Transient Stability Enhancement of a PMSG-Based System by Saturated Current Angle Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Main Contributions
- (1)
- An integrated electro-mechanical analysis is presented, demonstrating how the interplay of reactive power coupling and fixed-angle current limiting can lead to rotor overspeed, a critical failure mode often overlooked in purely electrical studies [8].
- (2)
- A dual-mechanism enhancement strategy is proposed. This strategy integrates an adaptive saturated current angle to eliminate detrimental CLC equilibrium points with a damping controller that ensures robust electro-mechanical stability, addressing synchronization [28,29] and mechanical damping [34] in a unified manner.
- (3)
- The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through comprehensive simulations, demonstrating its ability to prevent CLC trapping, ensure reliable fault ride-through, and significantly reduce fault recovery time.
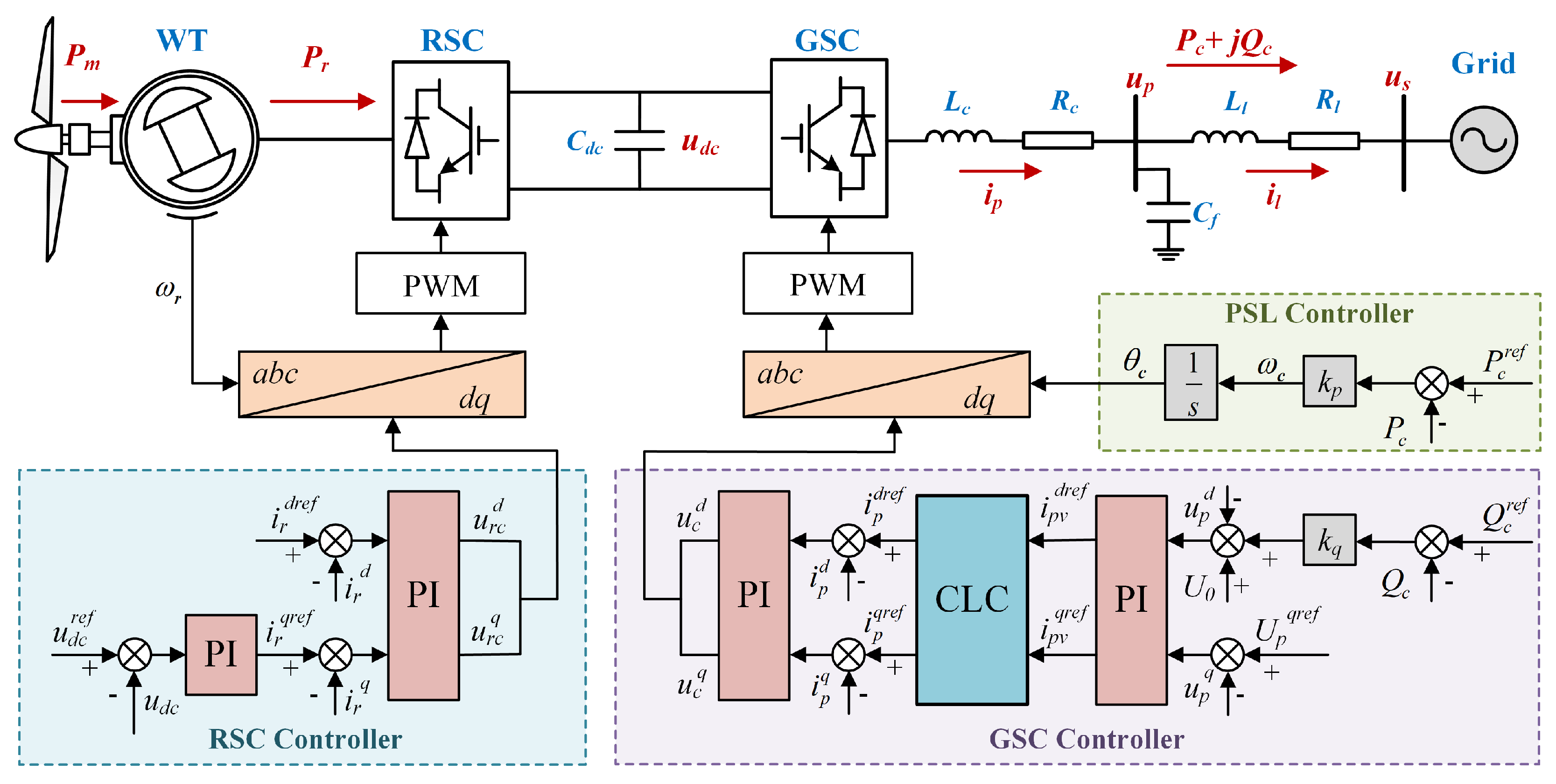
2. System Modelling
2.1. Rotor-Side Converter Control
- is the combined inertia constant of the wind turbine and generator.
- is the generator rotor speed.
- is the mechanical power captured from the wind.
- is the active power extracted by the RSC.
