ProposalLaneNet: Sparse High-Quality Proposal-Driven Efficient Lane Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- •
- We make full use of the narrow and diverse structure of lane lines and propose a novel detection strategy: stepwise forward guidance detection through a reference starting point to a reference lane. Compared with the traditional starting point guidance, the reference generated by this strategy is more flexible and more consistent with the actual situation of the lane.
- •
- For the first time, we propose a novel strategy to remove element-level operations in the FPN structure, which fully uses the sparsity of lanes and reduces the network’s redundant computation.
- •
- To the best of our knowledge, this marks the first application of attention results as fusion feature weights for integrating multi-layer features in lane detection, effectively substituting the conventional 1:1 mechanical proportional fusion in the FPN structure. This method is more rational and practical, leveraging the inherent image features for fusion.
- •
- Experiments show that our method achieves just the right balance of speed and accuracy on top of CULane and TuSimple datasets; these datasets are widely used in the field of lane detection, realizing the state of the art in speed and accuracy.
2. Related Work
2.1. Segmentation-Based Methods
2.1.1. Traditional Semantic Segmentation
2.1.2. Grid Semantic Segmentation
2.1.3. Instance Segmentation
2.2. Detection-Based Methods
2.2.1. Keypoint-Based Lane Detection
2.2.2. Curve-Based Lane Detection
2.2.3. Proposal-Based Lane Detection
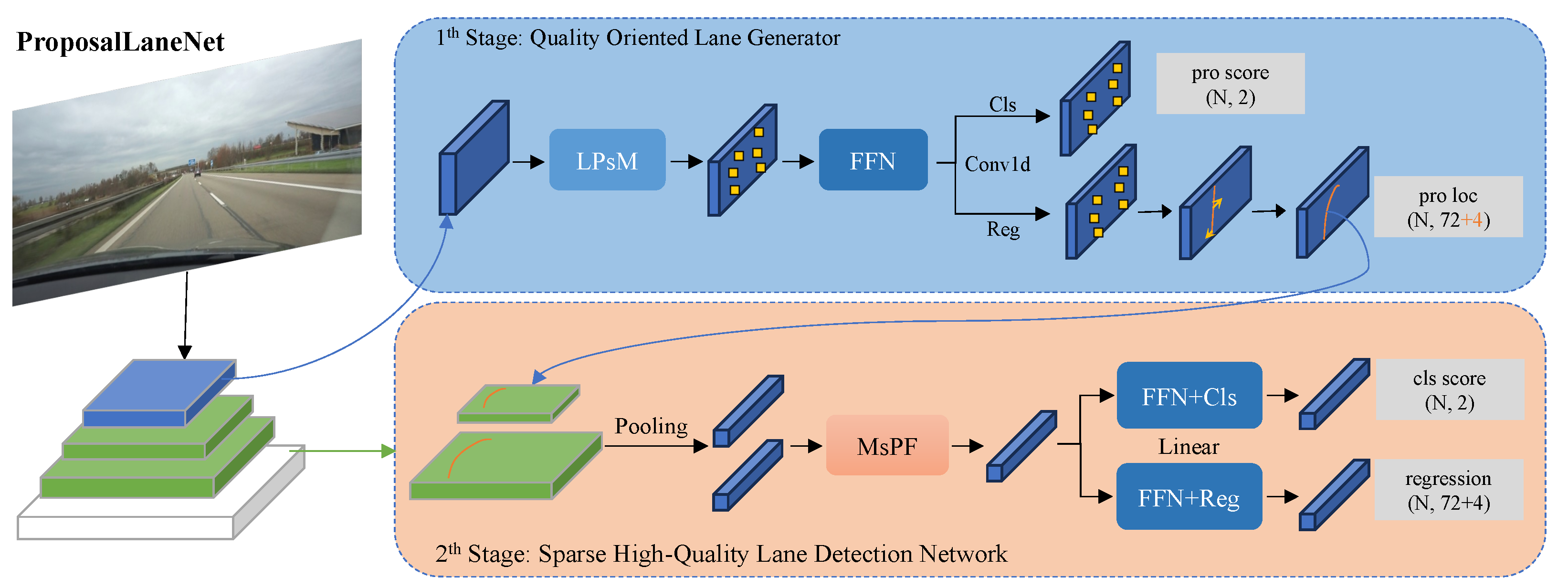
3. ProposalLaneNet
3.1. Overview
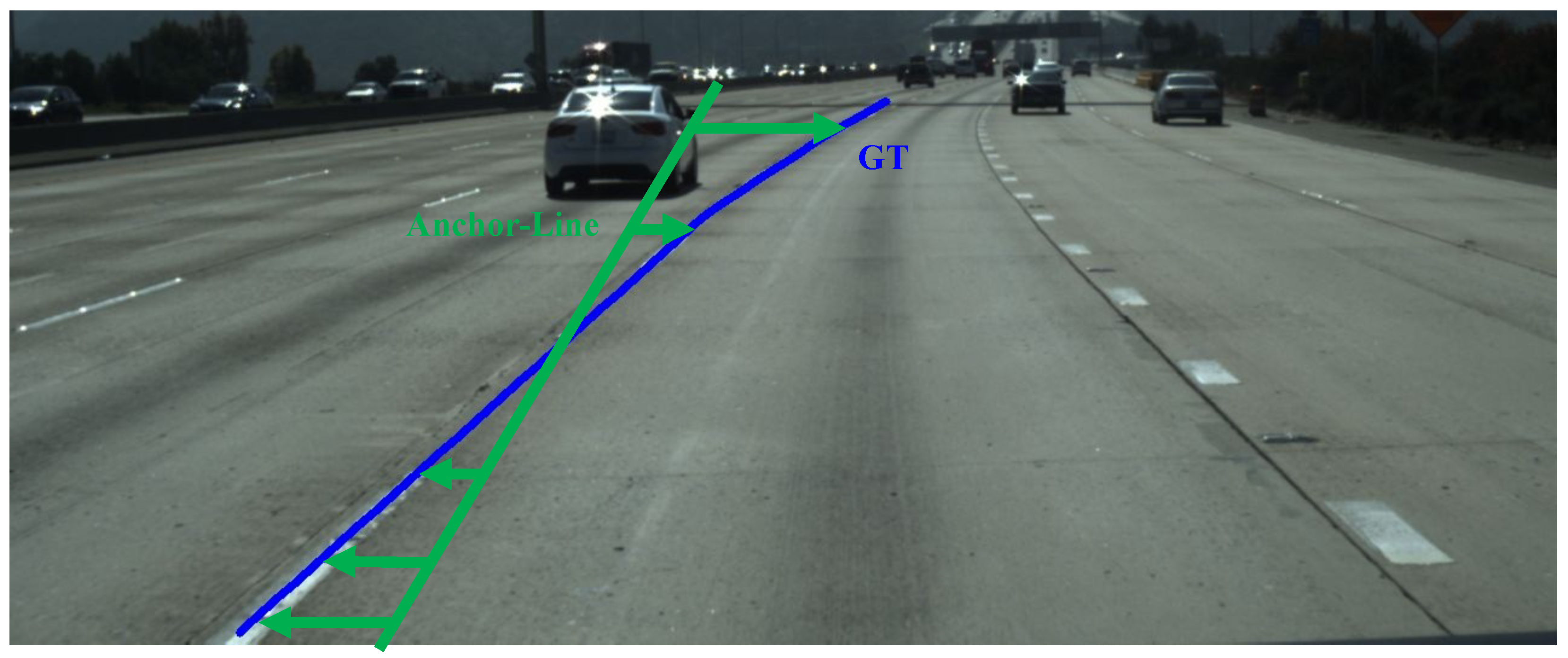
3.2. Quality Oriented Lane Reference
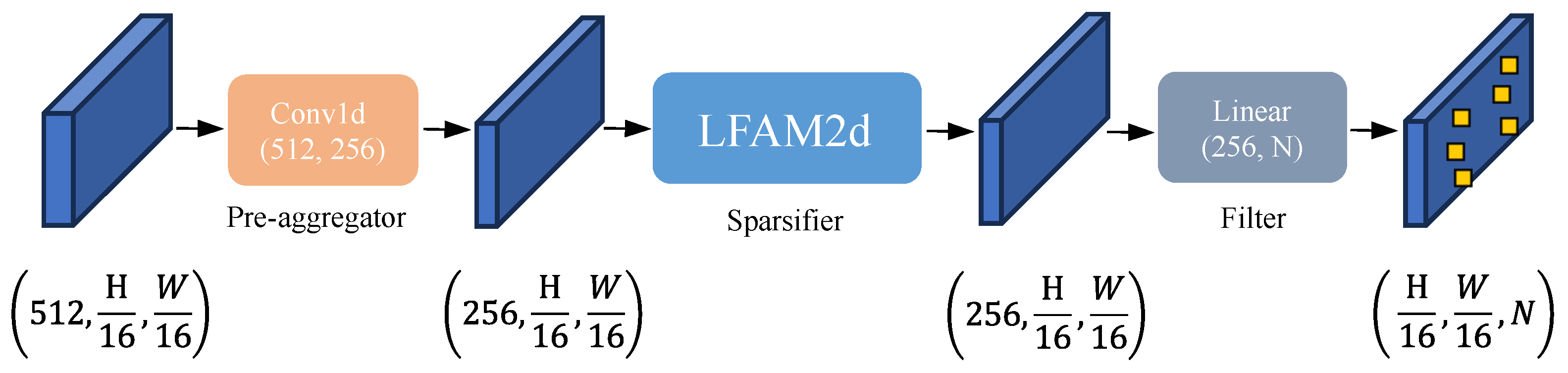
3.3. Lane Pre-Selection Mechanism
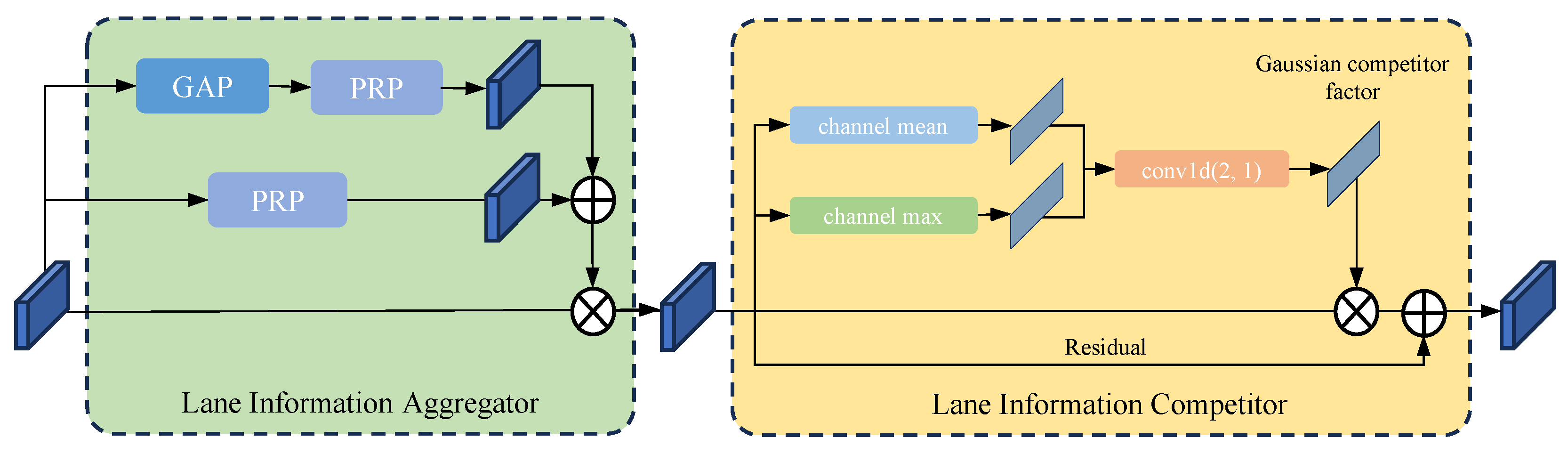
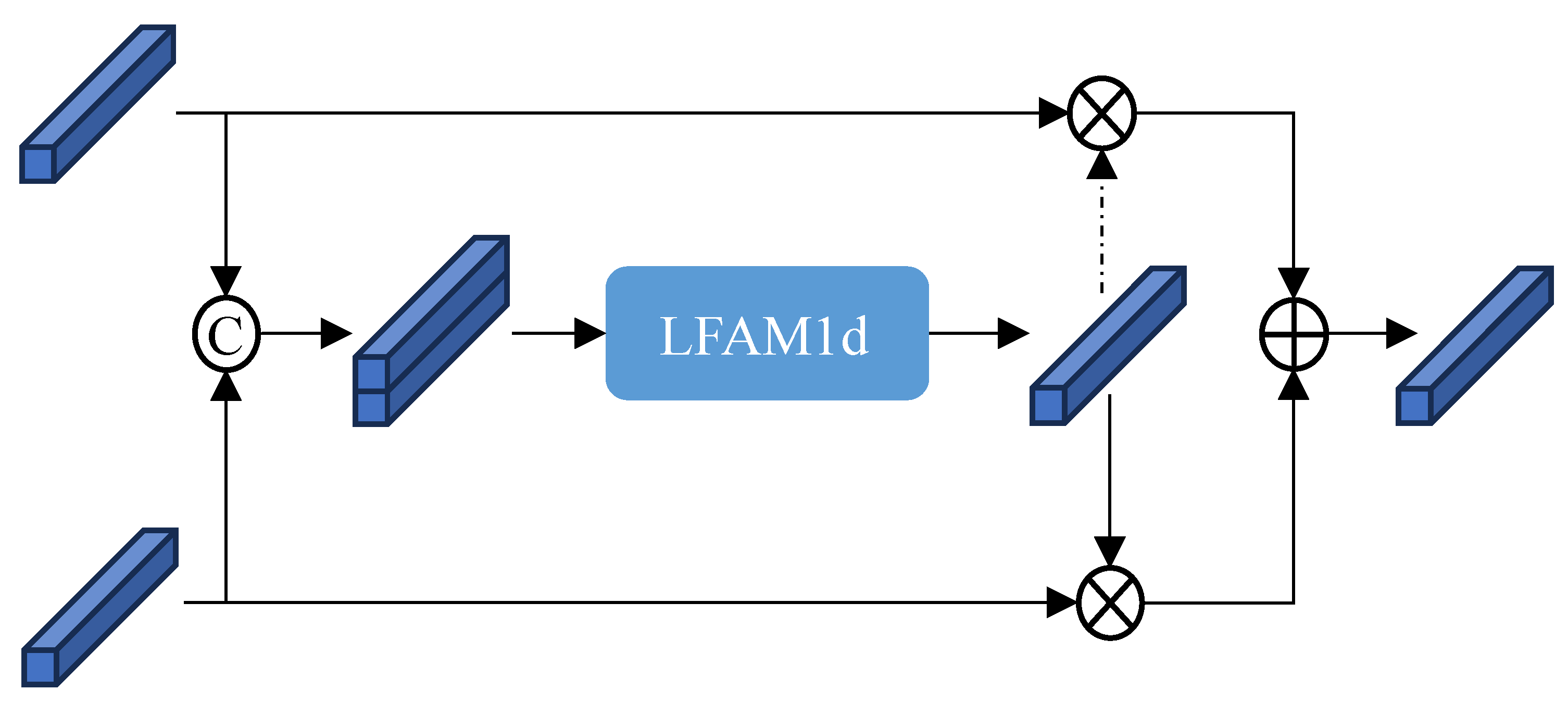
3.4. Lane Feature Attention Module
3.5. Multi-Scale Proposal Feature Fusion
3.6. Label Assignment and Loss Function
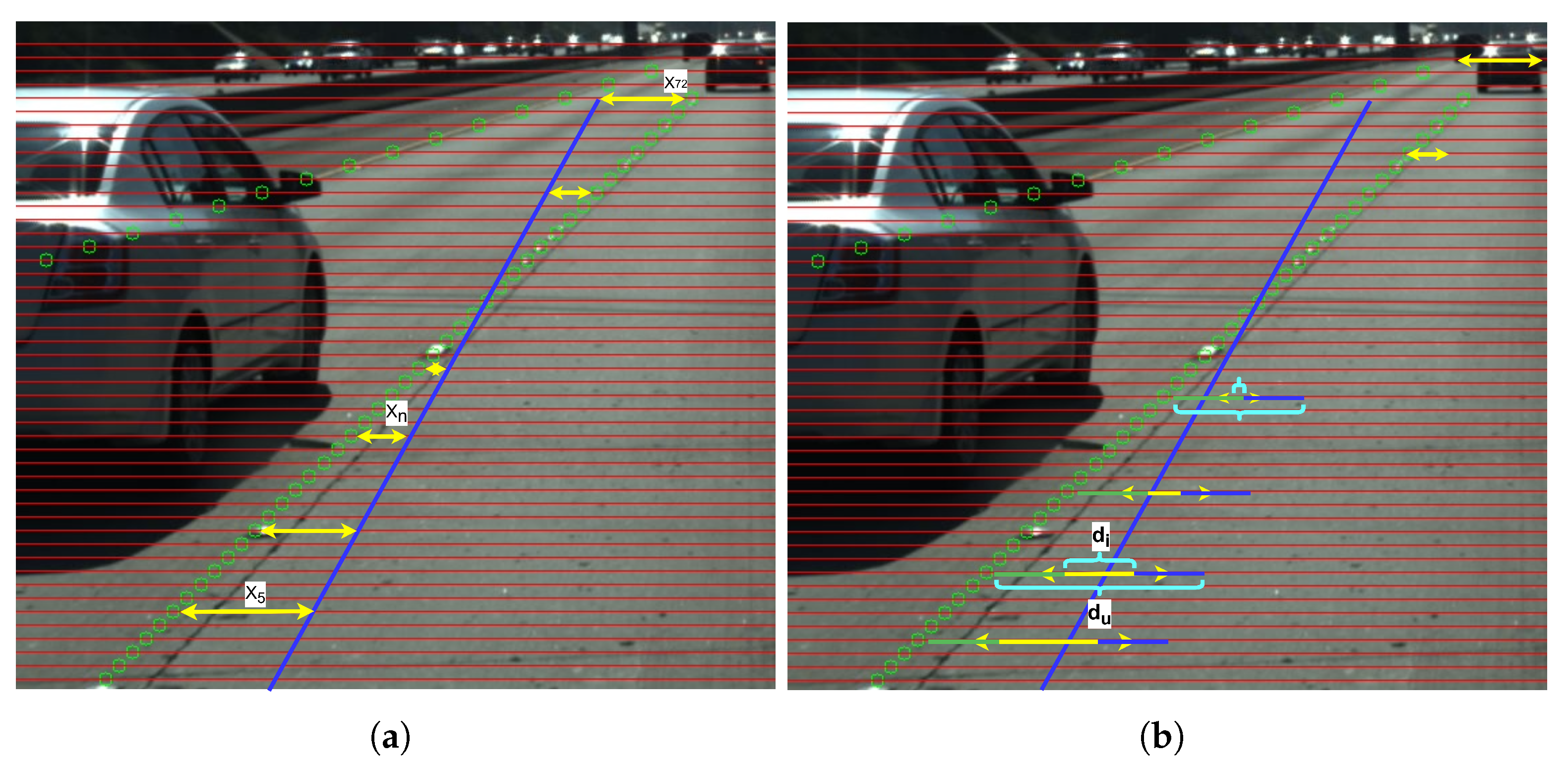
3.6.1. Definition of Lane Distance
3.6.2. Loss Function
3.6.3. Label Assigner
4. Experimental Settings
