1. Introduction
Industrial manufacturing increasingly relies on predictive maintenance to ensure reliability, safety, and resource efficiency. The concept of machinery health monitoring refers to the continuous assessment of a machine’s operational condition and remaining useful life (RUL) through sensor-based diagnostics and data analytics. This paradigm has evolved from simple condition monitoring toward intelligent, autonomous decision-support systems, yet challenges persist in scalability, explainability, and human integration.
1.1. Current Limitations in Machinery Health Monitoring
While such methodologies have long served the industry, they reveal critical deficiencies when challenged by the complexity and variability characteristic of modern industrial operations [
1]. A fundamental shortcoming of these systems is their lack of adaptability to evolving operational conditions and emerging failure patterns. Heavily dependent on historical data and expert-defined rules, traditional monitoring frameworks are inherently rigid, impeding their capacity to accommodate shifts in equipment behavior or the introduction of new process parameters [
2]. This rigidity frequently leads to increased false positives, delayed fault detection, and inefficient maintenance scheduling, all of which disrupt production continuity and elevate operational costs [
3]. Moreover, centralized architecture introduces bottlenecks in data processing and decision-making, undermining the system’s ability to respond promptly to real-time changes in operational states [
4]. The reliance on central processing units concentrates on analytical functions, resulting in latency issues and the creation of single points of failure that compromise overall system reliability [
5]. These limitations become especially pronounced in complex manufacturing environments, where numerous interconnected machines, each operating under distinct conditions, require simultaneous and coordinated monitoring.
1.2. Evolution Toward Autonomous Industrial Intelligence
The advent of artificial intelligence and advanced computational methods has revolutionized industrial monitoring systems, introducing autonomous decision-making and adaptive learning processes [
6]. Contemporary AI, particularly approaches grounded in multi-agent systems and distributed intelligence, surpasses the limitations of traditional centralized frameworks by fostering decentralized, self-organizing monitoring environments [
7]. Autonomous industrial intelligence marks a transition from reactive. to proactive supervision, wherein intelligent agents are capable of perceiving environmental conditions, anticipating potential failures, and independently initiating corrective measures [
8]. This progression entails the shift from static, rule-based systems to dynamic learning architectures that refine their diagnostic abilities through operational experience and environmental feedback [
8]. Key attributes of autonomous intelligence in industrial contexts include self-learning mechanisms that enhance system performance over time, distributed decision-making that lessens reliance on centralized control, predictive analytics for anticipating failures before their occurrence, and adaptive responses to unfamiliar operational scenarios [
9]. Together, these features enable the development of intelligent monitoring ecosystems that require minimal human intervention while ensuring high levels of accuracy and reliability [
10].
1.3. Multi-Agent Systems in Industrial Applications
Multi-agent systems (MASs) represent an effective framework for establishing autonomous industrial intelligence, as they distribute computational responsibilities among multiple specialized agents that collaborate toward shared objectives [
11]. In the realm of machinery health monitoring, multi-agent architectures offer significant advantages over traditional monolithic systems, providing enhanced scalability, superior fault tolerance, and greater adaptability to diverse monitoring needs [
12]. Within industrial settings, the implementation of multi-agent systems has proven highly effective in addressing complex monitoring challenges through coordinated agent interactions [
13]. Each agent within MASs can be tailored to focus on distinct aspects of the monitoring process, such as data acquisition, pattern recognition, fault diagnosis, or maintenance scheduling [
14]. This division of labor creates highly efficient monitoring ecosystems, wherein agents contribute specialized expertise while working collectively to ensure comprehensive coverage of industrial operations. Recent advancements in federated learning have further strengthened the capabilities of multi-agent systems by facilitating distributed learning across agents without necessitating centralized data consolidation [
15]. This approach is particularly advantageous in industrial environments where data privacy, bandwidth constraints, and limited computational resources render centralized learning impractical. Federated learning enables agents to exchange knowledge and enhance collective system performance while preserving data locality and minimizing communication overhead.
1.4. Research Gap and Motivation
Despite the considerable potential of multi-agent systems and autonomous intelligence within industrial applications, the current body of research lacks comprehensive frameworks that systematically guide the transition from traditional monitoring systems to fully autonomous industrial ecosystems. Existing studies often concentrate on isolated technical components, such as algorithm development or single-system implementations, without proposing holistic methodologies that encompass the breadth of industrial requirements and operational constraints [
16]. The absence of structured maturity models for autonomous industrial intelligence presents significant barriers for organizations aiming to adopt intelligent monitoring systems. In the absence of clear progression pathways and implementation strategies, companies face difficulties moving from conventional monitoring approaches to advanced autonomous solutions. This challenge is particularly acute in sectors such as ceramic manufacturing, where the integration of sophisticated artificial intelligence technologies must be balanced with established operational practices and rigorous safety standards [
17].
A further gap concerns the conceptual foundations of industrial AI. While the terms autonomous agents, multi-agent systems (MASs), and collaborative AI are frequently used, they do not fully capture the emerging paradigm needed for resilient, human-centric predictive maintenance. The proposed notion of Agentic AI extends beyond these frameworks. Autonomous agents emphasize independence in decision-making, MASs highlight distributed problem-solving, and collaborative AI focuses on human–machine teaming. By contrast, Agentic AI incorporates the dimension of agency: the ability of AI entities not only to act autonomously within predefined tasks, but also to proactively coordinate, negotiate, and reconfigure their roles in pursuit of system-level objectives while remaining accountable to human oversight. This reframing positions intelligent monitoring agents as intentional, goal-directed actors embedded in socio-technical ecosystems, where human operators, organizational policies, and technical agents co-evolve. Thus, Agentic AI represents not a re-labeling of MASs, but a step forward toward self-organizing, accountable, and human-centered industrial ecosystems [
18].
While Multi-Agent Systems (MASs) primarily focus on distributed task-solving and coordination among autonomous entities, Agentic AI extends this paradigm by integrating higher-order properties such as intentionality, adaptive role reconfiguration, and accountable autonomy. In MASs, decision hierarchies are typically predefined and reactive, whereas Agentic AI systems dynamically negotiate objectives and responsibilities according to contextual priorities and human oversight.
Table 1 summarizes the conceptual and functional distinctions between MASs and Agentic AI, highlighting the transition from cooperation-based autonomy to proactive, self-governing intelligence aligned with organizational goals.
Furthermore, previous research has not sufficiently addressed the critical equilibrium between autonomous operation and human oversight in industrial monitoring environments. While full automation promises enhancements in efficiency and responsiveness, industrial safety requirements and regulatory frameworks necessitate the retention of appropriate human involvement in pivotal decision-making processes. The development of effective human-centric autonomous systems demands careful consideration of user interaction modalities, system explainability, and robust fail-safe mechanisms. Additionally, comprehensive validation of autonomous monitoring systems in real-world industrial contexts is notably absent from the literature, as many investigations rely on laboratory simulations or simplified datasets rather than long-term industrial deployments [
19]. The intricate nature of industrial operations (including equipment interdependencies, environmental fluctuations, and production constraints) requires validation strategies that can demonstrate system efficacy under authentic operational conditions.
1.5. Objectives and Contributions
This study addresses the identified research gaps by proposing a comprehensive framework for implementing autonomous multi-agent systems in machinery health monitoring, with a particular focus on enabling the transition from reactive maintenance to self-organizing, intelligent industrial ecosystems. The research objectives are carefully structured to promote theoretical advancement and provide practical guidance for industrial organizations.
The primary objective is to develop an Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM), which offers a systematic pathway for the deployment of intelligent health monitoring systems across five progressive maturity levels, ranging from basic reactive sensing to fully autonomous industrial ecosystems.
Secondary objectives include (1) designing a multi-agent architecture that integrates sensing, reasoning, action, and coordination to achieve robust machinery health monitoring; (2) implementing federated learning mechanisms that facilitate distributed intelligence, safeguard data privacy, and minimize communication overhead; (3) validating the proposed framework within a ceramic tile manufacturing environment to demonstrate its applicability in traditional industrial sectors; and (4) quantifying improvements in system performance with respect to predictive accuracy, reductions in false positives, and operational efficiency. This research makes several significant contributions to the field of intelligent industrial monitoring.
First, it introduces the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model as an innovative theoretical construct, systematically organizing the evolution toward autonomous industrial intelligence. The AIMM equips organizations with a structured methodology for deploying intelligent monitoring systems while effectively managing complexity and ensuring operational continuity.
Second, the study presents a comprehensive multi-agent architecture that encompasses the full spectrum of monitoring requirements. Specialized agent roles—such as data collection, pattern analysis, maintenance scheduling, and system orchestration—collaborate to form an integrated monitoring ecosystem.
Third, the study demonstrates the practical utility of autonomous monitoring systems through implementation and validation in a ceramic tile manufacturing facility, providing empirical evidence of effectiveness under authentic industrial conditions and offering insight into implementation challenges and practical solutions.
From a methodological perspective, the research develops a federated learning framework tailored to industrial multi-agent systems, enabling distributed learning while addressing constraints related to data privacy, communication bandwidth, and resource allocation. Practically, this work equips industrial organizations with a scientifically grounded methodology for adopting autonomous machinery health monitoring. The framework encompasses agent design, system integration, performance evaluation, and strategies for human–machine collaboration, thereby facilitating a smooth transition to intelligent monitoring systems. The subsequent sections of this paper elaborate on the theoretical underpinnings of the AIMM, describe the multi-agent architecture and implementation methodology, present validation results from the ceramic manufacturing case study, and discuss the broader implications and future prospects of autonomous industrial intelligence.
