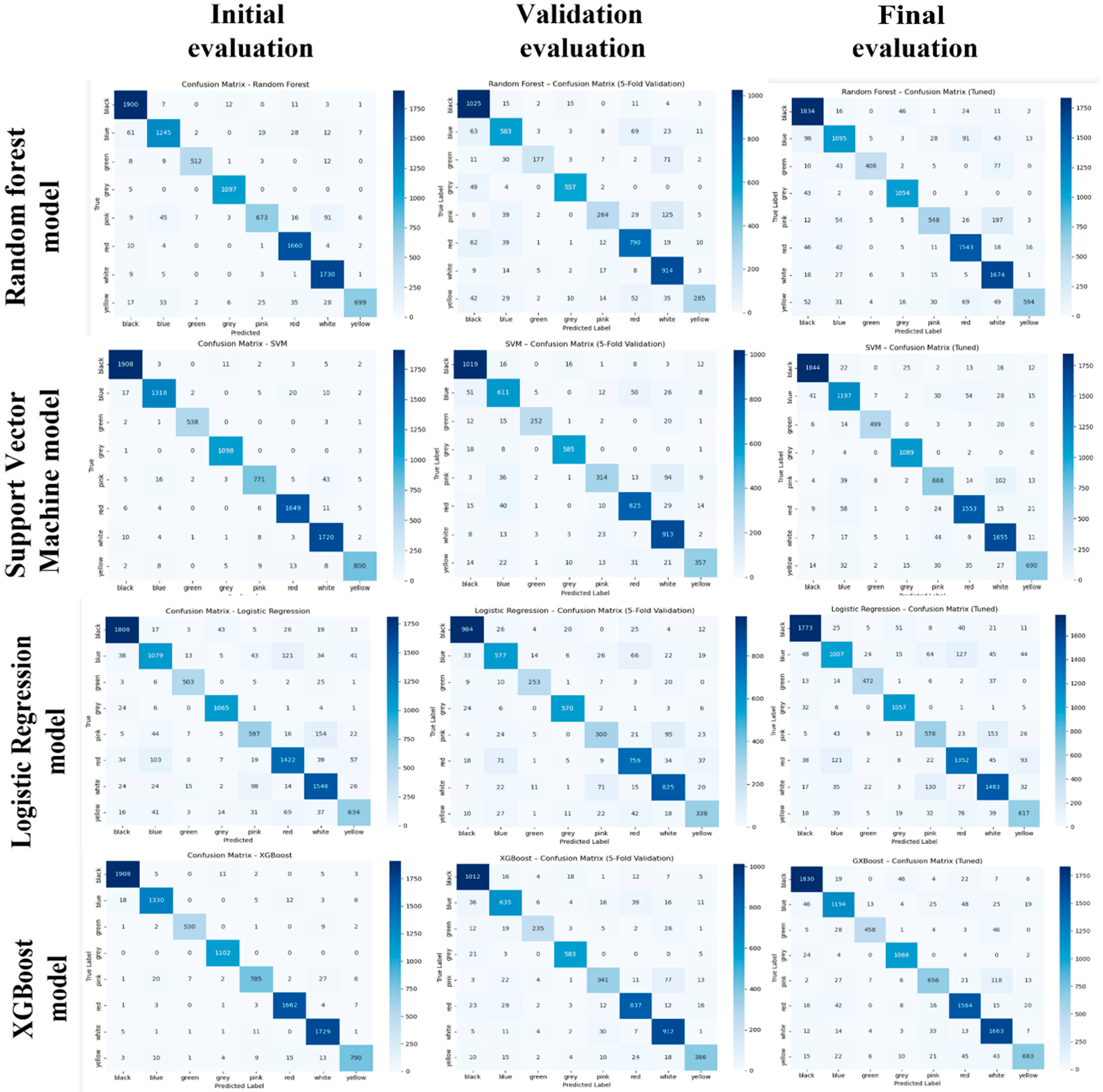
2.6. Evaluation of Classification Efficiency
3. Results (Part I): Non-Binary Multi-Colour Classification Using All Features
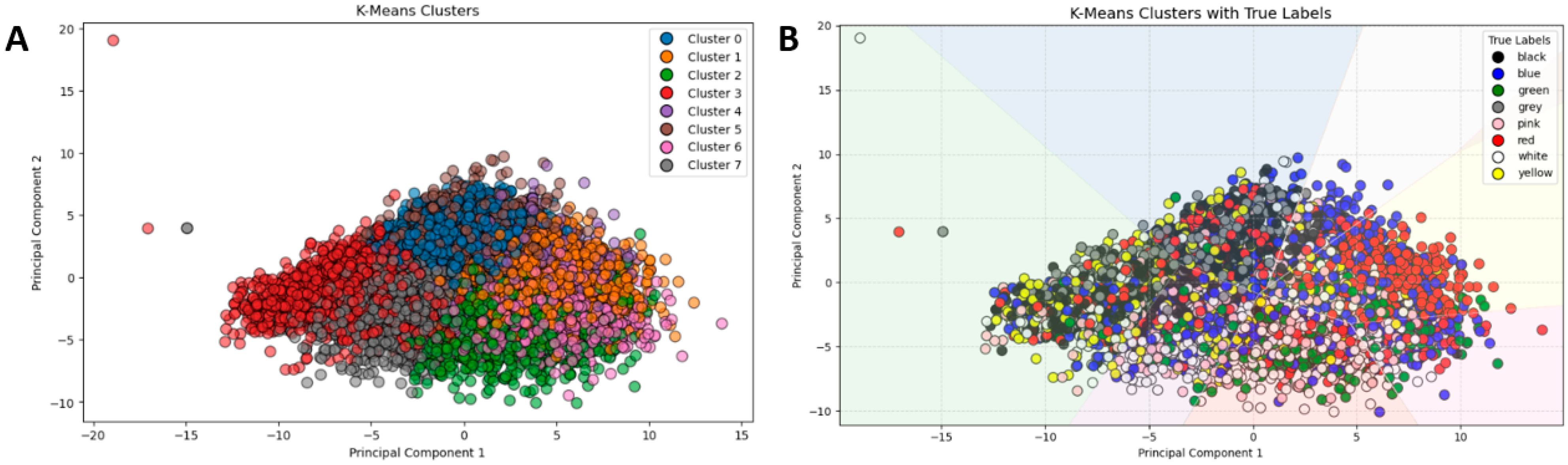
3.1. Clustering
3.2. Colour Classification
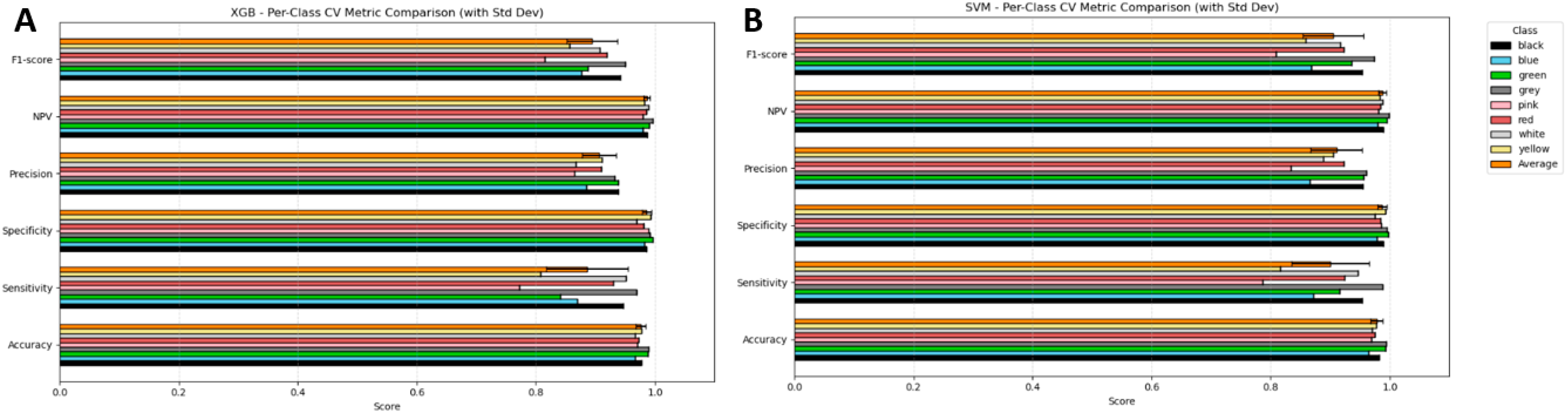
3.3. Multi-Colour Classification Metrics for XGBoost and SVM Classifiers
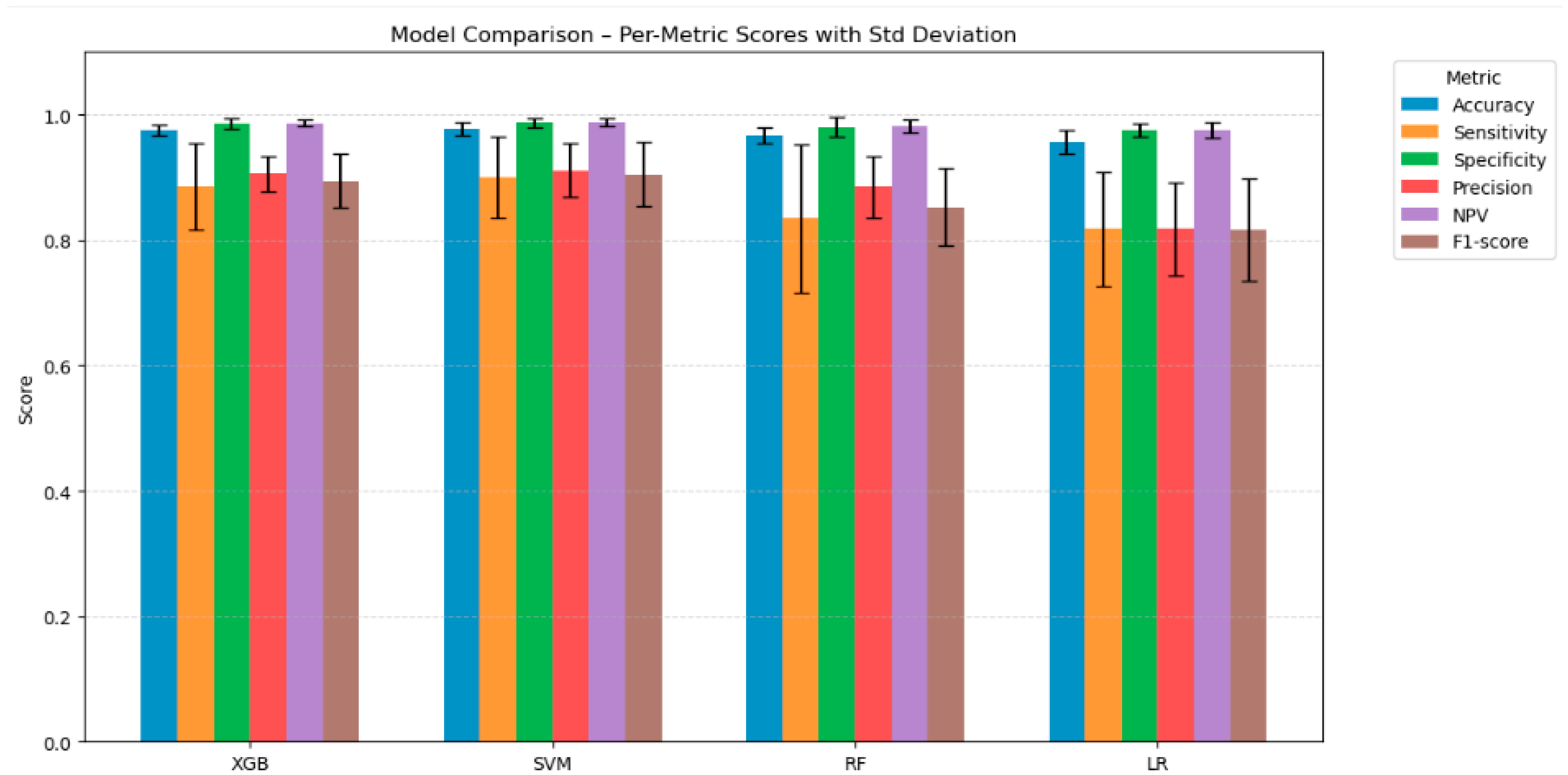
3.4. Average Classification Metrics for All Colours in Multi-Colour Classification
4. Results (Part II): Binary Two-Colour Classification for Feature Analysis
4.1. Classification Efficiency for SVM and RF for Grouped Features
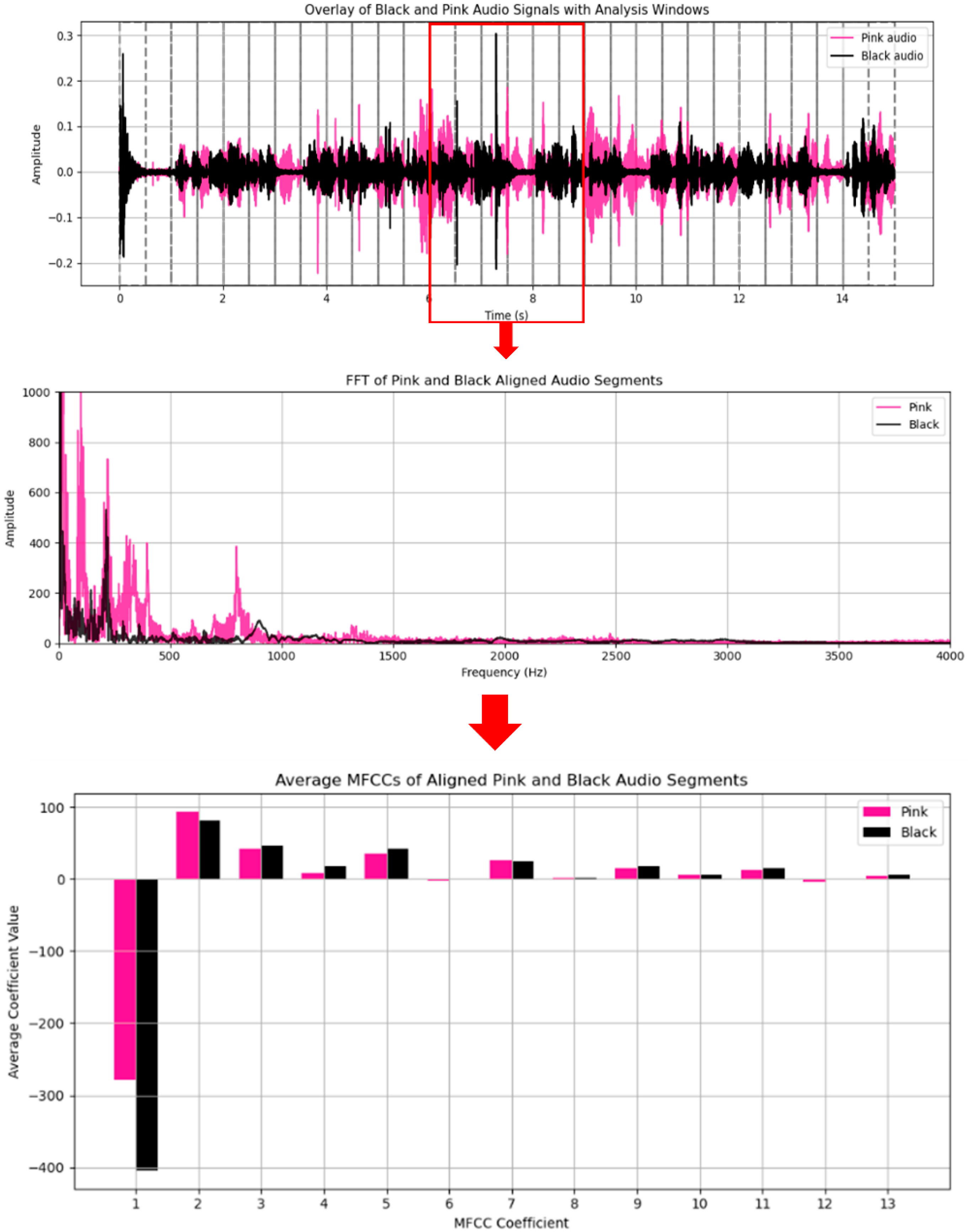
4.2. Feature Analysis
5. Discussion
Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| # | Short-Term or Mid-Term Features | LLD Data | MFCC Data | Chroma Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLD Average | 1 | zcr_mean | + | ||
| 2 | energy_mean | + | |||
| 3 | energy_entropy_mean | + | |||
| 4 | spectral_centroid_mean | + | |||
| 5 | spectral_spread_mean | + | |||
| 6 | spectral_entropy_mean | + | |||
| 7 | spectral_flux_mean | + | |||
| 8 | spectral_rolloff_mean | + | |||
| MFCC Average | 9 | mfcc_1_mean | + | ||
| 10 | mfcc_2_mean | + | |||
| 11 | mfcc_3_mean | + | |||
| 12 | mfcc_4_mean | + | |||
| 13 | mfcc_5_mean | + | |||
| 14 | mfcc_6_mean | + | |||
| 15 | mfcc_7_mean | + | |||
| 16 | mfcc_8_mean | + | |||
| 17 | mfcc_9_mean | + | |||
| 18 | mfcc_10_mean | + | |||
| 19 | mfcc_11_mean | + | |||
| 20 | mfcc_12_mean | + | |||
| 21 | mfcc_13_mean | + | |||
| Chroma Average | 22 | chroma_1_mean | + | ||
| 23 | chroma_2_mean | + | |||
| 24 | chroma_3_mean | + | |||
| 25 | chroma_4_mean | + | |||
| 26 | chroma_5_mean | + | |||
| 27 | chroma_6_mean | + | |||
| 28 | chroma_7_mean | + | |||
| 29 | chroma_8_mean | + | |||
| 30 | chroma_9_mean | + | |||
| 31 | chroma_10_mean | + | |||
| 32 | chroma_11_mean | + | |||
| 33 | chroma_12_mean | + | |||
| 34 | chroma_std_mean | + | |||
| LLD Std Dev | 35 | zcr_std | + | ||
| 36 | energy_std | + | |||
| 37 | energy_entropy_std | + | |||
| 38 | spectral_centroid_std | + | |||
| 39 | spectral_spread_std | + | |||
| 40 | spectral_entropy_std | + | |||
| 41 | spectral_flux_std | + | |||
| 42 | spectral_rolloff_std | + | |||
| MFCC Std Dev | 43 | mfcc_1_std | + | ||
| 44 | mfcc_2_std | + | |||
| 45 | mfcc_3_std | + | |||
| 46 | mfcc_4_std | + | |||
| 47 | mfcc_5_std | + | |||
| 48 | mfcc_6_std | + | |||
| 49 | mfcc_7_std | + | |||
| 50 | mfcc_8_std | + | |||
| 51 | mfcc_9_std | + | |||
| 52 | mfcc_10_std | + | |||
| 53 | mfcc_11_std | + | |||
| 54 | mfcc_12_std | + | |||
| 55 | mfcc_13_std | + | |||
| Chroma Std Dev | 56 | chroma_1_std | + | ||
| 57 | chroma_2_std | + | |||
