Personal Identification Using Embedded Raspberry Pi-Based Face Recognition Systems
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- -
- -
- Deep Learning Methods: With advancements in neural networks, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), facial recognition achieved unprecedented precision [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Models like DeepFace, FaceNet, and OpenFace excel in recognizing faces even in large datasets and challenging conditions, such as low light, varied expressions, and partial occlusions.
2. Materials and Methods
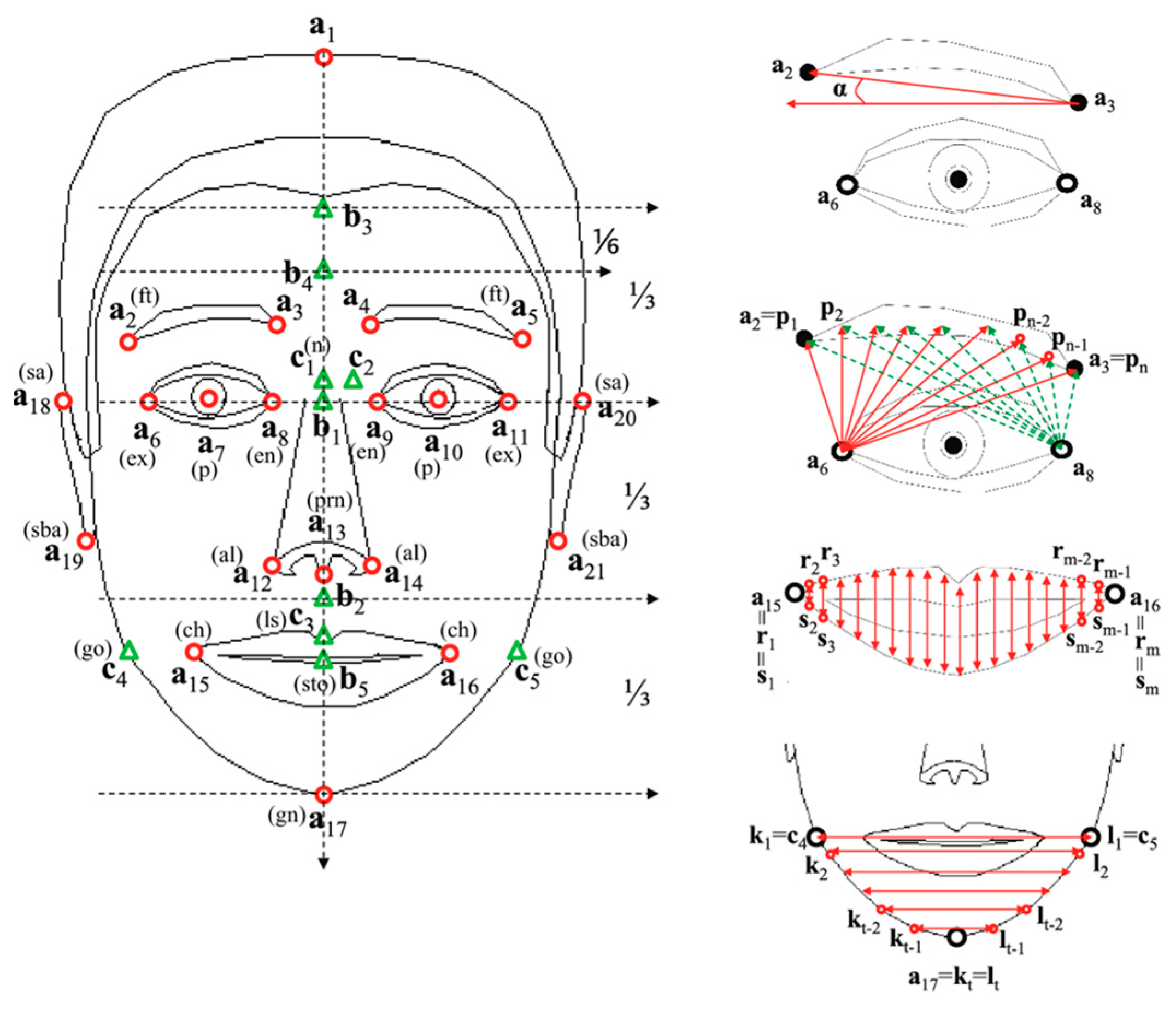
2.1. Characteristics Facial Features
- (a)
- Anthropometric:
- -
- Distance between the nose and eyes;
- -
- Distance between the centers of the eyes;
- -
- Distance between the mouth line and the eye line;
- -
- Distance between the farthest points of the eyes;
- -
- Distance from the center of the mouth to the furthest point of the eye.
- (b)
- Geometric:
- -
- Lip shape;
- -
- Nose shape;
- -
- Chin shape;
- -
- Forehead shape;
- -
- Shape of the ears;
- -
- Face oval.
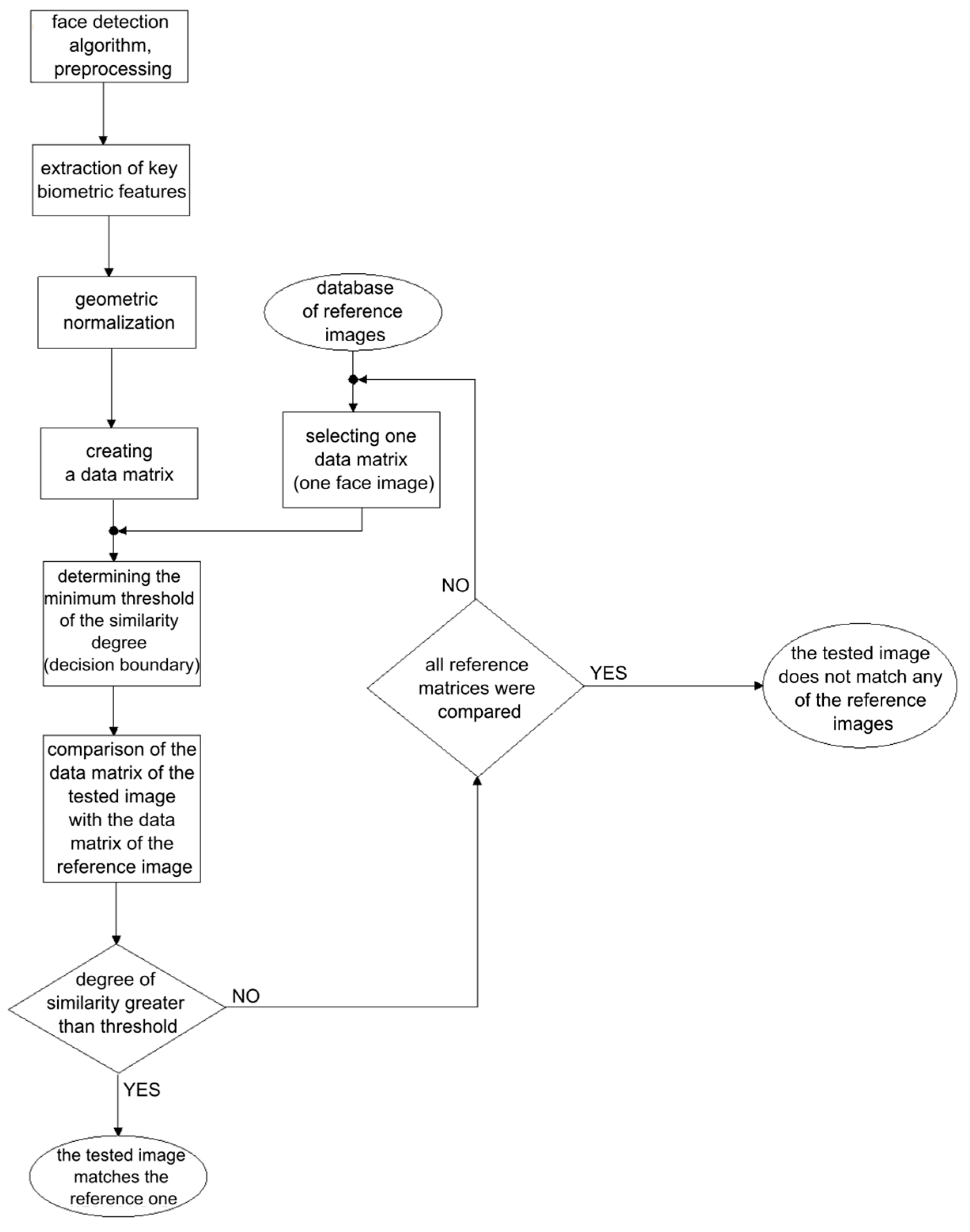
2.2. Biomimetic Facial Recognition System
2.3. Face Detection
- -
- Kawulok–Szymanek Algorithm: This method employs the Hough transform to detect image ellipses. The results are then verified using a support vector machine [58].
