Constructing Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles for an Extended-Range Electric Vehicle via Dynamic Programming Guided by Real-World Trip Dynamics and Road Terrain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Real Driving Emission Model
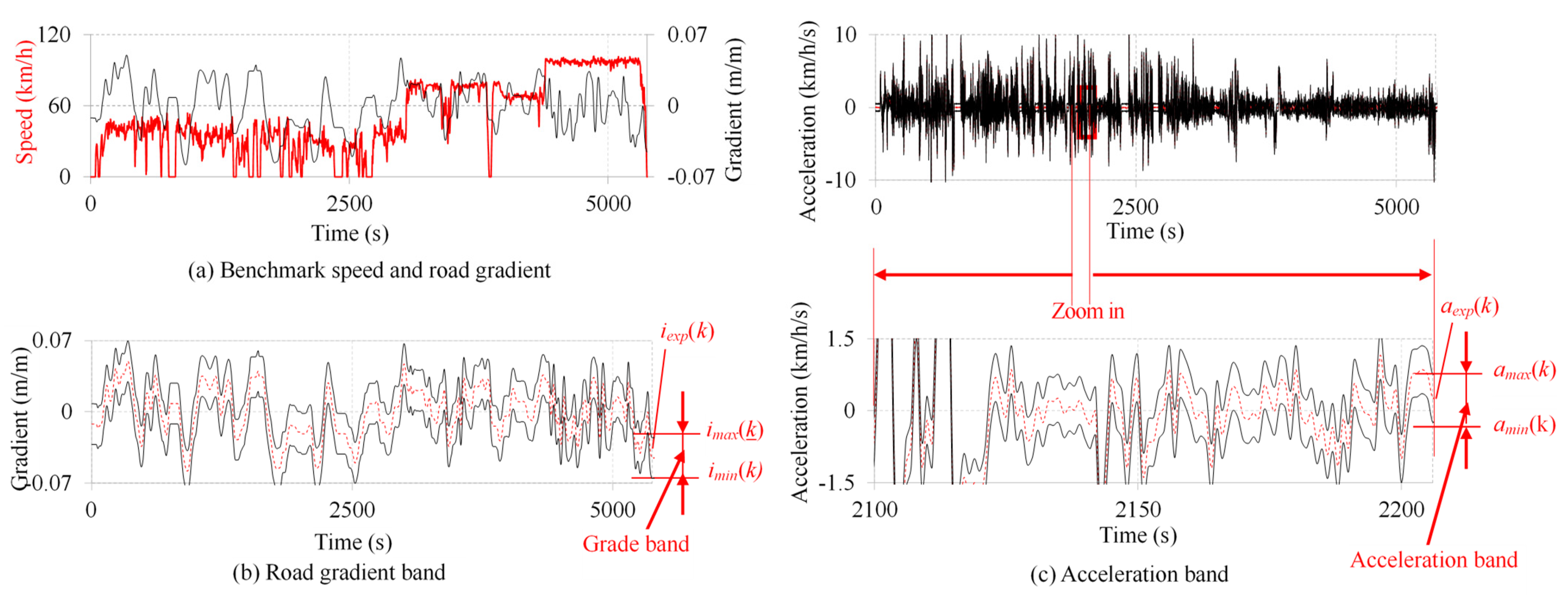
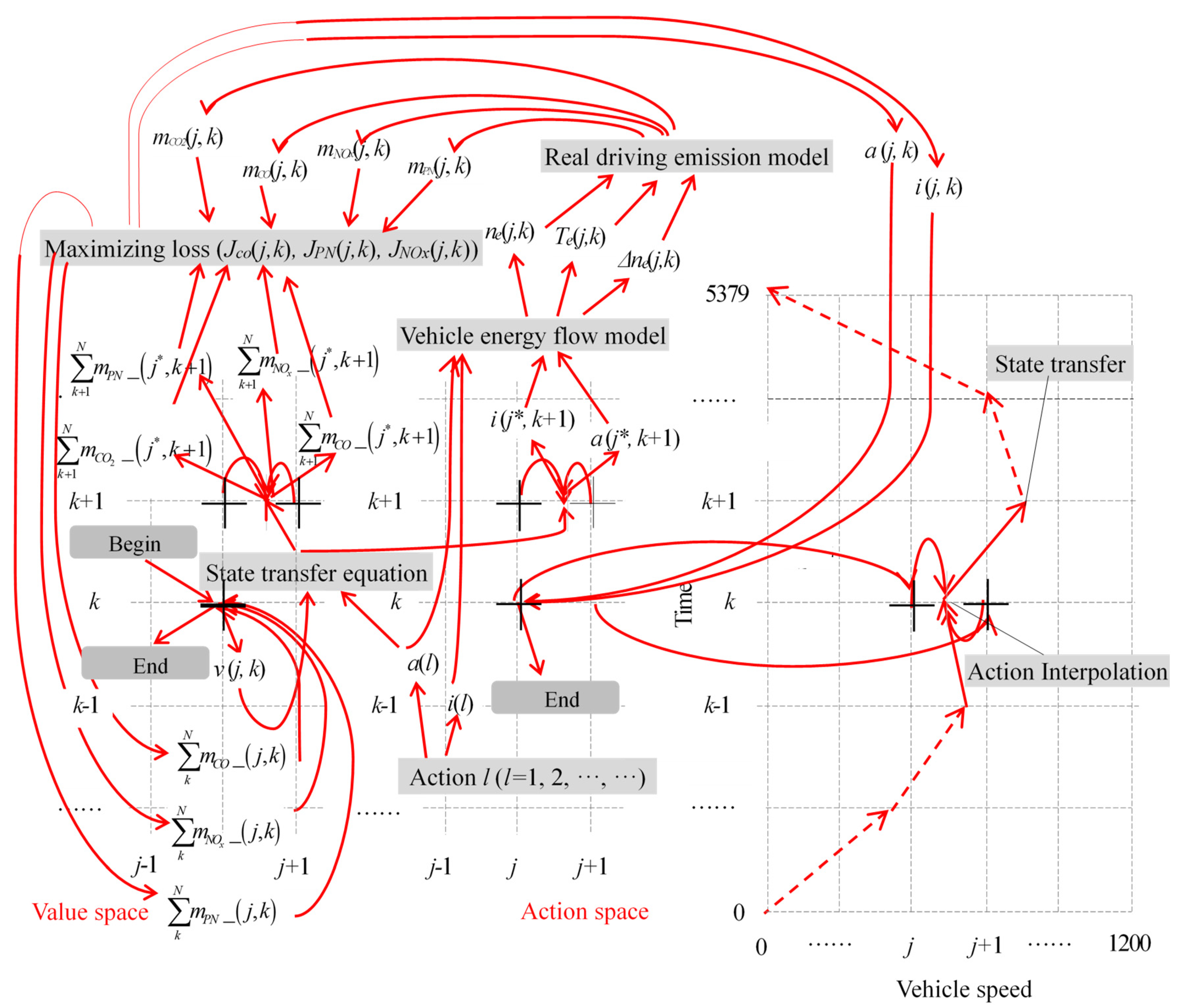
2.2. Multi-Stage Decision Optimization Model
2.3. DP Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. DP algorithm for Generating High-Emission Driving Cycle |
| Input: vehicle parameters, time step Δt, total stages N, baseline speed vexp(k), acceleration aexp(k), road grade iexp(k), real driving emission model. |
| 1 Initialize grids of speed v ∈ [vmin, vmax], acceleration a, and road grade i. |
| 2 for k = N − 1 to 1 do |
| 3 for each discrete speed v do |
| 4 for each action [a, i] around baseline do |
| 5 Compute next speed vnext = v + a·Δt |
| 6 Compute demanded power Pdem = f(v, a, i) |
| 7 Map Pdem → ne, Te → current emissions (CO2, CO, PN, NOx) |
| 8 Compute cumulative emissions: current emissions + future optimal emissions (from the value matrix at vnext) |
| 9 Evaluate emission metric J(v, a, i) |
| 10 end |
| 11 Select (a*, i*) = arg max J(v, a, i) |
| 12 end |
| 13 end |
| 14 Forward simulate with policy [a*(k), i*(k)] to generate cycle |
