Abstract
This study presents a dual-module architecture for image forgery detection in the context of cyber fraud investigation, designed to provide interpretable and court-admissible forensic evidence. The forgery segmentation module built on an encoder–decoder structure segments forged regions at the pixel level to produce a binary mask. The forgery classification module with two-stream structure integrates contextual and noise-residual cues from the raw image and the binary mask to determine the designated forgery method. The segmentation module achieves an F1-Score of 0.875 and an IoU of 0.78, while the classification module reaches an F1-Score of 0.94. The combined system attains an end-to-end F1-Score of 0.855 and AUC of 0.91, demonstrating reliable detection performance and enhanced explainability. These results highlight the framework’s potential for forensic image analysis and its practical applicability to real-world cyber fraud investigations.
1. Introduction
The proliferation of advanced image editing software, such as Photoshop and GIMP, leads to the development of sophisticated image forgery methods [1]. Modern forgery methods often extend beyond simple forgeries by incorporating post-processing to conceal traces of forgery. These additions make it difficult for human observers to visually determine the authenticity of an image. These sophisticated forgery methods are exploited for criminal activities that cause significant social problems. Their applications include creating fake news with forged images, fraudulent online advertisements, fabricating evidence, and defaming individuals. The widespread reach of the Internet amplifies this harm, as forged content is exposed to a vast audience, leading to increasingly severe damage [2,3].
Copy-move replicates a specific region and pastes it elsewhere within the same image [4]. This method creates the illusion that an object is larger or more numerous than in reality. In the context of cyber fraud, this approach is used to mislead viewers by artificially increasing the quantity of items depicted in an image. Additionally, Splicing combines elements from two or more different images to create a single composite image [5]. Its primary application in cyber fraud is to create a false context. By integrating subjects from different locations or times, this method can falsely depict events as occurring together, thereby deceiving the viewer. Also, Inpainting, also known as removal, deletes a specific object from an image [6]. The process functions by filling the designated area with pieces of surrounding area. Because this often involves copying existing pixels, it shares characteristics with copy-move method. In cyber fraud, inpainting is employed to maliciously remove critical information or objects, altering the image’s original meaning.
Forgery detection relies on traditional methods and deep learning methods. The traditional methods include frequency-domain analysis, camera artifact analysis, and object-based detection. A key characteristic of these methods is their dependence on manual feature extraction to identify evidence of forgery [7,8,9]. In addition, the advent of deep learning introduces a new paradigm. Modern research focuses on leveraging deep learning models to automatically detect image forgeries. These deep learning architectures outperform traditional methods by achieving faster and more accurate detection across various forgery methods [5], while advances in AI and computing hardware have further enhanced their automation and scalability. They utilize datasets of variously forged images to learn and identify subtle artifacts, such as fine regional differences, noise inconsistencies, and frequency distortions that occur in forged regions. Depending on the research objective, deep learning architectures are employed for tasks such as the binary classification of an image’s authenticity, the detection of forged regions, and the classification of the specific method [10,11,12,13,14].
Dense Fully Convolutional Network (Dense FCN) [10] accurately classifies forged regions within images on a per-pixel basis. This architecture is based on an encoder–decoder framework and incorporates dense connections linking all layers along with dilated convolutions that expand the internal spacing of the convolutional kernels to capture more subtle traces of forgery. However, it is noted that it only derives the presence of forgery as a binary mask and does not include the classification of specific forgery methods. ManTraNet [11] consists of two sub-networks: a feature extractor for image forgery traces and a local anomaly detector for pixel-wise localization. The feature extractor is pretrained on a pretext task that classifies 385 types of synthetic forgeries, which enables it to learn robust forgery traces and generalize to cases that have not been seen before. Localization is then formulated as local anomaly detection. Unfortunately, ManTraNet does not analyze forgery methods. Proposal Contrastive Learning (PCL) [12] adopts a dual-stream architecture utilizing contrastive learning, based on Learning Rich Features for Image Manipulation Detection [15]. This study proposes a method that processes color image features and noise features in parallel. This method is based on the Faster R-CNN [16] architecture and includes the process of generating candidate regions via the RPN. Furthermore, the proposed idea enhances the efficiency of forgery detection by integrating a proposed contrastive learning (PCL) head and implementing a PCL loss function. In the context of the noise stream, both SRM filtering and constrained convolutional layers are considered to differentiate from existing work. Notably, the PCL architecture produces only bounding-box detections for ground-truth and forged regions; it does not classify the forgery method. BusterNet [13] is a specialized network designed for copy-move forgery detection. The proposed idea employs a two-branch architecture followed by a fusion module. One branch detects target regions, while the other estimates source regions via autocorrelation-based visual similarity. The fused output possesses the ability to simultaneously localize both the source and target regions. While this design is noteworthy for source and target identifiability in copy-move forgery detection, it is not intended for general splicing or inpainting detection beyond copy-move. The Recompressed Image Difference [14] utilizes transfer learning for binary forgery discrimination. This approach first emphasizes the forged region by calculating the difference between an input image and its recompressed version. A pre-trained backbone is then fine-tuned on these different images to classify the image as authentic or forged. A key limitation of this method is that it does not perform forged region localization or identify different forgery methods.
