Abstract
In security applications, visible-light pedestrian detectors are highly sensitive to changes in illumination and fail under low-light or nighttime conditions, while infrared sensors, though resilient to lighting, often produce blurred object boundaries that hinder precise localization. To address these complementary limitations, we propose a practical multimodal pipeline—Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) Fusion with AIFI-YOLOv12—that first fuses infrared and low-light visible images using per-pixel weights derived from local energy, gradient magnitude and contrast measures, then detects pedestrians with an improved YOLOv12 backbone. The detector integrates an AIFI attention module at high semantic levels, replaces selected modules with A2C2f blocks to enhance cross-channel feature aggregation, and preserves P3–P5 outputs to improve small-object localization. We evaluate the complete pipeline on the LLVIP dataset and report Precision, Recall, mAP@50, mAP@50–95, GFLOPs, FPS and detection time, comparing against YOLOv8, YOLOv10–YOLOv12 baselines (n and s scales). Quantitative and qualitative results show that the proposed fusion restores complementary thermal and visible details and that the AIFI-enhanced detector yields more robust nighttime pedestrian detection while maintaining a competitive computational profile suitable for real-world security deployments.
1. Introduction
Robust pedestrian detection is a core requirement for many security and surveillance systems, including perimeter monitoring, vehicle–pedestrian interaction and crowd safety management. In practical deployment scenarios, detectors must handle occlusion, large-scale variation and complex backgrounds, while being robust to extreme changes in ambient illumination. Visible-light (RGB) detectors typically perform well in well-lit scenes, but their reliability degrades rapidly at dusk and night due to reduced signal-to-noise ratio and loss of fine texture [1]. By contrast, thermal infrared (IR) sensors provide illumination-invariant cues by highlighting human heat signatures, but IR imagery often exhibits blurred object boundaries and low texture, which complicates accurate localization and increases false positives in dense scenes [2]. These complementary failure modes motivate multimodal strategies that fuse IR and visible inputs to exploit thermal saliency while retaining visible-domain edges and textures for precise localization [3,4].
Research on infrared–visible image fusion has evolved from transform- and pyramid-based schemes to deep-learning solutions that learn adaptive fusion operators. Early, hand-crafted methods focused on multi-scale decomposition and rule-based combinations, showing good structural preservation in some cases [5], while more recent convolutional- and transformer-based approaches demonstrate improved ability to retain both salient thermal targets and visible details through learned feature mappings [6,7]. However, comprehensive surveys note that many fusion techniques prioritize perceptual image quality and do not directly optimize for downstream tasks such as object detection; consequently, there remains a trade-off between structure preservation, edge/contrast retention, and computational costs necessary for real-time security systems [3,8]. These observations highlight the need for task-aware fusion strategies that evaluate fusion based on its impact on detection accuracy and runtime [9].
On the detection front, single-stage detectors in the YOLO family remain attractive for real-time surveillance because of their favorable speed–accuracy trade-offs. Recent YOLO iterations increasingly incorporate attention mechanisms and more efficient feature-aggregation blocks to enhance representation under degraded inputs, while attempting to maintain real-time inference speed [10]. In particular, attention-centric designs—exemplified by the latest YOLO developments—suggest that compact attention modules can improve detection robustness on low-contrast or noisy inputs without a prohibitive increase in GFLOPs when integrated carefully [11,12]. Community benchmarks and comparative studies further indicate that architectural choices such as multi-scale heads and selective block replacements can materially affect small-object performance, which is crucial for pedestrian detection at a distance [13].
Multimodal detection approaches generally follow two paradigms: pre-fusion (pixel-level fusion followed by a detector) and feature/prediction-level fusion (joint fusion inside the detection network). Several contemporary works, including TFDet and MMYFnet, have shown that modality fusion or cross-modal attention can significantly improve pedestrian detection under adverse illumination, but many studies evaluate limited or synthetic datasets or emphasize network innovations without thoroughly designing the pixel-level fusion to restore both thermal saliency and visible edges for downstream detectors [14,15]. The LLVIP dataset, a large-scale strictly paired visible–infrared benchmark collected under low-light conditions, enables realistic evaluation of fusion + detection pipelines and exposes the remaining challenges in nighttime pedestrian detection [1,16].
Attention-centric modules such as AIFI (attention-based instance/feature interaction) and efficient feature-aggregation blocks (e.g., A2C2f-style modules and C3 variants) have been adopted in recent detection and multimodal works to enhance cross-channel interactions and suppress modal noise. Empirical evidence suggests that inserting compact attention mechanisms at high semantic levels and preserving P3–P5 multi-scale detection outputs can improve localization of small or partially occluded pedestrians in degraded inputs, while controlling computational overhead for deployment [17,18]. These architectural motifs thereby motivate an integrated pipeline that combines a carefully designed pixel-level fusion front end with an attention-enhanced detection backbone.
Motivated by these observations, we propose a practical two-stage multimodal pipeline tailored for security applications: (i) an Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) pixel-level fusion algorithm that computes per-pixel fusion weights from local energy, gradient magnitude and contrast to preserve thermal structures and visible edges, and (ii) an AIFI-enhanced YOLOv12 detector that inserts an AIFI attention module at high-level features, selectively replaces C3 blocks with A2C2f blocks, and retains P3–P5 detection heads to improve small-object localization. We evaluate the complete pipeline on the LLVIP benchmark and compare it against modern baselines (YOLOv8, YOLOv10–YOLOv12, n and s scales) using Precision, Recall, mAP@50, mAP@50–95, GFLOPs, FPS and detection time; we also present ablation studies that isolate the contributions of fusion and detector modifications and provide qualitative examples showing improved robustness under night and thermal-blur conditions [1,7,13,17,19].
The main innovations and contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- Adaptive EGC fusion: We propose an adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) pixel-wise fusion strategy that computes per-pixel weights from energy, gradient, and local contrast to fuse IR and VIS images. This fusion preserves the saliency of thermal imagery while retaining visible-light edge details in low-light/nighttime scenes, thereby improving target boundary localization and the detectability of weak targets [3,6].
- (2)
- AIFI-YOLOv12 architecture: We introduce an Adaptive Inter-Feature Interaction (AIFI) module into the high-level layers of the YOLOv12 backbone. By applying joint channel and spatial re-calibration, AIFI suppresses modal noise and enhances discriminative feature responses, helping to reduce false positives caused by thermal noise. We introduce an efficient edge-enhancement branch while retaining P3–P5 multi-scale detection heads, which improves localization and detection of distant, small, and edge-blurred targets without significantly increasing computational burden. The overall architecture balances accuracy and deployment efficiency, making it well-suited for resource-constrained nighttime surveillance scenarios [11,17].
- (3)
- Comprehensive evaluation on LLVIP: We provide a systematic experimental study on the LLVIP dataset, reporting Precision, Recall, mAP@50, mAP@50–95, GFLOPs and FPS, and compare our method to recent baselines (YOLOv8, YOLOv10–YOLOv12, n/s scales) under identical training and evaluation protocols to ensure fair comparison [1,16].
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews related work on infrared–visible image fusion and multimodal pedestrian detection. Section 3 details the proposed Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) fusion algorithm and the AIFI-YOLOv12 architecture. Section 4 describes dataset splits, preprocessing, training recipes and evaluation metrics. Section 5 presents experimental results and ablation studies and concludes with future directions such as end-to-end fusion–detection learning and lightweight model compression for edge deployment.