To address the persistent challenges in industrial predictive maintenance, this study introduces the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) as a structured roadmap for transitioning from reactive approaches to self-organizing, human-accountable intelligence ecosystems. The AIMM conceptualizes autonomy as a multi-dimensional construct, encompassing sensing, reasoning, coordinated action, and explainable human–machine collaboration. The framework is implemented and validated through a multi-agent monitoring architecture deployed in an industrial ceramic facility, where federated learning and adaptive edge analytics enable privacy-preserving, distributed intelligence. Building on and synthesizing existing research in multi-agent systems, federated learning, and industrial AI maturity models, the following section develops the theoretical framework that grounds the AIMM within current scientific discourse and positions it as a practical bridge between theoretical autonomy and real-world industrial implementation. Subsequent sections elaborate on the theoretical underpinnings of the AIMM, describe the multi-agent architecture and implementation methodology, present validation results from the ceramic manufacturing case study, and discuss broader implications and future prospects for autonomous industrial intelligence.
2. Theoretical Framework
This section develops the theoretical foundations underlying the proposed Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM). It serves as a structured literature review that consolidates the main research streams on intelligent industrial monitoring, multi-agent architectures, federated learning, and human-centric AI. By synthesizing these perspectives, the section positions the AIMM within the broader evolution of predictive maintenance—from rule-based diagnostics to distributed, explainable, and human-accountable intelligence systems. Each subsequent subsection (
Section 2.1,
Section 2.2,
Section 2.3 and
Section 2.4) examines a specific dimension of this evolution: (i) the conceptual basis of the AIMM as a maturity model for industrial autonomy; (ii) the design principles of multi-agent architectures that operationalize distributed intelligence; (iii) the role of federated learning in enabling privacy-preserving collaboration; and (iv) the integration of human expertise through explainable, trust-oriented interaction mechanisms. This theoretical groundwork anchors the empirical validation presented in later sections and clarifies how the AIMM extends beyond traditional multi-agent or collaborative AI paradigms toward fully agentic industrial ecosystems.
2.1. Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM)
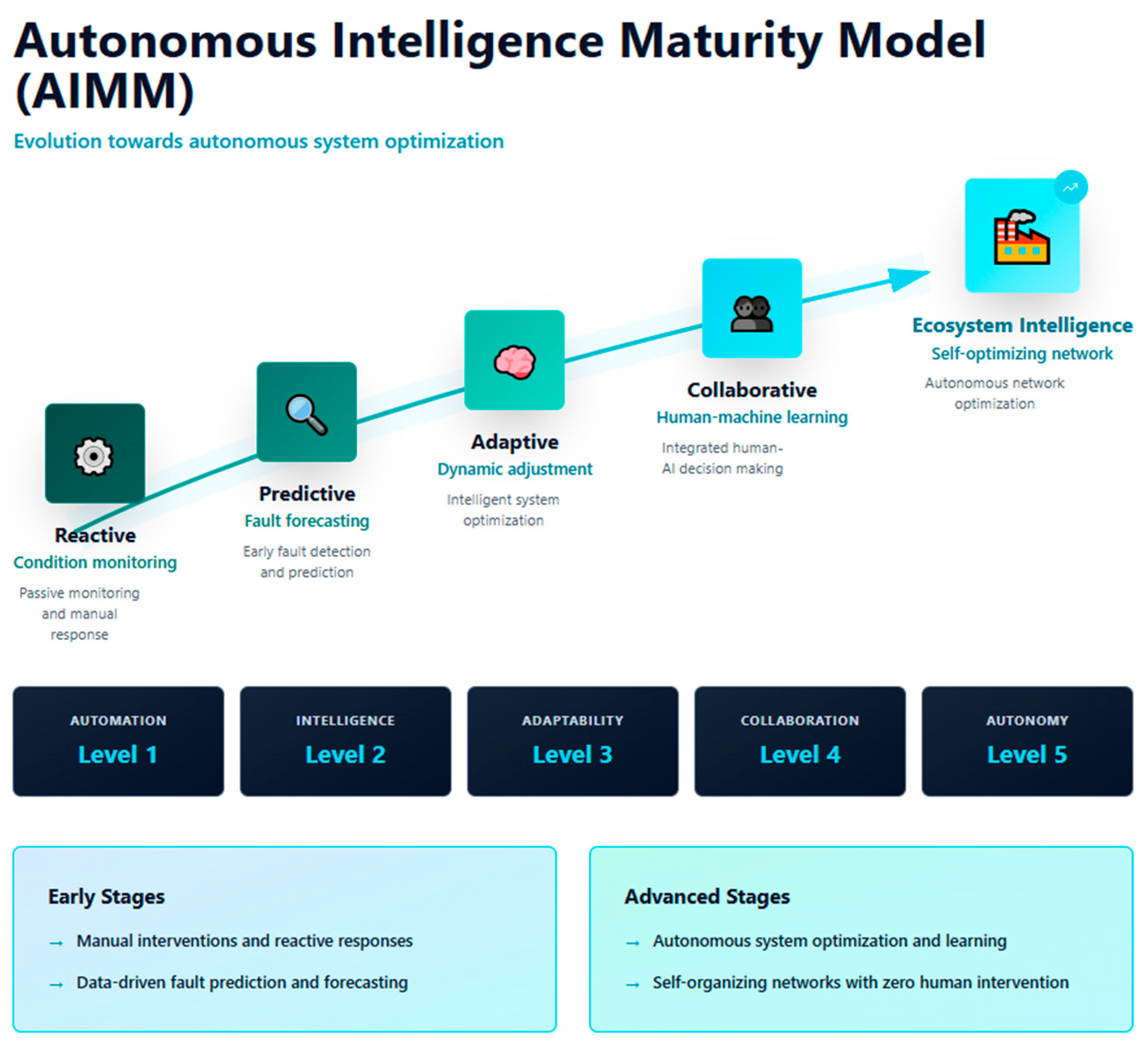
The Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) provides a structured framework for advancing from basic reactive systems to fully autonomous industrial intelligence ecosystems. The AIMM delineates five progressive maturity levels, each characterized by specific technological, organizational, and operational developments essential for autonomous machinery health monitoring [
20].
Level 1 represents a pre-autonomy baseline used as the reference point for subsequent progression toward autonomous intelligence. Systems at this level perform data acquisition and threshold-based alerting, while diagnostic interpretation and corrective actions remain entirely human-driven [
21]. Including this non-autonomous baseline enables quantitative comparison across AIMM maturity levels.
Level 2 introduces predictive intelligence, leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze historical operational data and anticipate equipment failures [
21]. These systems enhance diagnostic capabilities, supporting predictive maintenance and early warning functions, though they generally maintain a centralized structure and require ongoing model retraining.
Level 3, adaptive intelligence, marks a transition to self-learning systems capable of dynamically adjusting operational parameters and refining models in real time [
22]. This stage integrates online learning and adaptive control, enabling systems to autonomously optimize performance in response to changing environments. Distributed processing begins to replace centralized architectures, increasing resilience and scalability.
At Level 4, collaborative intelligence emerges through multi-agent architectures where specialized agents and human operators interact to fulfill comprehensive monitoring and maintenance objectives. The collaboration between autonomous agents and human expertise is facilitated by intelligent user interfaces and collaborative learning mechanisms, enhancing decision-making in complex industrial scenarios [
23]. At this stage, autonomy becomes collaborative: agents execute distributed reasoning and decision-making, while safety-critical approvals remain under human oversight, ensuring shared accountability and compliance with industrial safety standards. Federated learning is introduced here as an enabler of distributed collaboration, allowing cross-agent model updates under privacy and bandwidth constraints.
Level 5 represents ecosystem intelligence, where self-organizing agents autonomously coordinate maintenance and monitoring across interconnected production units. These systems demonstrate collective, adaptive behaviors, optimizing both structure and resource allocation to manage interdependencies and ensure robust, system-wide resilience [
24]. Hierarchical federated aggregation extends this collaboration across facilities, supporting ecosystem-level optimization and emergent autonomy.
The AIMM guides industrial organizations through the systematic adoption of autonomous intelligence, detailing the evolution from simple monitoring toward intelligent, resilient, and fully autonomous industrial ecosystems.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete AIMM framework, showing the progression from reactive intelligence through ecosystem intelligence, with the associated technological capabilities and organizational transformations at each maturity level.
Table 2 provides a comprehensive comparison of the five AIMM levels, detailing the technological requirements, decision-making mechanisms, human roles, and autonomy characteristics that distinguish each maturity stage.
2.2. Multi-Agent Architecture Design Principles
The implementation of autonomous intelligence at advanced AIMM levels necessitates sophisticated multi-agent architectures that distribute computational tasks, coordinate agent activities, and maintain overall system coherence. Designing such systems involves addressing key challenges in agent communication, task allocation, conflict resolution, and scalability [
25].
2.2.1. Agent Specialization and Role Definition
While
Section 2.1 defines the capabilities that characterize each AIMM maturity level, this subsection details the operationalization of these capabilities through agent design and interaction principles. The emphasis here is placed on the practical aspects of implementation, including interfaces, coordination rules, and protocols for handling failures, rather than revisiting the conceptual definitions of agent roles. In this context, effective machinery health monitoring is achieved by establishing precisely defined agent roles that facilitate complementary tasks and ensure comprehensive system oversight. The proposed architecture is structured around four principal agent types, each with clearly delineated operational domains:
Sensing Agents: Responsible for data acquisition and preprocessing across distributed sensor networks, including sensor calibration, data validation, and preliminary signal processing. These agents interface directly with physical equipment and the environment.
Reasoning Agents: Perform advanced analytics such as pattern recognition, fault diagnosis, and predictive modeling using machine learning and expert knowledge. They form the cognitive core of the monitoring system.