- -
- Deformable Part Model (DPM) Algorithm: this utilizes the Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) for face detection [59].
- -
- Viola–Jones Algorithm: this approach involves feature selection and AdaBoost classification [60].
- -
- Zhu–Ramanan Algorithm: this creates local models characterizing facial structure, leveraging biometric features regardless of head angle [4].
- -
- Maximum Margin Object Detection Algorithm (MMOD): using a support vector machine, MMOD employs face classification based on the HOG descriptor [61].
2.4. Locating Facial Landmarks
- -
- An algorithm using a set of regression trees;
- -
- CFSS algorithm—uses the assessment of the face oval, and then the final facial contour is adjusted using the regression method;
- -
- Zhu–Ramanan algorithm—in addition to detecting faces, it also returns the coordinates of matched models.
2.5. Geometric Normalization and Classification of Facial Landmarks
2.6. Face Classification
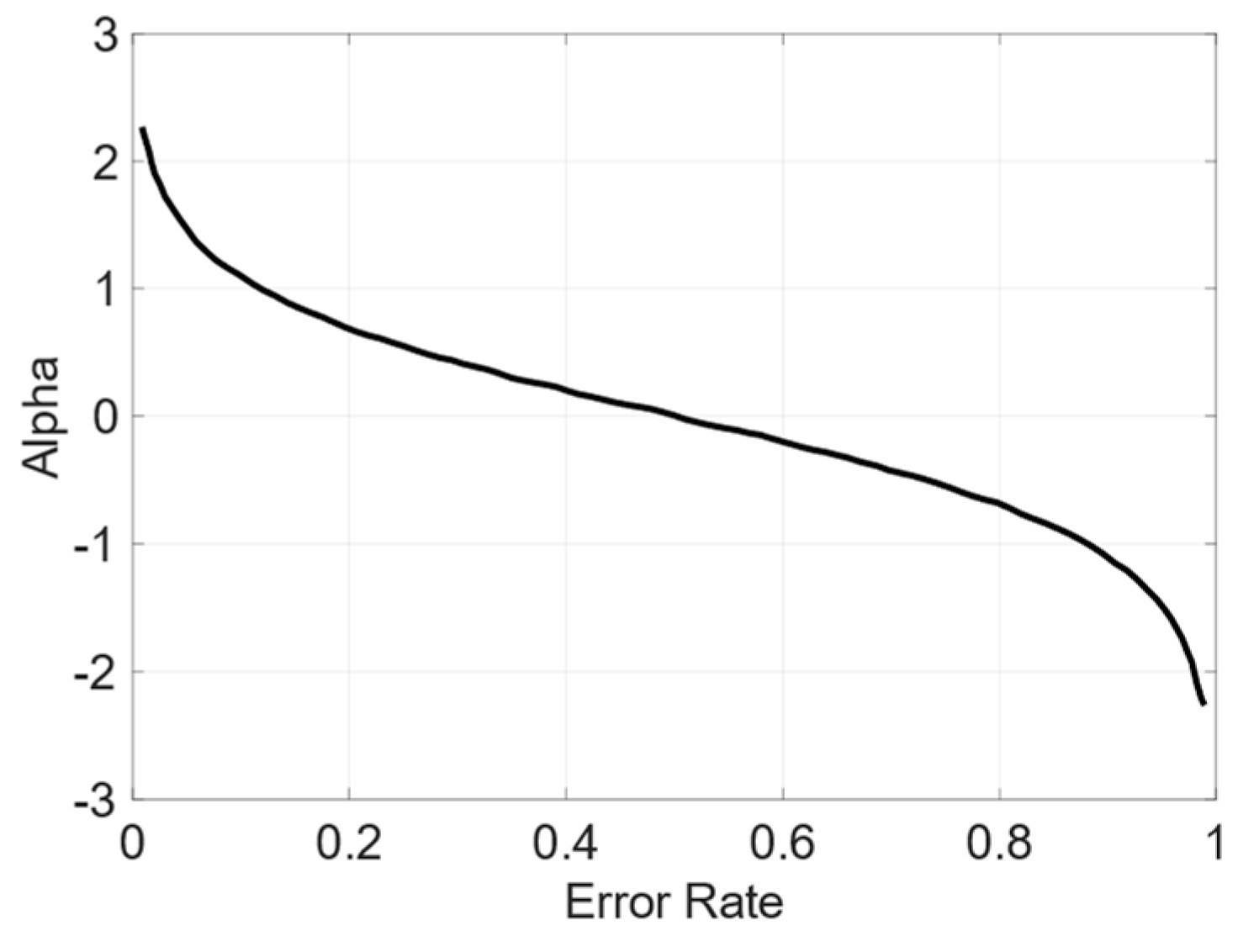
2.6.1. AdaBoost Machine Learning
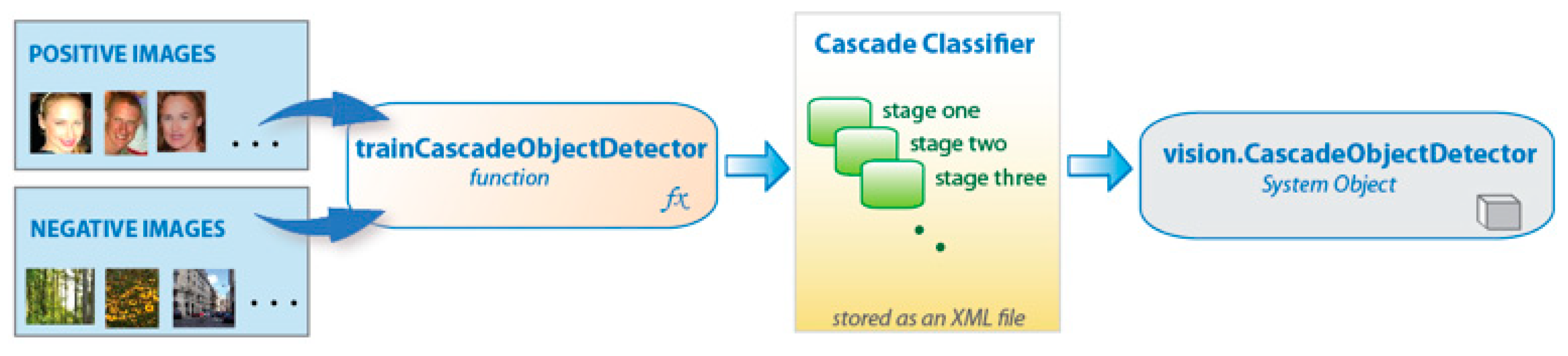
2.6.2. Cascading Haar Classifier
- -
- The selection of Haar-like features;
- -
- The creation of integral images;
- -
- Training with the AdaBoost algorithm;
- -
- The formation of cascade classifiers.
