Effect of Oblique Impact Angles on Fracture Patterns in Laminated Glass Plates Impacted by a 10 mm Steel Ball
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Test Specimens
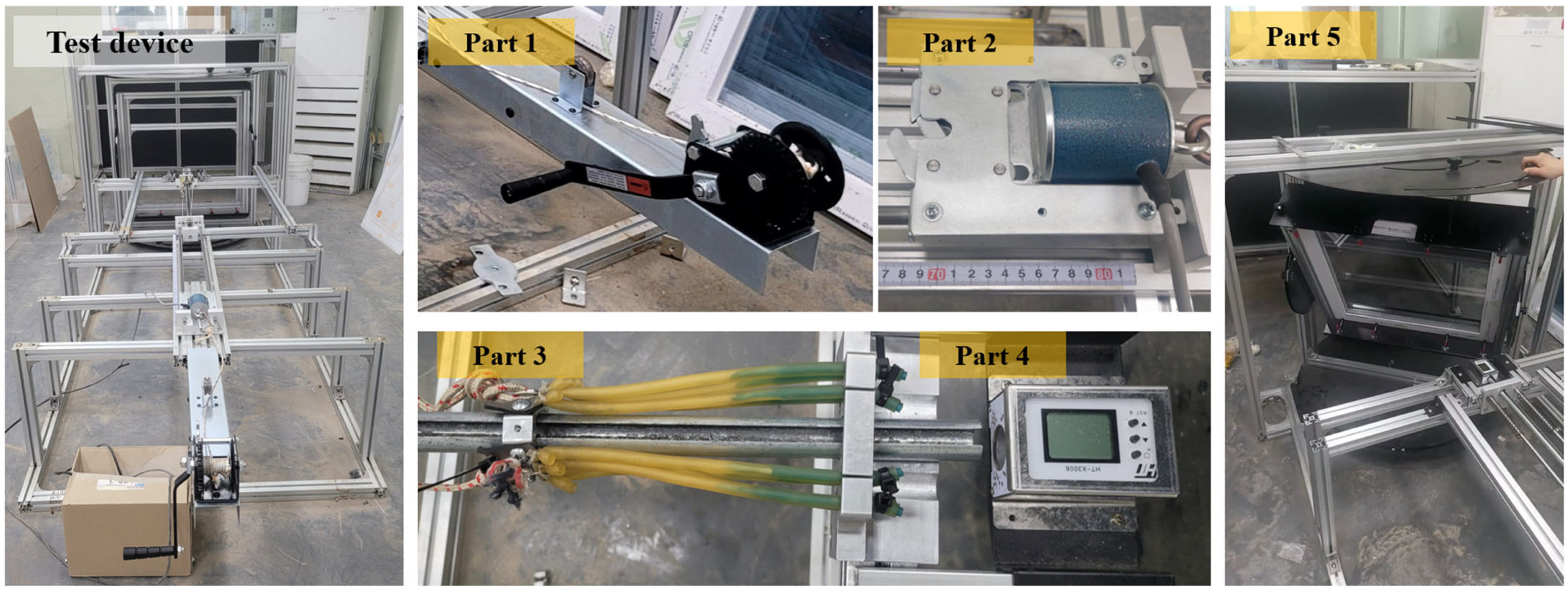
2.2. Test Setup
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Damage Pattern
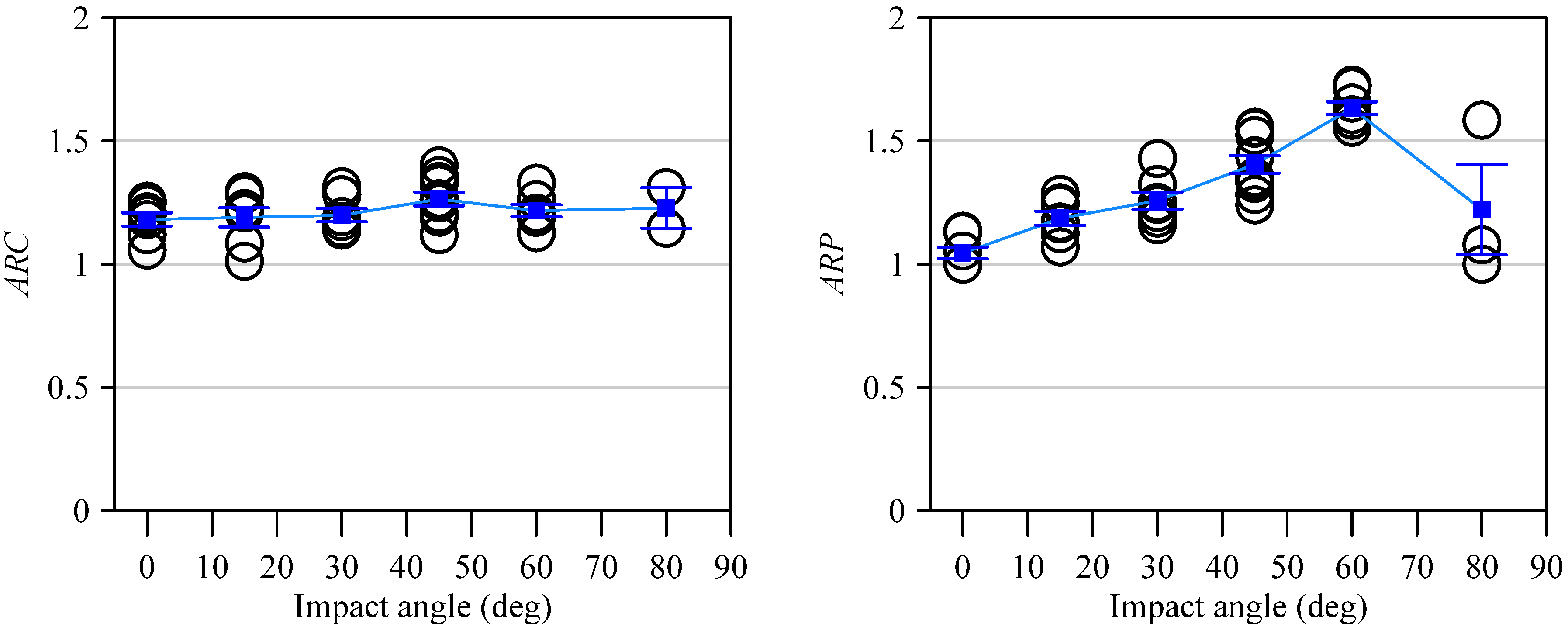
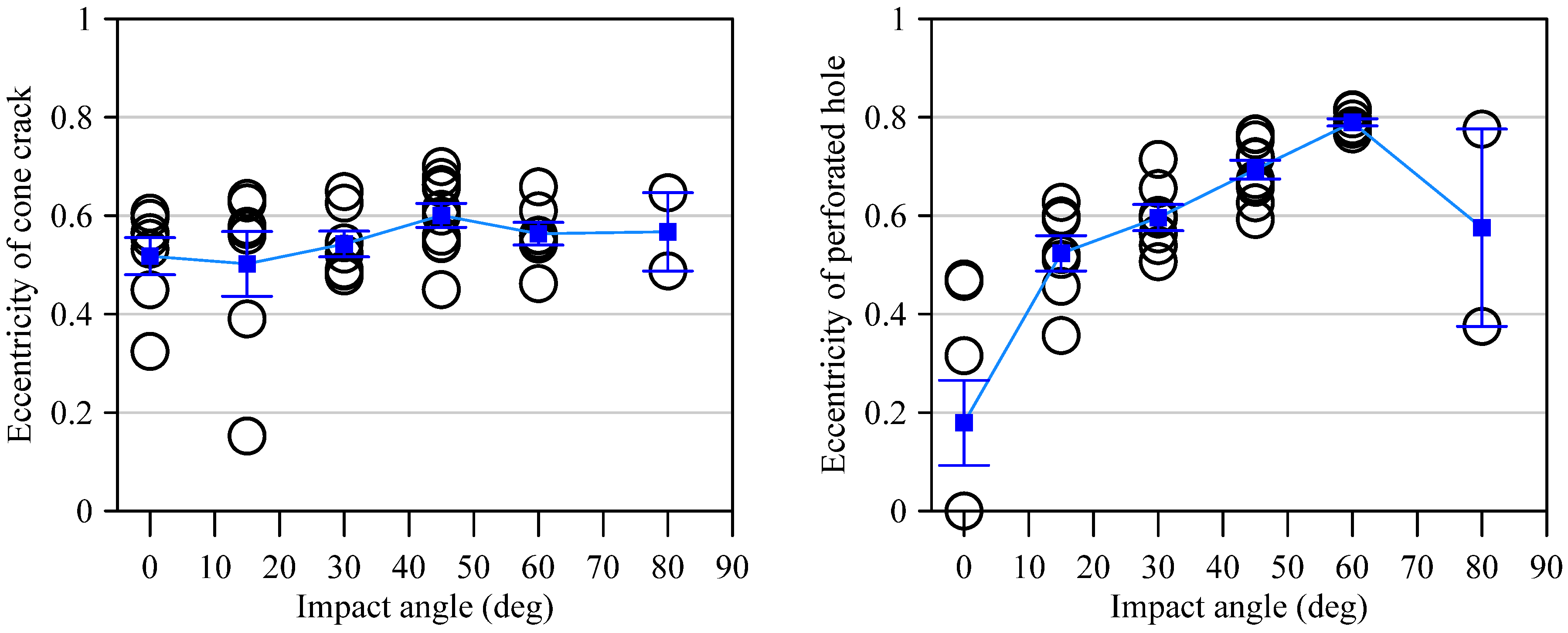
3.2. Eccentricity Analysis of Fracture Pattern
3.3. Limit Impact Angle
3.4. Differential Angular Sensitivity of Cone Cracks and Perforated Holes
3.5. Comparison of Tests Results with 8 and 10 mm Steel Balls
4. Conclusions
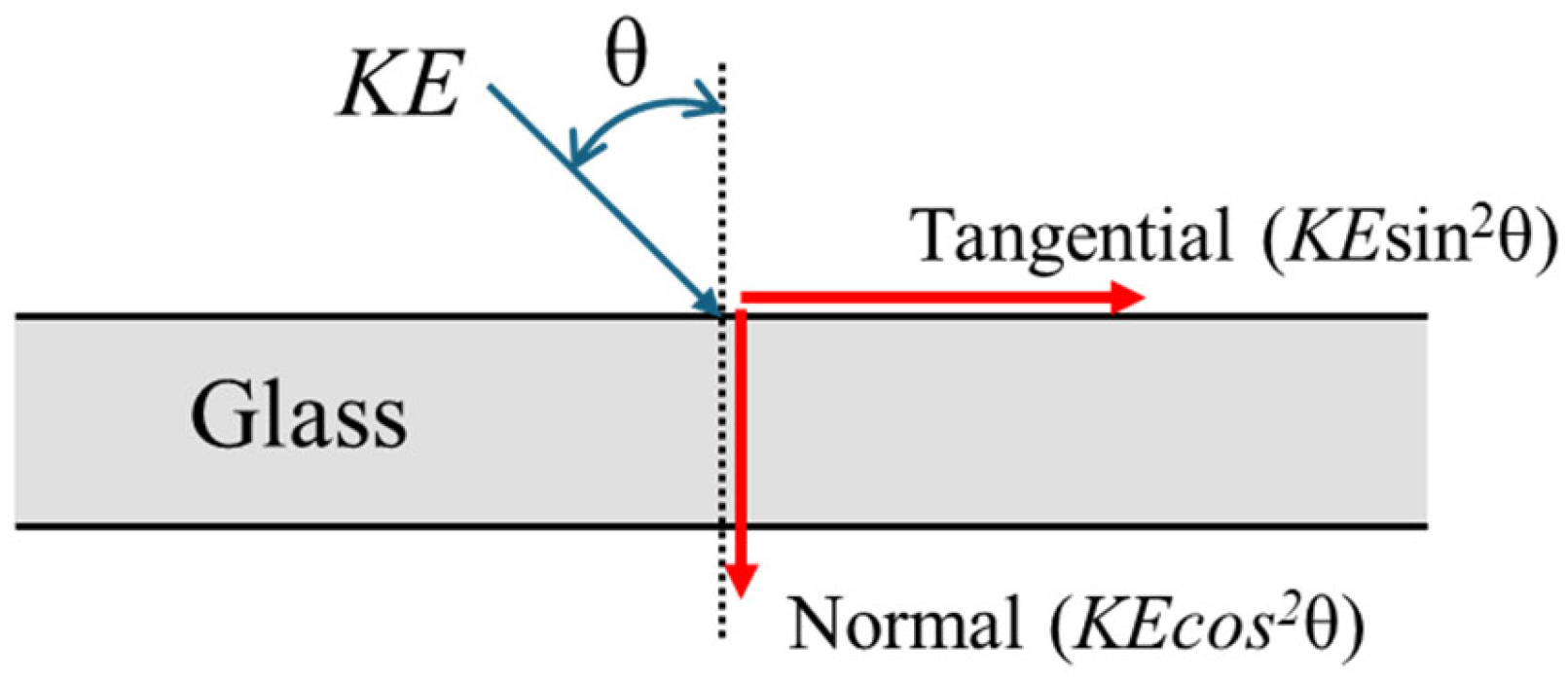
- The Cmax/KE and Cmin/KE values remained stable at 5.7–6.4 mm/J and 4.9–5.3 mm/J for angles from 0° to 45°, but dropped significantly to 0.7 and 0.6 mm/J at 80°. This change occurs because the normal impact energy component decreases from 0.5KE at 60° to only 0.03KE at 80°, showing that normal energy dominates the overall damage size.
