Abstract
The widening gap between life expectancy and healthy life years underscores the need for scalable, adaptive, and privacy-conscious healthcare solutions. In this study, we integrate the AMPER (Aim–Measure–Predict–Evaluate–Recommend) framework with Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), Automated Machine Learning (AutoML), and privacy-preserving Federated Learning (FL) to deliver personalized hypertension management. Building on sequential data modeling and privacy-preserving AI, we apply this framework to the MIMIC-III dataset, using key variables—gender, age, systolic blood pressure (SBP), and body mass index (BMI)—to forecast future SBP values. Experimental results show that combining BERT with Moving Average (MA) or AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models improves predictive accuracy, and that personalized FL (Per-FedAvg) significantly outperforms local models while maintaining data confidentiality. However, FL performance remains lower than direct data sharing, revealing a trade-off between accuracy and privacy. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of integrating AutoML, advanced sequence modeling, and FL within a structured health management framework. We conclude by discussing theoretical, clinical, and ethical implications, and outline directions for enhancing personalization, multimodal integration, and cross-institutional scalability.
1. Introduction
Recent decades have witnessed substantial advances in healthcare and technology, resulting in longer life expectancies across many populations. Yet, the extension of lifespan has not consistently translated into an equivalent increase in healthy life years, creating a widening gap between longevity and sustained well-being. This gap highlights the imperative for proactive, data-driven health management strategies aimed at preventing chronic diseases, enabling early detection, and delivering personalized interventions. In this context, Artificial Intelligence (AI)—and more specifically Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)—offers a promising avenue for enabling scalable, adaptive, and high-performing predictive models without requiring extensive manual configuration [1,2,3]. By automating the selection, optimization, and deployment of machine learning pipelines, AutoML can accelerate the translation of diverse and complex health data into actionable insights, thus playing a pivotal role in bridging the gap between extended lifespans and improved quality of life [4,5].
Despite the proliferation of health management services in recent years, many continue to be fragmented, lacking cohesive methodologies or comprehensive frameworks to support sustained and personalized interventions. To address this gap, the present study adopts the Digital Me paradigm, which conceptualizes an AI-enabled product–service system capable of continuously managing an individual’s physiological state. Within this paradigm, the AMPER (Aim–Measure–Predict–Evaluate–Recommend) framework offers a structured methodology to capture user objectives, measure health indicators, predict future states, evaluate progress, and deliver personalized recommendations. Such a staged and transparent architecture is well-suited for integrating advanced machine learning into personalized healthcare delivery.
A major technical hurdle in implementing the AMPER framework is the processing of large-scale sequential health data, such as longitudinal blood pressure measurements. Traditional deep learning architectures for sequence modeling—Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks—often exhibit limited efficiency in compressing and learning from high-volume clinical time-series. Recent advances in language models, particularly Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), have demonstrated substantial potential for modeling sequential dependencies in non-linguistic domains. By leveraging bidirectional attention mechanisms, BERT can capture complex temporal patterns in physiological signals, offering a promising alternative to conventional sequence models for health monitoring tasks such as blood pressure prediction.
Beyond selecting an appropriate model architecture, optimizing predictive performance and adapting to diverse user profiles require systematic model development pipelines. AutoML has emerged as a pivotal enabler in this regard, automating end-to-end processes including data preprocessing, feature engineering, model selection, and hyperparameter optimization. By reducing the need for manual intervention, AutoML not only democratizes access to advanced modeling but also enables iterative refinement of predictive models in real time. In healthcare applications, this capability can accelerate the deployment of personalized and adaptive models while maintaining methodological rigor. Furthermore, integrating AutoML into the AMPER pipeline facilitates scalable personalization by dynamically tailoring model configurations to the specific characteristics of individual users or cohorts.
The application of advanced modeling techniques to healthcare data, however, is constrained by stringent privacy requirements. Health records and genetic data are classified as sensitive personal information under law and international data protection frameworks. Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a compelling approach to reconcile the need for model training on rich, distributed datasets with the imperative to safeguard patient privacy. In FL, model parameters—not raw data—are exchanged between institutions or devices, enabling collaborative model development without centralizing sensitive information. This paradigm has already been piloted in large-scale medical initiatives, including collaborations between Intel Labs and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, and NVIDIA’s Clara FL platform for radiological imaging, demonstrating both feasibility and measurable performance gains in real-world contexts.
The present study proposes a personalized blood pressure management system that integrates the AMPER framework, BERT-based sequential modeling, AutoML-driven pipeline optimization, and privacy-preserving federated learning. Using the MIMIC-III database as a case study, we develop and evaluate predictive models for systolic blood pressure, comparing direct data-sharing approaches with personalized federated learning strategies. In doing so, this work not only advances methodological innovation at the intersection of AutoML and FL but also provides a reproducible framework for delivering adaptive, privacy-conscious healthcare services within the broader Digital Me vision.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 reviews the key theoretical foundations, including privacy-preserving AutoML, the personalized federated learning strategy, and the AMPER framework. Section 3 describes the development of a blood pressure management system by applying the AMPER framework to the MIMIC-III dataset, detailing each stage from Aim to Recommend. This section also presents the implementation of AutoML for pipeline optimization (BERT, MA+BERT, and ARIMA+BERT) and compares personalized federated learning (local and global models) with a direct data-sharing approach. Section 4 outlines the process of developing the prototype service interfaces through the application of the AMPER framework, illustrating how the system delivers personalized health recommendations. Section 5 concludes by summarizing the key findings, discussing practical implications, and identifying limitations and directions for future research.
2. Background
2.1. Privacy-Preserving AutoML
Automated machine learning or AutoML is an emerging field within artificial intelligence that aims to streamline the process of developing machine learning (ML) models by automating the stages of model creation, from data preprocessing and feature selection to model selection and optimization. It addresses the challenge of enabling users who may not have extensive statistical or programming backgrounds to harness the power of ML technologies effectively. This ability to democratize access to machine learning can lead to enhanced productivity and innovation across various domains, such as healthcare, finance, and environmental sustainability [1,2,3].
AutoML can be broadly described as the automation of the entire machine learning pipeline—including data preparation, feature engineering, model training, and evaluation—with the goal of improving model performance while lowering the technical barriers for users [1,6]. According to the literature, AutoML frameworks can implement numerous algorithms, allowing for the exploration of various model architectures and hyperparameters to identify the most effective models without significant manual intervention [1,2,3,4]. For instance, frameworks like Auto-Sklearn and TPOT have been recognized for their capabilities in generating robust models tailored to specific datasets [1,7].
Recent studies have proposed several core methodologies defining the functioning and advancement of AutoML systems. The search space model is a fundamental component that systematically explores potential ML configurations, while optimization techniques such as Bayesian optimization and random search are applied to evaluate and refine these candidates [8,9]. Such methodological rigor allows AutoML systems to optimize not only for accuracy but also for computational efficiency, which is essential given the growing volumes of data [5].
