Abstract
This study investigates semantic text segmentation enhanced by large language model (LLM) embeddings. We assess how effectively embeddings capture semantic coherence and topic closure by integrating them into both classical clustering algorithms and a modified graph-based methods. In addition, we propose a simple magnetic clustering algorithm as a lightweight baseline. Experiments are conducted across multiple datasets and embedding models, with segmentation quality evaluated using the boundary segmentation metric. Results demonstrate that LLM embeddings improve segmentation accuracy, highlight dataset-specific difficulties, and reveal how contextual window size and embedding choice affect performance. These findings clarify the strengths and limitations of embedding-based approaches to segmentation and provide insights relevant to retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
1. Introduction
The task of text segmentation is to partition a text into sequential fragments that each exhibit high internal semantic coherence. This requires a representation of meaning that captures semantic similarity across sentences. In our study, we use vector representations, or embeddings, generated by modern pre-trained LLMs. Embeddings encode textual information into dense vectors, and several methods for constructing them exist, each with different assumptions and interaction mechanisms [1,2]. These differences give embedding methods distinct properties that affect their suitability for intelligent systems. For developers, analyzing such properties is essential—for example, assessing interpretability, the ability to generalize across domains, and the capacity to support downstream tasks [3].
It is also important to consider whether a given type of embedding depends strongly on vocabulary [4] or on domain [5] and to what extent similarity between vector representations correlates with human judgments, as well as in which semantic dimensions this occurs. Other relevant factors include the granularity of meaning units, the importance of long-range semantic connections, the role of segment linearity, and how contextual information is incorporated. In this regard, text segmentation—where strict evaluation metrics are available—provides a particularly suitable testing environment. Much research in this direction has focused on identifying well-defined metrics and developing methods for obtaining suitable representations [6].
Depending on the subject area for which segmentation is required, it can be the subject of separate studies [7], for example, whether the text system is used for dialogues, encyclopedic text, or a text-cleaning process or whether the system is supplemented with synthetic data. This spread of input data parameters can also introduce a number of features into the methods and can require fine-tuning of the hyperparameters of the algorithms.
As a starting point for evaluating segmentation methods, some studies use a baseline estimate based on random segmentation [8,9,10,11]. How close the obtained estimate is to the random baseline may be explained or may require additional methods and calculations. However, even if some segmentation algorithms show results close to random, such a baseline estimate can serve as a measure of the complexity of the dataset. In addition, it leaves the opportunity to determine the reliability and stability of the obtained results.
The choice of vector representation of text data can be significant for obtaining a qualitative assessment of working with text data. At the same time, other indicators, such as stability and reliability, may directly depend on how these embedding models are formed and used. Embedding models also have their own historical and logical continuity. Although deep embeddings have recently been unrivaled in terms of representation quality, the properties embedded in them often reflect many problematic issues. The choice of trade-off between the complexity of the model, its availability, focus, etc., is still a relevant and practical task [3].
In this study, we investigate the extent to which accurate text segmentation can be obtained using computationally light algorithms, provided that high-quality embeddings from large language models are available. This question is particularly relevant for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems [12,13], where the quality of retrieved evidence depends critically on how textual data is partitioned into coherent units. In large-scale corpora and real-time applications, segmentation enables the extraction of semantically complete fragments that can be efficiently indexed, embedded, and retrieved in response to user queries. Importantly, this need persists regardless of the increasing context window sizes in modern LLMs: excessive inclusion of irrelevant context reduces answer fidelity, while inadequate fragmentation omits crucial semantic cues. Hence, segmenting texts into units that balance informativeness, coherence, and length remains a fundamental step toward improving both retrieval accuracy and model interpretability [14]. Performing such segmentation in a computationally efficient manner, without compromising semantic completeness, thus represents a practical requirement for deploying RAG methods at scale.
This leads to the compilation of computational experiments; these experiments aim to assess the quality of segmentation obtainable from various datasets, embedding models, and machine learning methods that formalize the idea of semantic proximity in classification or clustering problems.