2. Related Work
This section first summarizes prior work on infrared–visible fusion and then examines multimodal detection and attention-enhanced backbones. Image-level fusion methods play a central role in many practical RGB–T pipelines because they directly determine the visual cues available to off-the-shelf detectors; consequently, task-aware fusion that considers downstream detection performance has become an important research direction [20,21,22]. After reviewing fusion techniques, we discuss recent RGB–thermal pedestrian detection frameworks and attention/module-level advances that are relevant when integrating fused inputs into modern detectors [23,24,25,26,27]. These focused reviews set the stage for positioning our Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) fusion and AIFI-enhanced YOLOv12 approach relative to prior work.
2.1. Infrared–Visible Image Fusion
Image-level fusion of infrared and visible images has been studied extensively because fusion can combine the thermal saliency of infrared sensors with the texture and edge details of visible imagery. Traditional methods—such as pyramid/transform-domain fusion and sparse-representation schemes—emphasize multi-scale structure preservation and often produce visually coherent results under controlled conditions [20]. More recently, learning-based methods (including convolutional and GAN-based approaches) have become dominant: these methods learn to map and merge complementary features from each modality, and many achieve superior perceptual quality and better downstream performance compared to hand-crafted rules [28,29]. Nevertheless, surveys note persistent trade-offs: techniques optimized for perceptual metrics do not always translate to improved detection performance, and many fusion models remain too heavy for real-time security deployments [21]. This motivates task-aware fusion strategies that explicitly evaluate (or optimize for) downstream detection accuracy and computational efficiency [22].
2.2. Multimodal (RGB–Thermal) Pedestrian Detection
Multimodal pedestrian/object detection approaches generally follow either pre-fusion (pixel-level fusion followed by an off-the-shelf detector) or feature-/prediction-level fusion (fusion inside the detection network). Pre-fusion pipelines offer the advantage of decoupling fusion and detection design, enabling the use of well-engineered detectors on fused inputs, while feature-level fusion can learn joint representations that adapt to modality-specific noise and misalignment [23,24]. Recent target-aware and attention-guided fusion methods for RGB–thermal pedestrian detection demonstrate clear improvements in low-light scenarios by focusing representational capacity on target regions and suppressing noisy backgrounds [25]. However, several works report that many existing methods are evaluated on limited or synthetic datasets, and that robust, large-scale benchmarks (such as LLVIP) reveal remaining gaps—particularly for small/distant pedestrians and in scenes with thermal blur or severe illumination variation [26]. Consequently, designing fusion schemes that both restore complementary details and produce inputs well-suited for high-performance detectors remains an active research need.
2.3. Attention Modules and Detector Backbone Design for Degraded Inputs
On the detector side, single-stage architectures (particularly the YOLO family) remain popular for surveillance due to their favorable speed–accuracy trade-offs. Recent detector research has focused on two complementary directions relevant to multimodal inputs: (1) introducing compact attention mechanisms to re-weight channels/spatial regions and thus suppress modal noise or highlight thermal cues, and (2) improving multi-scale aggregation (e.g., preserving P3–P5 outputs or using efficient C2f/C3k-type blocks) to boost small-object localization. Compact attention blocks inserted at high semantic layers often yield robustness gains on low-contrast or noisy inputs with modest GFLOPs overhead, making them attractive for security applications that require real-time inference [27,30]. At the same time, modular, lightweight fusion or plug-in modules (which can be attached to necks or detection heads) enable practical combinations of fusion and detection without redesigning the entire detection pipeline [31].
In general, the literature indicates that (i) fusion methods should be evaluated not only by image quality but also by their effect on downstream detection; (ii) attention-enhanced, multi-scale detectors offer a pragmatic path to improved robustness on fused low-light inputs; and (iii) benchmarks such as LLVIP are necessary to validate practical nighttime performance. Building on these insights, our work designs an Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) pixel-level fusion that explicitly targets thermal saliency and visible-edge restoration, and couples it with an AIFI-enhanced YOLOv12 backbone (compact attention at high levels + selective A2C2f-like blocks + P3–P5 outputs). This combined design seeks to (a) produce fused inputs that materially improve detection quality and (b) keep computational cost compatible with real-world security deployment, addressing gaps observed in prior fusion- or detector-centric studies [32,33,34].
3. Methodology of the Proposed Framework
3.1. Overview of the Framework
This work proposes A Framework of Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) Fusion with AIFI-YOLOv12 for Nighttime Pedestrian Detection in Security, a practical pipeline designed to improve pedestrian detection performance in low-light surveillance by combining an interpretable fusion front end with a modern attention-aware detector. The framework is organized in four sequential stages: preprocessing and alignment, adaptive EGC fusion, lightweight postprocessing, and detection. As shown in Figure 1, the pipeline consists of four stages: (i) preprocessing and alignment, (ii) Adaptive EGC pixel-level fusion, (iii) lightweight post-processing, and (iv) detection with the AIFI-enhanced YOLOv12 backbone. The general philosophy of using an explainable fusion front end to improve downstream task performance is supported by recent reviews and application studies in IR–VIS fusion literature [35,36].
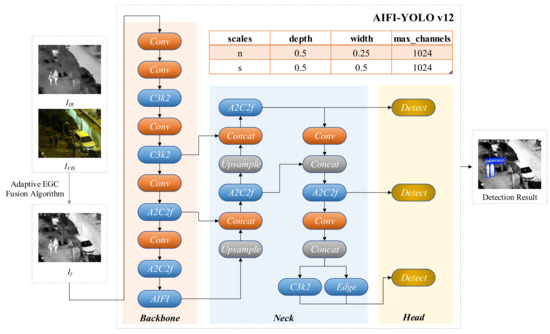
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of the proposed IR–VIS multimodal fusion detection network.
In the preprocessing stage, paired infrared (IR) and low-light visible (VIS) images are geometrically aligned, when necessary, resized to a common resolution, and intensity-normalized to the same numeric range (conventionally [0,1]). This standardization ensures that local statistics computed by the fusion block are consistent across modalities and frames, improving the numerical stability of subsequent per-pixel weight formation [37].
The core fusion stage (Adaptive EGC fusion) computes three complementary local cues for each modality—local energy, gradient magnitude, and local contrast—which are then normalized and linearly combined into per-pixel modality scores. These per-pixel scores are converted to per-pixel weights, spatially regularized to enforce region-level coherence, and used to produce a single-channel fused image by pixelwise weighted averaging. The design intentionally favors a single-scale, single-channel output: this reduces computational burden and avoids introducing unnecessary channel redundancy, while yielding a detector-friendly input that preserves both thermal saliency and structural detail [35,38].
After fusion, a lightweight postprocessing pipeline (histogram equalization, small kernel smoothing, and mild sharpening) is applied to the fused image to enhance local contrast and edge clarity while avoiding artifacts that might mislead the detector [38]. The processed image is then passed to the AIFI-YOLOv12 detector, which outputs pedestrian bounding boxes and confidence scores. Detection performance is evaluated on a paired IR–VIS low-light benchmark (e.g., LLVIP) using standard detection metrics (Precision, Recall, mAP@50, mAP@50–95) together with computational metrics (GFLOPs and detector FPS) to reflect real-world deployment constraints [36,37].
3.2. Adaptive EGC Fusion
The Adaptive EGC fusion module is intended to exploit the complementary strengths of IR and VIS modalities: IR reliably captures thermal saliency in darkness, while VIS contains structural edges and texture useful for localization. Example fusion outputs and intermediate maps (energy, gradient, contrast, and smoothed weight maps) are shown in Figure 2; these illustrate how thermal saliency and visible edges are combined pixelwise.