- Cone crack eccentricity increased only 15.4% maximum, while perforated hole eccentricity increased dramatically by 338.9% from 0.18 (0°) to 0.79 (60°). This 22-fold difference comes from different formation processes: cone cracks form through stress fields (following Hertzian contact theory), while perforated holes form through direct mechanical penetration that depends on the ball’s trajectory.
- A critical angle exists around 80° where only 50% of specimens achieved complete penetration because the normal energy (0.11–0.14 J) falls below the threshold needed for glass fracture (~0.8 J). Most energy (97%) goes into the tangential direction, causing the ball to deflect rather than penetrate.
- Comparisons between 8 mm and 10 mm steel balls showed similar trends in normalized parameters (Cmax/KE, Pmax/KE, aspect ratios), confirming that energy-based normalization works well for different projectile sizes in impact-resistant design.
- This work was limited to 5 mm thickness single-pane low-E glass with specific impact velocities (40–50 m/s) and 10 mm ball size. Future studies should investigate: (1) laminated glass with different interlayer materials, (2) various glass thicknesses and types, (3) lower or higher velocity impacts, (4) three-dimensional damage modeling, and (5) predictive models based on the dual damage mechanism identified in this study for better impact-resistant glazing design.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korea Flat Glass Window Association. Changho Story—Dictionary Definition. 2018. Available online: http://www.kfgwa.or.kr/fittings-story/fittings-overview (accessed on 31 December 2024). (In Korean).