- Edge Features: These features detect edges by comparing the sum of pixel intensities in two adjacent rectangular regions. For example, a vertical edge feature might compare the sum of pixels on the left side of a rectangle with the sum of pixels on the right side.
- Line Features: These features detect lines by comparing the sum of pixel intensities in three adjacent rectangular regions. For example, a horizontal line feature might compare the sum of pixels in the top, middle, and bottom regions of a rectangle.
- Four-Rectangle Features: These features detect diagonal patterns by comparing the sum of pixel intensities in four rectangular regions arranged in a grid.
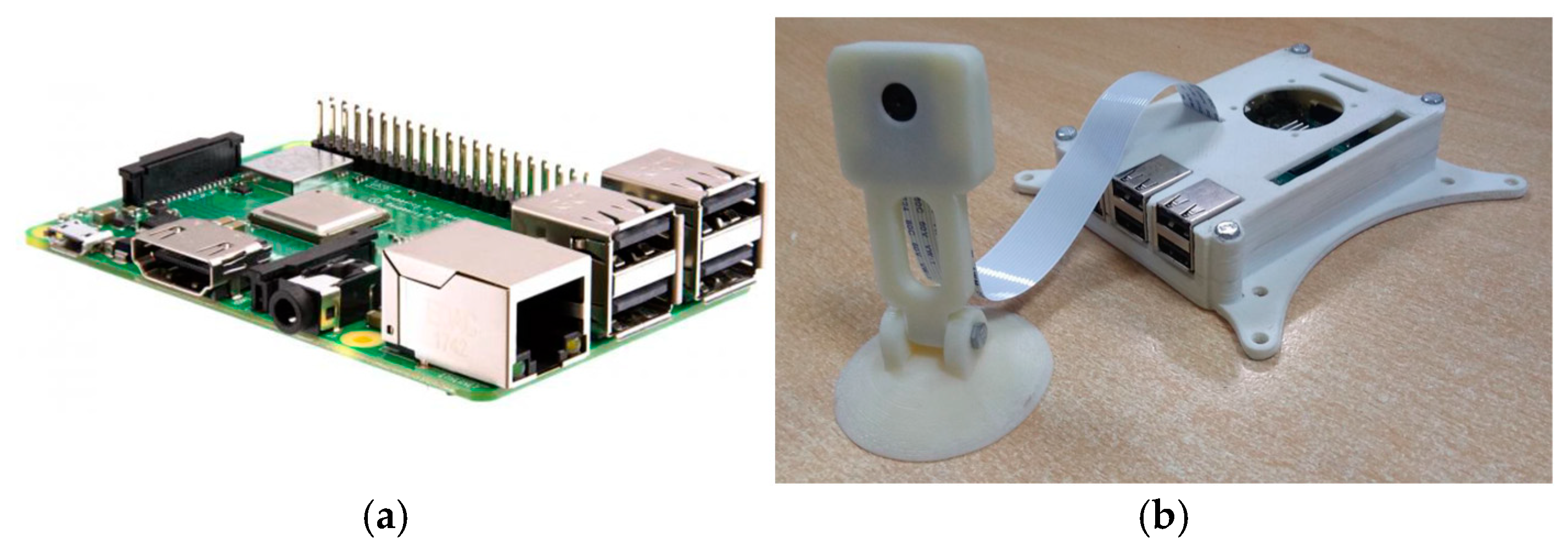
2.7. Hardware Setup
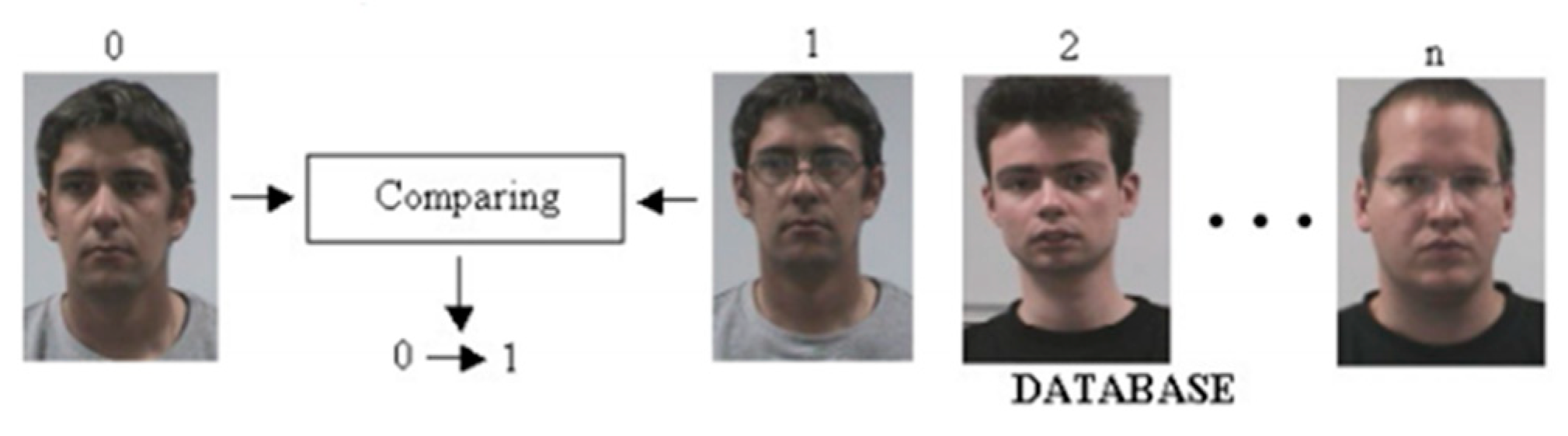
2.8. Face Recognition Application
- -
- Collecting data and sample images;
- -
- Creating the database;
- -
- Verifying faces;
- -
- The graphical user interface of the application.
