Featured Application
The combined use of naringinase and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus enables the development of an integrated process for grapefruit juice fermentation and debittering at its natural pH. This approach not only improves consumer acceptability by reducing the characteristic bitterness but also enhances the nutritional and functional value of the product through probiotic enrichment. The process has potential for application in the functional beverage industry as a strategy to create novel, consumer-friendly citrus-based products.
Abstract
Growing consumer awareness of the link between diet and health has increased interest in functional foods, including fermented juices. Grapefruit juice has potential health-promoting properties, but its bitter taste limits its acceptance by consumers. This study aimed to develop a fermentation process for debittering grapefruit juice at natural pH using Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and naringinase. Grapefruit juice was fermented with Lactic. rhamnosus using free naringinase and naringinase immobilized on carob gum and chitosan supports at 30 ± 0.2 °C for 72 h. Naringin concentration, bacterial cell count, total phenol content, organic acids, carbohydrates, antioxidant activity, and pH were analyzed. Naringinase immobilized on carob gum demonstrated the highest efficiency, hydrolyzing over 42% of naringin after 24 h (from 418.20 to 241.19 μg/mL). The free enzyme reduced the naringin concentration to 155.28 μg/mL after 48 h. The highest Lactic. rhamnosus cell count (2.05 × 109 CFU/mL) was achieved with the free enzyme. Total phenol content decreased from 42.24 to 16.58 mg GAE/100 mL when using naringinase immobilized on chitosan. The combined use of naringinase and Lactic. rhamnosus enables the development of an integrated process that improves consumer acceptance with potential applications in the functional beverage industry.
1. Introduction
In recent years, growing consumer awareness of the relationship between diet and health has contributed to a surge in interest in functional foods. Functional foods benefit the body, support specific functions, and provide essential nutrients [1]. Probiotics are widely used in commercial functional products of animal origin, such as yogurt and cheese [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Plant-based probiotic products are less common on the market and are usually limited to traditional cereal- or soy-based products [2,7]. Fruit and vegetable juices, due to the presence of essential nutrients, can be considered a suitable medium for probiotic bacteria [1].
The most commonly used commercial probiotic microorganisms in food are bacteria of the genera Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium [1,3,7]. Grapefruit juice, which can be a potential growth medium for lactic acid bacteria, was fermented using probiotic bacterial strains, including Lactiplantibacillus plantarum [8,9,10,11], Lactobacillus fermentum [11], Lacticaseibacillus casei [12], Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus [11], and Bifidobacterium longum [11,12,13]. However, the bitterness of citrus juices, caused by naringin, reduces consumer acceptance [14]. Naringin, a flavonoid glycoside, mainly causes the bitter taste of citrus fruits. Debittering can be achieved by hydrolyzing naringin using naringinase, an enzyme complex with α-L-rhamnosidase and β-D-glucosidase activities. Naringin can be hydrolyzed to rhamnose and prunin by α-L-rhamnosidase; afterward, β-D-glucosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of prunin to glucose and tasteless naringenin [15]. The use of free naringinase in citrus juice processing poses several practical difficulties related, among other things, to the inability to reuse or separate the enzyme from the reaction medium. Various immobilization techniques can partially solve these problems [16,17,18]. Due to its use in juice technology, it is necessary to immobilize naringinase on a natural carrier approved for food use [16,17,18]. Separating immobilized naringinase from heterogeneous citrus juice using magnetic carriers is particularly desirable.
Lactic. rhamnosus as a fermentation culture has well-documented probiotic properties [19,20,21]. In addition, this strain shows strong growth in various plant substrates [22,23,24], making it suitable for grapefruit juice fermentation. Tran et al. [11] used Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 01, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus B01725, Lactobacillus fermentum D13, and Bifidobacterium B7.5 to ferment grapefruit juice and reduce its naringin content while raising its initial pH to 6.3.
However, the presented study introduced the Lactic. rhamnosus strain into the juice exclusively as a probiotic culture. At the same time, naringinase was added separately, both in free form and immobilized on two different carriers. The study aims to remove bitterness simultaneously and produce probiotic grapefruit juice at its natural pH by using free and immobilized naringinase and probiotic bacteria in a combined fermentation process. The pH, Lactic. rhamnosus cell counts, concentrations of naringin, phenols, organic acids, and antioxidant capacity were determined in the juice before the combined process and after 24, 48, and 72 h of its duration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Lactobacillus casei subsp. rhamnosus (Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus) is a probiotic bacterial starter culture (from Serowar.pl, Szczecin, Poland) with low acidification and fermentation activity. Naringinase from Aspergillus niger KMS, cultured under submerged conditions, was isolated by concentrating the post-culture fluid through ultrafiltration, followed by protein precipitation using acetone, yielding a solid preparation with an activity of 816 µmol/(min·g) [25]. Polysaccharides were used for enzyme immobilization: carob gum (locust bean gum) obtained from Ceratonia siliqua (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and chitosan (medium molecular weight, 75–85% deacetylated). Naringin (assay 95%, HPLC) was from Sigma-Aldrich. Activators used for enzyme immobilization: a 50% aqueous solution of polyethyleneimine (Sigma-Aldrich), glutaraldehyde (25%, by volume, aqueous solution) was from Merck (Warsaw, Poland). Dextran aldehyde was obtained using the method described by Rajdeo [26].
