Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Blood Flow in Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft for Enhanced Flow Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of 3D Graft Geometrical Models
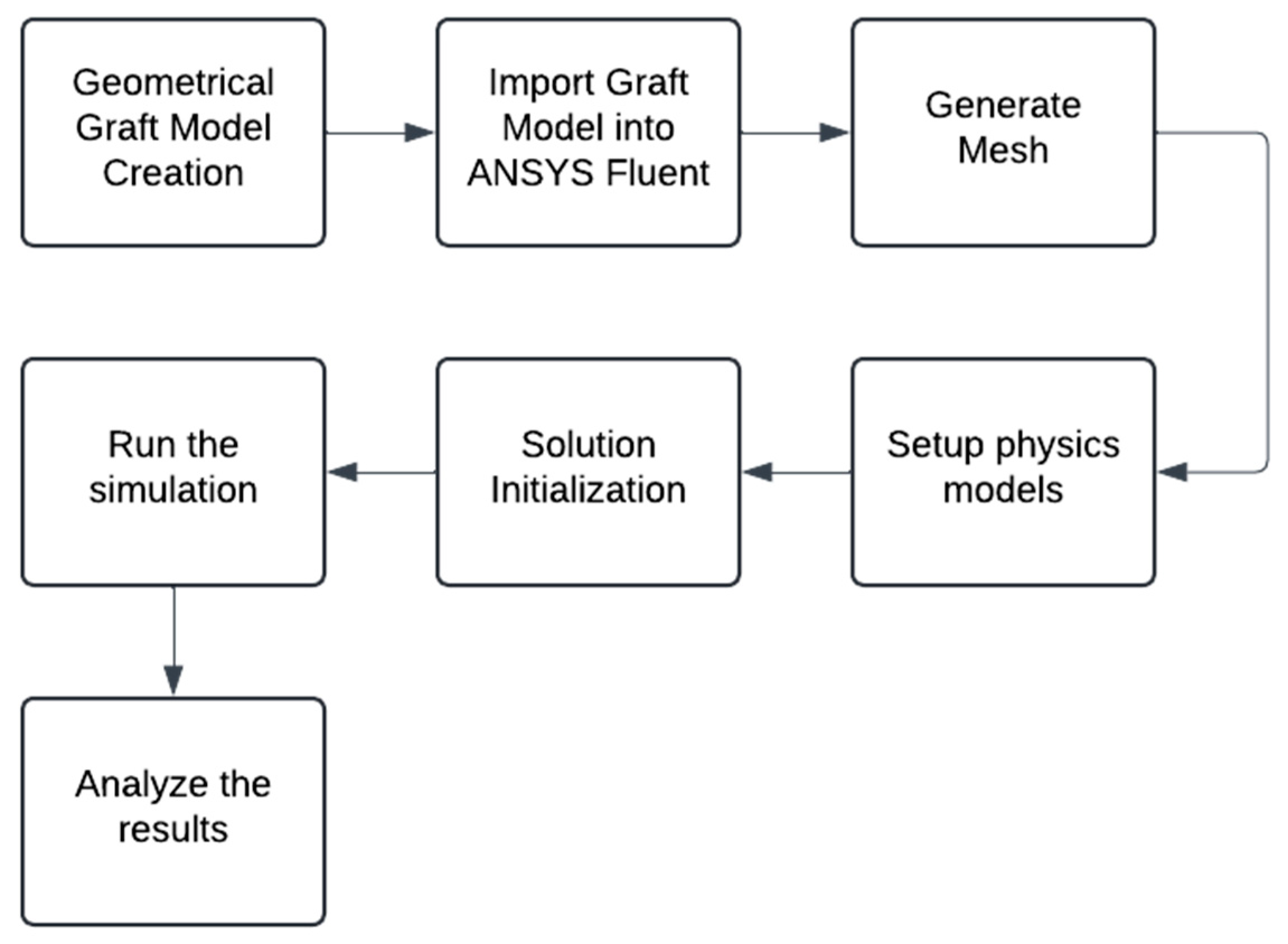
2.2. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Simulation
2.2.1. Geometry Import
2.2.2. Mesh Generation
2.2.3. Setup Physics Model
2.2.4. Solution Initialization
2.2.5. Running the Simulations
2.2.6. Analysis of the Results
2.3. Data Validation of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Process
2.4. Selection of the Best Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft
2.5. Comparison Between the Optimized and Conventional Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft (AVG)
3. Results
3.1. Data Validation
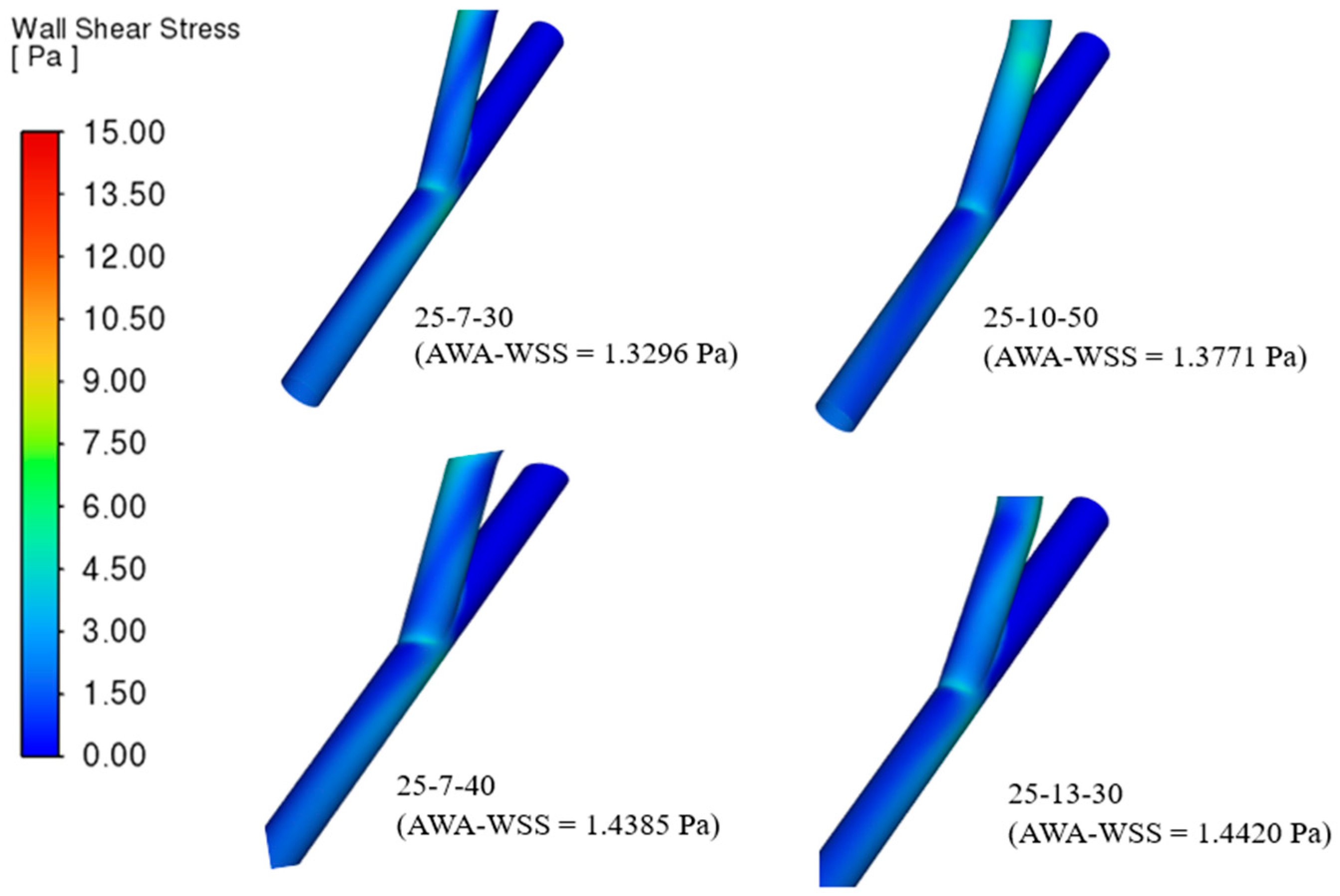
3.2. Area-Weighted Average Wall Shear Stress (AWA-WSS)
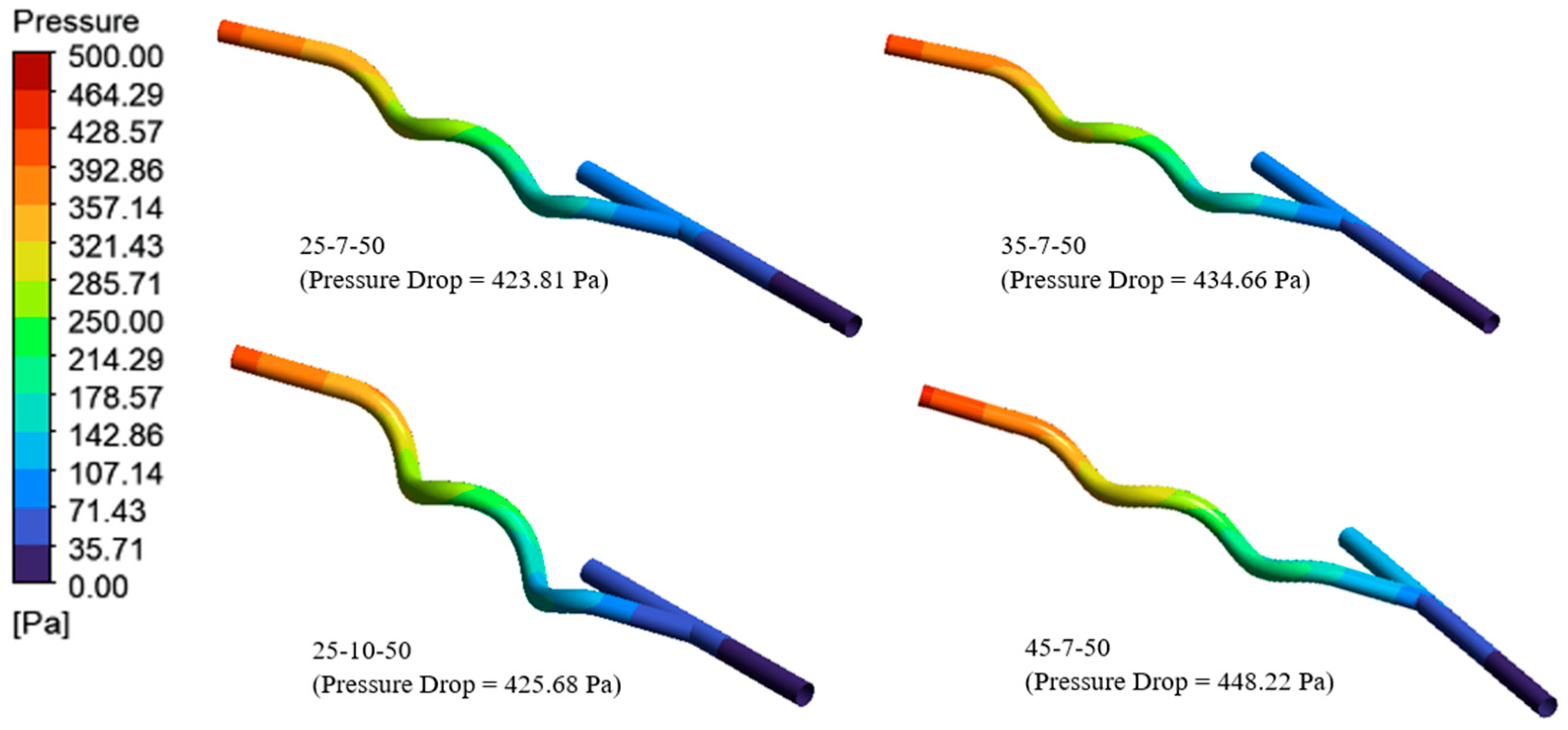
3.3. Pressure Drop
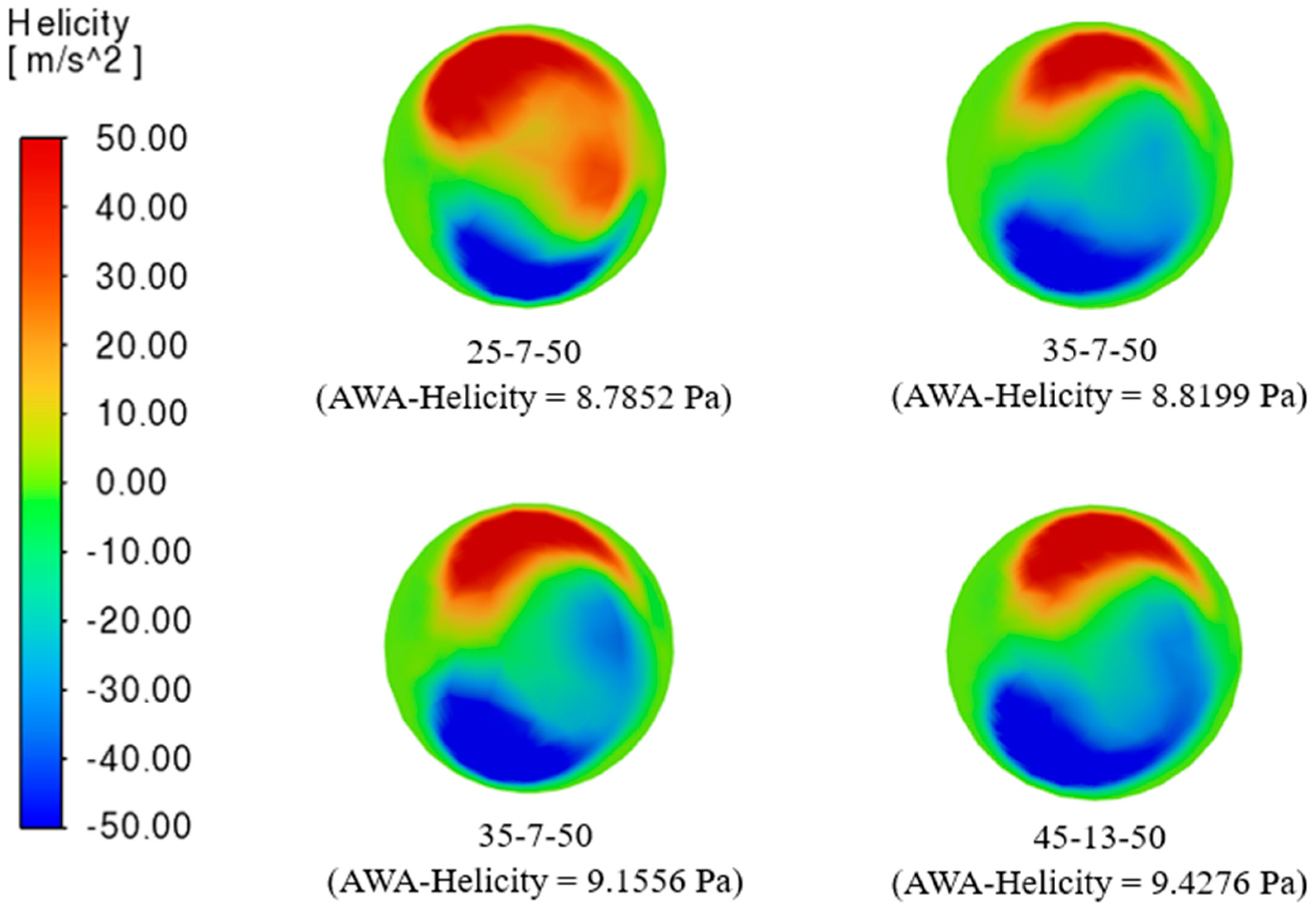
3.4. Helicity
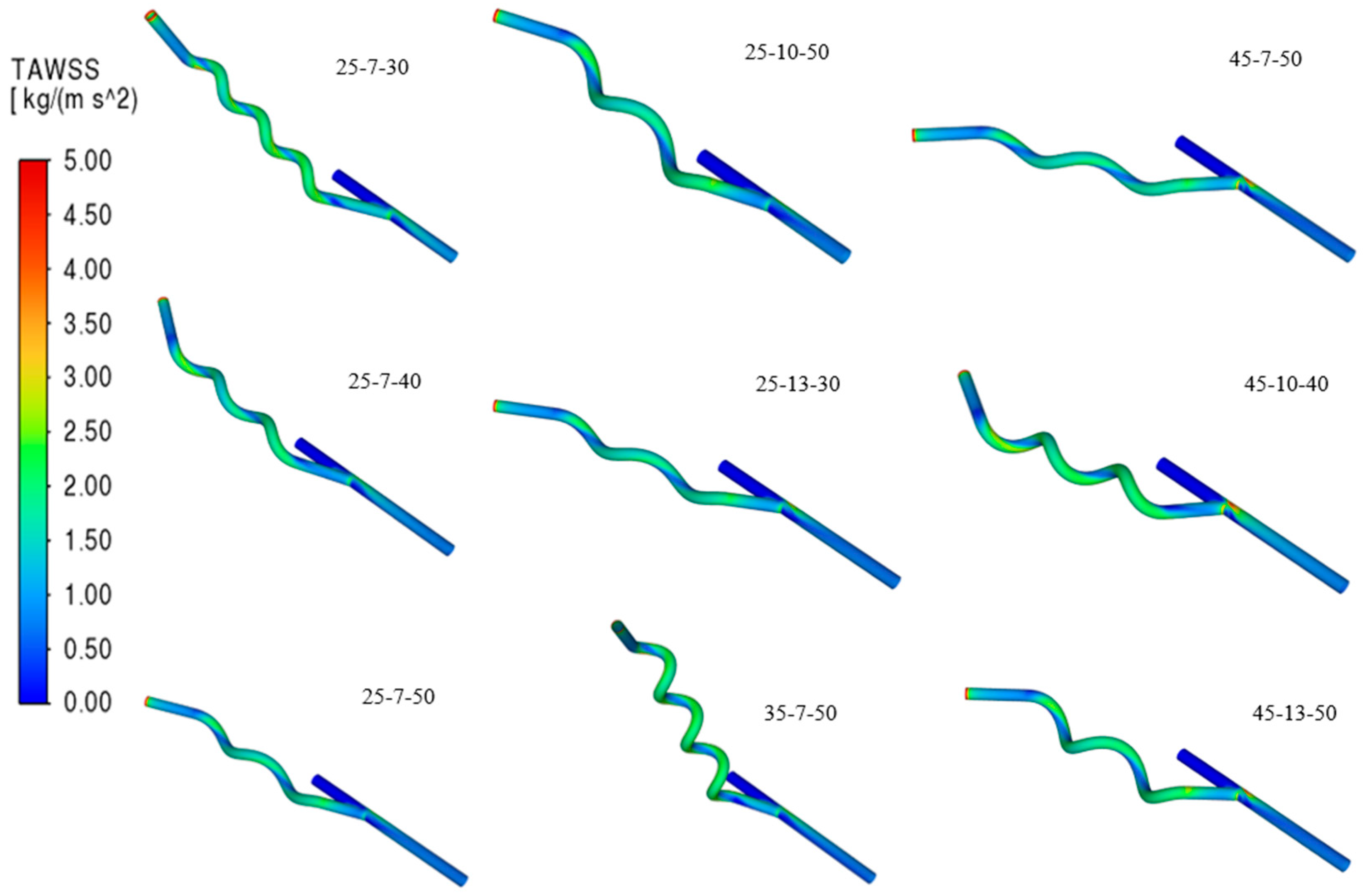
3.5. Selection of the Best Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft (AVG) Based on CFD Transient Simulations
3.6. Numerical Comparison Between the Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft and the Conventional Bypass Graft
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Anastomosis Angle, Helical Diameter, and Helical Pitch on Hemodynamic Parameters
4.2. Selection of the Best Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft (AVG) Based on CFD Transient Simulations