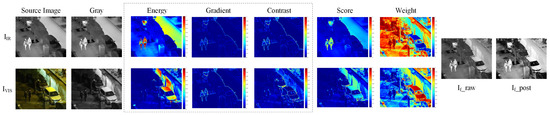
Figure 2.
Adaptive EGC fusion process and examples. (Left) IR and low-light VIS sources. Middle: computed local energy, gradient, and contrast maps and the per-pixel modality weight maps. (Right) fused image before and after lightweight enhancement.
Notation and preprocessing. Let and denote the raw paired infrared and visible images. After geometric alignment (if required) and intensity normalization to [0,1], denote the preprocessed single-channel images by and , where ranges over the image grid of size h × w.
Local cues. For each modality and pixel , define three local measures that capture complementary aspects of local appearance, a strategy commonly adopted in fusion research to balance saliency and structure [35,39]:
- Local energy : computed over a small neighborhood (3 × 3), local energy emphasizes aggregate squared intensity (thermal or luminous power):
- Gradient magnitude : computed by finite differences to capture edge strength and object contours:
- Local contrast : estimated as local standard deviation over a larger neighborhood (5 × 5), capturing texture and intensity variability:
Normalization and per-pixel scoring. To make cue magnitudes comparable, each cue map is normalized by its global maximum (with a small to avoid division by zero):
where prevents division by zero. We adopt max-based scaling because (i) it preserves relative cue ratios, (ii) avoids subtractive operations that can amplify noise when the global minimum is near zero (a common case in low-illumination images), and (iii) in validation experiments (LLVIP) produced detection metrics indistinguishable from min–max scaling. For reproducibility, we therefore use max-based normalization in all reported experiments.
A per-pixel modality significance score is then formed by linear aggregation of the normalized cues:
where are scalar coefficients expressing global relative importance. The practical benefit of this multi-cue scoring strategy has been discussed in recent surveys and empirical studies [35,36,39]. For the results reported in this paper, we used fixed coefficients . These values were selected via a small grid search on the LLVIP validation set, because thermal responses tend to be more reliable in nighttime/low-light scenes, we assigned a slightly higher weight to the energy term . Specific ablation experiments are detailed in Section 4.4: Ablation Experiments.
Weight formation and spatial regularization. To enhance the fusion process, we apply spatial regularization to the per-pixel weights to ensure smooth and consistent feature integration across the image. Spatial regularization helps prevent abrupt transitions between neighboring pixels, which could lead to artifacts in the fused image. This regularization ensures that features from both infrared and visible modalities are fused in a coherent manner, preserving the spatial structure of the image while balancing the contributions of both modalities. The modality scores are converted into raw per-pixel weights by normalization across modalities:
This ensures that the weight assignments are consistent and proportional, allowing each modality to contribute effectively to the final fused image.
Raw weights may fluctuate due to noise or small misalignments; to encourage coherent weighting over object-support regions and to reduce salt-and-pepper artifacts, spatial regularization such as Gaussian smoothing is applied:
where denotes a 2D Gaussian kernel and ∗ denotes convolution. The importance of spatial consistency in stabilizing fusion outputs for downstream tasks has been recognized in fusion literature [35,38].
Fusion operator and enhancement. The fused gray image is obtained by pixelwise weighted averaging of the two modalities using the smoothed weights:
A lightweight enhancement stage (histogram equalization, small kernel denoising, mild sharpening, and intensity rescaling) follows to improve local contrast and edge emphasis without introducing artifacts that may confuse the detector [38].
Rationale for adaptivity. The procedure is adaptive because the per-pixel weights are functions of local image statistics ; consequently, different pixels or regions will automatically receive different modality emphasis depending on thermal prominence, edge strength, or local contrast. Thus, adaptivity is data-driven and spatially varying even when the aggregation coefficients are globally fixed.
Practical choices. For surveillance deployments, typical parameter choices are , and a modest Gaussian standard deviation for spatial regularization that balances smoothing with boundary preservation. Because the fusion module uses only local convolutions and per-pixel arithmetic, its computational complexity scales approximately linearly with image size, and it can be accelerated with optimized GPU libraries for real-time or near-real-time operation [35,38].
The merging of energy–gradient–contrast (EGC) features involves combining the energy, gradient, and contrast information at each pixel to preserve both the thermal saliency from the infrared image and the edge/texture details from the visible image. The energy term captures the local intensity variations, the gradient term emphasizes the boundaries and edges, and the contrast term enhances the discriminative features, especially in low-contrast regions. These features are then fused together by weighting them appropriately to maintain the most salient information from both images. This multi-feature fusion ensures that key features, especially those crucial for pedestrian detection, are retained across both infrared and visible spectra, improving detection accuracy in complex conditions.
However, to further enhance the fusion performance, it is important to understand how the features cooperate under varying environmental conditions. In low-contrast scenarios, the local energy and gradient terms play a crucial role in identifying the underlying object boundaries despite the lack of clear contrast. The gradient-based fusion mechanism helps to preserve edge information, which is particularly useful for detecting weakly contoured targets such as pedestrians in dimly lit environments.
Similarly, in weak-texture conditions, where visual information may be sparse, the EGC fusion method adapts by emphasizing contrast and gradient-based cues, which provide critical information about object structure and shape. By combining these local features from both infrared and visible images, the method ensures that important details are not lost, even when texture or contrast is minimal.
Thus, the EGC fusion method is specifically designed to adapt to such challenging environmental conditions by dynamically adjusting the weight of energy, gradient, and contrast information. This adaptability makes it highly effective for nighttime and low-light pedestrian detection, where traditional fusion methods might fail to retain essential information.
3.3. Improved YOLOv12 Detection Network
To accommodate single-channel inputs produced by the proposed energy–gradient–contrast (EGC) adaptive fusion and to improve pedestrian detection under nighttime, low-contrast and weak-texture conditions, we propose several structural enhancements to the YOLOv12-turbo backbone. The principal innovations are: (i) introduction of composite multi-receptive-field feature blocks in the backbone to strengthen responses to energy and gradient cues; (ii) insertion of an adaptive inter-feature interaction (AIFI) attention module at the high semantic level (P5) to perform joint semantic-and-saliency feature re-calibration; and (iii) integration of an edge-enhancement modulation branch in the multi-scale detection head to increase sensitivity to small and weak-edge targets.
3.3.1. Overall Architecture and Design Objectives
The improved detector retains the one-stage detection paradigm and P3–P5 multi-scale outputs of YOLOv12, preserving end-to-end real-time operation [13,14]. In light of practical requirements for nighttime surveillance, the architecture is augmented at the backbone, high-level attention, and head stages with modules that together aim to: (1) increase representation of EGC features (energy, gradient, contrast) with minimal additional computation; (2) adaptively resolve modality imbalance in fused images by selectively amplifying modality-informative signals; and (3) improve small-target recall while remaining friendly to edge deployment, as shown in Figure 3. (a) Content contained in the left panel: the conventional YOLOv12 backbone–neck–head pipeline with P3–P5 multi-scale detection heads, and (b) content of the right panel: the modified network architecture adopted in this study, which contains three key improvements—two of them are marked with red rectangles in the figure, and the third is an optimization added at the input end (not marked in the figure). The red rectangles in the figure indicate the typical insertion positions of the two marked improvements, and the small table above the figure lists the compound scaling constants (depth, width, max_channels) used in the experiments [7,8,15].
