Neural Modelling of CO2 Emissions from a Selected Vehicle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology
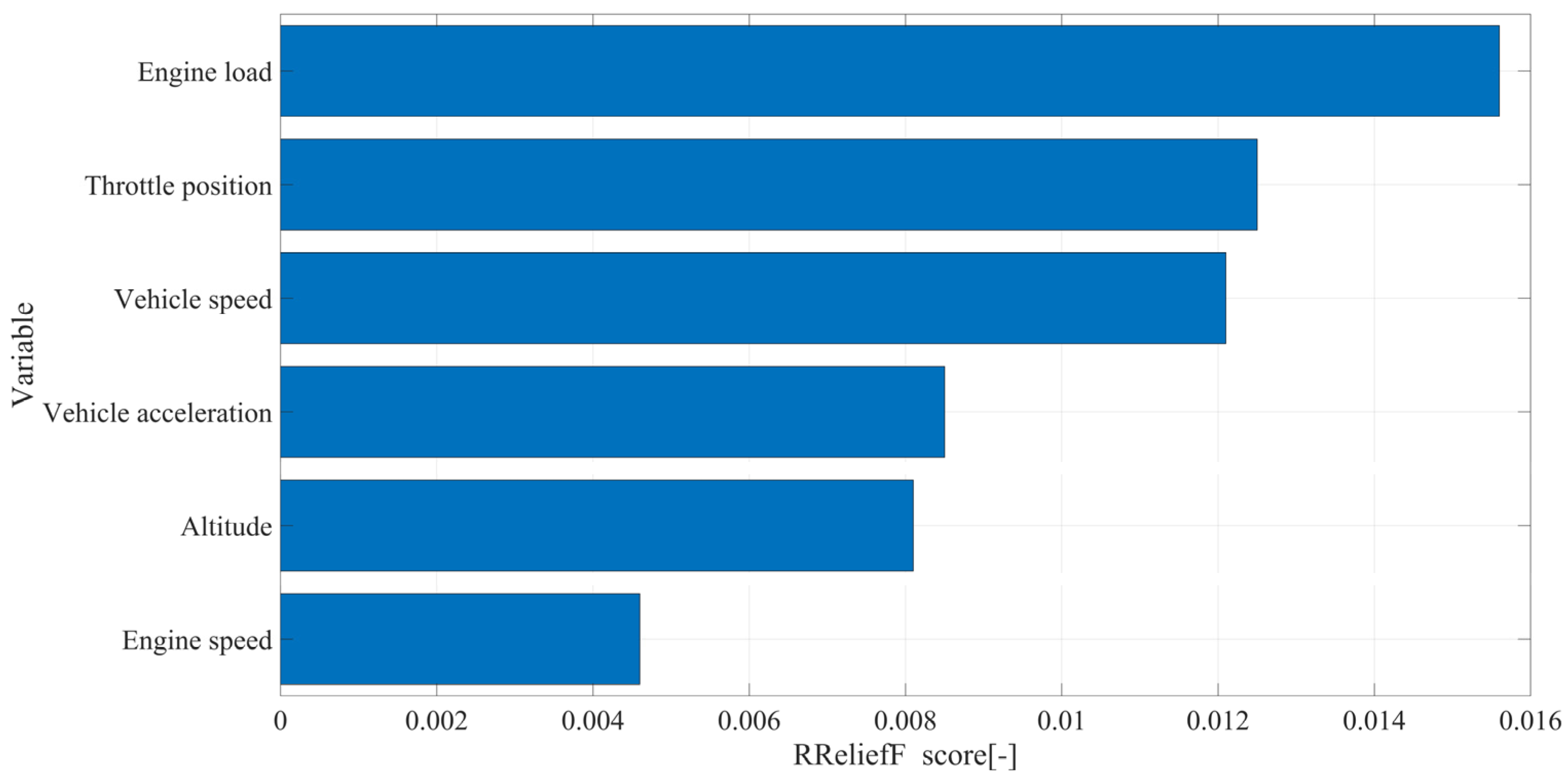
- engine speed,
- engine load,
- vehicle speed,
- vehicle acceleration,
- throttle position,
- altitude,
- CO2 emissions.
2.2. Modelling Methods
- x—input vector,
- W(i)—weight matrices of the i-th layer,
- b(i)—threshold value of the i-th layer,
- f(i)—activation function of the i-th layer,
- y—output vector [32].
- n—the number of observations,
- —the i-th observed (actual) value,
- —the average observed (actual) value.
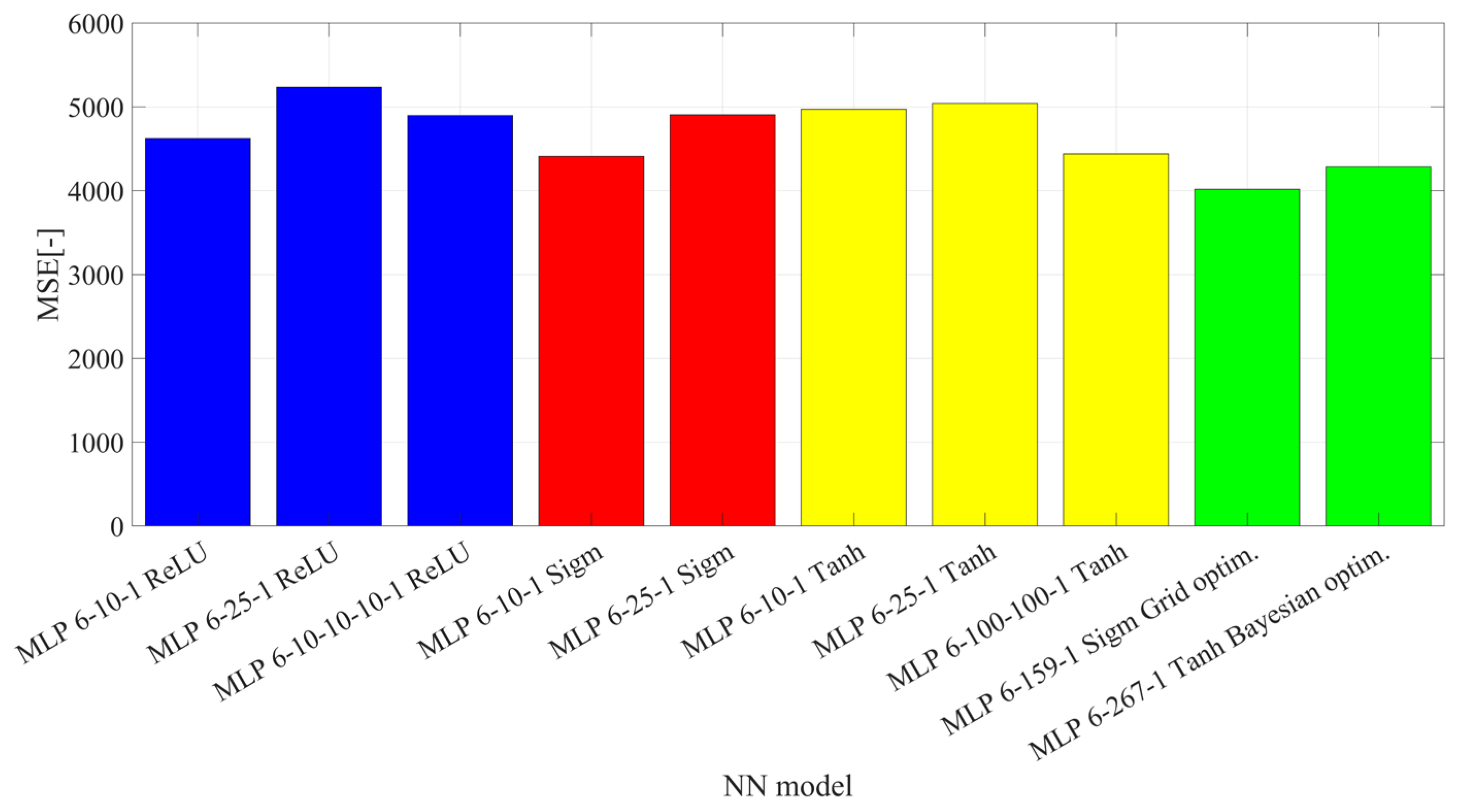
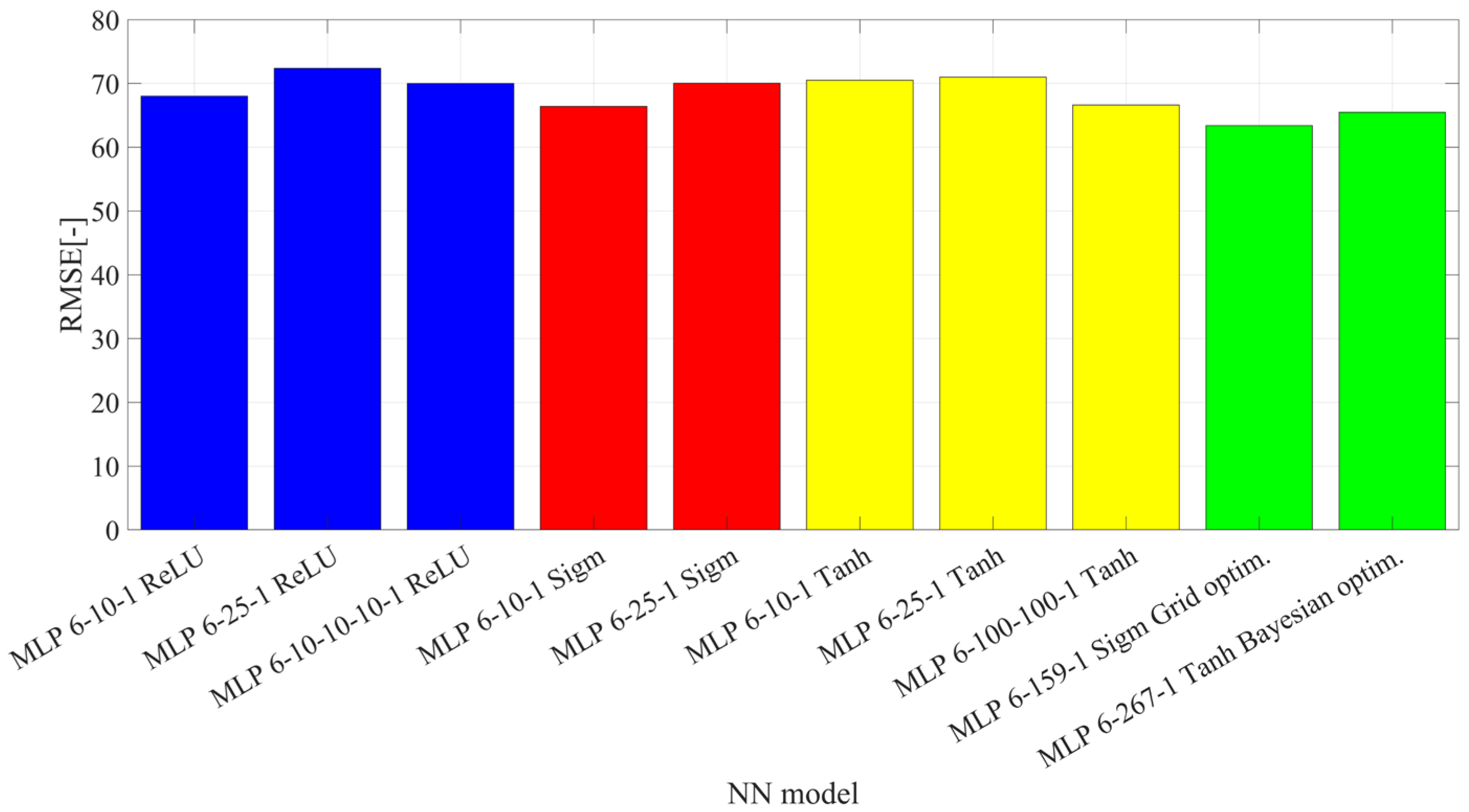
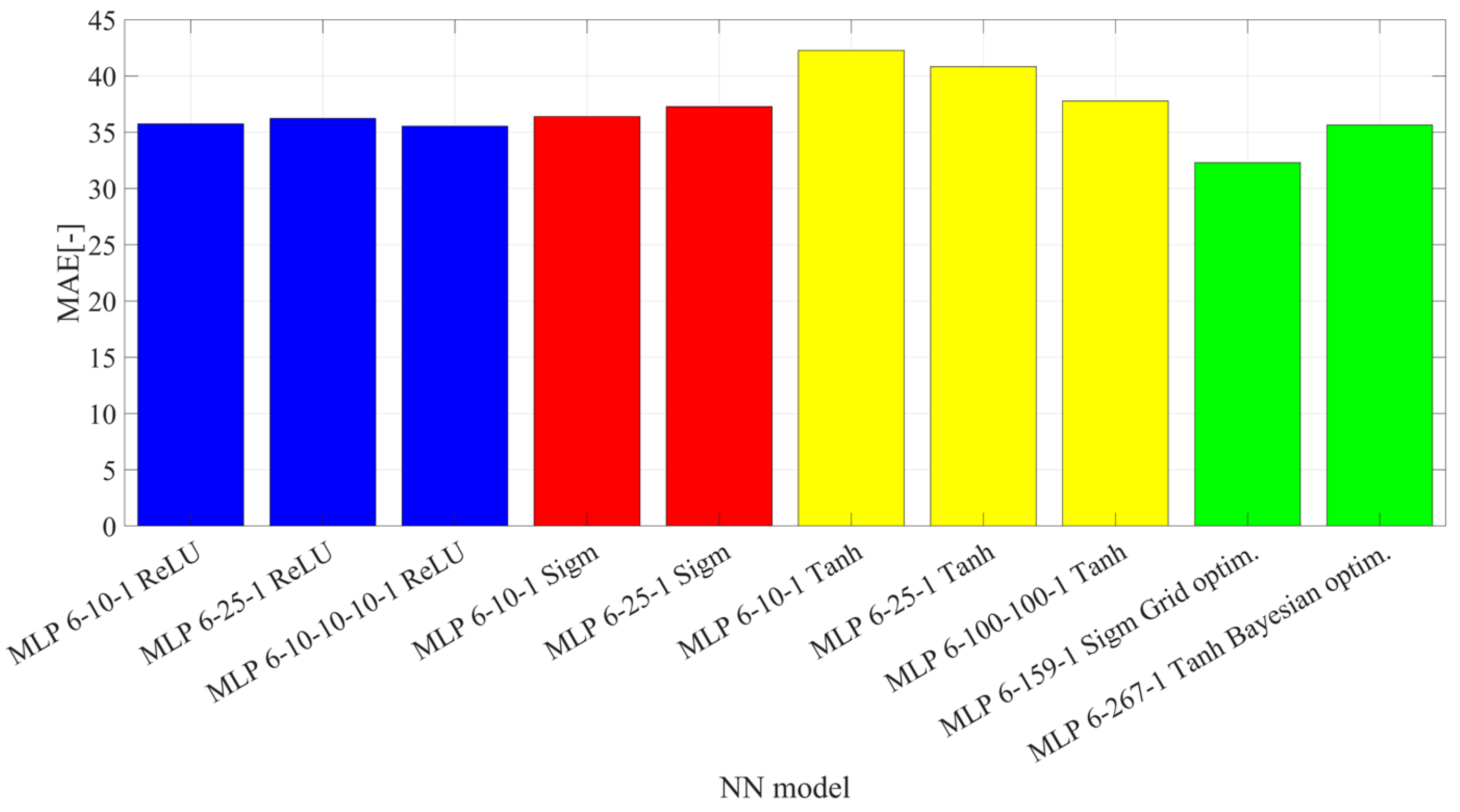
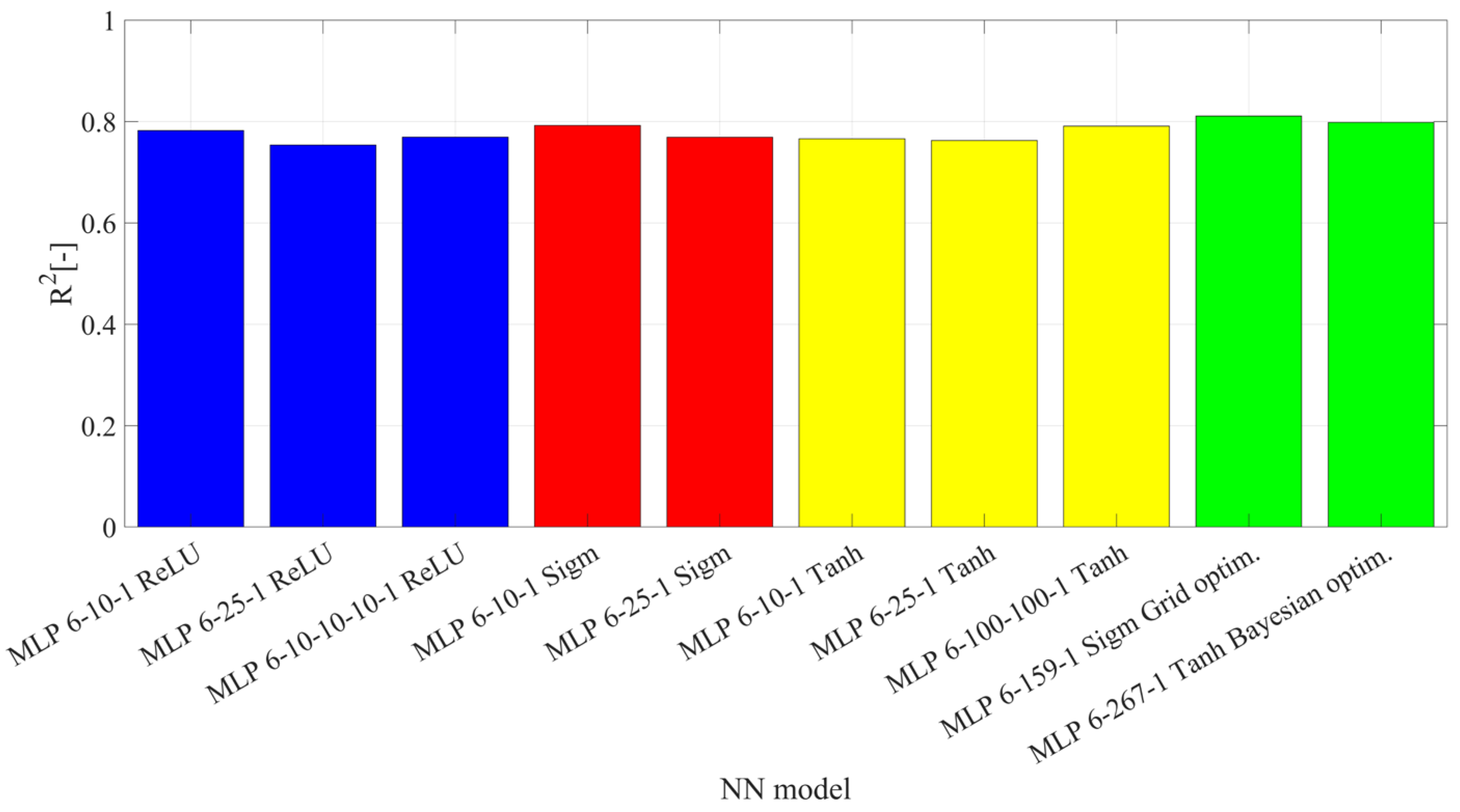
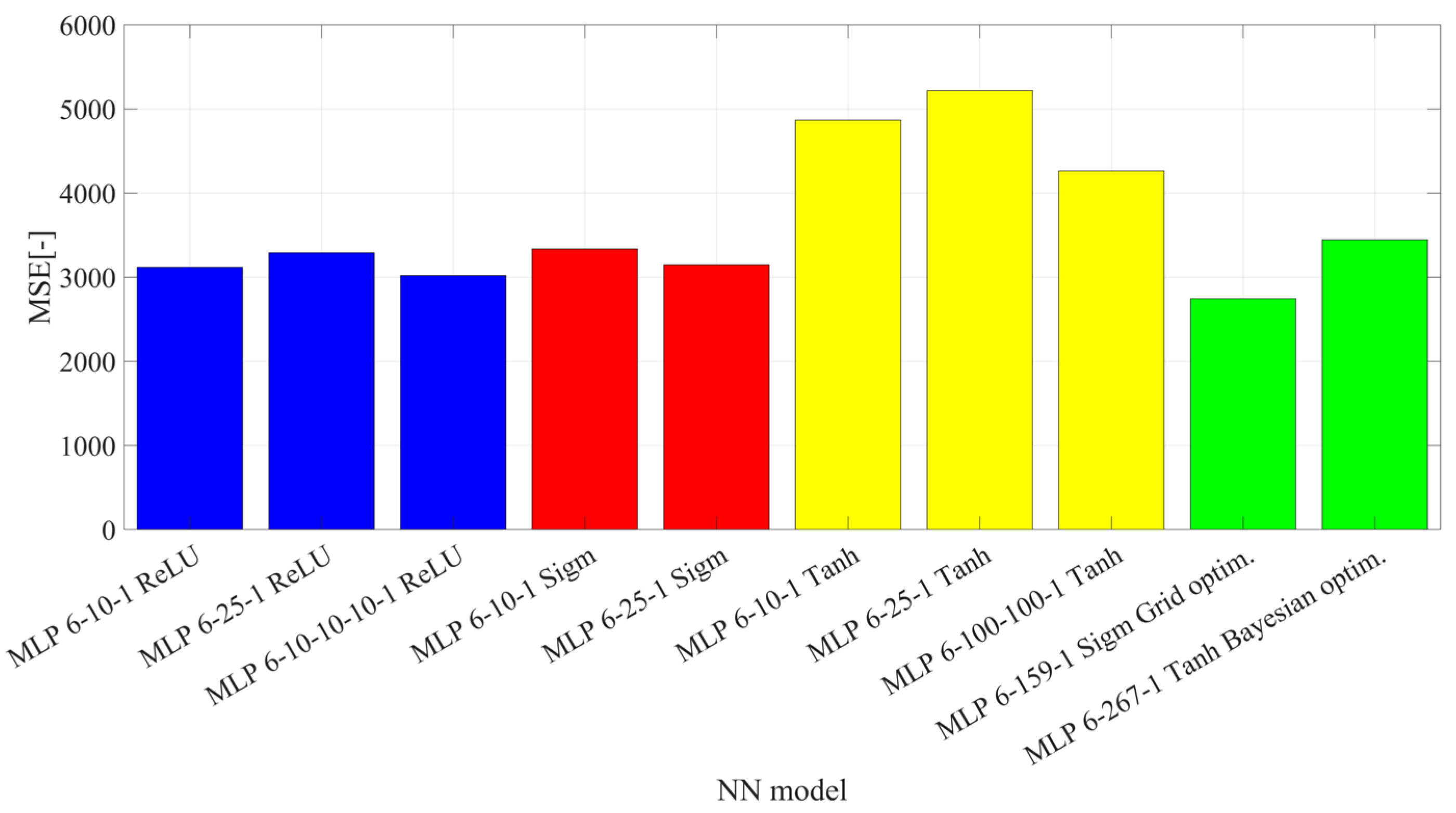
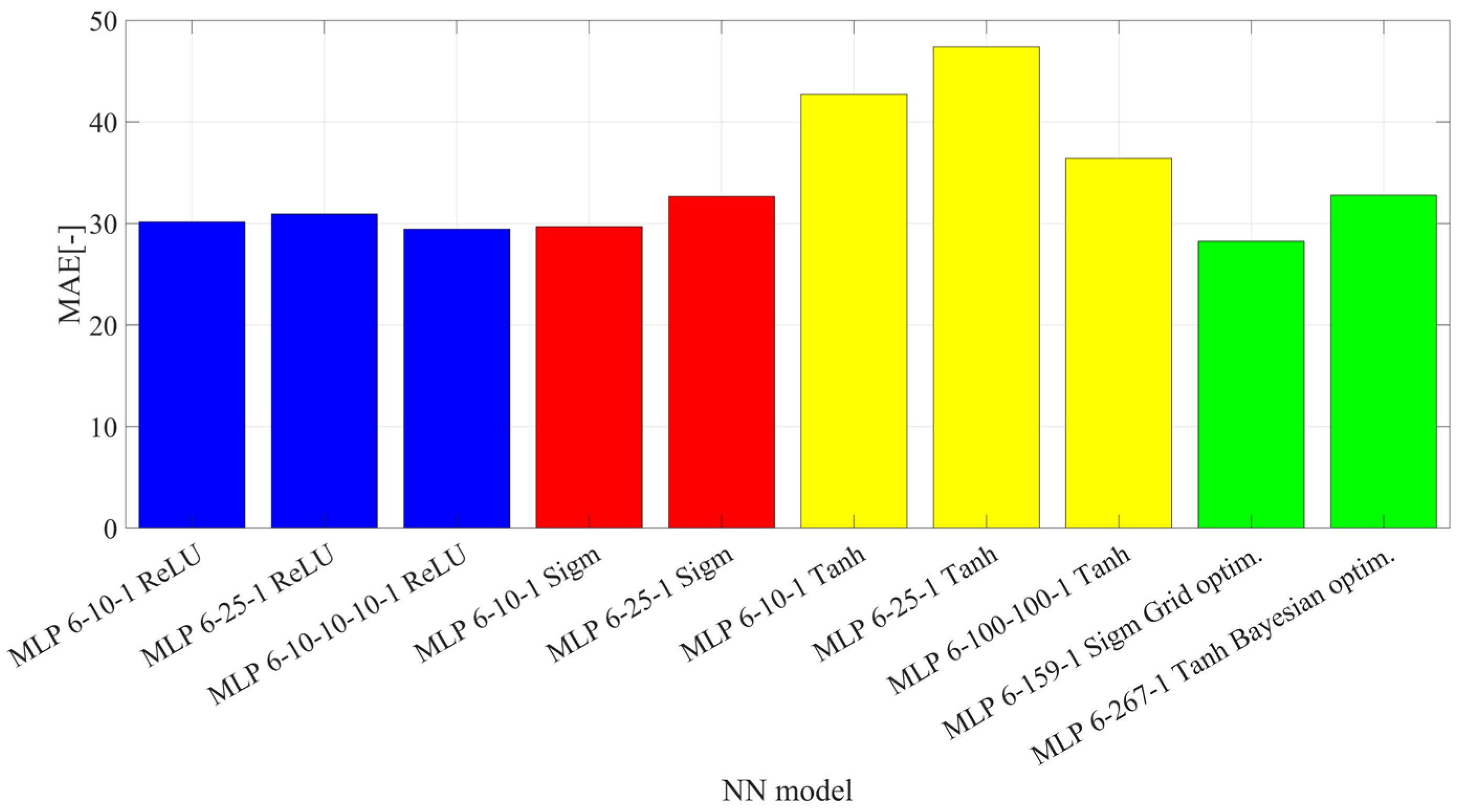
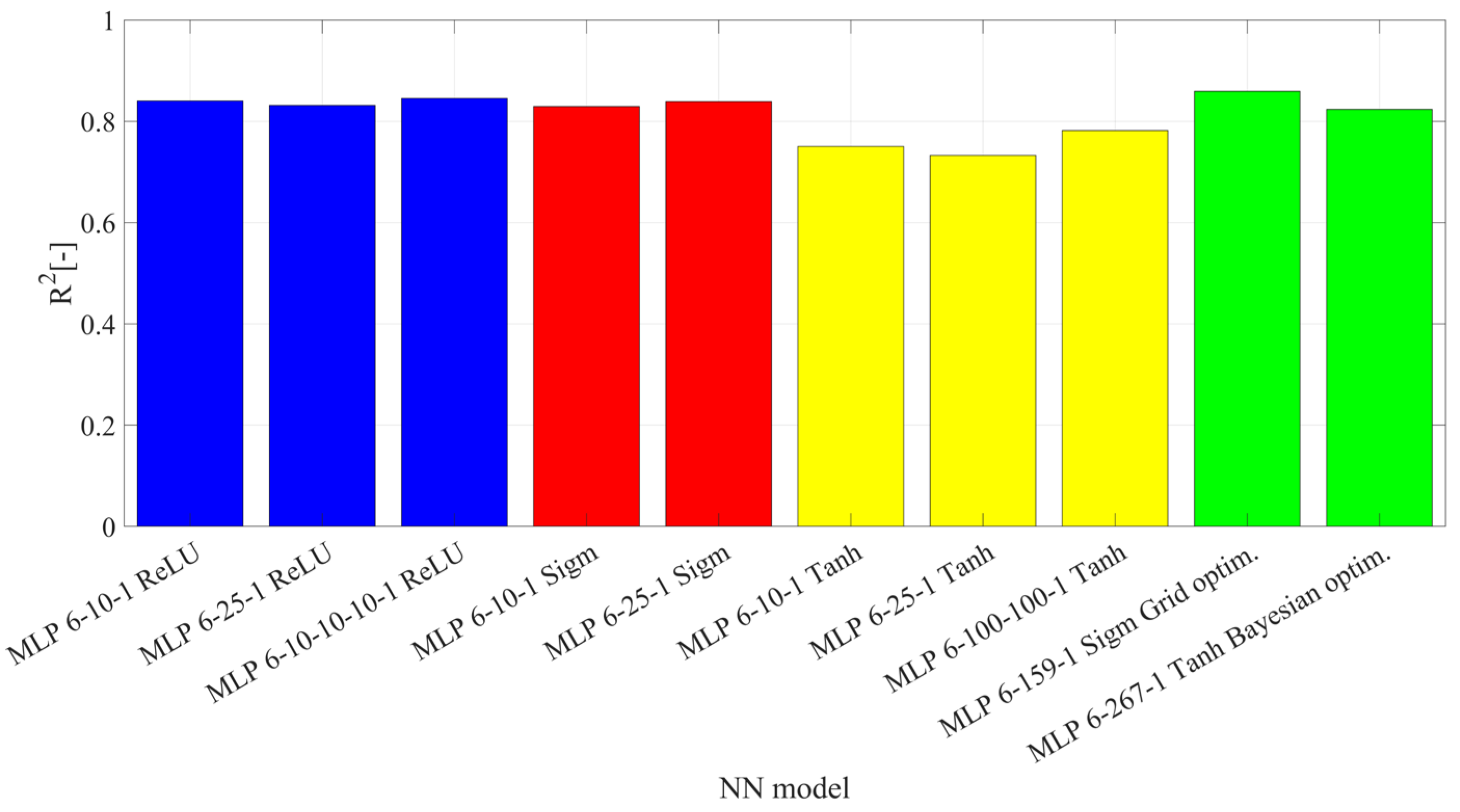
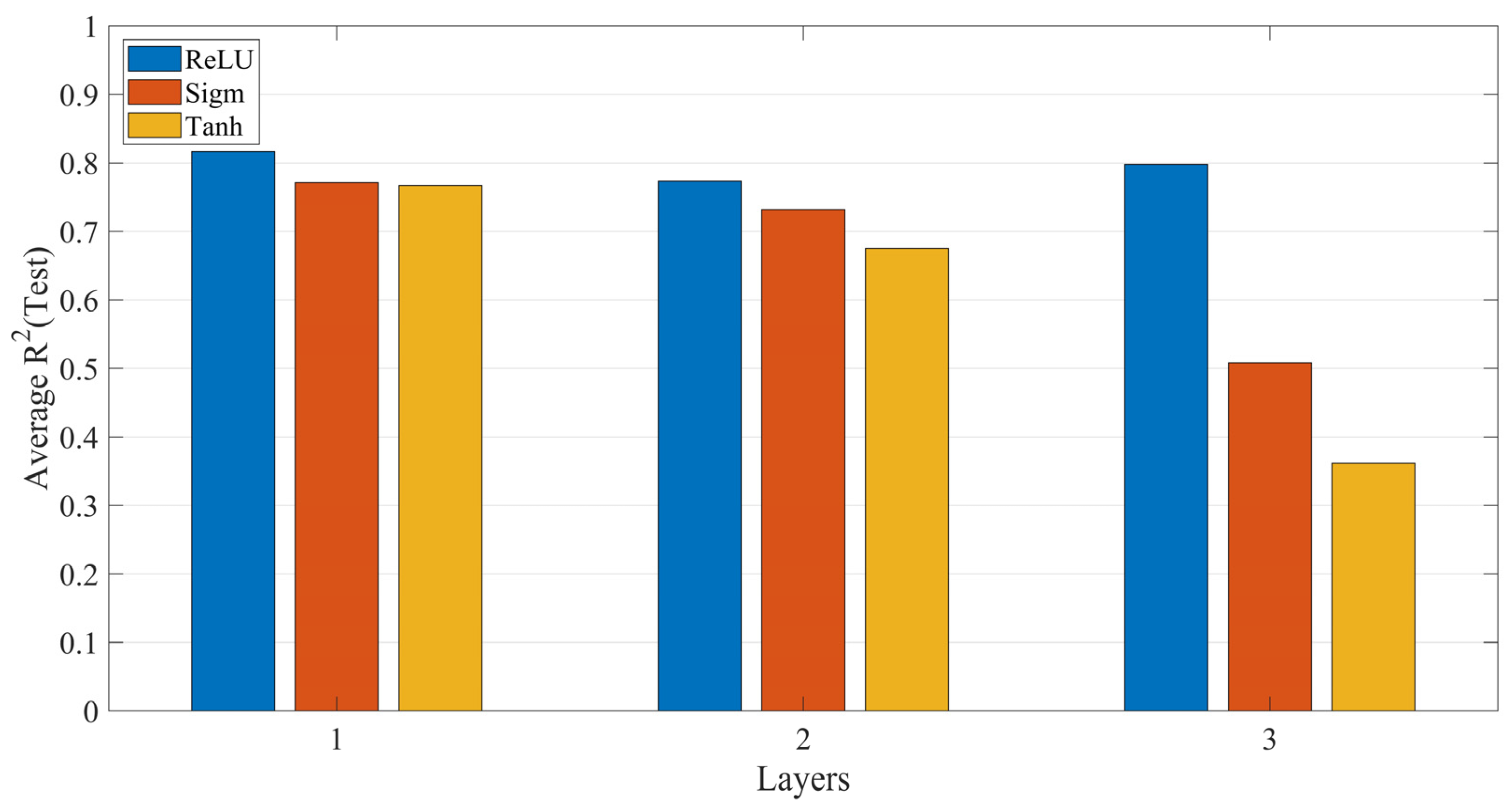
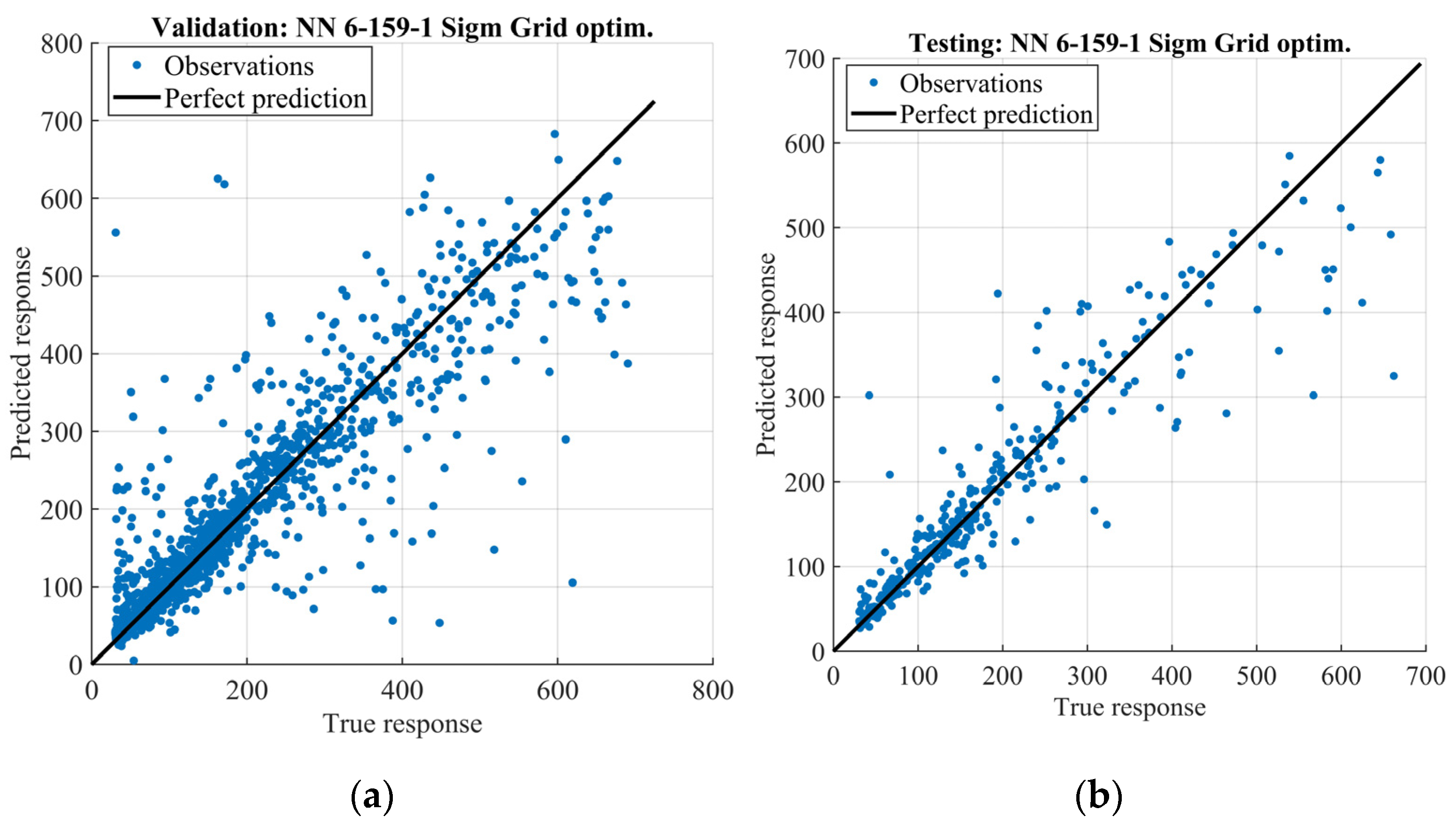
3. Results
- with 1, 2, or 3 hidden layers,
- with identical activation function in each layer: sigmoid, hyperbolic tangent, ReLU,
- with the same number of neurons in each layer: 10, 25, 100.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BFGS | Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| HDOP | Horizontal Dilution of Precision |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| LTSM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| MRMR | Minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| OBD | On-Board Diagnostics |
| PEMS | Portable Emissions Measurement System |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| RReliefF | Regressional ReliefF |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