Another reason for the experiments is consideration of overfitting issues, which can inevitably arise in machine learning problems. Many models, especially those with a large number of trainable parameters, can be subject to overfitting. The overfitting effect for text analysis methods may be expressed in various forms (which result in the same visible form as a low score on validation/test sets for boundary errors) to answer such questions as corpus field dependency, which may be the case for deep segmentation models. Hence, independent downstream tasks, like the search for semantic boundaries or cohesion, could clarify this issue. Hence, both internal checks aimed at the reliability and quality of the model, as well as external ones for comparison with alternative solutions, are needed.
We note that semantically significant units have different names/terms in this area, often due to the methods used, but in general they have logically justified meanings (topic cohesion, semantic granularity of tokens, etc.). In this study, generally accepted terms for segments are used (the term “linearity” is omitted, since the greatest emphasis is placed on sentences as the main text unit of analysis). In some cases, cluster terms are used, since the segmentation methods employed are closely related to clustering methods.
In summary, in this research we first introduce a systematic evaluation of how large language model (LLM) embeddings support semantic text segmentation when combined with both lightweight clustering methods and graph-based approaches. Second, we propose and analyze a simple yet robust baseline algorithm—termed Magnetic clustering—which demonstrates that, given appropriate embeddings, computationally efficient procedures can achieve results comparable to more sophisticated methods. Third, we conduct an extensive set of experiments across six datasets with varying structural characteristics, using the boundary similarity metric as a principled evaluation criterion. This provides empirical insights into the role of embedding models, context size, and hyperparameter optimization in segmentation performance.
2. LLM Embedding Models
Table 1 presents the list of models and references selected for computational experiments. Although a wide range of LLM-based models is available [15,16], in this study, we restrict attention to models that have been specifically trained or optimized for embedding tasks rather than text generation. The selected models provide diversity in scale and design philosophy: from lightweight universal encoders to very large architectures with specialized training for semantic retrieval and multi-functionality. This diversity allows us to examine how universal versus task-specific embeddings capture semantic relations in segmentation. Preliminary experiments also showed that these models can consistently detect topic shifts in simple baseline scenarios, which motivated their use as the foundation for systematic evaluations in this study.

Table 1.
Summary of LLM-based embeddings used in the experiments [17].
3. Segmentation Algorithms
A number of algorithms were used to conduct computational experiments. A basic segmentation algorithm using local vector similarity was implemented. Since one of the main tasks of the study is to test the hypothesis of applicability of basic algorithms, we focused on the following well-established (classical) algorithms: [23] Spectral Clustering [24], Agglomerative Clustering [25], Affinity Propagation [26], and KMeans++ [27,28]. A comparative analysis with the published algorithm GraphSeg from [11] and with a variant that substitutes embedding-based distances in this method (GraphSegSM) was also conducted.
All segmentation algorithms in this study operate on a similarity matrix derived from sentence embeddings. Let denote a document consisting of n sentences, and let be the embedding vector of sentence produced by a given LLM model. We construct the similarity matrix using cosine similarity:
Because we consider linear segmentation [3], only entries close to the main diagonal of S are stored and used, corresponding to local sentence neighborhoods (see Figure 1). This matrix serves as the common input for all subsequent algorithms—both clustering-based and graph-based—ensuring comparability across methods. For computational efficiency all similarity matrices were precomputed.
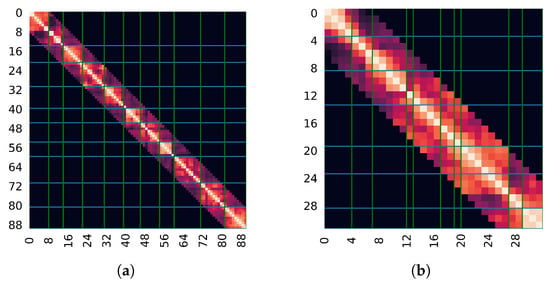
Figure 1.