4.3. Optimized Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsingh, R.; Bakaeen, F.G. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Practice Trends and Projections. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2025, 92, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, D.; Pigliafreddo, A.; Casarella, S.; Di Nunno, L.; Mantovani, D.; Boccafoschi, F. Biological Materials for Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts: Overview of Recent Advancements. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafron, J.M.; Heng, E.E.; Boyd, J.; Humphrey, J.D.; Marsden, A.L. Hemodynamics and Wall Mechanics of Vascular Graft Failure. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 1065–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, M.; Brenner, B. Pocket Companion to Brenner & Rector’s the Kidney, 7th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Edinburgh, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jennette, J.C.; Stone, J.R. Diseases of Medium-Sized and Small Vessels. In Cellular and Molecular Pathobiology of Cardiovascular Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 197–219. [Google Scholar]
- Donadoni, F.; Bonfanti, M.; Pichardo-Almarza, C.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Dardik, A.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V. An in Silico Study of the Influence of Vessel Wall Deformation on Neointimal Hyperplasia Progression in Peripheral Bypass Grafts. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 74, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadoni, F.; Pichardo-Almarza, C.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Dardik, A.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V. Multiscale, Patient-Specific Computational Fluid Dynamics Models Predict Formation of Neointimal Hyperplasia in Saphenous Vein Grafts. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2020, 6, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, J.M.; Kolega, J.; Meng, H. High Wall Shear Stress and Spatial Gradients in Vascular Pathology: A Review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 41, 1411–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Kang, H.; Fan, Y.; Sun, A.; Deng, X. Bioinspired helical graft with taper to enhance helical flow. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 3643–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabinejadian, F.; McElroy, M.; Ruiz-Soler, A.; Leo, H.; Slevin, M.; Badimon, L.; Keshmiri, A.; Sznitman, J. Numerical Assessment of Novel Helical/Spiral Grafts with Improved Hemodynamics for Distal Graft Anastomoses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.C.; Larman, A. Investigation of Spiral Blood Flow in a Model of Arterial Stenosis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Totorean, A.F.; Bernad, S.I.; Susan-Resiga, R.F. Fluid dynamics in helical geometries with applications for bypass graft. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 272, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apan, J.J.; Tayo, L.; Honra, J. Numerical Investigation of the Relationship between Anastomosis Angle and Hemodynamics in Ridged Spiral Flow Bypass Grafts. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzizisis, Y.S.; Coskun, A.U.; Jonas, M.; Edelman, E.R.; Feldman, C.L.; Stone, P.H. Role of Endothelial Shear Stress in the Natural History of Coronary Atherosclerosis and Vascular Remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 2379–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajihah, S.A.; Sankar, D.S. A Review on Non-Newtonian Fluid Models for Multi-Layered Blood Rheology in Constricted Arteries. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2023, 93, 1771–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Arteriovenous Graft Configurations. Master’s Thesis, Washington University, St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, P.; Ranade, R.; Choudhry, S. Accelerating Transient CFD through Machine Learning-Based Flow Initialization. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.15766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulwahhab, M.; Injeti, N.K.; Dakhil, S.F. CFD Simulations and Flow Analysis Through a T-junction Pipe. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2012, 4, 3392–3407. [Google Scholar]
- Bernad, S.I.; Bosioc, A.I.; Bernad, E.S.; Craina, M.L. Helical type coronary bypass graft performance: Experimental investigations. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Gao, L.; Jian, W.; Wang, L. Wall shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1083547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzirakis, K.; Kamarianakis, Y.; Kontopodis, N.; Ioannou, C.V. Selection of Bifurcated Grafts’ Dimensions during Aorto-Iliac Vascular Reconstruction Based on Their Hemodynamic Performance. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenakis, A.; Ruiz-Soler, A.; Keshmiri, A. Multi-Objective Optimisation of a Novel Bypass Graft with a Spiral Ridge. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimadge, M.; Chopade, M. CFD Analysis of Flow through T-Junction of Pipe. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 2017, 4, 906–911. [Google Scholar]
- Katritsis, D.; Kaiktsis, L.; Chaniotis, A.; Pantos, J.; Efstathopoulos, E.P.; Marmarelis, V. Wall shear stress: Theoretical considerations and measurement methods. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 49, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Hwang, D.; Choi, W.-R.; Baek, J.; Lee, S.J. Fluid-Dynamic Optimal Design of Helical Vascular Graft for Stenotic Disturbed Flow. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111047. [Google Scholar]
