Evaluation of Two-Stage Backwashing on Membrane Bioreactor Biofouling Using cis-2-Decenoic Acid and Sodium Hypochlorite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lab-Scale MBR Operation for Evaluating Permeability by Two-Stage Backwashing
2.2. Lab-Scale MBR Operation for Evaluation of Foulants
2.3. EPS’ Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Biofilm Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Two-Stage Backwash on MBR Permeability
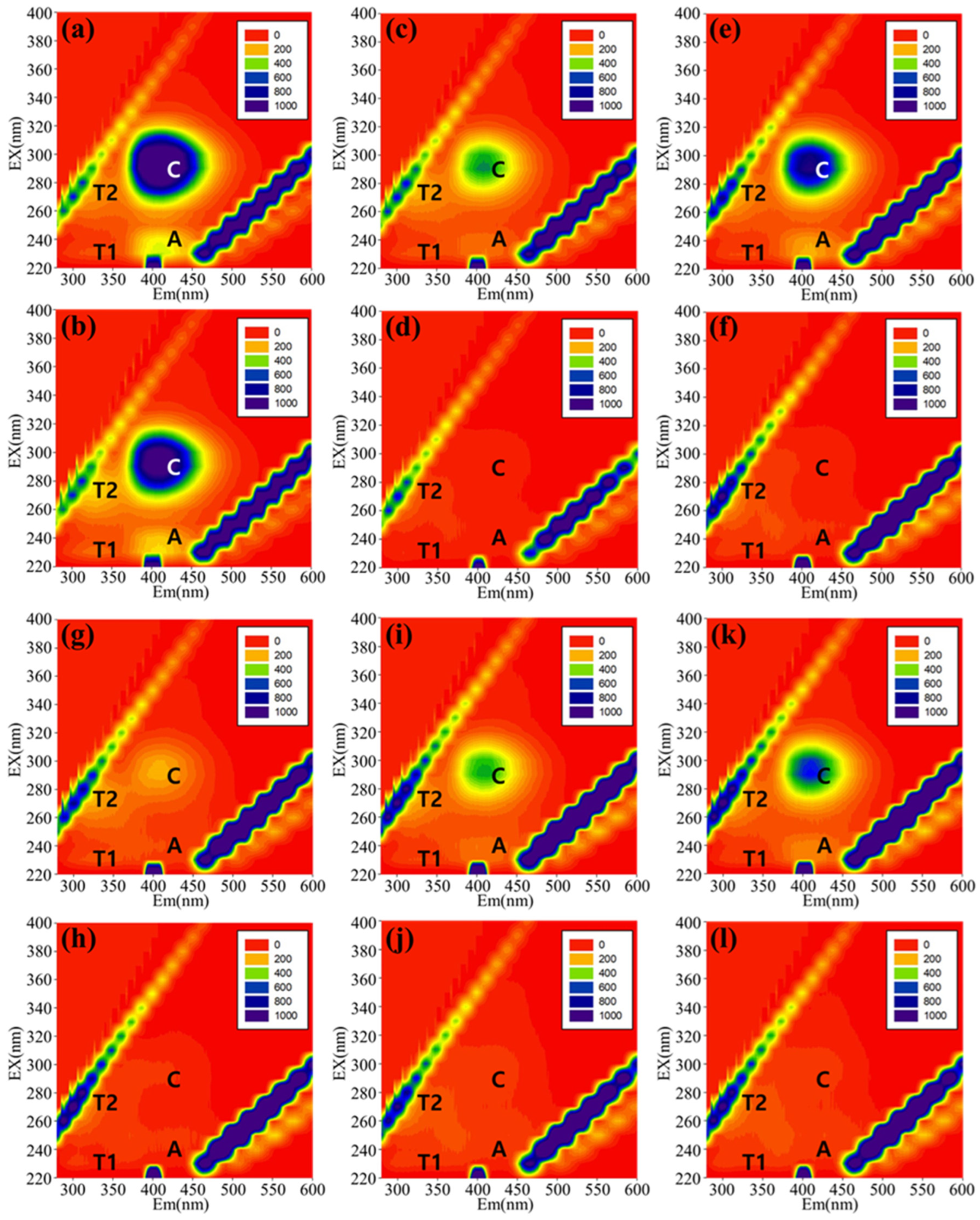
3.2. EEM Peak Composition by Backwashing
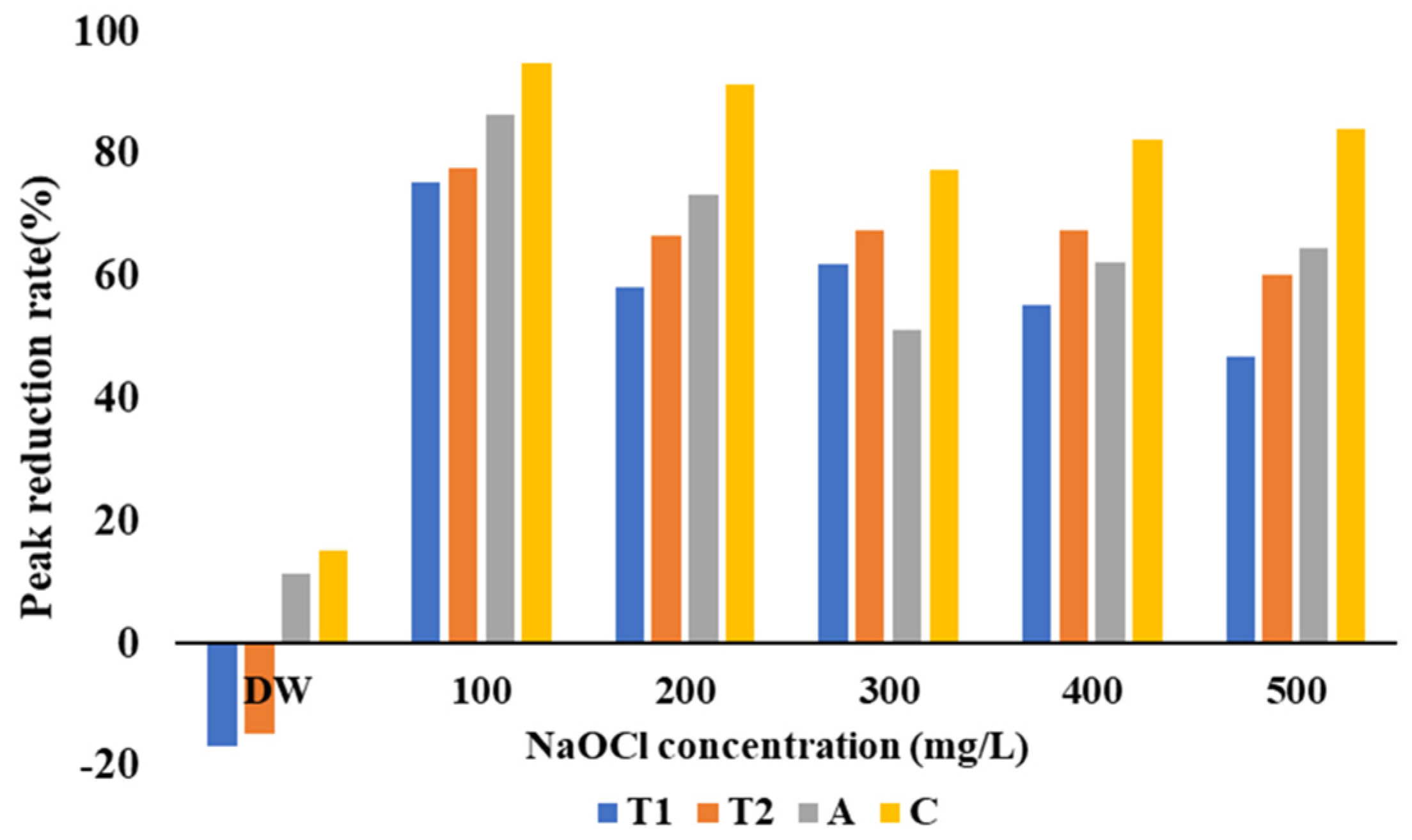
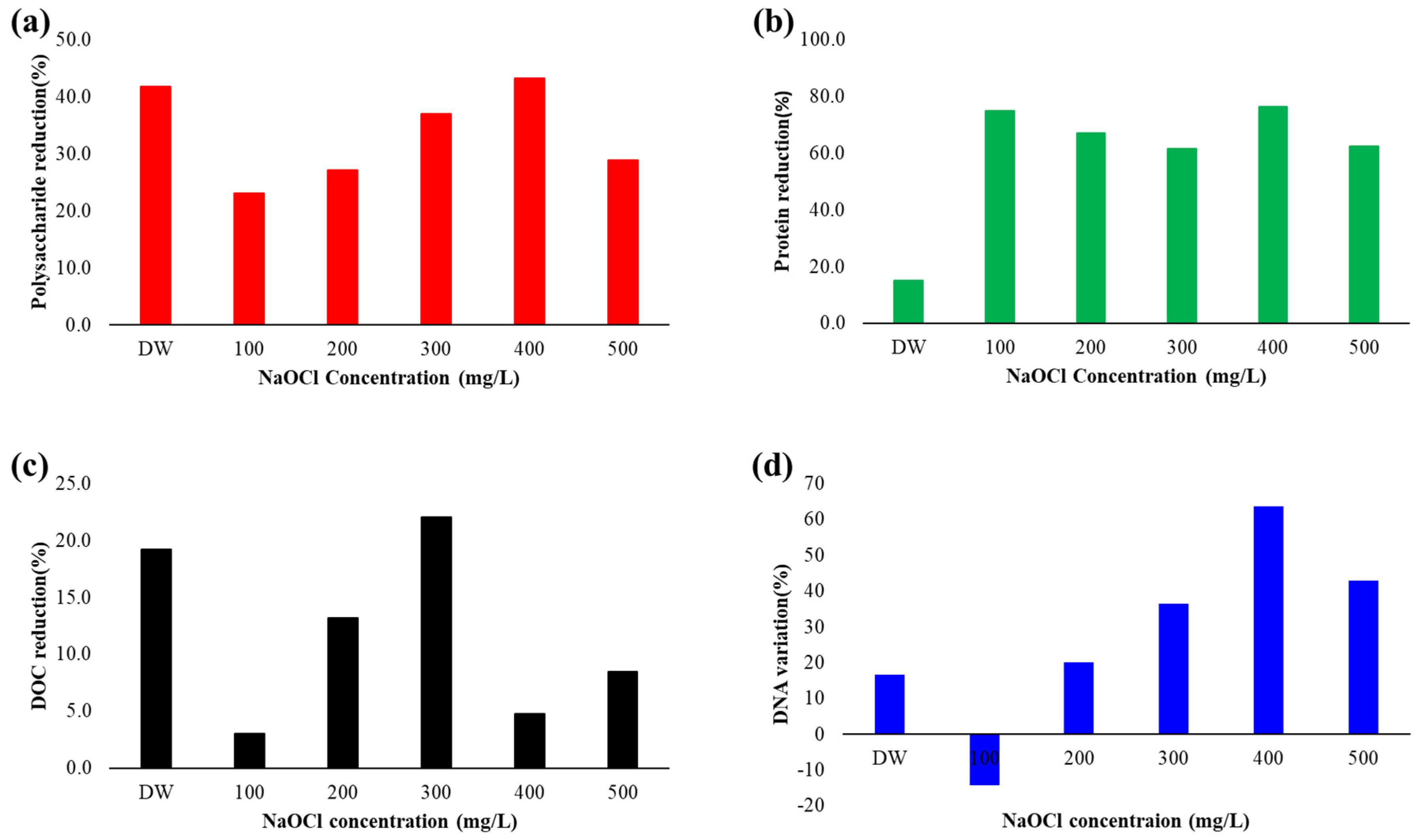
3.3. Biofouling Reduction by CDA and NaOCl
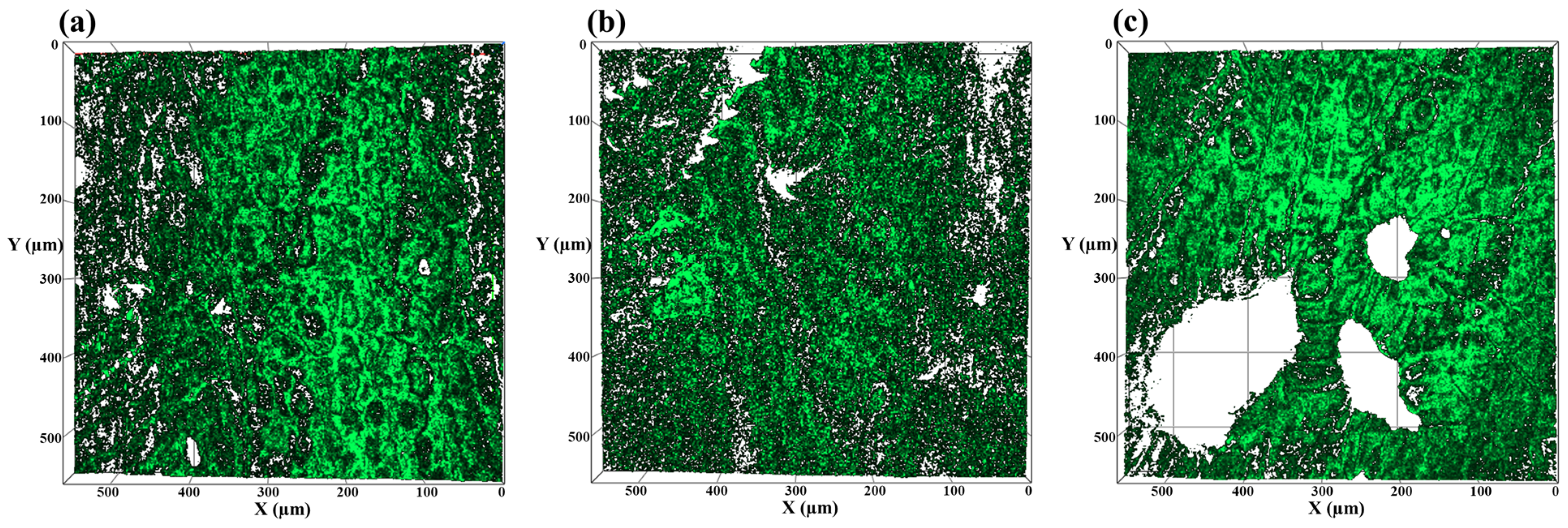
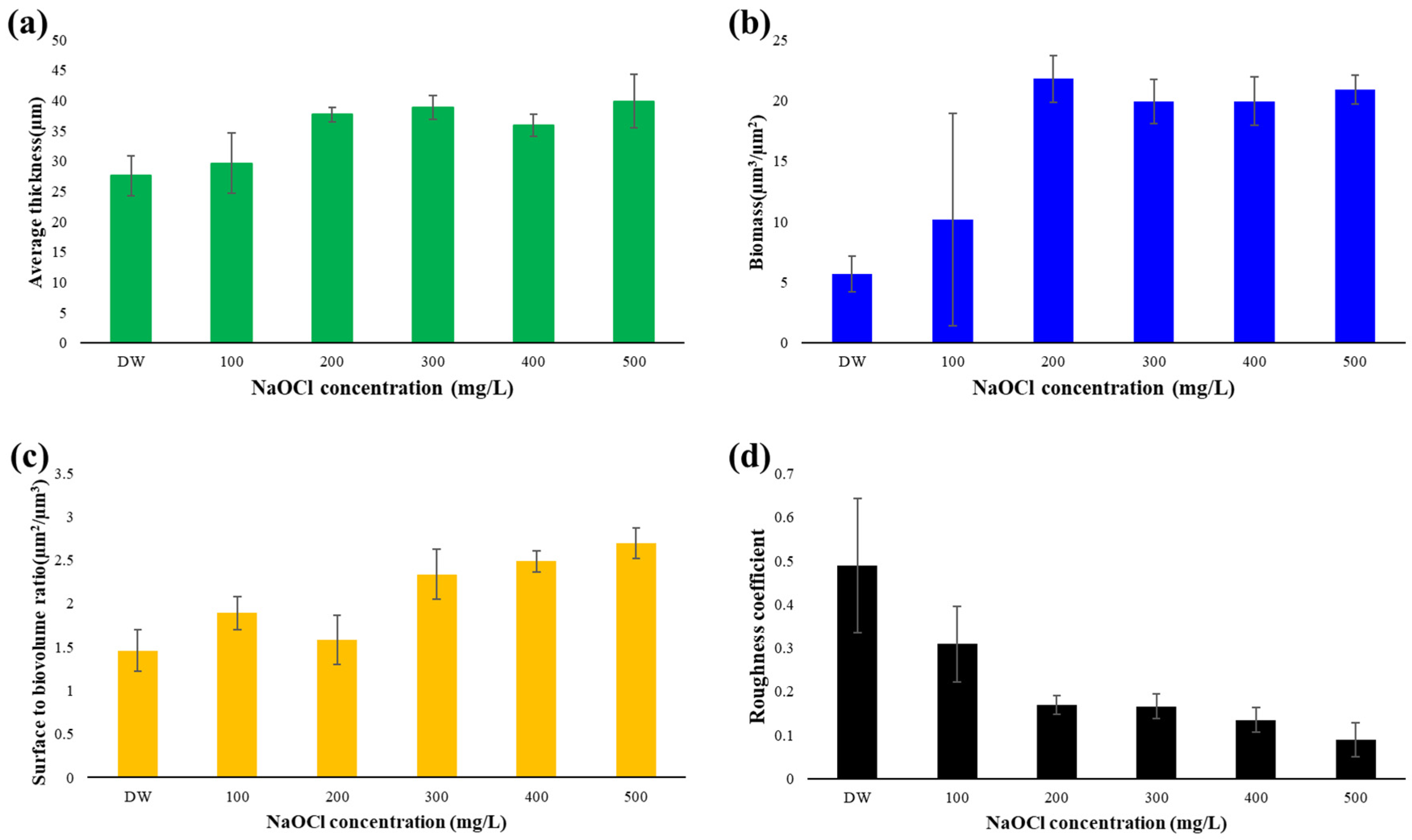
3.4. Surface Coverage Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane technologies in wastewater treatment: A review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, S.W.; Rice, J.S.; Nelson, K.D.; Vernon, C.R.; McManamay, R.; Dickson, K.; Marston, L. Comparison of potential drinking water source contamination across one hundred US cities. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.U.; Roy, H.; Islam, M.R.; Tahmid, M.; Fariha, A.; Mazumder, A.; Tasnim, N.; Pervez, M.N.; Cai, Y.; Naddeo, V. The advancement in membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology toward sustainable industrial wastewater management. Membranes 2023, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Bopape, M.F.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Richards, H. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komlenic, R. Rethinking the causes of membrane biofouling. Filtr. Sep. 2010, 47, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSawaftah, N.; Abuwatfa, W.; Darwish, N.; Husseini, G. A comprehensive review on membrane fouling: Mathematical modelling, prediction, diagnosis, and mitigation. Water 2021, 13, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, P.; Singh, C.K.; Sodhi, K.K.; Surya, J.N.; Singh, D.K. Biofilms: Understanding the structure and contribution towards bacterial resistance in antibiotics. Med. Microecol. 