Example of a heat map for the similarity matrix. Horizontal lines display the true segmentation, while vertical lines are the estimated clustering boundaries. Segmentation of sample texts from Abstracts (a) and PhilPapersAI (b) by Spectral Clustering.
3.1. Basic Segmentation Algorithms (Magnetic Clustering)
Unlike random segmentation for the baseline score shown in [8,9], our approach uses a basic segmentation algorithm to understand what an embedding metric can produce without large further investments. We call it Magnetic clustering because the basic principle of the algorithm “glues” adjacent text blocks together, analogous to a magnet. The direction of attraction is determined by the values of the similarity (proximity) matrix, taking into account the trainable parameters.
For the similarity matrix it is convenient to introduce an approximation for the values outside of the matrix indices:
In other words, coincides with the original entry inside the matrix, and outside the index range, it is approximated by the average of all entries lying on the diagonal with the same offset .
For every , the difference between the weighted similarities of the neighbors on the right and on the left is evaluated.
where represents the weights applied symmetrically to both sides of the position. from naturally defines a clustering partition. We say and are in the same cluster if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
- and have the same sign and
- and have different signs and
- For every belongs to the same cluster as or
In other words, the segment/clustering border is defined between positions such that and (e.g., Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Clustering defined by the segmentation algorithm partition. ‘+/−’ for .
The obtained represent only a tendency i-th unit toward left (negative) or right (positive) neighbors, and they may have high variance. Hence, as an intermediate step, a smoothing filter (function) has to be applied. This filter also works as an aggregator of semantic blocks of texts into higher-level semantically related blocks. For the given algorithm, the following parameters are subject to optimization: weights . We assume for , meaning that the relation between distant semantic elements can be neglected.
The proposed segmentation algorithm shows high stability with respect to parameter variations. For example, small changes in the optimal parameters do not result in notable changes in the final score. The same is true with respect to the filtering hyperparameters.
3.2. Adaptation of Clustering Algorithms for Segmentation
The following machine learning clustering algorithms [23] were used to assess the possibility of good clustering based on the calculated similarity matrix: Spectral Clustering, Agglomerative Clustering, Affinity Propagation, and KMeans++. An essential point is how the similarity matrix is constructed. The sentence embeddings generated by LLMs contain enough information for distinguishing the topic-centric scope of the texts. It is worth noting that different ways to compute the similarity matrix can be adapted. Preliminary computational results show that they do not yield advantages regarding the segmentation metrics. This can be explained by how the embedding models are trained. Our analysis indicates that cosine similarity provides the most stable form of similarity for this task.
For every algorithm, the width of the non-zero diagonal band is estimated as a hyperparameter per dataset. It corresponds to the level of granularity by which algorithms try to identify target segmentation blocks. Every applied algorithm has a specific parametric search space with three common parameters: , which is the number of sentences in the embedding (sliding window length of 1, 2, or 3 sentences); , which is the bandwidth of non-zero central diagonals in the similarity matrix; and , which is the embedding model from Table 1. The other adjustable parameters are defined by the specificity of algorithms: the mode for choosing the weights and filters in Magnetic clustering and the mode to evaluate the number of clusters in Spectral Clustering, Agglomerative Clustering, and KMeans++; the mode to determine the connectivity type in Agglomerative Clustering, and the mode to determine the damping factor in Affinity Clustering. Optimization was performed with the hyperparameter optimization library Optuna [29]. By setting the proper values (the optimum found) from the search space, the algorithm is adapted to dataset-specific characteristics.
3.3. Graph-Based Algorithms for Segmentation
Graph-based segmentation algorithms show promising concepts and results. We evaluate the method proposed in [11], which relies on composing graph cliques into a coherent segmentation structure. This approach introduces heuristics that estimate the similarity of sentences using word embeddings: it measures a fine-grained alignment of parsed sentence-unit embeddings weighted by information content, so nouns and verbs have higher weights. The algorithm produces a segmentation that relies on semantic similarity between sentences: it builds a graph structure that represents the semantic relatedness of text units: sentences are nodes, and edges connect semantically related sentences according to the heuristics. Segmentation is then derived by detecting the maximal cliques of semantically coherent sentences and merging them into larger units.