Additionally, ensemble learning is a central theory within AutoML. It combines predictions from multiple algorithms to improve accuracy beyond what individual models can achieve, thus capitalizing on the strengths of varied modeling approaches [4,5]. Furthermore, the integration of meta-learning allows AutoML systems to learn from previous tasks, significantly speeding up the training process by tailoring the modeling techniques to suit specific data properties [1,9]. This cross-task learning fosters adaptability and accelerates the deployment of effective models across diverse applications.
The rapid advancement of AutoML has transformed the landscape of predictive modeling by automating complex processes that previously required substantial human expertise. As AutoML systems become increasingly integral to data-driven decision-making, the demand for robust security and privacy safeguards has intensified. This is particularly critical in domains such as healthcare, finance, and education, where sensitive personal information is frequently processed and analyzed. Consequently, the intersection of AutoML and privacy has emerged as a pivotal area of inquiry.
With the proliferation of data-driven technologies, privacy concerns have intensified, especially when dealing with sensitive datasets containing personal information. Accordingly, AutoML methodologies must incorporate robust privacy-preserving techniques to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access. For example, Yuan et al. [2] argue that AutoML enables healthcare professionals to develop predictive models without sharing sensitive data with external parties, thereby mitigating privacy risks commonly associated with traditional machine learning approaches. This consideration is particularly crucial in the healthcare sector, where the handling of highly sensitive patient information requires strict safeguards; any unauthorized access can result in significant ethical and legal consequences [10].
2.2. Personalized Federated Learning Strategy
One prominent strategy employed alongside AutoML is Federated Learning (FL), which facilitates the training of models across decentralized devices without requiring data centralization. This approach inherently preserves user privacy by ensuring that raw data remains on the device, with only model updates being communicated [11,12]. By leveraging FL, organizations can capitalize on the efficiency of AutoML while maintaining compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). For example, Karras et al. [12] introduced FLIBD, an innovative framework designed to enhance privacy through distributed model training and effective management of large-scale IoT data. Such approaches highlight the potential of federated architectures to reconcile the demands of advanced machine learning with stringent privacy requirements.
Applications of FL in the medical field demonstrate the potential to overcome data-sharing constraints and risks of personal data leakage. For example, the NVIDIA Clara FL platform reports that, in a multi-hospital setting, models trained with FL exhibit improved predictive performance compared with models trained on data from individual hospitals alone. In the EXAM study, which predicts oxygen requirements in COVID-19, a global model constructed from data across 20 hospitals showed significant improvements in metrics such as AUC relative to local models. Furthermore, Google’s Gboard keyboard system, an FL case leveraging data from hundreds of millions of mobile users, suggests that FL can be applied at scale to sensitive personal data, such as medical self-records (e.g., symptom diaries).
Another approach to enhancing data privacy within AutoML workflows involves the adoption of on-premise solutions that localize the data processing environment. Elangovan et al. [13,14] demonstrate that on-premise AutoML platforms can effectively circumvent the risks inherent in external cloud services, which are often considered untrusted environments for handling sensitive information. By ensuring that all data processing occurs within the organization’s own infrastructure, these solutions minimize the risk of data leakage and maintain strict organizational control over sensitive datasets. The privacy-preserving mechanisms of AutoML can be summarized as follows. First, on-premises AutoML ensures that data preprocessing, feature extraction, and model training are all performed on the organization’s internal servers, thereby preventing external leakage at the source. Second, Differential Privacy (DP) introduces noise during the training process to reduce re-identification risk. For example, methods that add Gaussian noise to the local gradient g and use the resulting updates for parameter updates can be employed for privacy protection. Finally, Secure Aggregation techniques enable the server to average updates from clients only in encrypted form, thereby ensuring that the learning results of individual institutions are not exposed. We discussed these approaches in the discussion, incorporating the reviewers’ comments.
A noteworthy example of an innovative framework in this area is FLIBD (Federated Learning-Based IoT Big Data Management), introduced by Karras et al. [12], which enhances privacy through distributed model training and the effective management of large-scale IoT data [15]. The primary objective of FLIBD is to enable decentralized learning processes in which sensitive data remains localized on individual devices, thereby mitigating privacy risks and supporting compliance with data protection regulations such as the GDPR. A central feature of FLIBD is its capacity to safeguard user privacy by eliminating the need to upload raw data to centralized servers. Instead, only model parameter updates are exchanged, effectively protecting sensitive information from potential exposure. This methodology aligns with current privacy standards and enables organizations to harness the benefits of machine learning without compromising user confidentiality. However, FLIBD and similar federated learning frameworks present several challenges. First, synchronizing model updates across numerous devices can significantly increase communication overhead, potentially causing delays in achieving model convergence—particularly in large-scale applications. Additionally, the diversity of local data may result in model divergence; if updates from individual devices are not carefully managed, inconsistencies can arise, negatively affecting overall model performance. Finally, the implementation of FLIBD requires robust infrastructure and sophisticated management systems. This added complexity may pose a barrier for organizations with limited technical resources or expertise.
Although still in the early stages of practical adoption, federated learning has already shown notable promise for enhancing privacy within AutoML workflows. By enabling model training on heterogeneous datasets without exposing raw user data, federated learning addresses the growing privacy concerns driven by the rapid expansion of personal data through IoT devices [16]. This aligns with Alardawi et al. [15], who highlight that federated learning facilitates collaborative model development while avoiding the exchange of sensitive information, thereby reinforcing both privacy and security. Consequently, advancing the integration of federated learning and other privacy-preserving techniques into AutoML represents a compelling pathway for organizations aiming to balance innovation with stringent data protection.
2.3. AMPER Approach for Privacy-Preserving AutoML
The AMPER (Aim–Measure–Predict–Evaluate–Recommend) framework represents a structured data management approach for user state acquisition and learning optimization. AMPER sequentially guides data through five key phases. The framework begins by defining the user’s aim (‘A’), ensuring that all processes align with individual goals. It then measures (‘M’) the user’s current state through diverse variables, enabling accurate profiling, and predicts (‘P’) potential future states using minimally domain-dependent algorithms to enhance scalability and generalizability. Next, it evaluates (‘E’) predicted outcomes against the original aim to maintain alignment, and finally recommends (‘R’) targeted actions to guide users toward desired outcomes, thereby completing the adaptive learning loop.
From an AutoML perspective, the AMPER framework delivers significant value by systematizing the end-to-end management of user state data and model adaptation. By explicitly structuring the pipeline into Aim, Measure, Predict, Evaluate, and Recommend phases, AMPER enables seamless integration of automated model selection, state monitoring, and personalized feedback loops. This structured approach not only supports automated decision-making and model refinement but also facilitates interpretability and auditability—two critical challenges in practical AutoML deployments. By continually aligning system behavior with user-defined aims and providing a transparent path from data collection to actionable recommendations, AMPER reduces the complexity of managing adaptive learning systems and strengthens the reliability of AutoML solutions across diverse application domains.