- def proba1():
- def proba_0():
3. Verification System
3.1. Selecting the Similarity Threshold
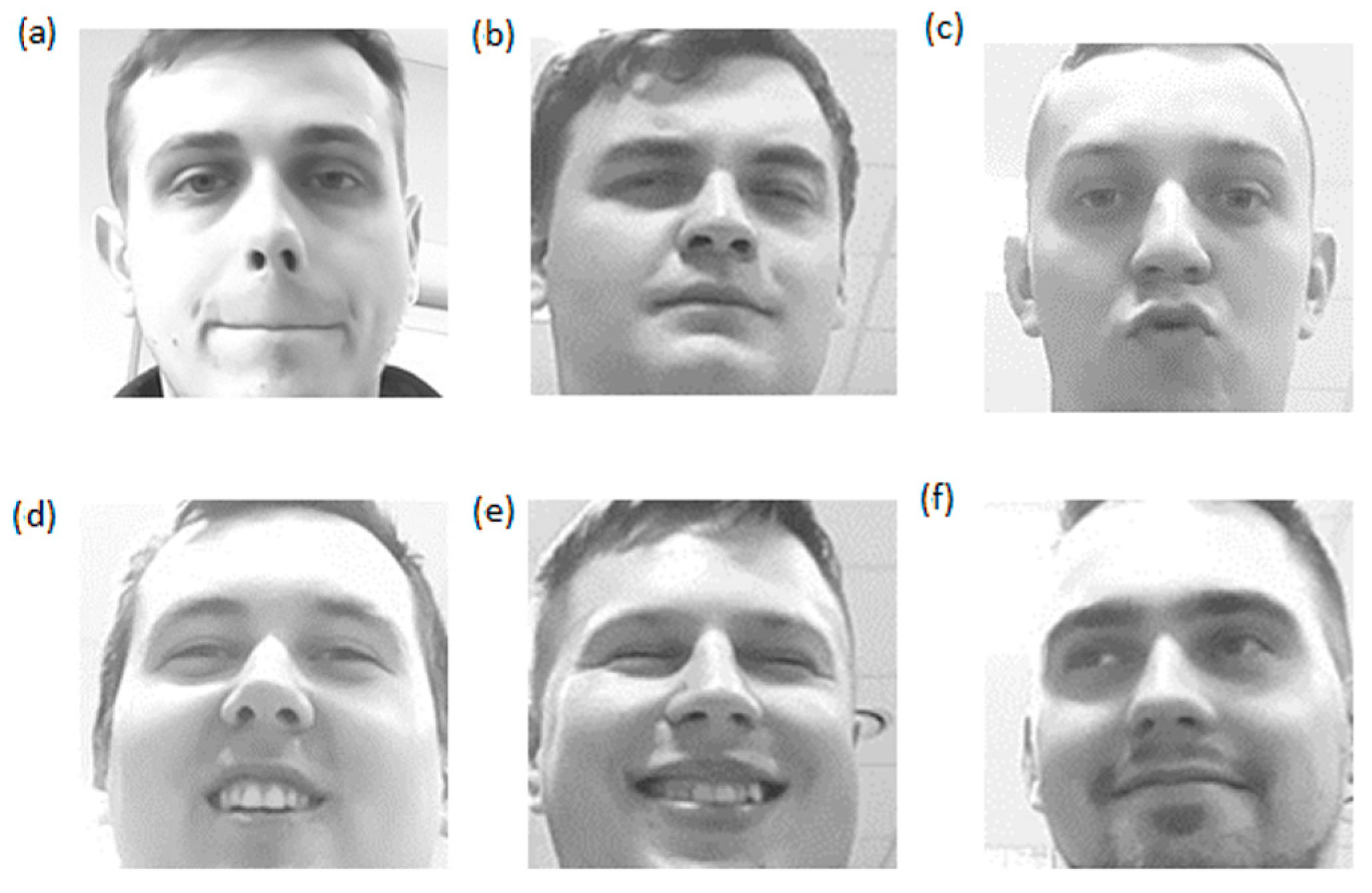
3.2. Efectiveness of Recognition Depending on Facial Expressions
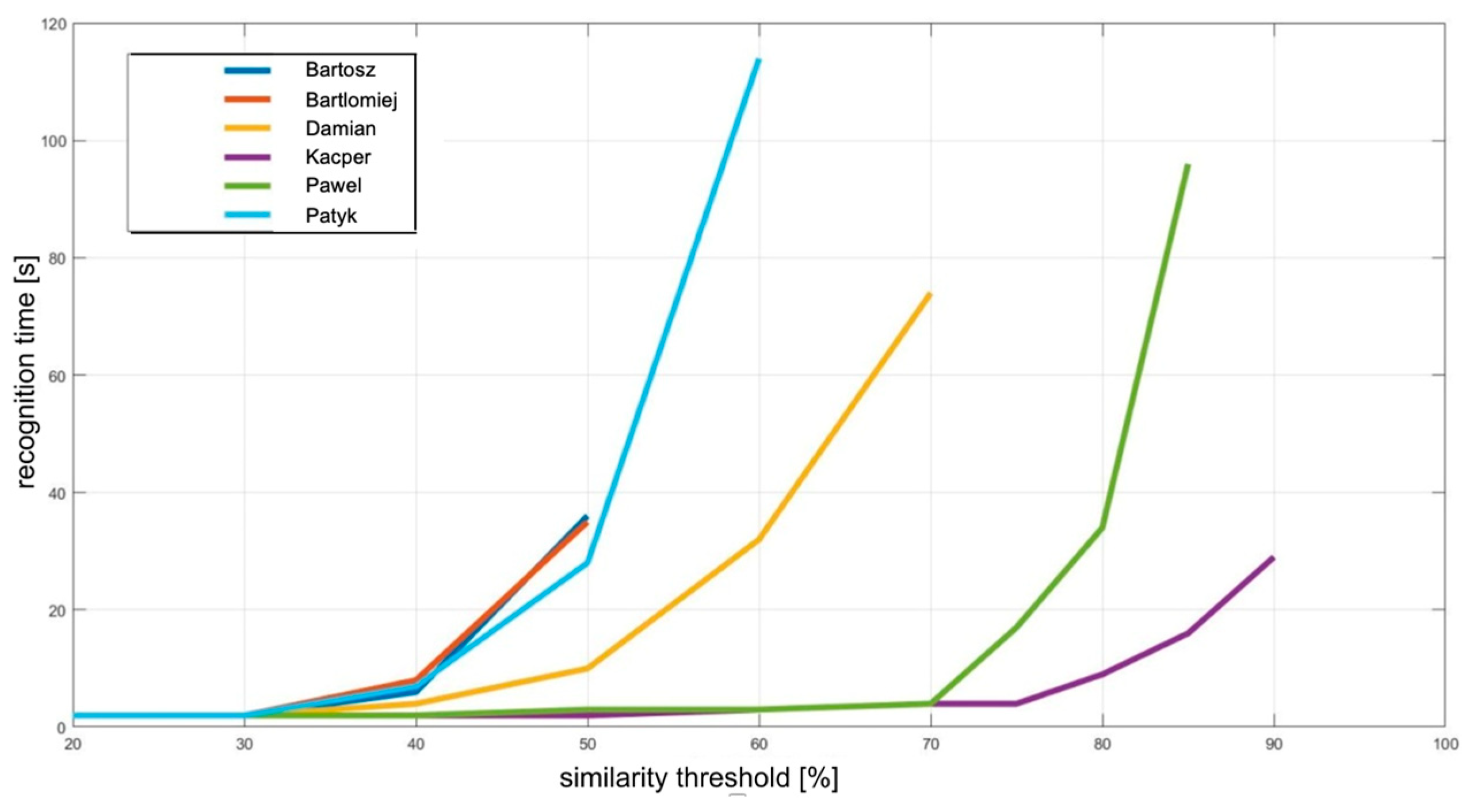
3.3. Performance and Effectiveness Test of the Face Recognition System
4. Conclusions
- -
- Database Size and Biometric Variations: To assess scalability and reliability, the system needs to be tested with larger databases, exceeding a thousand users, including individuals with significant biometric similarities.