2.2. Grid-Side Converter Control
3. Analysis of Transient Synchronization Stability
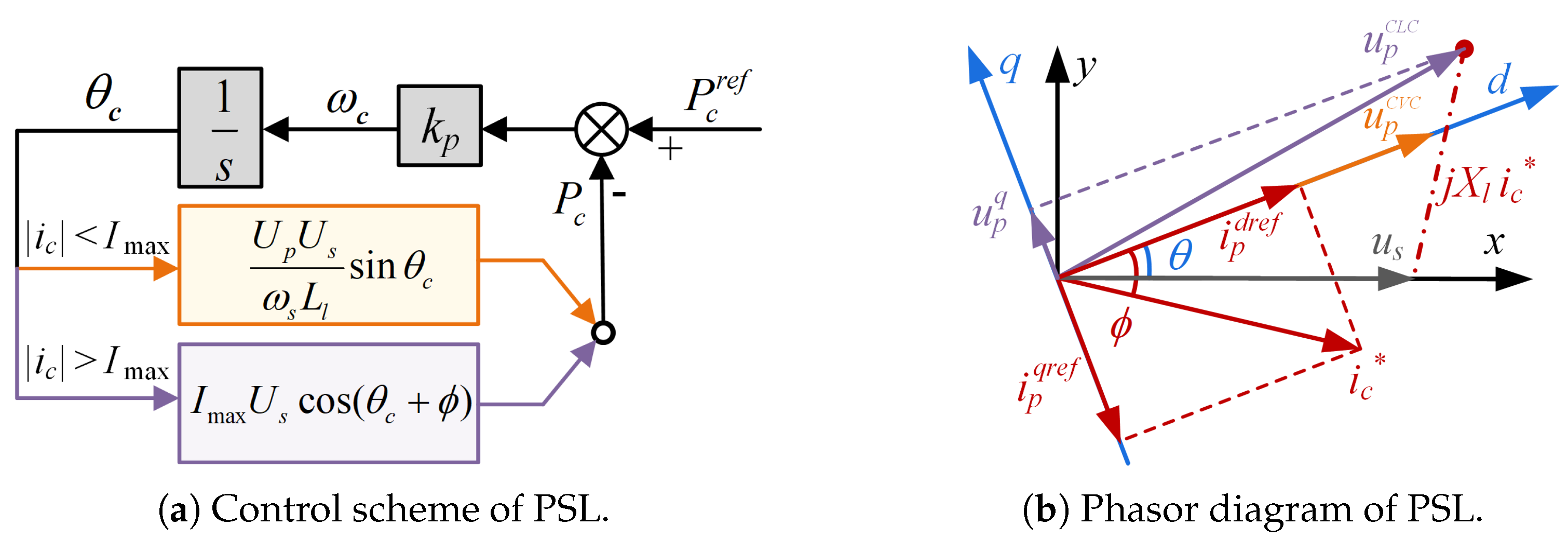
3.1. Impact of the Saturated Current Angle on System Stability
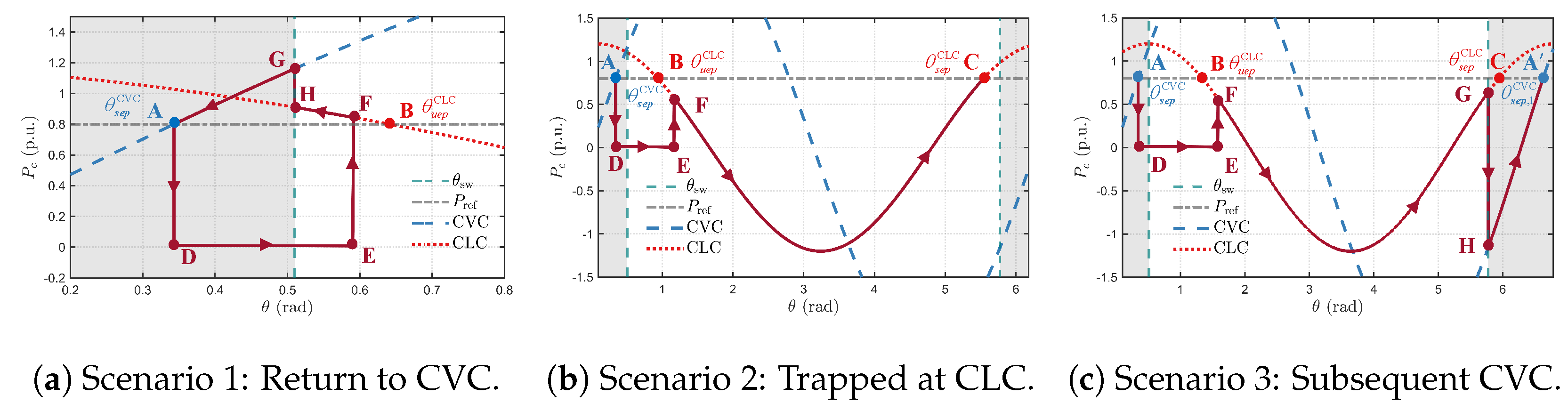
3.1.1. Scenario 1: Recovery to the Original SEP in CVC Mode
3.1.2. Scenario 2: Trapping at the SEP in CLC Mode
3.1.3. Scenario 3: Pole Slip to a Subsequent CVC SEP
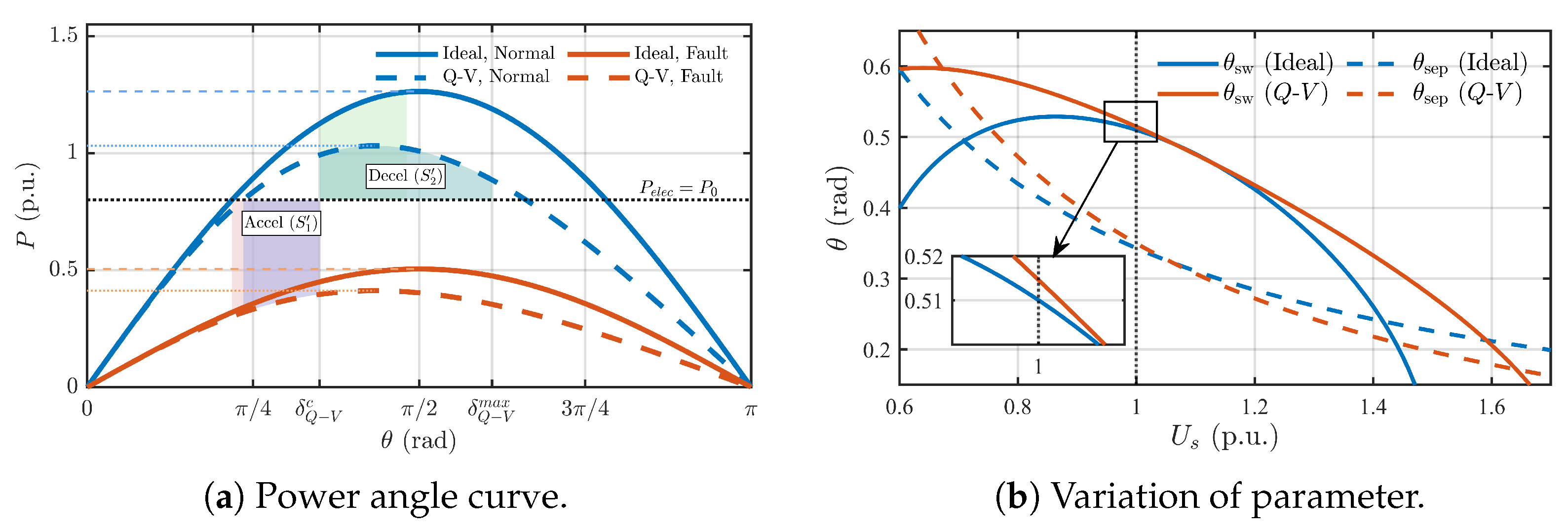
3.2. Effect of Reactive Power Control Loop
4. Transient Stability Enhancement Strategies
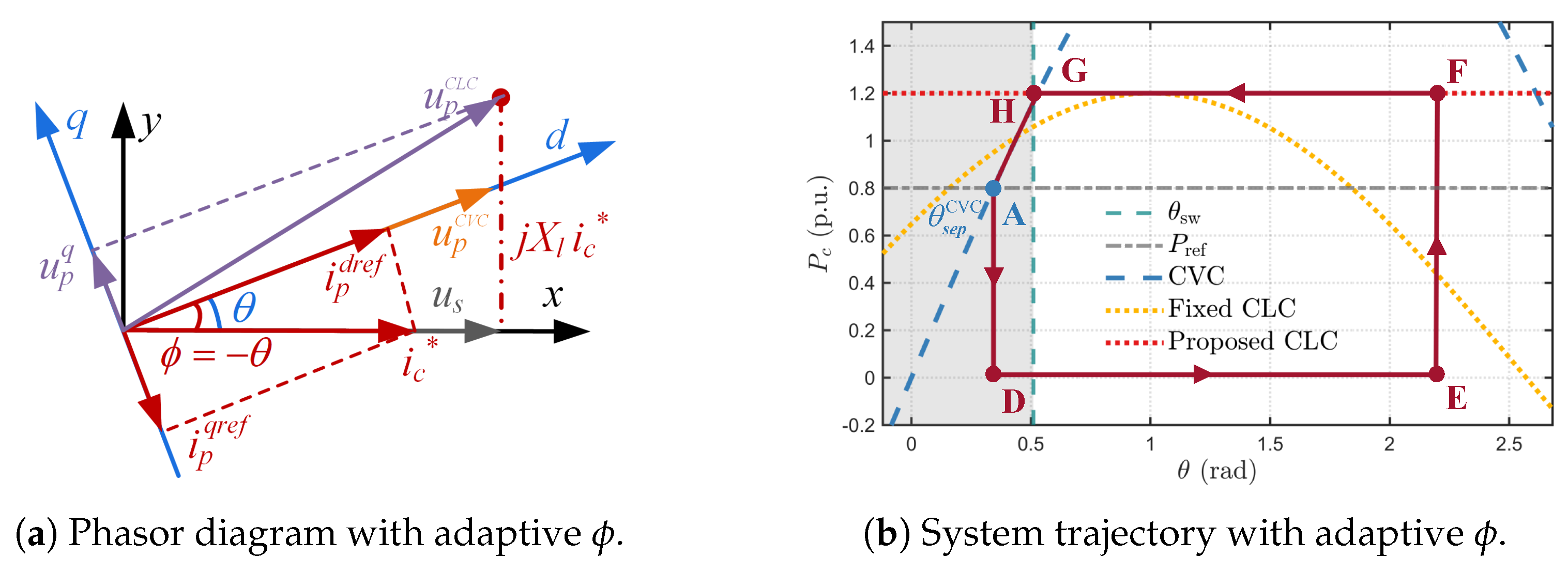
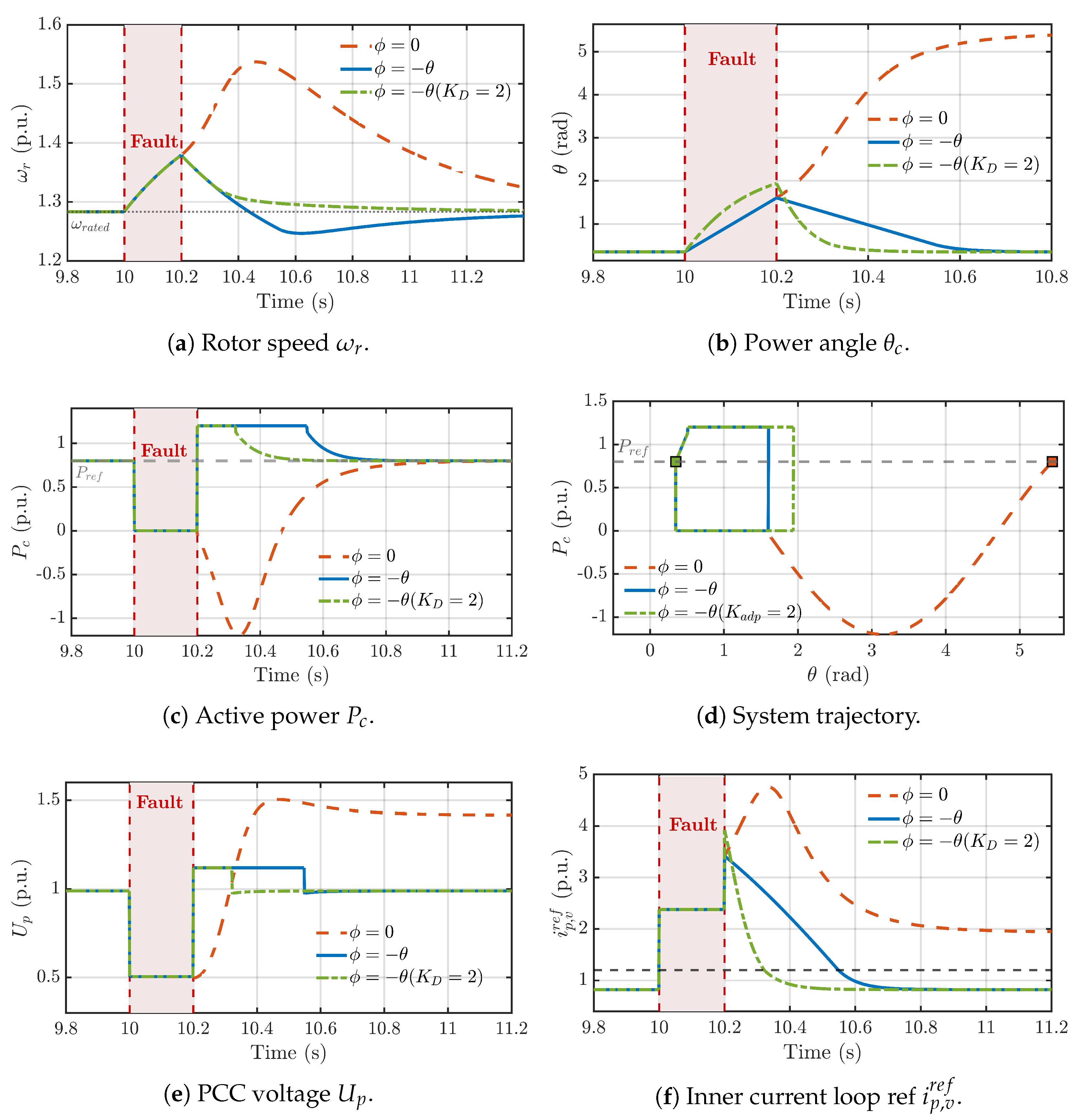
4.1. Adaptive Saturated Current Angle for Stabilizing at Original SEP
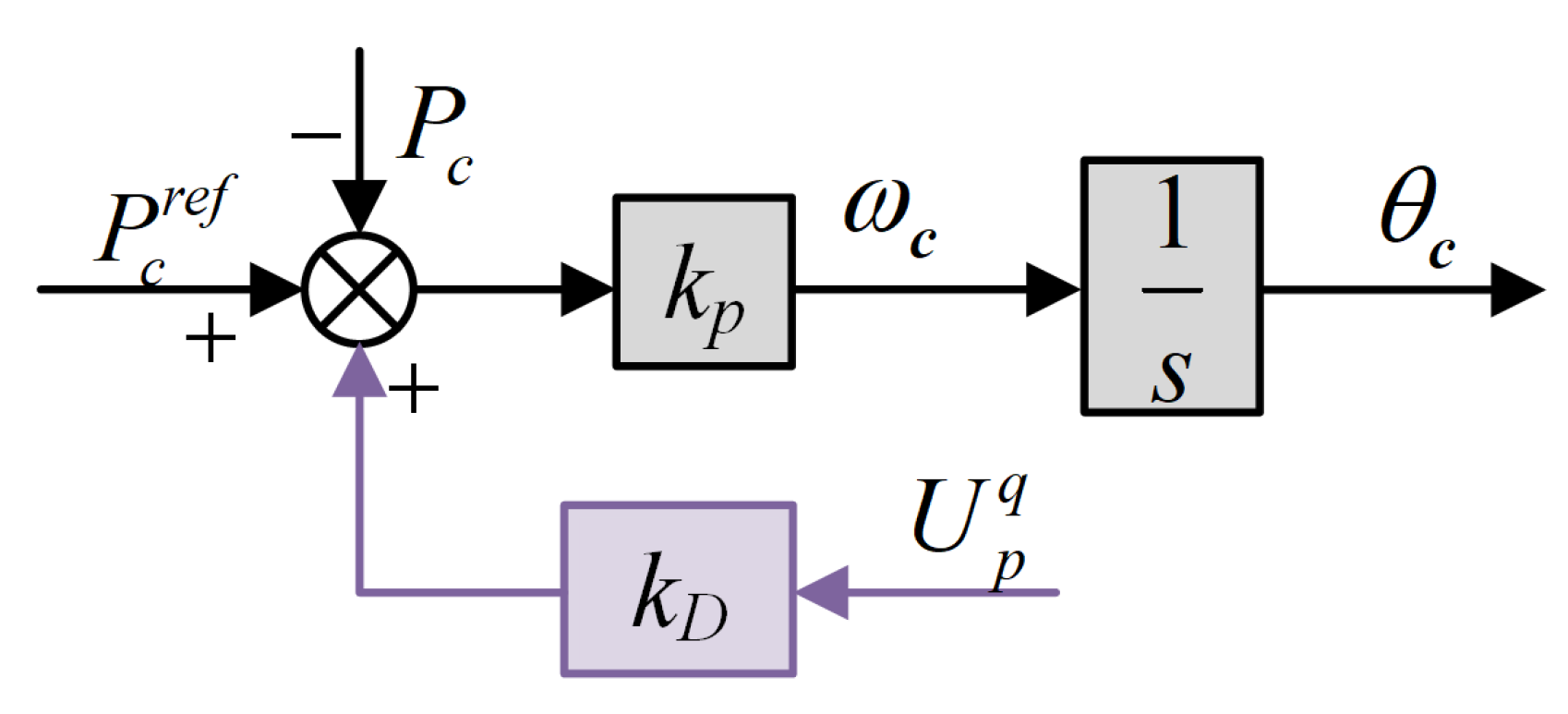
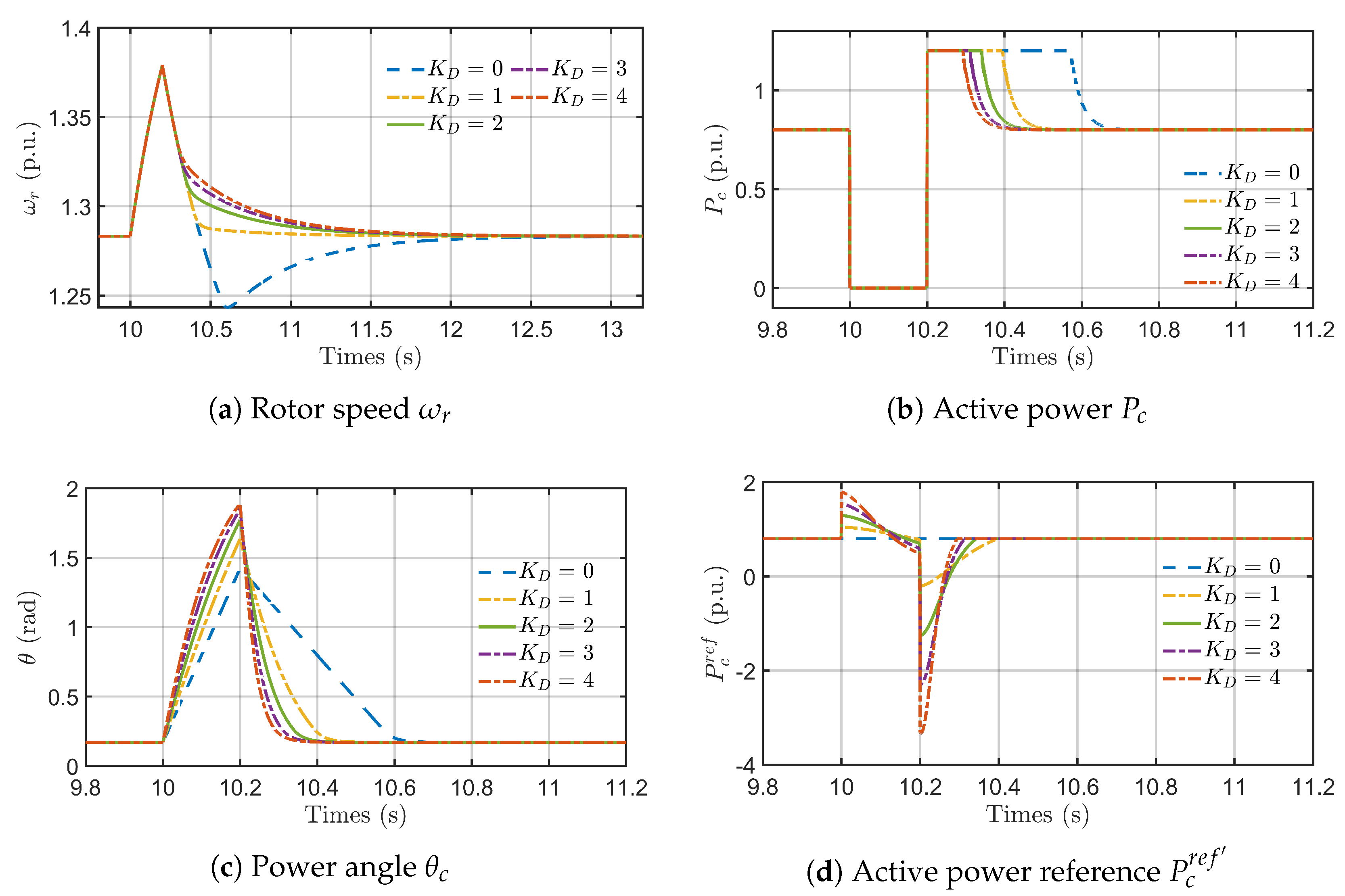
4.2. Damping Enhancement Strategy via Adaptive Active Power Reference Regulation
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Dynamic Response Analysis
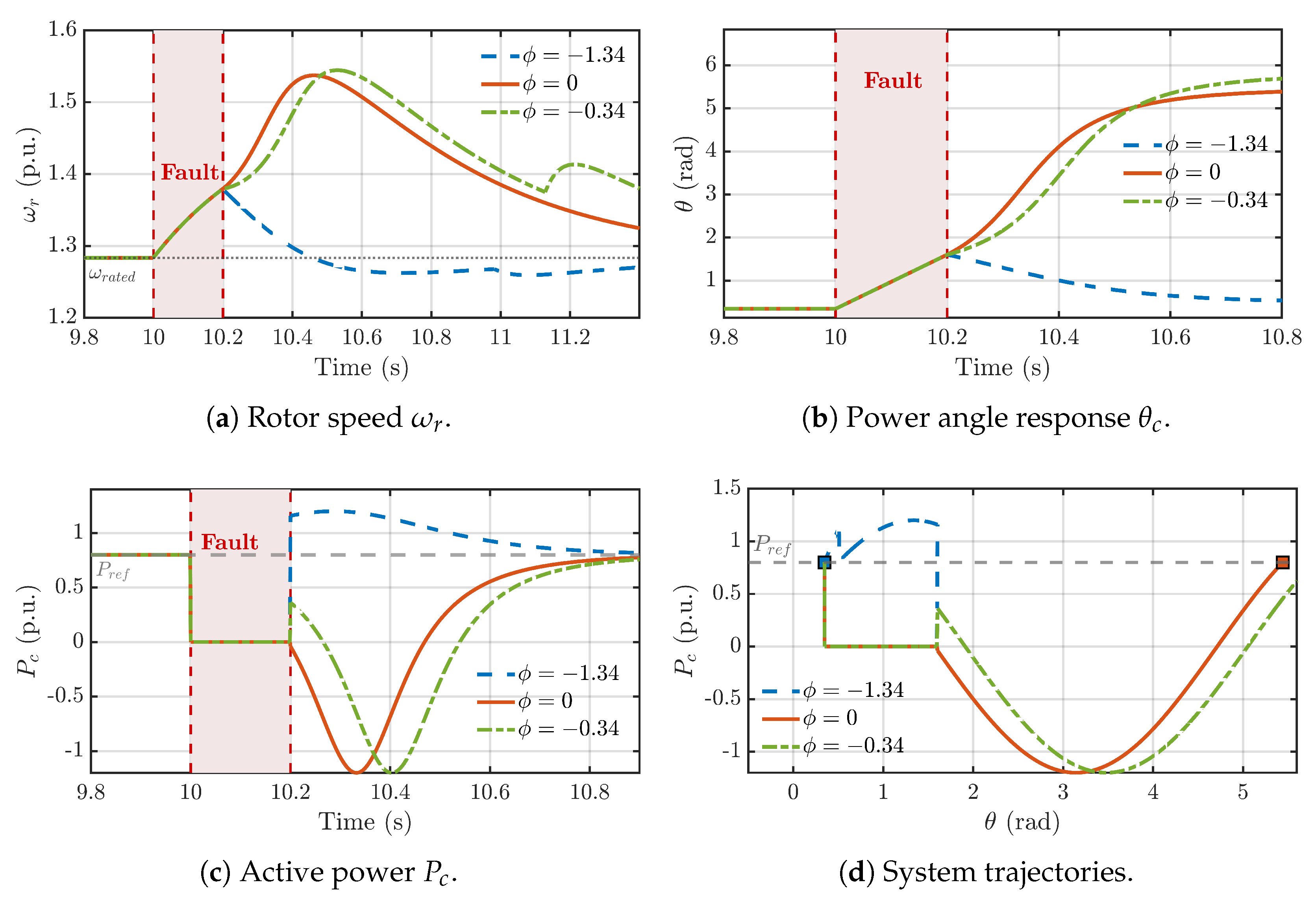
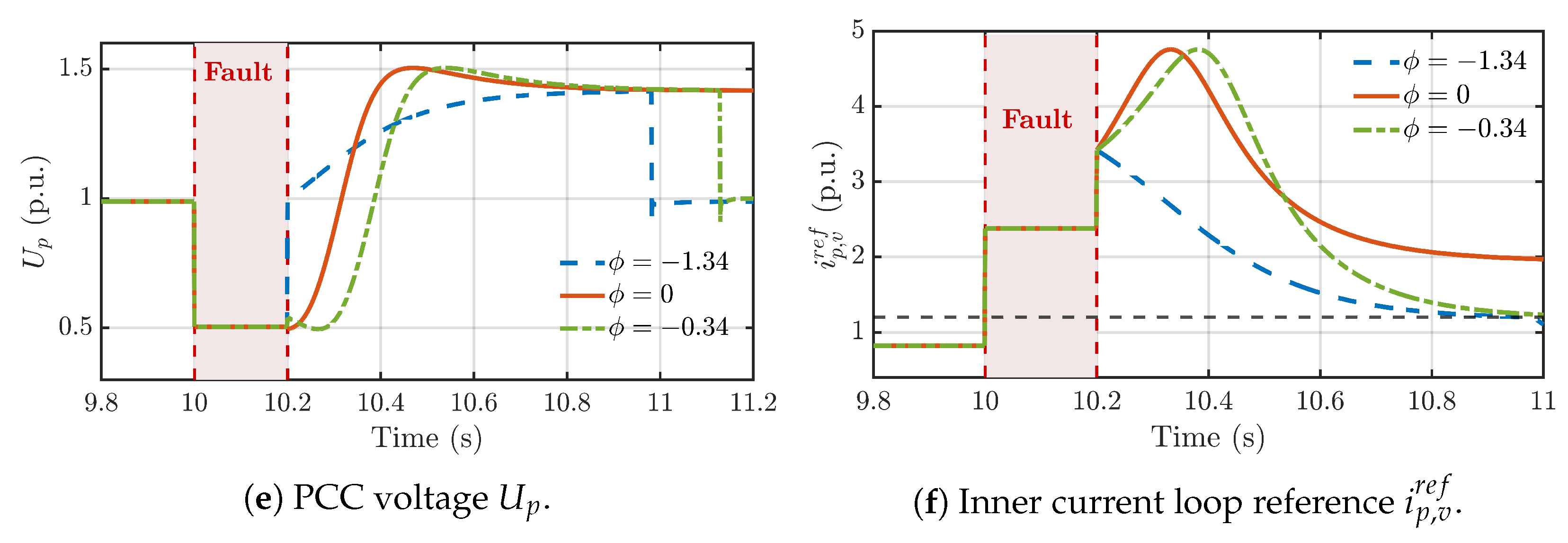
- Scenario 1 (Stable Recovery, rad): This angle lies within the safe operating range. As seen in the plots, after the fault is cleared, the rotor speed () peaks and then safely returns to its nominal value, while the power angle () successfully re-synchronizes to its original stable equilibrium point (SEP).
- Scenario 2 (Trapped in CLC, rad): When is outside the safe range, the system becomes trapped at the CLC’s SEP. The trajectory plot (d) shows the system stabilizing on the CLC power curve. This creates a sustained energy imbalance, causing the rotor speed (a) to accelerate continuously until an overspeed trip would occur.
- Scenario 3 (Pole Slip, rad): With an angle at the boundary of the safe range, the system avoids the CLC trap but undergoes a pole slip. The power angle (b) slips to a subsequent SEP near . This event injects a large amount of energy into the rotor, causing a rapid and severe over-acceleration seen in the rotor speed plot (a).