| 58 | chroma_3_std | + | |||
| 59 | chroma_4_std | + | |||
| 60 | chroma_5_std | + | |||
| 61 | chroma_6_std | + | |||
| 62 | chroma_7_std | + | |||
| 63 | chroma_8_std | + | |||
| 64 | chroma_9_std | + | |||
| 65 | chroma_10_std | + | |||
| 66 | chroma_11_std | + | |||
| 67 | chroma_12_std | + | |||
| 68 | chroma_std_std | + |
References
- Safran, A.; Sanda, N. Color synesthesia. Insight into perception, emotion, and consciousness. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylopoulos, M.I.; Ro, T. Synesthesia: A colorful word with a touching sound? Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragança, G.F.F.; Fonseca, J.G.M.; Caramelli, P. Sinestesia e percepção musical. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2015, 9, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.; Simner, J. Lexical-gustatory synaesthesia: Linguistic and conceptual factors. Cognition 2003, 89, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brang, D.; Rouw, R.; Ramachandran, V.S.; Coulson, S. Similarly shaped letters evoke similar colors in grapheme–color synesthesia. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarick, M.; Jensen, C.; Dixon, M.J.; Smilek, D. The automaticity of vantage point shifts within a synaesthetes’ spatial calendar. J. Neuropsychol. 2011, 5, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anash, S.; Boileau, A. Grapheme-Color Synesthesia and Its Connection to Memory. Cureus 2024, 16, e67524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagleman, D.M.; Kagan, A.D.; Nelson, S.S.; Sagaram, D.; Sarma, A.K. A standardized test battery for the study of synesthesia. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 159, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothen, N.; Meier, B. Acquiring synaesthesia: Insights from training studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothen, N.; Meier, B.; Ward, J. Enhanced memory ability: Insights from synaesthesia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1952–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilot, A.K.; Kucera, K.S.; Vino, A.; Asher, J.E.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Fisher, S.E. Rare variants in axonogenesis genes connect three families with sound-color synesthesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3168–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Khalil, R.; Acosta, L.M.Y. A case report of acquired synesthesia and heightened creativity in a musician after traumatic brain injury. Neurocase 2023, 29, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogaard, B.; Vanni, S.; Silvanto, J. Seeing mathematics: Perceptual experience and brain activity in acquired synesthesia. Neurocase 2013, 19, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.H.; Shenker, J.I. Non-optic vision: Beyond synesthesia? Brain Cogn. 2016, 107, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, E.M.; Brang, D.; Ramachandran, V.S. The cross-activation theory at 10. J. Neuropsychol. 