- -
- Hardware Impact: The current setup uses a standard Raspberry Pi-compatible camera module. Initial tests suggest that higher-resolution cameras could improve accuracy and facial feature detection, particularly when the reference images are of higher quality than the test images. Exploring the impact of hardware upgrades on system performance, especially under challenging conditions like poor lighting or occlusions, would be a valuable next step.
- -
- Algorithm and Library Performance: The system employs the Haar cascade classifier for face detection and data matrix generation, achieving high accuracy with frontal faces. However, its performance decreases with extreme facial angles. Leveraging additional tools from the OpenCV library, such as deep learning-based models, could mitigate these limitations and broaden the system’s capabilities.
- -
- Security Enhancements: While the system works well for access control in environments dealing with sensitive data, it is vulnerable to spoofing via printed photographs. Adding features like thermal imaging to differentiate living faces from static images or incorporating additional biometric verifications (e.g., fingerprint or retina scans) would enhance security.
- -
- Retail and Surveillance: tracking customer movements or behavior in stores.
- -
- Data Collection: gathering pedestrian statistics or analyzing consumer habits.
- -
- Media Analysis: measuring screen time for actors in media productions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, W.; Chellappa, R.; Phillips, P.J.; Rosenfeld, A. Face Recognition: A Literature Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2003, 35, 399–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethan, K.; Sachin Kumar, A. A Literature Survey on Online Voting System Using Face Recognition. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Commun. Technol. 2024, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Pentland, A. Eigenfaces for Recognition. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1991, 3, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahonen, T.; Hadid, A.; Pietikäinen, M. Face Recognition with Local Binary Patterns. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2004: Computer Vision—ECCV 2004, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; Pajdla, T., Matas, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Ross, A.; Prabhakar, S. An Introduction to Biometric Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2004, 14, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introna, L.D.; Nissenbaum, H. Facial Recognition Technology: A Survey of Policy and Implementation Issues; Center for Catastrophe Preparedness and Response, New York University: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 74, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kostka, G.; Steinacker, L.; Meckel, M. Between Security and Convenience: Facial Recognition Technology in the Eyes of Citizens in China, Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Public Underst. Sci. 2021, 30, 644–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.J. Surveillance Society: Monitoring Everyday Life, by Lyon, D., Buckingham and Philadelphia: Open University Press, 2001. xii+ 189 pp. $27.95 (paper). ISBN 0-33520546-1. The Inf. Soc. 2003, 19, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Bolle, R.; Pankanti, S. Biometrics: Personal Identification in Networked Society; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pushparani, M.; Indumathi, T. Human Authentication by Matching 3D Skull with Face Image Using SCCA. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2015, 10, 34247–34254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J. Biometrics on Mobile Phone. In Recent Application in Biometrics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manonmani, S.P.; Abirami, G.; Sri, V.N. Spoof Prevention for E-Banking Using Live Face Recognition. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2023, 5, 4600–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, L.; Bidgoli, A.M.; Javadi, H.H.S. Identifying People’s Faces in Smart Banking Systems Using Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, K.C.; Ramya, S.; Sandhiya, R. Face Recognition-Based Banking System Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 19724–19730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, R.; Poggio, T. Face Recognition: Features Versus Templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1993, 15, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhou, L.; el Ayachi, R.; Baslam, M.; Oukessou, M. Face Recognition in a Mixed Document Based on the Geometric Method. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 116, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, R.; Wibowo, M.O.B.; Satria, B.Y.; Winursito, A. Implementation of Face Recognition Using Geometric Features Extraction. J. Ilmiah Kursor 2022, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Huh, J.H. Face Recognition at a Distance for a Stand-Alone Access Control System. Sensors 2020, 20, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajja, T.K.; Kalluri, H.K. Face Recognition Using Local Binary Pattern and Gabor-Kernel Fisher Analysis. Int. J. Adv. Intell. Paradigms 2023, 26, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allagwail, S.; Gedik, O.S.; Rahebi, J. Face Recognition with Symmetrical Face Training Samples Based on Local Binary Patterns and the Gabor Filter. Symmetry 2019, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.B.; Tiwari, N. Local Binary Patterns Histograms (LBPH) Based Face Recognition. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.N.; Nguyen, M.H.; Pham, C. Masked Face Recognition with Convolutional Neural Networks and Local Binary Patterns. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yin, B.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Y. 3D Face Recognition Using Local Binary Patterns. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taigman, Y.; Yang, M.; Ranzato, M.; Wolf, L. DeepFace: Closing the Gap to Human-Level Performance in Face Verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, M. Research on Face Emotion Recognition Algorithm Based on Deep Learning Neural Network. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjdoubi, A.; Meddeber, M.; Yahyaoui, K. Smart City Surveillance: Edge Technology Face Recognition Robot Deep Learning Based. Int. J. Eng. Trans. A Basics 2024, 37, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, N. A Survey on Deep Learning Based Face Recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 189, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, N.A.B.M.; Rahman, N.H.B.A.; Ibrahim, Z.; Mangshor, N.N.A. Celebrity Face Recognition Using Deep Learning. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2018, 12, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzu’bi, A.; Albalas, F.; Al-Hadhrami, T.; Younis, L.B.; Bashayreh, A. Masked Face Recognition Using Deep Learning: A Review. Electronics 2021, 10, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.M.F.; Cardoso, P.V. O’Neil, Cathy. Weapons of Math Destruction: How Big Data Increases Inequality and Threatens Democracy. Crown: New York, 2016. Mural Int. 2017, 7, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hua, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, Y. Face, Facial Recognition Technology and Personal Privacy. Acta Bioethica 2023, 29, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz Ketley, I. Case Study: Code of Ethics for Facial Recognition Technology. In Proceedings of the Wellington Faculty of Engineering Ethics and Sustainability Symposium; Te Herenga Waka-Victoria University of Wellington: Wellington, New Zealand, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J. Facial Recognition Technology and Ethical Issues. In Proceedings of the Wellington Faculty of Engineering Ethics and Sustainability Symposium; Te Herenga Waka-Victoria University of Wellington: Wellington, New Zealand, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North-Samardzic, A. Biometric Technology and Ethics: Beyond Security Applications. J. Bus. Ethics 2020, 167, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buolamwini, J.; Gebru, T. Gender Shades: Intersectional Accuracy Disparities in Commercial Gender Classification. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency, New York, NY, USA, 23–24 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, I.D.; Buolamwini, J. Actionable auditing: Investigating the impact of publicly naming biased performance results of commercial AI products. In Proceedings of the AIES 2019—Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–28 January 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Perona, P.; Balakrishnan, G. Benchmarking Algorithmic Bias in Face Recognition: An Experimental Approach Using Synthetic Faces and Human Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.N.K. Fly in the Face of Bias: Algorithmic Bias in Law Enforcement’s Facial Recognition Technology and the Need for an Adaptive Legal Framework. Minn. J. Law Inequal. 2021, 39, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, I.; Morales, A.; Fierrez, J.; Obradovich, N. Sensitive loss: Improving accuracy and fairness of face representations with discrimination-aware deep learning. Artif. Intell. 2022, 305, 103682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klontz, J.C.; Jain, A.K. A case study of automated face recognition: The Boston marathon bombings suspects. Computer 2013, 46, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, O.A.; Ahmad, S.M.S.; Samsudin, K.; Hanafi, M.; Shafie, S.M.B.; Zamri, N.Z. Facial recognition for partially occluded faces. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2023, 30, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.R.; de Almeida, G.M.; Cuadros, M.A.d.S.L.; Campos, H.L.M.; Nunes, R.B.; Simão, J.; Muniz, P.R. Recognition of Human Face Regions under Adverse Conditions—Face Masks and Glasses—In Thermographic Sanitary Barriers through Learning Transfer from an Object Detector. Machines 2022, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.D.; Chen, L.; Chen, W. Thermal face recognition under different conditions. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, G.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. RGB-D face recognition with texture and attribute features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Ross, A.; Nandakumar, K. Introduction to Biometrics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-0-387-77325-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W. Facial action coding system: A technique for the measurement of facial movement. In Differences Among Unpleasant Feelings, Motivation and Emotion; Palo Alto: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Alisawi, M.; Yalçin, N. Real-Time Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Methods: Systematic Review. Intell. Methods Eng. Sci. 2023, 2, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, T.S.; Kandavalli, T.C.; Sugash, T.M.; Subramani, R. Smart Facial Emotion Recognition with Gender and Age Factor Estimation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 218, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores, A.R.; Barbosa, F.; Queirós, C.; Carvalho, I.P.; Griffiths, M.D. Recognizing emotions through facial expressions: A large-scale experimental study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhana Ranjini, M.M.; Jeyaraj, M.P.; Kumar, M.S.; Prasath, T.A.; Prabhakar, G. Haar Cascade Classifier-based Real-Time Face Recognition and Face Detection. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 6–8 July 2023; pp. 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Zhu, X.; Cai, H. Face Detection Algorithm Based on Improved AdaBoost and New Haar Features. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), Suzhou, China, 19–21 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoche, M.; Hörmann, S.; Rigoll, G. Cross-quality LFW: A database for analyzing cross-resolution image face recognition in unconstrained environments. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, FG 2021, Jodhpur, India, 15–18 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Richoz, A.R.; Stacchi, L.; Schaller, P.; Lao, J.; Papinutto, M.; Ticcinelli, V.; Caldara, R. Recognizing facial expressions of emotion amid noise: A dynamic advantage. J. Vis. 2024, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F.; Tian, Y. Comprehensive database for facial expression analysis. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, FG 2000, Grenoble, France, 28–30 March 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, P.; Vera-Rodriguez, R.; Fierrez, J.; Ortega-Garcia, J. Facial Soft Biometric Features for Forensic Face Recognition. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