In terms of privacy protection, AMPER’s staged data management process acts as a critical enabler of privacy-aware machine learning. By emphasizing measurement of only relevant user state variables, and by supporting localized processing of sensitive information, AMPER inherently minimizes the risk of data over-collection and exposure. This is particularly advantageous in regulated sectors, such as healthcare and finance, where granular control over data usage and flow is a legal and ethical imperative. Furthermore, the explicit separation between measurement, prediction, and recommendation phases makes it possible to enforce privacy-preserving mechanisms—such as anonymization or differential privacy—at specific points in the data pipeline, thus enhancing organizational capacity to comply with privacy requirements while retaining the flexibility and benefits of advanced machine learning.
The importance of robust data management is further amplified within federated learning environments, where decentralized data sources and device heterogeneity introduce new layers of complexity. In federated learning, data never leaves the user’s device; only model updates are shared, which inherently supports privacy. However, this decentralized setting also creates unique challenges for consistent user state tracking, cross-device synchronization, and the continuous improvement of model performance. Here, the AMPER framework becomes indispensable. By providing a clear protocol for capturing, evaluating, and acting upon user state data on each device, AMPER enables federated learning systems to maintain high levels of personalization and adaptivity without sacrificing data privacy or system integrity. Its iterative and modular design ensures that learning objectives and outcomes remain transparent, auditable, and user-aligned—even as they are distributed across heterogeneous and dynamic environments.
3. Model Design
According to the 2022 life tables from Statistics Korea, the life expectancy of Koreans rose from 80.87 years in 2012 to 82.7 years in 2022, an increase of about 1.83 years [17]. In contrast, healthy life expectancy is only 65.8 years, leaving a gap of roughly 17 years between lifespan and years lived in good health. This gap highlights the importance of addressing health management to ensure that increased longevity translates into a healthier life.
Although various health management services have been introduced, their development still lacks systematic procedures and robust methodological foundations. To address this limitation, the present study designs a data-driven health management service grounded in the Digital Me paradigm. Using the MIMIC-III database, which comprises clinical records from intensive care units in a U.S. hospital, the study focuses on the challenge of processing large-scale sequential data—an essential yet complex task due to the temporal nature and clinical importance of such data. Traditional sequence prediction models, including Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, often face inefficiencies related to data compression and long training times [18,19,20]. To overcome these limitations, this study explores the application of language models capable of handling large-scale sequential data, with particular attention to BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which has shown strong potential in sequence processing tasks but has been underutilized in clinical contexts. Specifically, the study evaluates the effectiveness of BERT for predicting systolic blood pressure, demonstrating its applicability to healthcare data analysis.
3.1. Digital Me Context and Privacy Preserving Approach
In 2020, Gartner, a leading research organization in the information technology sector, analyzed 1700 emerging technologies and identified five key trends anticipated to shape the digital economy over the next decade: Composite Architectures, Algorithmic Trust, Beyond Silicon, Formative Artificial Intelligence, and Digital Me [21].
Within the Digital Me paradigm, technologies that integrate digital sensing with human users are gaining prominence. Representative examples include health passports—digital systems that, similar to traditional passports, enable individuals to store and share their complete medical history with ease, and which have already been implemented in several countries—and digital twins, virtual counterparts that mirror an individual’s real-world state. Such constructs can function as identity representations in both physical and virtual environments. More advanced applications include bidirectional brain–machine interfaces (BMIs), wearable devices that enable two-way data exchange between the brain and a computer. Initially designed solely for recording neural electrical activity, recent innovations now permit direct neural stimulation, offering potential uses ranging from therapeutic treatments to the modulation of emotional states.
The definition of Digital Me varies across scholarly perspectives. This study adopts the definition proposed by Lee et al. (2025) [22], which conceptualizes Digital Me as:
“An AI-based product–service system (PSS) that enables real-time management of an individual’s state (e.g., health, beauty, memory, knowledge, finance, happiness). It is grounded in a hardware product that the user consistently carries, supported by a platform integrating services connected to the hardware, data cloud services, AI systems, and both hardware and software services.”
3.2. Hypertension Management in AI-Based Personal Healthcare
Hypertension is a pervasive chronic condition worldwide and a leading contributor to premature mortality. Its prevalence is particularly high among middle-aged and older adults, many of whom remain active participants in the workforce, thereby amplifying its societal and economic implications. In developed nations, lifestyle factors such as diets high in calories, limited physical activity, and sustained exposure to occupational and psychosocial stressors further exacerbate the risk. Consequently, hypertension prevention and management have emerged as critical public health priorities, both to safeguard individual well-being and to sustain the productivity of aging populations.
Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood against the inner walls of blood vessels. It is classified into systolic blood pressure—the peak pressure during cardiac contraction—and diastolic blood pressure—the lowest pressure during cardiac relaxation and ventricular filling [23]. Diagnostic thresholds for hypertension vary internationally. For example, as shown in Table 1, some countries define it as a systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher, or a diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher, while others adopt lower thresholds, such as 130 mmHg for systolic and 80 mmHg for diastolic pressure [24,25,26].

Table 1.
Hypertension diagnosis guideline [25].
Blood pressure is inherently dynamic, fluctuating in response to diverse temporal and contextual factors such as circadian rhythms, seasonal variations, physical activity, dietary intake, mental stress, and ambient temperature. For instance, it may rise transiently during exercise or psychological tension but return to baseline during rest—patterns that constitute normal variation. Hypertension, in contrast, is characterized by persistently elevated blood pressure even at rest. Accurate measurement requires standardized conditions, including a consistent time of day, stable posture, and a relaxed state [24].
Because blood pressure changes over time and under varying conditions, it can be represented as sequential data in which temporal patterns carry clinically significant meaning. Persistent hypertension imposes continuous strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of severe outcomes such as stroke, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. However, its often asymptomatic nature means that detection relies on regular measurement with a sphygmomanometer, and the disease may remain untreated until substantial damage occurs, earning it the designation of a “silent killer” [27]. Recognizing the sequential characteristics of blood pressure data, this study proposes a predictive approach that applies language model architectures to capture temporal dependencies and forecast blood pressure variations under specific conditions.
3.3. LLM for Sequential Data Processing in Hypertension Prediction
A language model (LM) is a computational framework that assigns probabilities to sequences of words to capture the statistical and contextual properties of language. Fundamentally, it aims to identify the most plausible ordering of words within a sequence. The most common training objective involves predicting the next word given a sequence of preceding words. Language models are generally classified into statistical models and artificial neural network–based models. In recent years, neural network–based architectures such as BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) have demonstrated exceptional performance and have become the dominant approach in natural language processing tasks. Given their capability to model complex sequential dependencies, these architectures offer strong potential for applications beyond natural language, including the analysis and prediction of physiological time-series data such as blood pressure measurements.