2011, 5, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, D.; Ghloum, J.K.; Gibson, L.C.; Watson, M.R.; Chen, L.M.; Akins, K.; Enns, J.T.; Hensch, T.K.; Werker, J.F. Reduced perceptual narrowing in synesthesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10089–10096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laeng, B.; Flaaten, C.B.; Walle, K.M.; Hochkeppler, A.; Specht, K. ‘Mickey Mousing’ in the Brain: Motion-Sound Synesthesia and the Subcortical Substrate of Audio-Visual Integration. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 605166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.H.; Kalckert, A.; Fink, G.R. Priming Letters by Colors: Evidence for the Bidirectionality of Grapheme–Color Synesthesia. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupé, J.M.; Dojat, M. A critical review of the neuroimaging literature on synesthesia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalwani, P.; Brang, D. Stochastic resonance model of synaesthesia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20190029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäncke, L.; Beeli, G.; Eulig, C.; Hänggi, J. The neuroanatomy of grapheme-color synesthesia. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.; Sinke, C.; Bleich, S.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Zedler, M. Investigation of the relationship between neuroplasticity and grapheme-color synesthesia. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1434309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Balsters, J.H.; Baechinger, M.; Van Der Groen, O.; Wenderoth, N.; Mantini, D. Estimating a neutral reference for electroencephalographic recordings: The importance of using a high-density montage and a realistic head model. J. Neural. Eng. 2015, 12, 56012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, J.M.; Prvulovic, D.; Linden, D.E.J.; Singer, W.; Stirn, A. Neuronal Correlates of Colour-Graphemic Synaesthesia: Afmri Study. Cortex 2006, 42, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C. Multisensory attention and tactile information-processing. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 135, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Calvert, G.A. Multisensory integration: Perceptual grouping by eye and ear. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, R322–R325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, J.P. Sensory Perception: Lessons from Synesthesia using Synesthesia to inform the understanding of Sensory Perception. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2013, 86, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, V.S.; Hubbard, E.M. Synaesthesia—A Window Into Perception, Thought and Language. J. Conscious. Stud. 2001, 8, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Grossenbacher, P.G.; Lovelace, C.T. Mechanisms of synesthesia: Cognitive and physiological constraints. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2001, 5, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, J.; Sinke, C.; Zedler, M.; Emrich, H.M.; Szycik, G.R. Reduced audio–visual integration in synaesthetes indicated by the double-flash illusion. Brain Res. 2012, 1473, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, E.M. Neurophysiology of synesthesia. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2007, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, D.P.; Lungu, L.; Friday, R.; Terhune, D.B. The chemical induction of synaesthesia. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 37, e2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wyke, M.A.; Binnie, C. Hearing words and seeing colours: An experimental investigation of a case of synaesthesia. Perception 1987, 16, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, J.E.; Aitken, M.R.F.; Farooqi, N.; Kurmani, S.; Baron-Cohen, S. Diagnosing and Phenotyping Visual Synaesthesia: A Preliminary Evaluation of the Revised Test of Genuineness (TOG-R). Cortex 2006, 42, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartulienė, R.; Saudargienė, A.; Reinytė, K.; Davidavičius, G.; Davidavičienė, R.; Ašmantas, Š.; Raškinis, G.; Šatkauskas, S. Voice-Evoked Color Prediction Using Deep Neural Networks in Sound–Color Synesthesia. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Eslinger, P.J. Colored hearing synesthesia: An investigation of neural factors. Neurology 1989, 39, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Sakata, H.; Kwee, I.L.; Nakada, T. Musical pitch classes have rainbow hues in pitch class-color synesthesia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goller, A.I.; Otten, L.J.; Ward, J. Seeing Sounds and Hearing Colors: An Event-Related Potential Study of Auditory-Visual Synesthesia. Available online: http://mitprc.silverchair.com/jocn/article-pdf/21/10/1869/1759787/jocn.2009.21134.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Takayanagi, K. Colored-hearing synesthesia. Jpn. Hosp. 2008, 27, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Adeli, H.; Zhou, Z.; Dadmehr, N. Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 123, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikin, A.; Johansson, N. Implicit associations between individual properties of color and sound. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2019, 81, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, G.; Marks, L.E. Synesthesia: Strong and weak. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 10, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asci, F.; Costantini, G.; Di Leo, P.; Zampogna, A.; Ruoppolo, G.; Berardelli, A.; Saggio, G.; Suppa, A. Machine-learning analysis of voice samples recorded through smartphones: The combined effect of ageing and gender. Sensors 2020, 20, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majkowski, A.; Kołodziej, M. Emotion Recognition from Speech in a Subject-Independent Approach. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbast, H. Voice Recognition Based on Machine Learning Classification Algorithms: A Review. Indones. J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 4414–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsurayyi, W.; Aleedy, M.; Alsmariy, R.; Almutairi, S. Gender Recognition by Voice Using Machine Learning. In International Conference on Advanced Network Technologies and Intelligent Computing; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume 6, pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, J.R. A deep learning model of perception in color-letter synesthesia. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Filiz, G. Synaesthesia is linked to a distinctive and heritable cognitive profile. Cortex 2020, 126, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindborg, P.; Friberg, A.K. Colour Association with Music Is Mediated by Emotion: Evidence from an Experiment Using a CIE Lab Interface and Interviews. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moos, A.; Simmons, D.; Simner, J.; Smith, R. Color and texture associations in voice-induced synesthesia. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, M.; Yokosawa, K. Synesthetic colors are elicited by sound quality in Japanese synesthetes. Conscious. Cogn. 2011, 20, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, E.; Ramachandran, V. Neurocognitive Mechanisms of Synesthesia. Neuron 2005, 48, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, T. pyAudioAnalysis: An Open-Source Python Library for Audio Signal Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszewicz, T.; Kania, D. Trajectory of Fifths Based on Chroma Subbands Extraction—A New Approach to Music Representation, Analysis, and Classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, Z.K.; Al-Talabani, A.K. Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient and its Applications: A Review. IEEE Access. 