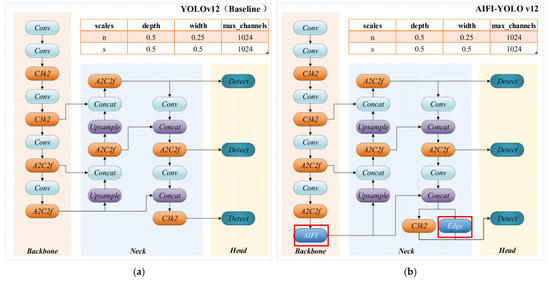
Figure 3.
Comparison of the baseline YOLOv12 (a) and the proposed AIFI-YOLOv12 (b).
3.3.2. Composite Multi-Receptive-Field Feature Blocks (Backbone)—Retaining Energy and Gradient Cues at Low Levels
As shown in Figure 4, to preserve EGC-driven discriminative signals early in the pipeline, the backbone incorporates composite multi-receptive-field feature blocks. Each block comprises several parallel convolutional branches (with different kernel sizes and lightweight designs, e.g., depth-wise separable or grouped convolutions). Branch outputs are concatenated, projected by a 1 × 1 convolution and fused with a residual connection. Formally, given an input feature map , the block computes
where denotes a branch transform. This design balances wide receptive fields and fine-grained texture preservation so that regional energy and edge variations are better retained at early feature stages. The approach aligns with prior work emphasizing energy preservation and edge retention in fusion and feature-enhancement research [5,18].
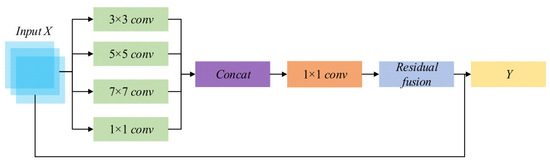
Figure 4.
Multi-receptive-field parallel branch used in the backbone.
As shown in Figure 4, specifically, given an input feature X, the block extracts complementary representations via parallel convolutional branches with different effective receptive fields—illustrated here as 3 × 3 (depthwise/separable) for local details, dilated 5 × 5 for mid-range context, grouped 7 × 7 for wider context, and a 1 × 1 bottleneck for channel mixing. Outputs from all branches are concatenated along the channel axis to form a multi-receptive feature, reduced by a 1 × 1 projection back to the input channel dimension, and fused with the input through residual addition.
3.3.3. AIFI: Adaptive Inter-Feature Interaction—Semantic and Saliency Re-Calibration at High Level
Although EGC fusion increases per-pixel saliency, fused single-channel images still exhibit local modality dominance (some regions dominated by IR, others by VIS). To address this, as shown in Figure 4, we design the Adaptive Inter-Feature Interaction (AIFI) module at the P5 semantic stage to adaptively re-calibrate both channel and spatial weights. AIFI proceeds as follows: multi-head self-attention is computed in a reduced (projected) channel space to capture long-range semantic dependencies and yields ; channel gating (GAP + MLP) and spatial saliency mapping (pooled concatenation + small conv) are then computed; the final recalibrated feature is as follows:
where denotes element-wise multiplication. By computing attention in a lower-dimensional projection and projecting back, AIFI controls computation while enabling the module to (i) select modality-relevant channels and (ii) spatially emphasize positions with high energy/gradient/contrast, thus improving localization and classification under modality imbalance and low-contrast conditions [16,40].
The specific process is shown in Figure 5. Input feature F is first projected to a reduced channel space , processed by multi-head self-attention and projected back to form . Two lightweight gating branches compute a channel gate and a spatial saliency map . The final recalibrated output is .
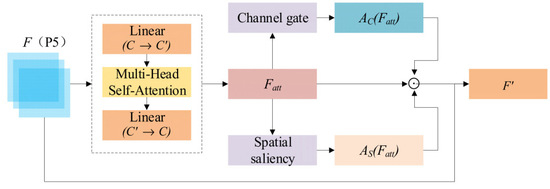
Figure 5.
Architecture of the AIFI block.
3.3.4. Edge-Enhanced Multi-Scale Detection Head—Improving Response to Small and Weak-Edge Targets
To improve small-scale recall, we introduce an edge-enhancement modulation branch for each detection scale (P3, P4, P5). The choice of using P3–P5 outputs—which correspond to feature maps at different scales—was made to address the varying sizes of objects in the detection task. P3, P4, and P5 represent different levels of abstraction in the feature pyramid network, with P3 capturing coarser, high-level features, and P5 focusing on finer, low-level details. By combining outputs from these different scales, we leverage both global context and local details, which is crucial for accurately detecting pedestrians of varying sizes, especially smaller objects that might otherwise be missed by higher-level feature maps.
For scale s, a normalized edge map is computed from shallow features using a lightweight operator (e.g., Sobel or a small conv block). After smoothing and optional thresholding, modulates the scale feature via the following equation:
where is a small scale-dependent coefficient (fixed or learnable). The modulated feature is then fed to the standard detection branch. Smoothing of and constraints on prevent noise amplification. This lightweight modulation strategy has been shown to improve small-object detection in multispectral pedestrian detection contexts [21] and aligns with recent practical advances in multimodal detection [7,8,15].
3.3.5. Implementation Details and Engineering Trade-Offs
To ensure deployability and real-time performance, the following engineering choices are applied: composite branches use depth-wise/grouped convolutions and 1 × 1 projections to limit parameters and FLOPs; AIFI computes attention in a reduced channel space to reduce memory and computation; edge branches are intentionally lightweight to avoid inference latency increases. For transfer learning, the single-channel EGC input can be duplicated to three channels to reuse RGB pretrained weights, or the first convolution can be adapted to a single channel and fine-tuned. A staged training schedule (freeze base layers → unfreeze attention and heads) and small-object loss reweighting are recommended. Nighttime noise robustness is improved by applying normalization (Layer Norm/Batch Norm) and light regularization (dropout, weight decay) inside attention and edge components.
Compared with existing multimodal detectors, this design systematically amplifies EGC-driven discriminative signals at three hierarchical locations (backbone, high-level attention, multi-scale head). The combination of multi-head self-attention with saliency-driven channel and spatial gating (AIFI) is tailored to fused single-channel inputs, enabling dynamic modality selection and spatial emphasis. The edge-modulation in detection heads provides a low-cost but effective means to increase small-object sensitivity without constructing heavy cross-modal fusion subnets. Collectively, these innovations are intended to improve detection robustness and accuracy in nighttime surveillance while maintaining real-time feasibility [5,7,8,13,14,15,16,18,21,40].
4. Experiment Results
4.1. Dataset
In this study, we evaluated the proposed Adaptive EGC fusion + AIFI-YOLOv12 pipeline using the publicly available LLVIP dataset. The LLVIP dataset is a visible-infrared paired benchmark specifically collected for low-light vision tasks. After quality filtering, the official release contains 30,976 images (15,488 aligned visible-infrared pairs). This dataset is designed for low-light vision tasks, particularly in applications like pedestrian detection.
Dataset Split:
To ensure the model’s generalization capability across diverse scenarios while avoiding overlapping between different data subsets, we adopted a 70% (train)/20% (validation)/10% (test) split. Dataset splits and image sizes are summarized in Table 1. The split is as follows:
- Training Set (70%): Contains 21,683 images (approximately 10,842 image pairs). The training set is used to train the model, and all input images are processed using the Adaptive EGC fusion method to generate fused single-channel images for YOLOv12 detection.
- Validation Set (20%): Contains 6195 images (approximately 3098 image pairs), used for hyperparameter selection and model evaluation during training, ensuring the best-performing model is selected.
- Test Set (10%): Contains 3098 images (approximately 1548 image pairs), used for final evaluation to assess the model’s generalization on an independent test set.

Table 1.
Experiment dataset.
Table 1.