Action Agents: Manage maintenance scheduling, resource allocation, and execution coordination. By interfacing with maintenance systems and human operators, they translate diagnostic outputs into practical interventions.
Coordination Agents: Oversee inter-agent communication, task distribution, and system optimization. Their role is essential in resolving conflicts and ensuring efficient resource utilization across the monitoring ecosystem.
Recent advances in multi-agent reinforcement learning confirm that role specialization enhances both fault diagnosis and resource allocation, especially in predictive maintenance scheduling [
26]. Moreover, multi-agent reinforcement strategies applied to critical assets such as turbofan engines illustrate how specialization improves resilience under dynamic conditions [
27].
2.2.2. Communication Protocols and Information Sharing
Robust communication protocols are vital for efficient information exchange, bandwidth optimization, and data security. The proposed hierarchical protocol structure operates at local, regional, and global levels, facilitating rapid responsiveness and bandwidth efficiency. Standardized message formats, priority assignments, and routing mechanisms enable interoperability between agents developed by different teams. Comprehensive security measures are implemented to protect operational data and maintain system integrity.
Recent surveys highlight that multi-agent communication remains a key bottleneck for collaborative intelligence, requiring optimization of routing and prioritization strategies [
28]. In addition, blockchain-based protocols are increasingly explored as a means to guarantee secure communication, traceability, and decentralized trust in industrial MAS deployments [
29]. These developments demonstrate the importance of designing communication layers that balance efficiency with robustness and security.
2.2.3. Learning and Adaptation Mechanisms
Multi-agent architectures support both individual agent learning and collective system improvement through collaborative knowledge sharing. Agents develop specialized competencies using experiential data and feedback, while advanced machine learning algorithms enhance decision-making and enable dynamic adaptation to changing conditions. System-wide collaborative learning promotes knowledge exchange, with federated learning methodologies advancing agent capabilities without centralized data aggregation, thus preserving data privacy. Meta-learning techniques further optimize learning strategies across diverse operational contexts. Integrating individual specialization with collaborative intelligence is essential for developing adaptive, scalable, and resilient multi-agent systems in complex industrial environments.
Clustered federated learning has recently been shown to enhance predictive performance while reducing training overhead and coping with heterogeneous device capabilities in industrial IoT environments [
30]. Moreover, systematic reviews of data and analytics maturity demonstrate that adaptive learning frameworks are crucial for scaling AI-driven decision support [
31]. Multi-objective reinforcement learning approaches also provide evidence of effective trade-offs between fault prediction accuracy and computational efficiency in real industrial case studies [
32,
33].
2.3. Federated Learning for Industrial AI
Federated learning is a pivotal technology for distributed intelligence in industrial multi-agent systems, enabling data privacy, bandwidth efficiency, and scalable computation. Its architecture supports both local specialization and system-wide advancement: each agent independently trains models using site-specific data, developing expertise tailored to individual contexts, while periodic aggregation synthesizes insights into a comprehensive global model [
34]. This collaborative approach ensures efficient knowledge sharing without the need for centralized data storage.
To safeguard sensitive industrial data, federated learning employs privacy-preserving techniques such as differential privacy, which protects individual data points by introducing controlled noise to model parameters, and secure aggregation protocols, which use cryptographic methods to prevent disclosure of agent-specific contributions [
35]. These measures maintain confidentiality while enabling collaborative model improvement. Industrial environments impose constraints related to reliability, limited computational resources, and restricted communication bandwidth. Federated learning addresses these challenges through asynchronous protocols that accommodate agent availability and adaptive scheduling aligned with computational capacity. Resource-aware algorithms dynamically adjust complexity to fit local constraints, and edge computing enhances local processing, reducing communication overhead and improving system responsiveness [
36]. Recent applications in the IIoT domain demonstrate cluster-assisted custom federated learning approaches which mitigate non-IID data issues and reduce training resource needs by grouping edge devices with similar data distributions, resulting in improved predictive performance under realistic constraints [
37]. Similarly, adaptive federated learning architectures for resource-constrained IoT show that multi-edge clustering and edge-AI node selection significantly improve accuracy and model convergence in heterogeneous and bandwidth-limited settings [
38].
Federated learning offers a robust framework for collaborative model development in complex industrial settings, balancing privacy, efficiency, and adaptability while optimizing collective intelligence across distributed platforms.
2.4. Human-Centric Collaborative Intelligence
This section addresses the importance of integrating human expertise with autonomous systems in industrial environments, emphasizing the need for collaborative intelligence. Human–machine interaction must be designed with adaptive interfaces that accommodate varying user expertise and operational contexts, ensuring clear and actionable information. Explainable AI enhances user comprehension by clarifying the rationale underlying automated decisions, which supports situational awareness and informed human oversight [
39]. To foster appropriate trust in autonomous systems, transparency mechanisms should provide insights into operations, decision-making, and system performance. Explicit communication of uncertainty and regular performance assessments help calibrate user trust, while fail-safe mechanisms and human override options safeguard operational safety and continuity [
40]. Continuous validation and systematic monitoring further sustain user confidence in system reliability.
Effective collaboration between human experts and automated agents is achieved through mechanisms that support knowledge integration and interactive learning. Human-in-the-loop strategies enable experts to refine algorithms, guide model development, and correct errors, while automated systems reveal complex patterns that broaden operator understanding [
41]. This bidirectional knowledge exchange establishes a synergistic partnership, leveraging both human insight and machine intelligence to enhance system adaptability and resilience in complex industrial settings.
The theoretical framework consolidates the conceptual basis for the proposed Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM), positioning it as both a synthesis and an evolution of existing paradigms in intelligent maintenance and distributed industrial AI. The AIMM emerges as the integrative outcome of the four dimensions discussed above: hierarchical autonomy, multi-agent coordination, federated learning for privacy-preserving collaboration, and human-centric explainability. Together, these elements form a structured pathway for transitioning from reactive, single-agent diagnostics to fully agentic industrial ecosystems capable of accountable, self-organizing behavior. Building upon this conceptual foundation, the next section translates the AIMM framework into a tangible implementation.
Section 3 (Materials and Methods) details the architecture, data infrastructure, and validation procedures adopted to operationalize the proposed multi-agent monitoring system within an industrial manufacturing environment.
3. Materials and Methods
This section operationalizes the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) within a real industrial context, translating its conceptual structure into an implementable multi-agent monitoring architecture. The methodology integrates hardware, software, and organizational components to enable distributed intelligence and privacy-preserving collaboration across production assets.
Section 3.1 describes the multi-agent system architecture, outlining the functional design and agent interactions;
Section 3.2 details the federated learning framework supporting decentralized model training;
Section 3.3 presents the industrial implementation environment and explains the experimental design, validation metrics, and statistical procedures employed. Together, these elements provide the methodological foundation for evaluating the effectiveness and scalability of Agentic AI in smart manufacturing ecosystems.
3.1. Multi-Agent System Architecture
This work presents a comprehensive framework for deploying autonomous intelligence in industrial equipment monitoring through a hierarchical multi-agent architecture. The system comprises four specialized agent types (sensing, reasoning, action, and coordination agents) distributed within an edge-computing environment. Sensing agents ensure reliable data acquisition and preliminary anomaly detection through advanced preprocessing and local analytics. Reasoning agents perform in-depth diagnostic analysis using a suite of machine learning models, including ensemble methods and deep learning networks, tailored to diverse industrial fault scenarios. Action agents translate diagnostic outputs into maintenance decisions via multi-criteria analysis and optimal resource allocation, while maintaining seamless integration with human operators through interactive dashboards. Coordination agents orchestrate inter-agent communication and system-wide optimization, resolving conflicts and ensuring global performance objectives are met through dynamic task allocation and distributed consensus algorithms [
42].
The federated learning framework further enhances system adaptability and privacy. Local models are continuously trained on equipment-specific data, and periodic aggregation refines a global model without centralizing sensitive information. Differential privacy, secure aggregation protocols, and data anonymization safeguard data confidentiality throughout the process [
43]. Recent studies have shown that hardware-aware and blockchain-enhanced aggregation strategies improve both scalability and resilience of federated systems in industrial settings [
44].
Communication strategies and resource-aware algorithms optimize bandwidth and computational load, supporting operational efficiency, as demonstrated in constrained IIoT environments where clustering and adaptive scheduling significantly improve training convergence and robustness [
45].
Figure 2 presents the complete multi-agent system architecture implemented in this study, illustrating the hierarchical organization of the four agent categories and their integration with the ceramic manufacturing equipment. The diagram shows the bidirectional communication flows between agent layers and the underlying federated learning infrastructure that enables distributed intelligence across the monitoring ecosystem.
3.2. Implementation Environment
The validation of the proposed multi-agent system was conducted within a ceramic tile manufacturing facility in Sassuolo, Italy, with an annual production capacity of 12 million square meters and 180 personnel [
46]. The production process encompasses raw material preparation, hydraulic pressing, drying, firing, and glazing, supported by diverse equipment including hydraulic presses (1600–3000 t), continuous dryers, roller hearth kilns (up to 400 m, 1200 °C), and glazing lines with spray booths [
47]. The facility operates on a three-shift schedule, 350 days annually, with high utilization rates for critical machinery and routine preventive maintenance during weekly and annual shutdowns.
A comprehensive sensor deployment strategy, aligned with ISO 10816 standards [
48], was implemented to monitor key equipment components such as bearing housings, gearbox casings, motor frames, and major supports. Hydraulic presses are fitted with accelerometers, temperature, and pressure sensors to monitor vibration, thermal conditions, and hydraulic profiles. Kilns utilize distributed sensing networks with vibration, temperature, infrared, and gas flow sensors for precise operational oversight. Glazing lines incorporate vibration and flow sensors to ensure accurate glaze application and stability. Use of ISO 10816-1 and -3 (or revised/related industrial vibration standards) provides guidance on acceptable vibration levels and sensor placement for rotating and non-rotating machine parts [
49].
