The Optimal Initial Displacement in Rotated Maxillary Incisor Teeth with Clear Aligner in Different Periodontal Conditions: A Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geometry Acquisition, Model Construction, and Periodontal Conditions
2.2. Aligner and Attachment Modeling: Material Properties
2.3. Meshing and Convergence Test
2.4. Boundary Conditions, Contact Definitions, Loading Protocol, and Software
2.5. Model Validation
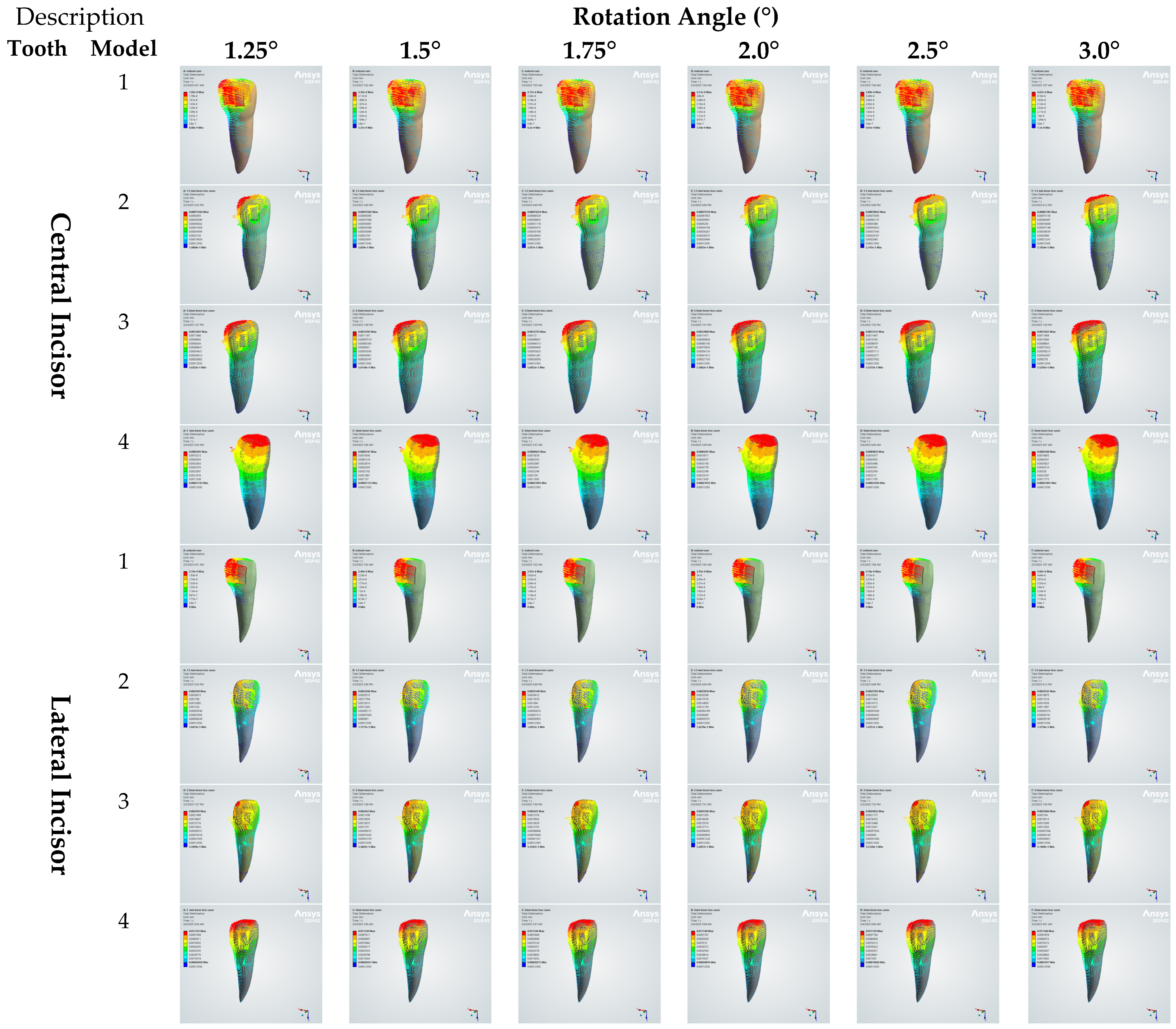
3. Results
3.1. PDL Stress Distribution
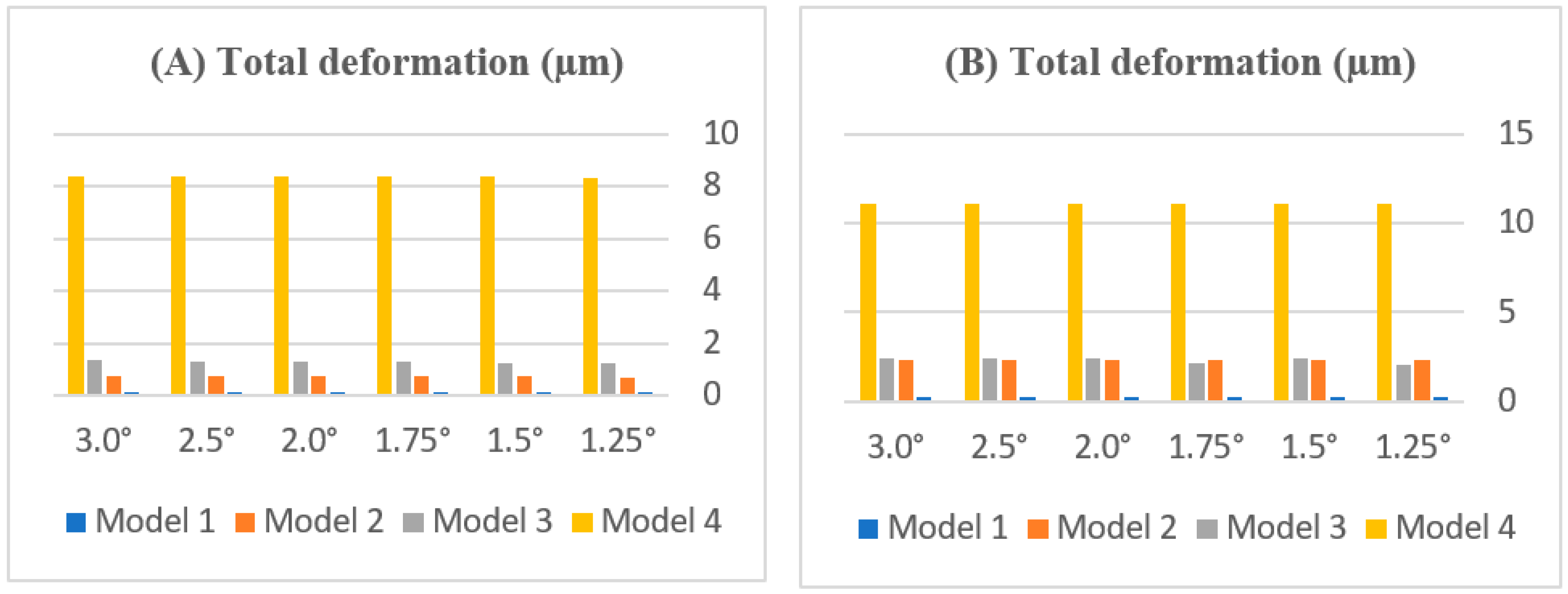
3.2. Total Deformation on Teeth
4. Discussion
4.1. PDL Stress Distribution and Rationale for Tooth-Specific Thresholds
4.2. Nonlinear Stress Redistribution with Progressive Bone Loss (Models 1–4)
4.3. Comparison with Previous Finite Element and Clinical Studies: Clinical Implications for Aligner Staging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis. |
| PDL | Periodontal Ligament. |
| CAT | Clear aligner therapy. |
| CEJ | Cementoenamel Junction. |
| µm | Micrometer. |
| MPa | Megapascal (unit of stress). |
| kPa | Kilopascal (1000 kPa = 1 MPa). |
| Normal Periodontal Condition | Simulated model with full alveolar bone support. |
| Reduced Periodontal Support | Simulated model with decreased alveolar bone height (bone loss). |
| Optimal Displacement | Range of initial tooth displacement considered biomechanically favorable. |
| Maxillary Incisors | Upper front teeth (central and lateral) evaluated in this study. |
| Von Mises Stress | Equivalent stress value used to assess stress distribution in structures. |
| PET-G | Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified. |
| Aligners | Clear thermoplastic orthodontic appliances used for tooth movement. |
| CBCT | Cone Beam Computed Tomography. |
| AAP/EFP | American Academy of Periodontology/European Federation of Periodontology. |
Appendix A
References