For this algorithm, the space of optimizable parameters is defined by two values: (1) The similarity threshold () is the cutoff value for adding an edge between two sentences in the semantic similarity graph. Only pairs of sentences whose similarity exceeds are connected. The parameter is considered in the real valued range of . (2) The minimum segment size () is the smallest number of sentences in a segment. Segments smaller than are merged with their most semantically related neighbor, thereby preventing the creation of very short and incoherent fragments. The parameter is considered in the integer range of .
The choice of parameter ranges reflects both methodological considerations and empirical observations across different datasets. The similarity threshold is limited to the above interval because values below this range tend to generate overly dense graphs in which nearly all sentences are connected, making clique detection uninformative, while values above this range produce graphs that are too sparse to form meaningful cliques. Similarly, the range for is set to in order to avoid trivial boundaries: segments shorter than three sentences often capture only noise or local fluctuations rather than genuine topic shifts, whereas segments longer than six sentences risk merging distinct semantic units and obscuring meaningful transitions. These ranges were selected to ensure robust behavior across different datasets, balancing sensitivity to fine-grained topical changes with stability against over-segmentation or under-segmentation.
We extend the original GraphSeg algorithm [11] into a modified framework, hereafter called GraphSegSM. The overall structure of GraphSegSM remains identical to GraphSeg: the text is represented as a graph where sentences are nodes, and edges connect semantically related sentences; segmentation is then obtained by detecting cliques of highly related sentences and merging them into larger coherent units. The key difference lies in how similarity between sentences is estimated. While the original GraphSeg algorithm relies on a heuristic combining word embeddings with information-content weighting, GraphSegSM replaces this heuristic with cosine similarity between sentence-level LLM embeddings. This modification ensures a consistent comparison with other clustering-based approaches in this study, which also operate on embedding-derived similarity matrices. To enable systematic evaluation, the search space of optimizable parameters in GraphSegSM is defined as the Cartesian product of the tuples , where and are as defined previously. This formulation allows GraphSegSM to preserve the structural advantages of the original graph-based method while leveraging the representational power of modern LLM embeddings.
4. Boundary Segmentation Metric
In this research, the boundary segmentation score is used as a primary evaluation metric [30]. Its advantages over various metrics such as Pk [31] and WinDiff [32] are discussed in [6]. The selection of the primary segmentation score allows us to compare in a formal way both embedding models and segmentation algorithms. The boundary segmentation score evaluates the proportion between wrong boundaries, near misses, and perfect matches:
A comparison of two segmentations to evaluate their difference involves the use of an edit distance function that produces sets of editing operations: insertion/deletion transpositions , and the set that specifies the matching boundary pairs. The numeric parameter defines how far a boundary can be misplaced to be counted as a near miss. That is, for boundary b from segmentation and from segmentation if there are no boundaries in their matching positions and , then . By default, it is set to two; hence only the pairs of boundaries whose positions differ by one are considered as “near misses", provided that their corresponding next positions are empty.
It is clear that for , the estimation score B penalizes a “near miss” half as much as each insertion/deletion editing pair. Also, it gives room for flexible approximations of segmentation with smooth borders. In our study it provides advantages for text segmentation since it is a normal situation that text-related topics vary smoothly, allowing variation in defining boundaries. Further, for some of the considered algorithms that evaluate text topics over neighboring contexts, this mechanism becomes inherited for defining proper evaluations with contextualized embeddings. Unlike cases where various boundary types are specified as in [30], we consider the case where the semantic difference between text blocks alone matters, and this difference defines a single boundary type. Hence, we remove from consideration the terms for penalizing substitutions between boundary types.