A multi-rate sampling protocol was employed, capturing high-frequency vibration data at 25.6 kHz and low-frequency parameters at 1 Hz, with strategic averaging to optimize fidelity. Data are stored locally with a 30-day retention period and archived centrally using compression techniques for efficient long-term storage. Automated backup procedures and continuous data quality monitoring—including signal-to-noise ratio analysis and sensor drift detection—ensure data integrity and system reliability. Daily quality reports support proactive maintenance and operational continuity. These methodologies align with recent deployments in edge-IoT and tiny-ML settings, where high sampling rates and robust data pipelines are used under industrial constraints to detect incipient faults early with minimal resource overhead [
50,
51].
This implementation framework facilitates real-time, holistic monitoring of ceramic production equipment, underpinning advanced fault detection and predictive maintenance capabilities in an industrial context.
3.3. Experimental Design and Validation Methodology
The experimental validation began with a three-month baseline period using traditional threshold-based monitoring to establish reference benchmarks. During this phase, naturally occurring faults, maintenance actions, and operational patterns were systematically recorded, and historical maintenance logs provided ground truth for fault detection evaluation. The multi-agent system was then deployed incrementally to minimize disruption. In the initial stage, sensing agents and basic anomaly detection were introduced. This was followed by the integration of reasoning agents equipped with advanced machine learning capabilities, and finally by the addition of action and coordination agents to complete the system architecture. Throughout the process, traditional and experimental systems operated in parallel, allowing for direct performance comparisons. A randomized split between control and experimental equipment groups, with monthly rotations, ensured unbiased results. Statistical significance was assessed using paired t-tests at an α level of 0.05.
Performance evaluation utilized key metrics, including sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F1-score for fault detection; detection latency; and false alarm rate as a measure of system reliability. Prognostic effectiveness was assessed through metrics such as Remaining Useful Life (RUL) prediction accuracy, prognostic horizon, and uncertainty quantification, with actual failure events serving as benchmarks [
52]. Operational efficiency was measured via Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and its components, as well as maintenance costs and energy efficiency, following practices in recent industrial case studies that forecast OEE under dynamic production conditions [
53]. Multi-agent system performance was characterized by inter-agent communication latency, task allocation efficiency, and coordination overhead. Learning progress was tracked through model accuracy improvements and federated learning convergence rates. Human–machine interaction was evaluated by operator acceptance and override frequency. This comprehensive set of metrics ensured rigorous technical and operational validation.
Statistical validation involved hypothesis testing to determine significant improvements in fault detection, reductions in false alarms and maintenance costs, and increased operational efficiency. Time series analysis decomposed performance trends, while change point detection identified significant shifts following system implementation, in line with methods proposed in recent RUL literature under variable operating conditions [
54]. Autocorrelation analysis confirmed the independence of observations, and correlational analyses revealed relationships among monitoring parameters and operational results. Cluster analysis facilitated the identification of equipment groups and failure patterns, supporting targeted optimization strategies. Uncertainty was quantified through confidence intervals derived from bootstrap resampling, and effect sizes were calculated to determine the practical significance of observed improvements. These analytical procedures were applied to a longitudinal dataset comprising 20 equipment units monitored over 12 months, which accumulated approximately 25,000 operating hours and 146 recorded failure events. To ensure robust model evaluation, the data were partitioned into training (70%), validation (15%), and testing (15%) sets using time-based blocking to prevent information leakage. In parallel, monthly operator surveys (n = 38, 86% response rate) provided complementary qualitative insights, employing 5-point Likert scales with anonymized and reverse-coded items to mitigate acquiescence bias. The integration of technical and human-centric data was further supported by economic modeling, based on assumptions including a baseline downtime cost of €1200 per hour, electricity at €0.22 per kWh, natural gas at €0.67 per Nm
3, and labor at €45 per hour. A sensitivity analysis with ±20% variation in input parameters confirmed a positive net present value and a payback period of less than two years, underscoring the financial viability of the proposed optimization strategies.
4. Results
4.1. Agent Performance Analysis
The deployment of specialized agents throughout the ceramic manufacturing facility yielded substantial enhancements in monitoring capabilities and operational efficiency. Sensing agents achieved a remarkable 99.7% data availability across all equipment units, marking a 12% improvement over conventional centralized systems. Advanced edge-based data preprocessing significantly reduced communication bandwidth requirements, lowering average usage from 2.4 GB to 0.77 GB per equipment unit each day. The quality of vibration data improved considerably, with the signal-to-noise ratio increasing from 18.3 dB to 27.8 dB due to sophisticated filtering and artifact rejection methods. Temperature sensor drift compensation further reduced measurement uncertainty from ±2.1 °C to ±0.8 °C, ensuring more precise thermal assessments. Local anomaly detection capabilities enabled the identification of 94% of extreme events within 30 s, a notable improvement compared to the average centralized response time of 156 s. Over the deployment period, the effectiveness of machine learning models consistently improved. Random Forest classifiers, for instance, achieved 89.3% accuracy in classifying hydraulic press faults, outperforming rule-based threshold systems, which reached only 76.4% [
55]. LSTM networks demonstrated 92.1% accuracy in predicting bearing degradation up to 72 h in advance. Isolation Forest algorithms excelled in identifying previously unseen fault patterns with a precision of 85.7% and a false positive rate of just 3.2%. Semi-supervised learning approaches successfully leveraged unlabeled operational data, enhancing model performance by an average of 7.8% across different equipment types. Optimized maintenance scheduling resulted in a 23% reduction in total maintenance costs and increased equipment availability from 87.2% to 91.6%. The multi-criteria decision analysis framework effectively balanced competing objectives, with 89% of automated maintenance recommendations accepted by operators without further modification. Resource optimization led to a 34% reduction in emergency maintenance interventions through improved scheduling and coordination. Task allocation efficiency was notably high, with 97% of tasks delegated to optimal agents within 15 s. Conflict resolution mechanisms successfully managed 156 inter-agent conflicts, with 92% resolved automatically and the remaining 8% escalated to human operators. Global optimization preserved system coherence, balancing individual agent objectives and yielding a 15% improvement in overall equipment effectiveness.
The multi-agent communication framework exhibited remarkable robustness under diverse network conditions and operational scenarios. Message delivery success rates consistently surpassed 99.8% across all communication channels, while the average latency for critical safety transmissions remained at 47 ms. The adoption of the MQTT protocol with an appropriate Quality of Service ensured reliable message delivery and minimized network overhead. During routine operations, total communication overhead was maintained at 1.2% of available network bandwidth, increasing modestly to 3.8% during coordinated maintenance activities. Efficient message compression, utilizing JSON optimization and binary encoding for numerical data, led to a 73% reduction in payload size. Hierarchical communication protocols facilitated effective traffic prioritization, guaranteeing sub-50 millisecond delivery times for safety-critical messages. The system’s resilience was further demonstrated during network disruptions, supported by automatic failover mechanisms that sustained connectivity throughout planned maintenance periods. Agent autonomy during communication failures averaged 4.7 h before any observable degradation in performance, enabling stable operation even during extended outages. This robust communication infrastructure underpinned the multi-agent system’s ability to maintain operational continuity and responsiveness in dynamic industrial environments [
56].
4.2. Predictive Accuracy Assessment
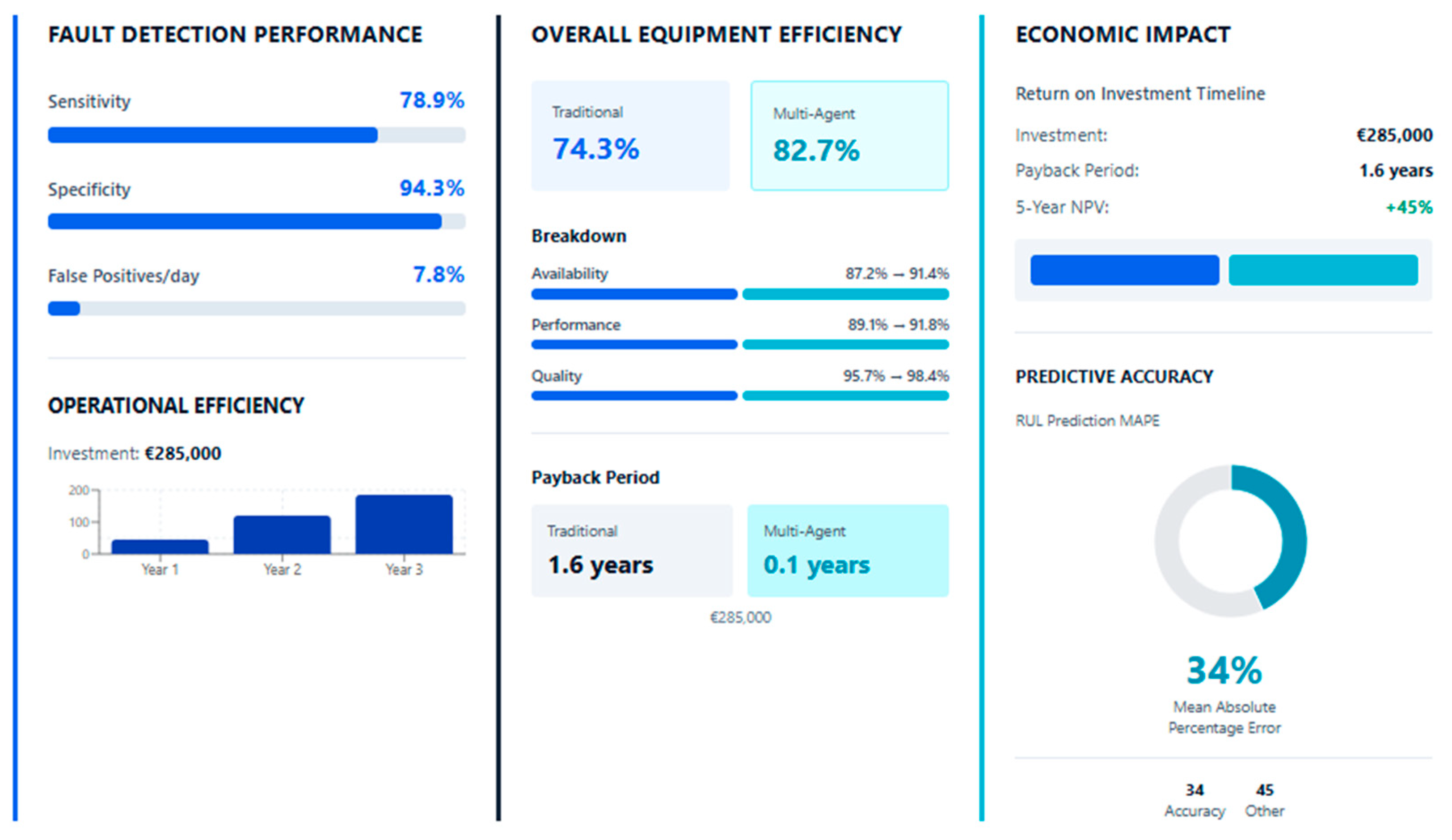
The deployment of multi-agent monitoring systems in ceramic manufacturing significantly enhanced fault detection performance and prognostic capabilities across all equipment categories. System sensitivity increased to 94.3%, up from 78.9% with baseline threshold monitoring, while specificity improved to 96.8%. Notably, hydraulic press monitoring attained 96.7% sensitivity for hydraulic faults and 94.2% for mechanical faults, with corresponding precisions of 91.8% and 89.3%. The overall F1-score reached 93.1%, indicating balanced sensitivity and precision.