2022, 10, 122136–122158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. On Splitting Training and Validation Set: A Comparative Study of Cross-Validation, Bootstrap and Systematic Sampling for Estimating the Generalization Performance of Supervised Learning. J. Anal. Test. 2018, 2, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Graber, A.; McBurney, R.N.; Balasubramanian, R. Sample size and statistical power considerations in high-dimensionality data settings: A comparative study of classification algorithms. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgeldawi, E.; Sayed, A.; Galal, A.R.; Zaki, A.M. Hyperparameter Tuning for Machine Learning Algorithms Used for Arabic Sentiment Analysis. Informatics 2021, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wang, X.; Zhan, Y. Environmental Sound Classification Algorithm Based on Region Joint Signal Analysis Feature and Boosting Ensemble Learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggio, G.; Costantini, G. Worldwide Healthy Adult Voice Baseline Parameters: A Comprehensive Review. J. Voice 2022, 36, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.H.; Ferrer, M.; Travieso, C.; Godino llorente, J.; Díaz-de-María, F. Characterization of Healthy and Pathological Voice Through Measures Based on Nonlinear Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2009, 17, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godino-Llorente, J.I.; Gomez-Vilda, P.; Blanco-Velasco, M. Dimensionality Reduction of a Pathological Voice Quality Assessment System Based on Gaussian Mixture Models and Short-Term Cepstral Parameters. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.H.L.; Gavidia-Ceballos, L.; Kaiser, J.F. A nonlinear operator-based speech feature analysis method with application to vocal fold pathology assessment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 45, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskidere, Ö.; Gürhanli, A. Voice Disorder Classification Based on Multitaper Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients Features. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 956249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, A.H.; Bashi, O.I.D.; Ali, N.H.N.; Al Kubaisi, Y.M. Lung disease recognition methods using audio-based analysis with machine learning. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, M.; Okada, Y.; Uchiyama, R.; Horiguchi, R.; Toyoshima, I. A New Regression Model for Depression Severity Prediction Based on Correlation among Audio Features Using a Graph Convolutional Neural Network. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ramadass, P.