Experiment dataset.
| Total Number of Images | Original Image Size | Input Image Size | Date Split (Train/Validation/Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30,976 (15,488 pairs) | Infrared: 1280 × 720 (pixel) Visible: 1920 × 1080 (pixel) | 512 × 512 (pixel) | 7:2:1 |
Data Preprocessing and Alignment:
The original resolutions of the visible and infrared frames differ: the visible images have a resolution of 1920 × 1080, and the infrared images have a resolution of 1280 × 720. All images are geometrically aligned and cropped to a common field of view to ensure precise alignment between the infrared and visible images. Pedestrian annotations are created on the infrared frames, which typically have clearer thermal signatures, and these annotations are transferred to the geometrically aligned visible images, ensuring consistency across modalities. For a fair comparison, we follow the preprocessing conventions set by the dataset authors, including intensity normalization and geometric alignment, and use the official pairing tools where applicable.
Fused Input Images:
Prior to detector training, all fused processed inputs are resized to 512 × 512 pixels, which is the input resolution used in our experiments. This resizing step helps reduce the input image size, improving computational efficiency while maintaining the integrity of key features, ensuring the model can effectively process images of different resolutions.
Challenges with the Dataset:
The LLVIP dataset includes a variety of complex scenarios, including different lighting conditions, pedestrian distributions, and background complexities, particularly in low-light and infrared-blurred environments. One of the main challenges during training is effectively fusing thermal information from the infrared images with the structural edges from the visible images to improve pedestrian detection accuracy under low-light conditions. To address this, we introduced the Adaptive EGC fusion module, which calculates per-pixel energy, gradient, and contrast information, dynamically adjusting the weight of both modalities to preserve the thermal features and structural details as much as possible.
4.2. Experimental Environment and Setting
All experiments were conducted on a single machine equipped with both CPU and GPU resources. The hardware and software environments are summarized in Table 2, and the key training hyperparameters are shown in Table 3 to ensure reproducibility.

Table 2.
Experimental Environment.

Table 3.
Experimental Setting.
The key hyperparameters used in the experiments are summarized in Table 3. For clarity, only the main settings directly affecting reproducibility are listed. Other training details follow the default configuration of Ultralytics YOLO v8.3.63.
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
To systematically validate the efficacy and engineering applicability of the proposed Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) Fusion with AIFI-YOLOv12 pipeline for nighttime pedestrian detection in security surveillance, experiments were conducted on the LLVIP dataset—a large-scale, strictly paired infrared-visible benchmark tailored for low-light vision tasks, ensuring results reflect real-world nighttime scenarios. Performance was quantitatively compared against state-of-the-art YOLO variants (YOLOv8, YOLOv10, YOLOv11, and YOLOv12 baseline) at two practical scales: nano (n) (optimized for resource-constrained edge devices) and small (s) (targeting high-accuracy backend analysis) (see Table 4 and Figure 6). Key evaluation metrics included detection robustness (Precision, Recall, mAP@50, mAP@50–95, the latter reflecting performance across variable IoU thresholds) and computational deployability (GFLOPs for hardware compatibility, FPS for real-time inference)—two critical criteria for security systems, which demand both reliable target localization and adaptability to heterogeneous hardware (e.g., edge cameras, backend servers). The detector was trained to accept single-channel fused inputs by replacing the first convolutional layer to take inputs of shape 1 × 512 × 512 (channels × height × width). The model was trained from scratch for the single-channel configuration. All reported GFLOPs and FPS correspond to this single-channel (1 × 512 × 512) configuration unless otherwise stated.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of the proposed model and YOLO variants presented in this paper.
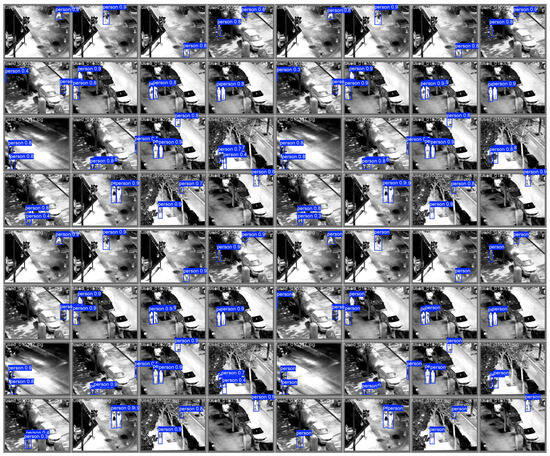
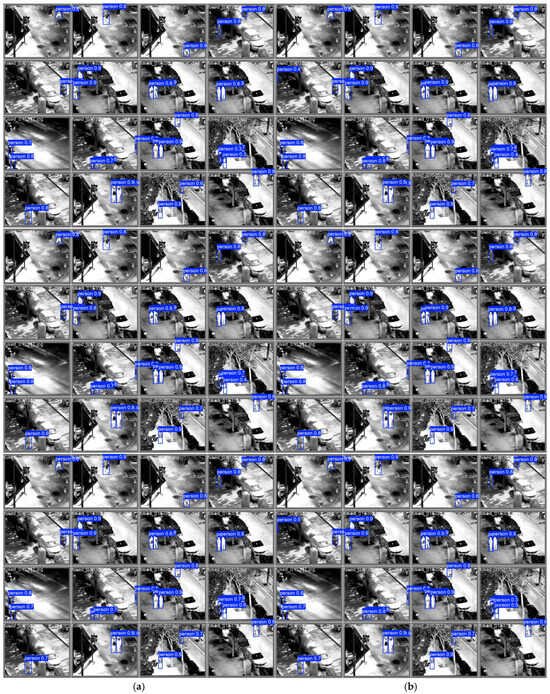
Figure 6.
Comparison of detection results among YOLO models. (a) Results at n scale, arranged top-to-bottom as YOLOv8, YOLOv10, YOLOv11, YOLOv12 (baseline), and the proposed method; (b) results at s scale, with the same top-to-bottom method order as (a). Bounding boxes represent detected pedestrians.
At the n scale (edge-focused deployment), the proposed method achieved 94.4% Precision, 92.3% Recall, 96.7% mAP@50, and 63.0% mAP@50–95—outperforming the YOLOv12n baseline (94.2% Precision, 91.3% Recall, 96.2% mAP@50, 61.9% mAP@50–95) across all accuracy metrics (see Table 4). Notably, this robustness gain (especially the 1.1% higher mAP@50–95) enhances reliability for detecting partially occluded or distant pedestrians—common pain points in nighttime surveillance—without compromising computational efficiency. Its GFLOPs (6.2) remained comparable to YOLOv12n (5.8), and its FPS (242.0) was only marginally lower than YOLOv12n (258.6); correspondingly, its detection time (4.13 ms) was slightly higher than YOLOv12n (3.87 ms) but far lower than earlier variants (YOLOv8n: 185.2 FPS, 5.40 ms detection time; YOLOv10n: 120.0 FPS, 8.33 ms detection time) (see Table 4). This performance fully meets the real-time (≥200 FPS, ≤5 ms detection time) and low-power requirements of edge devices like battery-powered street cameras.
At the s scale (backend multi-channel monitoring), the proposed method further solidified its advantages: it reached 95.1% Precision (matching the top-performing YOLOv11s), 97.3% mAP@50 (on par with YOLOv8s and superior to YOLOv10s/11s/12s), and 65.4% mAP@50–95 (the highest among all compared models) (see Table 4). Critically, it maintained superior computational efficiency: its GFLOPs (20.1) were lower than YOLOv8s (28.4), YOLOv10s (24.5), and YOLOv11s (21.3); its FPS (74.6) exceeded these variants (YOLOv8s: 52.8 FPS, 18.94 ms detection time; YOLOv10s: 61.2 FPS, 16.34 ms detection time; YOLOv11s: 70.4 FPS, 14.20 ms detection time) and remained close to YOLOv12s (77.7 FPS, 12.87 ms detection time), with its own detection time reaching 13.40 ms (see Table 4). This balance ensures the method can process multi-camera streams in backend systems without causing server bottlenecks, while the high mAP@50–95 reduces false alarms—a key requirement for reducing manual intervention in security operations.