In roller hearth kiln applications, the system achieved 92.4% sensitivity for thermal anomalies and 88.9% for mechanical faults, maintaining a high level of precision at 87.6% despite challenging conditions. For glazing line operations, sensitivity was 89.7% for pump faults and 91.3% for spray mechanism anomalies. Multi-class fault severity classification reached 86.4% accuracy, with critical faults detected at a sensitivity of 98.1% and minor faults at 82.3%, supporting both immediate intervention and proactive maintenance.
Prognostic performance also showed substantial improvements. The mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) for Remaining Useful Life (RUL) predictions averaged 18.6%—notably better than the 34.2% observed with traditional, manufacturer-based maintenance intervals. Main hydraulic press bearings yielded a MAPE of 14.3% and a predicted horizon up to 240 h, while electric motor insulation degradation forecasts achieved a MAPE of 22.1% with horizons reaching 480 h. Hydraulic system wear and valve forecasts resulted in MAPEs of 19.8% and 21.5%, respectively. Fluid contamination forecasting extended component lifespan by an average of 28%.
These results demonstrate that the multi-agent system delivers robust, reliable fault detection and predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and optimizes maintenance planning through advanced data-driven methodologies [
57]. Similar recent studies using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning approaches report comparable improvements in RUL accuracy and cost reduction, underlining the validity of the approach [
58]. Additionally, cost-optimised comparative evaluations of ML models confirm that ensembles and cost-sensitive metrics can push sensitivity and precision above 90% in industrial-scale predictive maintenance datasets [
59]. Methods addressing stochastic conditions in RUL prediction align with our observed performance gains in long horizon forecasts [
60].
4.3. False Positive Rate Reduction
The reduction in false positive alarms emerged as a pivotal factor for the acceptance and practical utility of the multi-agent system within industrial monitoring. The deployment of advanced contextual analysis and machine learning algorithms led to a 67% decrease in false positive alerts, lowering the daily average from 23.7 to 7.8 across all monitored equipment. Nuisance alarms during normal operational transients were reduced by 78%, owing to enhanced temporal pattern analysis and operational state correlation. Production mode recognition achieved an accuracy of 94.7%, allowing for context-aware alarm thresholds that distinguished effectively between startup, steady-state, and shutdown conditions.
Cross-parameter validation further minimized single-sensor false alarms by 54%, as correlation with related monitoring parameters provided greater diagnostic reliability. In particular, vibration alarms, when validated through temperature and operational load correlation, experienced an 89% reduction in false positives without compromising fault detection sensitivity. The implementation of dynamic threshold adjustment based on real-time operational conditions resulted in a 43% decrease in false alarms compared to static threshold methods. Machine learning-based optimization enabled the system to adapt to seasonal variations, changes in production mix, and equipment aging.
These improvements in alarm management significantly elevated operator confidence and response effectiveness. Surveys among maintenance technicians indicated an 82% rise in alarm confidence, with 94% of respondents expressing greater trust in automated monitoring recommendations. The reduced alarm fatigue contributed to a 31% improvement in response time to genuine alarms, underscoring enhanced system reliability.
Alarm prioritization was also notably effective. A three-tier classification system—distinguishing critical, warning, and informational alarms—yielded a 96% agreement with expert operator assessments. Critical alarms demonstrated a positive predictive value of 98.3%, ensuring immediate action for safety-critical events, while warning alarms achieved an 87.6% positive predictive value, supporting efficient maintenance planning without creating unnecessary urgency.
4.4. Operational Efficiency Improvements
Operational improvements in equipment effectiveness highlighted the impact of autonomous monitoring systems. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) increased from 74.3% to 82.7%, reflecting an 11.3% rise in production efficiency, which encompassed enhancements in equipment availability, performance, and product quality.
Implementation of predictive maintenance scheduling led to a 28% reduction in planned downtime through optimized timing and resource management. Maintenance window utilization increased substantially, while coordination across multiple equipment units reduced total downtime by 15%. Emergency interventions decreased by 43%, with condition-based maintenance strategies contributing to a 34% rise in Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and a 19% reduction in Mean Time To Repair (MTTR).
Energy efficiency also benefited from systematic monitoring. Specific energy consumption was reduced by 7.3%, facilitated by targeted replacement of degraded motors and optimization of operational parameters. Roller hearth kiln monitoring enabled a 4.8% decrease in natural gas usage, while combustion air management improved thermal efficiency by 2.3%. Heat recovery system maintenance further enhanced recovery efficiency by 12%.
In addition, acoustic monitoring for compressed air systems detected significant leaks, resulting in an 11% reduction in energy consumption following repairs. Compressor loading optimization provided an additional 6% savings. These advancements collectively demonstrate significant gains in operational reliability, resource optimization, and energy efficiency through integrated multi-agent monitoring and predictive maintenance frameworks.
4.5. Learning Curve Analysis
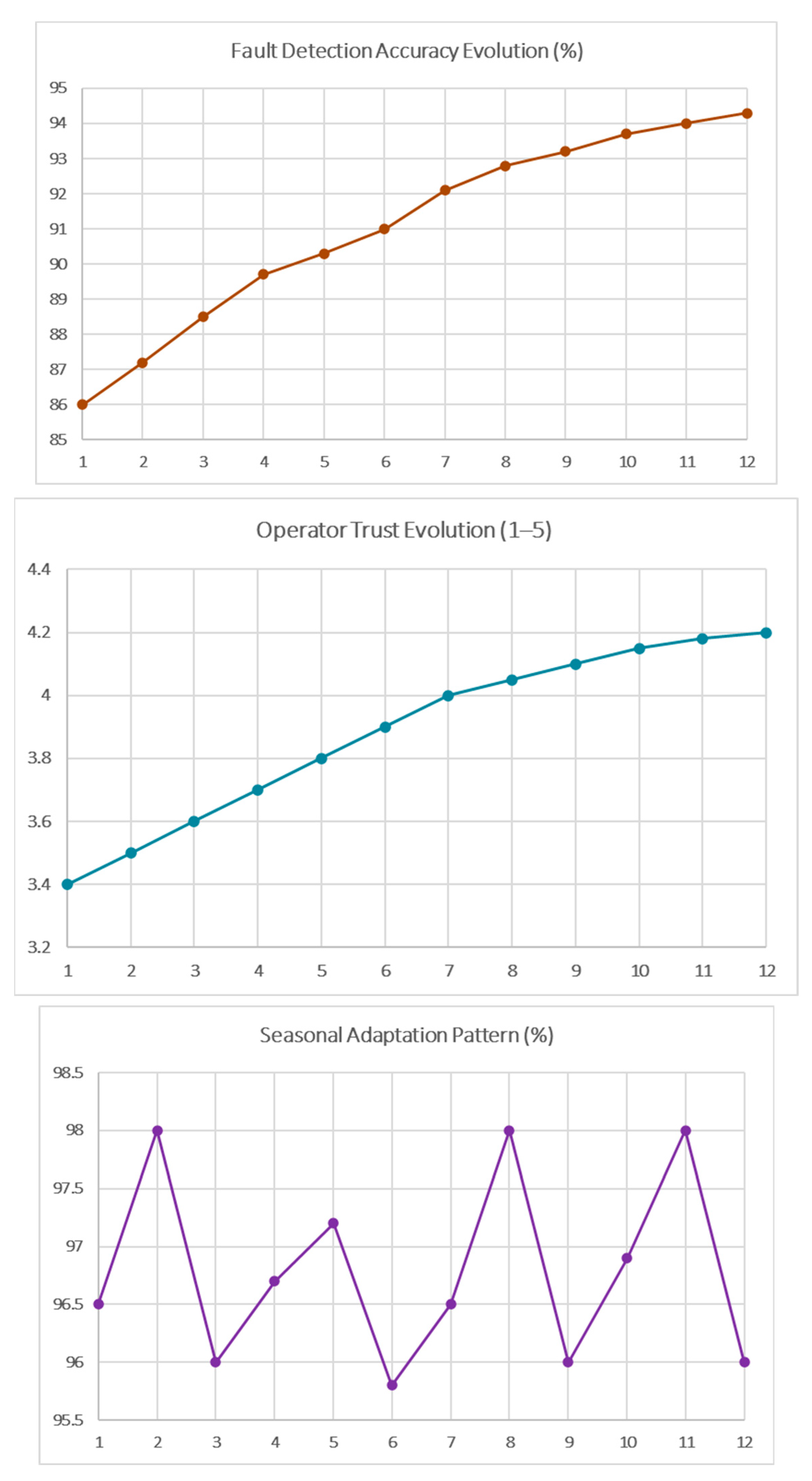
The performance of individual machine learning agents improved significantly throughout the deployment period [
61]. Fault detection accuracy increased from 82.4% in the first month to 94.3% after twelve months, following a logarithmic learning curve. Optimal model updates were achieved with every 100 new samples, balancing learning efficiency and computational demands. Domain adaptation strategies, particularly transfer learning, markedly accelerated model development for new equipment [
61]. Training time for achieving acceptable performance was reduced by 67%, from six weeks to two weeks, especially effective within similar equipment categories, such as hydraulic presses, where adaptation reached a 78% success rate. Seasonal adaptation mechanisms enabled models to accommodate operational variations, limiting performance degradation during transition periods to 3.7%.