- Parhi, S.K.; Patro, S.K. Data-driven prediction and intelligent optimization of strength, porosity and cost of concrete with supplementary cementitious materials. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2025, 10, 2567084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalla, S.; Kumar, N.S. Experimental investigations on performance efficiency characteristics of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) with enhanced sustainable mineral admixtures. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2025, 10, 2538978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Choi, N.S. Surface fracture response of glass eabric/epoxy lamina-bonded glass plates to impact with small-diameter steel ball. Compos. Res. 2000, 13, 75–82. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.K.; Park, C.K.; Seo, J.W.; Jeon, C.S. A Study on impact testing of a rolling-stock windscreen. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2013, 16, 365–371. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ha, Y.D.; An, T.S. Peridynamic Impact fracture analysis of multilayered glass with nonlocal Ghost interlayer model. J. Comput. Struct. Eng. Inst. Korea 2018, 31, 373–380. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Oh, W.T.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.C. Experimental Study and Finite Element Analysis about Vehicle Laminated Glass Subject to Headform Impact. Korean Soc. Automot. Eng. 2017, 25, 374–379. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Study on the effect of different sandwich materials on the impact resistance of laminated glass. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Mun, J.H.; Park, S.; Choi, C.; Hong, S. Damage Limit Velocity and Fracture Patterns in Single Glass Plates Impacted by Steel Balls of Varying Diameters. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Chan, A.H.C.; Cheng, Y. Parametric analyses on the impact fracture of laminated glass using the combined finite-discrete element method. Compos. Struct. 2022, 297, 115914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Shukla, V.K.; Rath, A.; Philip, S.A. Effect of 0.32 Caliber Bullets on Fiberglass at Various Firing Distances and Determination of Range of Firing from the Fracture Patterns on Fiberglass. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, N.P. Distinctive Impact Pattern of AK 47/56 Projectile on Glass Fracture. J. Forensic Sci. Crim. Investig. 