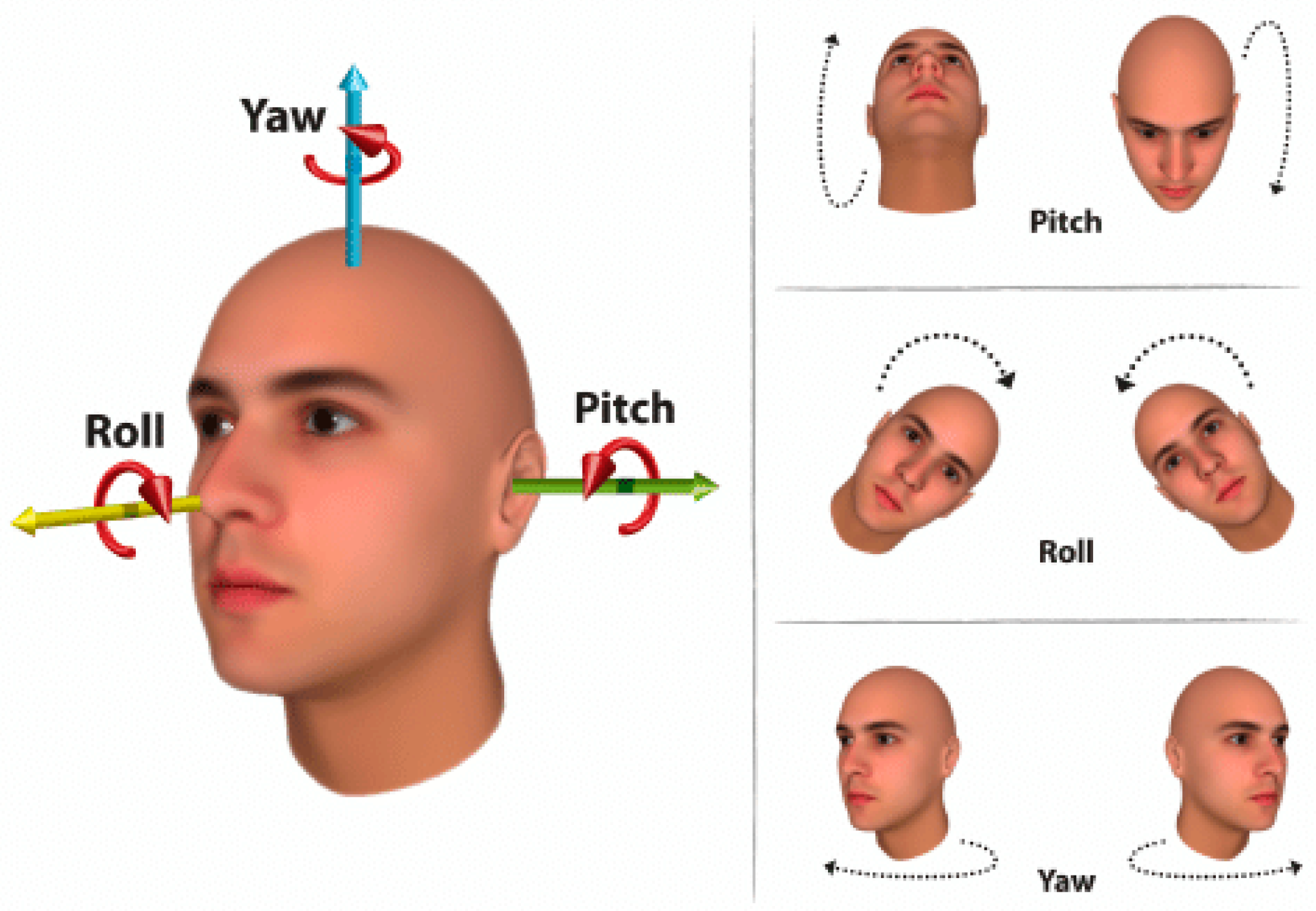
- Arcoverde, E.; Duarte, R.; Barreto, R.; Magalhaes, J.; Bastos, C.; Ing Ren, T.; Cavalcanti, G. Enhanced Real-time Head Pose Estimation System for Mobile Devices. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2014, 21, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalepa, J.; Szymanek, J.; Kawulok, M. Real-time People Counting from Depth Images. In Proceedings of the Beyond Databases, Architectures and Structures: 11th International Conference, BDAS 2015, Ustroń, Poland, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Iandola, F.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Deformable Part Models Are Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Shammi, U.A.; Kobashi, S. A Study on Face Detection Using Viola-Jones Algorithm in Various Backgrounds, Angles and Distances. Int. J. Biomed. Soft Comput. Hum. Sci. Off. J. Biomed. Fuzzy Syst. Assoc. 2018, 23, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Taskar, B.; Guestrin, C.; Koller, D. Max-margin Markov Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2003, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Su, G.; Du, C. Feature Points Extraction from Faces. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 26, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jaadi, Z. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Explained. Built In. 2022. Available online: https://builtin.com/data-science/step-step-explanation-principal-component-analysis (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Fei, H.; Fan, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, T.; Chen, R.; Bai, T. Cotton Classification Method at the County Scale Based on Multi-Features and Random Forest Feature Selection Algorithm and Classifier. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Chen, C.W. Human Facial Feature Extraction for Face Interpretation and Recognition. Pattern Recognit. 1992, 25, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.L. AdaBoost Tutorial. 2013. Available online: http://mccormickml.com/2013/12/13/adaboost-tutorial/ (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Murtaza, M.; Sharif, M.; Raza, M.; Shah, J.H. Analysis of Face Recognition under Varying Facial Expression: A Survey. Int. Arab. J. Inf. Technol. 2013, 10, 378–388. [Google Scholar]
- OpenCV. Cascade Classifier Tutorial. Available online: https://docs.opencv.org/3.4/db/d28/tutorial_cascade_classifier.html (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Ashtagi, R.; Malse, N.; Mohite, S.; Nipanikar, S.; Lanjewar, R. Face Recognition-Based Attendance System. In Advances in Information Communication Technology and Computing; Goar, V., Kuri, M., Kumar, R., Senjyu, T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; Volume 1074, pp. 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.J.; Sirotin, Y.B.; Vemury, A.R. The Effect of Broad and Specific Demographic Homogeneity on the Imposter Distributions and False Match Rates in Face Recognition Algorithm Performance. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS 2019), Tampa, FL, USA, 23–26 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowinski, S.; Pecolt, S.; Błażejewski, A.; Sobieraj, M. Design of a Low-Cost Measurement Module for the Acquisition of Analogue Voltage Signals. Electronics 2023, 12, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Hoang, T.; Kim, H.; Teoh, A.B.J.; Choi, D. AVET: A Novel Transform Function to Improve Cancellable Biometrics Security. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
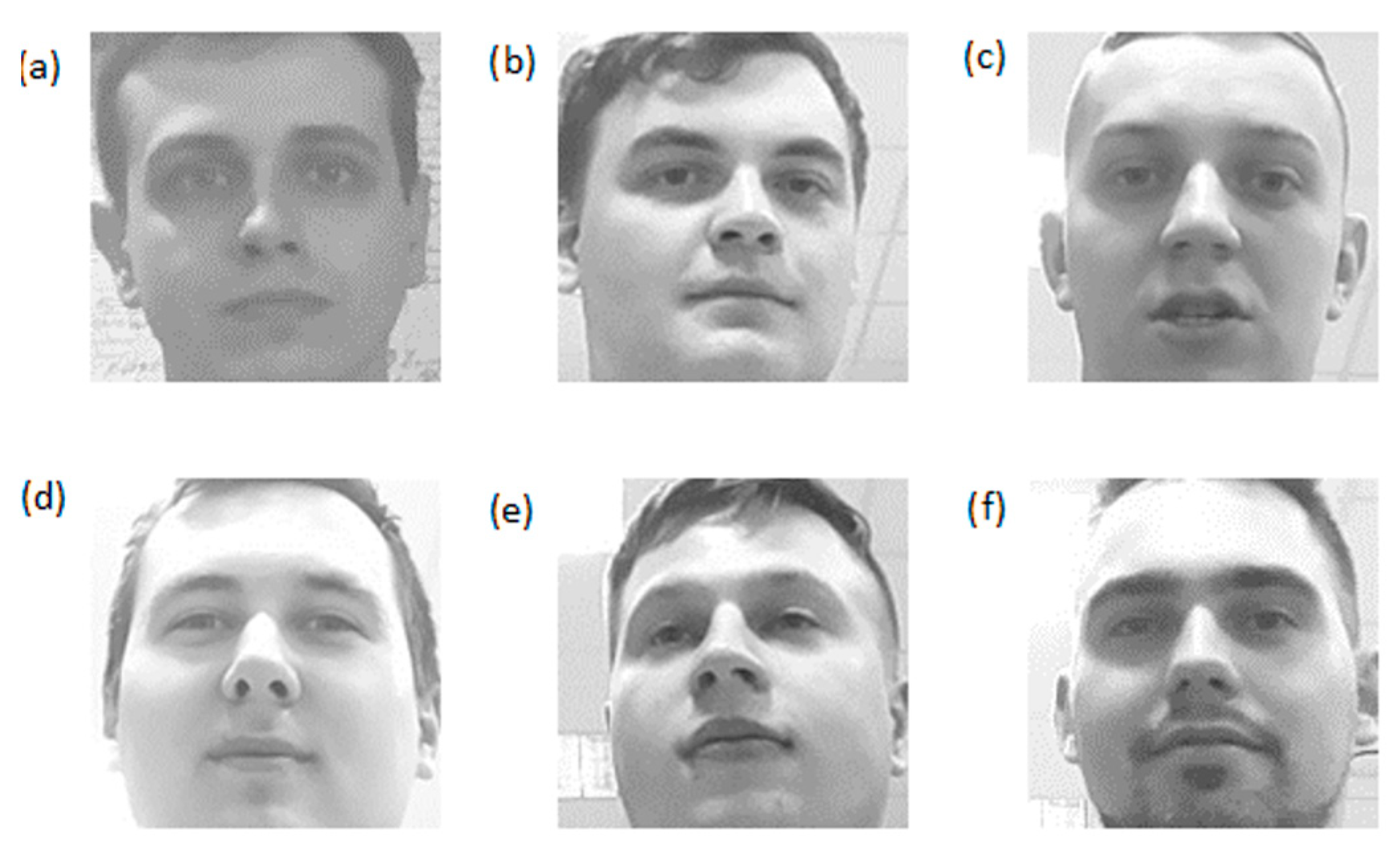





| Set Similarity Threshold [%] | User No. 1 (Kacper) | User No. 2 (Bartosz) | User No. 3 (Damian) | User No. 4 (Pawel) | User No. 5 (Patryk) | User No. 6 (Bartlomiej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper |
| 10 | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper |
| 20 | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper |
| 30 | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper |
| 40 | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper |
| 50 | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper |
| 60 | Kacper | unknown | Kacper | Kacper | Kacper | unknown |
| 70 | Kacper | unknown | Kacper | Kacper | unknown | unknown |
| 75 | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Kacper | unknown | unknown |
| 80 | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Kacper | unknown | unknown |
| 85 | Kacper | unknown | nieznana | Kacper | unknown | unknown |
| 90 | Kacper | unknown | nieznana | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| 95 | unknown | unknown | nieznana | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| 100 | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Set Similarity Threshold [%] | User No. 1 (Kacper) [s] | User No. 2 (Bartosz) [s] | User No. 3 (Damian) [s] | User No. 4 (Pawel) [s] | User No. 5 (Patryk) [s] | User No. 6 (Bartlomiej) [s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 |
| 10 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 |
| 20 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 |
| 30 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 | ~2 |
| 40 | ~2 | ~6 | ~4 | ~2 | ~7 | ~8 |
| 50 | ~2 | ~36 | ~10 | ~3 | ~28 | ~35 |
| 60 | ~3 | unknown | ~32 | ~3 | ~114 | unknown |
| 70 | ~4 | unknown | ~74 | ~4 | unknown | unknown |
| 75 | ~4 | unknown | unknown | ~17 | unknown | unknown |
| 80 | ~9 | unknown | unknown | ~34 | unknown | unknown |
| 85 | ~16 | unknown | unknown | ~96 | unknown | unknown |