Water and acetonitrile (HPLC grade) were also purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. All other chemicals were of analytical grade and were obtained from various sources. Fresh grapefruits were bought in a local supermarket.
2.2. Immobilization of Naringinase
Naringinase from Aspergillus niger KMS was immobilized on two types of magnetic carriers. The first carrier was obtained based on locust bean, activated with polyethyleneimine, and cross-linked with dextran aldehyde [16]. The second was a chitosan carrier activated with glutaraldehyde [27].
2.2.1. Immobilization and Stabilization of Naringinase on a Polysaccharide Magnetic Carrier
The carrier was obtained by combining magnetite microparticles and carob gum, followed by activation with a 5% polyethyleneimine solution for 3.5 h. The average particle size of the carrier used was 117.29 ± 12.31 µm. The process of immobilizing naringinase on the carob gum carrier was carried out by adding 7.5 mL of enzyme solution (5 mg/10 mL, 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0) to 150 mg of the carrier and incubating the mixture at 27 ± 0.2 °C for 4 h with continuous stirring (150 rpm). After completion of the immobilization step, 10 mL of a 20% dextran aldehyde solution was added to the system, and incubation was continued for another 20 h under the same conditions. After stabilization with dextran aldehyde, the resulting enzyme-carrier complex was separated from the solution using a neodymium magnet and then rinsed several times with phosphate buffer (0.01 M, pH 7.0) and distilled water.
2.2.2. Immobilization and Stabilization of Naringinase on a Chitosan Magnetic Carrier
Magnetic chitosan microspheres were prepared by applying reversed-phase suspension methodology, using 7.5% glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking reagent. Immobilization of naringinase on a chitosan carrier activated with glutaraldehyde. Before immobilization, 150 mg of magnetic chitosan carrier was incubated in phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.0) for 20 h. Then, 10 mL of naringinase solution (5 mg/10 mL, 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0) was added to the carrier, and the mixture was incubated for 2 h at 25 ± 0.2 °C. After immobilization, the carrier with the immobilized enzyme was separated using a neodymium magnet and then rinsed several times with phosphate buffer (0.01 M, pH 7.0) and distilled water [27].
2.3. Fermentation and Debittering of Grapefruit Juice
Freshly squeezed grapefruit juice, without any preliminary treatment, was neither filtered nor sterilized, and was fermented with a monoculture of Lactic. rhamnosus. The free naringinase and its immobilized forms were applied. These biocompatible supports allow repeated use of the enzyme and facilitate its separation from the reaction medium [27]. A total of 55 mL of freshly squeezed grapefruit juice and 2.8 mL of free enzyme (1 mg/mL) or 150 mg immobilized naringinase and 3 mg of the bacteria were mixed in a conical flask and incubated at 30 °C. Fermentation was carried out on a GFL 3031 shaker (Gesellschaft für Labortechnik mbH, Burgwedel, Germany). The flasks were placed in the shaker’s sockets at 95 rpm.
Samples were taken after 24, 48, and 72 h of fermentation. 5 mL of sample was taken each time, centrifuged at 10,956× g for 20 min, and the supernatant was used to determine naringin concentration, TPC, antioxidant activity, concentration of organic acids, and carbohydrates. The juice samples were not centrifuged or filtered to determine the bacterial count. Appropriate dilutions were obtained using sterile saline solution (0.9% NaCl).
2.4. Determination of Naringin Concentration
The concentration of naringin in the juice was determined using the Davis colorimetric method [28]. The Davis method is based on the reactions of naringin with alkaline diethylene glycol. One hundred μL of supernatant after centrifugation of juice, One hundred μL of (4.0 M) NaOH was added to 4.8 mL of diethylene glycol (90%, v/v) and incubated for 10 min at room temperature. The intensity of the yellow color produced was measured at 420 nm. The absorbance was then converted to naringin concentration using the regression equation characterizing the standard curve, prepared based on measuring the absorbance of aqueous naringin solutions in the concentration range of 50–1000 µg/mL.
2.5. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Cell Counts
The number of Lactic. rhamnosus cells was determined by plating appropriately diluted samples on MRS agar. After 24 h of incubation, the CFU/mL was counted.