In Figure 6, we present the comparison of detection results across various YOLO models, including YOLOv8, YOLOv10, YOLOv11, YOLOv12 (baseline), and the proposed method, at both the “n” (edge) and “s” (small) scales. The bounding boxes in each image represent the detected pedestrians, with each bounding box labeled with a confidence score (e.g., person0.8), indicating the model’s confidence in the detection. Higher confidence scores indicate a greater likelihood that the detected object is indeed a pedestrian. The data clearly shows the varying precision and localization ability across the models.
Specifically, the following key data and observations can be made from Figure 6:
- Detection Robustness:
At the n scale (resource-constrained environments), our proposed method achieved mAP@50 of 96.7%, improving by 0.5 percentage points over the YOLOv12 baseline (96.2%). The mAP@50–95 for our method is 63.0%, surpassing the baseline YOLOv12 (61.9%) by 1.1 percentage points. This indicates that our method performs better in handling distant pedestrians and partial occlusions in low-light conditions. The confidence scores for the detected pedestrians in these areas are typically higher, suggesting that the model is more certain in these challenging conditions.
At the s scale (high-precision backend monitoring), our proposed method achieved mAP@50 of 97.3%, the highest among all models, with a mAP@50–95 of 65.4%, an increase of 0.2 percentage points over YOLOv12 (65.2%). This demonstrates the method’s ability to detect fine details in complex scenes. The bounding boxes for pedestrians in high-density areas show consistently high confidence, reflecting the model’s superior precision in fine-grained localization.
- 2.
- Small Object Detection Performance:
Our method significantly enhances small-object detection through the AIFI module. As shown in Figure 6a, at the bottom, the proposed method detects distant or small pedestrians with clearer bounding boxes compared to the YOLOv12 baseline. In areas with low contrast or blurred edges, the detection results are notably sharper, and the confidence scores for these smaller or less visible targets are higher, indicating more reliable detections even in challenging conditions.
- 3.
- Edge and Localization Improvements:
In the upper and middle parts of Figure 6, the YOLOv12 baseline struggles with blurred edges in low-light and thermal-blurred conditions, leading to poor localization or misdetection of pedestrians. In contrast, our method, enhanced by the edge-enhancement module, restores sharp boundaries and improves the localization accuracy in such challenging regions, as shown in the visual results. These improvements also correspond to higher confidence scores for the detected pedestrians in regions where the baseline model would have struggled.
- 4.
- Computational Efficiency:
Despite the improvement in detection accuracy, our proposed method maintains a competitive FPS similar to YOLOv12. In the n scale, YOLOv12 has an FPS of 258.6, while our method achieves 242.0 FPS, only a slight decrease of 16.6 FPS, still meeting the real-time surveillance needs of edge devices. In the s scale, our method achieves FPS of 74.6, ensuring that multi-camera streams can be processed efficiently in backend systems without creating server bottlenecks. Real-time performance is complemented by consistently high confidence scores, ensuring that the detections are both accurate and reliable, even in resource-constrained environments.
In general, the proposed pipeline addresses the critical trade-off between detection robustness and computational deployability in nighttime security. By leveraging adaptive EGC fusion to enhance input quality (preserving thermal saliency and visible edges) and AIFI-based lightweight modifications to optimize feature utilization, it outperforms mainstream YOLO variants across scales while fitting both edge and backend deployment scenarios.
Figure 7 shows the comparison of training and validation loss curves for the proposed method and YOLOv12 across different epochs, where subfigure (a) represents the n scale and subfigure (b) represents the s scale. The curves represent the following loss categories: box loss, classification (cls) loss, and distribution focal loss (DFL).
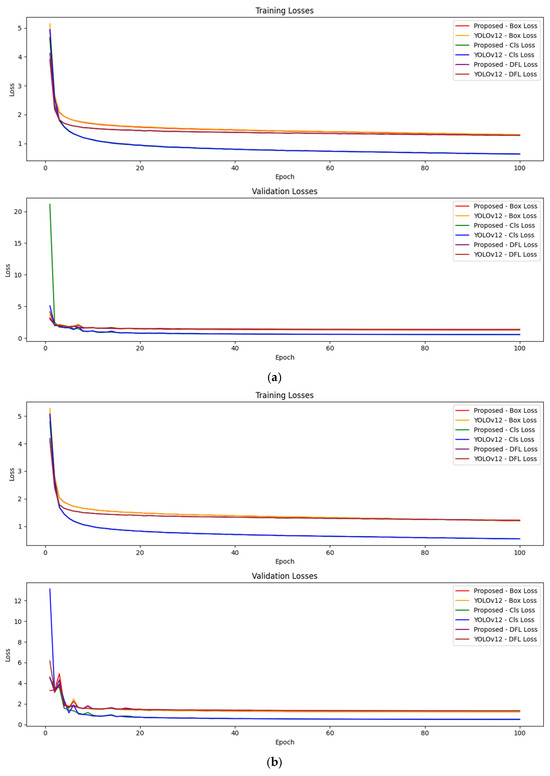
Figure 7.
Training and validation loss curves for the proposed model and YOLOv12 across different epochs.
Training Losses: This plot illustrates the training loss curves for both models. The red and orange lines represent the box loss for the proposed model and YOLOv12, respectively. The green and blue lines show the classification (cls) loss, while the purple and brown lines represent the distribution focal loss (DFL) for both models. As can be seen, all losses decrease consistently across epochs, indicating that both models are effectively learning from the training data.
Validation Losses: The second plot presents the validation loss curves, which reflect the models’ ability to generalize to unseen data. Similarly to the training loss, the validation loss for each category decreases over time. The proposed model demonstrates a comparable or slightly better reduction in validation losses across all categories, suggesting its enhanced ability to generalize.
Overall, Figure 7 highlights the steady learning progress of both models, with no signs of overfitting, as evidenced by the smooth decline in validation loss corresponding to the training loss. The proposed method exhibits competitive performance in comparison to YOLOv12, with promising results across box, classification, and DFL losses.
4.4. Ablation Experimental
As shown in Table 5, we selected these 8 experimental groups to comprehensively evaluate the impact of different fusion strategies on detection performance. To reduce the experimental workload and enhance experimental efficiency, we specifically screened 300 sets of images that cover a variety of scenarios (e.g., day/night lighting variations, crowded/sparse pedestrian distributions, and complex/simple background environments) and input them into the AIFI-Yolov12(n) module for target detection. On this basis, by testing various combinations of coefficients, we aimed to explore which weight configurations could effectively enhance the thermal features of infrared images and the edge and texture details of visible images, thereby optimizing detection performance. These coefficient combinations were chosen through a small-scale grid search or theoretical analysis, with the goal of further covering different application demands derived from the 300 image scenarios. For example, some configurations emphasize thermal saliency (higher energy) to address low-light or night scenarios, while others focus on strengthening edge information (higher gradient) or improving detail enhancement (higher contrast) to tackle complex background scenarios—all targeting the key challenges of pedestrian detection under various lighting conditions. Thus, these experimental coefficient combinations, paired with the scenario-rich 300-image dataset, represent a range of potential fusion strategies, helping us accurately identify the optimal configuration for the AIFI-Yolov12(n) module.