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. CULane
4.1.2. TuSimple
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1. Area-Based Evaluation Metrics
4.2.2. Distance-Based Evaluation Metrics
4.2.3. Model Inference Cost
4.3. Implementation Details
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Visualization Comparison
5.2. Performance Comparison with Classical Methods
5.3. Ablation Study
5.3.1. Ablation Study of Core Modules
5.3.2. Ablation Study of the High-Quality Proposal Generation Head On
5.3.3. Ablation Study on the Efficacy of Multi-Scale Proposal Fusion
5.3.4. Ablation Study on the Robustness of the Multi-Scale Proposal Fusion Method
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Ultra Fast Structure-Aware Deep Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Guo, S.; Tan, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, M.; Ma, L. Rethinking Efficient Lane Detection via Curve Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 22–24 June 2022; pp. 17041–17049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. CondLaneNet: A Top-to-down Lane Detection Framework Based on Conditional Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3753–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Cai, D.; He, X. CLRNet: Cross Layer Refinement Network for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–23 June 2022; pp. 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Ultra Fast Deep Lane Detection With Hybrid Anchor Driven Ordinal Classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, K.; Luo, J.; Wei, X.; Wei, X. Structure Guided Lane Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.05403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixão, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Keep your Eyes on the Lane: Real-time Attention-guided Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixão, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. PolyLaneNet: Lane Estimation via Deep Polynomial Regression. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Virtual, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 6150–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, S.; Hui, T.