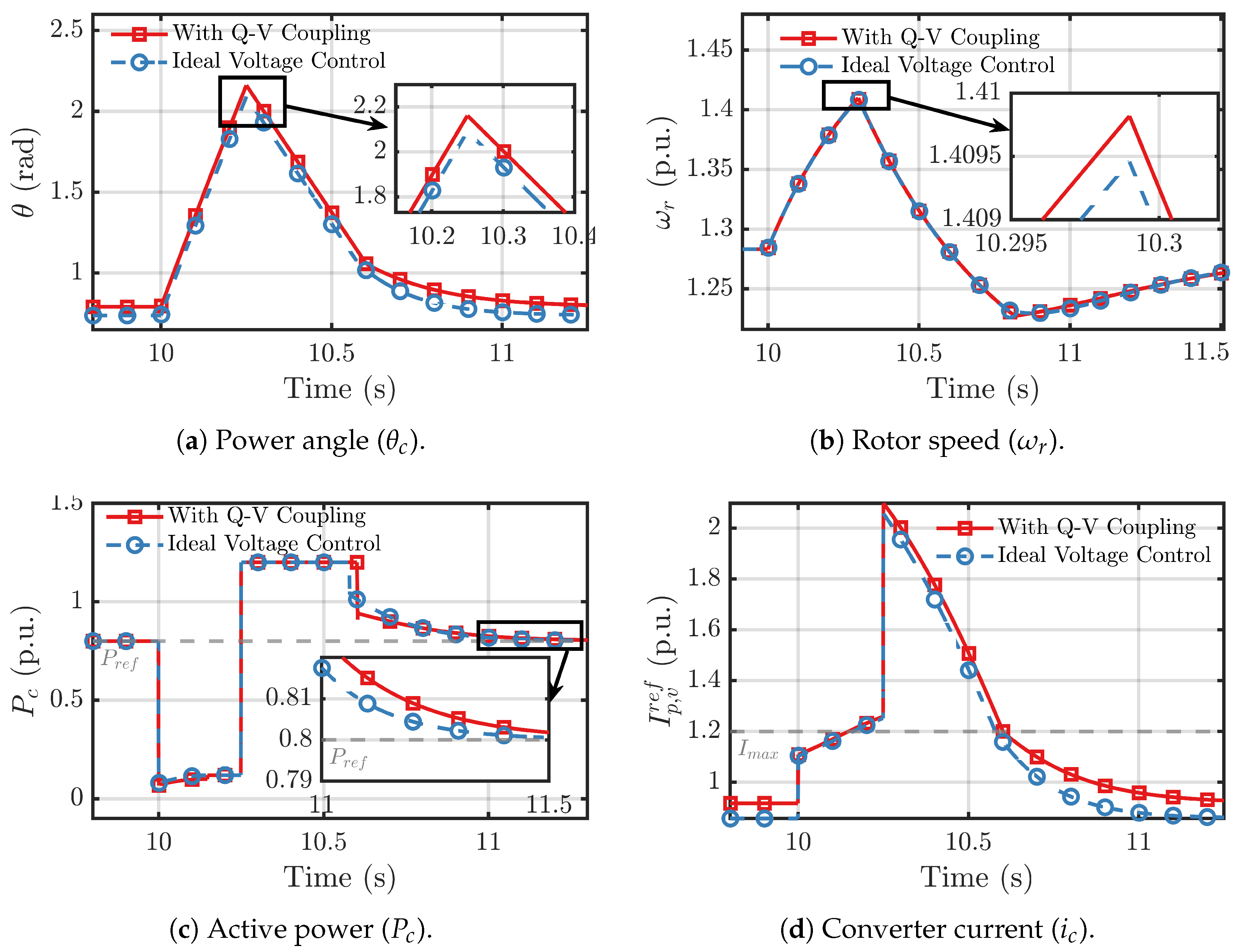
5.2. Performance of the Proposed Adaptive Control Strategy
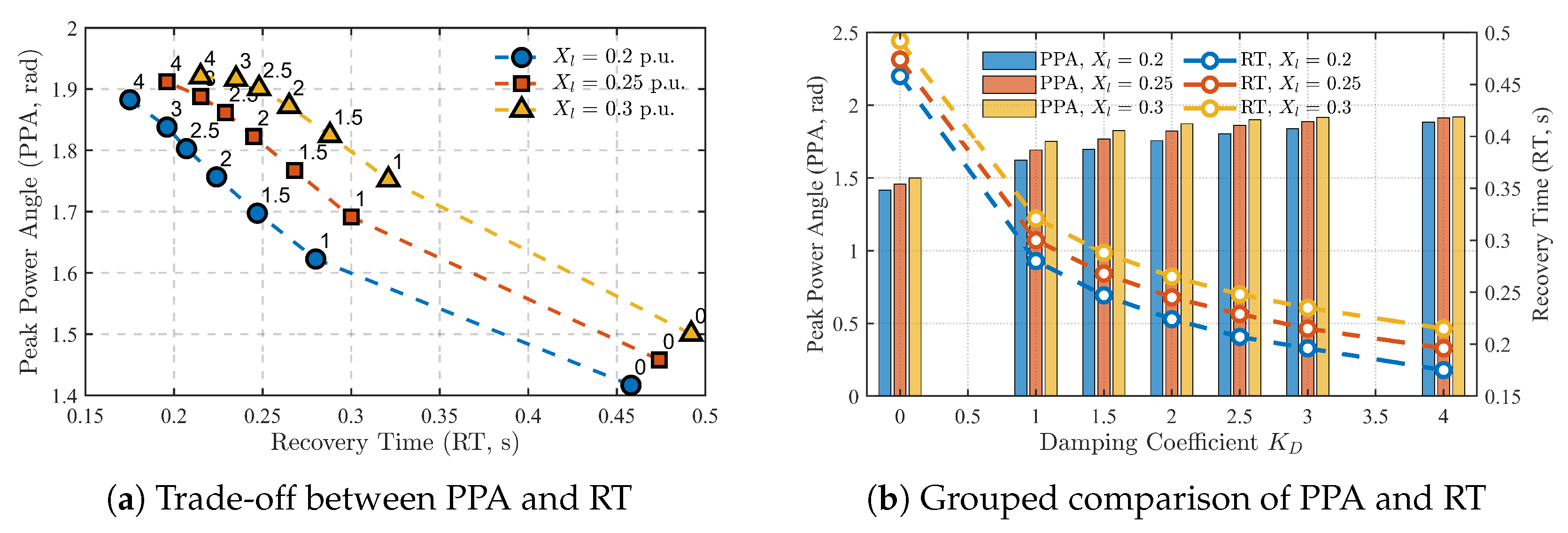
5.3. Discussion on Robustness and Parameter Tuning
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Description |
| GFL | Grid-Following |
| GFM | Grid-Forming |
| CVC | Constant Voltage Control |
| CLC | Current Limiting Control |
| PMSG | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator |
| SEP | Stable Equilibrium Point |
| UEP | Unstable Equilibrium Point |
| RSC | Rotor-Side Converter |
| GSC | Grid-Side Converter |
| MPPT | Maximum Power Point Tracking |
| PSL | Power Synchronization Loop |
| PCC | Point of Common Coupling |
References
- Gu, Y.; Green, T. Power System Stability with a High Penetration of Inverter-Based Resources. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 832–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Balasubramaniyan, S. Synchronization Stability and Control Strategies for PMSG-based Wind Energy Systems under Grid Fault Conditions. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 6148–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xin, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, K.; Hu, J. Transient Stability Analysis and Control Design of Droop-Controlled Voltage Source Converters Considering Current Limitation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qoria, T.; Wang, X.; Kadri, R. Grid-Forming Control VSC-based Including Current Limitation and Re-Synchronization Functions to Deal with Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 223, 109647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Harnefors, L.; Nee, H. Power-Synchronization Control of Grid-Connected Voltage-Source Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qoria, T.; Gruson, F.; Colas, F.; Kestelyn, X.; Guillaud, X. Current Limiting Algorithms and Transient Stability Analysis of Grid-Forming VSCs. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 189, 106726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Z.; Shen, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, Z. Transient Angle Stability of Virtual Synchronous Generators Using Lyapunov’s Direct Method. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 4648–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C. Transient Stability Analysis of Multiparallel Grid-Forming Converters Considering Active and Reactive Power Control Coupling and Current Limiting. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 13615–13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, Z.; Zha, X.; Sun, P.; Hu, Y.; Huang, M. An Iterative Equal Area Criterion for Transient Stability Analysis of Grid-Tied Converter Systems with Varying Damping. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, L. Weak Grid Characteristic Analysis and Operating Mode Selection for Voltage Support Enhancement of Wind Farms Connected to MMC-HVDC During Asymmetric Faults. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2025, 13, 2917–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Yao, J.; He, W.; Yang, D.; Gong, S.; Zhao, L. Transient Stability Analysis and Improved Control Strategy of PMSG-based Grid-forming Wind Energy Conversion System Under Symmetrical Grid Fault. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2025, 13, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Fang, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, T.; Goetz, S. Transient Angle and Voltage Stability of Grid-Forming Converters with Typical Reactive Power Control Schemes. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 13, 2917–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Guerrero, J. Impact of Reactive Power Control on Low-Frequency Oscillation of Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2025, 40, 3604–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Li, D.; Liang, Z.; Ye, N. Transient Synchronization Stability in Grid-Following Converters: Mechanistic Insights and Technological Prospects—A Review. Energies 2025, 18, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Mu, T.; Shao, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Du, Z. Segmental Equal Area Criterion for Grid Forming Converter with Current Saturation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 159, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Su, M.; Yuan, L.; Chen, S.; Dong, Z. Analysis and Enhancement of Transient Synchronization Stability for Grid-Connected VSG Considering Reactive Power Coupling and Fault Current Limitation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2025, 6, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J. Synchronous Instability Mechanism of P-f Droop-Controlled Voltage Source Converter Caused by Current Saturation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 5206–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qoria, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Colak, I. Variable Virtual Impedance-Based Overcurrent Protection for Grid-Forming Inverters: Small-Signal, Large-Signal Analysis and Improvement. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 3324–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihara, D.; Taoka, H.; Kikusato, H.; Hashimoto, J.; Otani, K.; Khaliqur, R.; Ustun, T. Theoretical Comparison of Current Limiting Algorithms in Grid-Forming Inverter in Terms of Transient Stability. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2025, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wang, X. Equivalent Circuit Model of Grid-Forming Converters with Circular Current Limiter for Transient Stability Analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 3141–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Song, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, P. Reactive Power Characteristics and FRT Strategy for Grid-Forming Converters with Virtual Impedance-Based Current Limiting. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025, 40, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandi-Nezhad, A.; Guo, Y.; Pal, B.; Yang, G. Modeling Fault Recovery and Transient Stability of Grid-Forming Converters Equipped with Current Reference Limitation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025, 40, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, R.; Yang, S.; Ye, H.; Du, Z. Transient Stability of Power Synchronization Loop Based Grid Forming Converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2843–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X. Design-Oriented Transient Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected Converters with Power Synchronization Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6473–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Bakhshizadeh, M.; Yang, G.; Kocewiak, Ł.; Pal, B.; Nadarajah, M. Nonlinear Stability Investigation of Type-4 Wind Turbines with Non-Autonomous Behavior Based on Transient Damping Characteristics. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 76059–76070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Du, W.; Mohiuddin, S.; Cheng, Y. Critical Clearing Time for Droop-Controlled Grid-Forming Inverters with Circular Current Limiting and Virtual Impedance Current Limiting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2025, 40, 1997–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fu, L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y. Transient Synchronization Stability of Grid-Forming Converter During Grid Fault Considering Transient Switched Operation Mode. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeckeland, N.; Yang, B.; Seo, G. Transient Stability-Enhancing Method for Grid-Forming Inverters Under Current Limiting. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 6714–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Liu, N.; Xu, H.; Mao, R.; Yang, Y. Transient Stability Enhancement Control for VSG Considering Fault Current Limitation and Reactive Power Support Constraints. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 40, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, M. Transient Synchronous Stability Analysis of PMSG Grid-Connected System Considering Transient Switching Control Under Severe Faults. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 7298–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounadja, E.; Yahdou, A.; Kacemi, W.M.; Belhadj Djilali, A.; Benbouhenni, H.; Iqbal, A. A New Third-Order Continuous Sliding Mode Speed and DC-Link Voltage Controllers for a PMSG-based Wind Turbine with Energy Storage System. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 6017–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadega, P.A.; Balogun, O.A. Modeling and Control of Grid-Connected Solar-Wind Hybrid Micro-Grid System with Multiple-Input Ćuk DC-DC Converter for Household & High Power Applications. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2022, 58, 191–224. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Hu, T.; Zheng, T.; Qian, M.; Li, C.; Cao, Z.; Yan, G. Enhanced Dynamic Support Strategies of Grid-Forming-PMSG Based on DC-voltagesynchronization: Frequency and Q Support Perspective. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 169, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Du, W.; Zhao, T.; Xie, H.; Wang, H.; Yi, S. Transient Synchronization Stability Analysis of a Grid-Connected Wind Farm with Multiple PMSGs. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 6934–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated Power () | 1.5 MVA | Active Power Ref | 0.8 p.u. |