2023, 16, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.G.; Basu, S.; Banerjee, T.; Shukla, V.K. Biofilm and wound healing: From bench to bedside. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzaki, S. Mechanisms of actions of sodium hypochlorite in cleaning and disinfection processes. Biocontrol Sci. 2006, 11, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Uchida, H. Intensive membrane cleaning for MBRs equipped with flat-sheet ceramic membranes: Controlling negative effects of chemical reagents used for membrane cleaning. Water Res. 2019, 150, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chew, J.W.; Liu, Y. An environmentally sustainable approach for online chemical cleaning of MBR with activated peroxymonosulfate. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 600, 117872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, D.L.; von Gunten, U. The chlorine dilemma. Science 2011, 331, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.Z.; Bérubé, P.R. Assessing the effects of sodium hypochlorite exposure on the characteristics of PVDF based membranes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5392–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, D. Effect of hypochlorite cleaning on the physiochemical characteristics of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekeç, Ö.; Gökalsın, B.; Karaltı, İ.; Kayhan, F.E.; Sesal, N.C. Effects of chlorine stress on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm and analysis of related gene expressions. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Kwon, J.-S.; Park, H.-S.; Ji, W.H.; Kim, H.-S.; Jang, A. Influence of sodium hypochlorite used for chemical enhanced backwashing on biophysical treatment in MBR. Desalination 2013, 316, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, J.E.; Tao, F.; Zhang, L.-H. Listening to a new language: DSF-based quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Tannières, M.; Moréra, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum quenching: Role in nature and applied developments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachosz, K.; Vu, M.T.; Nghiem, L.D.; Zdarta, J.; Nguyen, L.N.; Jesionowski, T. Enzyme-based control of membrane biofouling for water and wastewater purification: A comprehensive review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-S.; Lee, C.-H. Origin and evolution of quorum quenching technology for biofouling control in MBRs for wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.M.; Coleman, E.C.; Yeasmin, R.; Harrison, Z.L.; Kurakula, M.; Baker, D.L.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Fujiwara, T.; Jennings, J.A. Synthesis and characterization of 2-decenoic acid modified chitosan for infection prevention and tissue engineering. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, S.; Rahmani-Badi, A.; Babaie-Naiej, H.; Soudi, M.R. Unsaturated fatty acid, cis-2-decenoic acid, in combination with disinfectants or antibiotics removes pre-established biofilms formed by food-related bacteria. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ryu, J.; Jung, J.; Yu, Y.; Choi, S.; Kweon, J. Dispersive biofilm from membrane bioreactor strains: Effects of diffusible signal factor addition and characterization by dispersion index. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1211761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Jiang, Z.; Kim, J.; An, S.; Park, Y.; Kweon, J. Low-biofouling membrane bioreactor: Effects of cis-2-Decenoic acid addition on EPS and biofouling mitigation. Chemosphere 2024, 358, 142110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Approaches to dispersing medical biofilms. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, A.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Interspecies and interkingdom signaling via quorum signals. Isr. J. Chem. 2016, 56, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Amari, D.; Davies, D.G.; Sauer, K. cis-DA-dependent dispersion by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm and identification of cis-DA-sensory protein DspS. mBio 2023, 14, e02570-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunacheva, C.; Stuckey, D.C. Analytical methods for soluble microbial products (SMP) and extracellular polymers (ECP) in wastewater treatment systems: A review. Water Res. 2014, 61, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Halbouni, D.; Traber, J.; Lyko, S.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T.; Tacke, D.; Janot, A.; Dott, W.; Hollender, J. Correlation of EPS content in activated sludge at different sludge retention times with membrane fouling phenomena. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Sun, S.-H.; Xiao, K.; Huang, X. Two strategies of stubborn biofouling strains surviving from NaClO membrane cleaning: EPS shielding and/or quorum sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, K. [105] Determination of DNA concentration with diphenylamine. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968; Volume 12, pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q.; Harada, H. A novel integrated approach to quantitatively evaluate the efficiency of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extraction process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, P.; Schmidt-Emrich, S.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program COMSTAT. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz Nizer, W.S.; Inkovskiy, V.; Overhage, J. Surviving reactive chlorine stress: Responses of gram-negative bacteria to hypochlorous acid. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. Effect of sodium hypochlorite on typical biofilms formed in drinking water distribution systems. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strempel, N.; Nusser, M.; Neidig, A.; Brenner-Weiss, G.; Overhage, J. The oxidative stress agent hypochlorite stimulates c-di-GMP synthesis and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenal, U.; Reinders, A.; Lori, C. Cyclic di-GMP: Second messenger extraordinaire. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.Y.; Wu, Z. Acute responses of microorganisms from membrane bioreactors in the presence of NaOCl: Protective mechanisms of extracellular polymeric substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Formation mechanisms of emerging organic contaminants during on-line membrane cleaning with NaOCl in MBR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation− emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin, C.; Lesage, G.; Traber, J.; Pronk, W.; Heran, M. Three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence (3DEEM) for quick and pseudo-quantitative determination of protein-and humic-like substances in full-scale membrane bioreactor (MBR). Water Res. 2017, 118, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellman, J.B.; Hood, E.; Spencer, R.G. Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilusha, R.T.; Wei, Y. New insights into the microbial diversity of cake layer in yttria composite ceramic tubular membrane in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR). Membranes 2021, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thejani Nilusha, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y. Optimization of in situ backwashing frequency for stable operation of anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactor. Processes 2020, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.S.; Chu, K.H.; Choi, I.