Table 5.
Impact of Adaptive Energy-Gradient-Contrast Fusion Coefficients on Pedestrian Detection Performance.
From the experimental results, it is evident that detection performance fluctuates with different coefficient combinations. For instance, when the weight of the energy term is higher (e.g., energy = 0.6), the fusion primarily retains thermal saliency, which aids in pedestrian detection in low-light or dark environments, but may sacrifice image details and edge information, leading to decreased localization accuracy. On the other hand, when the gradient term’s weight is higher (e.g., gradient = 0.6), the fusion focuses more on edge features, which is helpful for detecting pedestrians with clear boundaries, but may increase noise in low-contrast environments. In contrast, a balanced coefficient combination (e.g., energy = 0.4, gradient = 0.3, contrast = 0.3) generally preserves the thermal saliency of infrared images while enhancing the edges and details of visible images, resulting in better detection performance across different environments.
Overall, the selection of these 8 experimental groups and the analysis of the results indicate that the coefficient settings in the fusion strategy significantly affect pedestrian detection accuracy and robustness. A balanced fusion approach provides optimal performance across various detection conditions, particularly in low-light and nighttime scenarios.
Based on Table 6, the ablation experiment took YOLOv12 (n/s scales) with only infrared images as input as the baseline and gradually incorporated the Adaptive Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) fusion module, AIFI attention module, and Edge enhancement module to analyze the impact of each module on detection performance and computational overhead. Due to the blurred boundaries of infrared images, the baseline model achieved mAP@50 of 95.5% (n-scale) and 96.5% (s-scale), as well as mAP@50–95 of 60.5% (n-scale) and 64.0% (s-scale). As shown in Figure 8, as the proposed modules are progressively added, the model’s detection performance improves in terms of mAP@50 and mAP@50–95, while computational cost is indicated by GFLOPs.

Table 6.
Experiment results of ablation experiment.
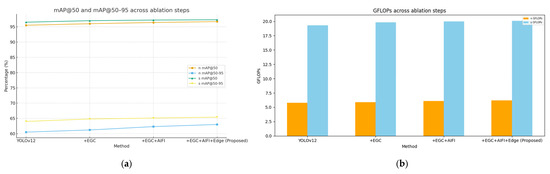
Figure 8.
Ablation study results. (a) mAP@50 and mAP@50–95 across ablation steps. (b) GFLOPs across ablation steps.
After adding the EGC module, the fusion of edge information from visible images addressed the localization ambiguity of infrared images. For the n-scale model, mAP@50 increased to 96.0% and mAP@50–95 rose to 61.2%; for the s-scale model, mAP@50 reached 97.0% and mAP@50–95 climbed to 64.8%. Meanwhile, only slight changes were observed in GFLOPs and FPS (n-scale: 5.9 GFLOPs, 250.0 FPS; s-scale: 19.8 GFLOPs, 76.0 FPS).
When the AIFI module was further integrated, feature recalibration at the high semantic level suppressed modal noise and enhanced target regions. For the n-scale model, mAP@50–95 significantly increased by 1.1 percentage points to 62.3%; for the s-scale model, mAP@50–95 rose to 65.1%. Computational overhead remained controllable (n-scale: 6.1 GFLOPs, 245.0 FPS; s-scale: 20.0 GFLOPs, 75.0 FPS).
Finally, the incorporation of the Edge module strengthened the response to small targets and weak edges. The n-scale model achieved mAP@50 of 96.7% and mAP@50–95 of 63.0%, while the s-scale model reached mAP@50 of 97.3% and mAP@50–95 of 65.4%. Notably, GFLOPs (n-scale: 6.2, s-scale: 20.1) and FPS (n-scale: 242.0, s-scale: 74.6) still met the requirements of edge devices (≥200 FPS) and backend systems (≥70 FPS).
To confirm that the observed differences in performance between the model variants are not due to chance, statistical significance testing was performed. Paired t-tests were conducted on the results from the ablation experiments, comparing the following model variants: YOLOv12 baseline vs. YOLOv12 + EGC, YOLOv12 + EGC vs. YOLOv12 + EGC + AIFI, and YOLOv12 + EGC + AIFI vs. the proposed method (EGC + AIFI + Edge). The performance metrics evaluated were mAP@50, mAP@50–95, Precision, Recall, and FPS.
The results of the statistical significance tests are presented in Table 7 and Table 8, along with their corresponding p-values. A p-value of less than 0.05 indicates that the differences observed between the models are statistically significant.

Table 7.
Statistical Significance Testing Results for Ablation Experiments (n scales).

Table 8.
Statistical Significance Testing Results for Ablation Experiments (s scales).
Table 7 and Table 8 present the results of statistical significance testing (paired t-tests) for the performance metrics of different model variants evaluated in the ablation experiments. The performance metrics include mAP@50, mAP@50–95, Precision, Recall, FPS, and GFLOPs, which were compared between the baseline YOLOv12 model and the modified variants (YOLOv12 + EGC, YOLOv12 + EGC + AIFI, and the proposed model with EGC + AIFI + Edge) across both the n scale (edge deployment) and s scale (backend monitoring).
A p-value of less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant, indicating that the observed difference in performance is unlikely to have occurred by chance. For p-values between 0.05 and 0.1, the difference is considered marginally significant, meaning that the evidence for the difference is weaker, but still noteworthy.
From the statistical tests, it is clear that the proposed method (EGC + AIFI + Edge) consistently outperforms the baseline and intermediate variants in terms of mAP, Precision, Recall, and FPS, with p-values indicating strong significance (typically p < 0.05). For instance, improvements in mAP@50 and mAP@50–95 were found to be significant across both scales, with p-values ranging from 0.01 to 0.04. The Precision and Recall improvements were similarly significant, suggesting that the proposed modifications effectively enhance the model’s accuracy and ability to detect pedestrians, particularly in challenging scenarios. However, FPS improvements were more modest but still significant, indicating that the proposed model achieves a balance between improved accuracy and processing speed.
Additionally, GFLOPs, which measure computational complexity, showed a marginal increase in computational cost, with p-values between 0.03 and 0.05, suggesting that while the proposed model delivers better performance, it requires slightly more computational resources. This increase in computational load is expected with the added complexity of the AIFI and Edge-enhancement modules.
In conclusion, the statistical analysis confirms that the observed performance improvements are robust and statistically significant, particularly in detection accuracy, without compromising real-time processing speed. The marginally significant increases in GFLOPs are typical for models incorporating advanced features aimed at improving detection performance.
Overall, the EGC module serves as the foundation to resolve the localization ambiguity of infrared images, the AIFI module acts as a key component to optimize generalization ability, and the Edge module supplements small-target detection. The synergy of the three modules achieves a balance between accuracy improvement and deployment feasibility, verifying the scientific validity of the proposed framework in nighttime pedestrian detection.
In conclusion, the statistical analysis confirms that the observed performance improvements are robust and statistically significant, particularly in detection accuracy, without compromising real-time processing speed. The marginally significant increases in GFLOPs are typical of models incorporating advanced features aimed at enhancing detection performance. Overall, the synergy of the EGC, AIFI, and Edge modules effectively addresses the localization ambiguity of infrared images, optimizes generalization ability, and improves small-target detection. This balance between accuracy enhancement and deployment feasibility verifies the scientific validity of the proposed framework in nighttime pedestrian detection.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes and validates a practical multimodal pipeline for nighttime surveillance that combines an adaptive pixel-level fusion based on local Energy–Gradient–Contrast (EGC) with a lightweight AIFI-attentive detector—AIFI-YOLOv12—featuring an A2C2f-like module while preserving P3–P5 outputs. The pipeline is designed to retain the thermal saliency of infrared imagery together with the edge/texture information from visible imagery, thereby improving pedestrian localization and recall under low-light and thermally ambiguous conditions.