Appendix A

Appendix B
References
- Kopfer, H.W.; Schönberger, J.; Kopfer, H. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions of a heterogeneous vehicle fleet. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2014, 26, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folęga, P.; Burchart, D.; Kubik, A.; Turoń, K. Application of the life cycle assessment method in public bus transport. Eksploat. Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2025, 27, 204539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, B.; Andrych-Zalewska, M.; Merkisz, J.; Chłopek, Z. The uniqueness of pollutant emission and fuel consumption test results for road vehicles tested on a chassis dynamometer. Eksploat. Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2025, 27, 195747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biszko, K.; Oskarbski, J. Modelowanie emisji z wykorzystaniem symulacji mikroskopowych. Transp. Miej. Reg. 2022, 5, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Rykała, M.; Grzelak, M.; Rykała, Ł.; Voicu, D.; Stoica, R.-M. Modeling Vehicle Fuel Consumption Using a Low-Cost OBD-II Interface. Energies 2023, 16, 7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijošius, J.; Žvirblis, T.; Rimkus, A.; Stravinskas, S.; Kilkevičius, A. Emissions, reliability and maintenance aspects of a dual-fuel engine (diesel-natural gas) using HVO additive and ANCOVA modeling. Eksploat. Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2026, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungan, M.S.; Arpa, O. Estimation of CO2 emissions from vehicles using machine learning and multi-model investigation. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2025, 73, e154287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M.; Kijek, M.; Gontarczyk, M.; Rykala, L.; Zelkowski, J. Fuzzy Modeling of Evaluation Logistic Systems. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference, Transport Means, Juodkrante, Lithuania, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Donateo, T.; Filomena, R. Real time estimation of emissions in a diesel vehicle with neural networks. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences, 75th National ATI Congress, Rome, Italy, 15–16 September 2020; Volume 197, p. 06020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Song, K.; Shi, J. Degradation generation and prediction based on machine learning methods: A comparative study. Eksploat. Niezawodn. Maint. Reliab. 2025, 27, 192168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Dubey, R.K. Deep learning model based CO2 emissions prediction using vehicle telematics sensors data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2021, 8, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, G.M.I.; Arfin Tanim, S.; Sarker, S.K.; Watanobe, Y.; Islam, R.; Mridha, M.F.; Nur, K. Deep learning model based prediction of vehicle CO2 emissions with eXplainable AI integration for sustainable environment. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, H.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Northrop, W.F.; Shekhar, S. Vehicle emissions prediction with physics-aware ai models: Preliminary results. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.00375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, E.T.; Panagiotopoulou, A.; Papadakis, A. A Review of OBD-II-Based Machine Learning Applications for Sustainable, Efficient, Secure, and Safe Vehicle Driving. Sensors 2025, 25, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.N.; Tolba, A.; Abouhawwash, M. Application of Deep Learning Initiatives for CO2 Emissions Forecasting. Clim. Change Rep. 2024, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tong, Z.; Haroon, M. Estimation of transport CO2 emissions using machine learning algorithm. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 133, 104276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurcan, F. Forecasting CO2 emissions of fuel vehicles for an ecological world using ensemble learning, machine learning, and deep learning models. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, G.; Oliver-Hoyo, M.T. Using the relationship between vehicle fuel consumption and CO2 emissions to illustrate chemical principles. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaras, G.; Zacharof, N.G.; Ciuffo, B. Fuel consumption and CO2 emissions from passenger cars in Europe–Laboratory versus real-world emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 60, 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, B.; Szczotka, A.; Woodburn, J.; Merkisz, J. Comparison of exhaust emission results obtained from Portable Emissions Measurement System (PEMS) and a laboratory system. Combust. Engines 2023, 62, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkisz, J.; Rymaniak, Ł. Determining