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Zhang, T. A Keypoint-based Global Association Network for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y. BSNet: Lane Detection via Draw B-spline Curves Nearby. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.06910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D.; Yuan, B.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Z. PETDet: Proposal Enhancement for Two-Stage Fine-Grained Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5602214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, T.; Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-End Object Detection with Learnable Proposals. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 14449–14458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving Into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Chen, X.; Fan, Z.; Zeng, G.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, J. Conditional DETR for Fast Training Convergence. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3631–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spatial as Deep: Spatial CNN for Traffic Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, D. RESA: Recurrent Feature-Shift Aggregator for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3547–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, W.; Qiu, Q. LaneNet: Real-Time Lane Detection Networks for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01726. [Google Scholar]
- Abualsaud, H.; Liu, S.; Lu, D.B.; Situ, K.; Rangesh, A.; Trivedi, M.M. LaneAF: Robust Multi-Lane Detection with Affinity Fields. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Lee, Y.; Azam, S.; Munir, F.; Jeon, M.; Pedrycz, W. Key Points Estimation and Point Instance Segmentation Approach for Lane Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 8949–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W. Focus on Local: Detecting Lane Marker from Bottom Up via Key Point. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 14117–14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, T.; Xiong, Z. End-to-end Lane Shape Prediction with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3693–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Line-CNN: End-to-End Traffic Line Detection With Line Proposal Unit. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Yang, W. ADNet: Lane Shape Prediction via Anchor Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 6381–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Liao, S.; Shao, L. Pixel-in-Pixel Net: Towards Efficient Facial Landmark Detection in the Wild. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3174–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Feng, W.; Fu, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, S. VIL-100: A New Dataset and A Baseline Model for Video Instance Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–18 October 2021; pp. 15661–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Qi, X.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L. DAB-DETR: Dynamic Anchor Boxes are Better Queries for DETR. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Gieseke, F.; Oehmcke, S.; Wu, Y.; Barnard, K. Attentional Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3559–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Pan, X.; Han, Y.; Song, S.; Huang, G. FLatten Transformer: Vision Transformer using Focused Linear Attention. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 5938–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TuSimple TuSimple/Tusimple-Benchmark: TuSimple Competitions for CVPR2017. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/TuSimple/tusimple-benchmark (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wang, D.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Deep Layer Aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Backbone | GFLOPs ↓ | FPS ↑ | GPU (TFLOPS) | Eff. | Total (%) ↑ | Normal (%) ↑ | Crowd (%)↑ | Dazzle (%) ↑ | Shadow (%) ↑ | No Line (%) ↑ | Arrow (%) ↑ | Curve (%)↑ | Cross (%) ↓ | Night (%) ↑ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Lane Segmentation | ||||||||||||||||
| SCNN [16] | (Ref. AAAI2018) | VGG16 | 328.4 | 7.5 | 5.1 | 1.47 | 71.60 | 90.60 | 69.70 | 58.50 | 66.90 | 43.40 | 84.10 | 64.40 | 1990 | 66.10 |
