Abstract
A critical factor contributing to the burden of childhood asthma is the lack of effective self-management in homecare settings. Artificial intelligence (AI) and lung sound monitoring could help address this gap. Yet, existing AI-driven auscultation tools focus on wheeze detection and often rely on subjective human labels. To improve the early detection of asthma worsening in children in homecare setting, we trained and evaluated a Deep Learning model based on spirometry-labelled lung sounds recordings to detect asthma exacerbation. A single-center prospective observational study was conducted between November 2020 and September 2022 at a tertiary pediatric pulmonology department. Electronic stethoscopes were used to record lung sounds before and after bronchodilator administration in outpatients. In the same session, children also underwent spirometry, which served as the reference standard for labelling the lung sound data. Model performance was assessed on an internal validation set using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. A total of 16.8 h of lung sound recordings from 151 asthmatic pediatric outpatients were collected. The model showed promising discrimination performance, achieving an AUROC of 0.763 in the training set, but performance in the validation set was limited (AUROC = 0.398). This negative result demonstrates that acoustic features alone may not provide sufficient diagnostic information for the early detection of asthma attacks, especially in mostly asymptomatic outpatients typical of homecare settings. It also underlines the challenges introduced by differences in how digital stethoscopes process sounds and highlights the need to define the severity threshold at which acoustic monitoring becomes informative, and clinically relevant for home management.
1. Introduction
Asthma self-management in homecare settings is a complex and challenging task for children and their parents. Effective symptom monitoring and timely adjustment of treatment require a high level of autonomy and experience [1,2]. Children and their caregivers often struggle to recognize early signs of asthma exacerbation, leading to underestimation of disease severity [2]. As a result, many tolerate high levels of daily symptoms, impacting their quality of life and increasing reliance on bronchodilators [1,3]. Inadequate or delayed recognition and management of exacerbations can result in more severe outcomes, including increased treatment side effects, repeated attacks, accelerated lung function decline, and life-threatening events [1,4]. Early detection and intervention at home could significantly reduce these risks [2,4].
In children, asthma is diagnosed primarily on clinical grounds and confirmed by means of spirometry. Unlike in adults, where non-allergic phenotypes are frequent and immunological profiling is often required, pediatric asthma is predominantly associated with atopy (88% of pediatric patients) [5]. Thus, diagnosis in children relies less on immunological parameters and more on clinical features, auscultation, and lung function assessment, such as spirometry [5].
Poorly controlled asthma is defined by clinical criteria such as frequent symptoms, reliever use, and exacerbations that play a crucial role in clinical assessment. These include wheezing or diminished breath sounds detected by means of auscultation [6]. Wheezing, in particular, is a critical component of clinical scoring systems used to guide decision-making during asthma exacerbations [7]. An automatic tool capable of monitoring these sounds in home settings could transform asthma management by enabling early intervention.
The growing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine offers promising solutions in the diagnosis, management, and treatment of respiratory pathologies [8,9]. AI has shown impressive success in diagnosing respiratory diseases, sometimes outperforming physicians [10]. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) are key components of AI that allow computers to mimic human cognitive tasks. While ML involves human-guided training and improvement through experience, DL requires no human intervention during training, extracting insights directly from raw data [10,11]. Several studies have demonstrated the potential of ML and DL for automatic lung sound analysis [12,13]. However, most of these studies rely on preliminary human-labelled data, which can induce bias and human error into prediction models [11,14,15]. Importantly, no existing studies have used spirometry, the gold standard for asthma diagnosis, to label these data [15,16].
This study aimed to enhance the early detection of asthma worsening in children at home, given the lack of reliable monitoring tools. By training a deep learning model on lung sounds labelled with spirometry, we aimed to provide an objective marker of airway obstruction that could support timely orientation and care and help reduce the short- and long-term complications of asthma.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Consideration
This observational, prospective, single-center study was conducted at the outpatient pediatric pulmonology unit of the Geneva University Hospitals (HUG) (Geneva, Switzerland), a tertiary care center in Switzerland, between November 2020 and September 2022. The study received approval from SwissEthics (study number 2019-01238). Written informed consent was obtained from all parents and assent from children aged ≥12 years.
