1. Introduction
Buildings are at the forefront of the global energy and climate challenge. The construction and operation of buildings collectively account for a significant share of the world’s energy consumption and carbon emissions. In 2023, the buildings and construction sector was responsible for about 34% of global energy-related CO
2 emissions and consumed ~32% of global energy, according to the latest UNEP/GlobalABC report [
1]. This level marked a rebound to the highest emission point on record, exceeding the pre-pandemic peak as energy demand in buildings reached roughly 132 exajoules, over one-third of global final energy consumption [
2]. Such figures highlight that improvements in building energy efficiency and shifts to low-carbon energy sources are imperative and urgent.
Despite incremental progress in efficiency, the buildings sector remains off track for international climate goals. Global building-related emissions have not decreased over the past 7 years and in fact grew about 1% from 2021 to 2022 [
2,
3]. Efficiency gains and cleaner technologies are being outpaced by growth in population, floor area, and comfort demands. For example, global floor area is expanding so rapidly, especially in emerging economies, that it offsets many efficiency improvements, “locking in” energy-intensive buildings for decades [
4]. Absent major changes, buildings are set to continue consuming enormous energy and emitting high carbon levels for the foreseeable future. Indeed, in 2022 the sector’s energy intensity (energy use per floor area) improved by only ~3.5%, a modest drop that still leaves it 15% above the trajectory needed to meet a net-zero by 2050 scenario [
2].
Encouragingly, a global consensus is emerging on the actions needed. The Paris Agreement’s first Global Stocktake highlighted that meeting climate targets requires doubling the rate of energy efficiency improvement by 2030 and tripling renewable energy capacity [
2]. The buildings sector is identified as a key player: global building energy intensity would need to fall by 37% from 2015 levels by 2030 to align with a net-zero path [
2]. Similarly, clean energy deployment in buildings must accelerate; for instance, as of 2022 only 6% of buildings’ final energy came from renewables, far behind the ~18% needed by 2030 [
2]. Investment levels also need a major boost: cumulative spending on efficient and zero-carbon buildings by 2022 should have been 40% higher (an extra
$800 billion globally) to get on track [
2]. These gaps underscore the scale of transformation required in how we design, construct, renovate, and operate buildings worldwide.
At the same time, there is a tremendous opportunity. It is estimated that half of the buildings that will exist in 2050 have not yet been built as of today [
2]. This means the decisions made now on new construction, by incorporating energy-efficient design, materials, and systems, can avoid future emissions for decades. Likewise, the vast existing building stock offers a chance for deep retrofits to dramatically cut energy use. With the right strategies, new buildings can be designed to be ultra-efficient or even net-zero energy, and old buildings can be upgraded to approach modern performance. The technologies needed to achieve high-performance building outcomes include high-performance insulation and glazing, efficient heat pumps, solar panels and smart control systems; such technologies are already mature, having been applied in zero-energy building projects that integrate envelope design, renewable energy systems and building energy management systems [
5] and demonstrated in occupied all-electric homes, where predictive control of heat pumps reduced daily heating energy use by approximately 19%, backup heating use by about 38% and maintained acceptable comfort levels even under cold outdoor conditions [
6].
The building sector exerts a profound impact on global energy consumption and climate change, yet it also represents one of the most significant avenues for cost-effective mitigation. Through the adoption of strategies ranging from improved design and advanced materials to intelligent energy systems and robust policy frameworks, it is possible to substantially reduce energy demand and associated emissions while ensuring healthy and comfortable indoor environments. This review synthesises insights from academic research and authoritative industry sources, including the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), and incorporates illustrative case studies and global initiatives to demonstrate practical pathways towards sustainable transformation.
This review is organized to provide a comprehensive examination of energy efficiency and decarbonization in buildings from a global perspective. Throughout this review, the term energy efficiency refers to the performance ratio of useful output to energy input, energy savings to the measured or estimated reduction in consumption achieved by efficiency or behavioural measures, and demand reduction to the lowering of end-use energy requirements through design or operational strategies. Following this introduction,
Section 2 describes the scoping review methodology, including eligibility criteria, search strategy, and data synthesis in accordance with the PRISMA-ScR framework.
Section 3 outlines the current energy and emissions profile of buildings worldwide to establish the context and urgency of action.
Section 4 discusses a spectrum of passive design strategies aimed at reducing energy demand, and
Section 5 focuses on advanced building envelope technologies that minimize thermal losses.
Section 6 examines efficient HVAC and lighting systems, along with intelligent automation and control technologies that optimize operational performance. In
Section 7, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar photovoltaics and solar thermal, is explored as a key strategy to decarbonize remaining energy needs.
Section 8 highlights the role of building energy modelling and simulation tools in supporting performance-driven design and retrofit decisions.
Section 9 considers retrofit approaches for existing buildings to achieve major efficiency improvements.
Section 10 explores the critical impact of occupant behavior on actual energy performance outcomes.
Section 11 analyses the influence of building policies, energy codes, and certification programs such as green building ratings in driving sectoral transformation.
Section 12 surveys emerging technologies and innovative directions that can support a systemic transition to low-carbon and sustainable buildings. Finally,
Section 13 concludes this paper.
2. Methodology
This scoping review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines, which are particularly suited for synthesizing evidence across emerging and multidisciplinary domains such as building energy efficiency and decarbonization. The primary objective was to systematically map the range of technological, policy, and market-oriented strategies relevant to reducing the operational and embodied carbon footprint of buildings. This study follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses–Scoping Review (PRISMA-ScR) methodology, which is appropriate for broad, multidisciplinary domains where evidence synthesis rather than quantitative meta-analysis is required. The approach focuses on mapping the scope, range, and nature of research on building decarbonization, rather than evaluating the statistical outcomes of individual studies. Although comprehensive, this review does not claim the exhaustiveness of a systematic review; instead, it aims to identify converging evidence, cross-domain interactions, and emerging trends across technologies, policies, and behavioural dimensions.
The review was guided by three overarching research questions:
What technological measures, both passive and active, are available to enhance energy efficiency and support the decarbonization of buildings across their lifecycle?
How do regulatory frameworks, building codes, and market-based instruments influence the adoption and scaling of these measures?
What future trends and innovations are expected to drive further improvements in building sector sustainability?
Eligibility Criteria: To reflect the multidisciplinary scope of the topic, eligible sources included peer-reviewed journal articles, conference proceedings, authoritative reports from intergovernmental organizations such as the International Energy Agency (IEA) and United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), national and regional policy documents, and industry white papers. Only sources explicitly addressing building energy efficiency or decarbonization strategies were considered. Studies were excluded if they focused exclusively on unrelated sectors, addressed energy efficiency without relevance to buildings, or were non-technical without analytical content. The inclusion period spanned from 2000 to 2025 to capture both established practices and recent innovations.
Information Sources and Search Strategy: Searches were conducted between July and September 2025 across Web of Science, Scopus, and IEEE Xplore using combinations of the following keywords: “building energy efficiency” OR “low-carbon buildings” OR “zero-emission buildings” AND “passive design” OR “building envelope” OR “retrofit” OR “renewable integration” OR “HVAC efficiency” OR “building policy” OR “energy codes” OR “green building certification”. Grey literature was identified through targeted searches of the IEA, UNEP GlobalABC, European Commission policy portals, and selected national energy agency repositories. Site-specific queries (e.g., site: iea.org, site: unep.org) and citation chaining from key references were used to ensure comprehensive coverage.
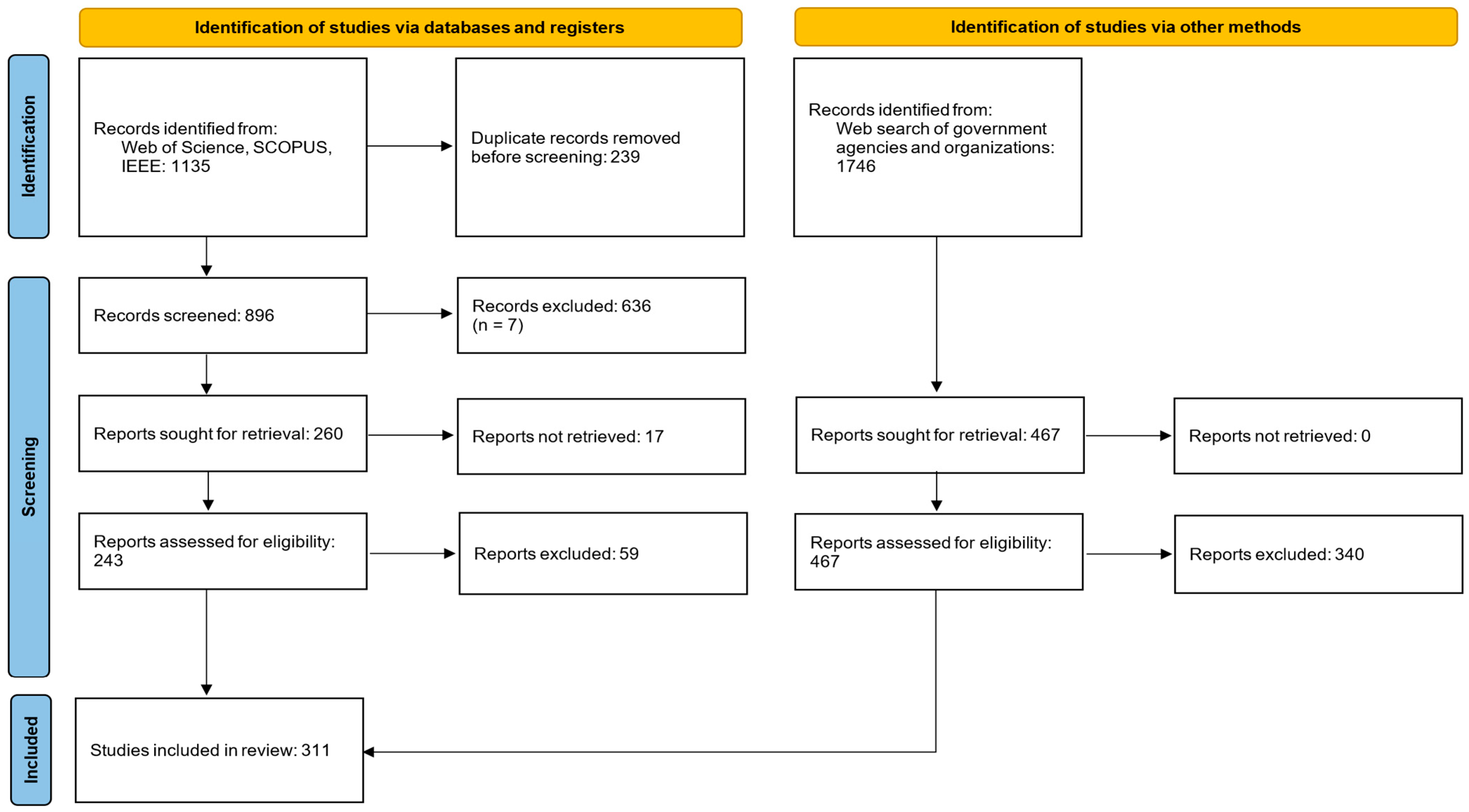
Source Selection: All retrieved records were imported into a reference management system, and duplicates were removed. Two reviewers independently screened titles and abstracts against the eligibility criteria. The full text of potentially relevant documents was assessed for inclusion. A PRISMA flow diagram,
Figure 1, documents the identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion stages, indicating the number of records retrieved from databases and grey literature, exclusions at each stage, and the final number of sources included in the synthesis.
Data Extraction and Synthesis: A structured data extraction form was used to capture key attributes from each source, including: (a) type and scope of energy efficiency or decarbonization strategy; (b) technological domain (e.g., passive design, HVAC systems, renewable integration, building automation); (c) policy or regulatory context; (d) reported performance outcomes (e.g., percentage energy savings, CO2 reduction); (e) identified barriers and enabling factors; and (f) projected trends or recommendations. Extracted data were verified by a second reviewer to ensure accuracy. Thematic synthesis was employed to organize findings into the core domains of the review: global building energy and emissions profile, passive and active efficiency measures, renewable integration, modelling tools, retrofitting, policies and certification, occupant behavior, and emerging innovations. Cross-cutting themes, such as the interaction between technology and policy or the role of behavioral engagement in achieving technical potential, were identified inductively and integrated into the narrative.
This methodology ensured comprehensive coverage of relevant literature, systematic source selection, and transparent synthesis, providing a robust evidence base to address the review’s research questions.
3. Global Energy and Emissions Profile of Buildings
Buildings consume roughly one-third of the world’s energy and produce a comparable share of energy-related greenhouse gas emissions. Breaking down the numbers, the operational energy use in buildings (for heating, cooling, lighting, appliances, etc.) accounts for about 30% of global final energy consumption and approximately 26% of energy-related CO
2 emissions, as of the latest assessments [
7]. If one also considers the indirect energy used to produce building construction materials (like cement, steel, and aluminum), the share rises further; overall, buildings operations plus construction are responsible for over one-third of global emissions [
7]. In absolute terms, building operations emitted on the order of 9–10 Gt CO
2 in 2022, and another ~2.5 Gt CO
2 came from manufacturing building materials, pushing the combined total to roughly 37% of global CO
2 [
2]. This carbon footprint encompasses emissions from on-site fuel combustion (direct emissions, e.g., natural gas for heating) as well as those from off-site power plants generating electricity or heat used in buildings (indirect emissions).
In terms of energy use, buildings span diverse end-uses and fuel types. Space heating and water heating dominate energy consumption in many regions, together they account for almost half of the energy use in buildings worldwide [
8]. Particularly in cooler climates, substantial energy is expended to keep indoor environments warm and provide hot water year-round. By contrast, space cooling (air conditioning and electric fans) has a smaller share globally but is the fastest-growing end-use, cooling-related electricity demand has more than tripled since 1990 and continues to surge in hotter regions and emerging economies [
9]. Already, air conditioners and fans consume nearly 20% of the electricity in buildings worldwide [
9], and without efficiency improvements, cooling energy demand could more than double again by 2050. Meanwhile, lighting and appliances/equipment make up most of the remainder of building electricity use. Lighting has historically been a major electricity load; for example, in commercial buildings of the U.S., it represents around 17% of electricity consumption [
10], but this is rapidly declining with the global shift to LED technology. Overall, electricity’s role is rising: electricity now provides about 35% of buildings’ final energy use (up from 30% in 2010) as many devices and systems electrify [
7]. The flip side is that fossil fuels like natural gas, oil, and coal still supply the other ~65% of building energy; direct fossil fuel use in buildings (for heating, cooking, etc.) has actually increased at ~0.5% per year since 2010 despite efficiency gains [
7]. This modest growth of fossil use, combined with the electricity share, underscores that decarbonizing building energy requires both reducing demand and cleaning the energy supply.