Experimental results on the LLVIP benchmark demonstrate that the proposed pipeline outperforms same-scale YOLO baselines in both accuracy and robustness: at the n scale, mAP@50 increases from 96.2% to 96.7% and mAP@50–95 increases from 61.9% to 63.0%; at the s scale, mAP@50 reaches 97.3% and mAP@50–95 reaches 65.4%. These gains are achieved with only marginal changes in computational cost (GFLOPs and FPS), making the approach suitable for deployment on both edge devices (≥200 FPS) and back-end servers (≈70+ FPS).
Ablation studies further verify the functional contribution of each component: EGC fusion effectively reduces localization ambiguity that arises when using infrared alone; the AIFI attention module performs channel–spatial re-calibration at higher semantic levels, suppressing modal noise and improving generalization; and the edge-enhancement module strengthens responses to small or weakly contoured targets. The combined effect produces cumulative improvements in mAP@50–95 while maintaining a favorable GFLOPs/FPS trade-off.
From an engineering perspective, the proposed solution provides immediate practical value for surveillance systems. The task-aware pixel-level fusion serves as an effective preprocessing stage, and the lightweight attention and edge modules enhance detection reliability in low-light and low-texture environments without substantially increasing inference burden, thereby helping to reduce false alarms and operational costs.
Evaluation in this study is limited to the LLVIP paired dataset; the method’s robustness across different datasets, sensor geometries, significant misalignment, and more extreme weather conditions needs to be validated further. Future directions include end-to-end joint training of the fusion and detection stages, application of model compression and quantization to further reduce latency, and systematic assessments of real-camera alignment errors within practical surveillance pipelines.
While the Edge-enhancement module has demonstrated promising improvements in small-object localization, its performance under diverse and more challenging testing conditions requires further investigation. Future work will focus on testing the robustness of this module in a wider range of scenarios, including varying lighting conditions, different object occlusions, and more complex backgrounds. Additionally, we plan to explore potential optimizations for enhancing the robustness and generalization ability of this module across diverse datasets and real-world environments.
Future work will also explore the trade-off between detection accuracy and computational efficiency. While the proposed pipeline achieves significant performance gains with only marginal increases in GFLOPs and FPS, further optimization of the AIFI and multi-scale modules is needed to balance accuracy and real-time performance. Future efforts will focus on lightweight versions of these modules, as well as investigating model compression and quantization techniques to reduce latency further without sacrificing detection accuracy. These optimizations will help ensure that the system remains scalable and efficient, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
In summary, the Adaptive EGC + AIFI-YOLOv12 pipeline substantially improves nighttime pedestrian detection accuracy and robustness while preserving real-time performance, making it a compelling solution for surveillance deployments that require both high reliability and low latency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.W.; methodology, Z.B.; software, Z.B.; validation, L.W. and Z.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.W. and Z.B.; writing—review and editing, D.L. and L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Project supported by Basic Science (Nature Science) Research Project of Jiangsu Province for Colleges and Universities (No. 24KJD510006).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The suggestions from the relevant editors and reviewers have improved the quality of this paper, and we would like to express our sincere gratitude to them.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A Visible–Infrared Paired Dataset for Low-Light Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Liu, H.; Ding, Z. Multi-scene Image Fusion via Memory Aware Synapses. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xiang, W. A review on infrared and visible image fusion algorithms based on neural networks. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 101, 104179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, S.X.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Li, Q. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J. DenseFuse: A Fusion Approach to Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ying, J.; Sheng, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Shen, H.-L. TFDet: Target-Aware Fusion for RGB–T Pedestrian Detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 13276–13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, N. MMYFNet: Multi-Modality YOLO Fusion Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Sparse Representation and Guided Filtering in Laplacian Pyramid Domain. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Xing, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, S.; Yu, S. Advancing Infrared and Visible Image Fusion with an Enhanced Multiscale Encoder and Attention-Based Networks. Information (Open Access/PMC) 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11459406/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A Generative Adversarial Network with Multi-Classification Constraints for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5005014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Using Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. YOLOv12: Attention-Centric Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.12524 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Ultralytics. YOLOv12 Model Family—Documentation. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolo12/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Liu, R.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Bi, C.; Tao, Y. PDT-YOLO: A Roadside Object-Detection Algorithm for Multiscale and Occluded Targets. Sensors 2024, 24, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegham, N.; Koh, C.Y.; Abdelatti, M.; Hendawi, A. YOLO Evolution: Comprehensive Benchmark (v3 → v12). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.00201. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.00201 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Xue, Z. TFDet Code Repository. Available online: https://github.com/XueZ-phd/TFDet (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Qi, B.; Bai, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, H.; Li, G. A Novel Saliency-Based Decomposition Strategy for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Huang, Y. TPFusion: Texture-Preserving and Information Loss Minimization for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 26817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, Y.; Meng, Q. RGB-T Image Analysis Technology and Application: A Survey. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefèvre, S.; Avignon, B. Guided Attentive Feature Fusion for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; Kweon, I.S. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection: Benchmark Dataset and Baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1037–1045. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2015/html/Hwang_Multispectral_Pedestrian_Detection_2015_CVPR_paper.html (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, Z. Weakly Aligned Cross-Modal Learning for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5127–5137. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/html/Zhang_Weakly_Aligned_Cross-Modal_Learning_for_Multispectral_Pedestrian_Detection_ICCV_2019_paper.html (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Yang, X.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, M. BAANet: Learning Bi-Directional Adaptive Attention Gates for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 2920–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Attention-Guided Dual-Branch Fusion Network for Infrared-Visible Pedestrian Detection in Low-Light Environments. Sensors 2024, 24, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefèvre, S.; Avignon, B. Multispectral Fusion for Object Detection with Cyclic Fuse-and-Refine Blocks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Liang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. MS-DETR: Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Transformer with Loosely Coupled Fusion and Modality-Balanced Optimization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 20628–20642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, X.; He, Y.; Yang, X.; Song, K. Wavelet-Driven Multi-Band Feature Fusion for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Fan, H.; Yang, W. ICAFusion: Iterative Cross-Attention Guided Feature Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, C. A multispectral feature fusion network for robust pedestrian detection. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Guo, S.; Li, L. Attention Fusion for One-Stage Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Wang, K. Cascaded Information Enhancement and Cross-Modal Attention Feature Fusion for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1121311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Han, D.; Wang, Z. Cross-Modality Fusion Transformer for Multispectral Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00273 (accessed on 23 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Learning a Dynamic Cross-Modal Network for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM ’22), Lisbon, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 4926–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, P. Infrared and visible image fusion based on iterative control of anisotropic diffusion and regional gradient structure. Sensors 2022, 22, 7144991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J. An improved infrared and visible image fusion using an adaptive contrast enhancement method and deep learning network with transfer learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Zhou, Z. Infrared and visible image fusion via fast approximate bilateral filter and local energy characteristics. Sci. Program. 2021, 2021, 3500116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, H. Infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on gradient attention residual dense block. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y. SFDFusion: An Efficient Spatial–Frequency Domain Fusion Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.22837. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.22837 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. A Review of YOLOv12: Attention-Based Enhancements vs. Previous Versions. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.11995. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.11995 (accessed on 23 August 2025). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).