- Pasta, S.; Agnese, V.; Gallo, A.; Consentino, F.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Gentile, G.; Raffa, G.; Maalouf, J.; Michelena, H.; Bellavia, D.; et al. Shear Stress and Aortic Strain Associations With Biomarkers of Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, J.; Urbina, J.; Valverde, I.; Tejos, C.; Irarrázaval, P.; Andia, M.; Uribe, S.; Hurtado, D. 3D Quantification of Wall Shear Stress and Oscillatory Shear Index Using a Finite-Element Method in 3D CINE PC-MRI Data of the Thoracic Aorta. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenti, C.; Ziegler, M.; Bjarnegård, N.; Ebbers, T.; Lindenberger, M.; Dyverfeldt, P. Wall Shear Stress and Relative Residence Time as Potential Risk Factors for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in Males: A 4D Flow Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Case–Control Study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2022, 24, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cai, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ao, H.; Wan, Y.; Luo, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Hemodynamic Evaluation of Different Stent Graft Schemes in Aortic Arch Covered Stent Implantation. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2021, 13, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauren, F.; Tayo, L.L. Finite Element Analysis of ACL Reconstruction-Compatible Knee Implant Design with Bone Graft Component. Computation 2023, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Soler, A.; Kabinejadian, F.; Slevin, M.A.; Bartolo, P.J.; Keshmiri, A. Optimisation of a Novel Spiral-Inducing Bypass Graft Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghista, D.N.; Kabinejadian, F. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Hemodynamics and Anastomosis Design: A Biomedical Engineering Review. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
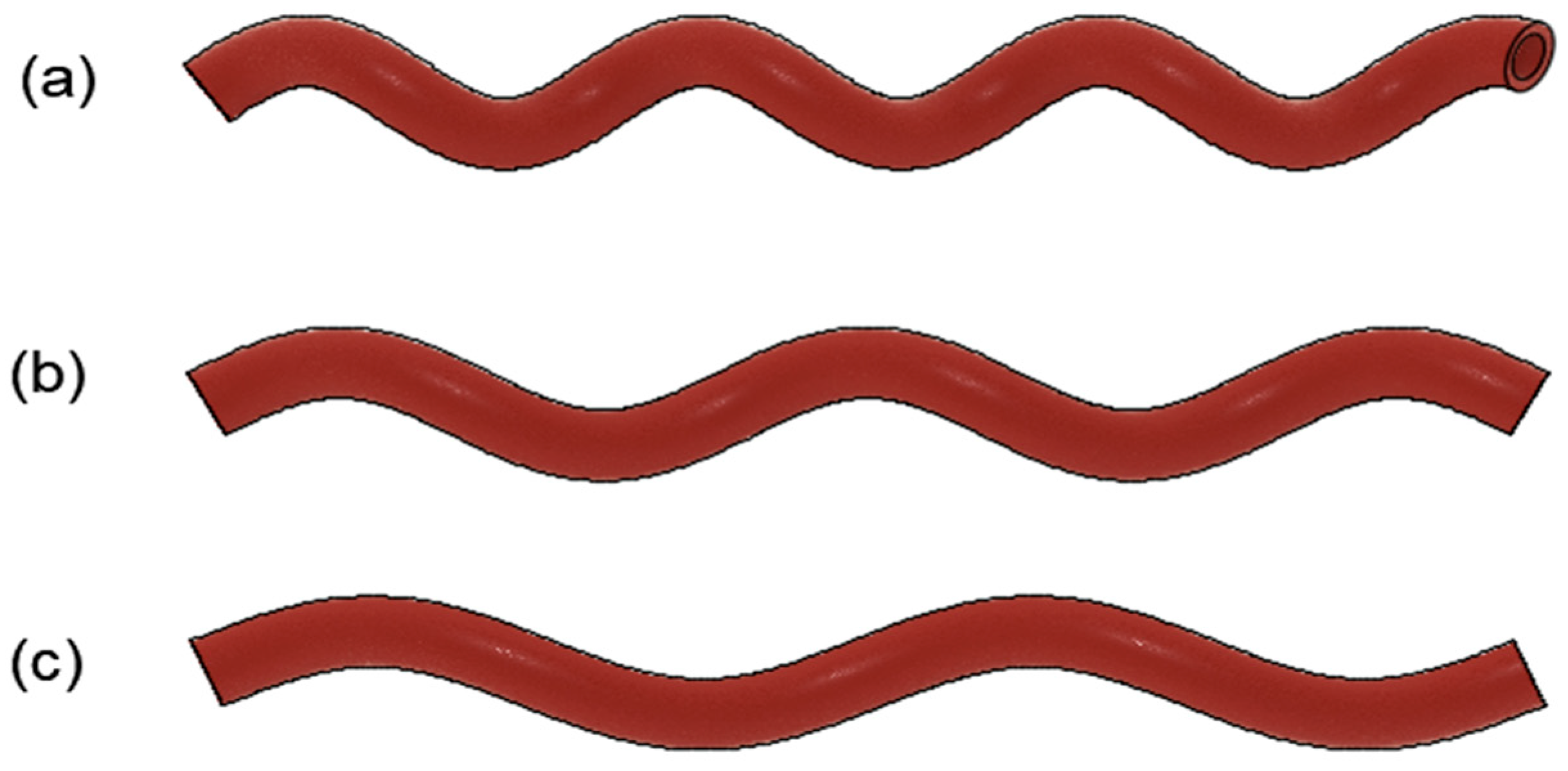
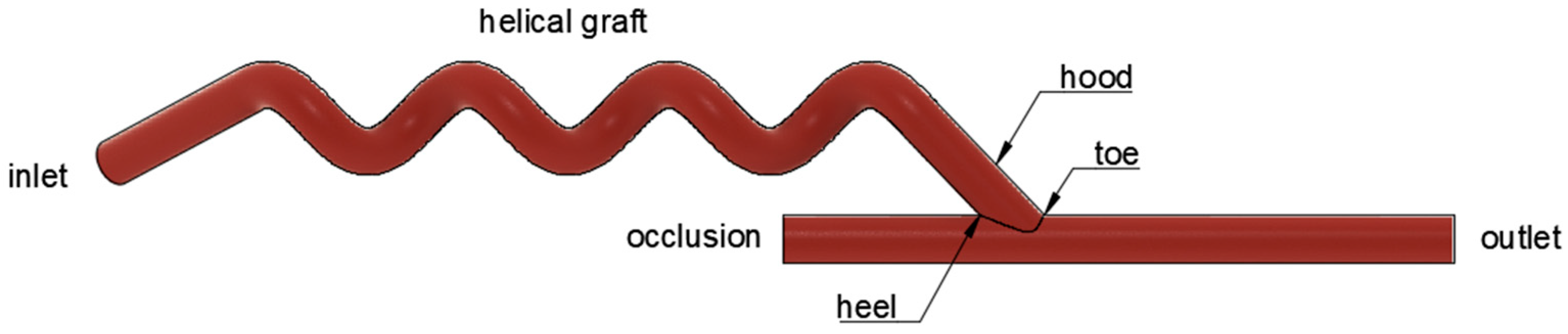
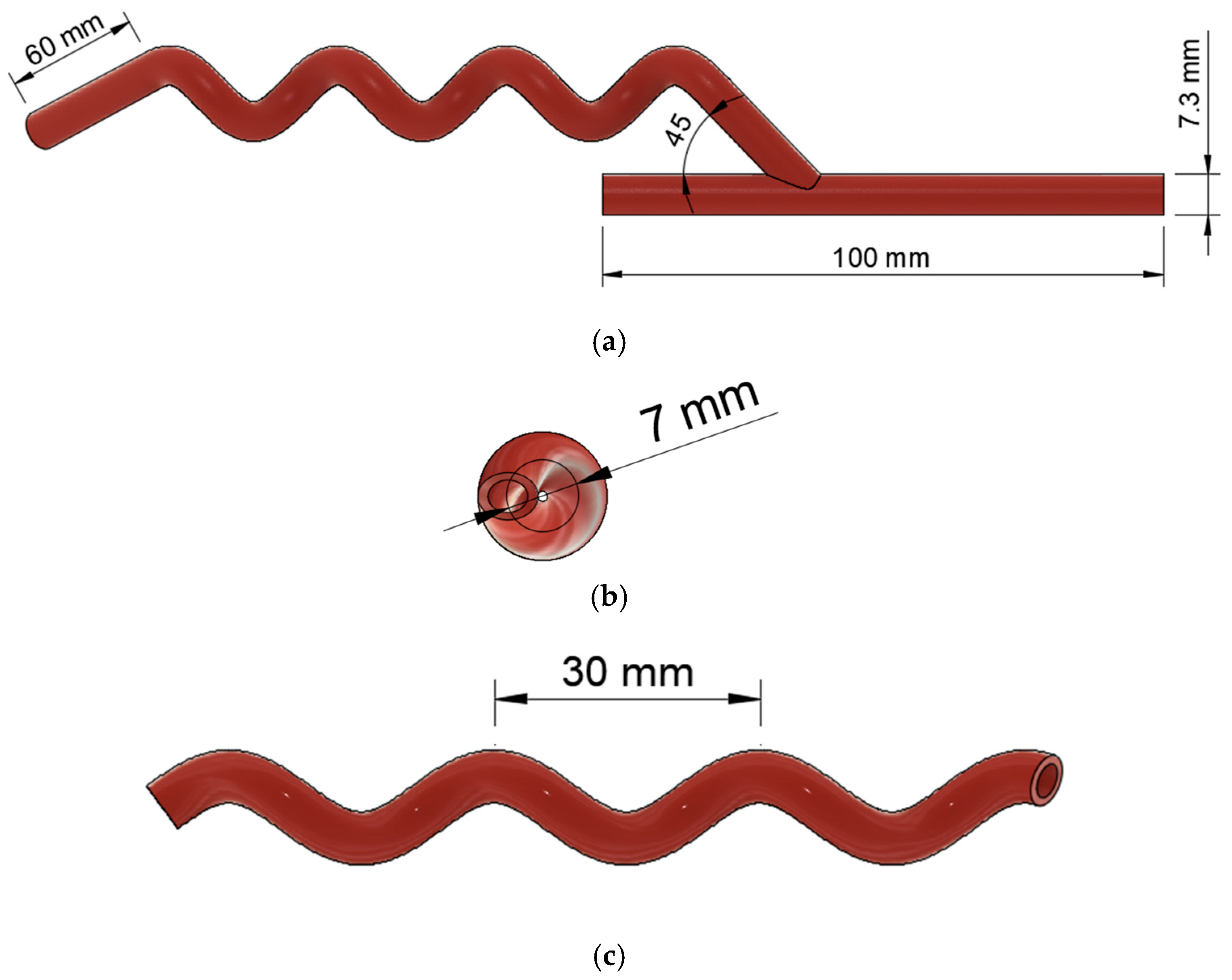
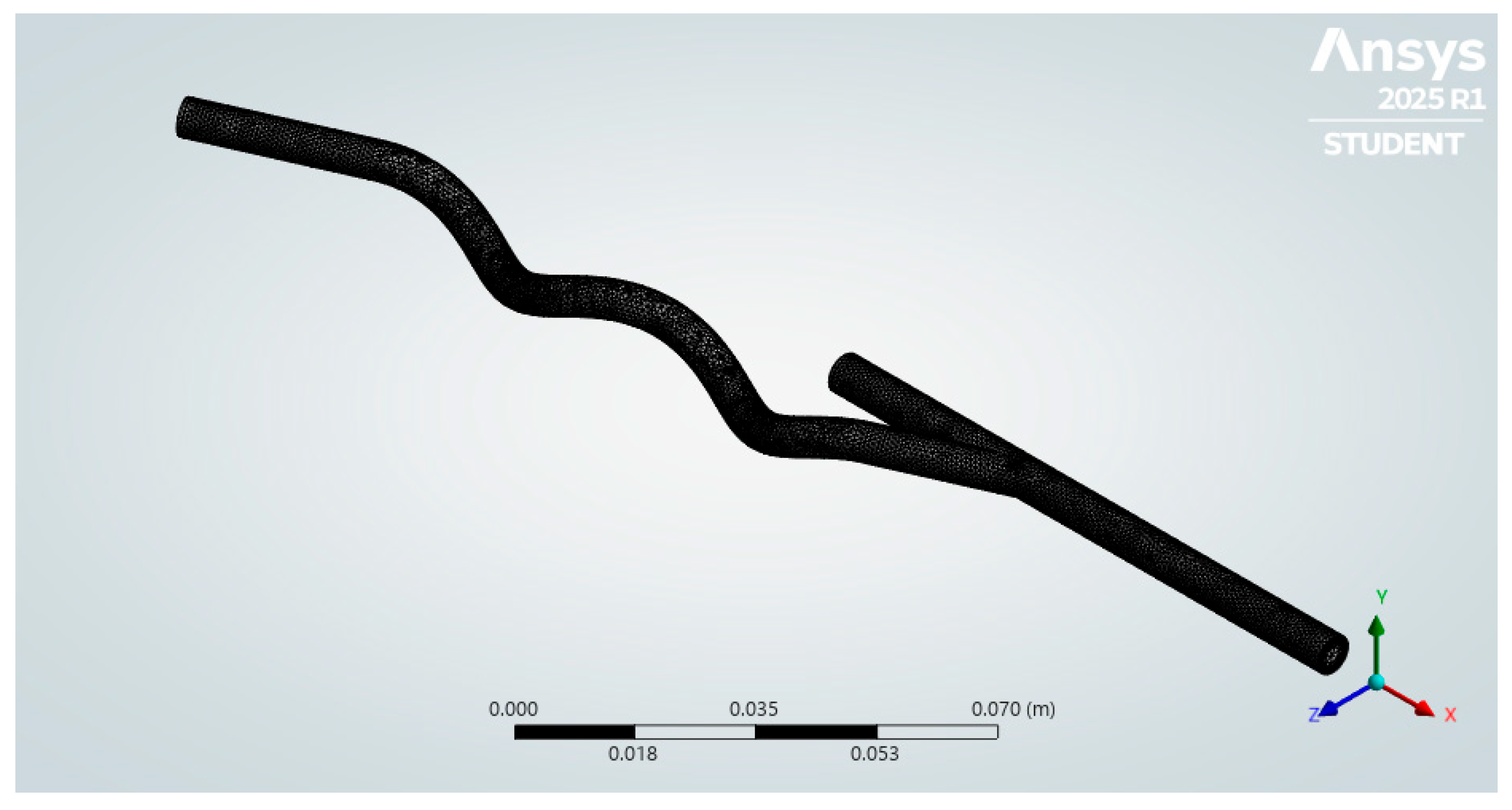
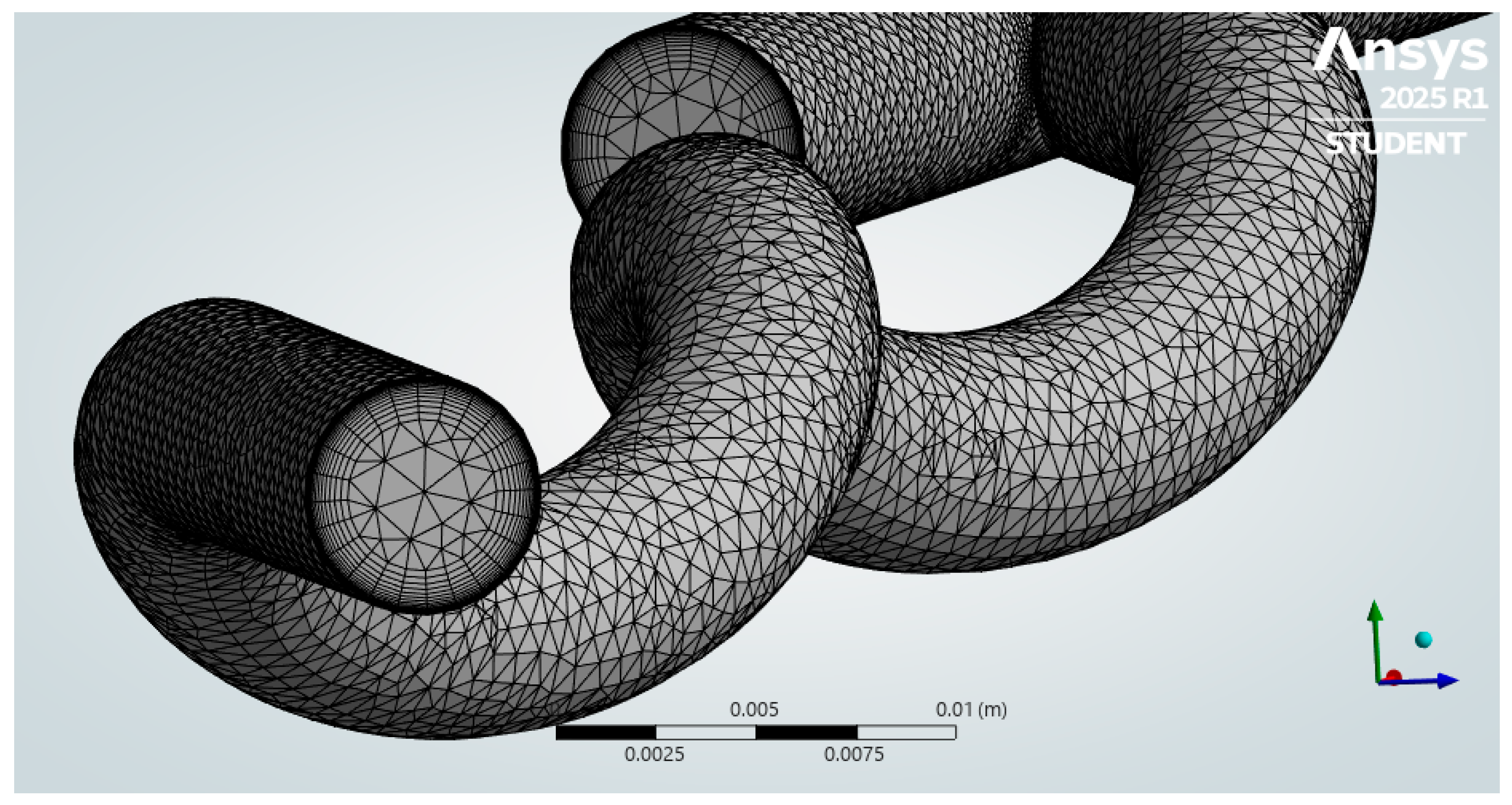
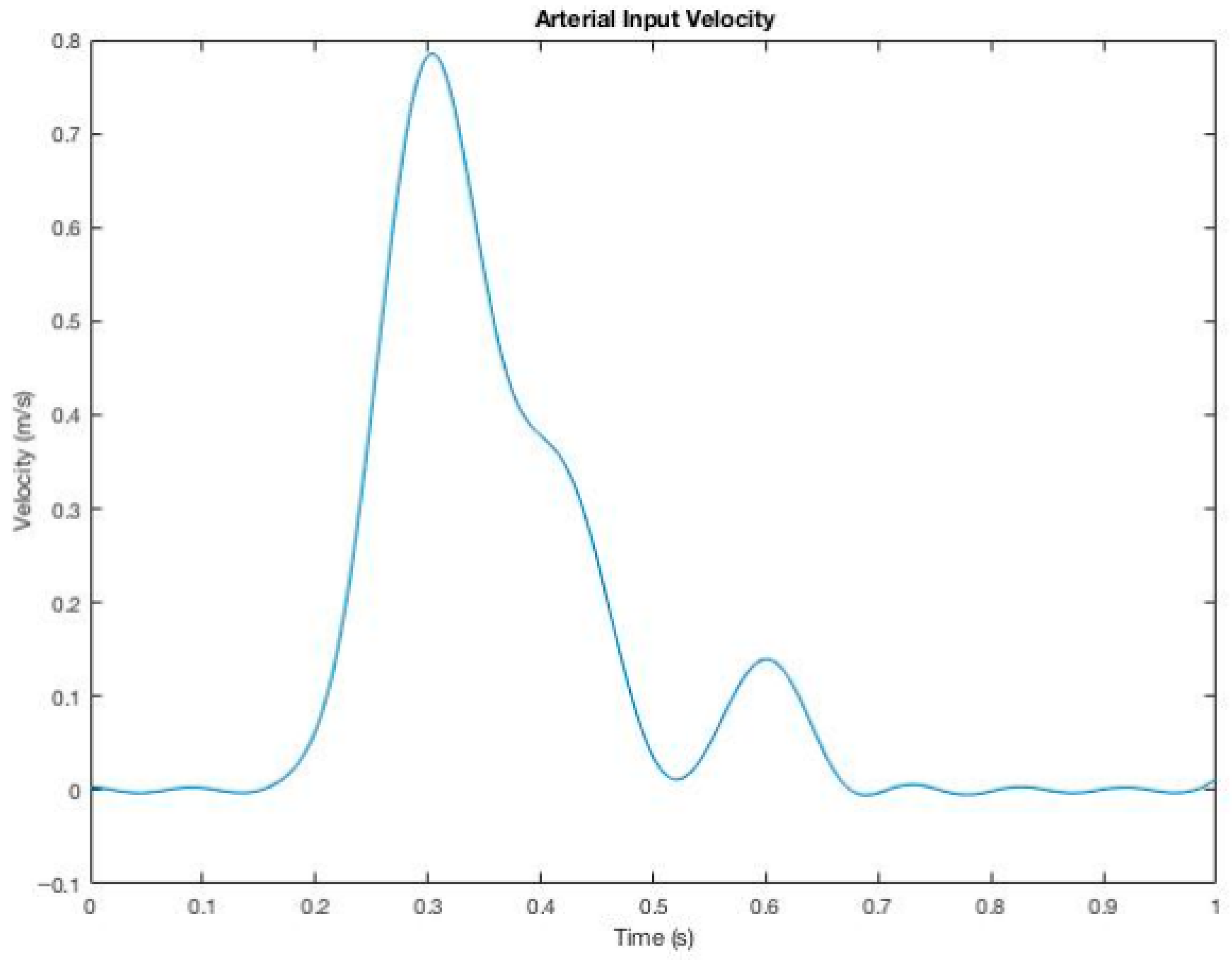
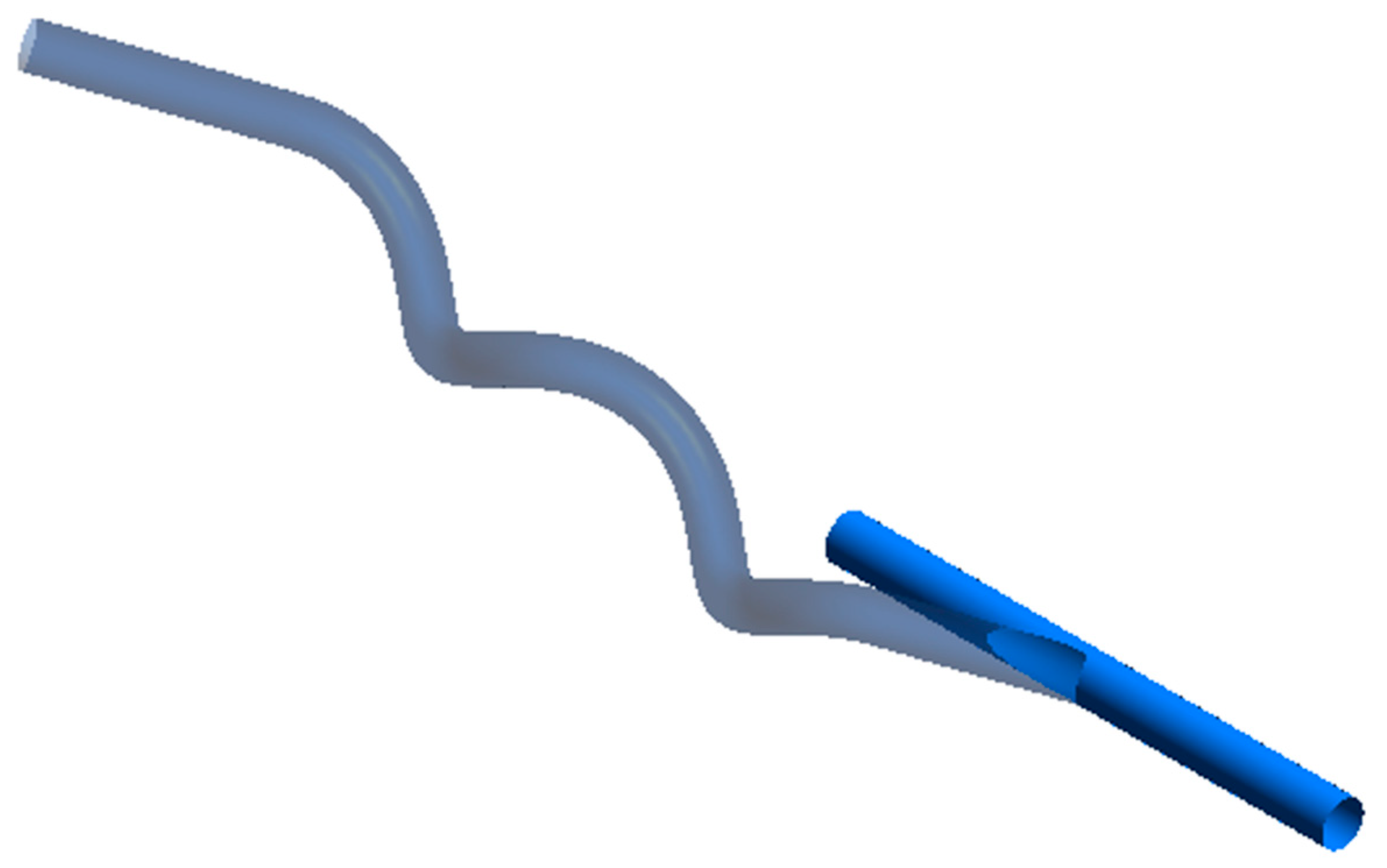
| Anastomosis Angle | Helical Diameter | Helical Pitch |
|---|---|---|
| 25° | 7 mm | 30 mm |
| 35° | 10 mm | 40 mm |
| 45° | 13 mm | 50 mm |
| Graft Model Number (AA-HD-HP) | Anastomosis Angle (AA) | Helical Diameter (HD) | Helical Pitch (HP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-7-30 | 25 | 7 | 30 |
| 25-7-40 | 25 | 7 | 40 |
| 25-7-50 | 25 | 7 | 50 |
| 25-10-30 | 25 | 10 | 30 |
| 25-10-40 | 25 | 10 | 40 |
| 25-10-50 | 25 | 10 | 50 |
| 25-13-30 | 25 | 13 | 30 |
| 25-13-40 | 25 | 13 | 40 |
| 25-13-50 | 25 | 13 | 50 |
| 35-7-30 | 35 | 7 | 30 |
| 35-7-40 | 35 | 7 | 40 |
| 35-7-50 | 35 | 7 | 50 |
| 35-10-30 | 35 | 10 | 30 |
| 35-10-40 | 35 | 10 | 40 |
| 35-10-50 | 35 | 10 | 50 |
| 35-13-30 | 35 | 13 | 30 |
| 35-13-40 | 35 | 13 | 40 |
| 35-13-50 | 35 | 13 | 50 |
| 45-7-30 | 45 | 7 | 30 |
| 45-7-40 | 45 | 7 | 40 |
| 45-7-50 | 45 | 7 | 50 |
| 45-10-30 | 45 | 10 | 30 |
| 45-10-40 | 45 | 10 | 40 |
| 45-10-50 | 45 | 10 | 50 |
| 45-13-30 | 45 | 13 | 30 |
| 45-13-40 | 45 | 13 | 40 |
| 45-13-50 | 45 | 13 | 50 |
| Variable | Selection Criteria |
|---|---|
| Area-Weighted Average Wall Shear Stress | Lowest (within 1 Pa to 6 Pa) |