The building sector’s trajectory is currently not aligned with climate goals. In the IEA’s Net Zero Emissions (NZE) by 2050 Scenario, buildings sector emissions would need to decrease by roughly 9% per year from now until 2030, implying a drop of over 50% this decade [
7]. Energy consumption in buildings would need to peak and start falling, declining by ~25% by 2030 even as population and floor area rise [
7]. This would entail massive efficiency improvements (e.g., deep retrofits, ultra-efficient new construction) and a shift away from fossil fuel heating. In particular, to get on track, all new buildings should be “zero-carbon-ready” by 2030, meaning designed to operate with very low energy demand and fully decarbonized energy sources [
7]. In addition, at least 20% of the existing building stock would need to be renovated to zero-carbon-ready levels by 2030 under the NZE scenario [
7]. Currently, we are far from these targets; for instance, only a handful of countries have mandatory requirements approaching net-zero performance for new buildings, and the global renovation rate is only around 1% per year [
2]. Hence, at current rates it would take a century to upgrade the building stock.
Regional disparities define the global picture. Developed economies tend to have stagnant or declining building energy use (through efficiency and saturation effects), whereas developing regions see rapid increases. About 80% of new building floor area growth by 2030 will occur in emerging economies, often in countries that lack stringent energy codes [
2]. For example, an estimated 2.4 billion square meters of new floorspace was added in 2022 in countries with no building energy code at all [
2]. This represents an enormous missed opportunity if those new buildings are constructed with subpar efficiency; they could lock in high energy needs for decades. In contrast, many advanced economies have implemented and continuously tightened building energy codes, resulting in much lower energy use intensities for new constructions. The European Union, for instance, has seen total building energy demand stabilize and even start to fall, aided by policies and mild weather in some years [
7]. In the U.S., building energy use has grown only modestly relative to GDP, but extreme climate events (e.g., hotter summers or colder snaps) have caused spikes in heating/cooling demand [
7]. Globally, the trend is still upward: in 2022, total buildings sector energy consumption increased by about 1% year-on-year [
7], a second consecutive annual rise after a brief dip in 2020’s pandemic. This upward tick reaffirms that the current pace of efficiency improvement (around 1% per year historically) is insufficient; it needs to accelerate to ~4% per year in terms of reducing energy intensity to meet climate goals [
8].
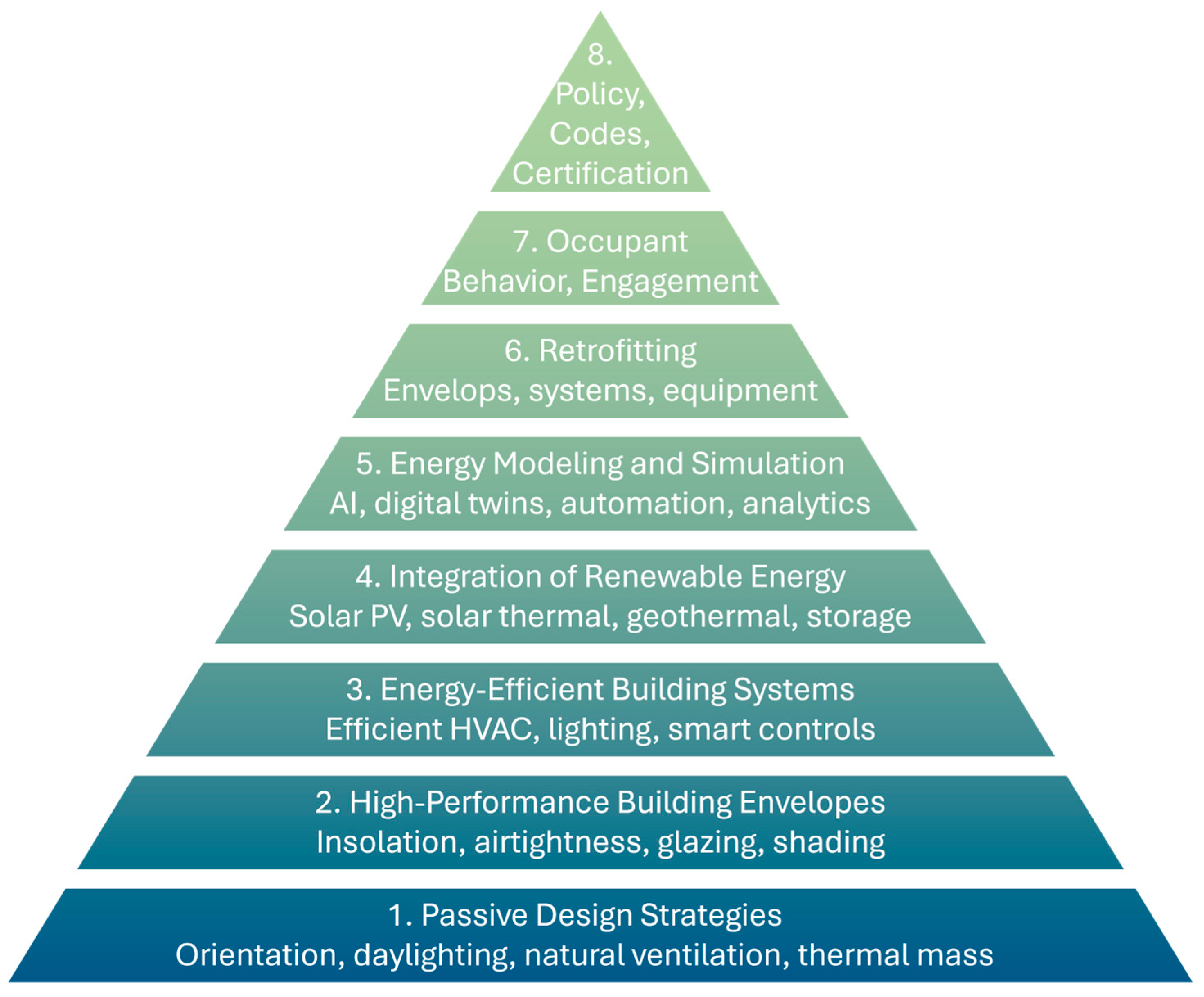
The buildings sector today remains one of the largest global sources of energy demand and carbon emissions, with current efficiency gains falling far short of the reductions required to meet international climate targets. This underscores the urgent need for a systematic and hierarchical approach to decarbonisation that prioritises demand reduction before supply-side substitution. To guide this analysis,
Figure 2 presents the conceptual framework adopted in this review. It organises building decarbonisation strategies into a sequential hierarchy that begins with passive design measures and high-performance envelopes, progresses through efficient building systems and renewable energy integration, and culminates in digital optimisation supported by behavioural engagement and policy interventions. This framework structures the narrative that follows, in which each subsequent section examines one layer of this hierarchy and synthesises evidence on its technical, economic, and regulatory implications.
4. Passive Design Strategies for Energy Efficiency
One of the most fundamental approaches to reduce building energy consumption is through passive design; that is, shaping a building’s form and features to naturally maintain comfortable conditions with minimal mechanical cooling or heating. Passive design measures take advantage of climate and site conditions (sun, wind, temperature, materials) to reduce or even eliminate the need for active energy-consuming systems. By preventing unwanted heat gains or losses and utilizing free solar heating, daylight, and ventilation, passive strategies directly cut the baseline demand on HVAC equipment and lighting. These strategies are effective across climates: in hot arid climates, combinations of shading, double glazing and natural ventilation can reduce residential energy consumption by up to ~24% [
11]; in tropical climates, optimal building orientation, cross-ventilation and adaptive façades lower cooling loads significantly [
12,
13]; in colder climates, high-performance insulation, thermal mass, glazing and airtight envelopes help maintain indoor comfort and reduce heating loads very substantially [
14]. Key passive design strategies include:
Building Orientation and Layout: By orienting a building properly on its site, designers can control solar exposure and wind. For example, facing the longest façade north/south (in many climates) can reduce excessive east–west solar gain. Locating and sizing windows to capture low-angle winter sun (for passive solar heating) while avoiding high-angle summer sun can significantly cut heating and cooling needs [
14]. Interior layouts can also place less-used or buffer spaces (stairwells, corridors) on the hot west side as thermal buffers.
Thermal Insulation and Mass: A well-insulated building envelope is critical for passive thermal control. Thermal insulation in walls, roofs, and floors helps retain heat in winter and exclude it in summer [
15]. Many studies confirm that adding insulation yields major savings; for instance, homes with insulated envelopes have been shown to use about 30% less energy on average than uninsulated homes in hot climates [
16]. Using high thermal mass materials (like concrete, brick, or stone) in the building structure can further even out indoor temperatures. Thermal mass absorbs heat during the day and releases it slowly at night, reducing temperature swings and shifting cooling loads to off-peak times.
High-Performance Glazing and Windows: Windows are typically the weakest link in the envelope thermally, but advanced glazing can substantially improve this. Double-glazed or triple-glazed windows with low-emissivity (low-E) coatings dramatically reduce heat transfer compared to single-pane glass, double glazing can cut heat loss through windows by 50% or more relative to single glazing [
17]. This keeps heat inside during winter and outside during summer. Proper window design also includes insulated frames and the use of inert gas fill (like argon) between glass panes. In hot climates, spectrally selective coatings can admit visible light for daylight while blocking infrared heat. As a result, efficient windows both lower heating needs and reduce unwanted solar heat gain, easing cooling loads.
Shading Devices: External shading can prevent a large fraction of solar radiation from hitting windows and walls. Overhangs, awnings, brise-soleil, and louvers are common shading devices that block high summer sun angles but still allow lower winter sun to penetrate (in heating-dominated climates). Movable shutters or adjustable louvers can respond to conditions. In tropical or hot regions, simply shading windows can reduce a building’s cooling energy by a significant amount, research in warm climates finds that shading and optimized glazing together cut cooling demand by around 18–28% [
18]. Additionally, shading of roofs (with roof overhangs or even installing photovoltaic panels above as a shade canopy) keeps the building cooler.
Natural Ventilation and Airflow: Exploiting natural breezes and buoyancy-driven flow (hot air rising) can often provide free cooling and fresh air [
19]. Passive ventilation design involves placement of operable windows, vents, or shafts to facilitate cross-breezes or stack ventilation. For instance, high vents at upper levels can let hot air escape (stack effect), drawing in cooler air from lower openings. Courtyards, atria, and wind catchers are traditional architectural elements that aid ventilation [
20]. In moderate climates and seasons, natural ventilation can sometimes wholly substitute for air conditioning, or at least reduce its usage hours, saving substantial energy.
Daylighting: Maximizing the use of natural light through windows, skylights, and light shelves reduces the need for artificial lighting during daytime. Good daylight design ensures adequate light penetration without causing glare or overheating. Light-colored interior surfaces and open layouts help distribute daylight. When effectively implemented, daylighting can cut lighting energy use by significant margins (often 50–80% in offices or schools) [
21], while also improving occupant well-being. However, it must be balanced with thermal considerations, hence innovations like tubular daylight devices or prismatic glazing that bring in light while limiting heat [
22].
These passive strategies, when integrated holistically, reinforce each other. For example, a case study in a hot climate might combine heavy roof insulation, reflective roofing, appropriately shaded windows, and strategic ventilation to maintain comfort with minimal cooling. Indeed, modeling studies in hot desert regions have shown that optimally designed envelope improvements (insulation, efficient glazing, shading, etc.) can achieve on the order of a 30–40% reduction in annual energy consumption [
16]. Field data likewise confirm large gains: a survey of homes in Saudi Arabia found that those with basic thermal insulation consumed about 32% less electricity on average (mostly for air-conditioning) than similar uninsulated homes [
16]. These savings represent a permanent reduction in load before any mechanical system is even considered.
Crucially, passive design is climate specific. The optimal set of measures in a cold, cloudy climate (where the priority is to conserve heat and allow solar gains) will differ from those in a hot, humid climate (where blocking sun and promoting ventilation are key). For instance, in a cold zone one might prioritize airtightness and south-facing windows for solar gain, whereas in a tropical climate one emphasizes shading, reflective roofs, and cross-ventilation. Designers often consult climatic data (temperature, humidity, sun path, wind roses) and use simulation tools to tune passive features appropriately. Building energy modeling often first assesses the impact of passive options in early design, since architectural decisions largely determine the magnitude of heating and cooling loads.
It is also worth noting that passive measures contribute not only to energy efficiency but also to resilience and comfort. A well-insulated, thermally massive building will stay habitable longer during power outages or extreme weather. Shaded and naturally ventilated spaces can provide comfort without grid power. These attributes are increasingly valued as we face more extreme heat waves and reliability challenges.
Globally, the promotion of passive design is recognised as a universally advantageous and cost-effective strategy that consistently delivers long-term benefits irrespective of future uncertainties [
14]. Leading green building standards and many national building codes now incorporate passive design requirements or incentives. The UNEP GlobalABC roadmap explicitly calls for “adopting passive design measures for all new buildings” as a priority action towards decarbonization [
2]. Implementation can range from modern high-tech solutions (like computer-optimized facade systems or electrochromic glass that dynamically tints to reduce glare and heat) to traditional vernacular techniques (like thick adobe walls and courtyard houses in desert regions). Both new construction and retrofits can benefit; for example, adding exterior window shading or extra insulation are common retrofit measures [
23]. While passive features sometimes add upfront cost (high-performance windows, insulation thickness, etc.), they typically pay back over time through energy savings and often come with co-benefits like improved comfort and lower HVAC maintenance [
24]. That is, passive design is the first and foundational pillar of energy-efficient buildings, upon which other strategies build.
In synthesis, passive design forms the foundation of the decarbonisation hierarchy by reducing intrinsic energy demand before any active system is introduced. As summarised in
Table 1, measures such as orientation, insulation, shading, glazing, and natural ventilation consistently deliver 20–40% reductions in thermal loads and up to 80% reductions in lighting energy use [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Their integration ensures that subsequent envelope, system, and renewable strategies operate on an inherently low-demand baseline, amplifying the overall energy and carbon reduction potential.