2.6. Determination of Total Phenol Content (TPC)
The Folin–Ciocalteu method determined the total phenol content (TPC). One hundred μL of juice, 6 mL of distilled water, and 0.5 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent were mixed. The reaction mixture was left for 1 min at 20 ± 0.2 °C. After this, 1.5 mL of 20% Na2CO3 solution and 1.9 mL of distilled water were added to each sample. The samples were mixed and heated in a water bath at 25 ± 0.2 °C until a stable blue color was obtained (approximately 40 min). The absorbance of the samples was then measured at a wavelength of λ = 760 nm in two replicates using a Marcel MEDIA spectrophotometer (Marcel Sp. z o.o., Zielonka, Poland). The total phenol content was expressed in mg/100 mL of juice in terms of gallic acid (GAE) [29,30].
2.7. Antioxidant Activity
The radical scavenging activities of the juice sample were determined using the stable radical DPPH. The juice was dissolved in methanol. 1 mL of 0.1 mM DPPH solution was added to 0.0345 mL of the test sample. After 20 min, at room temperature in the dark, the absorbance of the mixture was measured at a wavelength of 517 nm against methanol as a blank sample in two replicates [31]. The control sample was a mixture of DPPH solution with distilled water. The measurement results are given as the degree of radical scavenging, AA%:
where AA is the absorbance of the test sample, and AB is the absorbance of the control sample.
AA% = [(AB − AA)/AB] × 100,
2.8. Analysis of Organic Acids and Carbohydrates
The supernatant was then filtered through a 0.2 μm syringe filter (Shanghai Titan Scientific Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The cell-free supernatant of grapefruit juice was used to determine the concentration of organic acids and carbohydrates by the HPLC method (Aminex HPX-87H column, Aminex, PLC, Dublin, Ireland, UV-210 nm detector, and refractometric, temperature 65 °C, mobile phase 0.005 M H2SO4—flow rate 0.5 mL min). More details can be found in the Supplementary Materials.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Experiments were performed in triplicate, and results are presented as means ± standard deviation. Significance of differences (p < 0.05) was analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s test using STATISTICA v13.3 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration of Naringin
The hydrolysis of naringin, using both soluble and immobilized enzymes, was investigated, and the results are shown in Figure 1.
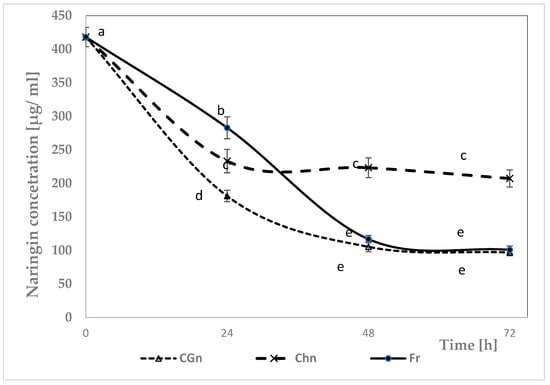
Figure 1.
Residual concentration of naringin after hydrolysis as a function of time. Fr—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + free naringinase; CGn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum; Chn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on chitosan; various letter markings indicate statistically significant differences at p < 0.05.
The concentration of naringin in fresh grapefruit juice was 418.20 ± 13.38 μg/mL. Naringinase was immobilized on a locust bean gum carrier and then stabilized, most effectively, hydrolyzing naringin contained in grapefruit juice. After just 24 h, over 42% of naringin was hydrolyzed to a concentration of 241.19± 9.64 μg/mL, which, according to Soares and Hotchkins [32], means that the bitterness of the grapefruit juice was not perceptible. The reaction was slightly slower in the case of the free enzyme. Naringin was reduced only to 155.28 ± 6.21 µg/mL after 48 h with free enzyme. The lowest catalytic activity was shown by naringinase immobilized on a chitosan carrier, with only 34% of naringin hydrolyzed after 72 h. After 72 h of reaction, the free enzyme and the enzyme immobilized on locust bean gum carrier hydrolyzed over 68% of the naringin in the juice, indicating similar activity of both forms.
Using the Lactip. plantarum 01 strain, Tran et al. [11] obtained a maximum decrease in naringin concentration (approximately 28%) after 24 h of grapefruit juice fermentation. Li et al. [10] added the strain Lactip. plantarum 1-1-2 to grapefruit juice, and after 42 h of fermentation, the concentration of naringin decreased from the initial value of >800 µg/mL to approximately 440 µg/mL.
Imece et al. [8] added probiotic bacteria Lactip. plantarum ACC 54, Lactip. plantarum ACC 28, and Lactip. plantarum 250, which exhibits naringinase activity, to grapefruit juice. The highest decrease (61.5%) in the amount of naringin in the samples was detected at the end of the third day.