2018, 8, 555746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshey, A.; Srivastava, A.; Yaday, V.K.; Nigam, K.; Kumar, A.; Das, T. Analysis of glass fracture pattern made by.177″ (4.5 mm) Caliber air rifle. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Harshey, A.; Das, T.; Abhyankar, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Nigam, K.; Anand, V.R.; Srivastava, A. Evidential significance of multiple fracture patterns on the glass in forensic ballistics. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhyankar, S.; Srivastava, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Nigam, K.; Harshey, A. Glass Fractures Made from Different Pellet Shapes—APreliminary Stduy. J. Forensic Sci. Crim. Investig. 2018, 8, 555739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, Y.S.; Salman, A.D.; Hounslow, M.J. Effect of impact angle and velocity on the fragment size distribution of glass spheres. Powder Technol. 2003, 138, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Sa, S.H.; Nam, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, J.P.; Goh, J.M.; Park, N.K. Forensic scientific analysis for glass breakdown patterns. J. Korean Soc. Saf. 2012, 27, 28–35. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Bocchese, F.; Brown, I.; Cornil, D.; Moskovkin, P.; Muller, J.; Kenny, S.D.; Smith, R.; Lucas, S. Low-E glass improvement by the understanding and control of the Ag growth. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 611, 155600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS L 2017; Low Emissivity Glass. Korean Standards and Certification: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018; p. 6. (In Korean)
- Hertz, H. Über die Berührung fester elastischer Körper. J. Reine Angew. Math. 1881, 92, 156–171. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, F.C.; Lawn, B.R. On the theory of Hertzian fracture. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 1967, 299, 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Farris, T.N.; Chandrasekar, S. Contact mechanics of Hertzian cone cracking. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1995, 32, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Choi, C. Experimental Study on Damage Patterns of Glass Pane Subjected to Low-Velocity Impact Loads. Protect. Facil. 2025, 2, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
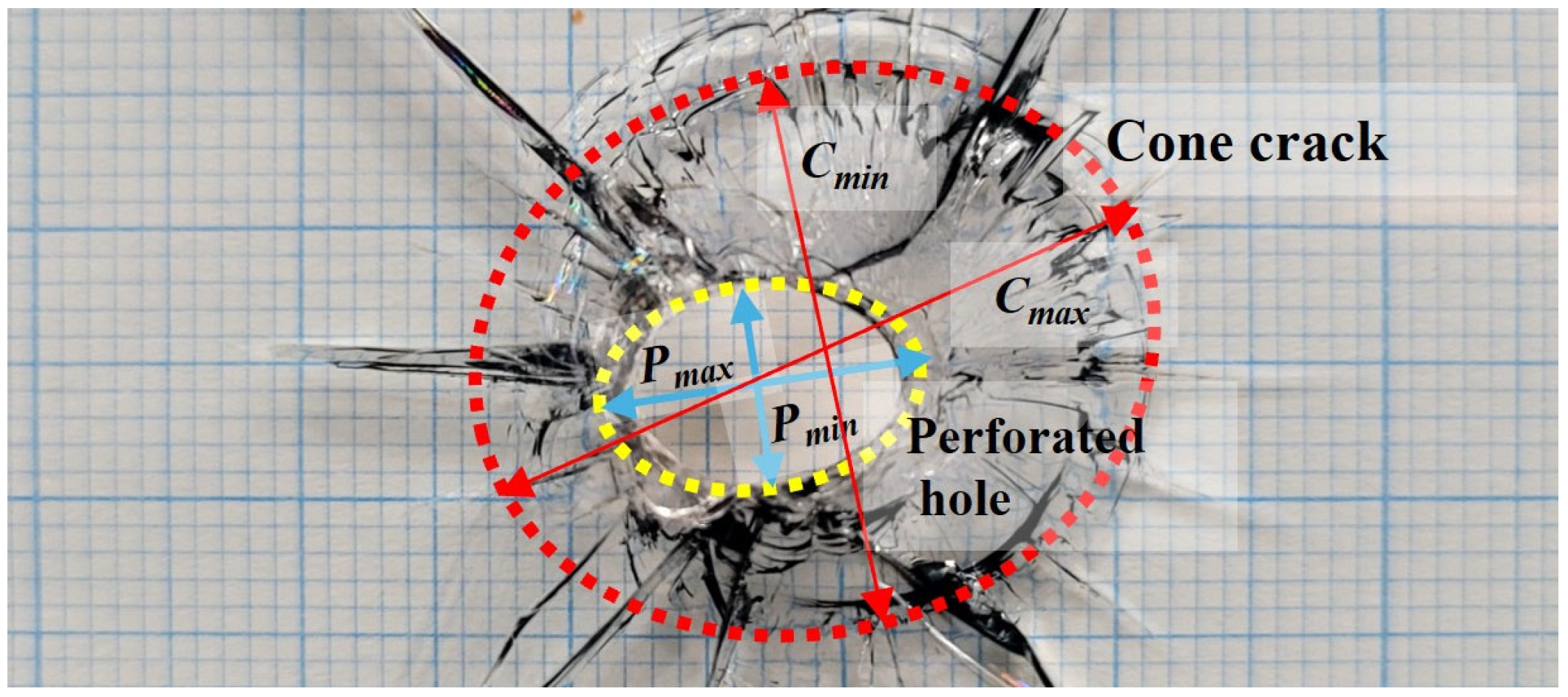

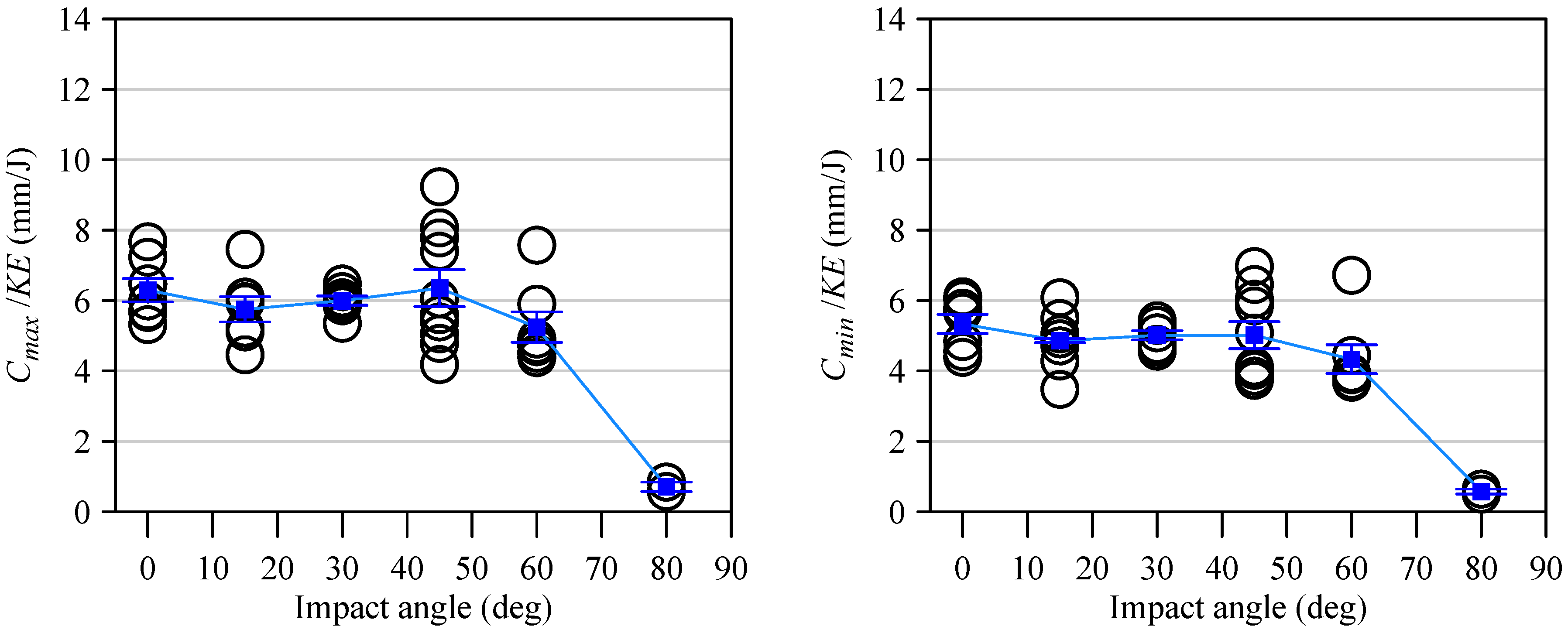
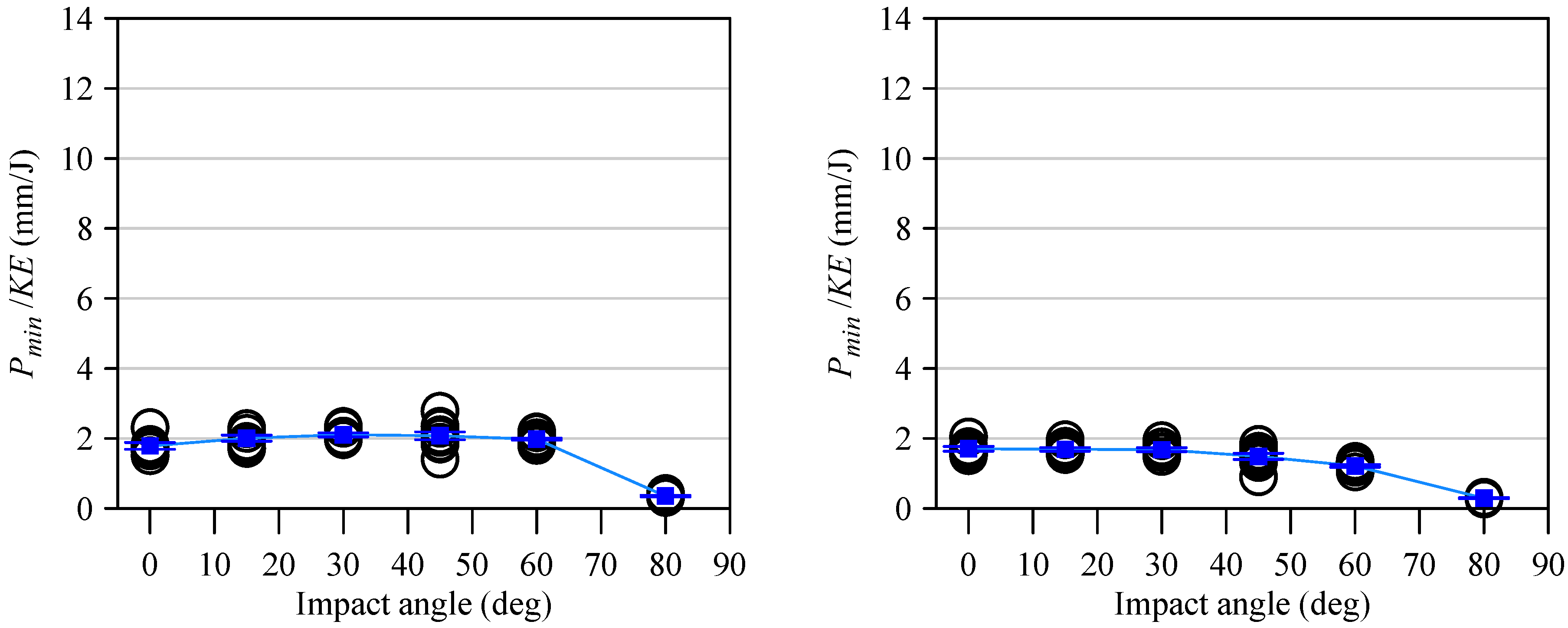