| Rated Voltage () | 690 V | Reactive Power Ref | 0 p.u. |
| Grid Voltage () | 1 p.u. | PCC Voltage Ref | 1 p.u. |
| Grid Frequency | 50 Hz | DC-Link Voltage Ref | 1200 V |
| Line Resistance () | 6 × 10−5 p.u. | DC-Link Capacitance | 0.04 p.u. |
| Line Reactance () | 1.2 × 10−4 p.u. | Current Limit () | 1.2 p.u. |
| WT Inertia () | 2 s | PSL Gain () | 7.85 |
| Rated wind speed | 12 m/s | Q-V Droop Gain () | 0.2 |
| Strategy | PPA (rad) | RT (s) | IAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.442 | 0.511 | 0.6995 | |
| 1.600 | 0.536 | 0.2555 | |
| 1.772 | 0.174 | 0.0916 |
| PPA (rad) | PRS (p.u.) | RT (s) | IAE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 1.4249 | 1.3781 | 0.461 | 0.2505 |
| 1.00 | 1.6373 | 1.3781 | 0.229 | 0.1248 |
| 2.00 | 1.7717 | 1.3781 | 0.174 | 0.0916 |
| 3.00 | 1.8502 | 1.3781 | 0.200 | 0.0700 |
| 4.00 | 1.8909 | 1.3781 | 0.181 | 0.0572 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Mu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Du, Z. Transient Stability Enhancement of a PMSG-Based System by Saturated Current Angle Control. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010861
Li H, Mu T, Zhang Y, Wu D, Li Y, Du Z. Transient Stability Enhancement of a PMSG-Based System by Saturated Current Angle Control. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010861
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huan, Tongpeng Mu, Yufei Zhang, Duhai Wu, Yujun Li, and Zhengchun Du. 2025. "Transient Stability Enhancement of a PMSG-Based System by Saturated Current Angle Control" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010861
APA StyleLi, H., Mu, T., Zhang, Y., Wu, D., Li, Y., & Du, Z. (2025). Transient Stability Enhancement of a PMSG-Based System by Saturated Current Angle Control. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010861