5. High-Performance Building Envelopes
Closely related to passive design, the concept of a high-performance building envelope deserves focused attention. The building envelope, that is the walls, roof, windows, foundation, and doors, is the barrier between indoors and outdoors. Its quality largely dictates how much energy is required to maintain comfortable indoor conditions. An optimized envelope minimizes heat transfer (both heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer) and uncontrolled air leakage, thus sharply cutting the heating and cooling loads [
25]. Upgrading envelope performance is often the most impactful retrofit one can do for an existing building, and for new buildings it is a cornerstone of achieving low-energy use [
26]. Key components and strategies for high-performance envelopes include:
Effective Insulation Systems: As noted earlier, insulation materials (fiberglass, mineral wool, foam boards, cellulose, etc.) slow down conductive heat flow through walls, roofs, and floors. The effectiveness of insulation is measured by its R-value (resistance) or inversely U-value (transmittance). High-performance envelopes target very low U-values. For example, Passive House standards (an international ultra-low-energy building standard) [
27] typically require wall U-values on the order of 0.10–0.15 W/m
2K, which corresponds to thick continuous insulation layers. Beyond thickness, quality installation (avoiding gaps or “thermal bridges” where heat can bypass insulation) is vital. Studies consistently show dramatic energy savings from insulation: one review found that adding or improving insulation can cut heating and cooling demand by 20–40% across varied climates [
16]. Even moderate levels of insulation yield diminishing returns at some point, but in most of the world’s existing buildings (especially older ones), current insulation levels are far below optimal. Retrofitting with exterior insulation and finish systems (EIFS) or cavity/blown insulation is a common strategy to upgrade thermal performance without major interior disruption [
28]. Importantly, insulation helps with summer cooling as well, a well-insulated roof, for instance, keeps out intense sun heat. In hot climates, roof insulation combined with reflective or “cool roof” coatings can substantially reduce AC loads [
29].
Thermal Bridge Mitigation: A thermal bridge is a path of least resistance for heat, often occurring at material junctions (e.g., a concrete slab edge or metal wall tie that spans from inside to outside) [
30]. High-performance design pays attention to eliminating or insulating these bridges. Techniques include wrapping building structures in continuous insulation, using thermally broken connectors, and careful design of penetrations [
31]. By addressing thermal bridges, one can improve overall envelope performance by several percentage points and also avoid cold spots that can cause condensation or mold.
Advanced Windows and Glazing: Windows deserve special emphasis because they typically have much higher U-values than insulated walls, even a good double-glazed window might be U = 1.1–1.5 W/m
2K, whereas an opaque wall might be 0.3. Therefore, window improvements yield big gains. Modern low-E double glazing with argon fill can cut heat losses roughly in half compared to single glazing [
17]. In cold climates, triple-glazed units with two low-E coatings and krypton/argon gas can approach or even below U = 0.7 W/m
2K, rivaling wall performance, these are used in Passive House projects commonly. In hot climates, specialized solar-control glass significantly reduces solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) while still transmitting light [
32]. Additionally, window frames (often aluminum, vinyl, wood, or composites) should be thermally broken or insulated, as frames can account for 10–20% of window heat loss. Another aspect is airtightness of window assemblies, high-performance windows come with robust weatherstripping and multi-point locks to ensure minimal air leakage when closed. The benefits of window upgrades are not just theoretical; for instance, replacing single-glazed windows with efficient double-glazing in a typical home can save on the order of 15% of heating energy in temperate climates and improve comfort by eliminating drafts [
17]. Though window retrofits can be costly, the non-energy benefits (better comfort, noise reduction) and carbon savings increasingly justify them, especially as part of deeper retrofit packages.
Airtight Construction: Uncontrolled air leakage through cracks and gaps in the envelope can be a huge energy drain; essentially, conditioned indoor air escaping and outside air infiltrating, which the HVAC then has to heat or cool [
33]. High-performance envelopes focus on achieving a high degree of airtightness. This involves careful sealing of all joints, penetrations (pipes, wiring, vents), and use of air barriers (special membranes or taped sheathing) in walls and roofs [
34]. Airtightness is often measured by blower door tests in terms of air changes per hour at 50 Pa (ACH50) [
35]. Traditional old buildings might have 5–10 ACH50 or higher (very leaky), whereas energy-efficient new buildings target below 3, 2, or even <1 ACH50. Passive House requires ≤0.6 ACH50, essentially extremely tight construction. The energy impact is significant: reducing infiltration can cut heating loads notably in cold climates and also improve cooling efficiency by keeping hot humid air out. However, a tight building then requires proper mechanical ventilation for fresh air (often with heat recovery—discussed later), to ensure indoor air quality.
Cool Roofs and Green Roofs: The roof is a critical envelope element, especially for low-rise buildings where it’s a large fraction of surface area. In hot climates or summer conditions, cool roofs with high solar reflectance and high thermal emittance (often white or light-colored coatings) can stay much cooler under the sun, thereby reducing heat transfer inside. For example, reflective roofs have been shown to remain more than 28 °C cooler than dark roofs under similar conditions, with cooling energy savings of 14–22% in tropical/subtropical climates [
36,
37,
38]. Meanwhile, green roofs provide thermal mass, shading, and evapotranspiration cooling, which reduce heat flux into the building and mitigate urban heat island effects. Green roofs reduce cooling loads significantly in hot climates [
39], and also provide insulation benefits in winter, along with environmental co-benefits [
40,
41].
Dynamic Facades: At the cutting edge, some high-performance envelopes incorporate dynamic or responsive elements—for example electrochromic glazing that can tint on demand to reduce glare and heat, or automated exterior blinds that deploy based on sun sensors. For instance, EC glazing has been found to reduce total energy consumption by 22.7–28.7% for windows oriented east, south, and west in a multi-aspect building, relative to static glazing [
42]. There are also phase-change materials (PCMs) integrated in walls that absorb and release latent heat to shave peak temperatures, delay peak indoor heat loads, and reduce cooling demand [
43]. These advanced features aim to adapt the envelope’s thermal properties in real-time to weather and occupant needs, optimizing energy use. While currently more expensive, as technology progresses they could become more common in high-performance designs [
44].
High-performance envelopes yield multiple benefits beyond energy. They improve thermal comfort, since surfaces like walls and windows stay closer to room temperature, avoiding drafts or cold radiation. They often improve acoustic comfort due to added mass and insulation (quieter interiors). They also enhance building durability by controlling moisture, as a well-insulated and airtight envelope with proper vapor barriers prevents condensation within assemblies and mold growth. These co-benefits make envelope upgrades an attractive investment, not just an energy measure.
It is important to consider that an envelope must be designed as a system. For example, if you make a building extremely airtight and insulated, you must also provide ventilation (preferably heat-recovery ventilation) to avoid indoor air becoming stale or humid. If you heavily shade a building to reduce cooling loads, you may need to compensate with design for daylight or a slight increase in lighting energy. Integrated design is needed to balance these aspects optimally.
Globally, building energy codes are increasingly incorporating higher envelope performance requirements. Many jurisdictions now mandate minimum insulation levels or window performance for new buildings, including the EU’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive [
45]. EU have moved toward “net-zero energy” and “zero-emission” building codes which essentially demand a combination of excellent envelope efficiency and on-site renewables [
46]. However, enforcement and compliance remain challenges in some areas, as specifications do not always translate to quality construction on site. Training of builders and use of on-site testing, like blower doors or infrared thermography to check insulation continuity, can help ensure real-world performance.
A high-performance envelope drastically reduces the heating and cooling needs of a building by insulating and sealing it against the external environment, while judiciously controlling solar gains and losses through advanced glazing and shading. It is the first line of defense in minimizing energy demand. Numerous studies and real-world projects validate that investing in the envelope yields large energy returns: for instance, deep retrofits focusing on insulation, windows, and airtightness in cold-climate houses commonly achieve 50% or more reduction in heating energy [
23]. Similarly, in hot climates, an upgraded envelope can turn a once-overheated building into one that needs only modest cooling.
High-performance envelopes consolidate passive gains by controlling heat transfer and air leakage with measurable precision.
Table 2 summarises the dominant envelope technologies, which achieve 20–40% reductions in heating and cooling energy through improved insulation and airtightness, while advanced glazing and cool roofs contribute an additional 14–30% [
16,
17,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41]. Within the hierarchy, the envelope defines the building’s thermal boundary, enabling smaller HVAC systems, higher comfort, and durable performance under future climatic stress.
6. Energy-Efficient Building Systems and Equipment
Even with the best passive design and envelope, most buildings will still require active systems for heating, cooling, ventilation, lighting, and powering appliances. These building service systems present enormous opportunities for efficiency gains through improved technologies and smarter operation. Over the past decades, there has been substantial progress in making HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and other building equipment more energy-efficient, just think of the evolution from incandescent bulbs to LED lights, or from fixed-speed air conditioners to variable-speed heat pumps [
47]. Key building systems for maximizing energy efficiency include:
Heating Systems: Heating can be provided by various means, including furnaces or boilers (burning gas, oil, biomass), electric resistance heaters, or increasingly heat pumps. Space and water heating together consume about 50% of building energy globally [
8], so efficiency improvements here are critical. Modern condensing gas boilers, for example, can reach over 90% thermal efficiency by capturing latent heat from flue gases (versus older boilers at 70–80%). However, the bigger revolution is shifting to electric heat pumps, which move heat rather than generate it by burning fuel. Heat pumps (air-source or ground-source) can achieve efficiencies of 300–400% (COP of 3–4) under favorable conditions, meaning they deliver 3–4 units of heat per unit of electricity input. According to IEA, heat pumps are a “central technology for decarbonizing heat” and their sales are growing at record rates [
8]. In many climates, a heat pump can reduce heating energy consumption (and emissions) drastically, especially if replacing electric resistance heat or inefficient boilers. Even in cold climates, new cold-climate heat pumps can perform well down to very low outdoor temperatures [
48]. Aside from the heat source, distribution efficiency matters too, well-designed hydronic (water-based) or air distribution systems with insulated ducts/pipes and advanced controls (like thermostatic radiator valves or smart thermostats) avoid losses and overheating.
Cooling and Air Conditioning: Cooling demand is increasing rapidly worldwide, and ensuring that new air conditioning systems are highly efficient is essential to prevent a future “AC energy crunch.” Global residential cooling demand is projected to rise steeply to 2050, particularly in developing countries, but efficiency improvements and policy interventions can reduce this growth substantially [
49] [
50]. Significant advances in efficiency have already been achieved. The transition from fixed-speed compressors to inverter-driven units enables modulation of capacity and reduces energy losses associated with on–off cycling [
51]. Performance metrics such as the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) have steadily improved, and best-in-class room air conditioners now achieve values approximately twice those of two decades ago [
52]. According to the International Energy Agency, effective policies could double average efficiency levels worldwide by mid-century and cut projected cooling energy demand growth by nearly half [
9]. High-efficiency heat pumps further enhance flexibility by providing both heating and cooling, thereby addressing two demands with a single investment. Natural cooling techniques, as emphasised in passive design strategies, reduce reliance on mechanical cooling, while in suitable climates evaporative or ground-coupled systems offer additional low-energy alternatives [
51]. In large commercial buildings, modern centrifugal and screw chillers with variable speed drives already reach coefficients of performance of 6–8 or higher, compared to older technologies [
51]. District cooling systems, which distribute centrally produced chilled water across multiple buildings, can also achieve energy savings through economies of scale and thermal storage integration [
49]. A major challenge, however, is the accelerating uptake of air conditioning in developing countries, where demand is expected to expand rapidly. Strong policy measures are needed to ensure that only high-efficiency units employing low global warming potential refrigerants are deployed.
Ventilation and Indoor Air Quality Monitoring: Modern energy-efficient buildings often incorporate mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (MVHR). These systems use heat exchangers to transfer heat between outgoing stale air and incoming fresh air, recovering typically 70–90% of the heat. Case studies in the UK and elsewhere have shown that MVHR can significantly reduce heat loss and improve indoor comfort when correctly installed and commissioned [
53,
54]. A recent review of mechanical ventilation strategies confirms that heat recovery systems often approach 90% efficiency, making them one of the most effective measures for reducing ventilation-related heating loads in airtight buildings [
55]. This allows continuous ventilation, which is critical for health in airtight buildings, with only a minimal energy penalty. In winter, MVHR pre-heats incoming cold air with exhaust air; in summer, some systems can bypass or use enthalpy exchangers to manage humidity. Fans used in ventilation should be efficient and appropriately sized, while ductwork must be airtight and well-designed to minimize pressure drops. In many commercial and institutional buildings, demand-controlled ventilation (DCV) is applied to save energy. Using CO
2 or occupancy sensors to adjust ventilation rates only to what is needed prevents over-ventilation and avoids unnecessary fan and conditioning energy use. Empirical studies further support these findings: CO
2-based DCV has achieved between 9% and 33% HVAC energy savings in office environments [
56], and DOE studies report average savings of ~17.8% across U.S. climate zones compared to occupancy-only sensing [
57]. Efficient ventilation therefore contributes simultaneously to lowering energy use and ensuring better air quality [
58].
Lighting Systems: The transformation of lighting has been one of the biggest energy-efficiency success stories. LED lighting has largely replaced incandescent and is rapidly replacing fluorescent lighting. LEDs use a fraction of the energy, they are about 75% less than incandescent bulbs and 30–40% less than typical fluorescent lamps, while lasting far longer [
59]. According to analyses, LEDs can reduce lighting energy consumption by 50–70% or more in many cases compared to conventional technologies, particularly in residential and commercial lighting retrofits. For example, replacing fluorescent troffers with LED fixtures has yielded 20–60% savings in U.S. retrofit projects using LED kits and controls (U.S. DOE “LED Retrofit Kits, TLEDs, and Lighting Controls”) and replacing lighting in large federal buildings (Forrestal Building) showed savings estimates up to 70% for certain retrofit options (DOE Headquarters Lighting Retrofit) [
60]. Globally, widespread LED adoption is projected to save hundreds of TWh of electricity annually and avoid on the order of 1.4 billion tons of CO
2 emissions if fully implemented; one scenario from the JRC “Status of LED Lighting World Market” estimates up to ~1400 TWh/year savings in the U.S. by 2035 under best-available technology trajectories, with comparable scaled effects globally, if similar adoption and efficiency improvements occur [
61]. In addition, smart lighting controls amplify savings: occupancy sensors that turn off lights when rooms are vacant and daylight sensors that dim artificial lights when daylight is sufficient both contribute significant energy reductions. For example, lighting energy savings of ~20% have been observed in office retrofits using occupancy sensors plus daylight dimming [
62]; occupancy sensors themselves have been shown to reduce lighting loads by between 20 and 60% depending on building type and usage when combined with daylight control [
63].