No. | Angle (°) | Velocity (m/s) | Cone Crack | Perforated Hole | Normalized Cone Crack | Nomalized Perforated Hole | ARC | ARP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (mm) | Cmin (mm) | Pmax (mm) | Pmin (mm) | Cmax/KE (mm/J) | Cmin/KE (mm/J) | Pmax/KE (mm/J) | Pmin/KE (mm/J) | |||||
| 0-1 | 0 | 40.79 | 24.90 | 20.73 | 7.96 | 7.04 | 7.23 | 6.02 | 2.31 | 2.04 | 1.20 | 1.13 |
| 0-2 | 0 | 43.90 | 23.89 | 22.60 | 6.70 | 6.70 | 5.99 | 5.67 | 1.68 | 1.68 | 1.06 | 1.00 |
| 0-3 | 0 | 44.33 | 21.63 | 17.84 | 7.44 | 7.06 | 5.32 | 4.39 | 1.83 | 1.74 | 1.21 | 1.05 |
| 0-4 | 0 | 45.20 | 27.38 | 24.46 | 6.38 | 6.38 | 6.47 | 5.78 | 1.51 | 1.51 | 1.12 | 1.00 |
| 0-5 | 0 | 45.93 | 24.93 | 21.11 | 7.71 | 6.80 | 5.71 | 4.83 | 1.77 | 1.56 | 1.18 | 1.13 |
| 0-6 | 0 | 46.10 | 24.91 | 20.03 | 7.25 | 7.25 | 5.66 | 4.55 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.24 | 1.00 |
| 0-7 | 0 | 47.51 | 35.84 | 28.53 | 8.25 | 8.25 | 7.67 | 6.11 | 1.77 | 1.77 | 1.26 | 1.00 |
| Average | 44.8 | 26.2 | 22.2 | 7.4 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 5.3 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 1.0 | |
| STDEV | 2.1 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 15-1 | 15 | 41.27 | 18.02 | 17.81 | 7.57 | 6.06 | 5.11 | 5.05 | 2.15 | 1.72 | 1.01 | 1.25 |
| 15-2 | 15 | 41.43 | 21.19 | 19.51 | 8.10 | 6.31 | 5.96 | 5.49 | 2.28 | 1.78 | 1.09 | 1.28 |
| 15-3 | 15 | 41.97 | 27.18 | 22.17 | 8.33 | 7.16 | 7.45 | 6.08 | 2.28 | 1.96 | 1.23 | 1.16 |
| 15-4 | 15 | 42.83 | 22.53 | 18.66 | 7.24 | 6.18 | 5.93 | 4.91 | 1.91 | 1.63 | 1.21 | 1.17 |
| 15-5 | 15 | 48.10 | 25.00 | 20.51 | 9.17 | 7.38 | 5.22 | 4.28 | 1.91 | 1.54 | 1.22 | 1.24 |
| 15-6 | 15 | 48.30 | 29.45 | 22.75 | 8.71 | 7.75 | 6.10 | 4.71 | 1.80 | 1.60 | 1.29 | 1.12 |
| 15-7 | 15 | 50.30 | 23.35 | 18.21 | 8.98 | 8.39 | 4.46 | 3.48 | 1.71 | 1.60 | 1.28 | 1.07 |
| Average | 44.9 | 23.8 | 19.9 | 8.3 | 7.0 | 5.7 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| STDEV | 3.9 | 3.8 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 30-1 | 30 | 40.63 | 22.11 | 18.54 | 8.01 | 6.62 | 6.47 | 5.43 | 2.34 | 1.94 | 1.19 | 1.21 |
| 30-2 | 30 | 42.88 | 23.13 | 20.16 | 7.77 | 6.70 | 6.08 | 5.30 | 2.04 | 1.76 | 1.15 | 1.16 |
| 30-3 | 30 | 43.18 | 24.13 | 18.36 | 7.98 | 6.72 | 6.25 | 4.76 | 2.07 | 1.74 | 1.31 | 1.19 |
| 30-4 | 30 | 43.93 | 24.06 | 21.14 | 8.13 | 6.50 | 6.02 | 5.29 | 2.04 | 1.63 | 1.14 | 1.25 |
| 30-5 | 30 | 45.83 | 25.91 | 22.10 | 9.96 | 6.97 | 5.96 | 5.08 | 2.29 | 1.60 | 1.17 | 1.43 |
| 30-6 | 30 | 45.99 | 23.44 | 20.47 | 8.72 | 7.02 | 5.35 | 4.68 | 1.99 | 1.60 | 1.15 | 1.24 |