- Dianiskova, S.; Rongo, R.; Buono, R.; Franchi, L.; Michelotti, A.; D’Antò, V. Treatment of mild Class II malocclusion in growing patients with clear aligners versus fixed multibracket therapy: A retrospective study. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2022, 25, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirlys, R.; Nedzinskaitė, R.; Rongo, R.; Severino, M.; Puisys, A.; D’Antò, V. Digital planning technique for surgical guides for prosthetic implants before orthodontic treatment. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongo, R.; Dianišková, S.; Spiezia, A.; Bucci, R.; Michelotti, A.; D’Antò, V. Class II malocclusion in adult patients: What are the effects of the intermaxillary elastics with clear aligners? A retrospective single center one-group longitudinal study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staderini, E.; Meuli, S.; Gallenzi, P. Orthodontic treatment of class three malocclusion using clear aligners: A case report. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2019, 9, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staderini, E.; Patini, R.; Meuli, S.; Camodeca, A.; Guglielmi, F.; Gallenzi, P. Indication of clear aligners in the early treatment of anterior crossbite: A case series. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2020, 25, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jian, F.; Long, H.; Lai, W. Effectiveness of clear aligners in achieving proclination and intrusion of incisors among Class II division 2 patients: A multivariate analysis. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassem, A.A.B. Does clear aligner treatment result in different patient perceptions of treatment process and outcomes compared to conventional/traditional fixed appliance treatment: A literature review. Eur. J. Dent. 2021, 16, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomanno, S.; Saran, S.; Laganà, D.; Mastrapasqua, R.; Grippaudo, C. Motivation, perception, and behavior of the adult orthodontic patient: A survey analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2754051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mir, C.; Brandelli, J.; Pacheco-Pereira, C. Patient satisfaction and quality of life status after 2 treatment modalities: Invisalign and conventional fixed appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 154, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Pereira, C.; Brandelli, J.; Flores-Mir, C. Patient satisfaction and quality of life changes after