Appliances and Plug Loads: In residential and commercial buildings, numerous devices such as refrigerators, cooking equipment, computers, servers, elevators, etc., collectively draw considerable power, often termed “plug loads” or equipment loads. Efficiency standards like ENERGY STAR [
64] and technology improvements have significantly reduced the energy demand of appliances. For example, a modern refrigerator uses only a quarter of the electricity of a typical 1970s model due to better compressors, insulation, and controls; today’s refrigerators use about 25% of the energy that 1970s models did [
65] and averages have dropped from ~1800 kWh/year in older models to ~500 kWh/year in many modern ones of comparable size [
66]. Washing machines and dishwashers have improved with motor and heater efficiencies and smarter cycles. Water heating has new efficient options like heat pump water heaters (using 2 to 3 times less energy than electric resistance) and solar thermal water heaters that can meet 50–70% of hot water needs from the sun in sunny climates. In office settings, computers and IT equipment have become more efficient, such as LCD or LED monitors versus old CRTs, and power management features in PCs. However, the proliferation of gadgets and electronics sometimes offsets these gains as many new types of devices are adopted by consumers. To manage this, strategies like advanced power strips that eliminate standby power draw, or scheduling systems that power down equipment after hours, are useful. Commercial buildings often face large miscellaneous loads like server rooms; employing efficient servers, virtualization, and cooling optimization in data closets can curb energy use.
Building-Level Controls and Integration: Beyond the efficiency of individual pieces of equipment, how systems are controlled and integrated is crucial. A prime example is thermostat control, where programmable thermostats are set to reasonable setpoints and adjusted during unoccupied periods or at night to prevent energy waste. Even a 1 °C widening of the thermostat band can save a few percent of heating/cooling energy. Modern smart thermostats learn occupancy patterns and self-adjust, often yielding 10–15% savings in homes by trimming heating/cooling when not needed [
67]. In commercial buildings, centralized Building Management Systems (BMS) or Building Automation Systems (BAS) coordinate all the HVAC, lighting, and safety systems. They can implement optimal start/stop (turning systems on at the latest possible time to still achieve comfort by occupancy), optimize energy use based on demand (e.g., shedding non-critical loads at peak times), and monitor performance. According to experts, simply commissioning and properly using a building automation system can typically cut building energy use by 5–15% through better scheduling and control [
68]. If all existing commercial buildings optimized their controls and fixed operational issues, studies suggest average savings on the order of 20–30% could be achieved [
69], essentially eliminating energy waste like simultaneous heating and cooling, lights on in empty areas, or fans running at high speed unnecessarily [
70]. Many of these measures cost little (like reprogramming controls or repairing a sensor) compared to the energy saved [
68].
Efficient Energy Distribution: Another often overlooked aspect is the efficiency of distribution systems, the ducts, pipes, and zone controls that deliver heating, cooling, and ventilation. Leaky air ducts in many buildings can lose 20–30% of the heat or cool air before it reaches rooms. Sealing ducts and insulating those running through unconditioned spaces prevents those losses [
71,
72]. Likewise, hot water distribution for heating or domestic hot water should be insulated to avoid heat loss, and pumps should be efficient with Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) control [
73]. Zoning (separating a building into areas with independent temperature control) prevents over-conditioning unused areas. For example, not all parts of a building need the same temperature at the same time; by zoning, you can cool only the occupied meeting rooms rather than the whole floor [
74].
Renewable-ready Systems: While focusing on efficiency, it is also wise to ensure systems are compatible with renewable energy integration. For instance, using electric heat pumps and electric cooking (induction stoves) instead of gas appliances makes it easier for a building to be powered entirely by clean electricity [
75]. Thermal storage (like water storage for heat/cold or building mass activation) can enable flexibility, allowing equipment to run when renewable power is abundant and pause when it is scarce [
76]. These considerations verge into the next topic of renewables, but it is worth noting that an energy-efficient building system not only reduces consumption but can also interact intelligently with the grid (demand response) to further overall energy sustainability [
77,
78].
For every major building system there are high-efficiency solutions available today, from condensing boilers and heat pumps for climate control to LEDs for lighting and ENERGY STAR appliances for plug loads. Employing these yields immediate energy and cost savings. When compounded across all systems, the reduction in an efficient building’s energy use relative to a standard one can be tremendous. For instance, a new green office building might use 50–70% less energy per square meter than a similar office building built decades ago, thanks to better equipment and controls in every subsystem. In existing buildings, systematic retro-commissioning and equipment upgrades often find 10–30% savings as “low-hanging fruit” [
79,
80]. When designing or retrofitting a building, it is ideal to right-size the systems after improving the envelope and passive features. A tighter, better insulated building will need a smaller furnace or chiller. Avoiding oversizing, which is common in practice due to safety factors, is important because oversized equipment cycles on/off inefficiently and costs more upfront. Integrated design will downsize HVAC equipment in concert with envelope upgrades and passive cooling/heating measures. Importantly, efficient systems not only cut energy but also often offer better performance, in terms of quieter HVAC, more consistent temperatures, better light quality, etc. The investment in efficiency typically pays back through utility savings, especially as energy prices or carbon costs rise.
Energy-efficient systems convert the reduced thermal demand of efficient envelopes into optimised operational performance. As shown in
Table 3, advanced heat pumps and condensing boilers lower heating energy by 30–70% [
47,
48], heat-recovery ventilation reduces ventilation losses by up to 90% [
53,
54,
55], and LED lighting with smart controls cuts electricity use by 50–70% [
59,
60,
61,
62,
63]. In the decarbonisation hierarchy, these technologies form the operational engine that transforms architectural efficiency into measurable carbon mitigation.
7. Integration of Renewable Energy in Buildings
After minimizing energy demand through passive design and efficient systems, the next step toward sustainable buildings is to supply the necessary energy from renewable sources. Integrating renewable energy technologies into buildings can drastically reduce or even eliminate reliance on fossil fuels for operating power, heating, and cooling. This section explores the main renewable options applicable at the building scale, their benefits, and considerations for implementation.
Solar Photovoltaics (PV): The most widely adopted renewable for buildings is solar PV, which converts sunlight into electricity. Rooftops and facades offer prime real estate for PV installation, effectively turning buildings into mini power plants. Rooftop solar panels can often generate a significant portion of a building’s electricity needs, especially for low-rise buildings with sufficient roof area relative to their consumption. For instance, a typical residential PV system of 5 kW might produce around 5000–7000 kWh per year depending on sun hours [
81]. Many commercial and industrial buildings have large flat roofs where solar arrays of hundreds of kW can be installed with little interference to operations. As of the mid-2020s, solar PV has become very cost-effective as the price of modules has plummeted, and many jurisdictions offer net metering or feed-in tariffs that allow building owners to sell excess solar power back to the grid or get credits. This can make on-site solar financially attractive. Furthermore, building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) are emerging, where PV cells are built into building materials like roof shingles, facade cladding, or windows (semi-transparent PV glass). Although BIPV can be costlier or less efficient than standard panels, it provides aesthetic integration and dual functionality, by acting as part of the weather enclosure while generating power. Given the global context, widespread adoption of building solar could allow rooftops alone to supply a very large share of demand: in the United States rooftop PV could provide about 39% of electricity sales [
82], while global analyses indicate rooftop PV could meet 20–50% of electricity demand in many countries [
83,
84]. In perspective, by 2022, there was over 1.2 terawatts of PV capacity installed globally (all scales), and this rose to over 1.6 terawatts by early 2024 [
85]. In some sunny regions, buildings with solar plus batteries are becoming net-zero energy on an annual basis, producing as much electricity as they consume, feeding into the grid during the day and drawing power at night. Achieving net-zero is easier for low-energy buildings (hence the importance of efficiency first). It is harder for high-rise buildings or those with limited area, but even there, solar can contribute a fraction of needs or be installed on neighboring structures (parking canopies with PV, etc.) [
86]. Notably, solar PV helps decarbonize not just electricity use but, indirectly, heating/cooling if those are electrified (e.g., running a heat pump on solar power).
Solar Thermal (Water Heating and Air Heating): Another direct use of solar is for solar thermal collectors, which capture the sun’s heat. The most common application is solar water heaters. Typically, roof-mounted collectors (either flat-plate or evacuated tube design) circulate a fluid that gets heated by the sun, and this heat is stored in a water tank for domestic hot water or space heating support. Solar water heating is a mature, cost-effective technology especially in regions with good sunshine and significant hot water needs (e.g., residential hot water, hotels, hospitals) [
87]. For example, countries like China, Turkey, Greece, and Israel have millions of households using solar water heaters, China alone accounts for roughly two-thirds of the world’s capacity, with over 690 million square meters of solar thermal panels installed by 2018 [
88]. A typical solar thermal system can supply 50–80% of a household’s annual hot water demand [
89], drastically cutting fuel or electricity use for water heating. Paybacks are often just a few years in sunny climates with expensive fuel. There are also solar air heaters (less common) that warm ventilation air and large-scale solar thermal arrays that feed into building heating or even district heating networks. In some cases, seasonal thermal storage can be employed, e.g., collecting solar heat in summer and storing in a large, insulated water tank or in ground boreholes to use in winter, but this is complex and site-dependent [
90].
Heat Pumps with Renewable Energy: While not a direct renewable source, coupling heat pumps with renewable electricity (like solar PV or wind) is an important integration strategy. When a building has solar PV, often the best use is to power a heat pump for heating/cooling and water heating, effectively converting solar power to thermal services with high efficiency [
91]. This is the concept behind net-zero energy buildings (NZEBs) and all-electric buildings: use an efficient electric-based design and provide the electricity via renewables [
92]. For example, a net-zero house might have extra solar panels in summer that feed into the grid, counterbalancing the electricity a heat pump uses from the grid in winter, achieving net zero over the year [
93]. Some advanced homes even use solar direct to heat in a simpler way, e.g., surplus solar PV midday can be diverted to an electric water heater (thermal storage) for later use, which can be more efficient than storing electricity in batteries depending on circumstances [
94].
Wind Power: On-site small wind turbines are another possibility, though far less common than solar for buildings. This is because wind turbines require sufficient wind speeds and tend to work best when mounted on towers clear of obstructions, conditions not often met in urban or suburban building settings [
95]. Small roof-mounted turbines exist, and architectural wind installations on tall buildings have been tried, but issues with turbulence, noise, and structural vibration have limited their uptake. Generally, small wind might be viable for rural properties or very tall free-standing buildings, but in cities solar is usually the preferred on-site renewable. That said, a few showcase projects have integrated wind; for instance, the Bahrain World Trade Center installed wind turbines between its twin skyscrapers [
96], and some eco-resorts use building-mounted wind. Another example: a case study in Istanbul integrating 40 small vertical turbines showed ~9.3% energy savings [
97]. Small-scale wind reviews confirm minimal contribution globally compared to solar, particularly in built-up areas, because of low wind speeds, turbulence, and site constraints [
95,
98].
Geothermal and Ambient Energy: Buildings can tap into renewable thermal energy from the ground or water bodies. Geothermal heat pump systems (also known as ground-source heat pumps) leverage the relatively stable ground temperature a few meters below the surface as a heat source in winter and heat sink in summer. While the heat pump itself uses electricity, the heat extracted from the ground is renewable in the sense that the ground is recharged by solar heat and geothermal heat from earth’s interior. Ground-source heat pumps are extremely efficient (often achieving COPs of 4 to 5) because of the mild source temperatures, thus significantly lowering the electric energy needed for heating/cooling [
99]. They are popular in certain regions (e.g., widespread in Sweden, Germany, the U.S. midwest, China for some district systems) especially for larger buildings or clusters where drilling boreholes is economical [
100,
101]. Another form is aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) or using lakes/oceans (water-source heat pumps) to draw renewable thermal energy [
102]. These systems enable a kind of renewable heating/cooling by shifting thermal energy seasonally. For example, some building complexes store cold in aquifers in winter to help with summer cooling, and vice versa. ATES systems have been demonstrated to provide large-capacity seasonal storage for buildings [
103], and studies show that low-temperature ATES can efficiently deliver heating and cooling while maintaining sustainable heat transport processes [
104]. Recent work also points out both technical and policy barriers as well as opportunities for wider deployment [
105].
Biomass and Other Renewables: In some contexts, biomass (wood pellets, biogas, etc.) is used in efficient boilers or CHP (combined heat and power) units to provide renewable heating and power [
106]. For instance, a rural campus might have a modern pellet boiler for heating instead of oil, since sustainably harvested biomass is considered carbon-neutral. Biogas from waste can be used in fuel cells or micro-turbines for buildings [
107]. Solar passive heating (as discussed in the passive design section) is effectively a renewable contribution too, as south-facing windows provide free solar heat gain. Daylight is a renewable source for lighting during the day. Even cooling can have renewable help via solar absorption chillers (solar heat driving an absorption refrigeration cycle) [
108,
109] or via nighttime radiative cooling panels on roofs [
110,
111]. However, these are niche compared to PV and solar water heating.
Energy Storage and Management: Key to maximizing renewable use in buildings is often energy storage that ca balance the mismatch between supply (sun, wind) and demand. Battery storage costs have been dropping, leading to more buildings installing batteries alongside PV. This allows storing excess midday solar to use in the evening, increasing self-consumption of solar energy and providing backup power [
112,
113]. Thermal storage, like insulated water tanks for solar hot water or even phase-change materials in air conditioning systems (ice storage), can store renewable thermal energy [
114]. Smart controls are used to manage when to draw from or charge storage, when to import or export to the grid, etc. For example, a building energy management system might pre-cool the building when solar power is abundant, effectively storing “cooling” in the building’s thermal mass, to reduce grid cooling later [
114].