Various forms of naringinase immobilization were used to reduce naringin concentration without the involvement of probiotic bacteria. Naringinase immobilization onto poly-dopamine (PDA)-coated magnetic nanoparticles was successfully used for debittering grapefruit juice, detecting a reduction in naringin of 56% after 24 h [17]. Naringinase immobilized on an aminated carrier converted almost 70% of the initial naringin after 24 h of reaction [33].
3.2. Changes of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Cell Counts
Changes in the number of Lactic. rhamnosus cells during the fermentation of grapefruit juice with of free and immobilized naringinase were investigated, and the results are presented in Figure 2.
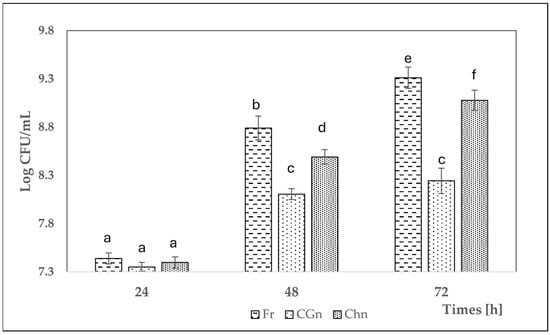
Figure 2.
The number of bacterial cells in grapefruit juice during fermentation and debittering. Fr—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + free naringinase; CGn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum; Chn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on chitosan; various letter markings indicate statistically significant differences at p < 0.05.
The tested lactic acid bacteria showed the ability to grow in grapefruit juice without adding nutrients. They utilized compounds contained in grapefruit juice in various metabolic processes. The highest final cell count of Lactic. rhamnosus—2.05 × 109 CFU/mL was found with free enzyme in a grapefruit juice sample. This sample was also characterized by intense bacterial growth throughout the experiment. In juice with naringin immobilized on a chitosan carrier, Lactic. rhamnosus reached a final concentration almost twice as low, at 1.2 × 109 CFU/mL. The lowest final concentration of Lactic. rhamnosus was observed in grapefruit juice with naringin immobilized on a magnetic carrier with locust bean gum, which was 1.75 × 108 CFU/mL. During fermentation, the concentration of naringin decreases, while the number of bacterial cells increases, which is typical for this process.
The results confirmed other authors’ findings on using grapefruit juice as a culture medium for lactic acid bacteria. Tran et al. [11] used probiotic lactic acid bacteria (Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 01, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus B01725, Lactobacillus fermentum D13, Bifidobacterium bifidum B7.5) to ferment grapefruit juice. In all cases, the cell count was higher than 108 CFU/mL after 24 h of fermentation [11]. Li et al. [10] tested six selected strains of lactic acid bacteria for fermentation and removal of bitterness from grapefruit juice, of which Lactip. plantarum 1-1-2 showed better growth than the other five strains (4.8 × 108 CFU/mL).
The lowest concentration of bacterial cells in the juice sample with naringin immobilized on a magnetic carrier with locust bean gum may be related to the adsorption of bacteria on the magnetic carrier with locust bean gum. This carrier showed high protein adsorption, as this carrier adsorbed naringin in the first stage of enzyme immobilization [16].
3.3. Total Phenol Content
Figure 3 shows changes in phenol content during the fermentation of grapefruit juice by Lactic. rhamnosus with free and immobilized naringinase.
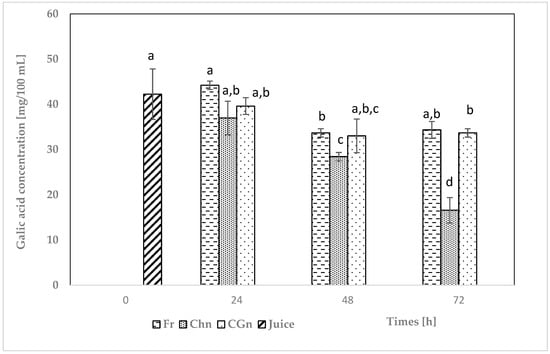
Figure 3.
Total phenol content in grapefruit juice during fermentation and debittering. Fr—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + free naringinase; CGn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum; Chn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on chitosan; various letter markings indicate statistically significant differences at p < 0.05.