Invisalign treatment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 153, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokeen, B.; Viloria, E.; Duong, E.; Rizvi, M.; Murillo, G.; Mullen, J.; Shi, B.; Dinis, M.; Li, H.; Tran, N.C. The impact of fixed orthodontic appliances and clear aligners on the oral microbiome and the association with clinical parameters: A longitudinal comparative study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 161, e475–e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yan, X.; Zhao, R.; Shan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jian, F.; Long, H.; Lai, W. Comparison of pain perception, anxiety, and impacts on oral health-related quality of life between patients receiving clear aligners and fixed appliances during the initial stage of orthodontic treatment. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, X.; Yan, X.; Tang, Z.; Lai, W.; Long, H. Orthodontic Practitioners’ Knowledge and Education Demand on Clear Aligner Therapy. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluccio, G. Is the use of clear aligners a real critical change in oral health prevention and treatment. La Clin. Ter. 2021, 172, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, C.-K.; Kim, B.-O. Orthodontic treatment for maxillary anterior pathologic tooth migration by periodontitis using clear aligner. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2011, 41, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, K.; Nazeer, M.R.; Ghafoor, R. Interdisciplinary management of gingiva l recession and pathologic teeth migration-Revisiting dental aesthetics. JPMA 2019, 69, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar]
- D’Antò, V.; Rongo, R.; Casaburo, S.D.; Martina, S.; Petrucci, P.; Keraj, K.; Valletta, R. Predictability of tooth rotations in patients treated with clear aligners. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.F.; Ford, P.J.; Symons, A.L. Periodontal disease and the special needs patient. Periodontology 2000 2017, 74, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiwattanapong, K.; Samruajbenjakun, B. Tissue response resulting from different force magnitudes combined with corticotomy in rats. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, H.E.; El-Beialy, A.R.; El-Ghafour, M.A.; Abouelezz, A.M.; El Sharaby, F.A. Root resorption associated with maxillary buccal segment intrusion using variable force magnitudes: A randomized clinical trial. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, C.; Hotokezaka, H.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Yozgatian, J.H.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Yoshida, N. Force magnitude and duration effects on amount of tooth movement and root resorption in the rat molar. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, C.I.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Wagener, F.A. Optimal force magnitude for bodily orthodontic tooth movement with fixed appliances: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, W.; Engelke, B.; Jung, K.; Dathe, H.; Fialka-Fricke, J.; Kubein-Meesenburg, D.; Sadat-Khonsari, R. Initial forces and moments delivered by removable thermoplastic appliances during rotation of an upper central incisor. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertan, E.; McCray, J.; Bankhead, B.; Kim, K.B. Force profile assessment of direct-printed aligners versus thermoformed aligners and the effects of non-engaged surface patterns. Prog. Orthod. 2022, 23, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Martines, E.; Mazzanti, V.; Arreghini, A.; Mollica, F.; Siciliani, G. Stress relaxation properties of four orthodontic aligner materials: A 24-hour in vitro study. Angle Orthod. 2016, 87, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, P.; Mazzanti, V.; Mollica, F.; Pellitteri, F.; Palone, M.; Lombardo, L. Stress relaxation properties of five orthodontic aligner materials: A 14-day in-vitro study. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-S.; Jiang, H.B.; Cha, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-M. Effects of thermoforming on the physical and mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials for transparent orthodontic aligners. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, I.; Moyano, J.; Pàmies, A.; Ruiz, G.; Artés, M.; Gil, J.; Puigdollers, A. Properties of superelastic nickel–titanium wires after clinical use. Materials 2023, 16, 5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanne, K.; Hiraga, J.; Kakiuchi, K.; Yamagata, Y.; Sakuda, M. Biomechanical effect of anteriorly directed extraoral forces on the craniofacial complex: A study using the finite element method. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1989, 95, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, N.J.; Wilson, A.N.; Jones, M.L.; Middleton, J. A stress analysis of the periodontal ligament under various orthodontic loadings. Eur. J. Orthod. 1991, 13, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geramy, A. Initial stress produced in the periodontal membrane by orthodontic loads in the presence of varying loss of alveolar bone: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2002, 24, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, J.; Jones, M.; Wilson, A. The role of the periodontal ligament in bone modeling: The initial development of a time-dependent finite element model. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1996, 109, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gill, G.; Kaur, H.; Amhmed, M.; Jakhu, H. Role of osteopontin in bone remodeling and orthodontic tooth movement: A review. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortona, A.; Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular round-shaped teeth: A finite element study. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, W. Force changes associated with different intrusion strategies for deep-bite correction by clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, S. The optimal orthodontic displacement of clear aligner for mild, moderate and severe periodontal conditions: An in vitro study in a periodontally compromised individual using the finite element model. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-H.; Hong, K.; Lim, D.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, B. Optimal position of attachment for removable thermoplastic aligner on the lower canine using finite element analysis. Materials 2020, 13, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toms, S.R.; Eberhardt, A.W. A nonlinear finite element analysis of the periodontal ligament under orthodontic tooth loading. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 123, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Li, N. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular teeth with different shapes: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2023, 27, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, X.; He, B.; Yao, J. Finite element method analysis of the periodontal ligament in mandibular canine movement with transparent tooth correction treatment. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-M.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-F.; Lin, C.-T.; Yao, W.-C.; Chiu, W.-T.; Lee, S.-Y. Damping effects on the response of maxillary incisor subjected to a traumatic impact force: A nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Dent. 2006, 34, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, S.; Shi, H.; Lu, R.; Yan, B.; Ma, S.; Markert, B. Viscoelastic properties of human periodontal ligament: Effects of the loading frequency and location. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, N.; Liu, M.; Cheng, K.; Jiang, D.; Yi, Y.; Ma, S.; Yan, B.; Lu, Y. Construction of human periodontal ligament constitutive model based on collagen fiber content. Materials 2023, 16, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Huang, C.; Li, N.; Lu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Yan, B.; Jiang, D. Formulation of Hyperelastic Constitutive Model for Human Periodontal Ligament Based on Fiber Volume Fraction. Materials 2025, 18, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q. The force effects of two types of polyethylene terephthalate glyc-olmodified clear aligners immersed in artificial saliva. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Fu, Y.; Shi, H.; Yan, B.; Lu, R.; Ma, S.; Markert, B. Tensile testing of the mechanical behavior of the human periodontal ligament. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramy, A. Alveolar bone resorption and the center of resistance modification (3-D analysis by means of the finite element method). Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2000, 117, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkantidis, N.; Christou, P.; Topouzelis, N. The orthodontic–periodontic interrelationship in integrated treatment challenges: A systematic review. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2010, 37, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarel, I.A.; Gasparello, G.G.; Mota-Júnior, S.L.; Pithon, M.M.; Taffarel, I.P.; Meira, T.M.; Tanaka, O.M. Distalization of maxillary molars with Invisalign aligners in nonextraction patients with Class II malocclusion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 162, e176–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castroflorio, T.; Sedran, A.; Parrini, S.; Garino, F.; Reverdito, M.; Capuozzo, R.; Mutinelli, S.; Grybauskas, S.; Vaitiekūnas, M.; Deregibus, A. Predictability of orthodontic tooth movement with aligners: Effect of treatment design. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toms, S.R.; Dakin, G.J.; Lemons, J.E.; Eberhardt, A.W. Quasi-linear viscoelastic behavior of the human periodontal ligament. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

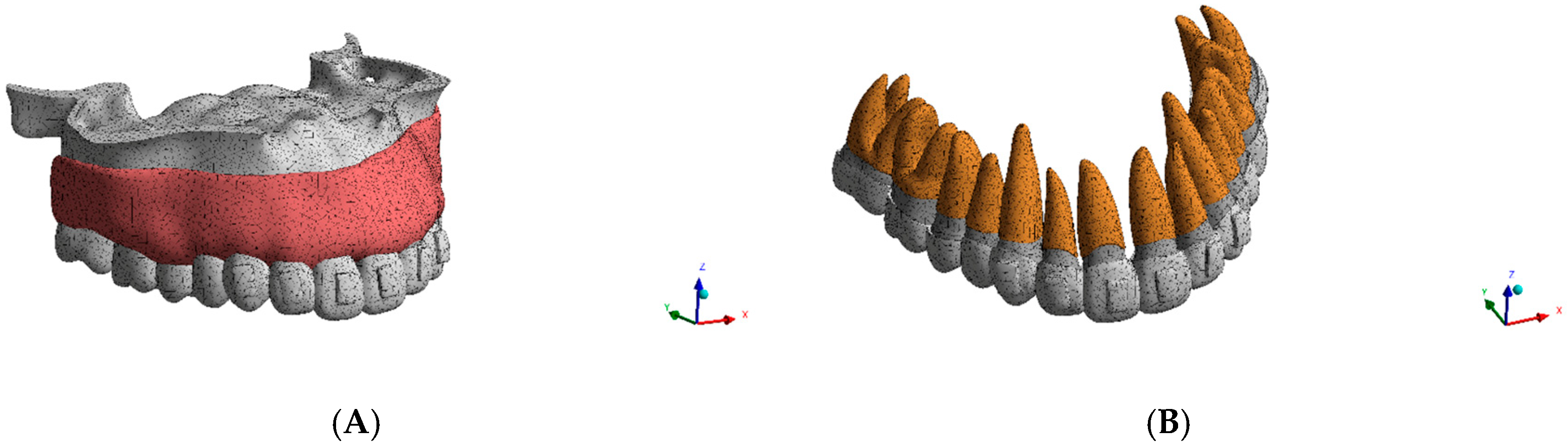
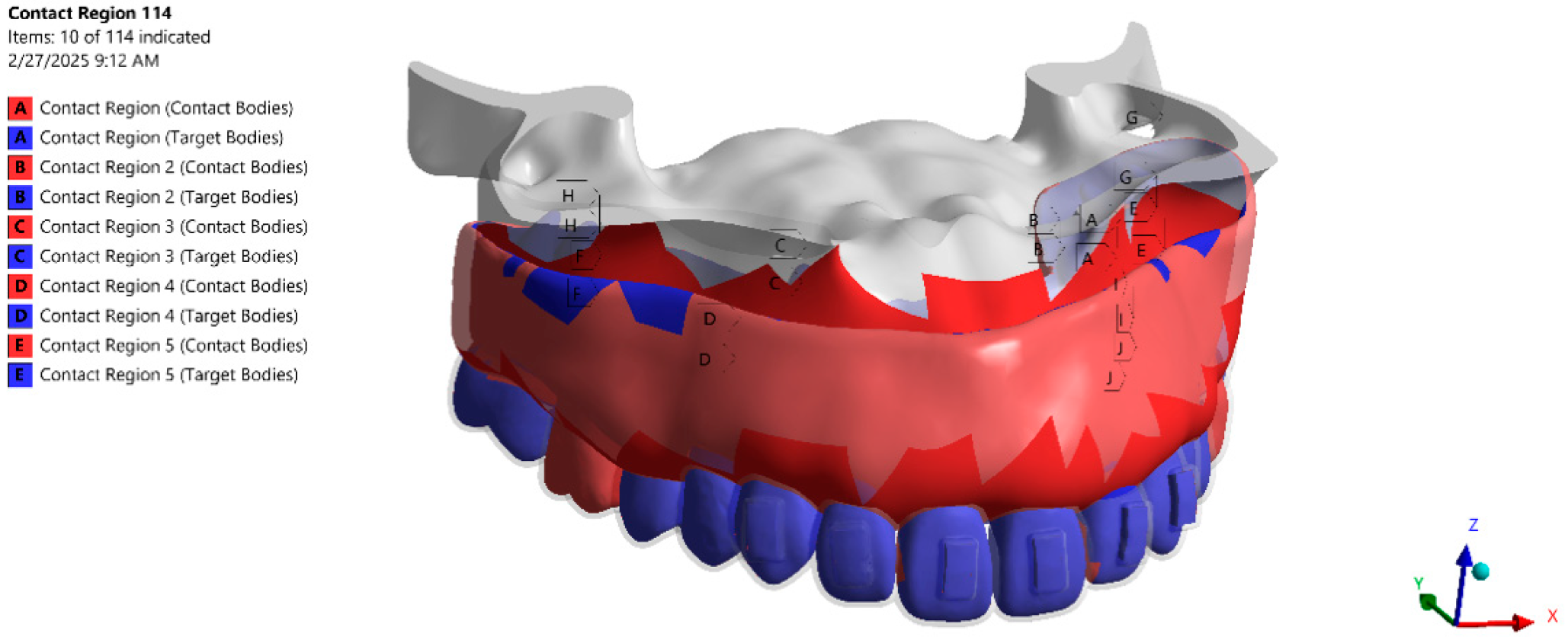
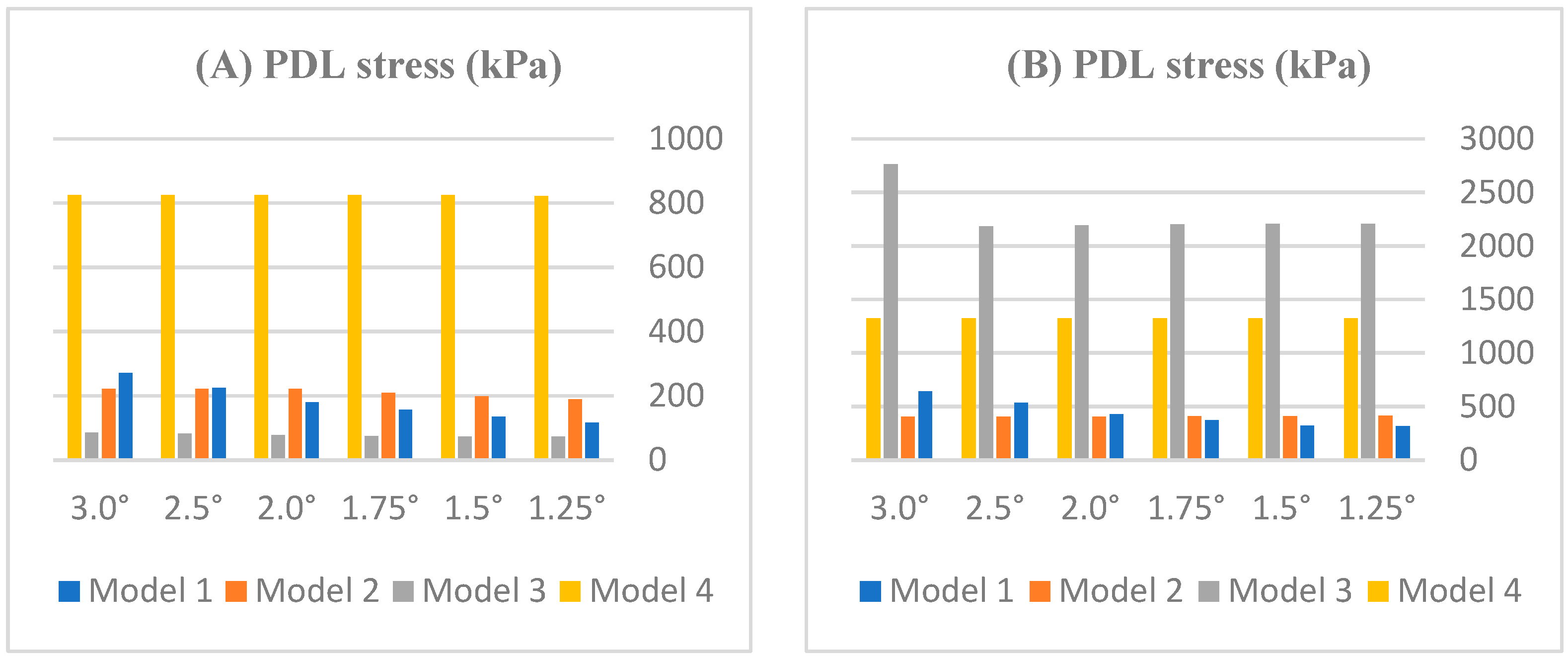
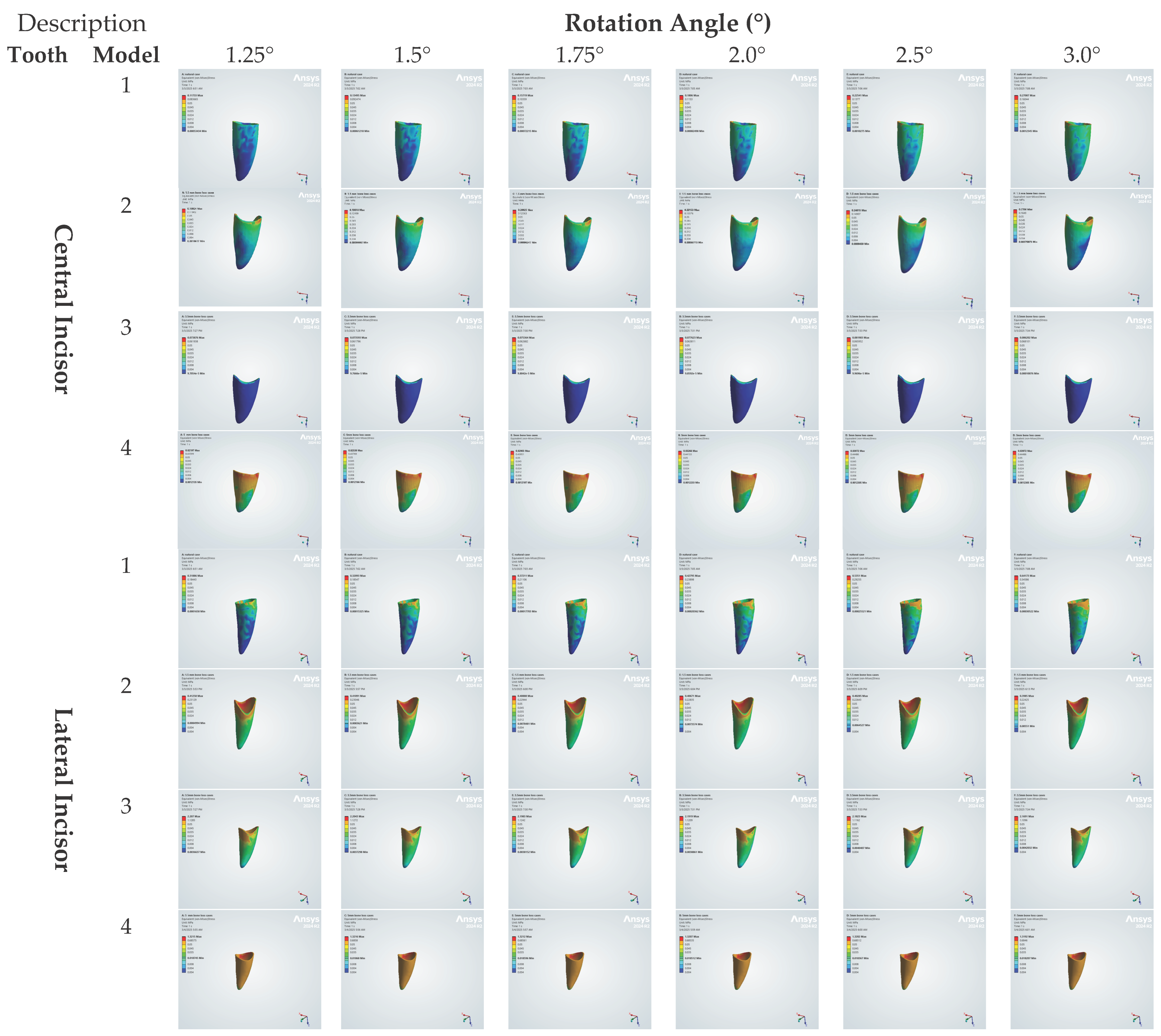
| Model | Stage | Nodes | Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Normal Periodontal Condition (0 mm bone loss) | 409,497 | 239,363 |
| 2 | Stage I periodontitis (1.5 mm bone loss) | 378,752 | 205,240 |
| 3 | Stage II periodontitis (3.5 mm bone loss) | 363,817 | 195,257 |
| 4 | Stage III periodontitis (5.0 mm bone loss) | 336,234 | 184,696 |
| Structure | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teeth | 20,000 | 0.30 | [39] |
| Cortical Bone | 13,700 | 0.30 | [39] |
| Cancellous Bone | 1370 | 0.30 | [39] |
| Gingiva | 3.45 | 0.45 | [39] |
| Attachment | 12,500 | 0.36 | [39] |
| Aligner | 528 | 0.36 | [39] |
| PDL | See reference [40] and Appendix A | ||
| Description | Rotation Angle (°) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth | Model | 1.25° | 1.5° | 1.75° | 2.0° | 2.5° | 3.0° |
| Central Incisor | 1 | 117.33 | 134.95 | 157.19 | 180.60 | 225.41 | 270.87 |
| 2 | 189.24 | 198.18 | 209.25 | 221.53 | 221.53 | 221.53 | |