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Selvam, K.P.; Shivahare, B.D.; Shah, M.A. Detection of Parkinson disease using multiclass machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwini, K.; Vincent, P.M.D.R.; Srinivasan, K.; Chang, C.Y. Deep Learning Assisted Neonatal Cry Classification via Support Vector Machine Models. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 670352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanushevskaya, I.; Gobl, C.; Chasaide, A.N. Voice quality in affect cueing: Does loudness matter? Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margo, C.E.; Harman, L.E. Helmholtz’s critique of Goethe’s Theory of Color: More than meets the eye. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2019, 64, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliot, A.J. Color and psychological functioning: A review of theoretical and empirical work. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, K. Some Experimental Observations Concerning the Influence of Colors on the Function of the Organism. Occup. Ther. 1942, 21, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, M. Color Appearance Models; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fetterman, A.; Liu, T.; Robinson, M. Extending Color Psychology to the Personality Realm: Interpersonal Hostility Varies by Red Preferences and Perceptual Biases. J. Pers. 2014, 83, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, A.; Imaizumi, S. Effects of color–emotion association on facial expression judgments. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonauskaite, D.; Abu-Akel, A.; Dael, N.; Oberfeld, D.; Abdel-Khalek, A.M.; Al-Rasheed, A.S.; Antonietti, J.P.; Bogushevskaya, V.; Chamseddine, A.; Chkonia, E.; et al. Universal Patterns in Color-Emotion Associations Are Further Shaped by Linguistic and Geographic Proximity. Psychol. Sci. 2020, 31, 1245–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonauskaite, D.; Mohr, C. Do we feel colours? A systematic review of 128 years of psychological research linking colours and emotions. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2025, 32, 1457–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithara, A.; Thomas, A.; Mathew, D. Study of MFCC and IHC feature extraction methods with probabilistic acoustic models for speaker biometric applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 143, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J. A Circumplex Model of Affect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Shao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Lu, X. Perceived Soundscape Experiences and Human Emotions in Urban Green Spaces: Application of Russell’s Circumplex Model of Affect. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
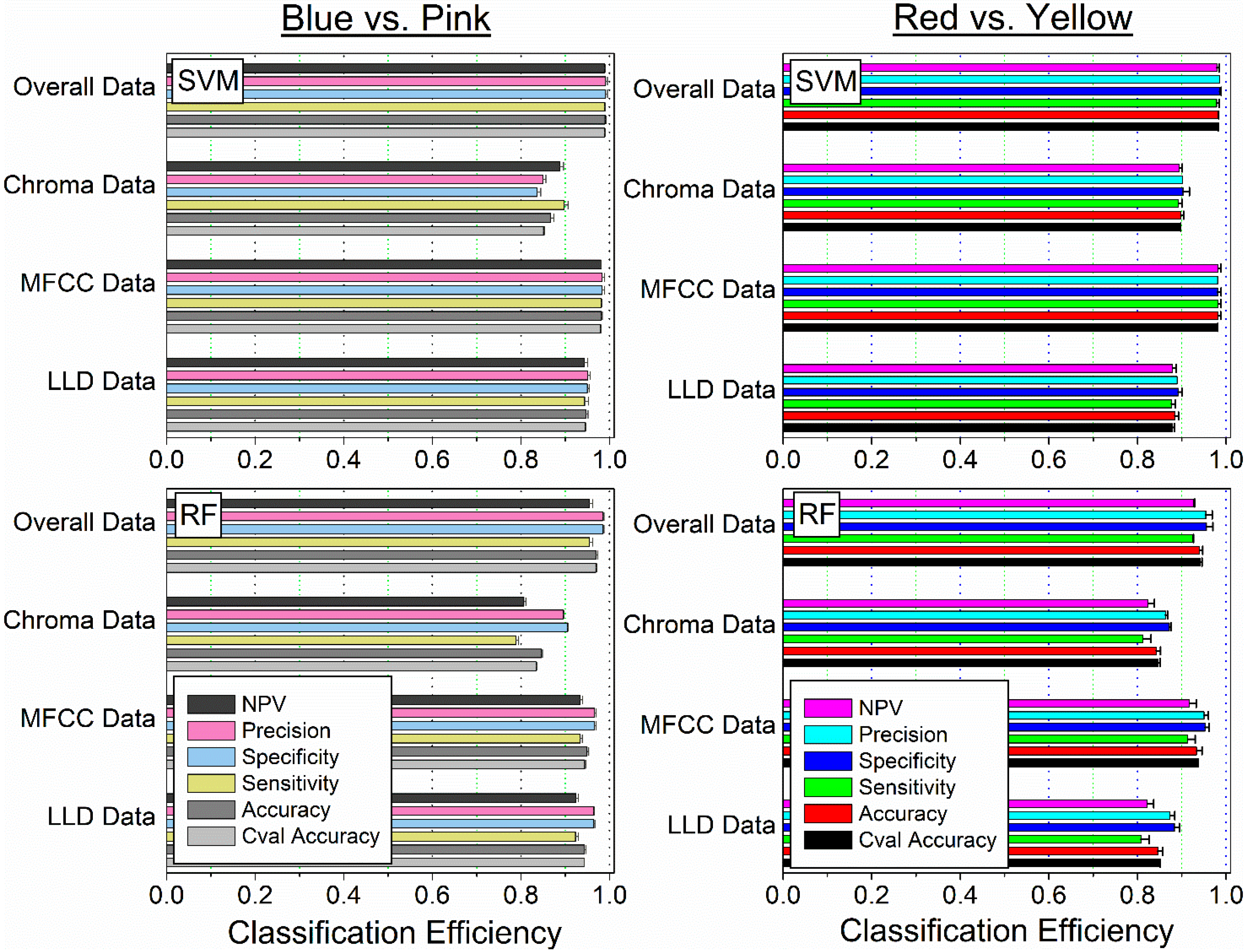

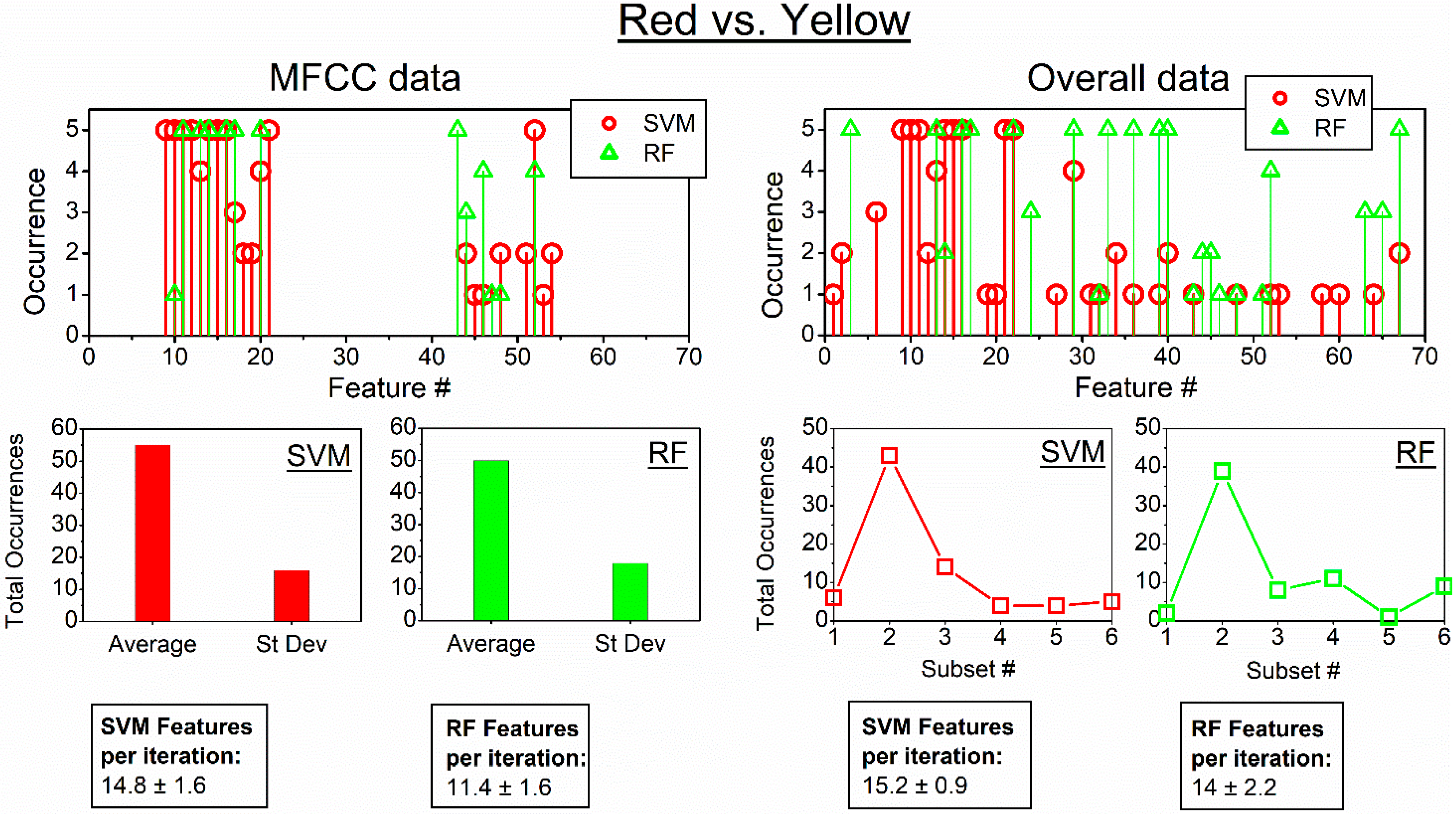