| Output: optimized action sequence [a*(k), i*(k)] and the corresponding high-emission driving cycle. |
3. Results and Discussions
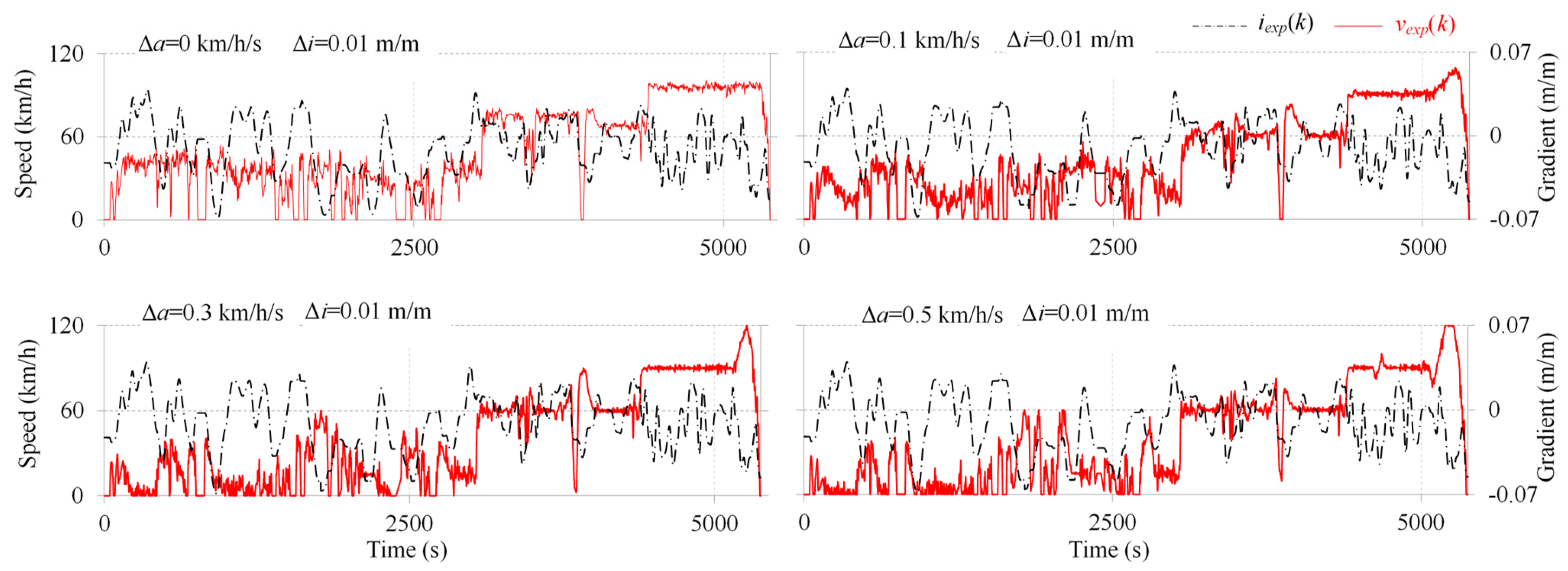
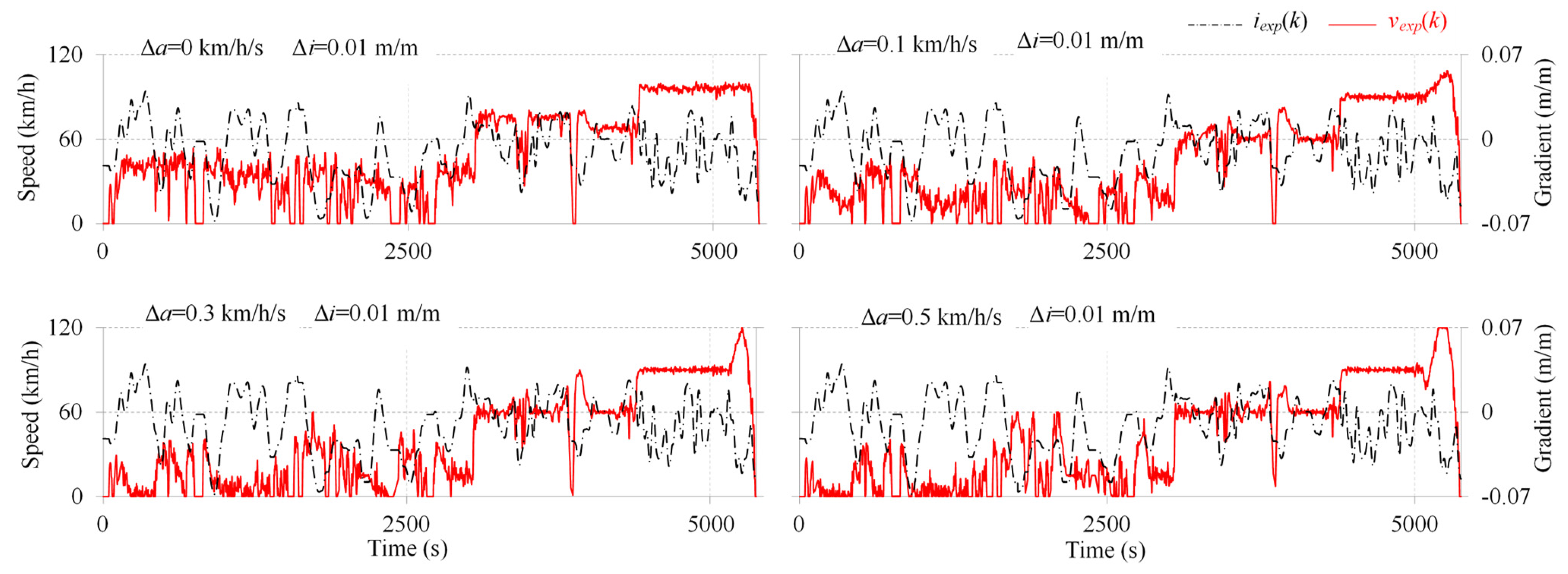
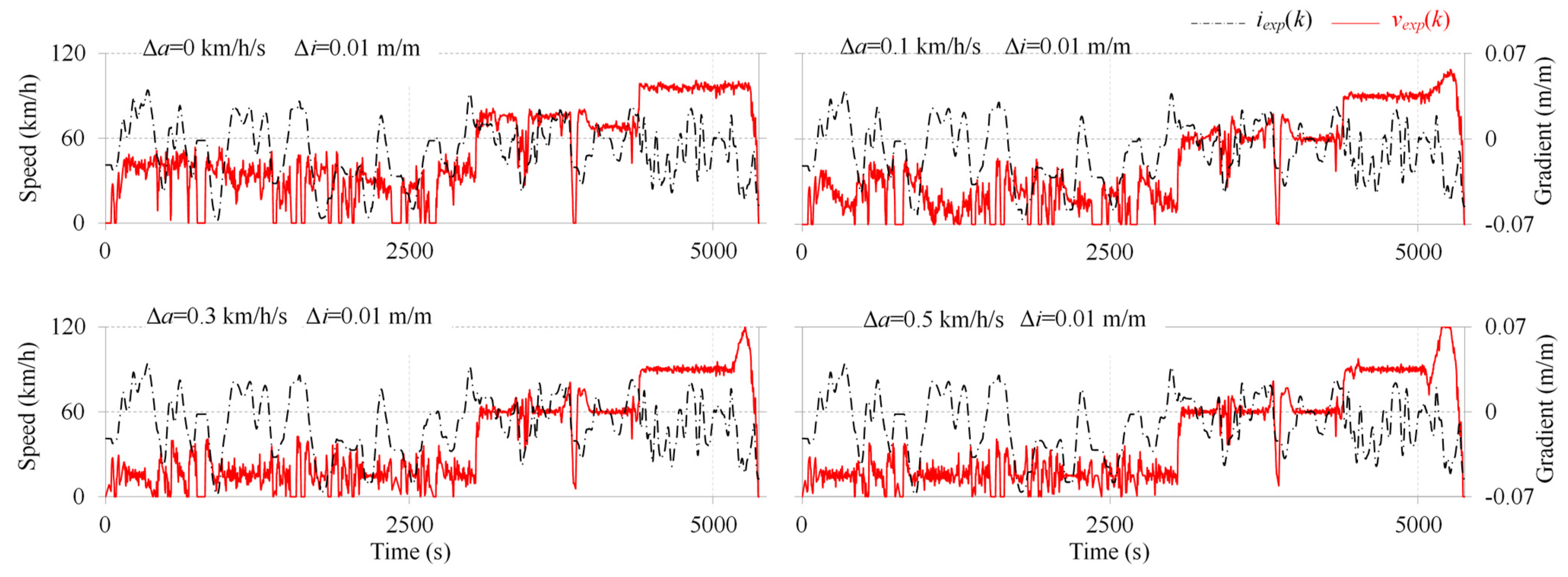
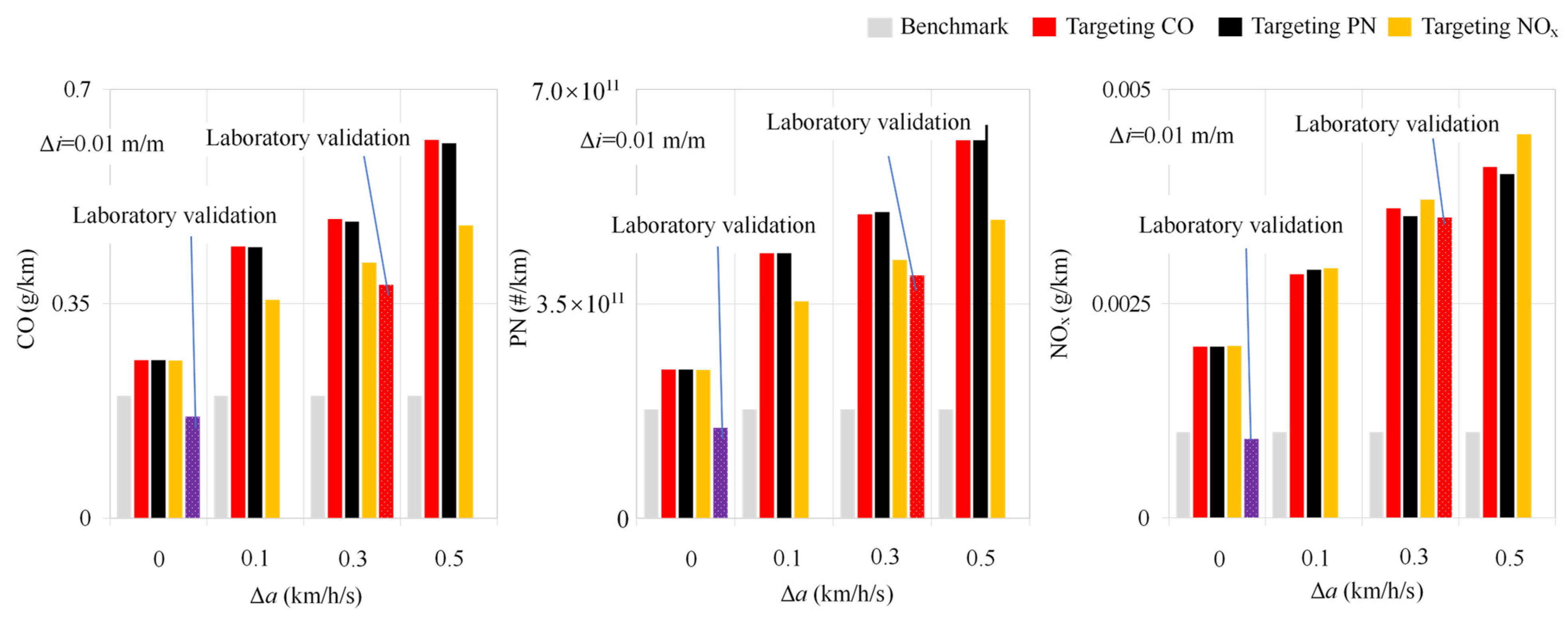
3.1. Characteristics of Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles
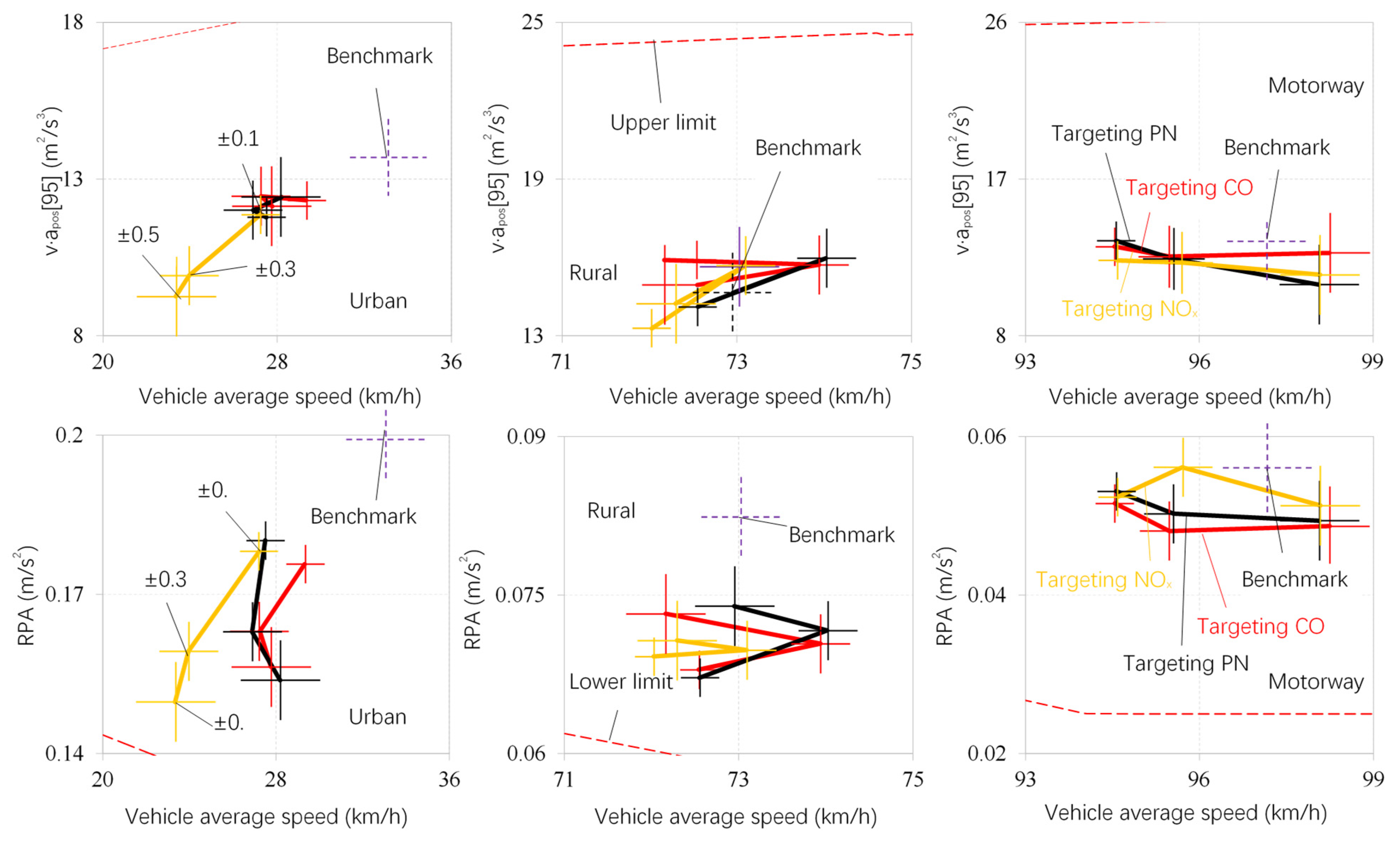
3.2. Verification of Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooftman, N.; Messagie, M.; Van Mierlo, J.; Coosemans, T. A review of the European passenger car regulations-Real driving emissions vs local air quality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 86, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.B.; Rodella, F.H.C.; Hoinaski, L. Regulating light-duty vehicle emissions: An overview of US, EU, China and Brazil programs and its effect on air quality. Clean Technol. Environ. 2021, 24, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallington, T.J.; Anderson, J.E.; Dolan, R.H.; Winkler, S.L. Vehicle emissions and urban air quality: 60 years of progress. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutuianu, M.; Bonnel, P.; Ciuffo, B.; Haniu, T.; Ichikawa, N.; Marotta, A.; Pavlovic, J.; Steven, H. Development of the world-wide harmonized light duty test cycle (WLTC) and a possible pathway for its introduction in the European