| 3 | 73.88 | 73.59 | 75.36 | 77.62 | 81.90 | 86.20 | |
| 4 | 821.97 | 825.39 | 825.39 | 825.39 | 825.39 | 825.39 | |
| Lateral Incisor | 1 | 318.86 | 320.93 | 372.11 | 427.95 | 535.10 | 641.73 |
| 2 | 412.58 | 410.91 | 408.80 | 406.71 | 406.71 | 406.71 | |
| 3 | 2207.0 | 2204.3 | 2198.3 | 2191.9 | 2182.3 | 2763.1 | |
| 4 | 1321.5 | 1321.6 | 1321.6 | 1321.6 | 1321.6 | 1321.6 | |
| Description | Rotation Angle (°) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth | Model | 1.25° | 1.5° | 1.75° | 2.0° | 2.5° | 3.0° |
| Central Incisor | 1 | 0.00195 | 0.00233 | 0.00271 | 0.00311 | 0.00389 | 0.00467 |
| 2 | 0.712 | 0.725 | 0.743 | 0.7572 | 0.757 | 0.757 | |
| 3 | 1.247 | 1.258 | 1.274 | 1.286 | 1.313 | 1.34 | |
| 4 | 8.349 | 8.37 | 8.37 | 8.37 | 8.37 | 8.37 | |
| Lateral Incisor | 1 | 0.00213 | 0.00249 | 0.00291 | 0.00335 | 0.00416 | 0.00502 |
| 2 | 2.338 | 2.32 | 2.314 | 2.3018 | 2.302 | 2.302 | |
| 3 | 2.103 | 2.432 | 2.117 | 2.416 | 2.402 | 2.38 | |
| 4 | 11.133 | 11.139 | 11.139 | 11.139 | 11.139 | 11.139 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-labani, A.G.; Taner, R.L.; Özdiler, O.; Dinçer, K.M. The Optimal Initial Displacement in Rotated Maxillary Incisor Teeth with Clear Aligner in Different Periodontal Conditions: A Finite Element Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910502
Al-labani AG, Taner RL, Özdiler O, Dinçer KM. The Optimal Initial Displacement in Rotated Maxillary Incisor Teeth with Clear Aligner in Different Periodontal Conditions: A Finite Element Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910502
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-labani, Abdullah G., R. Lale Taner, Orhan Özdiler, and K. Müfide Dinçer. 2025. "The Optimal Initial Displacement in Rotated Maxillary Incisor Teeth with Clear Aligner in Different Periodontal Conditions: A Finite Element Analysis" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910502
APA StyleAl-labani, A. G., Taner, R. L., Özdiler, O., & Dinçer, K. M. (2025). The Optimal Initial Displacement in Rotated Maxillary Incisor Teeth with Clear Aligner in Different Periodontal Conditions: A Finite Element Analysis. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910502