-H.; Mang, J.S.; Ko, K.B. Operating cost reduction of UF membrane filtration process for drinking water treatment attributed to chemical cleaning optimization. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Guo, W.; Lee, W. Formation of disinfection byproducts upon chlorine dioxide preoxidation followed by chlorination or chloramination of natural organic matter. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-L.; Huang, C.; Wang, W. Effect of cell integrity on algal destabilization by oxidation-assisted coagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-K.; Tang, X.; Tan, H.; Feng, F.; Xu, Z.-M.; Mahmood, Q.; Zeng, W.; Min, X.-B.; Tang, C.-J. Effect of scrubbing by NaClO backwashing on membrane fouling in anammox MBR. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, S.M.; Fisher, G.; Everett, B.A.; Tran, P.; Prindle, A. Secreted nucleases reclaim extracellular DNA during biofilm development. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, K.U.; Priyadarshanee, M.; Samantaray, D.P.; Das, S. Bacterial biofilm and extracellular polymeric substances in the treatment of environmental pollutants: Beyond the protective role in survivability. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C. EPS—Then and now. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Evaluation of Cis-2-Decenoic Acid and Vanillin as Quorum Sensing Compounds for Biofouling Reduction in Membrane Bioreactor Process. Ph.D. Thesis, Konkuk University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]


| Protocols | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic backwashing | Low cost, easy to apply, chemical-free | Cannot remove irreversible fouling |
