Generating Synthetic Facial Expression Images Using EmoStyle
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We hereby propose a systematic evaluation protocol of EmoStyle’s facial expression accuracy across 28 VA directions and 4 intensity levels, with the objective of quantifying the alignment between the intended and perceived emotions.
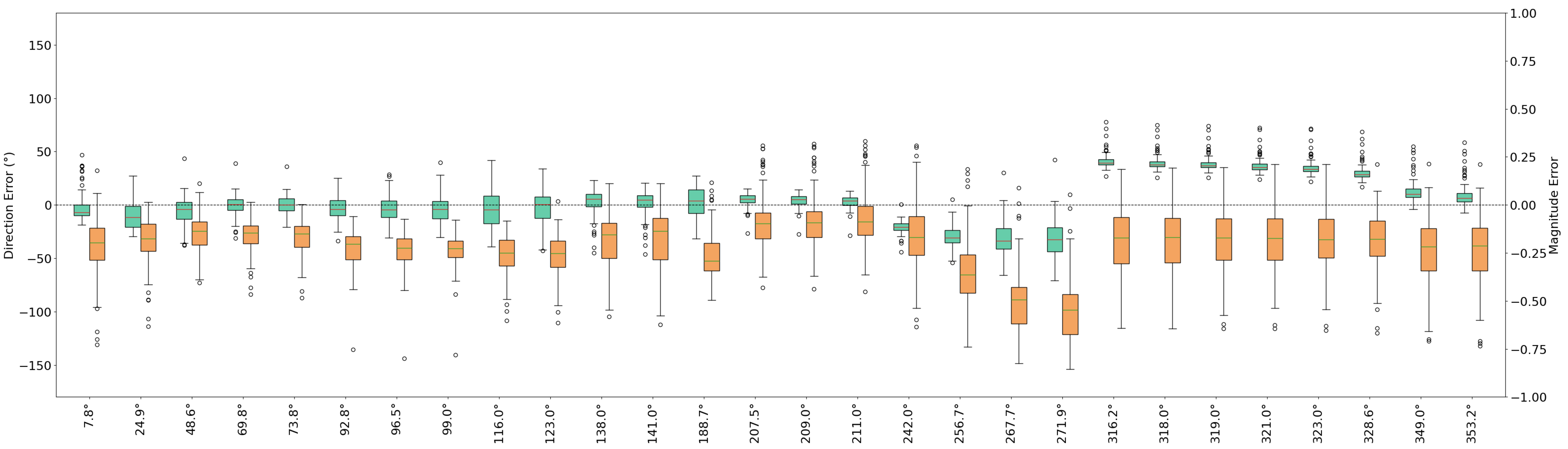
- Our evaluation identifies multiple weaknesses in EmoStyle’s ability to generate distinct and accurate facial expressions, notably a consistent failure region within the 242°–329° VA direction range.
- We explore simple image-quality-based filtering methods to improve the quality of the generated images.
- We release an open-source EmoStyle-based toolkit that comprises fixes to the original EmoStyle repository, an API wrapper, and experiment scripts (https://github.com/ClementDrn/emostyle-wrapper, accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Finally, the study provides practical recommendations for enhancing the image generation pipeline, including expression accuracy correction, artifact removal, sunglasses masking, and temporal consistency improvements.