The TPC in fresh grapefruit juice was 42.24 mg GAE/dL. Analysis of the data in Figure 3 shows that TPC decreased in all tested juice samples. After 72 h of fermentation, the final phenol content ranged from 16.58 to 34.34 g GAE/dL. The smallest decrease in phenol content compared to fresh grapefruit juice was recorded in the sample with Lactic. rhamnosus and immobilized on locust bean gum (CGn)—the phenol content after 72 h of fermentation was 33.68 mg GAE/100 cm3. In the case of juice with added bacteria and free enzymes, the differences in phenol content resulting from fermentation were not statistically significant. The most significant decrease in phenol content was observed in juice with Lactic. rhamnosus and naringinase immobilized on a chitosan carrier (Chn)—from 42.24 mg GAE/dL to 16.58 mg GAE/dL. A decrease in phenol content from 103.6 mg GAE/dL to 97.5 mg GAE/dL and from 103.6 mg GAE/dL to 100.6 mg GAE/dL after 24 h of fermentation was observed by Tran et al. [11] in grapefruit juice fermented by Lactic. rhamnosus B017250. Phenols can be used as nutrients by lactic acid bacteria [12]. In addition, phenolic compounds may increase nutrient consumption and thus stimulate bacterial growth [34]. The results obtained do not confirm the findings of other authors. Akarca and Baytal [35] found an increase in phenol content in grapefruit juice fermented by different species of Lactobacillus bacteria. The most significant increase was observed with Lactobacillus acidophilus bacteria, from 169.08 mg GAE/dL to 245.75 mg GAE/dL. The authors suggest that the increase in TPC during fermentation is related to the activity of lactic acid bacteria [35]. Phenol precursors are converted into phenolic compounds during fermentation, with some modifications to their structure. In this context, the enzyme β-D-glucosidase, produced by lactic acid bacteria, catalyzes the conversion of phenolic glycosides bound to sugar molecules into free phenolic acids [36]. In a study by Li et al. [10], after 3 days of fermentation of grapefruit juice by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1-1-2 bacteria, an increase in phenol content from 1.65 to 1.90 mg GAE/dL was observed. According to the authors, the higher TPC in fermented juice resulted from the degradation of grapefruit cell walls by enzymatic hydrolysis and the metabolism of flavonoids in grapefruit juice by Lactip. plantarum 1-1-2 [10].
3.4. Antioxidant Potentials
Figure 4 shows changes in DPPH free radical scavenging activity during the fermentation of grapefruit juice by Lactic. rhamnosus with free and immobilized naringinase. Analyzing the results presented in Figure 4, it was found that fresh grapefruit juice had the highest free radical neutralization activity against the DPPH radical (control sample)—24.81%. Fermented grapefruit juice with the addition of free naringinase showed a stable high level of antioxidant activity throughout the experiment. Grapefruit juice with Lactic. rhamnosus and naringinase immobilized on a chitosan carrier showed the weakest antioxidant activity throughout the experiment, despite a gradual increase, with the final value being only 12.84%, which was 51.1% of the activity of fresh grapefruit juice. Grapefruit juice with Lactic. rhamnosus and naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum showed the most dynamic increase in antioxidant activity, from a very low initial level (12.24%) to almost complete recovery of the antioxidant activity characteristic of fresh grapefruit juice (23.66%) on the third day of the experiment.
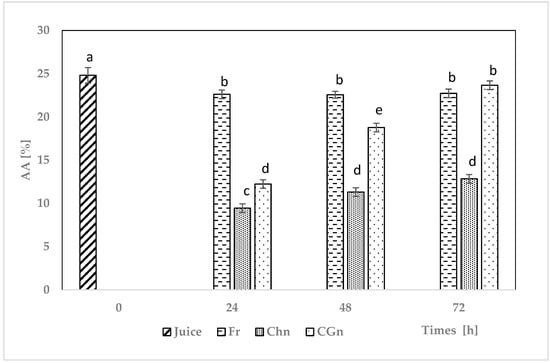
Figure 4.
DPPH free radical scavenging activity in grapefruit juice during fermentation and debittering. AA—Antioxidant activity, Fr—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + free naringinase; CGn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum; Chn—grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on chitosan; various letter markings indicate statistically significant differences at p < 0.05.
Akarca and Baytal [35] also observed an increase in the neutralization activity of free radicals against the DPPH radical. The antioxidant activity values of grapefruit juice samples fermented with various species of bacteria from the genus Lactobacillus were higher after 48 h of the process than the activity of fresh grapefruit juice (49.17%). It was found that the highest DPPH value was obtained in grapefruit juice by adding Lactip. plantarum (79.11%), and the lowest DPPH value was obtained in samples obtained by adding L. delbrueckii spp. Bulgaricus (50.65%). Li et al. [10] also observed an increase in the DPPH radical scavenging capacity in grapefruit juice after 17 h of fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1-1-2. According to the authors, this increase was related to the hydrogen atom supplied by antioxidants in fermented grapefruit juice. In addition, during fermentation, the bacteria hydrolyzed phenols, naringin, hesperidin, and eriocitrin into free phenols, such as naringenin and tangeretin, which have significantly higher antioxidant activity [10]. Quan et al. [37] found that the DPPH free radical neutralization values of fermented orange juices with different species of lactic acid bacteria increased at the end of fermentation. According to the authors, fermentation significantly increased the utilization of antioxidant active ingredients such as vitamin C, which has proton-donor properties.