2.2. Participants
We consecutively included children and adolescents aged 7 to 16 years with a prior diagnosis of asthma or a history of wheezing episodes suggestive of asthma, who were attending routine follow-up visits. We deliberately focused on outpatients to capture a population of asthmatic children with a low symptom profile. Participants with congenital heart disease or any chronic bronchopulmonary condition other than asthma were excluded. Spirometry tests were performed during a single outpatient visit for most participants; however, a subset returned for additional visits as necessitated by disease monitoring, contributing more than one spirometry record.
We did not implement techniques such as dropout or early stopping, since data were collected at a single visit per patient and the risk of overfitting related to repeated measures was not present in our design.
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Digital Lung Auscultation
Digital lung auscultation recordings were obtained utilizing two digital stethoscopes: the 3M™ Littmann® Stethoscope (3M Company, St.Paul, Minnesota, United States) with StethAssist® v.1.3 software (Solventum, Maplewood, Minnesota, United States), and the 3M™ Littmann® CORE Digital Stethoscope (3M Company, St.Paul, Minnesota, United States) with Eko™ software (Eko Health, Emeryville, California, United States). Lung sounds were recorded at eight thoracic sites (two anterior, two lateral, and four posterior) for 30 s per site, during two sessions (Figure 1), immediately after the first spirometry test and again 10 min after administration of salbutamol (4 × 100 μg). All files were saved in WAV format.
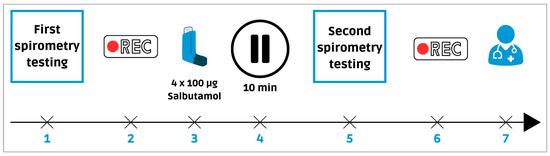
Figure 1.
Sequence of digital lung auscultation and spirometry recordings. Legend: (1) First spirometry test. (2) First digital lung sounds recording. (3) Bronchodilator administration. (4) 10 min break. (5) Second spirometry test. (6) Second recording. (7) Follow-up consultation with a pulmonologist.
All recordings were obtained in the same environment using the same protocol, which helps reduce variability and the risk of overfitting. Simultaneous use of both devices was attempted; however, the CORE stethoscope was favored when dual recordings were impracticable, owing to its superior sound amplification and noise-cancellation features.
2.3.2. Collection of Demographic and Clinical Data
During the first recording, as presented in Table 1, we collected demographic (age and sex) and clinical data (symptoms, medical history, and treatments) and Pediatric Respiratory Assessment Measure (PRAM) with Asthma Control Test (ACTp) scores [8,17]. All data were managed using the REDCap system hosted at the HUG [18,19].

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics in the case and control groups.
2.3.3. Spirometry Testing
Spirometry was performed using the Micro 5000 Spirometer (Medilan SA, Steinhausen, Switzerland). For each patient, the highest result of three independent measurements of forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and the FEV1/FVC ratio was recorded. Predicted values were adjusted for ethnicity, age, body height, and sex, using Global Lung Initiative (GLI) reference standards [20,21]. Each patient’s lung sound recording was matched to the corresponding spirometry test result, labelled as either “pathological for asthma” or “normal”, following the European Respiratory Society (ERS) guidelines [21]. Pathological results were defined as FEV1/FVC z-score < −1.64 (below the 5th percentile) or FEV1 z-score < −1.64, with a ≥10% improvement in FEV1 or FVC after bronchodilator inhalation [21].
2.4. Algorithm Development and Diagnostic Model
The asthma prediction model was based on the DeepBreath algorithm, developed by Heitmann et al. [13]. This deep learning model processes digital audio recordings and outputs the probability of asthma. Audio recordings were divided into non-overlapping 5 s sequences, independently presented to the model. During training, performance was assessed based on these 5 s splits. Audio recordings from both stethoscopes were processed similarly. The cohort was split into training (60%), validation (20%), and test (20%) sets. The training set was used to adjust the model parameters, while the validation set evaluated hyperparameter adjustments and assessed performance.