2. Related Work
2.1. Facial Expression Generation
2.2. Synthetic Data Generation
3. Method
3.1. Face Image Generation
3.2. Facial Expression Editing
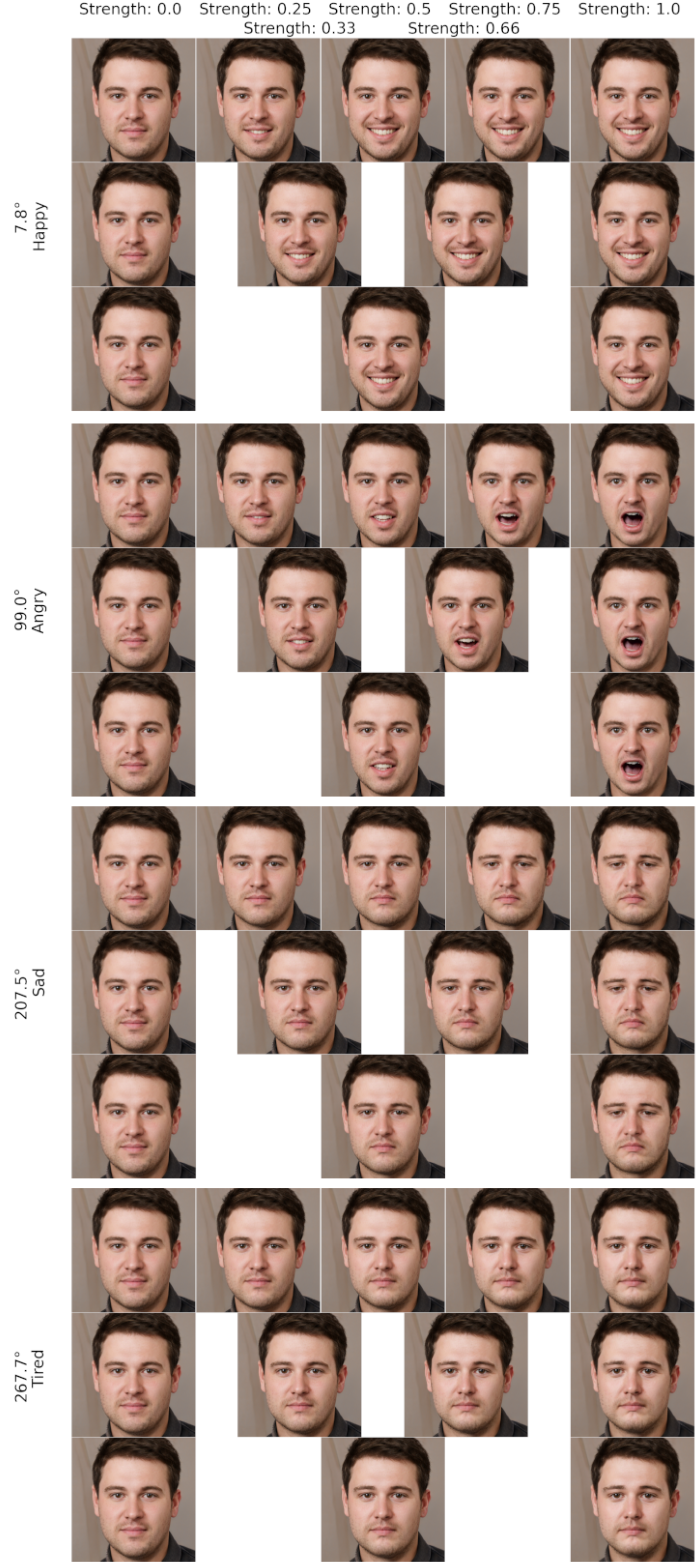
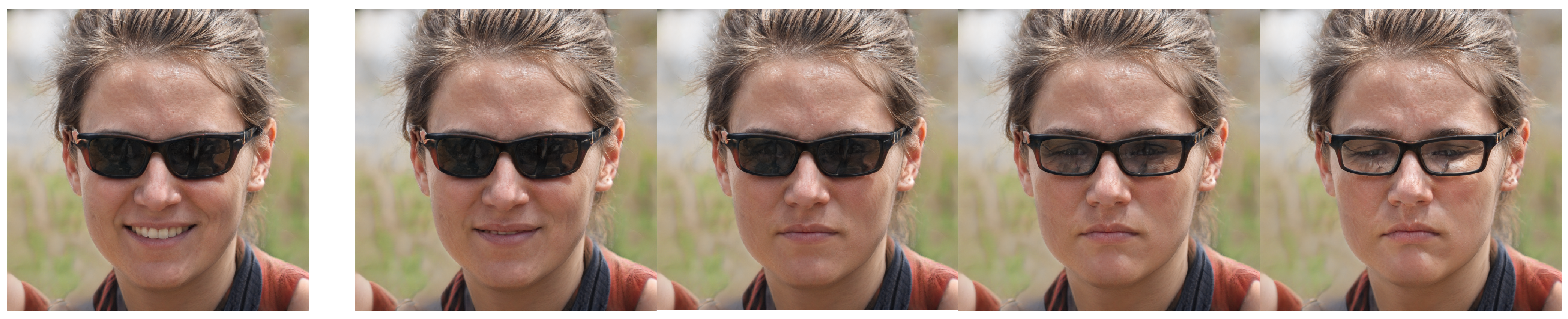
4. Experimental Results
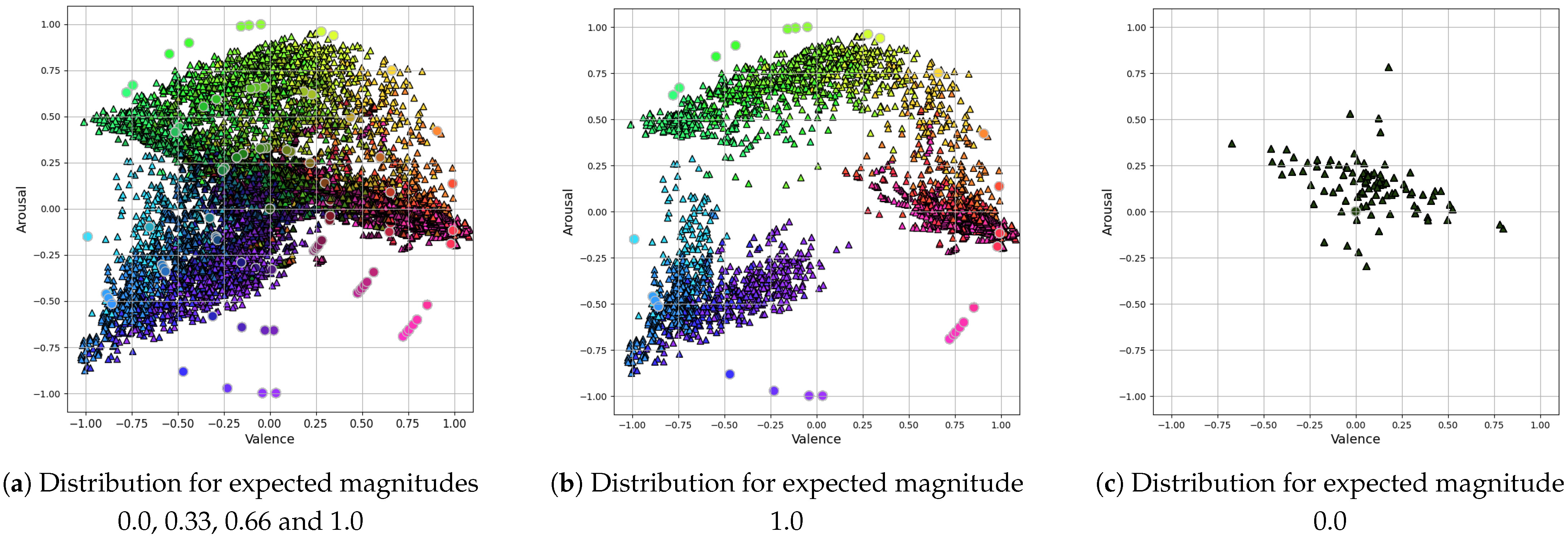
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Main Contribution
- This study proposes a systematic VA-space evaluation protocol that is applied to EmoStyle across a broad discretization of the VA space.
- We identify and analyze a consistent weakness in VA directions 242–329°, linked to training data imbalance.
- We provide practical insights on limitations of current quality filtering and accessory handling.
- An open-source toolkit is released with repository fixes, an API wrapper, and experiment scripts to enable reproducible research.