For a simple visualization of this metric, consider the example in Figure 3. For two segmentations, and , positional boundaries are denoted as . The boundaries and form a pair of matching boundaries, . The pair belongs to (a near miss), assuming . Finally, and are in , corresponding to two deletions and one insertion (boundary editing) [30].
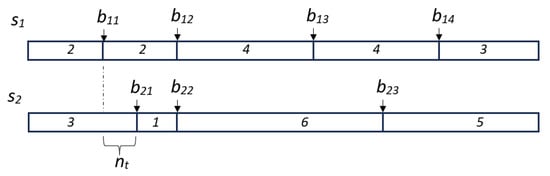
Figure 3.
Example of boundary segmentation.
5. Description of Datasets
To evaluate the quality of segmentation, it is wise to use different datasets that have different semantic characteristics. Based on the objectives of this study, it makes sense to consider datasets on which the algorithms described in the Section 3 are easy and convenient to use, and their characteristics reflect the variety of possible text fragments. An overview of the datasets used, together with their statistics, is given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of datasets.
We assume that there can be subjective (human perception-dependent) and objective segmentation with clearly expressed topic changes. For example, in the dataset from Wikipedia, there is a large number of border segments based on subjective ratings. In reality, these two types can be mixed as much as possible and may overlap. One of the reasons for using multiple datasets is a necessity to investigate the cases where subjective and objective boundaries coexist. We also included datasets with more objective boundaries, although in some cases the distinction is not always clear.
Below is a brief description of the datasets used.
5.1. Benchmarking Datasets in Text Segmentation Field
In this section, we describe classic datasets, which have been used repeatedly in the task of segmentation:
The Choi dataset [8] contains 922 artificial documents. Each of them is a set of segments (blocks) of sentences drawn from different sources. The segments are not related to each other, so as a rule, segmentation is relatively easy for many algorithms and typically yields high accuracy. Several studies have used this dataset for comparative segmentation evaluations, for example, see [33,34,35].
Manifesto consists of six fairly long texts of major political speeches [36,37]. It includes a human-generated segmentation according to strictly formed guidance. It is used to evaluate segmentation for semantic topic shifts and thematic changes [38,39].
Wiki-1024 contains texts from 1024 selected Wikipedia articles. Segmentation is determined by dividing the documents into sections and subsections. The original dataset has a large scale and makes it possible to train models with millions of parameters, such as deep networks of various architectures [10].
5.2. Datasets Generated in This Study
The following small datasets were created to increase the variety of text segmentation characteristics.
The Abstracts dataset is created by generating artificial documents and merging real abstracts of research articles into continuous texts. It is collected by a request for the online Scopus service (around 20k of abstracts) in the field of Information Retrieval. Segments are straightforward splits of documents by abstracts.
SMan was constructed in a similar way to the Abstracts dataset, but it uses random samples of Manifesto segments to generate artificial texts of political statements. Topics vary considerably due to mixing, though they generally follow the same slogan-like style.
PhilPapersAI is a selection of 336 articles on philosophy (in the field of modern philosophy of AI) based on papers from the philpapers.org archive. The archive is available at [40,41]. The files in the dataset were obtained in PDF format and had low parsing quality due to markup. With the OpenAI GPT-4o-mini LLM, 336 articles were restored and reprocessed with a breakdown by subsections. The texts processed by AI have a coherent and well-structured format. The LLM prompts required preserving the structure and style of the authors as accurately as possible.
These datasets are available at [42].
6. Experiments
Algorithm parameters were optimized using Optuna [29] (with a tree-structured hyperparameter search) for each dataset individually. The results obtained on independent test subsets are reported below.
During optimization, filtering and other parameters were adjusted to maximize the segmentation score, thereby aligning them with the task of identifying accurate boundaries corresponding to each dataset.
For independent testing, a portion of the dataset not involved in optimization was used. The results indicate that the scores remain consistent, showing that both filtering and other parameters were well adapted to the properties of each dataset. Boundary similarity scores are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Summary of results on test data. Higher boundary similarity scores correspond to better results.