The incorporation of annual seasonal pattern recognition improved forecast accuracy for temperature-sensitive equipment by 12%. Federated learning provides robust system-wide knowledge sharing while maintaining data privacy. Federated models reached 97% of the accuracy of centrally trained models, with only 2.1% of baseline data transmission required. Differential privacy measures effectively safeguarded against model inversion attacks, maintaining 94% of non-private model accuracy, and secure aggregation protocols ensured data security across 156 training rounds.
The allocated privacy budget allowed for twelve months of continuous learning with sustained privacy guarantees. Collaboration among agent types contributed to an 11% improvement in overall system performance compared to isolated learning. Coordination agents enhanced knowledge transfer efficiency by 23%, and cross-facility federated learning trials showed a 15% performance gain through shared learning with similar facilities. Overall, these strategies demonstrate the effectiveness of collaborative, privacy-preserving learning approaches for adaptive industrial monitoring systems.
Figure 3 illustrates the temporal evolution of system performance, demonstrating the adaptive learning capabilities that distinguish the multi-agent approach. The learning curves show continuous improvement in fault detection accuracy, progressive operator trust calibration, and successful seasonal adaptation with minimal performance degradation during transition periods.
4.6. Comparison with Traditional Systems
4.6.1. Quantitative Performance Comparison
Direct comparison between multi-agent autonomous monitoring and traditional threshold-based systems demonstrated substantial advantages across all measured performance dimensions.
Table 3 summarizes key performance metrics comparing baseline and multi-agent system performance.
These improvements compare favorably with recent studies; for instance, Li and Li [
62] reported F1-score accuracies around 95–96% using deep learning models on industrial sensor datasets, while Varalakshmi et al. [
63] demonstrated robustness under streaming conditions and unstable network environments. This alignment with the broader literature underscores the validity and generalizability of the performance gains achieved in the present study.
Statistical significance testing using paired
t-tests confirmed significant improvements across all metrics (α = 0.05). Effect size analysis using Cohen’s d indicated large practical significance for all major performance improvements (d > 0.8).
Figure 4 provides a comprehensive visual comparison of system performance metrics, highlighting the substantial improvements achieved across fault detection, operational efficiency, economic impact, and predictive accuracy dimensions. The dashboard format facilitates rapid assessment of the multi-agent system’s effectiveness relative to traditional monitoring approaches.
To complement the detailed quantitative metrics presented above, a concise summary of the main improvements achieved by the multi-agent monitoring system is reported in
Table 4. This table consolidates the most relevant performance indicators, allowing a direct comparison between the baseline threshold-based monitoring and the proposed agentic architecture. The values highlight significant gains across diagnostic accuracy, predictive precision, and operational efficiency, with all improvements statistically significant at
p < 0.05.
The summarized comparison emphasizes that the adoption of the multi-agent, federated framework yields substantial benefits across all major dimensions of machinery health monitoring. In particular, the marked reduction in false positives and the improvement in RUL prediction accuracy confirm the enhanced diagnostic reliability achieved through adaptive learning and distributed coordination. These quantitative outcomes provide the foundation for the subsequent discussion, which links the observed performance gains to the progressive maturity levels defined by the AIMM framework.
4.6.2. Qualitative Assessment Results
Operator feedback surveys conducted monthly throughout the validation period indicated consistently positive reception of the multi-agent monitoring system. On a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree, 5 = strongly agree), operators rated system usefulness at 4.3 ± 0.6, ease of use at 4.1 ± 0.7, and overall satisfaction at 4.4 ± 0.5.
Trust and Acceptance Metrics: System trust scores increased progressively from 3.1 ± 0.8 in month 1 to 4.2 ± 0.6 in month 12, indicating successful trust calibration through consistent performance. Alarm compliance rates (percentage of alarms receiving timely operator response) improved from 73% to 91%, reflecting increased confidence in system recommendations. Maintenance Technician Feedback: Maintenance personnel reported 89% satisfaction with predictive maintenance scheduling accuracy and 86% satisfaction with diagnostic support quality. Work order quality improved significantly, with 78% of maintenance tasks completed on the first attempt compared to 56% baseline. Skill development surveys indicated 67% of technicians felt the system enhanced their diagnostic capabilities.
4.6.3. Return on Investment Analysis
Economic analysis demonstrated compelling return on investment for the multi-agent monitoring system implementation. Total system implementation cost of €285,000 included hardware (€127,000), software development (€98,000), installation (€38,000), and training (€22,000). Cost Savings Quantification: Annual cost savings totaled €178,600, comprising maintenance cost reductions (€130,800), energy savings (€28,400), and production loss avoidance (€19,400). Simple payback period calculated to 1.6 years, with net present value of €447,300 over 5-year project horizon (discount rate 8%). Productivity Improvements: Production capacity increases through improved OEE generated additional revenue of €156,200 annually without capital investment in additional equipment. Quality improvements reduced product defects by 23%, avoiding waste disposal costs and improving customer satisfaction metrics. Risk Mitigation Value: Avoided catastrophic failures during the validation period prevented estimated €89,000 in emergency repair costs and production losses. Insurance premium reductions of 12% resulted from demonstrated risk management improvements through predictive monitoring.
5. Discussion
5.1. Technical Performance Evaluation
The experimental validation of the multi-agent autonomous monitoring system demonstrates a significant advancement over conventional industrial monitoring approaches. The system achieved a fault detection sensitivity of 94.3%, notably surpassing the typical 70–85% sensitivities reported for traditional vibration-based monitoring systems [
64]. This marked improvement is attributed to the integration of multiple specialized agents, which collectively contribute to enhanced monitoring capabilities.
The architecture’s specialization allowed tailored analytical strategies for different equipment types and failure modes, resulting in variable performance across categories. Hydraulic press monitoring reached 96.7% sensitivity, while kiln monitoring achieved 92.4%, highlighting the system’s adaptability. Multi-agent coordination proved highly effective, evidenced by a 97% task allocation efficiency and a 92% automated conflict resolution rate, minimizing the need for human intervention.
The federated learning framework addressed key industrial constraints, enabling privacy-preserving, facility-wide knowledge sharing without compromising data security. Centralized model training accuracy reached 97%, with communication overhead limited to 2.1%, a substantial improvement over traditional centralized approaches that typically consume significantly more bandwidth. This communication efficiency supports continuous learning without disrupting plant operations [
65].
Continuous learning approaches facilitated sustained improvements, with system accuracy increasing from 82.4% to 94.3% over a 12-month period. The system demonstrated robust adaptation to changing operational conditions, with only 3.7% performance degradation during seasonal transitions. Automatic adaptation mechanisms maintained high performance and reduced the need for manual recalibration, supporting long-term operational viability.
The multi-agent autonomous monitoring system offers substantial technical and operational benefits, including enhanced fault detection sensitivity, efficient resource allocation, secure federated learning, and adaptive performance in dynamic industrial environments.
The overall performance evaluation confirms the technical soundness and operational reliability of the proposed multi-agent system. Improvements in detection accuracy, resource efficiency, and communication robustness collectively demonstrate the system’s capacity to sustain autonomous learning and coordination over time. These findings substantiate the framework’s ability to evolve beyond isolated automation toward a structured, self-improving ecosystem of intelligent agents.
Results of AIMM Mapping
The empirical outcomes correspond to the progressive maturity stages defined by the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM).
L1 → L2: The transition from rule-based threshold monitoring to data-driven machine learning enabled a +15% increase in fault detection sensitivity and a substantial reduction in false alarms, marking the onset of predictive intelligence.
L2 → L3: Adaptive online learning mitigated seasonal drift (–3.7%) and improved model generalization, demonstrating the shift toward self-correcting and context-aware intelligence.
L3 → L4: Distributed agents achieved 97% task allocation efficiency and 92% automated conflict resolution under human oversight, evidencing the collaborative autonomy stage.
L4 → L5: Cross-facility federated learning delivered a +15% performance gain, establishing the foundations for ecosystem-level coordination and emergent autonomy.