2.4.1. Preprocessing and Model Training Details
The methodology applied in this study builds upon the framework established by Heitmann et al., adapting their approach to our dataset and context [13].
2.4.2. Preprocessing: Spectral Transformation
Digital lung auscultations were converted to log-mel spectrograms using the torchaudio library, closely following the preprocessing steps described by Heitmann et al. [13]. Audios were segmented with a Hann window of 256 samples and a hop length of 64 samples, corresponding to 64 ms windows with a 16 ms overlap at a 4000 Hz sampling rate. The resultant magnitude spectra between 250 and 750 Hz were mapped onto 32 mel frequency bands and converted to the logarithmic scale, focusing on this frequency range to reduce environmental noise. Each 5 s audio recording resulted in a log-mel spectrogram of dimensions 32 × 313 [13].
Before being fed into the convolutional neural network, the spectrograms underwent batch normalization applied independently to each frequency band [13,22]. To enhance model robustness, SpecAugment data augmentation was utilized during training, randomly masking temporal and frequency regions [13,23].
2.4.3. Model Architecture
The model architecture is derived from the PANN convolutional neural network, as adapted in Heitmann et al. [13,24]. It consists of five convolutional blocks, each comprising two convolutional layers with 3 × 3 kernels. Batch normalization was applied between convolutional layers to stabilize and accelerate training, with each convolutional layer followed by ReLU activation [13,25]. Downsampling was performed via 2 × 2 average pooling after the first four convolutional blocks. Dropout regularization was introduced both after downsampling operations and within fully connected layers [13].
Post convolution, the frequency dimension was further reduced using average pooling. Temporal information was smoothed by combining average and max pooling (window size 3, stride 1) across the time dimension. The resulting features were then passed through a fully connected layer with 1024 units activated by ReLU activation. Finally, an attention mechanism generated two feature time series whose scalar product was used to estimate the probability of pathological lung sounds [13].
2.4.4. Model Training
The model was trained with a binary cross-entropy loss function using batches of 64 samples. Optimization was performed with AdamW, with a weight decay rate of 0.005. A 1-cycle learning rate policy was applied, which progressively increases the learning rate up to a maximum of 0.001 before decreasing it below its initial value, replicating the training scheme of DeepBreath. To address class imbalance, balanced sampling ensured equal representation of pathological and normal recordings, as well as balanced input from Littmann and Eko digital stethoscopes [13].
2.5. Statistical Analysis Plan
Categorical variables were presented as percentages, and continuous variables as means with corresponding quartiles. Categorial variables were compared between groups using chi-square or Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables were first examined for normality of distribution using Shapiro–Wilk test. In addition, distributional characteristics were considered a priori in some case, as some variables displayed clear floor or ceiling effects (PRAM, SpO2), making a normal distribution unlikely, while Z-scores were considered normally distributed given their standardization against reference populations.
We used the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test and Welch’s t-test to compare groups.
A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Predictions from both stethoscopes were randomly sampled with replacement to compute 1000 AUROC values. A t-test was then performed on the two AUROC distributions, with the p-value set at <0.001.
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis assessed the algorithm’s discriminatory power, reflecting its ability to learn from training data and generalize to previously unseen examples in the validation set.
The confusion matrices, precision, sensitivity, and specificity metrics are computed from recording-based binary predictions. Specifically, a recording is considered predicted as “asthma” if more than half of its 5 s splits have a predicted value higher than 0.5. All statistical analyses were conducted using Python (Python Software Foundation, Beaverton, Oregon, United States, version 3.7.9) [26].
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Data
A total of 151 pediatric outpatients, 42.4% female and 57.6% male, were consecutively included (Table 2). 33.1% of patients with pathological spirometry results were categorized as cases, while 66.9% of patients with non-pathological spirometry results were categorized as controls (Table 2). Ten patients were excluded due to uninterpretable spirometry results in accordance with the ERS guidelines.

Table 2.
Clinical data in the case and control groups.
In total, patients were mostly non- or poorly symptomatic in both groups, and only a few of them were experiencing asthma exacerbation according to PRAM scoring during the outpatient visit, with no statistically significant difference between both groups. Furthermore, no patients required urgent management for asthma exacerbation, and all were discharged home after their follow-up visit (Table 2).