| 30-7 | 30 | 46.04 | 25.67 | 20.03 | 8.63 | 6.52 | 5.85 | 4.56 | 1.97 | 1.49 | 1.28 | 1.32 |
| Average | 44.1 | 24.1 | 20.1 | 8.5 | 6.7 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| STDEV | 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 45-1 | 45 | 41.78 | 33.36 | 25.17 | 8.49 | 6.62 | 9.23 | 6.97 | 2.35 | 1.83 | 1.33 | 1.28 |
| 45-2 | 45 | 42.17 | 27.24 | 21.52 | 10.23 | 6.72 | 7.40 | 5.85 | 2.78 | 1.83 | 1.27 | 1.52 |
| 45-3 | 45 | 42.47 | 30.11 | 22.54 | 8.55 | 5.51 | 8.06 | 6.04 | 2.29 | 1.48 | 1.34 | 1.55 |
| 45-4 | 45 | 45.84 | 33.84 | 28.08 | 6.13 | 3.94 | 7.78 | 6.46 | 1.41 | 0.91 | 1.21 | 1.56 |
| 45-5 | 45 | 46.04 | 22.17 | 17.75 | 8.91 | 7.18 | 5.05 | 4.05 | 2.03 | 1.64 | 1.25 | 1.24 |
| 45-6 | 45 | 47.20 | 27.92 | 23.41 | 9.42 | 6.56 | 6.05 | 5.08 | 2.04 | 1.42 | 1.19 | 1.44 |
| 45-7 | 45 | 47.42 | 22.26 | 18.69 | 9.81 | 7.39 | 4.78 | 4.02 | 2.11 | 1.59 | 1.19 | 1.33 |
| 45-8 | 45 | 49.10 | 20.87 | 18.64 | 9.45 | 6.56 | 4.18 | 3.74 | 1.89 | 1.31 | 1.12 | 1.44 |
| 45-9 | 45 | 49.11 | 27.94 | 20.55 | 10.13 | 7.57 | 5.60 | 4.12 | 2.03 | 1.52 | 1.36 | 1.34 |
| 45-10 | 45 | 51.34 | 29.42 | 21.02 | 10.05 | 7.43 | 5.39 | 3.85 | 1.84 | 1.36 | 1.40 | 1.35 |
| Average | 46.2 | 27.5 | 21.7 | 9.1 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 5.0 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.4 | |
| STDEV | 3.3 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 60-1 | 60 | 42.74 | 28.64 | 25.40 | 8.27 | 5.00 | 7.57 | 6.72 | 2.19 | 1.32 | 1.13 | 1.65 |
| 60-2 | 60 | 43.85 | 18.93 | 15.68 | 7.70 | 4.86 | 4.76 | 3.94 | 1.93 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 1.58 |
| 60-3 | 60 | 44.45 | 24.12 | 18.15 | 8.85 | 5.51 | 5.90 | 4.44 | 2.16 | 1.35 | 1.33 | 1.61 |
| 60-4 | 60 | 45.99 | 20.53 | 17.14 | 8.09 | 5.20 | 4.69 | 3.91 | 1.85 | 1.19 | 1.20 | 1.56 |
| 60-5 | 60 | 46.92 | 20.53 | 17.02 | 8.66 | 5.46 | 4.51 | 3.73 | 1.90 | 1.20 | 1.21 | 1.59 |
| 60-6 | 60 | 47.13 | 22.56 | 17.88 | 8.29 | 4.80 | 4.91 | 3.89 | 1.80 | 1.04 | 1.26 | 1.73 |
| 60-7 | 60 | 47.93 | 20.83 | 17.50 | 9.61 | 5.59 | 4.38 | 3.68 | 2.02 | 1.18 | 1.19 | 1.72 |
| Average | 45.6 | 22.3 | 18.4 | 8.5 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | |
| STDEV | 1.9 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 80-1 | 80 | 46.05 | ||||||||||
| 80-2 | 80 | 42.34 | ||||||||||
| 80-3 | 80 | 45.86 | 3.67 | 2.80 | 1.37 | 1.27 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 1.31 | 1.08 |
| 80-4 | 80 | 46.04 | 2.52 | 2.20 | 1.87 | 1.18 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 1.15 | 1.58 |