This progression empirically validates the AIMM as a practical maturity trajectory for autonomous industrial intelligence, illustrating how technological and organizational evolution unfold along the path from reactive monitoring to agentic, self-organizing ecosystems.
5.2. Industrial Implementation Challenges
Integration of the autonomous monitoring system in a ceramic manufacturing facility presented notable challenges, primarily related to interfacing with legacy equipment. This required the development of custom sensor solutions, thereby increasing installation complexity and extending timelines beyond initial projections. Installation time exceeded estimates by 23%, mainly due to compatibility issues with existing control systems and safety interlocks, a challenge frequently reported in Industry 4.0 adoption projects where legacy infrastructure slows deployment [
66]. Network infrastructure posed additional difficulties, especially in high-temperature zones near kilns, where standard industrial networking equipment required specialized protection. Addressing these constraints demanded hybrid communication strategies that combined wired and wireless technologies, ultimately enabling comprehensive facility coverage. From a human factors perspective, the transition required extensive change management beyond standard technical training. Initial operator compliance with automated recommendations was 73% in the first three months, rising to 91% as the system demonstrated reliable performance. This adaptation process underscores the necessity of gradual deployment and continuous performance validation to achieve operator acceptance. Organizational transformation was essential as maintenance practices shifted from reactive to predictive models. Transitioning from fixed-interval scheduling to condition-based recommendations mandated policy adjustments and workflow redesign, confirming that successful technical implementation must be supported by robust organizational change management. Strict industrial safety requirements constrained the degree of autonomous operation permitted, necessitating human oversight for safety-critical decisions. This conservative approach ensured compliance, with an 8% escalation rate to human operators for conflict resolution. Reliability standards demanded redundant communication channels and failsafe modes; the system achieved a 99.8% message delivery success rate, approaching but not fully meeting the 99.99% threshold often required for safety-critical environments [
67]. Further improvements in redundancy and fault tolerance will be needed for future deployments.
5.3. Human–Machine Collaboration Effectiveness
The deployment of the multi-agent autonomous monitoring system led to a marked increase in operator trust, with trust scores rising from 3.1 to 4.2 over the evaluation period. Maintenance technicians reported high satisfaction rates, with 89% approving of scheduling accuracy and 86% valuing the system’s diagnostic support. Notably, 67% of technicians experienced skill development, demonstrating the system’s capacity to augment human expertise. The integration of decision support tools resulted in an 89% acceptance rate for automated maintenance recommendations, while first-attempt work order completion improved from 56% to 78%. This reflects the effective synergy between autonomous decision making and human oversight. Over time, operator reliance on system explanations declined, indicating successful knowledge transfer and growing confidence in the system’s capabilities. Explainable AI mechanisms were instrumental for adoption and trust calibration, consistent with recent evidence showing that tailored explanations enhance operator trust and system transparency in industrial AI applications [
68]. Ninety-four percent of operators reported that the quality of system explanations enhanced their confidence in automated advice. The provision of uncertainty quantification and confidence intervals further enabled operators to calibrate their reliance on automation appropriately. Adaptive explanation systems, tailored to user expertise and operational context, facilitated transparency and effective human oversight without requiring deep AI expertise. The system fostered robust human–machine collaboration, supporting trust, skill development, and operational efficiency, aligning with broader findings on the human-centric orientation of Industry 5.0 [
69].
5.4. Scalability and Generalizability
The multi-agent monitoring system, though validated in a ceramic manufacturing context, is architected for cross-industry adaptability. Its modular agent design and standardized communication protocols facilitate application across various manufacturing sectors, necessitating only equipment-specific adjustments rather than fundamental reengineering. Empirical results from a facility with diverse machinery—including hydraulic presses, kilns, and glazing lines—demonstrate the system’s versatility in heterogeneous environments. The federated learning framework ensures robust data privacy and communication efficiency, features that are broadly relevant to numerous manufacturing domains [
70]. These mechanisms address industry-wide concerns, extending the system’s applicability beyond ceramics. Scalability analysis from deployment in a medium-sized facility (180 employees, 12 million m
2 annual capacity) indicates that communication overhead increases linearly, with baseline and peak values at 1.2% and 3.8%, respectively. The system effectively managed 20 monitored units, with modeling suggesting feasible expansion to 50–100 units without major architectural changes. However, larger facilities may encounter exponential growth in coordination complexity, necessitating the development of hierarchical management structures. Architecture’s modularity supports technological evolution, accommodating new machine learning algorithms and facilitating seamless integration of updated components. Standardized protocols and agent interfaces allow for technology upgrades without systemic disruption, supporting strategic industrial investments and long-term modernization plans.
Although the system was validated in a single ceramic tile facility over a 12-month period, this scope inevitably limits the generalizability of the findings. The ceramic sector, with its energy-intensive and equipment-diverse processes, provides a rigorous testbed, but further studies across multiple industries and longer timeframes are needed to fully assess long-term adaptation, reliability, and cross-sectoral applicability. To address this, the proposed AIMM framework should be interpreted as the transferable element: while the empirical study anchors the model in practice, the AIMM itself outlines a progression pathway that is industry-agnostic [
71]. By mapping the ceramic implementation to the AIMM’s maturity levels, organizations in other sectors (e.g., automotive, aerospace, process industries) can adapt the same staged adoption process to their own technological and organizational contexts. In this sense, the AIMM functions as the bridge between the local validation and the global generalizability of the results.
Beyond the ceramic sector, the proposed architecture can be adapted to other manufacturing domains (such as automotive, aerospace, and process industries) by tailoring sensing modalities and data governance policies while preserving the same federated multi-agent backbone. Variability in process dynamics, regulatory constraints, and data availability will influence specific implementation pathways, but the maturity logic defined by the AIMM remains consistent across sectors.
5.5. Safety and Explainability Considerations
The implementation of the autonomous monitoring system incorporated robust safety measures and explainable AI mechanisms to address stringent industrial requirements. Human oversight remained mandatory for safety-critical decisions, ensuring compliance with prevailing safety standards while optimizing automation for routine maintenance tasks. The system demonstrated a positive predictive value of 98.3% for critical alarms, supporting reliable decision-making in high-stakes scenarios. Failsafe operational strategies ensured uninterrupted monitoring during communication breakdowns, allowing autonomous operation for an average of 4.7 h in the event of network outages. This resilience provided adequate continuity for most industrial applications while upholding essential safety protocols.
Explainable AI played a crucial role in enhancing operator trust and system transparency. The adaptive explanation framework provided tailored information according to user expertise, which directly contributed to higher system acceptance and more effective utilization. The integration of uncertainty quantification enabled operators to calibrate trust and make informed, risk-based decisions, fostering a productive human–machine collaboration that balanced automation with human authority [
72]. Compliance with relevant industrial standards, such as those for condition and vibration monitoring and manufacturing operations management, was achieved through targeted design adaptations. Documentation and comprehensive audit trails facilitated regulatory compliance and supported ongoing process optimization. The system’s detailed performance monitoring and logging capabilities ensured both operational transparency and the continuous refinement of industrial processes.
5.6. Limitations and Future Research Directions
The current implementation of the multi-agent autonomous monitoring system exhibits several limitations that inform future research and development efforts. The validation period, set at 12 months, provides substantial insight but lacks comprehensive coverage of long-term equipment degradation and seasonal process variations. Extending the validation timeframe to multiple years would yield a more robust performance assessment.
While the system demonstrated effective mechanical and thermal monitoring, its chemical process monitoring capabilities remain limited. Future enhancements should focus on integrating advanced chemical analysis tools, especially for industries where such monitoring is essential. Technological improvements are required to advance system performance and applicability. Incorporating sophisticated sensor fusion methodologies—combining vibration, temperature, acoustic emission, ultrasonic, and chemical sensors—would substantially improve fault detection accuracy and monitoring scope. Augmenting edge computing resources to enable more advanced local data analysis would further decrease reliance on centralized communication, supporting efficiency and scalability. Research priorities include the development of explainable AI techniques tailored to industrial contexts, addressing the need for transparent, user-centric decision support systems. The expansion of cross-facility federated learning represents a significant opportunity to enhance performance through distributed knowledge sharing, while industry-wide standardization and data protection remain critical challenges [
73]. Integration with digital twin technologies is recommended to combine physics-based and data-driven models, enriching predictive maintenance capabilities and accuracy for remaining useful life estimation [
74]. Looking ahead, the automation of maintenance execution through robotic systems and automated spare parts management could enable fully autonomous maintenance cycles for routine tasks, contingent upon overcoming safety, reliability, and regulatory hurdles. Sustainability optimization, including carbon footprint monitoring, energy efficiency, and waste reduction, presents a promising direction for expanding the scope of autonomous monitoring systems to address contemporary environmental management requirements.
The successful deployment of autonomous multi-agent monitoring in ceramic manufacturing highlights its technical, economic, and collaborative advantages. Ongoing research is necessary to address current limitations, enhance system capabilities, and facilitate broader industrial adoption.
5.7. Positioning the AIMM as Theoretical Contribution
While quantitative validation provides strong evidence of technical and economic benefits, it is important to underline the role of the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) as the central theoretical innovation of this work. Unlike existing maturity models for digital manufacturing or predictive maintenance, which typically focus on technology adoption levels or digital readiness [
75], the AIMM explicitly integrates
Technological dimensions (sensing, analytics, distributed intelligence, and explainability);
Organizational transformation (human–machine collaboration, trust calibration, and workflow redesign);
Systemic resilience (ecosystem-level coordination and emergent autonomy).