However, as expected, due to the criteria used to classify the case and control groups, spirometric results differed significantly between groups. Patients in the pathological group showed a lower baseline FEV1/FVC Z-score (−1.4 vs. −0.1, p < 0.001) and lower FEV1 Z-score (−1.06 vs. 0.16, p < 0.001), together with a greater relative improvement in FEV1 after bronchodilator inhalation (14.5% vs. 3.0%, p < 0.001) (Table 2).
3.2. Predictive Capacity of the Algorithm
The algorithm distinguished healthy from pathological digital lung auscultation patterns validated by spirometric difference values in the training set, achieving an AUROC of 0.763. Performance in the training set was similar across devices, with AUROC values for the training set of 0.781 for the 3M™ Littmann® CORE digital stethoscope and 0.757 for the 3M™ Eko® CORE digital stethoscope (Figure 2). However, the model’s performance declined in the validation set, with AUROC values of 0.511 for the Littmann® and 0.352 for the Eko® stethoscope (Figure 3). Bootstrapped comparisons confirmed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) between the training and validation performances for both stethoscopes.
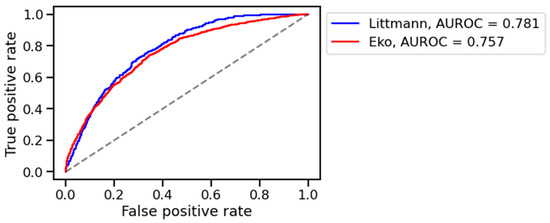
Figure 2.
AUROC on training set. Legend: L (blue): 3M™ Littmann® digital stethoscope, E (red): 3M™ Eko® CORE digital stethoscope.
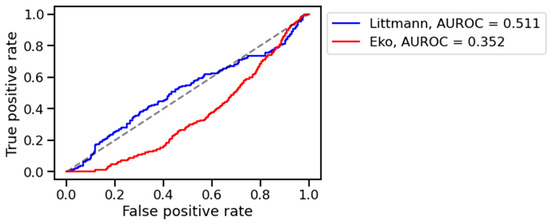
Figure 3.
AUROC on validation set. Legend: L (blue): 3M™ Littmann® digital stethoscope, E (red): 3M™ Eko® CORE digital stethoscope.
We investigated whether the poor generalization on the validation set was due to confusion between samples coming from two different stethoscopes. We trained and tested a model only on Eko recordings, and another one only on Littmann. The results are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
We observe a similar trend for both models: a training AUROC that increases with the amount of training data, and a validation AUROC at chance level. The AUROC for the Eko-only model is lower than the AUROC of our main model, which was trained on Eko and Littmann data. This suggests that the model does not necessarily get confused by recordings from two different stethoscopes and benefits from the larger amount of mixed data.
The confusion matrices for the training and validation sets are shown in Figure 4 and the precision, sensitivity, and recall are shown in Supplementary Table S2. We observe a significant drop in precision and sensitivity on the validation set, indicating that asthma cases unseen during training are difficult to detect.
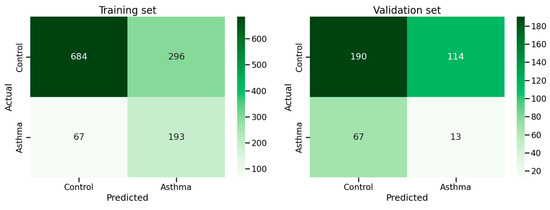
Figure 4.
Confusion matrices of training and validation sets.