Despite ongoing efforts, the buildings sector as a whole is still lagging in renewable uptake. In 2022, only about 6% of the final energy use in buildings was supplied by modern renewables (excluding traditional biomass) [
2], which is far below what is needed for climate targets. The target is to triple that share in the coming decade (to ~18% by 2030) [
2]. Reaching that will require not just on-site renewables but also cleaner grids, since buildings draw from the electricity grid. On the on-site front, solar PV is expected to do the heavy lifting, it is increasingly common to see new buildings with solar panels by design (some jurisdictions even mandate solar on new commercial or residential buildings). Net Zero Energy Buildings, which produce as much energy as they consume annually, are becoming more feasible and are being encouraged or required in places. The EU has nearly Zero-Energy Building mandates for new construction [
7], and California has net-zero goals for new homes [
115].
Case studies around the world demonstrate the possibilities: for instance, Australia and California have many net-zero homes thanks to good sun and progressive policy [
116]; in Europe, plus-energy buildings exist that generate surplus via solar and feed neighbors [
117]. In India, some IT campuses run partially on rooftop solar and biogas [
118]. Green Building certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) [
119] and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) [
120] give credit for on-site renewables, spurring adoption. Additionally, community or district solutions are emerging; that is, if one building cannot host enough renewables (e.g., a skyscraper), it can invest in nearby off-site renewables or be part of a district energy scheme that uses renewables.
Furthermore, it is important to note that building-integrated renewables also benefit the broader energy system by decentralizing generation and often producing power near the point of use will reduce transmission losses. A high penetration of photovoltaic on buildings can, however, create grid management challenges (e.g., backflow on distribution feeders at noon). To address this, many buildings with renewables will need to incorporate smart inverters and follow grid codes to help stabilize voltage and frequency. In the future, aggregating buildings with solar and batteries into virtual power plants could be a way to harness them for grid services. On the flip side, buildings can optimize their usage to times when their renewables produce. For example, scheduling EV charging at midday when the building’s solar array is active.
Hence, the integration of renewables transforms buildings from passive energy consumers into active participants in clean energy production. By covering roofs with solar panels, using the sun’s heat for hot water, tapping stable ground temperatures, and possibly coupling with storage, buildings can drastically reduce their net energy imports. Some can achieve net zero or even net exporters of green energy. This is a critical piece of the decarbonization puzzle: even after maximizing efficiency, fossil fuels in buildings (for heating, cooking, etc.) and grid electricity need to be replaced by renewables. Through a combination of on-site generation and drawing from increasingly renewable grids, a vision of zero-emission buildings is attainable.
Renewable energy integration represents the transition from efficiency to decarbonisation.
Table 4 synthesises the principal renewable pathways, where rooftop PV can supply up to 100% of a low-energy building’s annual electricity demand [
81,
82,
83,
84], solar thermal systems cover 50–80% of hot-water needs [
87,
88,
89], and geothermal heat pumps achieve seasonal coefficients of performance of 4–5 [
99,
100,
101]. Within the hierarchy, these measures replace residual fossil-based demand with clean generation, positioning buildings as active prosumers in the energy system.
8. Building Energy Modeling and Simulation
Designing a low-energy or net-zero building, or even deeply retrofitting an existing one, is a complex task with many interacting variables. To make informed decisions, architects and engineers rely on Building Energy Modeling (BEM) and sophisticated simulation software to predict a building’s energy performance before it is built, or to analyze an existing building’s behavior. Building energy modeling is essentially a computer-based physics simulation of the building, its systems, and how they respond to weather and occupant use patterns [
121]. This has become an indispensable tool in modern building design and retrofit planning, as well as for code compliance and green certifications.
A whole-building energy model takes into account the geometry of the building, the thermal properties of envelope materials, the efficiency and control of HVAC equipment, internal loads (people, appliances, lighting), and local climate data (temperatures, sun, wind, humidity) to calculate hour-by-hour energy flows and consumption over a typical year [
121]. With such a model, one can test different design options virtually and see their impact on energy use and comfort. For example, a designer could simulate adding 10 cm of insulation versus 20 cm, compare a gas boiler heating system to a heat pump, or try various glazing types to see the resultant annual heating/cooling loads and energy bills. This helps optimize the design for efficiency while meeting other constraints (budget, architectural aesthetics, etc.). It also helps ensure that aggressive energy targets, like Passive House criteria or net-zero performance, will be met in practice, by identifying the right combination of measures. Major use cases of BEM and simulation include [
121]:
Architectural Design Decisions: Energy modeling informs choices like orientation, massing, window-to-wall ratio, shading design, and envelope assemblies early in design [
122]. An architect might use simplified tools or early-stage models to guide these fundamental choices [
123], e.g., finding that adding exterior shading reduces peak cooling loads by X%, or that a certain facade option yields lower annual energy [
124,
125].
HVAC System Design and Sizing: Engineers use modeling to size heating and cooling equipment properly (avoiding oversizing) by simulating loads. It helps in selecting HVAC configurations, e.g., comparing a variable refrigerant flow system vs. a chiller/boiler system in an office building in terms of energy [
126,
127]. It can also simulate control strategies, like how a night setback thermostat will affect morning warm-up energy [
70,
128].
Compliance and Rating: Energy codes increasingly require performance-based compliance, meaning you demonstrate via an energy model that your building design uses less energy than a reference baseline. Programs like LEED [
119], or the EU’s building regulations [
45], or various national codes (Title 24 in California [
129], etc.) use models to assess if designs are meeting required performance levels or achieving certain percent improvements. Inherent performance ratings, like building energy labels, can be derived from standardized simulation comparisons [
121].
Retrofit Analysis: For existing buildings, a calibrated energy model (tuned to match utility data) can be used to test retrofit measures. For instance, one can model what happens if we replace windows, or if we add variable speed drives on pumps, and thereby prioritize the most impactful upgrades in a cost–benefit sense [
130,
131,
132].
Operational Optimization and Controls: BEM is also used for operational studies, e.g., evaluating different control strategies, like an optimal start HVAC sequence, or analyzing thermal comfort under various scenarios. There is a trend of using models in real-time (model predictive control) to optimize building management, though that is an advanced application [
133,
134]. For example, a field demonstration found that MPC saved approximately 40% of HVAC energy over existing control over two months in a commercial building [
135]. Also, data-enabled predictive control methods (like DeePC) have been shown to offer strong potential in managing system dynamics, reducing energy use while maintaining comfort [
136]. Unveiled challenges such as prediction errors, computational cost, and measurement/feedback delays are also reported in recent studies [
137]. BEM is also used for operational studies, e.g., evaluating different control strategies, like an optimal start HVAC sequence [
138], or analyzing thermal comfort under various scenarios [
128]. There is a trend of using models in real-time (model predictive control) to optimize building management, though that is an advanced application [
139].
Policy and Research: On a larger scale, building stock models (aggregating prototypical building simulations) inform policy decisions and development of new codes and standards [
140,
141]. For example, before implementing a new efficiency code, researchers model its impact on a representative set of buildings to estimate energy savings potential [
142].
Hence, building energy modeling and simulation becomes a crucial tool that underpins many of the strategies discussed in the previous sections: you simulate passive measures to quantify their benefit; you simulate different HVAC or renewable integration scenarios to choose the best; and you use models to verify that your building will meet code or certification thresholds. It is essentially the laboratory in which design hypotheses are tested without costly real-world trial and error.
There are many BEM software tools, ranging from very detailed to simplified [
123,
143]. EnergyPlus is a prominent detailed simulation engine (developed by the U.S. DOE), capable of modeling hour-by-hour or even sub-hourly performance including loads, systems, and plant [
144,
145]. Others include DOE-2 (older but still used, e.g., through interfaces like eQuest), TRNSYS (useful for multi-zone and renewable integration simulations), IES VE, IDA ICE, etc. These typically require detailed inputs and are used by specialists. For user-friendly design, interfaces like OpenStudio, DesignBuilder, or Honeybee (for Rhino/Grasshopper) provide ways to input geometry and parameters and run EnergyPlus or Radiance (for daylight) [
146,
147]. There are also simpler tools or early-design tools (like Sefaira, or even Excel-based calculators) that do quicker estimations to guide concept decisions.
The simulation accounts for various phenomena: heat transfer through envelope (conduction, convection, radiation), solar gains, internal gains, HVAC equipment part-load performance, sun control devices, natural ventilation if modeled, moisture sometimes, and increasingly daylight and lighting control (coupling thermal and lighting models to also predict lighting energy and daylight levels). Some tools integrate computational fluid dynamics (CFD) for detailed airflow analysis within spaces, though that is more niche and often separate from whole-building energy calcs.
A well-constructed energy model can reasonably predict trends and relative performance, but there are uncertainties [
148]. Models typically assume standard schedules for equipment and occupant densities, which may differ in reality. To improve confidence for existing buildings, models are calibrated by adjusting unknown inputs until the model’s output matches metered energy data within certain tolerances [
149]. Calibration uses techniques like inverse modeling or optimization. Once calibrated, the model can reliably evaluate changes. For new designs, calibration is not possible yet, so sensitivity analysis is done to see how robust the design is to various usage patterns.
There are international standards for how to do energy modeling for compliance, such as ASHRAE Standard 90.1 Appendix G (for evaluating percent improvement) [
150], or EN ISO 52016 [
151] in Europe for building energy calculation methods [
45]. These ensure consistency in modeling procedures. Many building codes allow a performance path where a model showing, say, 20% better than a baseline, is a way to comply (versus prescriptive insulation values, etc.). This performance approach encourages innovation because designers can trade-off measures as long as the total outcome is efficient.
Building energy modelling provides the analytical foundation that links design intent to operational performance. As detailed in
Table 5, simulation-driven design can reduce total energy consumption by over 30% through optimization [
121,
122,
123,
124,
125], while model predictive control and digital twins yield a further 20–40% reduction in HVAC energy use [
133,
134,
135,
136]. In the decarbonisation hierarchy, modelling ensures that passive, active, and renewable measures are co-optimised across the building lifecycle and verified through data-driven feedback.
9. Retrofitting Existing Buildings for Energy Efficiency
While new high-performance buildings are important, existing buildings represent the majority of the area floor and energy use in most countries [
152]. Many of these buildings were constructed in eras of cheaper energy and less stringent codes, meaning they often perform poorly by today’s standards [
153,
154]. Therefore, retrofitting, the process of upgrading and modifying buildings to improve their energy efficiency, is an indispensable strategy in the path toward a low-carbon building sector [
154,
155].
Globally, building floor area is dominated by existing stock, much of which will still be in use by 2050 [
1,
156]. In developed countries, annual new construction adds only on the order of one to two percent to total stock, meaning the vast majority of buildings in a given year were built previously [
157]. Even in rapidly growing economies, what is built in the next 10–20 years will remain for decades more [
1]. Climate targets cannot be met by focusing on new “green” buildings alone, the energy wastage of older buildings must be addressed. Studies indicate that retrofitting buildings to high efficiency is a key strategy for a low-/net-zero carbon future [
152,
157].
A wide range of measures that can improve a building’s energy performance include building envelope upgrades which aim to reduce the heating/cooling demand:
Adding or improving thermal insulation in walls, roof, and floors. For example, insulating external walls either from outside (with an external insulation finishing system) or inside can cut heat loss significantly. Roof insulation is often a quick win in older houses (e.g., adding attic insulation). Significant reductions in heating and cooling demand have been reported through ceiling and floor insulation [
158].
Window replacement or improvement. Replacing single-glazed or leaky windows with double or triple-glazed low-E windows is a common measure. If replacement is too costly, adding storm windows or window films can also reduce heat transfer. Upgrading windows not only saves energy but improves comfort (less draft, better temperature near windows). Energy savings of 39–53% have been documented when replacing single glazing with double glazing [
17], and reviews of advanced glazing systems confirm substantial benefits for both efficiency and comfort [
159].
Air sealing of the building. Identifying and sealing cracks, gaps, and joints (around window frames, utility penetrations, etc.) reduces infiltration. This might involve weatherstripping doors, sealing baseboards, and using caulk or foam in leaks. Professional blower door-guided air sealing can achieve major reductions in ACH for older homes. Studies report infiltration accounting for about 13% of energy use, with significant savings possible from sealing [
160]; losses of 25–40% of heating and cooling energy through leakage have also been reported [
161].
Addressing thermal bridges if possible (for instance, insulating exposed slab edges or adding insulating cladding over structural elements). Continuous insulation and thermally broken connectors have been shown to reduce effective U-values [
162], and balcony thermal breaks significantly reduce heat losses and discomfort [
163].
Cool roofs or roof coatings for buildings in hot climates, to reduce solar heat gain. Reflective roof coatings have been shown to reduce cooling loads by 18–93% depending on climate [
164], with other studies finding 14–22% annual load reductions [
37].
Window shading additions. Adding awnings, exterior shutters, solar control films, or brise-soleil to existing windows can cut cooling loads. Shading has been shown to reduce both peak cooling and lighting energy significantly [
165], and a case study in Darwin found reductions of 5–15% depending on shading design [
166].
Many passive retrofits, especially insulation and airtightness, are considered the “first step” because they directly reduce the size/capacity needed for system retrofits and provide ongoing savings. The “next step” is active retrofits, which replace or upgrade the building’s mechanical and electrical systems:
Heating system upgrades: Replacing an old furnace or boiler with a modern high-efficiency unit (like a condensing gas boiler or a heat pump). For example, an old 60% efficient oil boiler can be replaced with a 95% gas boiler or better yet a COP 3–4 heat pump, drastically cutting input energy [
48,
131]. In multi-unit buildings, sometimes converting a central boiler to distributed heat pumps per unit could be considered.
Cooling/AC system upgrades: Replacing aged chillers or room AC units with high-efficiency models (e.g., SEER 25+ mini-splits). Installing variable speed drives on fans, pumps, cooling tower fans, etc. Studies comparing VRF to chiller/boiler systems found 15–35% energy savings, while retrofitting condenser fans with VFDs achieved ~50% savings [
126,
127].
Control retrofit: Implementing modern controls like smart thermostats, zoning controls (so different floors or zones can be conditioned independently), demand-controlled ventilation in offices, and building automation in commercial buildings. Often older buildings have very rudimentary controls, so adding sensors and a control system can yield quick savings. Optimal start and setback controls improve performance [
138], and U.S. national lab studies report ~29% average savings from packages of control measures [
70].