The results presented in this study show a negative correlation between TPC and free radical neutralization activity against the DPPH radical. The increase in TPC and the associated increase in antioxidant activity may be due to the activity of β-D-glucosidase produced by Lactic. rhamnosus and β-D-glucosidase as a subunit of naringin. The decrease in TPC may be due to bacteria consuming certain phenols as an energy source. As a result, the amount of free phenolic compounds capable of neutralizing radicals is reduced. The simultaneous increase in antioxidant activity may be caused by the presence of naringenin, which, in the study by Li et al. [38], showed a more substantial DPPH radical scavenging effect than naringin.
3.5. Analysis of Carbohydrates and Organic Acids
Lactic acid bacteria utilize saccharides such as glucose and fructose as a source of carbon and energy [39,40,41,42]. Table 1 presents changes in glucose, fructose, and sucrose concentrations during the fermentation of grapefruit juice by Lactic. rhamnosus with the addition of free and immobilized naringinase.

Table 1.
Concentration of carbohydrates in grapefruit juice during fermentation and debittering.
The data in this table indicate that the bacteria utilized fructose most rapidly, followed by glucose and sucrose. After 48 h of fermentation, no fructose was observed in the juice. Fructose enters the phosphoketolase pathway [40]. They utilized glucose at a slightly slower rate. After 48 h of fermentation, less than 6.2% (w/v) glucose remained in the juice. The bacteria consumed sucrose the slowest; only after 72 h of fermentation did approximately 40% (w/v) of this saccharide remain in the juice. Tran et al. [11] found the exact order of saccharide consumption for Lactic. rhamnosus B01725.
The facultative heterofermentative bacterium Lactic. rhamnosus ferments saccharides into lactic acid and by-products such as CO2, acetic acid, and ethanol. Table 2 presents the changes in organic acid concentrations during the fermentation of grapefruit juice by Lactic. rhamnosus with the addition of free and immobilized naringinase.

Table 2.
Organic acid concentrations of grapefruit juice during fermentation and debittering.
Lactic acid concentration increased with fermentation duration up to 48 h. After 72 h, the concentration of this acid decreased. Acetic acid appeared in the final fermentation period, particularly in the presence of immobilized naringinase. Citrate and malate are the organic acids found in the most significant quantities in plants [39]. As can be seen from the data presented in Table 2, malic acid was metabolized by the bacterial strain used. After 48 h of fermentation, approximately 90% of this acid was metabolized. Malic acid is fermented by both homo- and hetero-lactic acid bacteria [39].
The initial citric acid concentration of 63.21 mM decreased only slightly during fermentation. In most samples collected after fermentation, the citric acid concentration did not differ significantly (p < 0.05) from the initial level. Studies conducted by other researchers do not confirm these results. Tran et al. [11] found no citric acid in grapefruit juice after fermentation with Lactic. rhamnosus B01725. Lactic. rhamnosus and other lactic acid bacteria can metabolize citrate to four-carbon compounds [43]. The differences in citric acid concentration between the presented fermentation and those reported by other authors may be because the process was conducted at low pH in this study. In the case of propionic acid, statistically significant differences were observed only in the case of grapefruit juice fermentation by the used Lactobacillus strain with the addition of immobilized naringinase on carob gum carrier.
3.6. Changes in pH of Grapefruit Juice
The pH changes were minimal during the fermentation of grapefruit juice with bacteria (Table 3). It may result from the intensive growth and metabolic activity of probiotic bacteria.

Table 3.
Changes in pH of grapefruit juice during bacterial fermentation.
The initial pH of the juice was 3.26. After 72 h, the pH slightly decreased to 3.00 for free naringinase. When naringinase immobilized on a carob gum carrier was used, the pH decreased to 2.78 after 72 h of fermentation. The smallest pH changes were observed when naringinase was immobilized on a chitosan carrier, where the juice’s pH decreased to 3.07 after 72 h. The grapefruit juice remained highly acidic throughout the process. However, the pH of the juices did not change significantly, indicating a high buffering capacity. Short-chain fatty acids are produced during fermentation, which lowers the pH values (Table 2).
The decrease in pH during the fermentation of probiotic products is of great importance for determining the fermentation time and maintaining product quality [11]. Many authors observe a decrease in pH during the fermentation of fruit juices [10,11,13].