4. Discussion
In this study, we developed and trained an AI model using lung-sound recordings labelled objectively by spirometry values, the gold standard for asthma diagnosis, under current European pediatric guidelines [21]. The previous studies often used human-labelled data based on the presence of wheezing as an asthma diagnosis indicator [9,13,14,16]. Yet, this practice remains subjective and biased. Firstly, because human labelling methods show inter-observer variability and could be influenced by recording quality, reviewer experience, and the limited frequency range detected by the human ear [9,27,28]. Secondly, given the exclusive use of wheezing as the principal diagnostic marker for asthma exacerbation, which is not only specific to asthma [13,14,27,29]. By contrast, our approach overcomes these limitations by linking every asthma label to a confirmed airflow limitation by respiratory functional results, and enabling the model to learn from the full spectrum of abnormal lung sounds present in every stage of asthma exacerbation. Islam et al. have shown that a multichannel lung sound analysis for asthma detection, focusing on comprehensive sound profiles, outperforms common classification based on the presence of wheezing, underscoring the value of wider acoustic profiling in asthma detection [29].
In our study, the population consisted mainly of children attending follow-up visits who were largely asymptomatic or presented with only mild symptoms, with PRAM scores low in both groups and not significantly different. Unlike the more symptomatic emergency department patients in the original DeepBreath study, participants had a mean ACTp score of 23.77 (SD 2.53), with none requiring urgent management for exacerbation (mean PRAM score 0.13, SD 0.45). However, the significant difference observed in spirometry results reflects the functional abnormalities in asthma, and their concordance with the classification criteria confirms that the “pathological” group truly represents patients with measurable reversible airway obstruction.
This discrepancy between poor clinical presentation and measurable functional changes highlights the difficulty in recognizing asthma exacerbations based on symptoms and underscores the need for objective monitoring tools for homecare. As we will see below, this deliberate selection aimed to facilitate early asthma exacerbation detection but may have contributed to the model’s modest validation performance because of the scarcity of pronounced adventitious sounds. It suggests a threshold of asthma severity below which AI models struggle to detect asthma exacerbations based only on lung sounds.
In terms of performance, we observed an AUROC of 0.763 in the training set, demonstrating the potential to distinguish healthy patients from those with asthma. However, the performance fell to 0.398 in the validation set. This drop suggests that the algorithm struggled to generalize to previously unseen recordings, indicating limited recognition of meaningful asthma patterns outside the training phase. This was unexpected, given DeepBreath’s strong diagnostic performance (AUROC of 0.912 during internal validation) [13]. Several factors may explain this decline. First, our outpatient cohort may have been too small to effectively train the model to detect early asthma exacerbation, particularly given the very low occurrence of abnormal lung sounds. Second, even though we limited the risk of overfitting by using single-visit data and standardized recording conditions, we acknowledge that the observed drop in validation performance suggests that some degree of overfitting may still have occurred, also likely due to the limited size of the training set.
Moreover, an important implication of our findings is the variability introduced by different digital stethoscopes. We observed a significant difference in performance between the Littmann® and Eko® CORE stethoscopes across both the training and validation sets (p < 0.001). In the validation set, AUROC values were 0.511 for the Littmann® and 0.352 for the Eko® CORE, although we favored the Eko® device for 74% of the recordings. Despite its advanced features, the Eko® CORE’s poorer performance may be attributed to digital filtering or noise suppression. Such processing, even if designed to improve recording quality, may inadvertently attenuate subtle acoustic signatures relevant for asthma detection [28]. To assess this, we performed a qualitative spectral analysis, which revealed systematic differences between the log-mel spectrograms of the two stethoscopes. Namely, the Eko stethoscope amplified certain frequencies and suppressed others compared to the Littmann. We further investigated whether the poor generalization on the validation set was due to confusion between samples coming from two different stethoscopes, but the conclusion is uncertain. The conclusion we draw is that more data leads to a better AUROC on the training set. And generalization to a validation set seems difficult but may possibly occur after crossing a certain amount of training data. In-depth spectral analyses and input standardization techniques to minimize the differences between spectrograms of different stethoscopes should be explored in future work.
Further analysis of the misclassified cases could offer valuable insights to guide model refinement.
A key goal for future studies will also be to identify the severity threshold at which acoustic features become informative. By deliberately including patients across a broader range of PRAM scores and examining performance breakdown at each level of severity, such studies could determine the “balance point” where acoustic monitoring begins to add diagnostic value and can meaningfully support home monitoring.