5.2. Limitations
5.3. Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AU | Action Unit |
| FER | Facial Expression Recognition |
| FID | Fréchet Inception Distance |
| FIQA | Face Image Quality Assessment |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| LPIPS | Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| VA | Valence and Arousal |
Appendix A



References
- Li, S.; Deng, W. Deep Facial Expression Recognition: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 1195–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, P.; Sevilla, J.; Besiroglu, T.; Heim, L.; Ho, A.; Hobbhahn, M. Machine Learning Model Sizes and the Parameter Gap. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R. Dynamic Programming. Science 1966, 153, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo Márquez, A. The curse of dimensionality. In Digital Maintenance Management: Guiding Digital Transformation in Maintenance; Springer Series in Reliability Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Hasani, B.; Mahoor, M.H. AffectNet: A Database for Facial Expression, Valence, and Arousal Computing in the Wild. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 10, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, S.R.; Russo, F.A. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS): A dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, D.; Zafeiriou, S. Aff-Wild2: Extending the Aff-Wild Database for Affect Recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1811.07770. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian Benitez-Quiroz, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Martinez, A.M. EmotioNet: An Accurate, Real-Time Algorithm for the Automatic Annotation of a Million Facial Expressions in the Wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ramis, S.; Buades Rubio, J.M.; Perales, F.; Manresa-Yee, C. A Novel Approach to Cross dataset studies in Facial Expression Recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 39507–39544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, F.; Huber, M.; Siebke, P.; Rieber, T.; Damer, N. SFace: Privacy-friendly and Accurate Face Recognition using Synthetic Data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.10520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A. Exposing.ai. Available online: https://exposing.ai (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I.; Seitz, S.; Miller, D.; Brossard, E. The MegaFace Benchmark: 1 Million Faces for Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.00596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; Gao, J. MS-Celeb-1M: A Dataset and Benchmark for Large-Scale Face Recognition. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.08221. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Shen, L.; Xie, W.; Parkhi, O.M.; Zisserman, A. VGGFace2: A dataset for recognising faces across pose and age. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1710.08092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Mathur, A.; Narayanan, A. Mitigating Dataset Harms Requires Stewardship: Lessons from 1000 Papers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.02922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, S.I. Synthetic Data for Deep Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wei, J.; Liu, F.; Si, C.