| RESA [17] | (Ref. AAAI2021) | ResNet-34 | 41.0 | 45.5 | 13.45 | 3.39 | 74.50 | 91.90 | 72.40 | 66.50 | 72.00 | 46.30 | 88.10 | 68.60 | 1896 | 69.80 |
| RESA [17] | (Ref. AAAI2021) | ResNet-50 | 43.0 | 35.7 | 13.45 | 2.65 | 75.30 | 92.10 | 73.10 | 69.20 | 72.80 | 47.70 | 88.30 | 70.30 | 1503 | 69.90 |
| Instance & Grid Lane Segmentation | ||||||||||||||||
| UFLD [1] | (Ref. ECCV2020) | ResNet-18 | 8.4 | 323 | 10.6 | 30.47 | 68.40 | 87.70 | 66.00 | 58.40 | 62.80 | 40.20 | 81.00 | 57.90 | 1743 | 62.10 |
| UFLD [1] | (Ref. ECCV2020) | ResNet-34 | 16.9 | 175 | 10.6 | 16.51 | 72.30 | 90.70 | 70.20 | 59.50 | 69.30 | 44.40 | 85.70 | 69.50 | 2037 | 66.70 |
| LaneAF [19] | (Ref. LRA2021) | ERFNet | 22.2 | 24 | 10.6 | 2.26 | 75.63 | 91.10 | 73.32 | 69.71 | 75.81 | 50.62 | 86.86 | 65.02 | 1844 | 70.90 |
| LaneAF [19] | (Ref. LRA2021) | DLA-34 | 23.6 | 20 | 10.6 | 1.89 | 77.41 | 91.80 | 75.61 | 71.78 | 79.12 | 51.38 | 86.88 | 72.70 | 1360 | 73.03 |
| CondLaneNet [3] | (Ref. ICCV2021) | ResNet-18 | 10.2 | 220 | 10.1 | 21.78 | 78.14 | 92.87 | 75.79 | 70.72 | 80.01 | 52.39 | 89.37 | 72.40 | 1364 | 73.23 |
| CondLaneNet [3] | (Ref. ICCV2021) | ResNet-34 | 19.6 | 152 | 10.1 | 15.05 | 78.74 | 93.38 | 77.14 | 71.17 | 79.93 | 51.85 | 89.89 | 73.88 | 1387 | 73.92 |
| CondLaneNet [3] | (Ref. ICCV2021) | ResNet-101 | 44.8 | 58 | 10.1 | 5.74 | 79.48 | 93.47 | 77.44 | 70.93 | 80.91 | 54.13 | 90.16 | 75.21 | 1201 | 74.80 |
| UFLDv2 [5] | (Ref. TPAMI2022) | ResNet-18 | - | 330 | 35.6 | 9.27 | 74.7 | 91.7 | 73.0 | 64.6 | 74.7 | 47.2 | 87.6 | 68.7 | 1998 | 70.2 |
| UFLDv2 [5] | (Ref. TPAMI2022) | ResNet-34 | - | 165 | 35.6 | 4.63 | 75.9 | 92.5 | 74.9 | 65.7 | 75.3 | 49.0 | 88.5 | 70.2 | 1864 | 70.6 |
| Keypoint-Based Lane Detection | ||||||||||||||||
| FOLOLane [21] | (Ref. CVPR2021) | ERFNet | - | 40 | 14.0 | 2.86 | 78.80 | 92.70 | 77.80 | 75.20 | 79.30 | 52.10 | 89.00 | 69.40 | 1569 | 74.50 |
| GANet-S [9] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-18 | 21.27 * | 153 | 14.0 | 10.93 | 78.79 | 93.24 | 77.16 | 71.24 | 77.88 | 53.59 | 89.62 | 75.92 | 1240 | 72.75 |