| 90 | ~29 | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Set Similarity Threshold [%] | User No. 1 (Kacper) | User No. 2 (Bartosz) | User No. 3 (Damian) | User No. 4 (Pawel) | User No. 5 (Patryk) | User No. 6 (Bartlomiej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 10 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 20 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Pawel | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 30 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 40 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 50 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 60 | Kacper | Bartlomiej | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 70 | Kacper | unknown | Kacper | Pawel | Pawel | Bartlomiej |
| 75 | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Pawel | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| 80 | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Pawel | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| 85 | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Pawel | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| 90 | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Pawel | unknown | unknown |
| 95 | unknown | unknown | unknown | Pawel | unknown | unknown |
| 100 | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Conditions | User No. 1 (Kacper) | User No. 2 (Bartosz) | User No. 3 (Damian) | User No. 4 (Pawel) | User No. 5 (Patryk) | User No. 6 (Bartlomiej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In daylight | ||||||
| A | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| B | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| C | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| D | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | unknown | Bartosz |
| E | Kacper | unknown | Damian | Kacper | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| In artificial light | ||||||
| A | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| B | Pawel | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| C | Kacper | Bartosz | unknown | Pawel | Pawel | unknown |
| D | unknown | unknown | Damian | Kacper | unknown | unknown |
| E | Kacper | unknown | unknown | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| In a darkened room | ||||||
| A | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| B | Pawel | Bartlomiej | unknown | unknown | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| C | unknown | unknown | Kacper | unknown | Damian | unknown |
| D | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| E | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Attempt Number | User No. 1 (Kacper) | User No. 2 (Bartosz) | User No. 3 (Damian) | User No. 4 (Pawel) | User No. 5 (Patryk) | User No. 6 (Bartlomiej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| 2 | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| 3 | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| Time in which the system recognized the user [s] | ||||||
| 1 | ~12 | ~12 | ~16 | ~9 | ~15 | ~12 |
| 2 | ~14 | ~15 | ~13 | ~13 | ~13 | ~14 |
| 3 | ~12 | ~11 | ~15 | ~12 | ~10 | ~14 |
| Type of Facial Expression | User No. 1 (Kacper) | User No. 2 (Bartosz) | User No. 3 (Damian) | User No. 4 (Pawel) | User No. 5 (Patryk) | User No. 6 (Bartlomiej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| smile | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| sadness | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| surprise | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| duck face | Kacper | unknown | Damian | Pawel | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| clenched lips | Kacper | Bartosz | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| anger | Kacper | Bartosz | Kacper | Pawel | unknown | Bartlomiej |
| puffed cheeks | Pawel | Patryk | Damian | Pawel | Patryk | Bartlomiej |
| User | Recognition Result | Recognition Time [s] |
|---|---|---|
| User No. 1 (Kacper—25 years old) | Kacper | ~11 |
| User No. 2 (Maciej—29 years old) | Maciej | ~10 |
| User No. 3 (Wojciech—43 years old) | Wojciech | ~9 |
| User No. 4 (Janusz—49 years old) | Janusz | ~12 |
| User No. 5 (Marcin—35 years old) | Marcin | ~11 |
| User No. 6 (Piotr—39 years old) | Piotr | ~9 |
| User No. 7 (Dawid—27 years old) | Dawid | ~12 |
| User No. 8 (Filip—16 years old) | Filip | ~8 |
| User No. 9 (Olimpia—19 years old) | Olimpia | ~11 |
| User No. 10 (Dorota—51 years old) | Dorota | ~10 |
| User No. 11 (Beata—46 years old) | Beata | ~10 |
| User No. 12 (Karolina—22 years old) | Karolina | ~14 |
| User | Recognition Result | Recognition Time [s] |
|---|---|---|
| User No. 1 (Kacper—25 years old) | Kacper | ~15 |
| User No. 2 (Maciej—29 years old) | unknown | - |
| User No. 3 (Wojciech—43 years old) | Wojciech | ~11 |
| User No. 4 (Janusz—49 years old) | Janusz | ~24 |
| User No. 5 (Marcin—35 years old) | Marcin | ~11 |
| User No. 6 (Piotr—39 years old) | unknown | - |
| User No. 7 (Dawid—27 years old) | Dawid | ~20 |
| User No. 8 (Filip—16 years old) | Filip | ~16 |
| User No. 9 (Olimpia—19 years old) | Olimpia | ~9 |
| User No. 10 (Dorota—51 years old) | Dorota | ~19 |
| User No. 11 (Beata—46 years old) | unknown | - |
| User No. 12 (Karolina—22 years old) | Karolina | ~10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pecolt, S.; Błażejewski, A.; Królikowski, T.; Maciejewski, I.; Gierula, K.; Glowinski, S. Personal Identification Using Embedded Raspberry Pi-Based Face Recognition Systems. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020887
Pecolt S, Błażejewski A, Królikowski T, Maciejewski I, Gierula K, Glowinski S. Personal Identification Using Embedded Raspberry Pi-Based Face Recognition Systems. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(2):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020887
Chicago/Turabian StylePecolt, Sebastian, Andrzej Błażejewski, Tomasz Królikowski, Igor Maciejewski, Kacper Gierula, and Sebastian Glowinski. 2025. "Personal Identification Using Embedded Raspberry Pi-Based Face Recognition Systems" Applied Sciences 15, no. 2: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020887
APA StylePecolt, S., Błażejewski, A., Królikowski, T., Maciejewski, I., Gierula, K., & Glowinski, S. (2025). Personal Identification Using Embedded Raspberry Pi-Based Face Recognition Systems. Applied Sciences, 15(2), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020887