This paper proposes a forgery detection architecture that integrates two distinct modules: one for segmenting forged regions and another for classifying the forgery method. In the proposed architecture, the segmentation module initially detects the forged region within the suspect image. Subsequently, this detected region is passed as a form of binary mask to the classification module, which then classifies the forgery method using the corresponding binary mask to derive the result.
The experimental results show the IoU of 0.78 and the F1-Score of 0.875 for the segmentation, and the F1-Score of 0.94 for the classification which lead to the end-to-end F1-Score of 0.855 and AUC of 0.91 for the overall architecture. Proposed two-stage detection approach aims to move beyond the numerous existing deep learning-based forgery detection methods. Instead of merely determining an image’s authenticity, the objective is to enhance explainability by simultaneously localizing which region is forged and identifying what the forgery method is. This comprehensive approach enhances the validity of forgery evaluations, improves an investigator’s ability to analyze forgeries, and increases the overall explainability, thereby enabling the use of such evidence in legal contexts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset and Experimental Environment
With deep learning architecture design, datasets for image forgery receive active attention. Studies span various forgery methods and propose dataset design protocols aimed at building versatile, robust models. The datasets used in this paper are detailed below.
The DEFACTO copy–move dataset [17] is described as having applied the alpha matting [18] technique to solve the visual artifact problem that occurs at the initial object boundary, and the location is limited so that it is duplicated only on the same x-axis or y-axis as the original object, so that there is no disharmony in terms of the content of the image. Accordingly, imaging contents, such as people walking in the sky, are not preprocessed in a form that does not fit the real world. The CoMoFoD dataset [19] is widely used as a benchmark dataset for testing copy-move forgery and consists of 260 forged image sets. Five types of operations are used, such as translation, rotation, scaling, combination, and distortion. It applies techniques such as JPEG compression, blurry noise addition, and color reduction. The DEFACTO splicing dataset [17] partially restricts the categories existing in MS COCO dataset [20] and selects only objects that do not significantly affect the context of the image. Therefore, rather than people, whose appearance changes with viewpoint, it uses objects or equipment with relatively stable appearance as splice sources. Furthermore, to reduce occlusion, the pasted objects are randomly inserted into relatively flat regions. Great Splicing Dataset [21], unlike the DEFACTO dataset [17] uses the Photoshop Program to manually create 5000 splicing datasets based on the images of BossBase database [22]. The dataset is designed to allow neural networks to learn the splicing region more effectively and includes a high-resolution and standardized production process. The DEFACTO inpainting Dataset [17] removes images with complex backgrounds to produce the inpainting dataset, and the dataset is produced using the representative algorithm, exemplar-based inpainting [23].
This paper mainly utilizes the DEFACTO dataset [17], selected from the publicly available datasets previously described. DEFACTO contains a large volume of images and evenly includes the three forgery methods relevant to this research: copy-move, splicing, and inpainting. The dataset is automatically generated from MS COCO [20] and provides precise annotations. It employs representative images and 91 object categories from MS COCO, refining object masks through alpha matting [18].