BERT is a pre-trained language model introduced by Google for applications in natural language processing (NLP). It is built upon the transformer architecture and trained on a curated dataset comprising approximately 3.3 billion words. Unlike the full transformer, BERT employs only the encoder component. In BERT, the input representation is formed by summing three types of embeddings—token, segment, and positional—which are subsequently processed through layer normalization and dropout. Token embeddings are generated using the WordPiece method, enabling subword-level representation. Segment embeddings distinguish between sentences in paired inputs by assigning different segment identifiers, while positional embeddings encode token order following the transformer’s positional encoding mechanism.
During pre-training, BERT employs two unsupervised learning objectives. The first, Masked Language Modeling (MLM), randomly masks a subset of tokens within the input and trains the model to predict the masked tokens. The second, Next Sentence Prediction (NSP), trains the model to determine whether a given sentence logically follows another. After pre-training, BERT can be fine-tuned for a range of natural language processing tasks through transfer learning, including sentence-pair classification, single-sentence classification, question answering, and sequence labeling [28].
3.4. Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Personalized AI
While advanced language models such as BERT can effectively capture sequential dependencies in physiological data like blood pressure, their deployment in healthcare applications is often constrained by strict privacy regulations and the sensitivity of personal medical records. Traditional centralized training approaches require aggregating data into a single repository, which increases the risk of data breaches and may violate privacy laws. Federated Learning (FL) addresses this challenge by enabling collaborative model training across multiple devices or institutions without transferring raw data to a central server. Instead, only model parameters or updates are shared, allowing the creation of robust, personalized AI models while safeguarding patient confidentiality. This section introduces the concept of Federated Learning, highlights its differences from conventional distributed learning, and discusses its potential for privacy-preserving hypertension prediction systems.
Unlike conventional datacenter-based distributed learning, which assumes that each dataset is independent and identically distributed (IID) and trains a shared model in parallel, Federated Learning operates in environments where data is heterogeneous, often non-IID, unbalanced, and distributed across a large number of clients with limited communication capacity [29,30]. A useful analogy can be drawn from the medical field: physicians in different hospitals treat patients using their own expertise and resources. They periodically share treatment insights and diagnostic techniques during conferences, thereby improving collective medical knowledge without exchanging sensitive patient records. Similarly, in Federated Learning, an initial global model is sent to local devices or institutional servers, where it is trained using private data. Only the updated model parameters are then sent back to a central server, aggregated, and redistributed to participating clients. This cyclical process incrementally improves the shared model while preserving data privacy. In contrast to traditional methods such as data anonymization or encrypted transmission, FL eliminates the need to transfer raw data altogether, offering a more robust privacy-preserving framework. As a result, it enables the development of personalized AI systems capable of leveraging sensitive or non-shareable datasets—such as those containing detailed physiological signals—for applications like hypertension prediction.
Through FL, models can be trained individually using data collected from personal devices such as smartphones, incorporating both physiological measurements and relevant personal information. Each locally trained model reflects the unique characteristics of its respective user. These personalized models are then aggregated via federated learning to construct a unified application capable of predicting hypertension status. Figure 1 presents the prototype results of this application in the experimental stage. In this design, sensor data from blood pressure monitors are transmitted to the application, where they are combined with personal information to train individualized AI models locally. The federated aggregation process integrates these models into a single global model, which can predict future blood pressure levels based on the current state and provide personalized targets for blood pressure reduction. This framework enables ongoing, tailored blood pressure management and can be concretely implemented within the Digital Me paradigm using the AMPER (Aim–Measure–Predict–Evaluate–Recommend) framework, wherein the developed model delivers core predictive and recommendation functionalities.
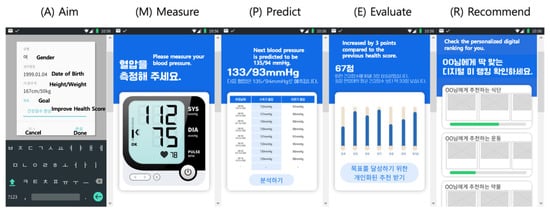
Figure 1.
AMPER framework applied to personalized hypertension prediction.
In the proposed hypertension prediction framework, AutoML is employed to design and optimize personalized models within a federated learning (FL) environment, with BERT serving as the core predictive architecture. On each user’s device, the AutoML pipeline automatically preprocesses raw sensor data from blood pressure monitors, addresses missing or noisy values, and performs feature engineering to capture temporal and contextual indicators such as circadian patterns, activity levels, and stress-related fluctuations. Leveraging AutoML’s search and optimization capabilities, the system fine-tunes BERT to model the sequential dependencies inherent in blood pressure data, adapting the model to each user’s unique physiological and behavioral profile. These locally trained BERT models remain on the device, and only parameter updates are transmitted to a central server for federated aggregation. This process enhances the global model’s predictive power without exposing any raw personal or medical data, ensuring compliance with strict privacy regulations such as the GDPR. Within the Digital Me paradigm and the AMPER framework, this integration of AutoML, BERT, and FL enables continuous, personalized blood pressure prediction and management, while safeguarding the confidentiality of sensitive health information.
4. Applying AMPER
4.1. Data
The MIMIC-III (Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III) database is an open-access resource developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) using data collected from the intensive care units of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. It contains de-identified health records for 61,532 patients—comprising 53,432 adults and 8,100 neonates—who were admitted to the ICU between 2001 and 2012. The dataset includes a wide range of clinical information, such as demographic profiles, vital signs, laboratory measurements, medication prescriptions, caregiver notes, imaging reports, and mortality outcomes [31,32].
The MIMIC-III database is structured as a relational database consisting of 26 tables in total. For this study, the primary tables utilized are ADMISSIONS, CHARTEVENTS, PATIENTS, and PRESCRIPTIONS. The ADMISSIONS table records information on hospital admissions and discharges, while the CHARTEVENTS table stores all charted clinical observations for patients. The PATIENTS table provides demographic details for each individual, and the PRESCRIPTIONS table contains data on medications prescribed, including dosage and administration times.
This study focuses on developing a healthcare service for managing hypertension. Blood pressure is closely associated with obesity, as excess adipose tissue requires an increased blood supply, and neurohormonal changes linked to obesity can contribute to elevated blood pressure. In recent years, the prevalence of hypertension among younger individuals—without other underlying conditions or family history—has risen, with many cases attributable to obesity. Obesity status can be readily assessed through the body mass index (BMI), calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. A BMI above 25 kg/m2 is associated with approximately twice the risk of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia, whereas a BMI above 30 kg/m2 is linked to more than a 1.5-fold increase in mortality from these conditions [33]. Accordingly, in this study, gender, age, systolic blood pressure (SBP), weight, and height were extracted from the MIMIC-III database as key input variables.