This multi-dimensional perspective positions the AIMM not merely as a supportive framework but as a roadmap for industrial transition from reactive monitoring toward fully autonomous ecosystems. The model’s five levels provide structured guidance for organizations to assess their current capabilities, identify implementation gaps, and plan progressive adoption strategies. The ceramic case study demonstrates the AIMM at work within a specific industrial context, but the conceptual structure is industry-agnostic. By linking maturity levels to generic technological and organizational milestones, the AIMM offers a transferable framework that can be adapted across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, or process industries. Thus, empirical validation serves to anchor the AIMM in practice, while the model itself provides the broader conceptual contribution to the literature on industrial AI maturity. Although validated in a single ceramic facility, the approach is designed to generalize across process- and discrete-manufacturing sectors. Future multi-site deployments will further test the robustness of AIMM-driven architectures under varying operational, regulatory, and environmental conditions. The AIMM framework conceptually aligns with existing autonomy models, such as adaptive autonomy frameworks in human–machine teaming [
76], cognitive multi-agent systems emphasizing self-regulation and goal adaptation [
77], and emerging AI agency frameworks addressing ethical and operational accountability [
78]. This theoretical orientation also converges with recent reflections on sustainable and human-centric autonomy. D’Adamo [
79] argues that the transition toward sustainability and technological progress cannot rely solely on innovation but must be grounded in a “we-oriented” model of collective responsibility and intergenerational collaboration. His vision of sustainable communities emphasizes agency as a shared, distributed capacity, one that balances technological autonomy with social trust, education, and ethical stewardship.
In this respect, the AIMM resonates with this socio-ethical interpretation of autonomy: it frames agentic intelligence not merely as self-governance within machines, but as a systemic property of sustainable industrial ecosystems. By linking intentional technological behavior with human accountability and collaborative values, the AIMM contributes to aligning industrial AI maturity with the broader goals of sustainable community building.
However, the AIMM differs by providing a maturity-based structure that integrates these theoretical perspectives into a coherent trajectory of industrial transformation, linking cognitive, organizational, and socio-technical evolution within a unified model. Each of the five AIMM levels can also be interpreted through an agentic progression that reflects the gradual development of intentional and accountable autonomy.
Levels 1–2 establish operational awareness and algorithmic decision support, marking the transition from reactive sensing to predictive intelligence.
Level 3 introduces adaptive agency, where systems begin to self-correct and refine behavior in response to dynamic operating conditions.
Level 4 represents collaborative autonomy, as intelligent agents and human experts jointly govern decision-making within transparent, explainable interfaces.
Level 5 achieves ecosystem-level agency, where distributed agents coordinate, negotiate, and reconfigure their functions across interconnected industrial networks.
This structured evolution embeds agency, the capacity to act intentionally and responsibly, into the very logic of industrial intelligence, positioning the AIMM as a theoretical bridge between cognitive autonomy and human-centric governance.
6. Conclusions
This study successfully developed and validated a comprehensive framework for autonomous multi-agent machinery health monitoring, demonstrating the practical feasibility of transitioning from reactive maintenance systems to self-organizing industrial intelligence ecosystems. The research addresses critical gaps in industrial AI implementation by providing both theoretical foundations through the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) and practical validation through real-world deployment in ceramic manufacturing operations.
6.1. Primary Research Contributions
A key contribution of this study lies in the introduction of the Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) as a novel theoretical framework. Unlike existing maturity models, which primarily assess digital readiness or isolated technological adoption, the AIMM integrates technological, organizational, and systemic dimensions of industrial intelligence. By explicitly linking levels of autonomy to human–machine collaboration, explainability, and ecosystem resilience, the AIMM provides a structured roadmap for guiding industries in their transition from reactive monitoring to fully autonomous, human-centric ecosystems. The empirical validation in the ceramic case study demonstrates the framework’s applicability, but the AIMM’s design is inherently cross-industry, making it transferable to diverse manufacturing contexts. The Autonomous Intelligence Maturity Model (AIMM) introduces a structured framework for advancing autonomous industrial intelligence through five maturity levels. Its multi-agent architecture effectively allocates monitoring roles (sensing, reasoning, action, and coordination), achieving higher fault detection sensitivity (94.3%) and specificity (96.8%) compared to traditional systems and reducing false positive alarms by 67%. The federated learning framework supports secure, distributed knowledge sharing with 97% centralized training accuracy and only 2.1% communication overhead, overcoming previous challenges in industrial AI deployment while protecting data privacy.
6.2. Practical Industrial Impact
The validation of autonomous multi-agent monitoring systems in ceramic manufacturing yielded significant operational improvements. Overall Equipment Effectiveness increased from 74.3% to 82.7%, reflecting an 11.3% rise in production efficiency without added capital investment. Gains were observed in availability (from 87.2% to 91.6%), performance (from 89.1% to 91.8%), and quality (from 95.7% to 98.4%), demonstrating broad enhancement across key metrics.
Economic analysis confirmed the financial viability of autonomous monitoring systems, with a simple payback period of 1.6 years and a net present value of €447,300 over five years. Annual cost savings reached €178,600, derived from reduced maintenance costs (€130,800), energy savings (€28,400), and avoided production losses (€19,400). Predictive maintenance strategies achieved a Mean Absolute Percentage Error of 18.6% for Remaining Useful Life predictions, a 45.6% improvement compared to scheduled maintenance approaches, resulting in a 43% reduction in emergency interventions and extended asset lifespan.
Human–machine collaboration was strengthened, with operator trust scores rising from 3.1 to 4.2 and 94% of operators reporting increased confidence in system-generated recommendations. Automated maintenance recommendations were accepted without modification in 89% of cases. Maintenance technicians reported satisfaction levels of 89% for scheduling accuracy and 86% for diagnostic support, and 67% indicated skill development as a result of system integration. Explainable AI mechanisms were instrumental, with 94% of operators stating that explanations increased their trust in automated decisions.
System scalability was demonstrated through modular architecture and standardized communication, enabling successful monitoring of diverse equipment types and facilitating cross-facility federated learning. Trials across multiple facilities showed a 15% performance improvement through knowledge sharing, highlighting the framework’s adaptability and potential for industry-wide application.
Safety and regulatory requirements were addressed through multiple redundancies and oversight processes. Human approval remained necessary for safety-critical decisions, and the system achieved a positive predictive value of 98.3% for critical alarms. Compliance with industrial standards such as ISO 13374, [
80] ISO 10816 [
48], and IEC 62264 [
81] was maintained, and comprehensive documentation ensured regulatory reporting and continuous improvement. The system was resilient to communication failures, maintaining autonomous operation for up to 4.7 h on average and achieving a 99.8% message delivery success rate, closely aligning with industrial reliability standards.
The deployment of autonomous multi-agent monitoring systems in ceramic manufacturing validated their technical effectiveness, economic benefits, scalability, and ability to enhance human–machine collaboration, safety, and regulatory compliance. These results establish the framework’s potential for broader industrial adoption and continued advancement toward fully autonomous, intelligent manufacturing ecosystems.
6.3. Limitations and Implementation Considerations
While a 12-month validation period is significant for industrial research, it may not reflect all seasonal and long-term system changes; extending this to 3–5 years would allow for better assessment of performance and adaptation. Mechanical and thermal monitoring dominated implementation, with limited chemical monitoring integration, which could be necessary for other uses. Integration was more complex than anticipated, taking 23% longer due to legacy system compatibility issues. Network challenges in high-temperature areas led to hybrid communication solutions, increasing complexity but improving coverage. These experiences underscore the need for realistic resource planning and infrastructure requirements. Organizational change management was more demanding than expected, needing broader efforts beyond technical training. Shifting from reactive to predictive maintenance required policy updates and workflow redesign, emphasizing the importance of thorough organizational change planning alongside technology deployment.
6.4. Future Research Priorities
Key research areas from this implementation include: developing advanced, explainable AI for industrial use to boost operator understanding and transparency; tackling data protection and standardization in cross-facility federated learning; combining digital twin technologies with data-driven methods to improve RUL prediction accuracy; integrating autonomous maintenance with robotics, which will require addressing safety and regulatory issues; and enhancing sustainability by incorporating carbon monitoring, energy efficiency, and waste reduction into autonomous systems.
6.5. Industrial Implementation Roadmap
Organizations should adopt a structured AIMM-based process for autonomous monitoring system implementation. Phase 1 builds sensing agents and anomaly detection for data collection and operator training. Phase 2 introduces reasoning agents with machine learning for predictive maintenance and increased trust. Phase 3 finalizes multi-agent architecture with action and coordination agents for full autonomy. Key success factors are effective change management, gradual deployment, robust communication planning, and realistic timelines. Proven economic and operational gains make investment in autonomous monitoring highly justifiable. The implementation roadmap presented here should be read in direct connection with the AIMM. Each roadmap phase (sensing → reasoning → full multi-agent orchestration) corresponds to specific AIMM levels, providing industries with a structured method to benchmark their current state and plan subsequent adoption steps. While the roadmap was demonstrated within a ceramic tile facility, its alignment with the AIMM ensures replicability across different industrial domains. This dual structure—a practical roadmap plus a theoretical maturity model—facilitates both immediate implementation and long-term strategic planning for industry-wide adoption of agentic AI.
6.6. Concluding Remarks
This research shows that autonomous multi-agent systems can transform industrial machinery health monitoring, offering both theoretical and practical guidance for adopting advanced manufacturing technologies. Validation in ceramic manufacturing highlights readiness for wider use and areas for further study. The system improves technical performance, economic outcomes, and human–machine cooperation, while the federated learning framework protects data privacy and boosts communication efficiency. The AIMM offers a structured approach to intelligent monitoring, supporting scalability and adaptability for broad deployment. Future work should address limitations and explore integration with digital twins, robotics, and sustainability platforms. This study underscores the value of AI in manufacturing, demonstrating its ability to enhance operations while maintaining human oversight and safety.