| Chemical enhanced backwashing | Low cost, superior cleaning efficiency | Can cause damage to membrane and microorganism |
| Two-stage backwashing | Superior cleaning efficiency, reduced dosage of NaOCl, more sustainable | Complex to apply, additional cost |
| Substance | Concentration(g/L) |
|---|---|
| Glucose | 0.4000 |
| Yeast extract | 0.0140 |
| BactoTM peptone | 0.1150 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 0.1048 |
| KH2PO4 | 0.0218 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 0.0320 |
| FeCl3·6H2O | 0.0001 |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 0.0033 |
| MnSO4·5H2O | 0.0029 |
| NaHCO3 | 0.2555 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Song, W.; Kim, C.; Jiang, Z.; Han, J.; Kweon, J. Evaluation of Two-Stage Backwashing on Membrane Bioreactor Biofouling Using cis-2-Decenoic Acid and Sodium Hypochlorite. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020874
Park S, Song W, Kim C, Jiang Z, Han J, Kweon J. Evaluation of Two-Stage Backwashing on Membrane Bioreactor Biofouling Using cis-2-Decenoic Acid and Sodium Hypochlorite. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(2):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020874
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sungjin, Wonjung Song, Chehyeun Kim, Zikang Jiang, Jiwon Han, and Jihyang Kweon. 2025. "Evaluation of Two-Stage Backwashing on Membrane Bioreactor Biofouling Using cis-2-Decenoic Acid and Sodium Hypochlorite" Applied Sciences 15, no. 2: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020874
APA StylePark, S., Song, W., Kim, C., Jiang, Z., Han, J., & Kweon, J. (2025). Evaluation of Two-Stage Backwashing on Membrane Bioreactor Biofouling Using cis-2-Decenoic Acid and Sodium Hypochlorite. Applied Sciences, 15(2), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020874