Pk scores are shown in Table 4 for consistency, as this metric has good interpretability and appears frequently in segmentation studies.

Table 4.
Summary of results on test data. – corresponds to a random segmentation algorithm (picking segmentation boundaries at random). Lower scores correspond to better results.
7. Optimizable Parameters and Result Overview
It is important to identify non-trivial patterns in the results produced by machine learning algorithms. Accordingly, we explain the outcomes not only in terms of model efficiency but also with respect to complementary analytic measures, such as stability under different types of errors.
Texts in natural language often show a nested semantic structure. Even if an algorithm is capable of recognizing semantic closure, its parameters have to be tuned in order to align with the corresponding layer of the hierarchy. In other words, algorithm tuning refers to the process of identifying optimal hyperparameters that correspond to specific datasets and specific types of segmentation.
Comparing the heat maps in Figure 1 for text data from the artificial Abstracts dataset (a) and the natural Wiki dataset (b), it is easy to see the granularity of different levels in the second case. This granularity can be useful and of interest for some tasks, but it can also be an obstacle for others—for example, when identifying hierarchical semantics versus simplifying to a flat list of topics. This also leads to systematic errors on naturally segmented texts, as the smoothness of such texts introduces an advanced level of complexity.
The use of lightweight, computationally efficient machine learning algorithms increases the stability of results by enabling evaluation over batches of segmented texts. In our experiments, as shown in Table 4 and Table 5, the batch size varied between 100–300 texts. This approach helps to avoid overfitting and yields more dataset-oriented results. On the other hand, it decreases the resulting scores, since the adaptability of classical machine learning algorithms to the segmentation task may be relatively low.

Table 5.
Summary of results on model choice and context embedding sizes that achieved the highest scores. One, two, or three consecutive sentences were passed for the embedding (window length). Models a–d refer to the embedding models from Table 1.
Additionally, the stability of results can be evaluated via the stability of the corresponding optimal parameters—i.e., whether the hyperparameter search space has converged to a stable minimum. Verification experiments, as illustrated in Figure 4, can be conducted by evaluating parameters in the neighborhood of the possible minimum.

Figure 4.
Heat maps for optimal parameters. The number of sentences in the embedding (y-axis) and the width of the diagonal bandwidth in the similarity matrix (x-axis) are optimized by the boundary segmentation score. (a) Choi and (b) Abstracts.
Table 5 demonstrates several patterns regarding the embedding models used:
- Magnetic clustering resolves segmentation tasks well on simpler datasets (Choi and Abstracts) but performs poorly on more challenging cases where coherent blocks depend on human perception.
- Magnetic clustering results on PhilPapersAI indicate systematic errors, which can be interpreted in different ways.
- In the majority of cases, the nomic-embed model outperforms the others.
- Context size deeply affects most evaluations; LLM-based embeddings over two consecutive sentences generally provide higher scores.
- Our hypothesis on the applicability of basic algorithms is partially confirmed. With the help of simple (computationally efficient) algorithms, it is possible to obtain results comparable to those of computationally expensive ones, for example, those based on graph methods.
8. Concluding Remarks
This article set out to examine what kinds of analytical insights can be gained from vector-based text representations generated by LLMs in the task of distinguishing semantic patterns. By combining clustering techniques with graph-based approaches, we compared a range of embedding models and assessed how well they capture semantic relations and the internal closure of topics.
Our focus was on identifying both the strengths and the limitations of such representations when applied to text segmentation as an unsupervised task. Lightweight machine learning methods allowed us to highlight the extent to which segmentation quality depends not only on the underlying representation but also on the simplicity or sophistication of the algorithm applied. We further observed that contextual information can significantly reinforce semantic coherence. The research opens possibilities to link segmentation metrics more explicitly with different types of errors. While this extension lies beyond the present study, it points to a promising path for improving both evaluation methodology and segmentation performance.