Lighting retrofit: One of the most popular retrofits due to ease and quick payback. This involves changing out incandescent or fluorescent lighting with LED fixtures, often also installing occupancy sensors or timers especially in commercial settings (hallways, bathrooms, storages). Upgrading lighting can reduce that component of energy by 50% or more [
59] and additional savings of 20–60% can be achieved with occupancy/daylight controls [
62,
63].
Appliance/HVAC auxiliary upgrades: Replacing old refrigerators, pumps, fans, motors with energy-efficient models (e.g., ECM motors in air handlers). Refrigerators now use about 75% less energy than 1970s models [
65].
Adding ventilation heat recovery: In a retrofit, if feasible, adding an HRV/ERV to capture exhaust heat can be done when ventilation systems are being improved. Studies confirm MVHR reduces heat loss and improves comfort [
53,
54].
Renewable energy systems: While not efficiency per se, adding solar PV or solar thermal panels is often part of an extensive retrofit. For example, an apartment might get a rooftop PV system to handle common area electricity, or a solar thermal system to preheat domestic hot water, reducing boiler load. Rooftop PV systems can typically produce 5000–7000 kWh/year for a 5 kW installation [
81], and solar thermal can cover 50–80% of annual hot water demand [
89].
The combination of passive and active retrofits often yields the best results, e.g., tighten envelope to reduce load, then installing a right-sized efficient HVAC system. Retrofitting just one or the other may give suboptimal results (like a super-insulated house still running a 30-year-old furnace, or a high-efficiency furnace in a very leaky house).
These are low-cost or no-cost changes such as re-commissioning existing systems, adjusting thermostat setpoints, educating occupants on energy-saving practices, or improving maintenance (cleaning filters, tuning boilers). Strictly speaking, this is not “retrofit” in construction terms, but it is often part of energy retrofit programs. For example, simply reminding office staff to turn off computers and lights after hours, or using smart plugs to shut off equipment, can produce significant savings (one Efficiency Vermont program found an office cut energy 30% through behavioral changes alone [
79]). Similarly, performing retro-commissioning on an old commercial building, which involves fixing broken sensors, balancing airflows, optimizing control setpoints, typically can save 5–15% of energy at a very low cost [
80].
Retrofit projects vary widely in depth: Shallow retrofits might implement a few isolated measures with fast paybacks (lighting, basic HVAC tweaks, insulation in accessible areas). These often yield 10–30% energy savings [
167,
168]. Deep retrofits (or “deep energy retrofits”) aim for high reductions, often 50% or more energy savings, by addressing the building holistically, typically envelope upgrades plus systems replacement and controls, possibly renewables too [
169]. Deep retrofits often coincide with major building renovations or end-of-life equipment replacement cycles. They require more upfront investment and coordination, but deliver large gains and future-proof the building against rising energy costs or carbon penalties [
170].
One concept in deep retrofits is the EnerPHit standard (Passive House retrofit) which prescribes very low energy use targets for retrofits, typically requiring insulation of all opaque surfaces, high-performance windows, airtightness, and balanced ventilation with heat recovery [
171,
172]. Achieving this in older buildings is challenging, but projects have done so; for example, a 1960s house in London retrofitted to EnerPHit reported heating energy use cut by ~75% in some reports [
173], and a 1960s apartment block retrofit in Europe achieved ~55% reduction in measured heating energy [
174]. Another approach is Net Zero Energy Renovations, where in addition to deep efficiency measures, sufficient on-site renewables are added to cover the remaining energy needs annually [
154,
175].
Retrofitting can be more complex than new builds because of constraints: occupancy (people living/working in the building during works), existing structures that may not easily accommodate added insulation (historic facades that cannot be altered, etc.), and split incentives (landlords pay for upgrades but tenants get the energy savings).
Upfront cost is a major barrier. Many cost-effective retrofits still have multi-year pay-back periods, which building owners might be hesitant to undertake without incentives or regulatory pressure. For example, in Germany retrofit insulation measures show pay-back times from 8 to 32 years, averaging about 15 years [
176]. Many SME retrofit projects report pay-backs under 5 years for simple upgrades like lighting or HVAC, but deep renovation packages often exceed 10 years [
177]. IEA deep retrofit case studies similarly show simple pay-back periods up to ~20 years for many projects [
178]. Some jurisdictions are moving toward requiring minimum energy performance. For example, the EU is considering mandates that worst-performing buildings must be renovated by certain deadlines [
45].
Another challenge is heritage and aesthetics. Retrofitting historic buildings externally can be sensitive. Solutions like internal insulation despite losing some interior area or aerogel-based plasters (thin insulation) are being explored for such cases to preserve facades [
179,
180]. High-performance secondary glazing can improve old windows where replacing them is undesirable for heritage reasons [
181].
When done right, retrofits can significantly reduce energy bills for owners/occupants, increase property value, and provide healthier indoor environments (due to better ventilation and moisture control) [
182]. Neighborhoods with retrofitted buildings benefit from improved local air quality if heating shifts away from old combustion systems (coal/wood stoves replaced by heat pumps, e.g.) [
182]. On a macro level, retrofit programs create jobs and spur economic activity in the construction sector [
183,
184]. During economic downturns or in stimulus plans (e.g., post-COVID green recovery plans), building retrofit programs are often highlighted for their triple benefits of job creation, reducing consumer energy costs, and cutting emissions [
183]. The IEA notes a need for expanding the energy efficiency workforce in the buildings sector to achieve higher retrofit rates [
183].
Despite the benefits, many barriers persist. Aside from cost and split incentives, there is the “hassle factor”, owners may be reluctant due to disruption during construction. There might be informational barriers, not knowing what measures are best or whom to trust to do the work. Furthermore, technical limitations on some buildings (structural capacity for adding insulation cladding, lack of space for new equipment, etc.) can limit what can be done easily. Also, rebound effect can occur: if a home becomes much more efficient and cheaper to heat, occupants might choose to heat it more or raise thermostat settings, eating into some savings.
Retrofitting converts the existing building stock from a liability into a principal mitigation asset.
Table 6 summarises evidence indicating that deep retrofits combining insulation, HVAC upgrades, and controls can achieve 50% or more reductions in total energy use [
154,
171,
172,
173,
174], while shallow retrofits yield 10–30% improvements [
167,
168]. As a mid-hierarchy strategy, retrofitting consolidates passive and active measures within a scalable framework that enables mass decarbonisation of ageing buildings.
10. The Role of Occupant Behavior and Engagement
Even the best-designed, most efficient building can underperform if its occupants use it in inefficient ways [
148,
185]. Conversely, occupant awareness and smart behavior can yield energy savings in any building, often at negligible cost [
186]. Therefore, understanding and influencing occupant behavior is a key piece of the energy efficiency puzzle [
187]. Studies have shown that occupant behavior can lead to wide variations in actual energy consumption [
148]. Key occupant-driven factors include:
Thermostat settings and schedules: Some people prefer higher indoor temperatures in winter or much cooler in summer, reflecting well-documented variation in thermal comfort preferences and acceptable ranges in standards such as ASHRAE Standard 55 [
188]. Each degree (°C) change can alter heating energy use by roughly 5–7% depending on climate and system, with the European Commission estimating about 7% per 1 °C reduction in heating setpoint [
189]. If occupants do not use setbacks, energy is wasted maintaining comfort when not needed; using programmed setbacks typically yields measurable savings. Conversely, diligent use of thermostat setbacks or smart scheduling can save considerable energy, with simulations indicating that night setbacks of 2–4 °C for 8 h can save about 5–15% annually [
190] and field guidance from DOE indicating up to ~10% a year with daily 7–10 °F setbacks.
Use of windows and shading: Occupants influence ventilation and passive heat gains by opening windows or adjusting blinds. In some climates, people might open windows for fresh air even with air conditioning running, which increases energy losses (for example, in tropical Southeast Asia many occupants do this, reducing efficiency) [
191]. Or they might forget to open shades on a cold sunny day, missing free solar heat, or forget to close them on a hot day, increasing cooling load, studies comparing exterior shades vs. interior blinds show up to ~10–20% savings in HVAC energy by better shading [
192]. Proper occupant use of operable elements (windows, vents, blinds) in naturally ventilated or mixed-mode buildings is crucial. If a building is designed to take advantage of natural ventilation but occupants don’t open windows, it will underperform compared to predicted models that assume ideal window use [
193]. Conversely, strategic window opening in mornings/evenings for cooling can reduce AC needs; for example, in school classrooms, window-opening behaviors are shown to reduce energy consumption risks or losses when appropriately timed (while avoiding large openings during times of high external temperature) [
194].
Electrical/appliance use: Occupant choices on appliance usage (how often and when they use washers, dryers, ovens) and behavior like leaving lights on or electronics in standby all add up. “Plug loads” in offices (computers, monitors, personal heaters, coffee machines) are highly occupant-driven. Offices that implement good practices, e.g., enabling PC sleep modes, educating staff to turn off equipment at day’s end, see much lower after-hours electricity usage than those that do not. In some offices, plug loads account for 20% of total building electricity usage, of which a large share comes from computers and monitors [
195]. One field example: using a combination of software, hardware, and behavior (switching off unused equipment, power-management, awareness campaigns) reductions of 43% in plug and process loads have been achieved [
196].
Hot water usage: In residences, behaviour significantly affects hot water heating—longer showers, leaving hot water running while doing other tasks, or letting water run to warm up, all increase energy use. Efficient fixtures (low flow shower heads, better insulation, efficient heaters) can reduce demand, but occupant habits are key. For example, a field study in Italian households found on average 27.8 L/person/day hot water consumption, representing ~26–31% of total daily water use [
197]. Studies of showers show that about 20% of shower water is “behavioural waste” (cold or unused water before the user begins showering properly) due to delays in getting the desired temperature or adjusting mixes [
198]. Interventions giving real-time feedback to users have reduced hot water consumption by 12–16% relative to baseline in some trials [
199].
Space usage and occupancy patterns: In schools and offices, energy is often wasted when occupants use only part of a building (e.g., certain rooms or wings) but the whole area is conditioned. For example, classrooms or offices may be empty much of the time but still heated or cooled. Enabling zoning (heating/cooling only occupied zones), educating building users, or implementing occupancy-based controls can significantly reduce this waste. Studies in office buildings show that occupancy-based HVAC control over a fraction of zones can yield substantial savings—one university campus experiment achieved about 17.8% electric energy savings for HVAC in those controlled zones [
200]. Another experimental study in a university building showed that simple occupancy-based control strategies produce large savings without compromising comfort or indoor air quality [
201]. In educational buildings, systematic reviews indicate that mixed-use spaces and underutilized rooms are frequent sources of energy waste [
202]. Simulation studies for small office buildings also find that occupancy density and the schedule of occupancy are among the strongest predictors of energy consumption, implying that unused or lightly occupied zones are major contributors to inefficiency [
202].
Maintenance and tuning influenced by occupants: Sometimes occupants disable or override energy-saving features due to discomfort or misunderstanding [
190,
203]. For instance, someone might frequently adjust a thermostat to extremes if they are impatient, leading to inefficient operation and negating programmed control strategies [
204]. Or they might disable or bypass an automated lighting sensor they find annoying, which can leave lights on until long timeouts; U.S. Department of Energy field research notes that overly complex connected lighting systems often end up disabled in practice [
205], and studies have shown that occupants in spaces with occupancy sensors are less likely to switch lights off manually, increasing reliance on the sensors [
206,
207].
The aggregate effect of behavior is often captured in the concept of the Energy Performance Gap, which is the difference between a building’s designed or modeled energy use and its actual measured use [
186]. A significant part of this gap in many cases is attributed to occupant behavior being different from standard assumptions [
208]. Models assume certain schedules and usage patterns, but real life can deviate. For instance, an office building might be assumed to shut down at 6 pm, but if cleaning crews turn on lights at night or some employees work late regularly, actual usage will be higher. It’s been suggested at times that “occupants are the main cause” of performance gap in some contexts [
208], although other factors such as system faults and weather variations may also contribute.
To harness the potential of occupant behavior for energy savings, many approaches focus on engagement, feedback, and incentives. Simply informing occupants about the energy costs of their actions and training them on how to use building systems effectively can make a difference. To address these challenges, a range of strategies have been developed to influence, guide, and support occupant behaviour in ways that contribute to reducing the energy performance gap. These strategies combine behavioural insights with technological and organisational measures, aiming to balance energy efficiency with occupant comfort and agency. They can be broadly categorised as follows:
Energy Feedback: Providing real-time or periodic feedback to occupants about their energy usage can motivate changes. For residential users, in-home displays showing electricity usage, especially when paired with smart meters, have been found to typically reduce consumption by around 2–10% on average, with a large meta-analysis reporting about 7.4% across field experiments and UK government trials finding 2.5–7.3% depending on design [
209]. Similarly, more granular feedback such as a breakdown by appliance via smart plugs or sub-metering can highlight where energy is going, and reviews note that feedback with appliance-level detail is often more effective than aggregate-only feedback when well-designed [
210]. Some utilities or apps send reports comparing a household’s usage with similar neighbours, leveraging social norms to encourage improvements; large randomised field experiments of these normative comparisons show average electricity reductions of about 2% with effects that persist over time [
211]. In commercial buildings, dashboards in lobbies showing real-time energy performance can create awareness among employees and visitors and support organisational sustainability goals; U.S. national lab studies describe and evaluate such public-facing displays in federal and campus buildings [
212,
213,
214].
Occupant Control and Incentives: Giving occupants some control but also aligning incentives is important. In many lease situations, a split-incentive problem arises, the tenant might pay the energy bill, giving them reason to save, but often they have limited control over building-wide HVAC settings. Or if the landlord pays (like in gross leases), tenants have no financial incentive to conserve. This landlord–tenant “principal–agent” problem is well documented in international analyses and city surveys [
215,
216]. Green leasing practices attempt to address this by sharing benefits of savings and clarifying roles and data sharing between parties [
217]. Programs such as EPA’s ENERGY STAR Tenant Space provide recognition pathways for office tenants and encourage sub-metering and collaboration with landlords [
218]. Some buildings run incentives or recognition for energy-saving behaviors, e.g., “energy champion” teams that consistently shut down equipment properly or friendly competitions; systematic reviews of office interventions report measurable savings from social rewards and team competitions, though persistence varies [
219,
220]. Cost-sharing provisions explicitly embed incentives: New York City’s model Energy-Aligned Clause lets tenants retain 20% of their share of predicted savings each year as a performance buffer while owners recover capital costs, aligning both parties around efficiency [
221].