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, J.; Zheng, S.; Peng, D.; Yang, D.; Zhou, D.; et al. Best Practices and Lessons Learned on Synthetic Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.07503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.; Baltrušaitis, T.; Hewitt, C.; Dziadzio, S.; Johnson, M.; Estellers, V.; Cashman, T.J.; Shotton, J. Fake It Till You Make It: Face analysis in the wild using synthetic data alone. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.15102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaipuria, N.; Zhang, X.; Bhasin, R.; Arafa, M.; Chakravarty, P.; Shrivastava, S.; Manglani, S.; Murali, V.N. Deflating Dataset Bias Using Synthetic Data Augmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; White, J.; Kalkan, S.; Gunes, H. Investigating Bias and Fairness in Facial Expression Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1912.04958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, A.; Miasayedzenkau, M.; Makaravets, D.; Pirshtuk, D.; Akbulut, E.; Holzmann, D.; Renusch, T.; Reichert, G.; Ritter, H. Face Generation and Editing with StyleGAN: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 3557–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal, R.; Zhu, P.; Mitra, N.J.; Wonka, P. StyleFlow: Attribute-conditioned Exploration of StyleGAN-Generated Images using Conditional Continuous Normalizing Flows. ACM Trans. Graph. 2021, 40, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, B.; Lim, A. EmoStyle: One-Shot Facial Expression Editing Using Continuous Emotion Parameters. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 6373–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J. A Circumplex Model of Affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumarola, A.; Agudo, A.; Martinez, A.M.; Sanfeliu, A.; Moreno-Noguer, F. Ganimation: Anatomically-aware facial animation from a single image. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; Shen, L.; Luo, Y. A chinese face dataset with dynamic expressions and diverse ages synthesized by deep learning. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lim, S.N. Unconstrained Facial Expression Transfer using Style-based Generator. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.06253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Aldausari, N.; Mohammadi, G. 2CET-GAN: Pixel-Level GAN Model for Human Facial Expression Transfer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.11570. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Zafeiriou, S. Affect Analysis in-the-wild: Valence-Arousal, Expressions, Action Units and a Unified Framework. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15792. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Sricharan, K.; Chellappa, R. ExprGAN: Facial Expression Editing with Controllable Expression Intensity. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.03842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.W.; Kim, S.; Choo, J. StarGAN: Unified Generative Adversarial Networks for Multi-Domain Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1711.09020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Song, B.C. Optimal Transport-based Identity Matching for Identity-invariant Facial Expression Recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.12172. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasnejad, I.; Sridharan, S.; Nguyen, D.; Denman, S.; Fookes, C.; Lucey, S. Using Synthetic Data to Improve Facial Expression Analysis with 3D Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Luo, C.; Xian, X.; Li, B.; Song, S.; Khan, M.H.; Xie, W.; Shen, L.; Ge, Z. SynFER: Towards Boosting Facial Expression Recognition with Synthetic Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.09865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1812.04948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlett, T.; Rathgeb, C.; Henniger, O.; Galbally, J.; Fierrez, J.; Busch, C. Face Image Quality Assessment: A Literature Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, F. MagFace: A Universal Representation for Face Recognition and Quality Assessment. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.06627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paplu, S.H.; Mishra, C.; Berns, K. Real-time Emotion Appraisal with Circumplex Model for Human-Robot Interaction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.09813. [Google Scholar]
- Toisoul, A.; Kossaifi, J.; Bulat, A.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Pantic, M. Estimation of continuous valence and arousal levels from faces in naturalistic conditions. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, A.V.; Savchenko, L.V.; Makarov, I. Classifying emotions and engagement in online learning based on a single facial expression recognition neural network. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 2132–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, A. Facial Expression Recognition with Adaptive Frame Rate based on Multiple Testing Correction. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; Krause, A., Brunskill, E., Cho, K., Engelhardt, B., Sabato, S., Scarlett, J., Eds.; JMLR, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 202, pp. 30119–30129. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Wen, F. GIQA: Generated Image Quality Assessment. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.08932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlsby, N.; Giurgiu, A.; Jastrzebski, S.; Morrone, B.; De Laroussilhe, Q.; Gesmundo, A.; Attariyan, M.; Gelly, S. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; JMLR, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA; pp. 2790–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Laine, S.; Härkönen, E.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Alias-Free Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
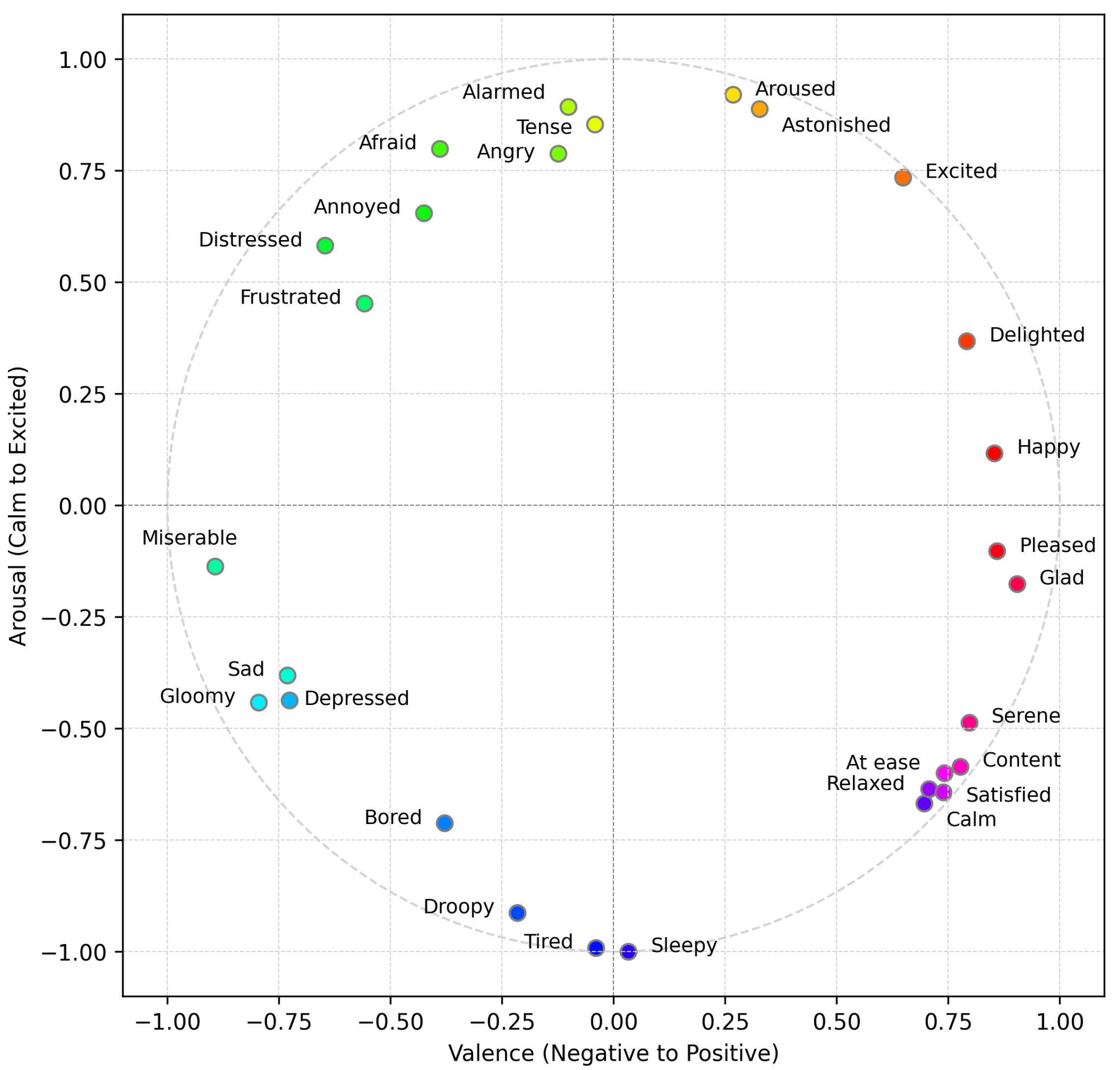



| Emotion | Angle (°) | Valence | Arousal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Happy | 8 | ||
| Delighted | 25 | ||
| Excited | 49 | ||
| Astonished | 70 | ||
| Aroused | 74 | ||
| Tense | 93 | ||
| Alarmed | 97 | ||
| Angry | 99 | ||
| Afraid | 116 | ||
| Annoyed | 123 | ||
| Distressed | 138 | ||
| Frustrated | 141 | ||
| Miserable | 189 | ||
| Sad | 208 | ||
| Gloomy | 209 | ||
| Depressed | 211 | ||
| Bored | 242 | ||
| Droopy | 257 | ||
| Tired | 268 | ||
| Sleepy | 272 | ||
| Calm | 316 | ||
| Relaxed | 318 | ||
| Satisfied | 319 | ||
| At ease | 321 | ||
| Content | 323 | ||
| Serene | 329 | ||
| Glad | 349 | ||
| Pleased | 353 |
| Emotion | Angle (°) | Dir. MAE (°) | Mag. MAE | Val. MAE | Arous. MAE | Dist. MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Happy | 8 | 10.2 ± 8.3 | 0.22 ± 0.15 | 0.23 ± 0.17 | 0.14↓± 0.08 | 0.30 ± 0.14 |