In practical terms, the proposed approach may benefit RAG systems, where precise segmentation improves evidence retrieval and response fidelity. It is also relevant for downstream tasks such as automatic summarization, question answering, topic tracking, and document indexing in large-scale corpora, including scientific and legal texts. In these applications, accurate segmentation contributes directly to efficiency, reliability, and interpretability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.; methodology, A.K. and K.Y.; software, A.K.; validation, R.M. and A.K.; formal analysis, R.M., A.K. and K.Y.; investigation, A.K. and K.Y.; resources, A.K.; data curation, A.K. and K.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.; writing—review and editing, R.M. and A.K.; visualization, A.K.; supervision, R.M.; project administration, R.M.; funding acquisition, A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan (grant no. AP23486904).
Data Availability Statement
This research uses six datasets for text segmentation. The datasets are freely available via the Mendeley Data service at https://doi.org/10.17632/cj22rpfdbb.1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nguyen, D.Q. A survey of embedding models of entities and relationships for knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the Graph-Based Methods for Natural Language Processing (TextGraphs), Barcelona, Spain, 13 December 2020; Ustalov, D., Somasundaran, S., Panchenko, A., Malliaros, F.D., Hulpuș, I., Jansen, P., Jana, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kusner, M.J.; Blunsom, P. A Survey on Contextual Embeddings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.07278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghinassi, I.; Wang, L.; Newell, C.; Purver, M. Recent Trends in Linear Text Segmentation: A Survey. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; Al-Onaizan, Y., Bansal, M., Chen, Y.N., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; pp. 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toleu, A.; Tolegen, G.; Makazhanov, A. Character-based Deep Learning Models for Token and Sentence Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Turkic Languages Processing (TurkLang 2017), Kazan, Russia, 18–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Conneau, A.; Kiela, D.; Schwenk, H.; Barrault, L.; Bordes, A. Supervised Learning of Universal Sentence Representations from Natural Language Inference Data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1705.02364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, C. Evaluating Text Segmentation. Master’s Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Galley, M.; McKeown, K.R.; Fosler-Lussier, E.; Jing, H. Discourse Segmentation of Multi-Party Conversation. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Sapporo, Japan, 7–12 July 2003; pp. 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, F.Y.Y. Advances in domain independent linear text segmentation. In Proceedings of the 1st Meeting of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, WA, USA, 29 April–4 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Solbiati, A.; Heffernan, K.; Damaskinos, G.; Poddar, S.; Modi, S.; Calì, J. Unsupervised Topic Segmentation of Meetings with BERT Embeddings. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.12978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshorek, O.; Cohen, A.; Mor, N.; Rotman, M.; Berant, J. Text Segmentation as a Supervised Learning Task. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers), New Orleans, LO, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Walker, M., Ji, H., Stent, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavaš, G.; Nanni, F.; Ponzetto, S.P. Unsupervised Text Segmentation Using Semantic Relatedness Graphs. In Proceedings of the Fifth Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics, Berlin, Germany, 11–12 August 2016; Gardent, C., Bernardi, R., Titov, I., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ding, Y.; Ning, L.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Yin, D.; Chua, T.S.; Li, Q. A Survey on RAG Meeting LLMs: Towards Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’24, New York, NY, USA, 1–8 February 2024; pp. 6491–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, K.; Pan, J.; Bi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.10997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Portes, J.; Havens, S.; Zaharia, M.; Carbin, M. Long Context RAG Performance of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Adaptive Foundation Models: Evolving AI for Personalized and Efficient Learning, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, C.; Shen, T.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Hua, K.; Hu, W.; Tao, Z.; Ma, S. LLMs are Also Effective Embedding Models: An In-depth Overview. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2412.12591. [Google Scholar]