| GANet-M [9] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-34 | 30.72 * | 127 | 14.0 | 9.07 | 79.39 | 93.73 | 77.92 | 71.64 | 79.49 | 52.63 | 90.37 | 76.32 | 1368 | 73.67 |
| GANet-L [9] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-101 | 89.45 * | 63 | 14.0 | 4.50 | 79.63 | 93.67 | 78.66 | 71.82 | 78.32 | 53.38 | 89.86 | 77.37 | 1352 | 73.85 |
| Curve-Based Lane Detection | ||||||||||||||||
| BézierLaneNet [2] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-18 | 7.5 * | 213 | 13.4 | 15.90 | 73.67 | 90.22 | 71.55 | 62.49 | 70.91 | 45.30 | 84.09 | 58.98 | 996 | 68.70 |
| BézierLaneNet [2] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-34 | 15.82 * | 150 | 13.4 | 11.19 | 75.57 | 91.59 | 73.20 | 69.20 | 76.74 | 48.05 | 87.16 | 62.45 | 888 | 69.90 |
| BSNet [10] | (Ref. ARXIV2023) | ResNet-18 | - | 197 | 10.6 | 18.58 | 79.64 | 93.46 | 77.93 | 74.25 | 81.95 | 54.24 | 90.05 | 73.62 | 1400 | 75.11 |
| BSNet [10] | (Ref. ARXIV2023) | ResNet-34 | - | 133 | 10.6 | 12.55 | 79.89 | 93.75 | 78.01 | 76.65 | 79.55 | 54.69 | 90.72 | 73.99 | 1445 | 75.28 |
| BSNet [10] | (Ref. ARXIV2023) | ResNet-101 | - | 48 | 10.6 | 4.53 | 80.00 | 93.75 | 78.44 | 74.07 | 81.51 | 54.83 | 90.48 | 74.01 | 1255 | 75.12 |
| BSNet [10] | (Ref. ARXIV2023) | DLA-34 | - | 119 | 10.6 | 11.23 | 80.28 | 93.87 | 78.92 | 75.02 | 82.52 | 54.84 | 90.73 | 74.71 | 1485 | 75.59 |
| Proposal-Based Lane Detection | ||||||||||||||||
| LaneATT [7] | (Ref. CVPR2021) | ResNet-18 | 9.3 | 250 | 13.4 | 18.66 | 75.13 | 91.17 | 72.71 | 65.82 | 68.03 | 49.13 | 87.82 | 63.75 | 1020 | 68.58 |
| LaneATT [7] | (Ref. CVPR2021) | ResNet-34 | 18.0 | 171 | 13.4 | 12.76 | 76.68 | 92.14 | 75.03 | 66.47 | 78.15 | 49.39 | 88.38 | 67.72 | 1330 | 70.72 |
| LaneATT [7] | (Ref. CVPR2021) | ResNet-122 | 70.5 | 26 | 13.4 | 1.94 | 77.02 | 91.74 | 76.16 | 69.47 | 76.31 | 50.46 | 86.29 | 64.05 | 1264 | 70.81 |
| CLRNet [4] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-18 | 11.9 | 102 * | 7.76 | 13.14 | 79.58 | 93.30 | 78.33 | 73.71 | 79.66 | 53.14 | 90.25 | 71.56 | 1321 | 75.11 |
| CLRNet [4] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-34 | 21.5 | 68 * | 7.76 | 8.76 | 79.73 | 93.49 | 78.06 | 74.57 | 79.92 | 54.01 | 90.59 | 72.77 | 1216 | 75.02 |