the environmental indicators for vehicles of different categories in relation to CO2 emission based on road tests. Combust. Engines 2017, 56, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkisz, J.; Dobrzynski, M.; Kubiak, K. An impact assessment of functional systems in vehicles on CO2 emissions and fuel consumption. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 118, 00030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasocki, J.; Chłopek, Z.; Godlewski, T. Driving style analysis based on information from the vehicle’s OBD system. Combust. Engines 2019, 58, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, A.; Komorska, I. Driving style analysis and driver classification using OBD data of a hybrid electric vehicle. Transp. Probl. 2020, 15, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, E. Independent driving pattern factors and their influence on fuel-use and exhaust emission factors. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2001, 6, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykała, Ł.; Rubiec, A.; Przybysz, M.; Krogul, P.; Cieślik, K.; Muszyński, T.; Rykała, M. Research on the Positioning Performance of GNSS with a Low-Cost Choke Ring Antenna. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malon, K.; Łopatka, J.; Rykała, Ł.; Łopatka, M. Accuracy Analysis of UWB Based Tracking System for Unmanned Ground Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 New Trends in Signal Processing (NTSP), Demänovská Dolina, Slovakia, 10–12 October 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cellina, M.; Strada, S.; Savaresi, S.M. Vehicle fuel consumption virtual sensing from GNSS and IMU measurements. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Bilbao, Spain, 24–28 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Andrych-Zalewska, M.; Chłopek, Z.; Merkisz, J.; Pielecha, J. Research on the results of the WLTP procedure for a passenger vehicle. Maint. Reliab. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2024, 26, 176112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feature Selection. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/stats/feature-selection.html (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Yuan, L.; Lu, W.; Xue, F.; Li, M. Building feature-based machine learning regression to quantify urban material stocks: A Hong Kong study. J. Ind. Ecol. 2023, 27, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neural Networks: Activation functions. Available online: https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/neural-networks/activation-functions?hl=pl (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Osowski, S.; Cichocki, A.; Siwek, K. MATLAB w Zastosowaniu do Obliczeń Obwodowych i Przetwarzania Sygnałów; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Warszawskiej: Warsaw, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rykała, M.; Rykała, Ł. Economic Analysis of a Transport Company in the Aspect of Car Vehicle Operation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osowski, S. Metody i narzędzia eksploracji danych; BTC: Warsaw, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rykała, M. A Study of the CO2 Emissions of a Passenger Vehicle on a Selected Example Using Mathematical Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, Military University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Lu, Y. Accuracy evaluation of multi-GNSS Doppler velocity estimation using android smartphones. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 46, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, M. Experimental studies on the relationship between HDOP and position error in the GPS system. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2022, 29, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.X.; Enge, P. How many GNSS satellites are too many? IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, H.; Givigi, S.; Noureldin, A. Automotive speed estimation: Sensor types and error characteristics from obd-ii to adas. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 28 April–1 May 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 124–130. [Google Scholar]
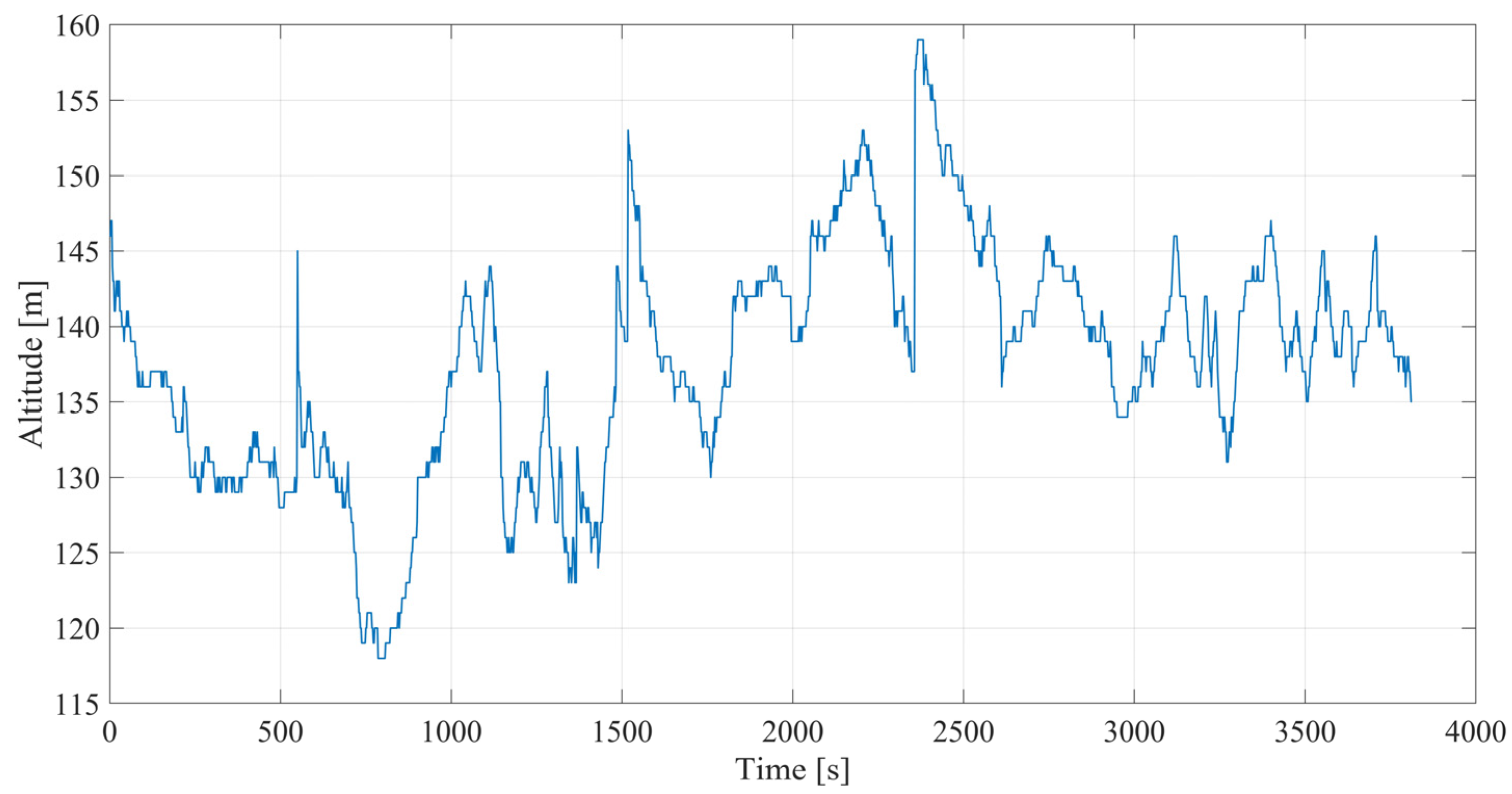
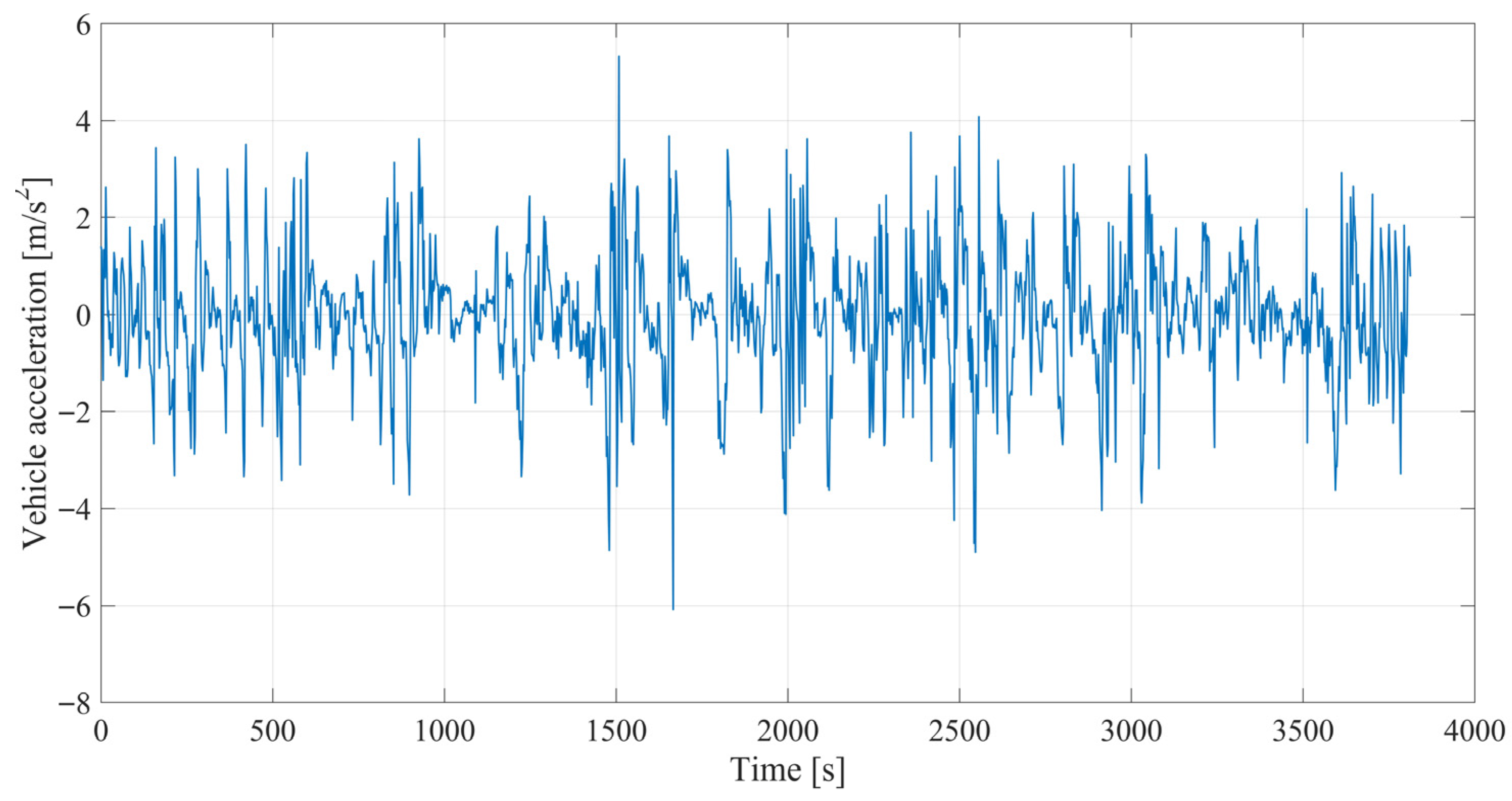
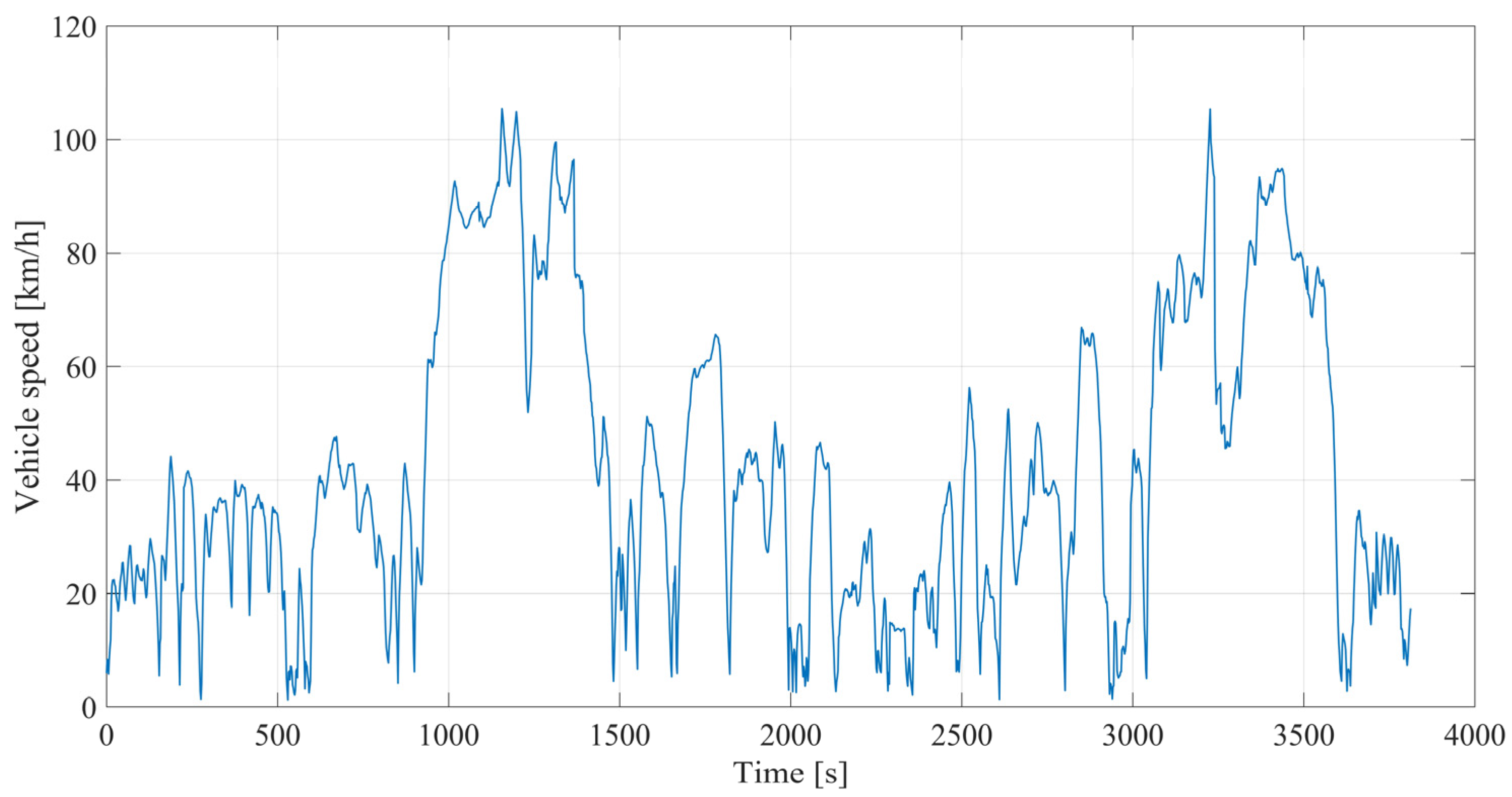
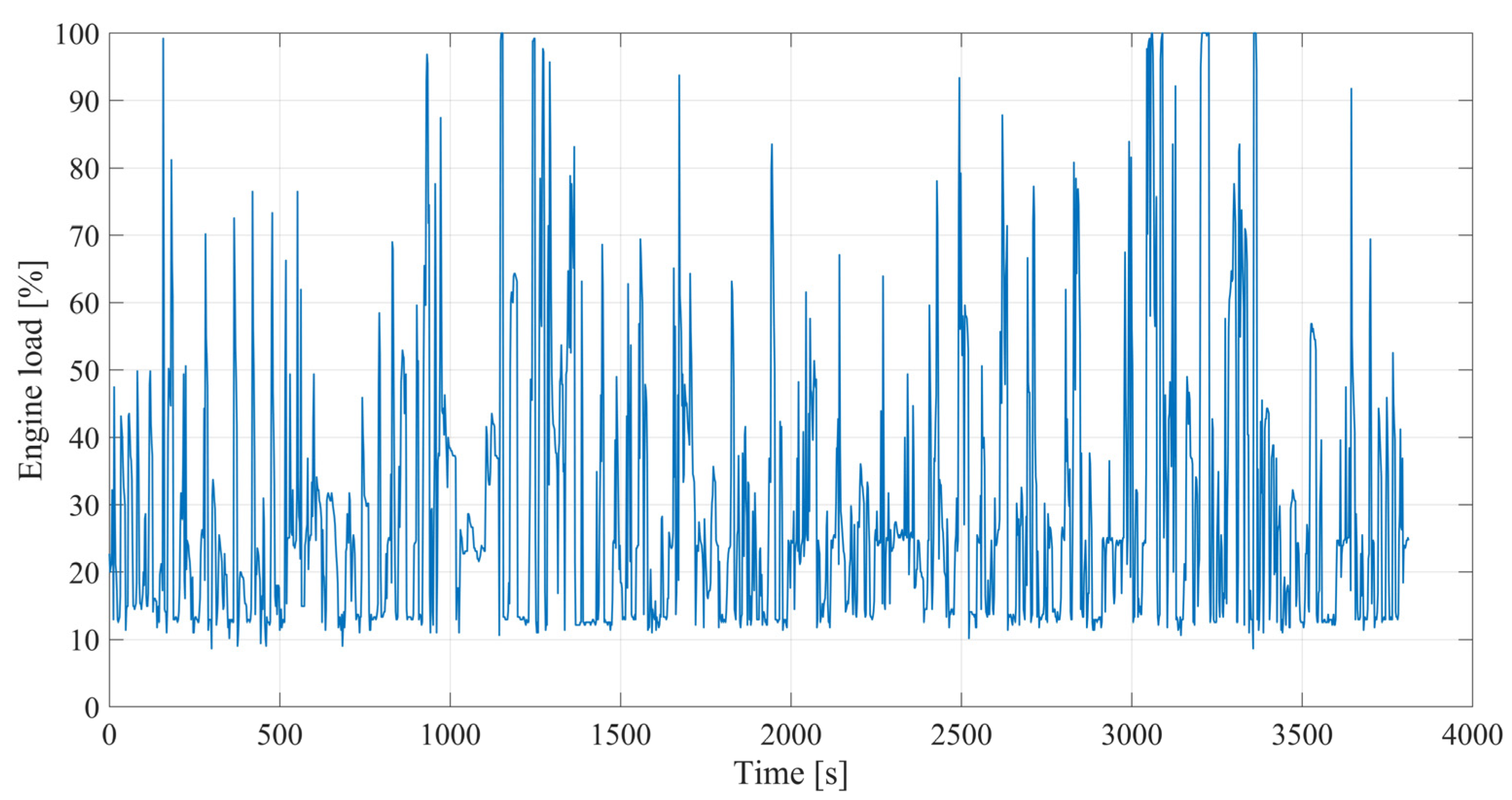
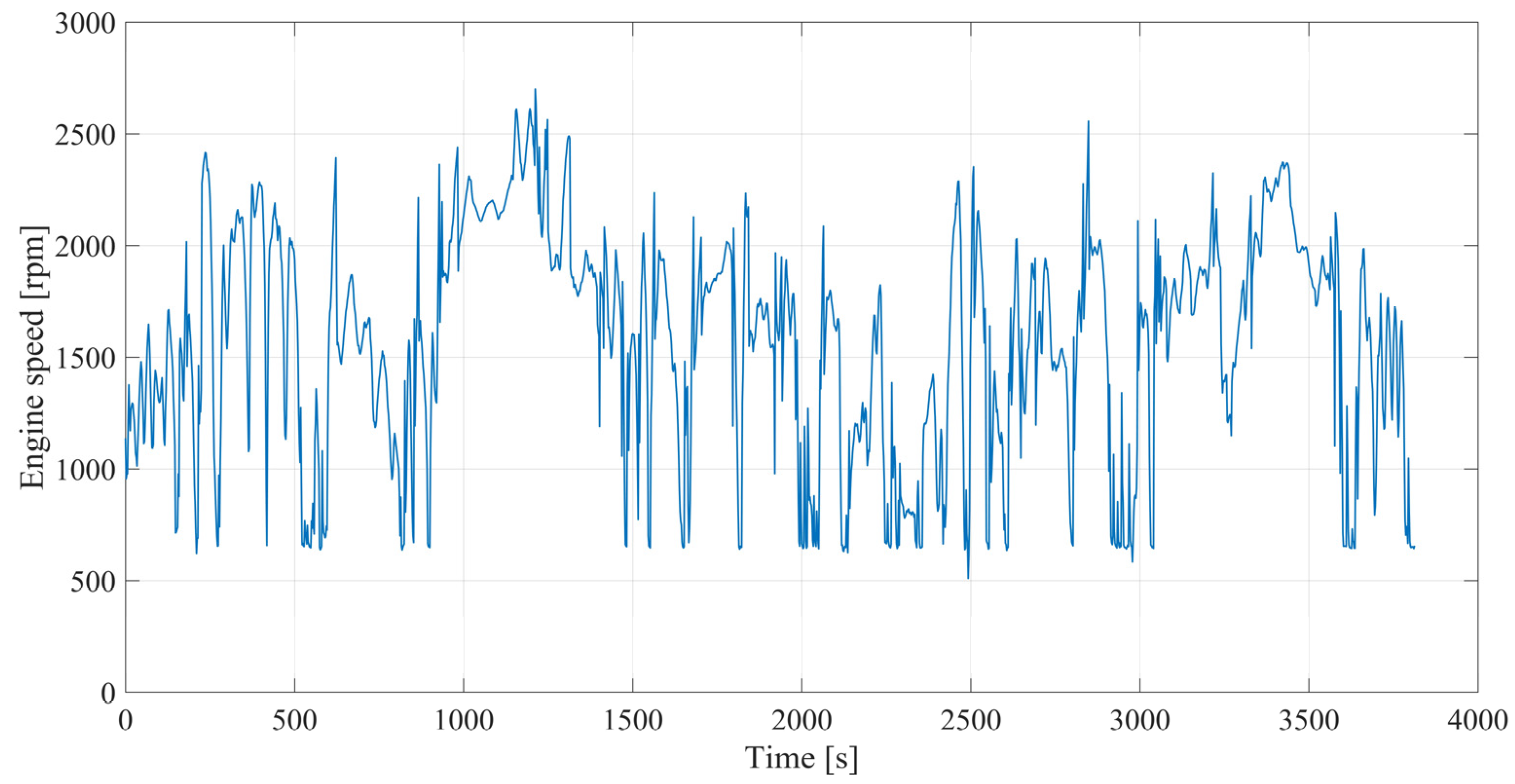


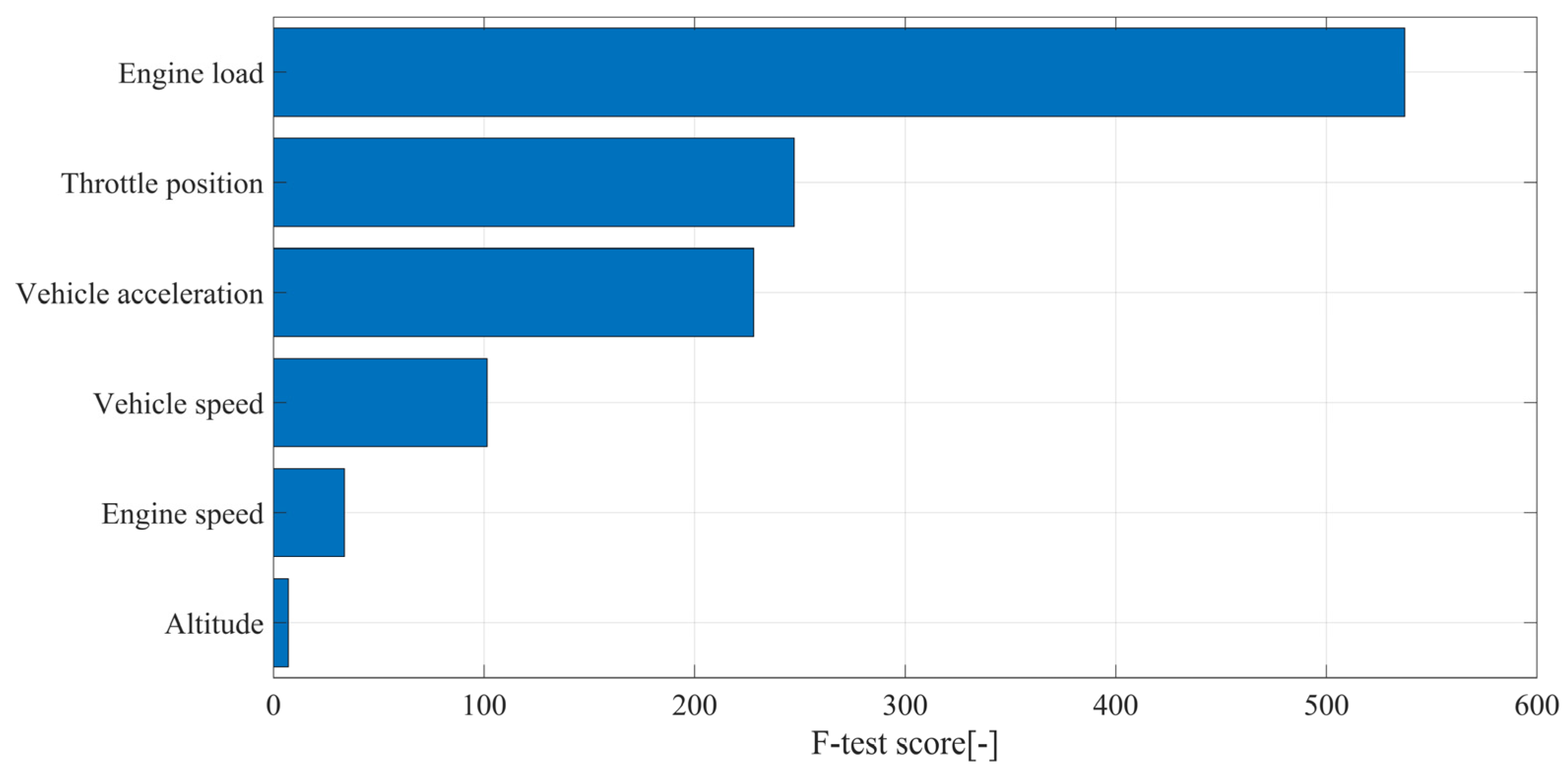
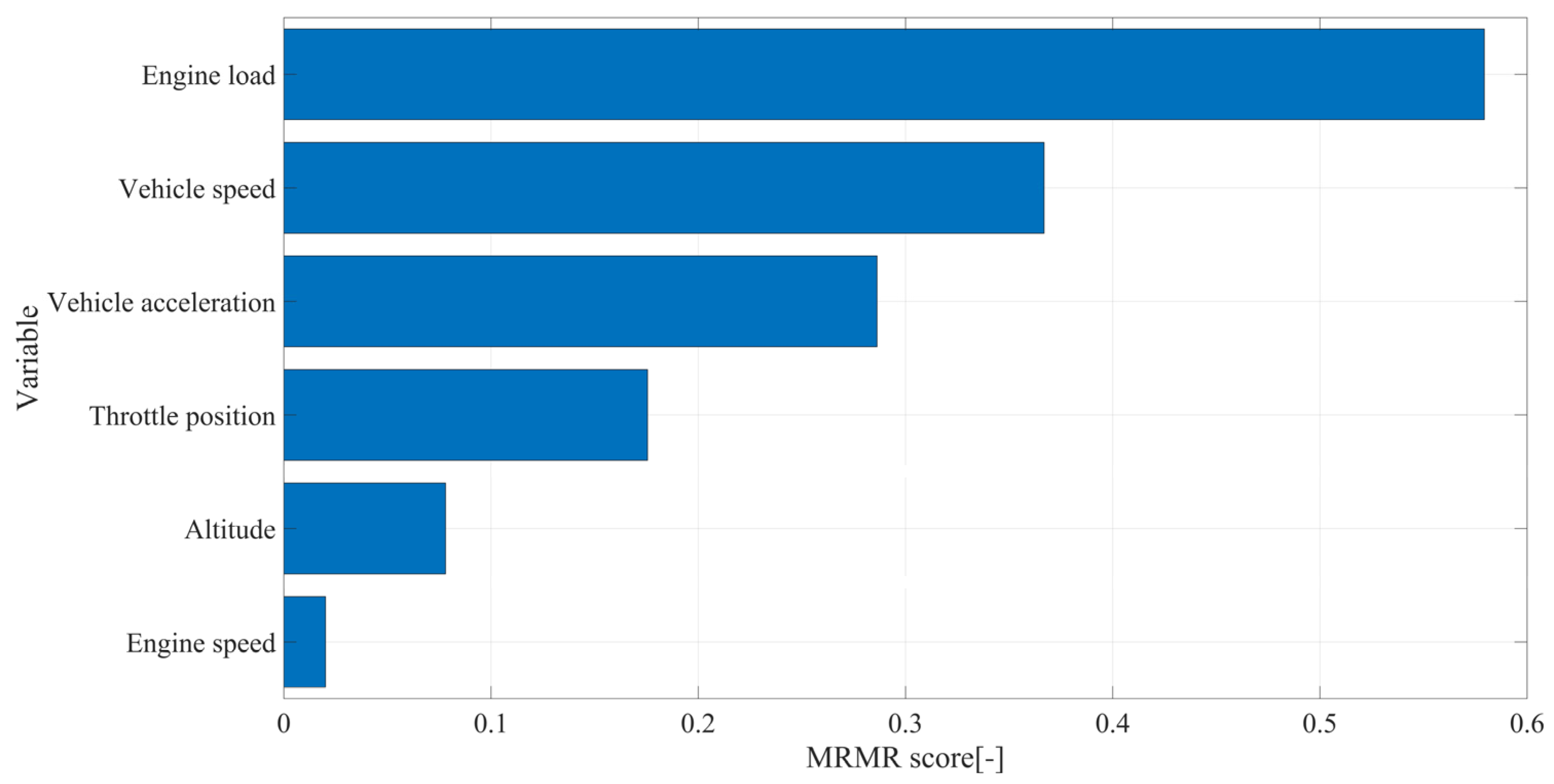

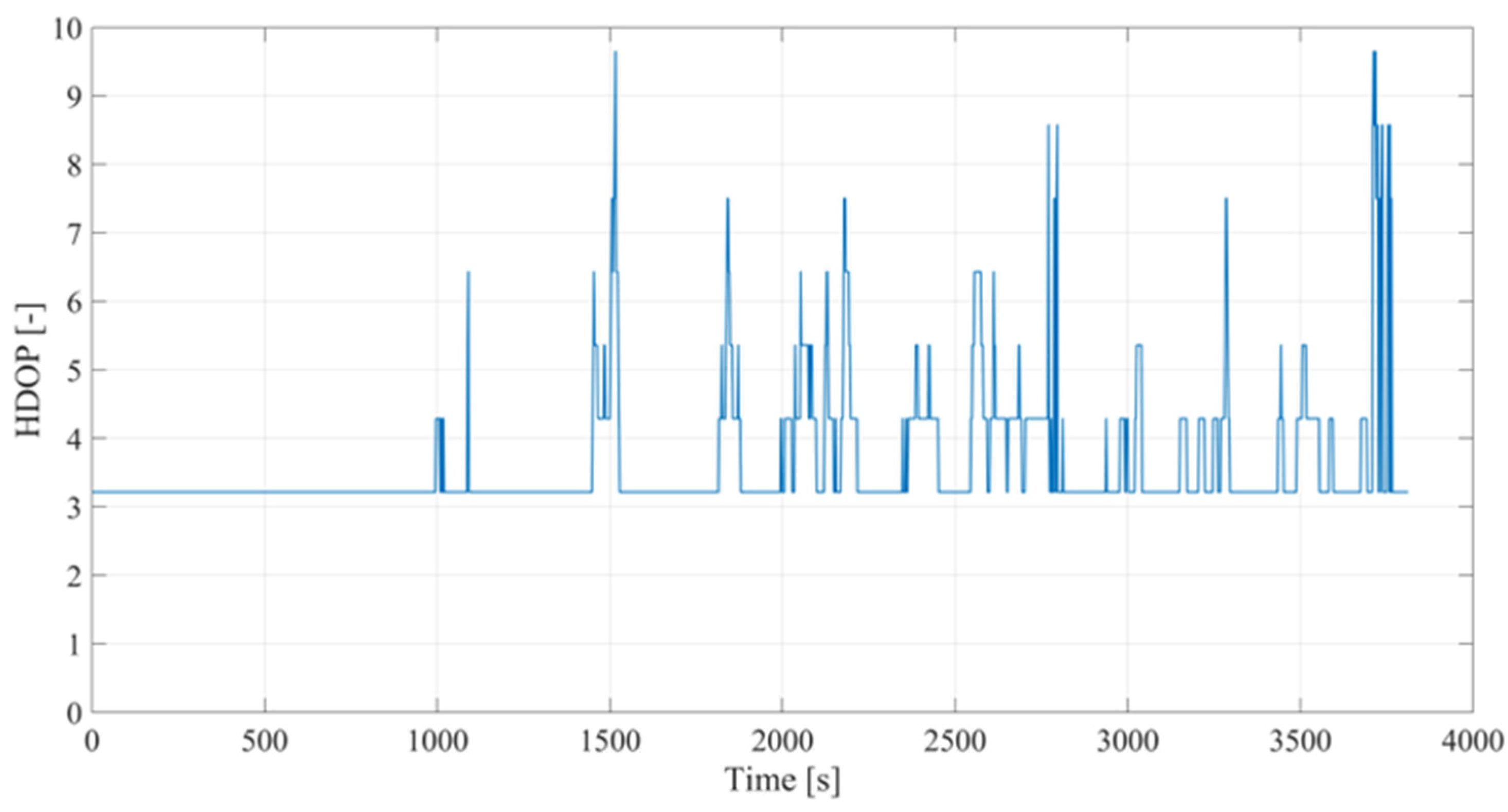
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Mazda |
| Model | 3 |
| Body type | Sedan |
| Weight | 1280 kg |
| Fuel | Gasoline |
| Engine displacement | 1998 cm3 |
| Maximum engine power | 88 kW at 6000 rpm |
| CO2 emission norm | EURO 5 |
| Parameter Type | Parameter Name | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Altitude (m) | Read from GNSS |