legislation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 40, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.D.K.; Axon, C.J. Using natural driving experiments and Markov chains to develop realistic driving cycles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 137, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.F.; Yang, X.H.; Pei, B.; Xu, H.M.; Wu, B.Y.; Su, W.H. Development of a representative transient cycle for evaluating real driving emissions of heavy-duty diesel engines. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.P.; Zou, F.M.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.H.; Gong, K.M. A novel optimization-based method to develop representative driving cycle in various driving conditions. Energy 2022, 247, 123455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzayyin, O.A.; Salem, H.; Hassan, M.A. A representative urban driving cycle for passenger vehicles to estimate fuel consumption and emission rates under real-world driving conditions. Urban Clim. 2021, 36, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.M.; Zeng, X.H.; Song, D.F. Construction of high-precision driving cycle based on Metropolis-Hastings sampling and genetic algorithm. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 118, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.A.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Ong, H.C.; Ashik, F.R.; Hassan, M.M.; Murshed, M.T.; Imran, M.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Rahman, M.A.; Hasan, M.A.; et al. State-of-the-art of establishing test procedures for real driving gaseous emissions from light- and heavy-duty vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/646 of 20 April 2016 amending Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 as regards emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 6). Off. J. Eur. Union 2016, L 109, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Varella, R.A.; Faria, M.V.; Mendoza-Villafuerte, P.; Baptista, P.C.; Sousa, L.; Duarte, D.O. Assessing the influence of boundary conditions, driving behavior and data analysis methods on real driving CO2 and NOx emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahariar, G.M.H.; Bodisco, T.A.; Zare, A.; Sajjad, M.; Jahirul, M.I.; Van, T.C.; Bartlett, H.; Ristovski, Z.; Brown, R.J. Impact of driving style and traffic condition on emissions and fuel consumption during real-world transient operation. Fuel 2022, 319, 123874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.W.; Niu, H.M.; Jia, Z.Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Mao, H.J. Comparison of vehicular emissions at different altitudes: Characteristics and policy implications. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 367, 125679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.C.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.L.; Xiang, G. Testing and evaluation of cold-start emissions in a real driving emissions test. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 86, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Chang, H.; Han, J.L.; Wu, D.M.; Gong, X.K.; Fu, M.M. Measuring the route topography impact on real driving emissions based on neural network models. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, J.; Pischinger, S.; Krysmon, S.; Sterlepper, S.; Dorscheidt, F.; Doucet, M.; Reuber, C.; Gorgen, M.; Scharf, J.; Nijs, M.; et al. Statistically supported real driving emission calibration: Using cycle generation to provide vehicle-specific and statistically representative test scenarios for Euro 7. Int. J. Engine Res. 2020, 21, 1783–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysmon, S.; Classen, J.; Pischinger, S.; Trendafilov, G.; Duezguen, M.; Dorscheidt, F. RDE calibration-evaluating fundamentals of clustering approaches to support the calibration process. Vehicles 2023, 5, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Andert, J.; Neumann, J.; Querel, C.; Scheel, T.; Aktas, S.; Ehrly, M.; Schaub, J.; Kotter, M. Hardware-in-the-loop-based virtual calibration approach to meet real driving emissions requirements. SAE Int. J. Engines 2018, 11, 1479–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, J.; Krysmon, S.; Dorscheidt, F.; Sterlepper, S.; Pischinger, S. Real driving emission calibration-review of current validation methods against the background of future emission legislation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserburger, A.; Didcock, N.; Hametner, C. Efficient real driving emissions calibration of automotive powertrains under operating uncertainties. Eng. Optim. 2023, 55, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, F.; Peng, Z.J.; Pei, Y.Q. The NOx emission characteristics of gasoline vehicles during transient driving cycles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 109, 103386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.D.; Ge, Y.S.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.X.; Su, S.; Li, C.B.; Tao, T.H. Evaluating the filtration efficiency of close-coupled catalyzed gasoline particulate filter (cGPF) over the WLTC and simulated RDE cycles. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.; Tomas, R.; Ferreira, E.; Bahmankhah, B.; Coelho, M.C. Driving aggressiveness in hybrid electric vehicles: Assessing the impact of driving volatility on emission rates. Appl. Energy 2021, 284, 116250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.C.