| CLRNet [4] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | ResNet-101 | 42.9 | 46 | 10.6 | 4.34 | 80.13 | 93.85 | 78.78 | 72.49 | 82.33 | 54.50 | 89.79 | 75.57 | 1262 | 75.51 |
| CLRNet [4] | (Ref. CVPR2022) | DLA-34 | 18.5 | 66 * | 7.76 | 8.51 | 80.47 | 93.73 | 79.59 | 75.30 | 82.51 | 54.58 | 90.62 | 74.13 | 1155 | 75.37 |
| ADNet [24] | (Ref. ICCV2023) | ResNet-18 | - | 87 | 35.6 | 2.44 | 77.56 | 91.92 | 75.81 | 69.39 | 76.21 | 51.75 | 87.71 | 68.84 | 1133 | 72.33 |
| ADNet [24] | (Ref. ICCV2023) | ResNet-34 | - | 77 | 35.6 | 2.16 | 78.94 | 92.90 | 77.45 | 71.71 | 79.11 | 52.89 | 89.90 | 70.64 | 1499 | 74.78 |
| ProposalLaneNet | ResNet-18 | 9.88 * | 135 * | 7.76 | 17.40 | 80.09 | 93.50 | 78.66 | 72.76 | 79.76 | 53.01 | 90.40 | 71.77 | 818 | 75.49 | |
| ProposalLaneNet | ResNet-34 | 19.33 * | 93 * | 7.76 | 11.98 | 80.52 | 93.77 | 78.84 | 73.53 | 84.12 | 54.19 | 90.79 | 72.71 | 1054 | 75.83 | |
| ProposalLaneNet | DLA-34 | 16.27 * | 83 * | 7.76 | 10.70 | 81.02 | 93.90 | 79.92 | 75.32 | 83.85 | 55.47 | 90.24 | 74.27 | 964 | 76.24 | |
| ProposalLaneNet | DLA-34 | 16.27 * | 83 * | 7.76 | 10.70 | 81.35 | 94.14 | 80.48 | 76.75 | 84.46 | 57.51 | 90.70 | 76.15 | 1335 | 76.69 | |
| Method | Backbone | F1-Measure ↑ | Accuracy ↑ | False Positives ↓ | False Negatives ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RESA | ResNet34 | 96.93 | 96.82 | 3.63 | 2.48 |
| PolyLaneNet | EfficientNetB0 | 90.62 | 93.36 | 9.42 | 9.33 |
| E2E | ERFNet | 96.25 | 96.02 | 3.21 | 4.28 |
| UFLD | ResNet34 | 88.02 | 95.86 | 18.91 | 3.75 |
| UFLDv2 | ResNet34 | 96.22 | 95.56 | 3.18 | 4.37 |
| SGNet | ResNet34 | - | 95.87 | - | - |
| LaneATT | ResNet34 | 96.77 | 95.63 | 3.53 | 2.92 |
| CondLaneNet | ResNet101 | 97.24 | 96.54 | 2.01 | 3.50 |
| FOLOLane | ERFNet | 96.59 | 96.92 | 4.47 | 2.28 |
| ADNet | ResNet18 | 96.90 | 96.23 | 2.91 | 3.29 |
| ProposalLaneNet | ResNet18 | 97.74 | 96.34 | 2.82 | 1.72 |
| Baseline | LPsM | MsPF | AWFM | F1-Measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 74.70 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | 78.92 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 80.23 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 81.02 |