| Input | Vehicle speed (km/h) | Read from GNSS |
| Input | Vehicle acceleration (m/s2) | Calculated from vehicle speed |
| Input | Engine load (%) | Read from OBD |
| Input | Engine speed (rpm) | Read from OBD |
| Input | Throttle position (%) | Read from OBD |
| Output | CO2 emission (g/km) | Read from OBD |
| Variable | Minimum | Mean | Std. Dev. | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude (m) | 118.00 | 137.59 | 7.59 | 159.00 |
| Vehicle speed (km/h) | 1.26 | 42.23 | 26.17 | 105.44 |
| Vehicle acceleration (m/s2) | −6.09 | −0.04 | 1.26 | 5.32 |
| Engine load (%) | 8.62 | 29.24 | 19.67 | 100.00 |
| Engine speed (rpm) | 509.75 | 1572.88 | 499.75 | 2699.75 |
| Throttle position (%) | 0.03 | 8.64 | 9.96 | 82.35 |
| Variable | CO2 Emission |
|---|---|
| Altitude (m) | 0.05 |
| Vehicle speed (km/h) | −0.30 |
| Vehicle acceleration (m/s2) | 0.39 |
| Engine load (%) | 0.69 |
| Engine speed (rpm) | −0.19 |
| Throttle position (%) | 0.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rykała, M. Neural Modelling of CO2 Emissions from a Selected Vehicle. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212037
Rykała M. Neural Modelling of CO2 Emissions from a Selected Vehicle. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212037
Chicago/Turabian StyleRykała, Magdalena. 2025. "Neural Modelling of CO2 Emissions from a Selected Vehicle" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212037
APA StyleRykała, M. (2025). Neural Modelling of CO2 Emissions from a Selected Vehicle. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212037