| 80-5 | 80 | 46.63 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 1.00 | |||||
| 80-6 | 80 | 46.86 | ||||||||||
| Average | 45.6 | 3.1 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| STDEV | 1.7 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | |
| Steel Ball (mm) | Cmax/KE (mm/J) | Cmin/KE (mm/J) | Pmax/KE (mm/J) | Pmin/KE (mm/J) | ARC | ARP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 10 | ||
| Angle (°) | 0° | 8.87 (3.3) | 6.29 (0.9) | 7.41 (1.9) | 5.34 (0.7) | 1.50 (0.6) | 1.79 (0.3) | 1.32 0.5 | 1.71 (0.2) | 1.17 (0.1) | 1.18 (0.1) | 1.12 (0.0) | 1.05 (0.1) |
| 15° | 8.83 (1.2) | 5.75 (1.0) | 7.04 (0.8) | 4.86 (0.1) | 1.83 (1.0) | 2.01 (0.2) | 1.55 0.7 | 1.69 (0.1) | 1.25 (0.1) | 1.19 (0.1) | 1.13 (0.1) | 1.19 (0.1) | |
| 30° | 6.88 (0.9) | 6.00 (0.3) | 6.07 (0.7) | 5.01 (0.3) | 2.30 (0.4) | 2.11 (0.1) | 1.59 0.2 | 1.68 (0.1) | 1.13 (0.0) | 1.20 (0.1) | 1.45 (0.1) | 1.26 (0.1) | |
| 45° | 6.77 (0.7) | 6.35 (1.7) | 5.87 (0.6) | 5.01 (1.2) | 2.30 (0.4) | 2.08 (0.4) | 1.56 0.2 | 1.49 (0.3) | 1.15 (0.0) | 1.26 (0.1) | 1.47 (0.1) | 1.40 (0.1) | |
| 60° | 7.01 (1.7) | 5.24 (1.1) | 6.25 (2.1) | 4.33 (1.1) | 1.80 (0.5) | 1.98 (0.1) | 1.08 0.2 | 1.21 (0.1) | 1.15 (0.1) | 1.22 (0.1) | 1.66 (0.2) | 1.63 (0.1) | |
| 80° | 1.37 (0.1) | 0.71 (0.2) | 1.11 (0.3) | 0.57 (0.1) | 0.50 (0.0) | 0.35 (0.1) | 0.50 0.0 | 0.29 (0.0) | 1.29 (0.2) | 1.23 (0.1) | 1.00 (0.0) | 1.22 (0.1) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S. Effect of Oblique Impact Angles on Fracture Patterns in Laminated Glass Plates Impacted by a 10 mm Steel Ball. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10898. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010898
Kim S. Effect of Oblique Impact Angles on Fracture Patterns in Laminated Glass Plates Impacted by a 10 mm Steel Ball. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10898. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010898
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sanghee. 2025. "Effect of Oblique Impact Angles on Fracture Patterns in Laminated Glass Plates Impacted by a 10 mm Steel Ball" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10898. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010898
APA StyleKim, S. (2025). Effect of Oblique Impact Angles on Fracture Patterns in Laminated Glass Plates Impacted by a 10 mm Steel Ball. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10898. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010898