To ensure reliable mask supervision and stable learning conditions, the dataset is pre-filtered by removing images where the forged region constitutes less than 1.5% of the total pixel count, as well as those whose spatial resolution falls below 400 × 400 pixels. This preprocessing step reduces the effect of label noise originating from extremely small alterations and guarantees that the model is trained on samples with sufficient spatial detail to distinguish forged regions from authentic content. As a consequence, the dataset focuses on cases where the forged regions are of meaningful size and discernible at moderate resolution. While this strategy narrows the scope of the analysis, it reflects practical tendencies in cyber fraud. Extremely minute forgeries or visually degraded images typically lack the persuasive impact necessary to deceive victims in real-world fraud scenarios and are thus less frequently employed. Accordingly, the exclusion of such cases does not compromise the relevance of the proposed model for its intended forensic application, which prioritizes the detection of forgeries capable of influencing human perception and decision-making.
The dataset comprises 13,333 image and mask pairs. The train, validation, and test splits contain 9300, 1991, and 2042 images, respectively, corresponding to 69.75%, 14.93%, and 15.32%, with identical counts for the paired masks. Detailed information is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detailed information of dataset used in the experiment.
As the experimental environment, the hardware specifications and operating system information used in this paper are listed below:
- GPU: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 (24 GB VRAM)
- CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-10980XE @ 3.00 GHz
- RAM: Samsung DDR4 PC4-21300 32 GB x4 (total 128 GB)
- Operating System: Ubuntu 22.04
2.2. Proposed Architecture
2.2.1. Architecture Overview
Figure 1 summarizes the overall architecture. The input to the architecture is a color image requiring authenticity analysis, denoted as the raw image. Within the architecture, the segmentation module identifies and segments the forged regions, and produces a corresponding binary mask aligned with the raw image. This mask, together with the raw image, is then processed by the classification module, which determines the specific forgery method applied.
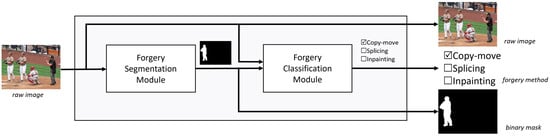
Figure 1.
Overview of the proposed architecture.
Inside the architecture, both modules are built upon an EfficientNet [24]-based pretrained on ImageNet [25] which offers high-quality features that are well-suited to forgery localization and three forgery methods classification, yielding an overall design that is computationally efficient yet accurate. EfficientNet is adopted as the backbone for its compound scaling and parameter efficiency, which delivers strong transfer performance with a favorable trade-off between accuracy and compute cost [24].
2.2.2. Forgery Segmentation
The forgery segmentation module receives the raw image, and the binary mask which indicates the forged region within the raw image, as the input data for training. The module consists of two parts: the encoder and the decoder.
Image feature maps are extracted using EfficientNet-B7 [24] as the base network in the encoder, while the decoder follows a U-Net [26] style network built with tailored convolutional layers. The encoder is initialized with ImageNet–pretrained weights [25], so rich boundary and texture cues for forgery are captured, while spatial resolution is restored in the decoder via upsampling and skip connections. Finally, a sigmoid activation is applied at the output layer, and a single-channel mask is produced.
At the encoder, the spatial resolution is halved by a stride-2. Four intermediate encoder features are tapped for skip connections, and the deepest feature is used as the bridge input to the decoder. At the decoder, the feature map is upsampled, and the corresponding skip features are concatenated channel-wise. Detailed structure is described in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Structure of the forgery segmentation module.
2.2.3. Forgery Classification
The forgery classification module receives the raw image, its corresponding binary mask indicating the forged region, and the corresponding forgery method associated with that region as the input data for training. The module consists of two streams: the noise stream and the context stream.
At the entrance of the noise stream which adopts Spatial Rich Model (SRM) high-frequency stream [27], the Multiply block gates the image by element-wise multiplication with the mask. This removes large, clean backgrounds and restricts the SRM filters to the candidate region, thereby increasing the effective signal-to-noise ratio of forgery residuals before SRM processing. In parallel, the context stream begins with the Concatenate (image, mask) block, which appends the binary mask as an additional channel rather than masking out pixels. This conditioning preserves background appearance while explicitly indicating where forgery is suspected, enabling early layers to capture global context and later layers to encode foreground–background contrast and object boundaries.