The gender of each patient was obtained from the GENDER column in the PATIENTS table. For cohort analysis, it is more meaningful to use the patient’s age at the time of their first admission rather than their age at the time of data extraction. To calculate this, the earliest admission date was identified for each SUBJECT_ID by selecting the minimum value of the ADMITTIME column in the ADMISSIONS table. The patient’s date of birth, available in the DOB column of the PATIENTS table, was then subtracted from this earliest admission date to determine age in years. For instance, if the date of birth is recorded as 2108-01-26 00:00:00 and the earliest admission date is 2149-11-09 13:06:00, the calculated age would be 41 years.
Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and body mass index (BMI) values were obtained from the CHARTEVENTS table in the MIMIC-III database. The CHARTEVENTS table stores a chronological log of all charted clinical data for patients. Each medical observation or procedure recorded in the chart is identified by an itemID, and the corresponding label for each itemID can be verified through the D_ITEMS table. To retrieve SBP measurements, the set of itemIDs associated with systolic blood pressure was used, yielding a total of 6,214,947 records. The specific itemIDs utilized for SBP extraction are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Systolic blood pressure (SBP)-related ItemIDs [34].
Finally, to compute the body mass index (BMI), measurements of patient weight and height were extracted from the CHARTEVENTS table using the corresponding itemIDs. BMI was then calculated as body weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. The specific itemIDs used for retrieving weight and height data are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Body mass index-related ItemIDs [34].
The extracted dataset was preprocessed to improve data quality and ensure the reliability of subsequent analyses. First, gender values originally stored as strings (e.g., “male,” “female”) were converted into a binary format (0, 1) for consistency and computational efficiency. In the MIMIC-III database, patient ages greater than 89 years are anonymized by assigning a value of 300; therefore, records with ages exceeding 89 or below 0 were excluded. For systolic blood pressure (SBP) data, decimal values and extreme outliers, such as 141,146.04, were addressed by converting the VALUENUM column to an integer type and filtering values outside the normal physiological range using an interquartile range (IQR) method. After completing the preprocessing procedures, the resulting dataset comprised 560,736 SBP records from 8911 patients as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Distribution of systolic blood pressure (SBP) measurements before (a) and after (b) preprocessing.
4.2. Aim
Health management extends beyond exercise and dietary control; it also requires setting goals that are both realistic and personally relevant. Goal setting is a critical first step in initiating behavioral change, as it provides a clear direction and fosters the motivation needed to sustain effort. Conversely, objectives that are misaligned with an individual’s circumstances may be unattainable and demotivating. Establishing achievable targets encourages a positive mindset and allows individuals to find satisfaction in the process of improvement. In contrast, overly ambitious goals may result in physical strain, illness, or injury. For example, in weight management, determining an appropriate rate of weight loss over a defined period enables the formulation of realistic long-term objectives and short-term milestones. The accumulation of small, attainable successes can reinforce motivation and facilitate the achievement of the ultimate objective. In this study, the initial target is defined as improving health indicators, specifically blood pressure scores, through a structured and personalized approach.
4.3. Measure
Healthcare data can be collected through a diverse array of measurement modalities, including wearable devices, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, smartphone applications, portable health gadgets, and genetic information analysis. Such technologies enable comprehensive, multidimensional assessment of an individual’s health status. In this study, the MIMIC-III database is employed, which contains data generated in intensive care units (ICUs) and recorded via the Philips CareVue Clinical Information System (models M2331A and M1215A; Philips Healthcare, Andover, MA, USA) and the iMDsoft MetaVision ICU system (iMDsoft, Needham, MA, USA) [31,32].
4.4. Predict
This study seeks to develop a predictive model for forecasting future systolic blood pressure (SBP) values using real patient data. The input features include gender, age, current SBP measurements, and body mass index (BMI), all of which were tokenized prior to model training. The prediction target is the patient’s future SBP value. For instance, if the data for patient SUBJECT_ID 36 are given as in Table 4, the input sequence is formatted as:
“<CLS> 1 69 32.78 <SEP> 147.0 <SEP> 152.0 <SEP> 124.0 <SEP> 118.0 <SEP> 151.0 <SEP> 143.0 <SEP> 158.0 <SEP>…”

Table 4.
Information for SUBJECT_ID = 36.
Table 4.
Information for SUBJECT_ID = 36.
| Sequence | Subject ID | Gender | Age | SBP | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 36 | 1 | 69 | 147 | 32.78 |
| 1 | 36 | 1 | 69 | 152 | 32.78 |
| 2 | 36 | 1 | 69 | 124 | 32.78 |
| 3 | 36 | 1 | 69 | 118 | 32.78 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 10 | 36 | 1 | 69 | 158 | 32.78 |
Here, <CLS> and <SEP> represent special tokens used in the BERT architecture, numerical values denote patient attributes and historical SBP measurements, and the model is trained to predict the next SBP value (e.g., 159.0). In this work, BERT was selected for its ability to capture bidirectional contextual dependencies within a sequence, a property that is particularly advantageous for identifying temporal patterns in physiological time-series data and improving the accuracy of future blood pressure predictions.
For clinical diagnosis of hypertension, guidelines recommend obtaining average blood pressure measurements over a period of 5–7 days, recorded both in the morning and evening [24]. In line with this standard, the present study segmented systolic blood pressure (SBP) data into 7-day intervals for primary analysis, and additionally performed comparative experiments using 30-day intervals. For each segment, the final SBP value was designated as the prediction label. The dataset was then partitioned into training, validation, and testing subsets in a 70:15:15 ratio. Given the sequential nature of SBP measurements, the Time2Vec method was applied to encode temporal information as vector representations during the embedding stage [35].
Systolic blood pressure (SBP) values in medical datasets are inherently time-dependent and may exhibit identifiable temporal patterns, including seasonality and long-term trends. To capture and model these dynamics, preliminary experiments were performed using the Moving Average (MA) and AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models to analyze SBP trajectories. The insights from these analyses were then incorporated into a predictive framework employing the BERT model to forecast future SBP values [36]. The experimental environment comprised both hardware and software components. On the hardware side, computations were performed using an 11th Generation Intel Core i7-11700K CPU (3.6 GHz; Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and a GeForce RTX 3080 D6X GPU (NVIDIA Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with 10 GB of memory. On the software side, all experiments were conducted in a Python 3.7.0 environment.
Using the patients’ systolic blood pressure (SBP) data, three predictive models—BERT, BERT combined with Moving Average (MA), and BERT combined with AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)—were employed to forecast future SBP values. These predictions were then compared against the actual measured values, referred to as the ground truth. The comparative results are presented in Figure 3 and Figure 4. In each figure, the blue line represents the ground truth SBP measurements, while the orange line depicts the SBP values predicted by the respective model.