| Delighted | 25 | 14.9 ± 7.9 | 0.19 ± 0.12 | 0.16 ± 0.13 | 0.25 ± 0.13 | 0.33 ± 0.11 |
| Excited | 49 | 10.7 ± 9.3 | 0.15↓± 0.09 | 0.12↓± 0.10 | 0.19 ± 0.15 | 0.25↓± 0.14 |
| Astonished | 70 | 7.0↓± 6.5 | 0.16↓± 0.09 | 0.11↓± 0.08 | 0.16 ± 0.10 | 0.21↓± 0.11 |
| Aroused | 74 | 7.0↓± 5.6 | 0.17↓± 0.09 | 0.10↓± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.09 | 0.22↓± 0.10 |
| Tense | 93 | 9.6 ± 7.0 | 0.23 ± 0.09 | 0.13↓± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.10 | 0.29 ± 0.10 |
| Alarmed | 97 | 10.7 ± 7.8 | 0.24 ± 0.10 | 0.15 ± 0.10 | 0.25 ± 0.10 | 0.31 ± 0.11 |
| Angry | 99 | 11.4 ± 8.8 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | 0.16 ± 0.11 | 0.25 ± 0.10 | 0.31 ± 0.11 |
| Afraid | 116 | 13.8 ± 10.0 | 0.26 ± 0.10 | 0.21 ± 0.16 | 0.24 ± 0.10 | 0.35 ± 0.13 |
| Annoyed | 123 | 11.7 ± 9.7 | 0.26 ± 0.11 | 0.20 ± 0.16 | 0.23 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.13 |
| Distressed | 138 | 9.2↓± 7.5 | 0.20 ± 0.14 | 0.17 ± 0.15 | 0.18 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.13 |
| Frustrated | 141 | 8.6↓± 7.3 | 0.19↓± 0.15 | 0.16 ± 0.16 | 0.16↓± 0.07 | 0.25↓± 0.14 |
| Miserable | 189 | 12.0 ± 7.9 | 0.27 ± 0.11 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 0.16↓± 0.12 | 0.36 ± 0.08 |
| Sad | 208 | 6.8↓± 4.1 | 0.15↓± 0.09 | 0.14 ± 0.08 | 0.11↓± 0.09 | 0.20↓± 0.09 |
| Gloomy | 209 | 6.1↓± 3.9 | 0.14↓± 0.09 | 0.13 ± 0.08 | 0.11↓± 0.09 | 0.19↓± 0.09 |
| Depressed | 211 | 5.2↓± 3.8 | 0.14↓± 0.09 | 0.12↓± 0.07 | 0.10↓± 0.09 | 0.17↓± 0.09 |
| Bored | 242 | 20.9 ± 6.0 | 0.20 ± 0.13 | 0.18 ± 0.13 | 0.33 ± 0.13 | 0.41 ± 0.09 |
| Droopy | 257 | 29.8 ± 8.5 | 0.36 ± 0.16 | 0.23 ± 0.15 | 0.50 ± 0.12 | 0.58 ± 0.09 |
| Tired | 268 | 32.8 ± 12.8 | 0.50 ± 0.16 | 0.26 ± 0.16 | 0.60 ± 0.12 | 0.68 ± 0.09 |
| Sleepy | 272 | 33.0 ± 15.1 | 0.55 ± 0.16 | 0.27 ± 0.16 | 0.63 ± 0.12 | 0.71 ± 0.09 |
| Calm | 316 | 41.2 ± 7.1 | 0.20 ± 0.15 | 0.16 ± 0.10 | 0.64 ± 0.08 | 0.67 ± 0.08 |
| Relaxed | 318 | 39.6 ± 7.1 | 0.20 ± 0.15 | 0.15 ± 0.09 | 0.62 ± 0.08 | 0.65 ± 0.08 |
| Satisfied | 319 | 38.8 ± 7.1 | 0.20 ± 0.15 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.61 ± 0.08 | 0.64 ± 0.08 |
| At ease | 321 | 37.1 ± 7.3 | 0.19 ± 0.15 | 0.14 ± 0.10 | 0.59 ± 0.08 | 0.61 ± 0.09 |
| Content | 323 | 35.3 ± 7.5 | 0.19 ± 0.15 | 0.13↓± 0.10 | 0.57 ± 0.09 | 0.59 ± 0.09 |
| Serene | 329 | 30.3 ± 7.6 | 0.20 ± 0.14 | 0.12↓± 0.11 | 0.49 ± 0.09 | 0.52 ± 0.11 |
| Glad | 349 | 12.9 ± 10.0 | 0.24 ± 0.15 | 0.23 ± 0.16 | 0.20 ± 0.11 | 0.32 ± 0.17 |
| Pleased | 353 | 9.7 ± 10.8 | 0.24 ± 0.16 | 0.25 ± 0.17 | 0.13↓± 0.11 | 0.29 ± 0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darne, C.G.D.; Quan, C.; Luo, Z. Generating Synthetic Facial Expression Images Using EmoStyle. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910636
Darne CGD, Quan C, Luo Z. Generating Synthetic Facial Expression Images Using EmoStyle. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910636
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarne, Clément Gérard Daniel, Changqin Quan, and Zhiwei Luo. 2025. "Generating Synthetic Facial Expression Images Using EmoStyle" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910636
APA StyleDarne, C. G. D., Quan, C., & Luo, Z. (2025). Generating Synthetic Facial Expression Images Using EmoStyle. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10636. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910636