The two streams are concatenated, transformed by a 256-unit fully connected layer with dropout 0.5 for strong stochastic regularization [28], and mapped to class probabilities by a Softmax layer. During training, the Softmax output is compared with the ground -truth forgery method label using cross-entropy; the loss is back-propagated through both streams. Only the Softmax output is used, and the classified label corresponds to the maximum probability. Detailed structure is described in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Structure of the forgery classification module.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Results of Forgery Segmentation Module
Figure 4 shows the training dynamics of the forgery segmentation module in terms of the F1-Score and IoU. Both metrics exhibit a steep increase during the first few epochs, followed by gradual stabilization, indicating effective convergence of the model. The consistent trend of the two curves demonstrates that the module achieves balanced optimization between pixel-level sensitivity and region-level segmentation accuracy. Minor oscillations observed in the later epochs are primarily attributed to small forged regions that remained in the dataset even after filtering out samples with less than 1.5% forged area.

Figure 4.
F1-Score and IoU curves of the segmentation module across epochs.
Quantitatively, the segmentation module achieves a Precision of 0.823, Recall of 0.934, F1-Score of 0.875, and IoU of 0.78 on the DEFACTO test set. These results confirm that the module accurately localizes forged pixels while maintaining reasonable precision. A single pixel-level confusion matrix, shown in Figure 5, visualizes the balance between forged (GT = 1) and authentic (GT = 0) regions, illustrating a low proportion of false negatives and a moderate number of false positives. This pattern indicates that the model favors higher recall, effectively minimizing missed forged areas at the expense of a slight over-segmentation. Table 2 summarizes the quantitative performance of the segmentation module.

Figure 5.
Pixel-level confusion matrix of the forgery segmentation module.

Table 2.
Quantitative results of the forgery segmentation module.
Figure 6 presents representative examples of the segmentation results for the three forgery methods: copy-move, splicing, and inpainting. The forged regions are highlighted as orange overlays on the suspicious image throughout this paper. In each case, the module accurately identifies the forged areas and produces masks that closely match the ground-truth, confirming the module’s robust pixel-level segmentation capability and generalization across different forgery methods.
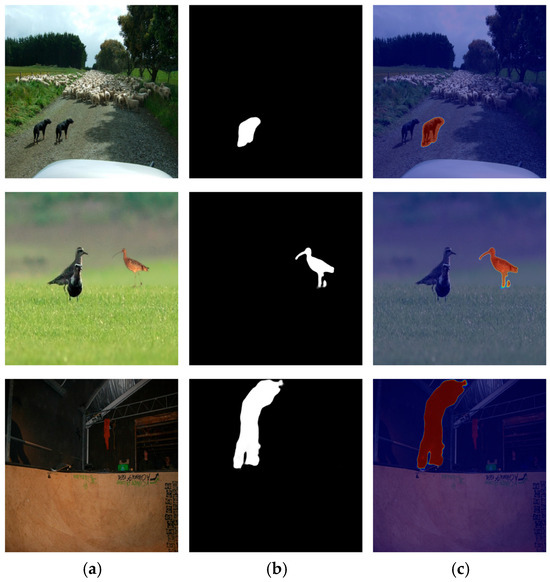
Figure 6.
Representative segmentation results for copy-move, splicing, and inpainting; (a) raw image, (b) binary mask and (c) region highlight.
3.2. Results of Forgery Classification Module
Figure 7 presents the training dynamics of the forgery classification module, represented by the F1-Score across epochs. The F1-Score curve shows a steady and smooth increase, followed by convergence around 0.94, demonstrating that the module effectively learns discriminative features from both the raw image and the corresponding binary mask. Minor fluctuations in the validation curve indicate limited variance across batches but do not affect the overall stability, confirming consistent generalization.
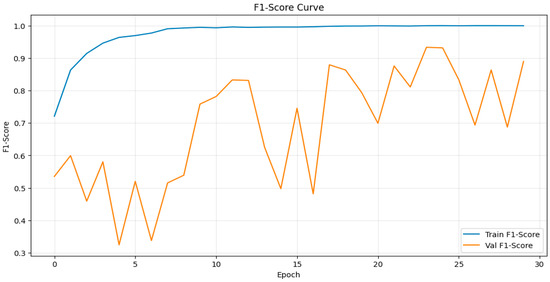
Figure 7.
F1-Score curve of the classification module across epochs.