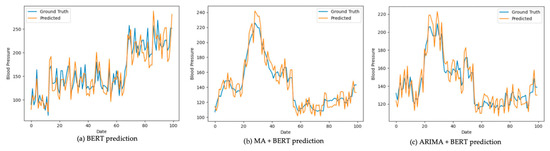
Figure 3.
Prediction result comparison (7-day interval).

Figure 4.
Prediction result comparison (30-day interval).
Model performance was assessed using three error metrics that quantify the difference between the predicted values and the actual measurements: Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE). The results indicate that integrating BERT with either the Moving Average (MA) or AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models yielded lower MAE, MSE, and RMSE values compared to using BERT alone as shown in Table 5. This performance improvement was particularly evident when the models were trained and evaluated on 30-day interval data.

Table 5.
Results of the prediction models.
Within the federated learning framework, two primary approaches to model training are commonly employed: Federated Stochastic Gradient Descent (FedSGD) and Federated Averaging (FedAvg) [29]. Lee et al. (2025) [22] report that FedAvg is generally preferred, as it produces results comparable to FedSGD without notable performance differences. Given the absence of a universally accepted federated learning library, implementations can be developed from scratch using a client–server architecture or built upon existing frameworks such as TensorFlow Federated (2.17.0) or PySyft (0.8.7) for PyTorch (1.10.2), with either approach being valid. In this study, the federated learning component employs Per-FedAvg, an enhanced variant of the FedAvg algorithm. Per-FedAvg incorporates model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML) to identify an effective model initialization, enabling rapid adaptation to heterogeneous data distributions across clients.
Algorithm 1 illustrates the personalized FedAvg (Per-FedAvg) Algorithm [37,38]. The algorithm takes as input the initial iterate and the fraction of active users . For each iteration , the server selects a subset of users uniformly at random, with the size of this subset being . The server then sends the current model weights to all users in . Each user sets their local model to . Then, for each inner iteration , the user computes the stochastic gradient using their dataset , and updates their local model using this gradient. This update process employs two learning rates, . After all inner iterations, each user sends their updated model back to the server. The server updates its global model by averaging the received models:
| Algorithm 1: Pre-FedAvg Algorithm [37,38] |
| Input: Initial iterate , fraction of active users . for to do Server chooses a subset of users uniformly at random and with size ; Server sends to all users in ; for all do Set ; for to do Compute the stochastic gradient using dataset ; Set ; Set ; end for Agent sends back to server; end for Server updates its model by averaging over received models: ; end for |
This study applies the personalized FedAvg (Per-FedAvg) algorithm by organizing patient data according to patient identifiers and distributing it across virtual devices. The process begins with the central server constructing an initial global model, which is then distributed to all virtual devices. At this stage, the global model is randomly initialized, meaning it has not undergone any prior training. Each virtual device uses its local dataset to train a local model, and the resulting trained weights are sent back to the central server.
The procedure of the algorithm is as follows: First, the server initializes the global parameter and distributes it to each client. Subsequently, client k updates its parameters based on the loss function with respect to its local dataset .
Here, denotes the local learning rate. Each client transmits its updated parameter to the server, and the server constructs a new global parameter by computing a weighted average of these parameters.
Here, denotes the number of data samples at client , and represents the total number of data samples. By repeating these procedures, personalized model learning becomes feasible in a federated learning environment. However, real medical data exhibit non-IID characteristics. Differences in the amount of data across hospitals, patient cohort characteristics, and disease distributions can adversely affect model convergence. To mitigate this, this study (1) divides hospitals into a small-sample group (<52 cases) and a representative-sample group (≥52 cases) and compares learning performance, and (2) applies a weighted average across clients proportional to each client’s data count. This design reduces bias arising from data imbalance and contributes to stabilizing learning across clients.
In this experiment, the initial global model is based on the BERT with ARIMA architecture, which achieved the highest predictive performance among the evaluated models and consists of 240,191 parameters. Each device trains its local model using the distributed global model, and the updated weights are then transmitted to the central server. The server aggregates these weights—typically by averaging—to update the global model parameters, which are subsequently redistributed to all devices. Using the updated global model, each device retrains and refines its local model.
To evaluate the error rate between the predicted and actual values, and to enable a direct comparison with the results of the standalone prediction algorithms, the same performance metrics—Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)—were employed. The performance outcomes of the prediction algorithm incorporating personalized federated learning (PFL) are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Results of the prediction model with PFL (30-day interval data).
As a result, the PFL model—integrating the weights of local and global models—exhibited lower overall performance compared to the data-sharing approach. Nevertheless, it demonstrated notable improvements over the local model, with reductions of 16.27% in MAE, 32.03% in MSE, and 17.54% in RMSE. These findings indicate that federated learning can serve as an effective alternative in scenarios where direct data sharing is infeasible.
Additionally, the performance of personalized federated learning was analyzed by comparing patient groups with relatively small and large amounts of data. Patients were divided into two groups—small and large—based on the median number of records held across all patients, which was 52. The small group consists of 3347 patients with fewer records than the overall median (52), while the large group comprises 3109 patients with more records than the median. In the small group, the median number of records per patient is 42, ranging from 30 to 52. In contrast, the large group has a median of 88 records, with the smallest dataset containing 54 records and the largest containing 6762. Table 7 presents the results of the prediction algorithm applying personalized federated learning (PFL) to both groups.

Table 7.
Comparing small and large sample groups in PFL predictions (30-day interval data).
As a result, the small group achieved a 5.59% reduction in MAE compared to the all-patient group, whereas the large group recorded a 10.42% increase. A similar pattern was observed for MSE: the small group showed a 1.87% decrease, while the large group exhibited a 22.30% increase. For RMSE, the small group experienced a 7.15% reduction, in contrast to the 15.90% increase in the large group. These findings indicate that the quantity of data held by each patient significantly influences the performance of the personalized federated learning model, clearly revealing performance disparities between small- and large-data groups.
4.5. Evaluation
In this study, the blood pressure status of users was evaluated using the reference standards provided by the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS). According to this standard, a user’s blood pressure is converted into a score out of 100 points for assessment.
For example, consider a 53-year-old male whose target systolic blood pressure is 135 mmHg, with an actual measurement of 145 mmHg and a predicted value of 150 mmHg. According to the NHIS standard, the average systolic blood pressure for this demographic is 125 mmHg. The differences from the average are −10, −20, and −25 mmHg, respectively. Taking the absolute values and converting them to scores out of 100 using the formula yields scores of 90, 80, and 75 for the target, measured, and predicted values, respectively.
Similarly, for a 35-year-old female with a target systolic blood pressure of 110 mmHg, an actual measurement of 95 mmHg, and a predicted value of 100 mmHg, the NHIS average is 112 mmHg. The differences from the average are +2, +17, and +12 mmHg, which correspond to scores of 98, 83, and 88, respectively. This scoring method allows for the assessment of a user’s current condition and serves as a practical metric for evaluating changes before and after health interventions.