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J.; Han, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.L. Investigating the impact of route topography on real driving emission tests based on large data sample at data window level. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB18352.6-2016; Limits and Measurement Methods for Emissions from Light-Duty Vehicles. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Xu, H.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.L.; Han, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.K. Energy management strategies for extended-range electric vehicles with real driving emission constraints. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumis, E.G.; Alafouzos, A.I. Study of diesel engine performance and emissions during a Transient Cycle applying an engine mapping-based methodology. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantz, H.; Jacobs, K.; Mecke, K. Utilizing Minkowski functionals for image analysis: A marching square algorithm. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 12, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R.E.; Dreyfus, S.E. Applied Dynamic Programming; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.K.; Du, B.C.; Han, J.L. Energy management strategies for hybrid diesel vehicles by dynamic planning embedded in real-world driving emission model. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 65, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jian, C. Constructing Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles for an Extended-Range Electric Vehicle via Dynamic Programming Guided by Real-World Trip Dynamics and Road Terrain. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111762
Chen Y, Xu H, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Jian C. Constructing Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles for an Extended-Range Electric Vehicle via Dynamic Programming Guided by Real-World Trip Dynamics and Road Terrain. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111762
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Hualong Xu, Li Zhang, Qing Zhang, and Chengzhi Jian. 2025. "Constructing Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles for an Extended-Range Electric Vehicle via Dynamic Programming Guided by Real-World Trip Dynamics and Road Terrain" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111762
APA StyleChen, Y., Xu, H., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., & Jian, C. (2025). Constructing Emission-Intensive Driving Cycles for an Extended-Range Electric Vehicle via Dynamic Programming Guided by Real-World Trip Dynamics and Road Terrain. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111762