| Pressure drop | Lowest (below 667 Pa) |
| Helicity | Highest |
| Time-Averaged Wall Shear Stress (TAWSS) | Highest (greater than 0.4 Pa) |
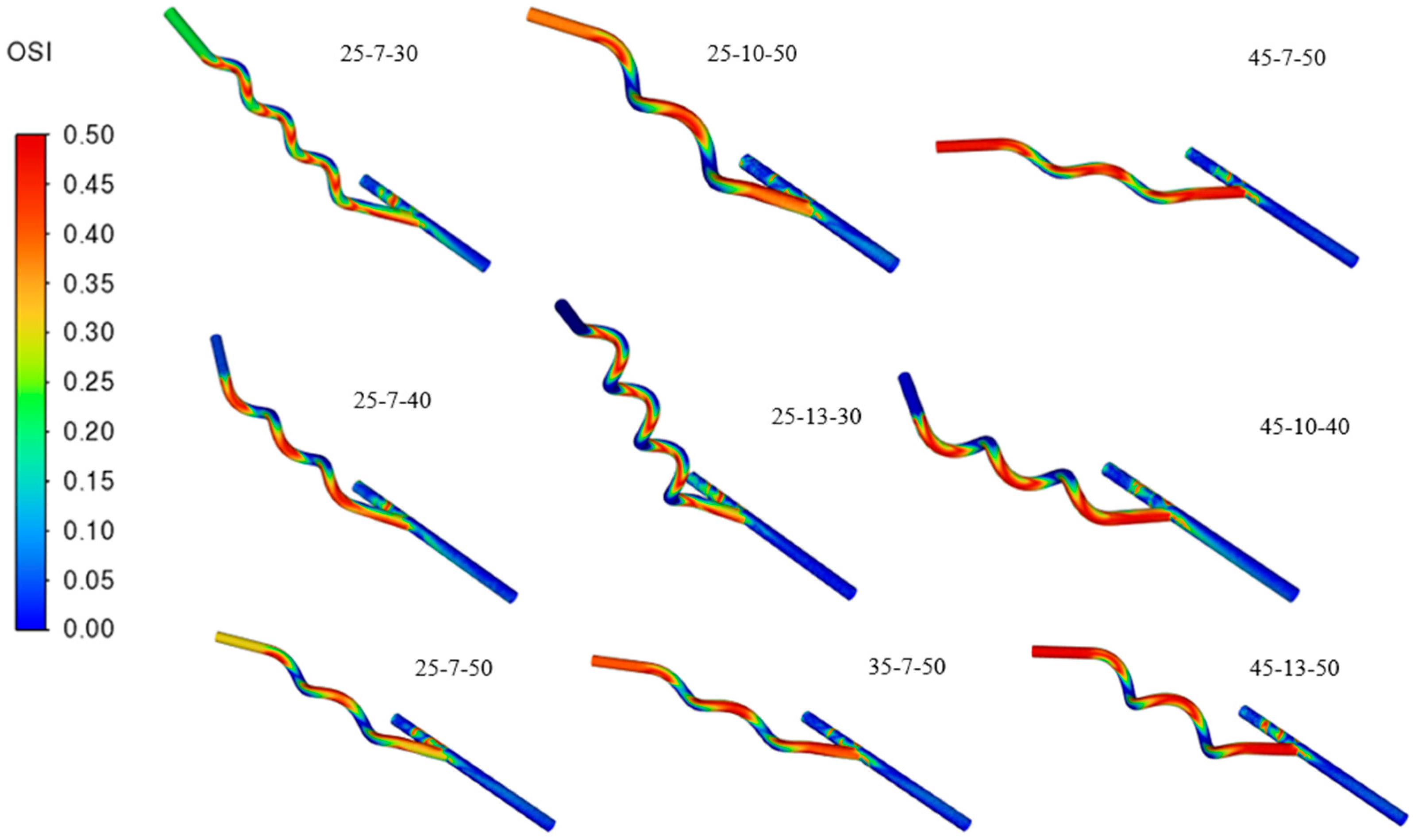
| Oscillatory Shear Index (OSI) | Lowest (less than 0.2) |
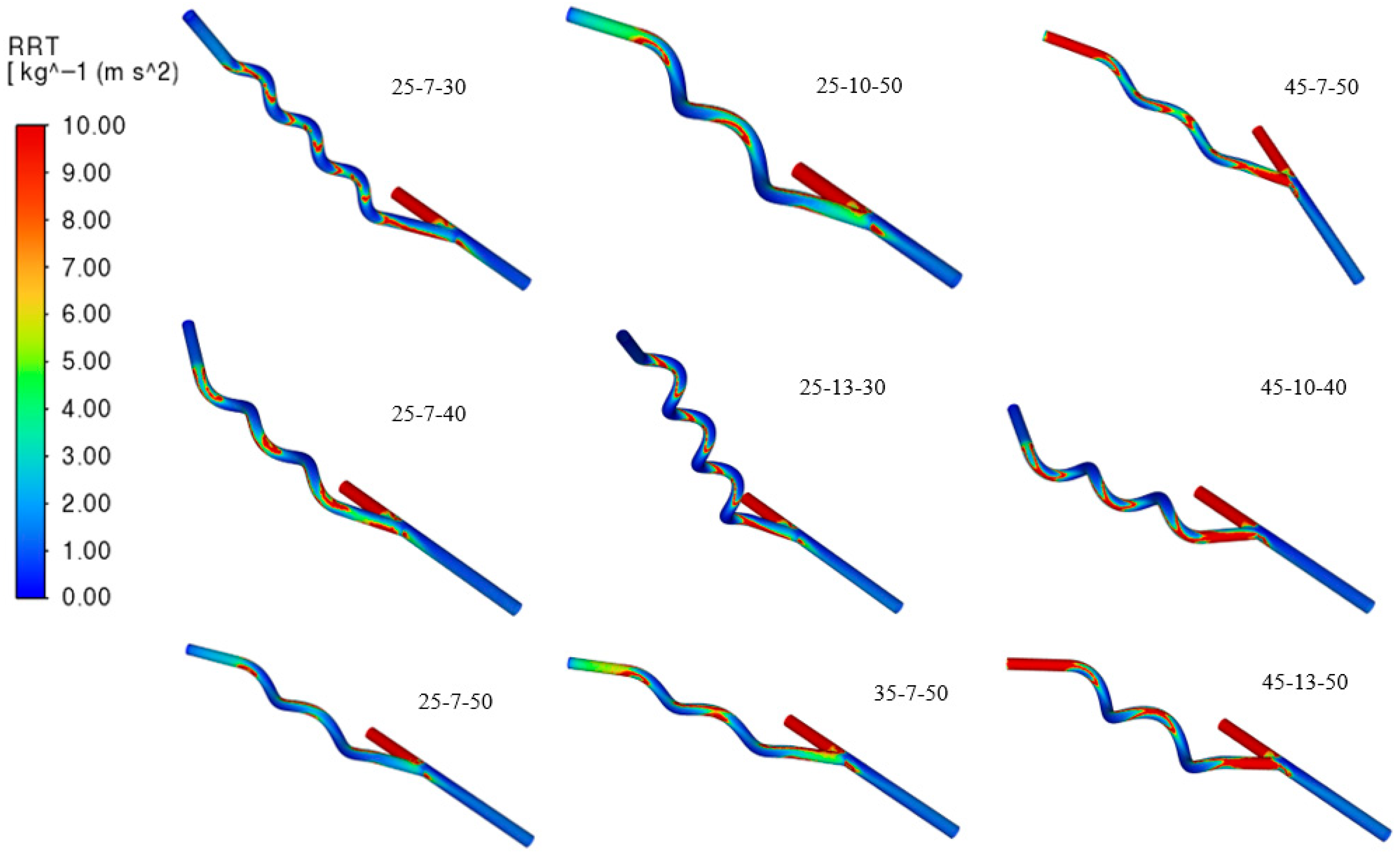
| Relative Residence Time (RRT) | Lowest |
| Variable | T-Joint Pipe (Literature) | T-Joint Pipe (CFD Results) | % Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | 2.05 | 2.05 | 0% |
| Outlet at 90° | 1.36 | 1.1275 | 18.69% |
| Outlet at 90° | 1.20 | 1.2009 | 0.0749% |
| Variable | T-Joint Pipe (Literature) | T-Joint Pipe (CFD Results) | % Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet | 2903 | 2903 | 0% |
| Outlet at 90° | 1814.23 | 1765.88 | 2.70% |
| Outlet at 90° | 1588.68 | 1669.79 | 4.98% |
| Graft Model Number (AA-HD-HP) | Helicity () | Graft Model Number (AA-HD-HP) | Helicity () |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-7-30 | 4.6273 | 35-10-50 | 6.9158 |
| 25-7-40 | 4.9942 | 35-13-30 | 2.0481 |
| 25-7-50 | 7.5508 | 35-13-40 | 1.7373 |
| 25-10-30 | 0.9351 | 35-13-50 | 7.3802 |
| 25-10-40 | 2.8613 | 45-7-30 | 6.0879 |
| 25-10-50 | 7.5971 | 45-7-40 | 5.0317 |
| 25-13-30 | 5.9899 | 45-7-50 | 9.1556 |
| 25-13-40 | 1.0925 | 45-10-30 | 7.2323 |
| 25-13-50 | 2.8248 | 45-10-40 | 8.7852 |
| 35-7-30 | 4.9607 | 45-10-50 | 7.1352 |
| 35-7-40 | 6.5121 | 45-13-30 | 8.3653 |
| 35-7-50 | 8.8199 | 45-13-40 | 8.2986 |
| 35-10-30 | 2.2792 | 45-13-50 | 9.4276 |
| 35-10-40 | 6.8687 |
| Graft Model Number (AA-HD-HP) | TAWSS (Pa) | OSI | RRT (Pa−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-7-30 | 1.4222 | 0.1983 | 1.6144 |
| 25-7-40 | 1.2242 | 0.1673 | 1.7940 |
| 25-7-50 | 1.1562 | 0.1756 | 1.7660 |
| 25-10-50 | 1.2648 | 0.2076 | 1.4419 |