4.6. Recommendations for Service Implementaion
There is an old saying, “illness will make itself known”. PatientsLikeMe—often described as the “Facebook for patients”—was launched in 2004 by three engineers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) to explore treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Over time, it has grown into a global community of approximately 250,000 members, including patients with serious illnesses across the United States and beyond. On this platform, patients document the progression of their symptoms, the side effects and efficacy of medications, and the recurrence or management of their conditions, while sharing experiences and insights with others.
The accumulated data is professionally analyzed and fed back to patients, helping them better understand and predict their conditions. To develop algorithms that accurately predict an individual’s illness, it is essential to incorporate not only the individual’s own health data but also large-scale healthcare datasets from patients with the same or similar conditions. The richer and more interconnected the data, the more precisely personalized healthcare services can be delivered. Accordingly, this study proposes a methodology to identify users similar to the target individual, analyze their behavioral patterns, and recommend actions most likely to improve the target individual’s health score.
The PRESCRIPTIONS table of the MIMIC-III database can serve as a valuable resource for drug recommendation. This table contains detailed information on medications prescribed to patients, including dosage and prescription time. However, since the MIMIC-III database is derived from intensive care unit (ICU) settings, it contains a disproportionately high number of prescriptions for critically ill patients, which should be taken into account when designing a recommendation system.
Suppose we aim to recommend medication to a 53-year-old female patient with a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg and a body mass index of 29.13. By searching for patients with similar profiles in Table 8, SUBJECT_ID 1 and SUBJECT_ID 3 emerge as relevant matches. If these patients received a certain medication and subsequently showed improvement in their blood pressure scores, this outcome could form the basis for recommending the same medication to the target patient. In this scenario, DRUG A, prescribed to SUBJECT_ID 1, could be considered as a recommendation candidate.

Table 8.
Sample data for recommendations.
In this business scenario, the recommendation process can be further enhanced by integrating AutoML into the pipeline. In our research context, AutoML can be configured to automatically explore and optimize various time-series modeling approaches, including the baseline BERT model as well as its enhanced variants such as BERT+MA and BERT+ARIMA. Through automated model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and performance evaluation, AutoML can dynamically determine which configuration is most effective for predicting patient-specific systolic blood pressure trajectories and deriving associated drug recommendations. This approach enables the recommendation agent to adaptively select the optimal time-series prediction model for each patient case, improving personalization and ensuring that the system remains robust even as new data or changing health patterns are introduced.
5. Concluding Remark
This study proposed and experimentally validated a healthcare service built upon the AMPER (Aim–Measure–Predict–Evaluate–Recommend) framework, with the overarching goal of maximizing users’ health status. To handle large-scale sequential data, BERT-based models were employed, achieving comparable or superior performance in blood pressure prediction compared to conventional deep learning models. In addition, privacy concerns associated with data sharing were addressed by applying personalized federated learning (PFL), which—despite performing slightly worse than centralized data sharing—surpassed existing local models by 16.27%, 32.03%, and 17.54% in MAE, MSE, and RMSE, respectively.
Importantly, the primary contribution of this work does not lie in proposing novel algorithms, but in integrating individually validated components into a unified pipeline within the AMPER framework for real-world medical data analysis. Specifically, this involves (1) automating hyperparameter search and model selection via AutoML, (2) representing patient time-series data using a BERT-based sequence model, and (3) enabling PFL in non-IID environments through Per-FedAvg. While each of these components has been investigated independently in prior studies, their integration within a single cohesive system allows the simultaneous pursuit of two often competing objectives—predictive accuracy and privacy preservation. Thus, the contribution of this study is a design- and system-level advancement that demonstrates how these technologies can be synergistically applied in clinical settings.
In contrast to prior reviews that question the clinical applicability of federated learning in healthcare due to methodological flaws and privacy concerns [30], our study demonstrates a system-level integration that mitigates these limitations through the AMPER framework. Unlike prior works focusing primarily on device-level privacy safeguards [39], our contribution highlights how federated learning can simultaneously achieve predictive accuracy and privacy preservation in large-scale sequential clinical data, thereby establishing its practical viability for blood pressure prediction and other clinical applications. This design- and system-level advancement underscores the potential of integrating validated technologies into a unified framework, setting the stage for further exploration of their clinical utility in real-world healthcare environments.
Future research directions are as follows. First, although this study confirmed the validity of the AMPER structure, further investigation is required to integrate it more effectively into health management services. This entails gaining a deeper understanding of its applicability in real-world clinical settings and optimizing its operationalization. Second, while federated learning in this study was performed with a single iteration—reducing both time and cost—its performance could be further stabilized and improved through multiple iterations. Therefore, research on iterative training strategies to enhance both stability and efficiency is warranted. Finally, there is a need to develop methods that improve predictive performance while safeguarding privacy. Potential approaches include data augmentation using generative AI, as well as transforming or synthesizing insufficient datasets to increase diversity, thereby enhancing both privacy protection and model performance.
Despite the encouraging results, several limitations warrant consideration. First, the proposed framework was evaluated exclusively on the MIMIC-III dataset, which—while comprehensive—reflects the clinical practices, patient demographics, and measurement protocols of a single healthcare environment. This limits the generalizability of the findings to broader, more heterogeneous populations. Second, the predictive modeling relied on a relatively constrained set of input variables (e.g., gender, age, SBP, BMI), which, although clinically relevant, may omit other influential physiological or behavioral factors such as medication adherence, dietary patterns, or stress levels. Incorporating a richer set of multimodal data could potentially enhance predictive performance. Third, while the integration of AutoML, BERT, and personalized federated learning demonstrated practical feasibility, the federated learning experiments were simulated under controlled conditions with virtual clients. Real-world deployments would need to contend with non-stationary data distributions, intermittent device connectivity, and variable computational resources, which could adversely affect convergence and model robustness. Fourth, the adoption of the Per-FedAvg algorithm, although effective in the present context, may not represent the optimal personalization strategy for all data regimes, particularly in scenarios with extreme data sparsity or high client heterogeneity. The PFL model proposed in this study demonstrated somewhat lower performance compared with data sharing. This can be explained by several factors. First, even within the same hospital, patient cohort characteristics differ substantially; in particular, the data used in this study are ICU-centered, and the distribution of physiological signals differs markedly from that of general ward patients. Consequently, even for data from a single hospital, patient-level data characteristics are heterogeneous, causing local updates to be biased toward certain groups. During the server aggregation stage, these biased updates may conflict with one another, thereby limiting the optimization of the global model and leading to performance degradation relative to data sharing. Second, there is information loss in the aggregation process. Because PFL blends local and global parameters, sparse patterns or rare cases specific to a particular hospital may be diluted, resulting in degraded performance. Third, there is a limit on the number of training rounds. Due to communication and resource constraints in this study, we could not secure a sufficient number of rounds, and as a result the model did not converge fully. Nevertheless, despite these limitations, PFL showed an improvement of 31.37% over the Local Model (trained solely on individual patient data). This suggests that FL approaches can provide tangible performance gains in environments where data sharing is not possible, relative to simple local training. Therefore, even though PFL exhibited lower performance than data sharing, it can serve as a meaningful alternative in sensitive contexts such as healthcare data. Finally, the study did not conduct a comprehensive comparison with alternative privacy-preserving techniques such as secure multiparty computation or homomorphic encryption, which could offer complementary strengths. Addressing these limitations through cross-institutional validation, expanded feature integration, and field deployment studies would be essential steps toward translating this framework into a clinically viable, privacy-conscious healthcare solution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K. and K.J.L.; methodology, S.K.; software, S.K.; validation, S.K., A.P. and K.J.L.; formal analysis, S.K.; investigation, S.K.; resources, S.K.; data curation, A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K. and T.K.; writing—review and editing, T.K.; visualization, T.K.; supervision, T.K.; project administration, A.P.; funding acquisition, A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea (grant no. NRF-2023S1A5A8080527).