| Blue vs. Pink | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | |||||||
| Fold | C-val Accuracy | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | NPV | Optimal Features |
| 1 | 95% | 97% | 96% | 98% | 98% | 96% | 9, 11, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 43 |
| 2 | 95% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 9, 10, 11, 13, 15, 16, 18, 19, 21, 43 |
| RF | |||||||
| Fold | C-val Accuracy | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | NPV | Optimal Features |
| 1 | 92% | 93% | 91% | 95% | 95% | 91% | 9, 11, 13, 16, 17, 18, 19, 43 44, 45, 46, 52 |
| 2 | 92% | 93% | 92% | 95% | 95% | 92% | 9, 11, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 43, 48 |
| Red vs. Yellow | |||||||
| SVM | |||||||
| Fold | C-val Accuracy | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | NPV | Optimal Features |
| 1 | 96% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21, 46, 52, 54 |
| 2 | 96% | 97% | 96% | 98% | 98% | 96% | 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 45 |
| RF | |||||||
| Fold | C-val Accuracy | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | NPV | Optimal Features |
| 1 | 91% | 92% | 90% | 93% | 93% | 91% | 9, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 21, 46, 51, 52 |
| 2 | 91% | 91% | 89% | 93% | 92% | 89% | 9, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 19, 21, 43, 46, 52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartulienė, R.; Ragaišė, D.; Maciulevičius, M.; Raišutis, R.; Davidavičius, G.; Saudargienė, A.; Šatkauskas, S. Colour Classification Analysis Based on MFCC Acoustic Feature Sets and Machine Learning Algorithms in Sound–Colour Synaesthesia. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212059
Bartulienė R, Ragaišė D, Maciulevičius M, Raišutis R, Davidavičius G, Saudargienė A, Šatkauskas S. Colour Classification Analysis Based on MFCC Acoustic Feature Sets and Machine Learning Algorithms in Sound–Colour Synaesthesia. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212059
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartulienė, Raminta, Diana Ragaišė, Martynas Maciulevičius, Renaldas Raišutis, Gustavas Davidavičius, Aušra Saudargienė, and Saulius Šatkauskas. 2025. "Colour Classification Analysis Based on MFCC Acoustic Feature Sets and Machine Learning Algorithms in Sound–Colour Synaesthesia" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212059
APA StyleBartulienė, R., Ragaišė, D., Maciulevičius, M., Raišutis, R., Davidavičius, G., Saudargienė, A., & Šatkauskas, S. (2025). Colour Classification Analysis Based on MFCC Acoustic Feature Sets and Machine Learning Algorithms in Sound–Colour Synaesthesia. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212059