Quantitative evaluation on the DEFACTO test set further validates the module’s effectiveness. The F1-Score reaches 0.94, with the confusion matrix in Figure 8 revealing that most errors occur between copy-move and splicing classes due to their similar structural artifacts. In contrast, the inpainting class achieves a precision of 0.97, showing that the high-frequency SRM-based noise stream successfully captures subtle residual cues that distinguish removed-object forgeries from compositional ones. Table 3 summarizes the class-wise performance of the classification module, including precision, recall, and F1-Score for each forgery method.

Figure 8.
Class-level confusion matrix of the forgery classification module.

Table 3.
Quantitative results of the forgery classification module.
Representative qualitative results are provided in Figure 9. Each row corresponds to one forgery method, displaying the raw image, the binary mask, and the final classification output. The classification output is rendered as a checklist, with a check mark on the predicted forgery methods: copy-move, splicing, or inpainting. The module consistently produces accurate predictions across all methods, verifying its robustness and generalization to diverse forgery patterns.

Figure 9.
Representative classification results for copy-move, splicing, and inpainting; (a) raw image (b) binary mask and (c) forgery method.
While the module attains high absolute scores across classes in Table 3 and produces stable qualitative outputs in Figure 9, residual confusion between copy-move and splicing remains. In particular, boundary-like textures and loss of global context can cause externally inserted content to resemble duplicated patterns, and vice versa. This ambiguity constitutes a key limitation of the current design. Its causes and potential remedies are discussed in Section 4, including the addition of explicit self-similarity features for copy-move and boundary or lighting-consistency cues for splicing, along with stronger multi-scale context modeling and hard-negative mining strategies.
3.3. Overall Architecture
The proposed dual-module architecture combines the forgery segmentation and classification components in a sequential workflow, enabling a comprehensive analysis of both where and how an image has been forged. In the first stage, the segmentation module segments the forged region and produces a binary mask aligned with the raw image. In the second stage, the classification module processes this mask together with the suspicious image to infer the specific forgery method. This design allows each module to specialize in its respective task while ensuring coherent interaction between them during inference.
Evaluation on an unseen test dataset yields an overall end-to-end F1-Score of 0.855 and AUC of 0.91, demonstrating that the combined architecture maintains strong consistency between forged region segmentation and forgery method classification. The segmentation module achieves an F1-Score of 0.875 and IoU of 0.78, while the classification module attains an F1-Score of 0.94. These results confirm that the proposed dual-stage approach performs competitively with recent state-of-the-art models while offering enhanced interpretability and modularity.
Figure 10 illustrates representative end-to-end examples of the full workflow. Each row displays the raw image, the binary mask generated by the segmentation stage, and the final classification result. The forged regions are clearly highlighted with orange overlays and the predicted forgery methods correspond accurately to copy-move, splicing, and inpainting forgeries. The outputs demonstrate not only the visual precision of segmentation but also the classifier’s ability to capture contextual and high-frequency cues relevant to each forgery method.
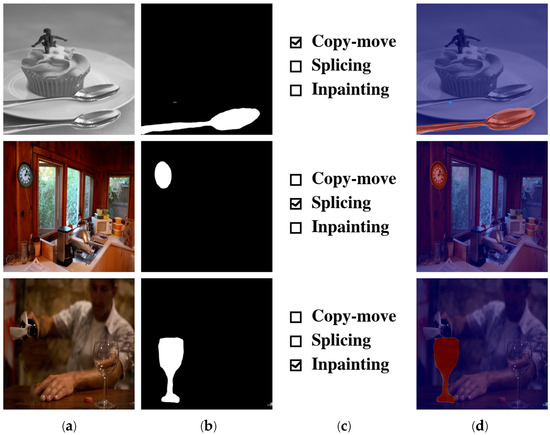
Figure 10.
Representative results of overall architecture for copy-move, splicing, and inpainting; (a) raw image, (b) binary mask, (c) forgery method and (d) region highlight.