- Oro, E.; Granata, F.M.; Ruffolo, M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Embedding Models and LLMs for IR and QA Across English and Italian. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollama developers. Ollama Project. Available online: https://ollama.com/search?c=embedding (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum, Z.; Morris, J.X.; Duderstadt, B.; Mulyar, A. Nomic Embed: Training a Reproducible Long Context Text Embedder. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J. AnglE-optimized Text Embeddings. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.12871. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Shakir, A.; Koenig, D.; Lipp, J. Open Source Strikes Bread-New Fluffy Embeddings Model. 2024. Available online: https://www.mixedbread.com/blog/mxbai-embed-large-v1 (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Chen, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, P.; Luo, K.; Lian, D.; Liu, Z. BGE M3-Embedding: Multi-Lingual, Multi-Functionality, Multi-Granularity Text Embeddings Through Self-Knowledge Distillation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.03216. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.X.; Shi, J. Multiclass Spectral Clustering. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2003), Nice, France, 14–17 October 2003; IEEE Computer Society: Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, N.; Dubey, K.A.; Guruganesh, G.; Zaheer, M.; Ahmed, A.; McCallum, A.; Mergen, G.; Najork, M.; Terzihan, M.; Tjanaka, B.; et al. Scalable Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’21, Singapore, 14–18 August 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtlehner, C.; Sebag, M.; Zhang, X. Scaling analysis of affinity propagation. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 066102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. A k-means clustering algorithm. JSTOR Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussabayev, R.; Mladenovic, N.; Jarboui, B.; Mussabayev, R. How to Use K-means for Big Data Clustering? Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-Generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. In Proceedings of the The 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2623–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, C. Evaluating Text Segmentation using Boundary Edit Distance. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–9 August 2013; Schuetze, H., Fung, P., Poesio, M., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 1702–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Beeferman, D.; Berger, A.; Lafferty, J. Statistical Models for Text Segmentation. Mach. Learn. 1999, 34, 177–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevzner, L.; Hearst, M.A. A Critique and Improvement of an Evaluation Metric for Text Segmentation. Comput. Linguist. 2002, 28, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.; Hirst, G. Lexical cohesion computed by thesaural relations as an indicator of the structure of text. Comput. Linguist. 1991, 17, 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Branavan, S.; Barzilay, R.; Karger, D.R. Global Models of Document Structure using Latent Permutations. In Human Language Technologies: Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Boulder, CO, USA, 31 May–5 June 2009; Ostendorf, M., Collins, M., Narayanan, S., Oard, D.W., Vanderwende, L., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Hearst, M.A. Text Tiling: Segmenting Text into Multi-paragraph Subtopic Passages. Comput. Linguist. 1997, 23, 33–64. [Google Scholar]
- Budge, I.; Klingemann, H.D.; Volkens, A.; Bara, J.; Tanenbaum, E. Mapping Policy Preferences. Estimates for Parties, Electors, and Governments 1945–1998; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, P.; Franzmann, S.; Al-Gaddooa, D.; Burst, T.; Ivanusch, C.; Regel, S.; Riethmüller, F.; Volkens, A.; Weßels, B.; Zehnter, L. The Manifesto Data Collection. Manifesto Project (MRG/CMP/MARPOR). Version 2024a. 2024. Available online: https://manifesto-project.wzb.eu/datasets/MPDS2024a (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Riedl, M.; Biemann, C. TopicTiling: A Text Segmentation Algorithm based on LDA. In Proceedings of the ACL 2012 Student Research Workshop, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 8–14 July 2012; Cheung, J.C.K., Hatori, J., Henriquez, C., Irvine, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Beeferman, D.; Berger, A.; Lafferty, J. Text Segmentation Using Exponential Models. In Proceedings of the Second Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Providence, RI, USA, 1–2 August 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ostendorff, M. Dataset philpapers-2023-10-28. 2023. Available online: https://huggingface.co/datasets/malteos/philpapers-2023-10-28/tree/main/data (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Ostendorff, M.; Rehm, G. Efficient Language Model Training through Cross-Lingual and Progressive Transfer Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.09626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krassovitskiy, A. Six Small Datasets for Text Segmentation, 2025. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/cj22rpfdbb/1 (accessed on 7 October 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).