| 25-13-30 | 1.4604 | 0.1461 | 1.4621 |
| 35-7-50 | 1.1688 | 0.2020 | 1.3562 |
| 45-7-50 | 1.1937 | 0.2214 | 1.3036 |
| 45-10-40 | 1.3443 | 0.1734 | 1.3550 |
| 45-13-50 | 1.2843 | 0.2136 | 1.3079 |
| Hemodynamic Parameter | Helical Bypass Graft | Spiral Ridged Bypass Graft | % Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area-Weighted Average WSS (Pa) | 1.4420 | 2.39 | 49.48% |
| Helicity (J/kg) | 1.1980 | 1.57 | 26.88% |
| Area of <1 Pa on host artery wall (mm2) | 8.08 | 10.00 | 21.24% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benitez, J.; Monzon, J.; Abenojar, W.J.; Honra, J.; Tayo, L. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Blood Flow in Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft for Enhanced Flow Performance. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011064
Benitez J, Monzon J, Abenojar WJ, Honra J, Tayo L. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Blood Flow in Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft for Enhanced Flow Performance. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011064
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenitez, Jericho, Jericho Monzon, Wynston Jay Abenojar, Jaime Honra, and Lemmuel Tayo. 2025. "Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Blood Flow in Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft for Enhanced Flow Performance" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011064
APA StyleBenitez, J., Monzon, J., Abenojar, W. J., Honra, J., & Tayo, L. (2025). Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Blood Flow in Helical Arterio-Venous Bypass Graft for Enhanced Flow Performance. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11064. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011064