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://physionet.org/content/mimiciii/1.4 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karmaker, S.K.; Hassan, M.M.; Smith, M.J.; Xu, L.; Zhai, C.; Veeramachaneni, K. AutoML to Date and Beyond: Challenges and Opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yu, K.; Xie, F.; Liu, M.; Sun, S. Automated Machine Learning with Interpretation: A Systematic Review of Methodologies and Applications in Healthcare. Med. Adv. 2024, 2, 205–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Kannath, S.K.; Mathew, J.; Sylaja, P. AutoML Accurately Predicts Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Large Vessel Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1259958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musigmann, M.; Nacul, N.G.; Kasap, D.N.G.; Heindel, W.; Mannil, M. Use Test of Automated Machine Learning in Cancer Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Lei, D.; Tan, C.; Guo, H. Machine Learning Models for Slope Stability Classification of Circular Mode Failure: An Updated Database and Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) Approach. Sensors 2022, 22, 9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Hallin, C.A.; Koren, M.; Issa, A.A. AutoML Classifier Clustering Procedure. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 37, 4214–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkar, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, Q.V.; Wang, D.; Weisz, J.D. Model LineUpper: Supporting Interactive Model Comparison at Multiple Levels for AutoML. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI ’21), College Station, TX, USA, 14–17 April 2021; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, M.; Tornede, A.; Mohr, F.; Hüllermeier, E. AutoML for Multi-Label Classification: Overview and Empirical Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 3037–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutiérrez, L.; Hassan, R.; Li, Y.; Tan, T.F.; Cheng, H.; Teo, Z.L.; Lim, G.; Ting, D.S.W. Clinical Performance of Automated Machine Learning: A Systematic Review. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2023, 53, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, W.N.; Cohen, I.G. Privacy in the Age of Medical Big Data. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuveneers, D. AutoFL: Towards AutoML in a Federated Learning Context. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, A.; Karras, C.; Giotopoulos, K.C.; Tsolis, D.; Oικονόμου, Κ.; Sioutas, S. Federated Edge Intelligence and Edge Caching Mechanisms. Information 2023, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, K.; Lim, G.; Ting, D.S.W. Medical Image Classification with On-Premise AutoML: Unveiling Insights through Comparative Analysis. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, K.; Lim, G.; Ting, D.S.W. A Comparative Study of an On-Premise AutoML Solution for Medical Image Classification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alardawi, A.S.; Odeh, A.; Aboshgifa, A.; Belhaj, N. Challenges and Opportunities in Federated Learning. Int. Sci. Technol. J. 2022, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggirala, J. Federated Learning on Mobile Devices: Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions. Int. Sci. J. Eng. Manag. 2024, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H. Results of the Life Table Created in 2022. Available online: https://kostat.go.kr/board.es?mid=a10301060900&bid=208&act=view&list_no=428312&tag=&nPage=1&ref_bid= (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning Long-Term Dependencies with Gradient Descent Is Difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations Using RNN Encoder–Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long. Short-Term. Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, K. 5 Trends Drive the Gartner Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies. 2020. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/5-trends-drive-the-gartner-hype-cycle-for-emerging-technologies-2020 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Lee, K.J.; Jeong, B.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. Towards Minimally Domain-Dependent and Privacy-Preserving Architecture and Algorithms for Digital Me Services: EdNet and MIMIC-III Experiments. In Proceedings of the 58th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS 2025), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2025; pp. 1348–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Hypertension. Available online: https://hqcenter.snu.ac.kr/archives/jiphyunjeon/%EA%B3%A0%ED%98%88%EC%95%95 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- 2022 Hypertension Treatment Guidelines. Available online: https://www.koreanhypertension.org/reference/guide?mode=read&idno=10081 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; Simone, G.; Desormais, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hypertensive Heart Disease. Available online: https://hqcenter.snu.ac.kr/archives/jiphyunjeon/%EA%B3%A0%ED%98%88%EC%95%95%EC%84%B1-%EC%8B%AC%EC%A7%88%ED%99%98?cat=194 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; y Arcas, B.A. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS 2017), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; pp. 1273–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Kairouz, P.; McMahan, H.B.; Avent, B.; Bellet, A.; Bennis, M.; Bhagoji, A.N.; Bonawitz, K.; Charles, Z.; Cormode, G.; Cummings, R.; et al. Advances and Open Problems in Federated Learning. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2021, 14, 1–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Pollard, T.; Mark, R. MIMIC-III Clinical Database. Available online: https://physionet.org/content/mimiciii/1.4/ (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.H.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, a Freely Accessible Critical Care Database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comorbidities of Obesity. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Available online: https://general.kosso.or.kr/html/?pmode=obesityDisease (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Wang, S.; McDermott, M.B.; Chauhan, G.; Ghassemi, M.; Hughes, M.C.; Naumann, T. MIMIC-Extract: A Data Extraction, Preprocessing, and Representation Pipeline for MIMIC-III. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning (CHIL ’20), Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–4 April 2020; pp. 222–235. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, S.M.; Goel, R.; Eghbali, S.; Ramanan, J.; Sahota, J.; Thakur, S.; Wu, S.; Smyth, C.; Poupart, P.; Brubaker, M. Time2Vec: Learning a Vector Representation of Time. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.05321. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; Holden-Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Kaplan, Z.; Niu, D.; Li, B. Optimizing Federated Learning on Non-IID Data with Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2020—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 1698–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah, A.; Mokhtari, A.; Ozdaglar, A. Personalized Federated Learning with Theoretical Guarantees: A Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning Approach. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 3557–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.T.; Kaladevi, A.C.; Kumar, V.V.; Shankar, A.; Alqahtani, F. Privacy Enhanced Edge-AI Healthcare Devices Authentication: A Federated Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025, 71, 5676–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).