Behavioral Programs and Gamification: Some organizations have tried gamification, turning energy saving into a game or competition. For example, dormitories in universities competing to lower their energy usage relative to baseline have shown measurable reductions, including multi-campus competitions with average electricity cuts of about 3–4% during events and top-performing dorms around 28%, and studies reporting larger reductions when feedback is real time rather than weekly [
222,
223]. Similarly, an office building running an energy reduction challenge between floors or departments can draw on dashboards, leaderboards and competitions; peer-reviewed demonstrations in offices report meaningful savings, for example an Energy and Buildings study that deployed a mobile gamification platform and suggested about 20% electricity reduction in the office environment [
224]. Group contests and comparative feedback in workplaces have also reduced organisational energy use in controlled studies [
225]. These programmes often spur short term savings while the competition is active, especially when supported by real-time monitoring and frequent feedback [
222,
223]. Gamification taps into people’s competitive or collaborative spirit and can make a mundane task like turning off lights more engaging, a conclusion echoed in systematic reviews of gamified energy interventions [
226].
Comfort and behaviour: Energy saving works when comfort is preserved. Widening temperature setpoints while offering personal comfort options such as fans and flexible clothing can maintain comfort and enable substantial HVAC savings; laboratory and modelling studies show that elevated air speed increases acceptable temperatures and extended setpoints reduce cooling energy use [
227,
228]. Discomfort often drives wasteful responses such as desk heaters in over-cooled offices; large field datasets show offices are frequently too cold, and commissioning or HVAC rebalancing improves comfort and curbs waste [
68,
229]. Efficiency improvements can also trigger rebound, where some of the engineering savings are taken as extra comfort so realised savings are lower; evidence for residential heating shows substantial direct rebound, especially among tenants and lower-income households [
230,
231,
232].
Cultures also play a significant role. It is also interesting to observe that occupant behavior norms differ worldwide. In some cultures, it is normal to put on a sweater at home in winter and keep heating moderate; in others, people heat to T-shirt conditions. Likewise for cooling, acceptable indoor temperature varies. Societal attitudes (and energy prices historically) shape these. Public campaigns can sometimes shift norms; for instance, Japan’s “Cool Biz” campaign encouraged offices to set AC to 28 °C in summer and employees to dress lighter, which reportedly saved a lot of electricity during energy crises [
233]. Similar efforts can propagate new norms (like not expecting to wear a suit in a 35 °C summer without AC blasting).
Occupant behaviour forms the behavioural layer that determines whether technical potential becomes realised performance. As shown in
Table 7, thermostat and feedback interventions reduce energy use by 5–15% [
190,
209], occupancy-based controls achieve 10–30% [
200], and engagement programmes and green leases ensure persistence of savings [
217,
218,
219,
220]. In the decarbonisation hierarchy, behavioural engagement integrates human agency with technology, closing the performance gap and sustaining long-term efficiency gains.
11. Policies, Codes, and Certification Programs
Technological solutions for efficient, low-carbon buildings are of limited use without a regulatory and market environment that drives their adoption. That’s where policies, building energy codes, and certification programs come into play. Governments and industry bodies around the world have implemented various measures to improve building energy performance, ranging from mandatory codes for new construction to voluntary rating systems that recognize exemplary buildings. This section surveys the landscape of such measures, highlighting how they contribute globally to raising efficiency and what gaps remain.
Building Energy Codes and Standards, also called building energy efficiency standards, are regulations that set minimum requirements for the energy performance of new buildings, and sometimes also major renovations. They are one of the most powerful tools policymakers have, as they essentially ensure that each new generation of buildings is more efficient than the last. Many countries have had energy codes since the 1970s or 1980s (often triggered by oil crises), but the stringency varies widely. Some key examples include:
In the European Union, the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) requires all new buildings from 2021 onward to be nearly zero-energy buildings (nZEB) [
234]. The 2024 recast of the EPBD (Directive (EU) 2024/1275) goes further, requiring zero-emission new buildings by 2030 and new public buildings by 2028 [
45]. It also sets renovation targets for existing stock: for non-residential buildings, renovation of the 16% worst-performing by 2030 and 26% by 2033; for residential buildings, national trajectories to reduce average primary energy use by 16% by 2030 and 20–22% by 2035, with at least 55% of the reduction coming from the worst-performing homes [
46].
In the United States, energy codes are primarily adopted at the state and local level but guided by model codes: the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) for residential buildings and ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1 for commercial buildings [
150,
235]. Over time these model codes have incrementally improved; for example, the U.S. Department of Energy determined that the 2021 IECC delivers ~40% greater efficiency than the 2006 edition [
236]. Some states lead with very strict codes; for instance, California’s Title 24 has long pursued zero-net-energy policy goals for new homes and now includes a prescriptive solar PV requirement for newly constructed buildings, with solar-ready and battery-ready provisions in recent cycles [
129]. Others lag with older codes or have no statewide residential energy code, leaving adoption to local jurisdictions [
237]. Additionally, ASHRAE published in 2023 Standard 228-2023, the first method to evaluate zero-net-energy and zero-net-carbon building performance in operation, providing a framework for voluntary use and potential future adoption [
238].
In China the building energy codes that have been steadily strengthened. In 2022, China introduced the General Code for Building Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Utilization (GB 55015-2021), in force from 1 April 2022, which sets mandatory efficiency requirements for new, expanded and renovated buildings and promotes renewables [
239,
240]. Enforcement in China varies, and national overviews note that urban codes are mandatory while some rural residential codes have been voluntary; major cities often adopt stricter local codes (e.g., Beijing DB11 standards and Shanghai’s Construction-Related Energy Conservation Regulations) [
241,
242,
243]. China’s building codes are tailored to climate zones such as severe cold, cold, hot-summer–cold-winter, hot-summer–warm-winter, and temperate, as defined in GB 50176-2016 (Thermal Design Code for Civil Buildings) [
244].
Many other countries have codes at various stages. Some developing countries are just adopting or updating them. India has an Energy Conservation Building Code for commercial buildings and an Eco-Niwas Samhita for residential, currently voluntary at the national level and implemented by states [
245]. Middle Eastern countries with high AC loads such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia have strengthened efficiency requirements and green standards, alongside energy-pricing reforms [
246,
247]. In Latin America, Mexico’s NOM-020-ENER-2011 is a mandatory residential envelope standard, Brazil operates the largely voluntary PBE Edifica building efficiency labelling, and Chile’s Energy Efficiency Law introduces mandatory energy ratings and tighter thermal rules [
248,
249,
250].
However, a major issue is coverage and enforcement. As of 2022, 81 countries had some form of building-energy code, yet 2.4 billion m
2 of floor space were added that year in countries with no codes, with the largest gaps in low-income regions [
2]. Some regions are catching up: Kenya introduced a National Building Code in 2022 with efficiency provisions, and Indonesia and Vietnam have national or large-building regulations [
251,
252,
253]. Gulf states also now use green building guidelines in new developments, e.g., Abu Dhabi Estidama [
254] and Saudi Mostadam programme [
255].
Governments also drive efficiency by leading through public buildings. Many require new government buildings to meet higher standards or green certifications, and retrofits of schools and hospitals demonstrate long-term savings. In the EU, the revised Energy Efficiency Directive requires renovation of 3% of public-sector floor area annually and upgrades to NZEB/ZEB levels [
256].
Some countries are pioneering net-zero or zero-emission codes. Denmark has integrated whole-life-carbon rules in BR18, including an LCA requirement and a GWP cap for larger new buildings, aligning code practice with zero-emission principles [
257]. In Canada, British Columbia’s Zero Carbon Step Code sets an operational-carbon pathway that jurisdictions can adopt en route to zero-emissions new construction by 2030 [
258].
Many major cities have set ambitious building energy or emissions targets. New York City imposes operational GHG caps for large buildings under Local Law 97 [
259]. London requires major developments to be net-zero-carbon in operation and to monitor actual energy use [
260]. Toronto’s Green Standard sets tiered performance requirements that ratchet toward near-zero by 2030 [
261]. Singapore applies BCA Green Mark 2021 to new and existing buildings and regulates minimum standards for new builds and major retrofits [
262]. Paris implements national tertiary-sector disclosure and reduction obligations [
263]. Global city coalitions such as C40 promote net-zero operational carbon for all new buildings by 2030 [
264].
Green Building Certification Programs have played a significant role in pioneering and spreading best practices. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), developed by the U.S. Green Building Council in the late 1990s, has become a globally recognised certification [
119]. Projects earn points across categories such as energy, water and materials and are certified at Certified, Silver, Gold or Platinum levels; energy carries substantial weight of 33 points in the score [
265]. As of 2024 there are 195,000+ LEED projects in 186 countries worldwide [
266]. Similar programs in other countries include: the UK-origin BREEAM rating system [
120], Green Star in Australia [
267], CASBEE in Japan [
268], DGNB in Germany [
269], and HQE in France [
270]. There are also programmes that focus specifically on operational energy performance, such as ENERGY STAR for Buildings in the United States [
271] and NABERS in Australia [
272]. In residential markets, widely used certifications include Passivhaus, which sets stringent limits on heating and cooling demand [
273], and the DOE Zero Energy Ready Home programme in the United States [
274].
There is debate on whether design-time certification always guarantees superior measured energy performance. Some studies find limited or mixed operational energy advantages on average for certified buildings [
275,
276]. However, certification has influenced markets, as studies report rent and/or price premia and, in some cases, higher occupancies for certified office buildings, supporting the business case for developers and investors [
277,
278].
In addition to building codes and certification programs, governments offer incentives such as subsidies, tax credits and grants for energy upgrades and renewable installations. During the COVID recovery and the 2022 energy crisis, European policy packages promoted insulation and heat pump adoption [
279]. In the United States, the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act introduced major incentives via tax credits and rebates [
280]. Emerging economies often rely on international climate finance for public-sector retrofits and efficient lighting programmes [
281]. Utilities in many countries also offer rebates for energy-efficient HVAC and appliances as part of demand-side management strategies, as documented in U.S. federal guidance and UK regulator materials [
282].
Synthesising the policy evidence, mandatory performance codes provide the structural backbone for energy transformation, while voluntary certification and incentive schemes accelerate diffusion beyond compliance. As shown in
Table 8, building codes such as the EU Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) and the U.S. International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) establish binding minimum performance thresholds that reduce the energy intensity of new construction and major renovations [
45,
150,
234,
235]. Complementing these, market-based incentives under the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and European retrofit subsidies have demonstrated their capacity to accelerate investment in deep energy renovation by reducing payback periods and increasing consumer uptake [
279,
280]. Certification schemes including LEED, BREEAM, and NABERS act as voluntary market differentiators that encourage innovation, disseminate best practices, and promote knowledge diffusion [
119,
120,
272]. Finally, public disclosure mandates such as New York City’s Local Law 97 and the London Energy Planning Guidance enhance transparency and accountability by linking operational performance with regulatory penalties and recognition [
259,
260]. The combination of regulatory compulsion, financial support, and transparent benchmarking yields the most robust long-term market transformation, as consistently observed in jurisdictions with progressive building codes and disclosure frameworks [
1,
2,
7,
264].
12. Synthesis: Linking Challenges, Strategies, and Enabling Conditions
The preceding sections have demonstrated that decarbonising the building sector requires a coordinated set of technological, behavioural, and policy interventions that act in concert across the building lifecycle. When viewed in relation to the challenges outlined in
Section 1 and
Section 3, these measures form an integrated framework capable of addressing the structural, operational, and institutional barriers that continue to impede progress. The synthesis presented here maps how the reviewed strategies respond to the sector’s most pressing needs and highlights the cross-cutting enablers that determine their effectiveness.
Global building-related emissions remain high because of four interlinked barriers: excessive operational energy demand, slow renovation rates, limited renewable energy adoption, and fragmented policy governance. Each barrier corresponds to specific solutions reviewed in
Section 4,
Section 5,
Section 6,
Section 7,
Section 8,
Section 9,
Section 10 and
Section 11, and their alignment reveals the extent to which the sector already possesses the technical means to decarbonise.
Table 9 summarises this correspondence, linking the challenges identified in the early sections with the strategies discussed throughout the review.
This alignment illustrates that the sector’s decarbonisation cannot be achieved through isolated interventions. Each strategy addresses a specific dimension of the problem but achieves its full potential only when combined with complementary measures. Passive and envelope strategies lower baseline energy demand; efficient systems and renewable energy supply meet residual needs sustainably; digital tools ensure design precision, operational monitoring, and verification; and behavioural and policy instruments sustain performance and scale adoption. Together, these strategies form a self-reinforcing cycle of demand reduction, operational efficiency, and carbon substitution.
Three cross-cutting enablers emerge across the literature as essential for maximising the effectiveness of this hierarchy of measures. The first is integrated design and lifecycle thinking, which ensures that architectural, engineering, and operational decisions are made coherently and that early design intent translates into measured performance. Building energy modelling and simulation play a central role by allowing the co-optimisation of passive and active measures and by linking design evaluation with operational feedback from retrofitted buildings. The second enabler is digitalisation and data-driven optimisation, encompassing building management systems, sensor networks, and predictive control. These technologies enable adaptive operation, real-time diagnostics, and continuous performance benchmarking, directly supporting regulatory compliance and performance disclosure. The third enabler is policy and governance alignment, which transforms technological capability into widespread practice through coherent building codes, market incentives, and certification programmes. When combined, these enablers integrate technical efficiency, user engagement, and institutional accountability into a single systemic framework.
Despite the maturity of the technologies reviewed, significant gaps remain. Retrofit deployment remains far below the required pace, particularly in existing and heritage buildings where technical and financial barriers persist. Behavioural and institutional inertia continues to contribute to the energy performance gap, while the fragmentation of data across systems and stakeholders limits continuous optimisation. Furthermore, regulatory asymmetries between regions impede the global harmonisation of efficiency standards and investment mechanisms. Overcoming these residual challenges requires convergence between the technological, digital, and policy dimensions of the sector. This trajectory points directly toward the emerging innovations discussed in the following section, where artificial intelligence, digital twins, industrialised retrofits, and circular construction represent the next evolutionary stage in translating integrated decarbonisation strategies into large-scale, measurable outcomes.