Figure 11 illustrates representative failure cases of the full workflow. Each row displays the raw image, segmentation result, segmentation ground-truth, final classification result and classification ground-truth. In the first example, a copy-move image yields a failure: the upper forged area is cropped, global context is reduced, and the segmentation mask resembles an external insertion, leading to a splicing decision. In the second example, a spurious activation appears around the bird’s head, producing a distant false positive; edge and specular textures in that region imitate the forged region and steer the decision toward copy-move. These failures indicate that context loss and texture confusion can propagate through the architecture and affect the final output.

Figure 11.
Representative failure results of overall architecture for copy-move and splicing; (a) raw image, (b) segmentation result (c) segmentation ground-truth (d) classification result and (e) classification ground-truth.
A comparative evaluation against prior studies further highlights the effectiveness of the proposed architecture. Table 3 reports overall end-to-end performance (Precision, Recall and F1-Score) for representative methods under comparable settings. The proposed architecture attains an overall F1-Score of 0.855 and an AUC of 0.91, while remaining compact compared with multi-branch and attention-based models such as Dense FCN [10], ManTraNet [11], PCL [12], and BusterNet [13] as shown in Table 4. These results indicate that precise segmentation and robust classification can be achieved through a compact dual-module design without sacrificing overall detection quality. A detailed overview of these architectures is provided in Section 1.

Table 4.
Comparison with previous studies.
Taken together, these results verify that the proposed architecture surpasses existing single-stage detectors in both overall performances (such as F1-Score and AUC) and explainability, providing reliable evidence for real-world forensic image analysis, where the credibility of visual evidence and interpretability of results are of paramount importance.
4. Discussion
This study presents a dual-module architecture for image forgery detection, designed to enhance interpretability and forensic reliability by jointly performing forgery segmentation and forgery classification. The architecture integrates two specialized modules: an encoder–decoder structured segmentation network based on EfficientNet-B7 for pixel-level localization, and a dual-stream classification network employing both noise- and context-based feature representations. This modular design enables independent optimization of each task while maintaining seamless interaction in the combined workflow.
Experimental results demonstrate strong quantitative and qualitative performance across all evaluation stages. The segmentation module achieves an F1-Score of 0.875 and an IoU of 0.78, accurately identifying forged regions within diverse images. The classification module reaches an F1-Score of 0.94, correctly distinguishing between copy-move, splicing, and inpainting forgeries. When the two modules are integrated, the full architecture attains an overall end-to-end F1-Score of 0.855 and AUC of 0.91 on unseen test data, confirming the robustness and complementarity of the proposed dual-stage architecture.
Beyond numerical performance, the architecture offers substantial methodological advantages. By decoupling segmentation and classification, it allows flexible model updates and targeted performance improvements in either stage without retraining the entire system. The architecture’s interpretability, producing both a visible segmentation mask and an explicit forgery method label, facilitates evidence-based analysis suitable for real investigative and legal contexts, addressing the critical demand for transparency in AI-driven forensic applications.
The dual-module architecture provides clear investigative orientation and decisive clues for suspect inference. The segmentation module indicates where to focus, and the classification module specifies the forgery method, enabling assessment of whether the criminal purpose involved copy-move to inflate the apparent quantity of an object, splicing to compose images, or inpainting to remove suspicious regions. Accordingly, this architecture evaluates how the forged image may have been used for criminal purposes and supports investigators’ analysis. This information contributes to the targeted acquisition of critical evidence in subsequent procedures and, in some cases, can play a decisive role. Although the direct court application of machine-learning systems may be limited, the critical leads inferred and documented by investigators from the system’s segmentation masks and method labels can satisfy expectations of evidentiary clarity and transparency, thereby serving as a practical tool for proving offenses and guiding subsequent procedures. Further limitations to consider include that classification reliability decreases when segmentation is inaccurate, and generalization to entirely novel forgery methods remains weak, which present meaningful directions for future work.
In addition, a residual source of error lies in the ambiguity between copy-move and splicing forgeries. Although both achieve high F1-Scores, they occasionally exhibit overlapping visual characteristics—especially when boundary-like textures or reduced global context make duplicated patterns resemble externally inserted content. As this confusion has forensic implications due to the different manipulation intents, future work should incorporate self-similarity cues for copy-move and boundary consistency cues for splicing, alongside refined context modeling.
Comparative evaluation with recent state-of-the-art methods demonstrates that the proposed dual-module architecture achieves comparable or superior accuracy while remaining computationally efficient. The results suggest that a carefully balanced combination of the segmentation module and the classification module is sufficient to deliver high-precision localization and reliable classification without excessive model complexity.