| Study | Shared Features | Decoupled Features | Conv Stacks | Linear Layers | Auxiliary Segmentation | F1-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | ✓ | 76.15 | ||||
| ✓ | ✓ | 76.78 | ||||
| ✓ | ✓ | 77.73 | ||||
| ✓ | ✓ | 77.19 | ||||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 78.92 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 78.27 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 77.82 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 78.52 |
| Method | F1@50 (%) | Flops (GFLOPs) | Params (M) | Input-Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADDF | 79.48 | 15.86 | 15.72 | (320, 800) |
| FPNX | 79.59 | 17.8 | 18.22 | (320, 800) |
| MsPFX | 80.75 | 15.86 | 15.74 | (320, 800) |
| Baseline + LsPM | w.o.seg | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 78.92 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 76.82 |
| ProposalLaneNet | w.o.seg | F1 (%) |
| ✓ | 81.02 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 80.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Tao, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, D. ProposalLaneNet: Sparse High-Quality Proposal-Driven Efficient Lane Detection. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10803. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910803
Chen B, Tao L, Zhao W, Li D. ProposalLaneNet: Sparse High-Quality Proposal-Driven Efficient Lane Detection. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10803. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910803
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Baowang, Liufeng Tao, Wenjie Zhao, and Dengfeng Li. 2025. "ProposalLaneNet: Sparse High-Quality Proposal-Driven Efficient Lane Detection" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10803. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910803
APA StyleChen, B., Tao, L., Zhao, W., & Li, D. (2025). ProposalLaneNet: Sparse High-Quality Proposal-Driven Efficient Lane Detection. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10803. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910803