13. Emerging Technologies and Future Directions in Sustainable Buildings
Looking ahead, the building sector is poised for continued transformation through innovation. Achieving the ambitious goal of truly sustainable, zero-carbon buildings worldwide will be aided by emerging technologies and approaches that are now on the horizon or in early adoption. This section explores some future directions and cutting-edge developments in building energy efficiency and sustainability, spanning smart digital technologies, advanced materials, and integrated design concepts.
13.1. AI-Native Digital Twins and Predictive Autonomy
Digital twins that fuse high-resolution sensing with physics-based and data-driven models are moving beyond visualization into closed-loop control, fault anticipation, and portfolio-scale optimization. Recent work proposes architectures that combine building digital twins with AI services for predictive control, diagnostics, and grid services, positioning the twin as an operational brain rather than a static replica. For example, the AI–DT Integration Framework conceptually integrates AI into each phase of the digital twin lifecycle, enabling systems to transition from mere replication toward proactive decision making and autonomy [
283].
In the building domain specifically, there is increasing research on “AI-driven digital twin architectures” that embed machine learning services with twin models for control and diagnostics [
284]. Field deployments of model predictive control (MPC) in buildings, when paired with digital twin models, have shown measurable energy savings, albeit typically in pilot settings and under controlled conditions [
285]. These empirical and review works also highlight the remaining challenges in realizing robust, scalable implementation in occupied buildings (such as occupant comfort, uncertainties, and reliability).
Near-term priorities include self-calibrating twins that continuously align model predictions to metered data. For instance, continuous calibration frameworks for physics-based building models have been proposed to adapt to dynamic changes in building conditions [
286]. The literature also explores self-evolving or self-adapting twin systems that can update themselves via Bayesian or learning-based approaches [
287].
Another priority is learning controllers that coordinate thermal storage, batteries, and flexible end-uses (e.g., HVAC loads, electric loads) to participate in local flexibility or demand response markets. While fewer full demonstrations exist in operational buildings, reviews of integrating ML and digital twins in smart buildings highlight this direction as a key research frontier [
288].
Together, these capabilities will be foundational for grid-interactive efficient buildings at scale, effectively bridging digital twins, AI, and control to deliver scalable autonomy in building operations.
13.2. Next-Generation Envelope Materials and Photonic Cooling
Vacuum insulated glazing (VIG) is advancing rapidly, delivering wall-like thermal insulation (low U-values) with thin profiles and strong retrofit potential for glazing-dominated buildings. Recent studies report that VIG can reduce U-values below 1.0 W·m
−2·K
−1 without greatly increasing thickness, making it applicable where frame depth is constrained [
289]. Field experiments of VIG retrofit show large reductions in heat gains and more stable interior surface temperatures compared to single or conventional glazing; for example, the inside surface temperature in a Hong Kong test dropped from ~50.2 °C (single glass) to ~29.9 °C (VIG retrofit) and heat fluxes were reduced by ~85% [
290].
Radiative sky cooling has matured from laboratory demonstrations to building-scale coatings and photonic meta surfaces that reject heat via the atmospheric window while reflecting solar irradiance. A 2024 review surveys advances in materials, durability, and building-scale applications, reporting measured sub-ambient cooling and its translation into reduced HVAC loads in hot climates [
291]. Another 2025 review highlights emerging deployment of radiative cooling in real buildings and integration into energy systems [
111]. Photonic structures: meta surfaces, selective thermal emitters, switchable surfaces, are now being designed for high emissivity in the 8–13 µm atmospheric window while reflecting solar wavelengths, enabling daytime cooling [
292]. Recent works push toward “directional” or “adaptive” thermal emitters that aim to reduce winter heat losses while maximizing summer cooling, directional emitters for façade thermoregulation [
293]. The next research frontier is controllable or seasonally adaptive surfaces that dynamically balance winter penalties and summer gains, enabling envelopes that respond to seasonal or operational constraints.
13.3. Hybrid Solar Technologies and Advanced Heat Pumps
Photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) collectors increase rooftop energy yield by co-producing electricity and useful heat from the same aperture. Recent reviews and performance studies describe higher exergy utilisation, improved PV efficiency via cooling, and viable manufacturing pathways, which together strengthen the business case, especially for dense urban sites and low-temperature heating networks. For example, an exergetic analysis shows that PVT systems can achieve exergy efficiencies in the 13–15% range under realistic operating conditions, complementing their thermal and electrical outputs [
294]. Another study on PVT configurations shows that cooling the PV module via the thermal side can reduce PV cell temperature, thereby boosting electrical output while extracting low-temperature heat [
295].
On the demand side, the transition to natural refrigerants is accelerating. Propane (R-290) heat pumps combine very low global warming potential (GWP) with promising efficiency and cold-climate performance; they are increasingly favored under tightening European and global rules on permissible refrigerants. Recent experimental work has demonstrated an 8 kW R-290 heat pump for hot water with favorable COPs in relevant regimes [
296]. Magnetic refrigeration remains pre-commercial for space conditioning but has advanced through improved magnetocaloric materials and system integration. Recent publications assess scaling challenges, device compactness, and performance benchmarking of magnetocaloric heat pumps (MCHPs) as alternatives without fluorinated gases [
297].
13.4. Industrialized Deep Retrofits and Additive Manufacturing
Deep renovation is increasingly treated as a product. Prefabricated overcladding and roof cassettes, inspired by the Energiesprong model, enable rapid retrofit by wrapping existing buildings in high-performance envelopes that can integrate windows and on-site renewables. Recent reviews highlight advances in prefabricated panel types and materials, with documented gains in airtightness and shortened installation times, although challenges remain in supply chain scale-up and standardisation [
298].
Additive manufacturing is opening new pathways for façade innovation. Experiments with hollow-core and multi-material 3D-printed elements show significant thermal benefits from optimised internal geometries, while reviews emphasise potentials such as integrated shading, energy coupling and bio-based feedstocks [
299,
300]. Scaling, codes and long-term hygrothermal validation remain critical research frontiers before mainstream adoption.
13.5. Coupling Buildings and Mobility for Flexibility and Resilience
Vehicle-to-building (V2B) as a subset of vehicle-grid integration (VGI) is increasingly documented as a mechanism for using parked EV batteries to serve building loads and provide backup power. A comprehensive review of V2G and related technologies discusses how bidirectional charging can support local load balancing and resilience services [
301]. A recent case study of V2B in an office complex demonstrates flexibility in supplying building demand during off-peak hours through coordinated scheduling of EV discharge [
302]. Another study quantifies the flexibility potential of EVs in building settings, estimating how much dispatchable capacity can be harnessed from parked EVs [
303]. Integrated approaches (e.g., managing EV energy partitioning, real-time optimization) are described in recent work on home/work V2B algorithms that aim to maximize local PV self-consumption while satisfying mobility constraints [
304].
On the national or grid scale, reports and roadmaps now treat vehicle grid integration, including V2B, as a strategic flexibility asset to shape demand, support renewables, and enhance resilience. For example, the U.S. DOE’s “Vehicle-to-Grid Integration Assessment” positions EVs as mobile storage devices able to provide grid services, including supporting backup to buildings or microgrids [
305]. A related DOE “Future of Vehicle Grid Integration” report frames EVs not just as loads but as two-way assets for grid and building integration [
306].
However, important open questions remain. User incentives and business models are crucial to encourage EV owners to make battery capacity available for V2B. The need for interoperable charger and communication standards is widely documented in policy and technical reports. Finally, battery degradation under repeated stationary cycling (charging/discharging for building service) is an active research issue, the tradeoffs between flexibility value and battery life must be carefully managed.
13.6. Toward Circular and Ultra-Low-Embodied-Carbon Buildings
Operational carbon reductions are increasingly complemented by strategies targeting embodied carbon, since in low-energy or net-zero buildings embodied carbon can account for a majority share of total emissions. (Arup & partners) “Net-zero buildings: Halving construction emissions today” notes that embodied carbon can already represent over 50% of a new project’s footprint in some scenarios [
307].
Low-carbon binders and recycled aggregates are among the leading mitigation pathways. A comprehensive review of sustainable concrete systems discusses how substituting portions of conventional cement with alternative binders (e.g., fly ash, slag, calcined clays) plus use of recycled aggregates can reduce embodied carbon while maintaining structural performance [
308]. Recycled materials in construction more broadly are surveyed by Wu et al. (2025), showing how reused concrete, recycled aggregates and waste streams are being reintegrated into building materials and the associated lifecycle benefits [
309].
Design for disassembly (DfD) is increasingly recognised as a cornerstone of circular construction, enabling components to be recovered, reused, or repurposed at the end of a building’s life. A recent systematic scoping review maps DfD strategies, barriers, and enablers across diverse building types, highlighting practices such as modular design, reversible connections, and material standardisation while also noting challenges related to cost, regulation, and industry adoption [
310].
Digital tracking, material passports, and digital twins are increasingly proposed to support traceability, reuse, and circular supply chains. A 2025 systematic review examines current methodologies for creating material passports, noting their role in documenting material composition, life cycle data and enabling reuse decisions [
311].
Thus, aligning procurement rules and building codes with verifiable embodied carbon metrics or classes (e.g., via mandated EPDs, minimum reuse requirements, or carbon budget constraints) is likely to play a decisive role in scaling diffusion of circular, ultra-low-embodied structures.
13.7. Bridging Remaining Gaps Through Emerging Technologies
The emerging technologies reviewed in this section collectively represent the next phase in overcoming the systemic gaps identified in
Section 12. Although mature efficiency measures, renewable integration, and policy instruments have already established a strong foundation for decarbonisation, progress remains constrained by four persistent barriers: the limited scalability of deep retrofits, the fragmentation of building data across systems and stakeholders, the persistence of behavioural and operational inefficiencies, and the uneven regulatory alignment between regions. Each of these challenges can be directly addressed by the frontier innovations now reshaping the building sector, which together provide the technological realisation of the integrative, digital, and governance-oriented enablers identified in the synthesis framework.
AI-native digital twins and predictive autonomy offer a pathway to overcome the persistent data and performance fragmentation that hinders operational optimisation. By combining real-time sensing, physics-based modelling, and adaptive machine learning, digital twins transform buildings into continuously self-calibrating systems capable of diagnosing inefficiencies and responding dynamically to changing conditions. These systems address the behavioural and institutional inertia described in
Section 12 by automating performance management and linking operational data to policy benchmarks such as building codes and certification criteria. Through continuous monitoring and model-based optimisation, digital twins create a feedback mechanism between design intent and actual performance, reducing the energy performance gap and supporting data transparency across the value chain.
Industrialised retrofit solutions, including prefabricated façade and roof cassettes inspired by the Energiesprong model, directly tackle the challenge of slow renovation rates and high labour intensity. By standardising production, reducing on-site construction time, and integrating high-performance envelopes with on-site renewable energy systems, these approaches lower both the cost and disruption associated with deep retrofits. They provide a scalable mechanism to upgrade existing building stock, particularly in regions where traditional renovation approaches are economically or logistically prohibitive. When combined with digital twin diagnostics and automated quality verification, industrialised retrofits enable mass customisation of renovation packages with predictable energy and carbon outcomes.
Advanced materials and envelope innovations further close the remaining efficiency gap by enhancing thermal performance and resilience beyond the limits of conventional construction. Vacuum-insulated glazing, radiative cooling surfaces, and phase-change composites provide adaptive control of heat transfer while maintaining architectural flexibility. These technologies support resilience under extreme climate conditions and reduce residual thermal loads, complementing the operational intelligence provided by digital systems. The convergence of material science and digital control thus enables envelopes that not only conserve energy but actively regulate building thermodynamics.
Circular construction, material passports, and low-carbon binders address the emerging priority of embodied carbon reduction, which has become increasingly dominant as operational emissions decline. By enabling traceability, reuse, and life-cycle accountability, these practices counteract the regulatory asymmetries highlighted in
Section 12 and foster harmonised standards for embodied carbon reporting. They also provide the material foundation for a circular economy in the built environment, ensuring that decarbonisation extends beyond operation to encompass production and end-of-life phases.
Coupling buildings with mobility and distributed energy systems, such as through vehicle-to-building and hybrid photovoltaic–thermal configurations, offers a complementary solution to the remaining flexibility and resilience challenges. These integrations enable buildings to function as active participants in the wider energy system, capable of balancing renewable generation variability, providing backup power, and participating in local flexibility markets. Such grid-interactive functions address both the operational and systemic dimensions of decarbonisation by aligning building performance with the dynamics of a renewable-based energy infrastructure.
Together, these emerging technologies represent a coherent technological response to the barriers that have constrained progress in building decarbonisation. They bridge the gap between mature efficiency measures and systemic transformation by combining automation, modularity, and circularity within a digital and policy-aligned framework. In doing so, they operationalise the three enablers identified in
Section 12—integrated design, digitalisation, and governance alignment—and provide the foundation for a globally scalable transition toward zero-emission and climate-resilient building ecosystems.
14. Conclusions
The building sector accounts for roughly one-third of global energy use and carbon emissions, making it a critical focus for climate mitigation. This review finds that substantial reductions can be achieved through a clear hierarchy of interventions that begins with passive design and high-performance envelopes to minimise energy demand; continues with efficient HVAC, lighting, and control systems to improve operational performance; and culminates in renewable energy integration to decarbonise remaining loads. Together, these measures can reduce building energy use by more than half while maintaining indoor comfort and resilience. Technological solutions for deep efficiency are already mature and widely demonstrated. Passive and envelope upgrades provide permanent savings, while efficient systems combined with renewable generation enable near-zero operational emissions. Retrofitting existing buildings remains the largest opportunity, capable of achieving 30% to 50% energy savings when supported by targeted policies and financing mechanisms. Behavioural engagement and regulation are equally decisive. Occupant behaviour can influence 10 to 30% of total energy use, highlighting the need for user feedback and smart controls. Mandatory codes, financial incentives, and certification programmes have proven effective in scaling best practices when implemented coherently and supported by transparent disclosure. Future progress will depend on integrating emerging technologies such as AI-enabled digital twins, advanced envelope materials, industrialised retrofits, and circular construction within harmonised policy frameworks that address both operational and embodied carbon. The tools for transformation already exist, and what is now required is coordinated implementation at scale to deliver a zero-emission, climate-resilient, and economically sustainable building sector.