Future studies to enhance the model’s robustness could require focusing on recruiting children presenting with acute exacerbation in the pediatric emergency department to evaluate and calibrate the model’s sensitivity and specificity across the full spectrum of asthma severity. Incorporating additional clinical variables, such as respiratory rate, pulse oximetry, patient-reported symptoms, or recent medication use, may help capture early, non-acoustic indicators of asthma exacerbations. These strategies could enhance the clinical relevance of lung sound analysis anchored to spirometry, ultimately supporting the development of a reliable, home-compatible tool for early detection of asthma exacerbations. These could empower parents by helping them recognize early symptoms of exacerbation, enabling them to initiate treatment according to the child’s personalized action plan or to seek urgent medical care when necessary.
5. Conclusions
Our study highlights both the potential and the current limitations of AI-based approaches to asthma diagnosis using lung sounds. Building upon previous methods that relied on subjective human wheeze-based labelling, our work introduces an objective approach by anchoring lung sounds to spirometry as an objective reference.
Despite encouraging training performance, the model did not achieve sufficient accuracy in the validation set, in mostly asymptomatic outpatients.
This outcome raises two central hypotheses for future research. First, it remains unclear whether there is a severity threshold of asthma below which acoustic features are not informative, thus limiting the utility of lung sound monitoring for early detection. Addressing this will require including patients across a broader spectrum of disease severity and analyzing the performance of the model at each severity level to identify the “balance point” where lung sound monitoring adds diagnostic value.
Second, our findings highlight the need to systematically address technical variability introduced by digital stethoscopes, as device-related processing may inadvertently suppress relevant frequencies for the diagnosis of early asthma attacks. Addressing this will require spectral analyses and calibration studies to better understand device-related variability.
Tackling both these questions is essential to defining the scope and practical utility of AI-based auscultation in pediatric asthma management. Our next step will be to address these challenges, we also plan to explore integrating lung sounds with other clinical variables that can conveniently be monitored at home, such as patient-reported symptoms and respiratory rate, for a more comprehensive approach to early asthma detection.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app151910662/s1, Table S1: AUROC breakdown for both stethoscope; Table S2: precision, sensitivity, and recall in training and validation set.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C.-L. and I.R.-M.; software, J.D. and M.-A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C.-L.; writing—review and editing, H.C.-L., J.N.S., L.L., A.G., C.B.-A., and I.R.-M.; supervision, I.R.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by the Foundation GERTRUDE VON MEISSNER.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of “Commission cantonale d’éthique de la recherche CCER, République et Canton de Genève” (protocol code 2019-01238, 10 August 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The code used for training and evaluating the model is available at the following GitHub repository: https://github.com/EPFLiGHT/Asthmoscope-MDPI-2025, accessed on 20 August 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
A.G. and A.P. are co-developers of a smart stethoscope, ‘Pneumoscope’, which is intended for potential commercialization. All other authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ACTp | Asthma Control Test |
| AUROC | Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| IC | Inhaled corticosteroids |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DLA | Digital lung auscultation |
| ERS | European Respiratory Society |
| FEF 25–75 | Forced Expiratory Flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| GLI | Global Lung Initiative |
| HUG | Geneva University Hospitals |
| LABA | Long-acting beta2-agonist |
| ML | Machine learning |
| PRAM | Pediatric Respiratory Assessment Measure |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| WAV | Waveform Audio File |
References
- Holgate, S.T.; Price, D.; Valovirta, E. Asthma out of Control? A Structured Review of Recent Patient Surveys. BMC Pulm. Med. 2006, 6, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, I.; Pearce, N. Global Burden of Asthma among Children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2014, 18, 1027–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaron, S.; Boulet, L.; Reddel, H.; Gershon, A. Underdiagnosis and Overdiagnosis of Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.; Wilson, N.; Bush, A. Difficult to Control Asthma in Children. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 7, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, J.; Hervás, D.; Marco, N.; Manuel Milan, J.; Dolores Martos, M. Calculating the Prevalence of Atopy in Children. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2009, 37, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Managment and Prevention; Global Initiative for Asthma: Fontana, WI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pasterkamp, H.; Kraman, S.S.; Wodicka, G.R. Respiratory Sounds. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 974–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalut, D.S.; Ducharme, F.M.; Davis, G.M. The Preschool Respiratory Assessment Measure (PRAM): A Responsive Index of Acute Asthma Severity. J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevat, A.C.; Kalirajah, A.; Roseby, R. Digital Stethoscopes Compared to Standard Auscultation for Detecting Abnormal Paediatric Breath Sounds. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, G.; Le Moine, O. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: Today and Tomorrow. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 509744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalovic, M.; Das, N.; Burgel, P.-R.; Daenen, M.; Derom, E.; Haenebalcke, C.; Janssen, R.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Liistro, G.; Louis, R.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Outperforms Pulmonologists in the Interpretation of Pulmonary Function Tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, S.A. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Cognitive Computing: What Do These Terms Mean and How Will They Impact Health Care? J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2358–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitmann, J.; Glangetas, A.; Doenz, J.; Dervaux, J.; Shama, D.M.; Garcia, D.H.; Benissa, M.R.; Cantais, A.; Perez, A.; Müller, D.; et al. DeepBreath—Automated Detection of Respiratory Pathology from Lung Auscultation in 572 Pediatric Outpatients across 5 Countries. npj Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywalski, T.; Piecuch, M.; Szajek, M.; Bręborowicz, A.; Hafke-Dys, H.; Kociński, J.; Pastusiak, A.; Belluzzo, R. Practical Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Algorithms in Pulmonary Auscultation Examination. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exarchos, K.P.; Beltsiou, M.; Votti, C.-A.; Kostikas, K. Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Asthma: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Existing Literature. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, A.; Scrafford, C.G.; Tielsch, J.M.; Levine, O.S.; Checkley, W. Computerized Lung Sound Analysis as Diagnostic Aid for the Detection of Abnormal Lung Sounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.A.; Sorkness, C.A.; Kosinski, M.; Schatz, M.; Li, J.T.; Marcus, P.; Murray, J.J.; Pendergraft, T.B. Development of the Asthma Control Test: A Survey for Assessing Asthma Control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap)—A Metadata-Driven Methodology and Workflow Process for Providing Translational Research Informatics Support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Minor, B.L.; Elliott, V.; Fernandez, M.; O’Neal, L.; McLeod, L.; Delacqua, G.; Delacqua, F.; Kirby, J.; et al. The REDCap Consortium: Building an International Community of Software Platform Partners. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 95, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanjer, P.H.; Stanojevic, S.; Cole, T.J.; Baur, X.; Hall, G.L.; Culver, B.H.; Enright, P.L.; Hankinson, J.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Zheng, J.; et al. Multi-Ethnic Reference Values for Spirometry for the 3–95-Yr Age Range: The Global Lung Function 2012 Equations. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1324–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Miller, M.R.; Thompson, B.; Aliverti, A.; Barjaktarevic, I.; Cooper, B.G.; Culver, B.; Derom, E.; Hall, G.L.; et al. ERS/ATS Technical Standard on Interpretive Strategies for Routine Lung Function Tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; JMLR.org: Lille, France, 2015; Volume 37, pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.S.; Chan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.-C.; Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V. SpecAugment: A Simple Data Augmentation Method for Automatic Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 2613–2617. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Cao, Y.; Iqbal, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Plumbley, M.D. PANNs: Large-Scale Pretrained Audio Neural Networks for Audio Pattern Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Proc. 2020, 28, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G. Rectified Linear Units Improve Restricted Boltzmann Machines Vinod Nair. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; Volume 27, pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Python Software Foundation Python. Available online: https://www.python.org/psf-landing/ (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Kevat, A.; Kalirajah, A. Artificial Intelligence Accuracy in Detecting Pathological Breath Sounds in Children Using Digital Stethoscopes. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjoune, Y.; Nguyen, T.N.; Doroshow, R.W.; Shekhar, R. Technical Characterisation of Digital Stethoscopes: Towards Scalable Artificial Intelligence-Based Auscultation. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2023, 47, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Bandyopadhyaya, I.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Saha, G. Multichannel Lung Sound Analysis for Asthma Detection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 159, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).