4. Conclusions
Fermentation of the juice with Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and simultaneously removing the bitter taste can be carried out at the natural acidic pH of this juice. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus primarily utilized fructose as a carbon and energy source during juice fermentation, followed by glucose. Using an immobilized naringinase on chitosan and carob gum reduced the number of bacteria obtained from the fermentation. Naringinase during grapefruit juice fermentation removed naringin to values below the detection limit for its bitterness in this juice, with free naringinase and naringinase immobilized on magnetic carob gum carrier demonstrating the highest bitterness removal efficiency. Free and immobilized naringinase also caused a reduction in polyphenol content during fermentation compared to fresh grapefruit juice. Changes in total phenol content caused variation in the fermented juice’s antioxidant activity, but adding free enzymes did not significantly change it. In contrast, using immobilized enzyme caused an initial decrease and then an increase with the duration of the process.
The following research stage on fermentation and simultaneous removal of bitterness from grapefruit juice should be a sensory analysis of this product, and determining its shelf life.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app151910858/s1. Information on the HPLC for determining organic acids and carbohydtares.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.G., J.B.-B. and Z.G.; methodology, K.G., J.B.-B. and Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, K.G., J.B.-B. and Z.G.; writing—review and editing, Z.G.; supervision, Z.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Fr | grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + free naringinase |
| CGn | grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum |
| Chn | grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on chitosan |
| Fr-1d, Fr-2d, Fr-3d | grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + free naringinase after 1, 2, and 3 days of fermentation |
| CGn-1d, CGn-2d, CGn-3d | grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on locust bean gum after 1, 2, and 3 days of fermentation |
| Chn-1d, Chn-2d, Chn-3d | grapefruit juice + Lactic. rhamnosus + naringinase immobilized on chitosan after 1, 2, and 3 days of fermentation |
References
- Perricone, M.; Bevilacqua, A.; Altieri, C.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. Challenges for the Production of Probiotic Fruit Juices. Beverages 2015, 1, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P.; Pissaridi, K.; Argyro, B.; Kanellaki, M.; Los Koutinas, A. Dairy and non-dairy probiotic beverages. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. Vol. 2016, 7, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Vieira, K.C.; Ferreira, C.D.S.; Bueno, E.B.T.; De Moraes, Y.A.; Toledo, A.C.C.G.; Nakagaki, W.R.; Winkelstroter, L.K. Development and viability of probiotic orange juice supplemented by Pediococcus acidilactici CE51. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Santiago, V.; Aguil, I.; Schorn-García, D.; Ezenarro, J.; Rico, D.; Martín-Diana, A.B.; Anguera, M.; Abadias, M. Effects of Lacticaseibacillus casei fermentation on the physicochemical, nutritional, volatile, and sensory profile of synbiotic peach and grape juice during refrigerated storage. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2025, 5, 101002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, F.; Juan, B.; Espadaler-Mazo, J.; Capellas, M.; Huedo, P. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KABP051: Stability in Fruit Juices and Production of Bioactive Compounds During Their Fermentation. Foods 2024, 13, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yang, N.; Jiang, T.; Xu, H.; Lei, H. Fermentation of kiwifruit juice from two cultivars by probiotic bacteria: Bioactive phenolics, antioxidant activities and flavor volatiles. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, Z.; Ahmad, S.; Wani, S.M.; Rouf, M.A.; Bashir, I.; Sc, M. Probiotic-fortified fruit juices: Health benefits, challenges, and future perspective. Nutrition 2023, 115, 112154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imece, A.; Sengul, M.; Cetin, B.; Aktas, H. Effect of probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains on some properties of grapefruit juice and naringin. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 108, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nualkaekul, S.; Gurjot, S.; Dimitris, C. Survival of freeze dried Lactobacillus plantarum in instant fruit powders and reconstituted fruit juices. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Han, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Debittering and Antioxidant Activity of Fermented Grapefruit Juice with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1-1-2. Shipin Kexue/Food Sci. 2024, 45, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.M.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, V.D.; Bujna, E.; Dam, M.S.; Nguyen, Q.D. Changes in bitterness, antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of grapefruit juice fermented by Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains. Acta Aliment. 2020, 49, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irkin, R.; Dogan, S.; Degirmenioglu, N.; Diken, M.E.; Guldas, M. Phenolic content, antioxidant activities and stimulatory roles of citrus fruits on some lactic acid bacteria. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2015, 67, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nualkaekul, S.; Salmeron, I.; Charalampopoulos, D. Investigation of the factors influencing the survival of Bifidobacterium longum in model acidic solutions and fruit juices. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gous, A.G.S.; Almli, L.; Coetzee, V. Levels of a Grapefruit-Like Model Beverage on the Sensory Properties and Liking of the Consumer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Use of Naringinase to Modify the Sensory Quality of Foods and Increase the Bioavailability of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Immobilization of Naringinase from Aspergillus Niger on a Magnetic Polysaccharide Carrier. Molecules 2020, 25, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmins, S.D.; Henríquez, A.; Torres, C.; Wilson, L.; Flores, M.; Pio, E.; Jullian, D.; Urbano, B.; Braun-Galleani, S.; Ottone, C.; et al. Immobilization of Naringinase onto Polydopamine-Coated Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Juice Debittering Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Temiño, Y.; Ruíz, M.O.; Ortega, N.; Ramos-Gómez, S.; Busto, M.D. Immobilization of naringinase on asymmetric organic membranes: Application for debittering of grapefruit juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 73, 102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, L. Thirty Years of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG A Review. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdenelli, M.; Ghelefi, F.; Silvi, S.; Orpianesi, C.; Cecchini, C.; Cresci, A. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from human faeces. Eur. J. Nutr. 2009, 48, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Cen, Q.; Cui, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Sun, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A. Lactobacillus rhamnosus: An emerging probiotic with therapeutic potential for depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 211, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancib, N.; Nancib, A.; Boudjelal, A.; Benslimane, C.; Blanchard, F.; Boudrant, J. The effect of supplementation by different nitrogen sources on the production of lactic acid from date juice by Lactobacillus casei subsp. Rhamnosus. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 78, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güney, D.; Güngörmü, M. Development and Comparative Evaluation of a Novel Fermented Juice Mixture with Probiotic Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Hekmat, S. Development of Probiotic Fruit Juices Using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 Fortified with Short Chain and Long Chain Inulin Fiber. Fermentation 2018, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Naringinase Biosynthesis by Aspergillus niger on an Optimized Medium Containing Red Grapefruit Albedo. Molecules 2022, 27, 8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajdeo, K.; Harini, T.; Lavanya, K.; Fadnavis, N.W. Immobilization of pectinase on reusable polymer support for clarification of apple juice. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 99, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodakowska-Boczniewicz, J.; Garncarek, Z. Immobilization of naringinase from Penicillium decumbens on chitosan microspheres for debittering grapefruit juice. Molecules 2019, 24, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.B. Determination of Flavanones in Citrus Fruits. Anal. Chem. 1947, 19, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrzejewska, K.; Bogusławska-Wąs, E. Comparison of selected microbiological and biochemical parameters of kombucha beverages. Żywność. Nauk. Technol. Jakość 2020, 4, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczyńska, A. Methods for determining the antioxidant activity of bee honey. Bromatol. I Chem. Toksykol. 2009, 3, 870–874. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, N.F.F.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Bitterness reduction in grapefruit juice through active packaging. Packag. Technol. Sci. 1998, 11, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, P.; Arrieta, R.; Torres, C.; Guerrero, C.; Wilson, L. Amination of naringinase to improve citrus juice debittering using a catalyst immobilized on glyoxyl-agarose. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervert-Hernández, D.; Pintado, C.; Rotger, R.; Goñi, I. Stimulatory role of grape pomace polyphenols on Lactobacillus acidophilus growth. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 136, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarca, G.; Baytal, F. Effects of fermentation on the quality characteristics and biological activities of citrus juices. Process Biochem. 2023, 130, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruç, S.Ö.; Çakır, I. A research on production of fermented watermelon juice by probiotic culture. GIDA J. Food 2019, 44, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J. Effect of Six Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains on Physicochemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Activities and Sensory Properties of Fermented Orange Juices. Foods 2022, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, X.; Nong, J.; Zhao, G.; Xiao, X. One-pot biocatalytic synthesis and antioxidant activities of highly lipophilic naringin derivatives by using bi-functional whole-cells. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintsis, T. Lactic acid bacteria as starter cultures: An update in their metabolism and genetics. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouhandeh, H.; Zunumi Vahed, S.; Hejazi, M.S.; Hahaei, M.R.; Akbari Dibavar, M. Isolation and Phenotypic Characterization of Lactobacillus Species from Various Dairy Products. Curr. Res. Bacteriol. 2010, 3, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, U.D.S.; Science, L. Effect of inulin on the growth and metabolism of a probiotic strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in co-culture with Streptococcus thermophilus. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancib, A.; Nancib, N.; Meziane-Cherif, D.; Boubendir, A. Joint effect of nitrogen sources and B vitamin supplementation of date juice on lactic acid production by Lactobacillus casei subsp. rhamnosus. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helland, M.H.; Wicklund, T.; Narvhus, J.A. Growth and metabolism of selected strains of probiotic bacteria in maize porridge with added malted barley. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 91, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).