The dual-module architecture can be extended toward multi-modal and domain-specific datasets, such as forensic image analysis from surveillance, social media, or cybercrime evidence. Further improvements may include self-supervised pretraining for domain adaptation, integration of frequency-domain representations, and interpretability-driven visualization to enhance the credibility of forensic results. Ultimately, the proposed architecture establishes a foundation for explainable, modular, and evidence-driven image forgery detection suitable for real-world investigative environments including cyber fraud investigation.
Author Contributions
Data curation, software, investigation, visualization, resources, writing—original draft, D.K.; Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, validation, supervision, funding acquisition, writing—review & editing, H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Hallym University Research Fund, 2025 (HRF-202506-010) and by Development of an Integrated Analysis and Inference System for Cybercrime Investigation Clues Program through the Korea Institutes of Police Technology (KIPoT) funded by the Korean National Police Agency (RS-2025-02218280).
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in the DEFACTO Dataset at https://defactodataset.github.io/. accessed on 3 June 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gill, N.K.; Garg, R.; Doegar, E.A. A review paper on digital image forgery detection techniques. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 3–5 July 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Novel Deep Learning-Based Facial Forgery Detection for Effective Biometric Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Deb, S.; Das, A.; Kar, N. Image forgery detection techniques: Latest trends and key challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 169452–169466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Warif, N.B.; Wahab, A.W.A.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Ramli, R.; Salleh, R.; Shamshirband, S.; Choo, K.-K.R. Copy-move forgery detection: Survey, challenges and future directions. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 75, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjardi, F.Z.; Latif, A.M.; Zarchi, M.S.; Sheikhpour, R. A survey on deep learning-based image forgery detection. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 144, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalmio, M.; Sapiro, G.; Caselles, V.; Ballester, C. Image inpainting. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–28 July 2000; pp. 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, A.C.; Farid, H. Exposing Digital Forgeries by Detecting Duplicated Image Regions; University of Califomia: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, A.C.; Farid, H. Exposing digital forgeries by detecting traces of resampling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, J.; Fridrich, J.; Goljan, M. Digital camera identification from sensor pattern noise. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2006, 1, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Li, H.; Tan, S.; Li, B.; Huang, J. Image tampering localization using a dense fully convolutional network. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 2986–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; AbdAlmageed, W.; Natarajan, P. Mantra-net: Manipulation tracing network for detection and localization of image forgeries with anomalous features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 18–20 June 2019; pp. 9543–9552. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, B.; Qiu, S.; Dai, T.; Xia, S.-T. Toward effective image manipulation detection with proposal contrastive learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4703–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Abd-Almageed, W.; Natarajan, P. Busternet: Detecting copy-move image forgery with source/target localization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 168–184. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.H.; Ghalwash, A.Z.; Elsayed, H.A.-G.; Salama, G.I.; Ghalwash, H.A. Enhancing digital image forgery detection using transfer learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 91583–91594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Han, X.; Morariu, V.I.; Davis, L.S. Learning rich features for image manipulation detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1053–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoudi, G.; Tajini, B.; Retraint, F.; Morain-Nicolier, F.; Dugelay, J.L.; Pic, M. Defacto: Image and face manipulation dataset. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruña, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Rhemann, C.; Rother, C.; Tang, X.; Sun, J. A global sampling method for alpha matting. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 2049–2056. [Google Scholar]
- Tralic, D.; Zupancic, I.; Grgic, S.; Grgic, M. CoMoFoD—New database for copy-move forgery detection. In Proceedings of the ELMAR-2013, Zadar, Croatia, 25–27 September 2013; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.; Liang, J. GreatSplicing: A Semantically Rich Splicing Dataset. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, P.; Filler, T.; Pevný, T. “Break our steganographic system”: The ins and outs of organizing BOSS. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Information Hiding, Prague, Czech Republic, 18–20 May 2011; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Daisy, M.; Buyssens, P.; Tschumperlé, D.; Lézoray, O. A smarter exemplar-based inpainting algorithm using local and global heuristics for more geometric coherence. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 4622–4626. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Fridrich, J.; Kodovsky, J. Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).