Research on Position Tracking Performance Optimization of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel nonlinear function with the characteristics of large-error small-gain and small-error large-gain is proposed to solve the chattering problem existing in the conventional nonlinear function ;
- (2)
- A time-delay compensation function is designed to address the asynchronization issue of the input signals (control quantity and system output quantity) of the extended state observer (ESO) in the traditional ADRC, thereby improving the performance of the ESO;
- (3)
- The Newton-Raphson algorithm is proposed for the self-tuning of ADRC parameters; a novel evaluation function is designed for position control to reduce overshoot; and simultaneously, the novel nonlinear function and the time-delay compensation module are combined, making the controller performance superior to that of single improved strategies such as PSO-ADRC and shark optimization-ADRC.
2. Establishment of PMSM Mathematical Model
3. Design on the Improved ADRC
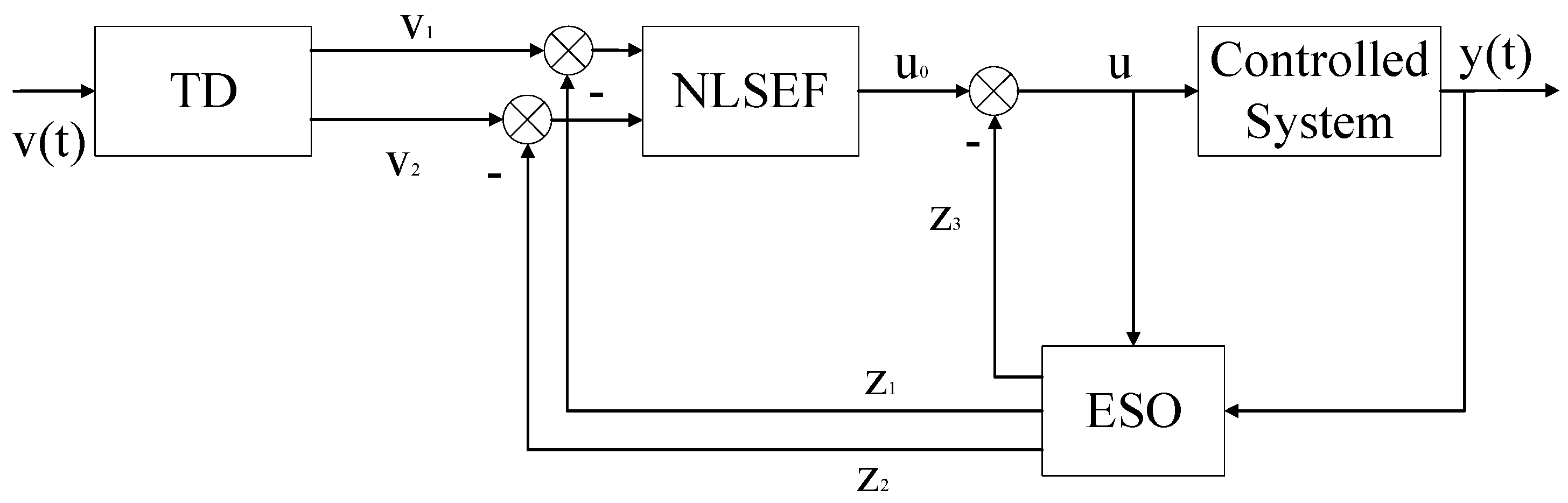
3.1. ADRC Theoretical Framework
3.2. Nonlinear Function Optimization
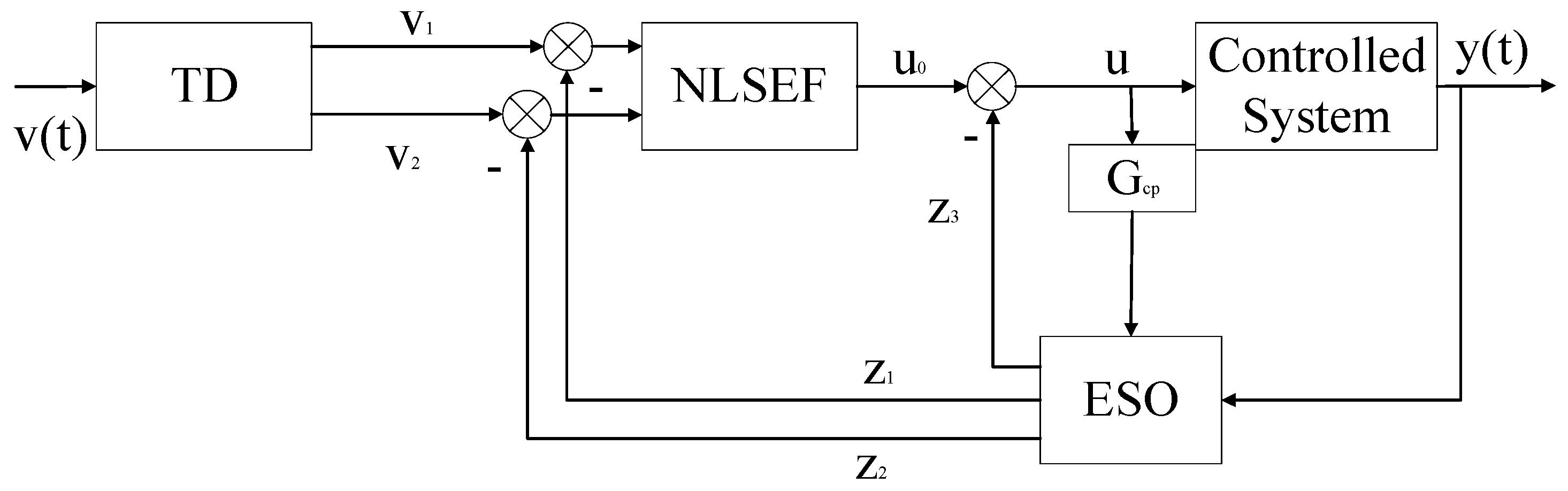
3.3. Delay Compensation Module for ESO Input Synchronization
- The total disturbance is zero;
- The actual system dynamics are bounded (i.e., does not grow infinitely due to state variations);
- Disturbances are estimable and bounded values.
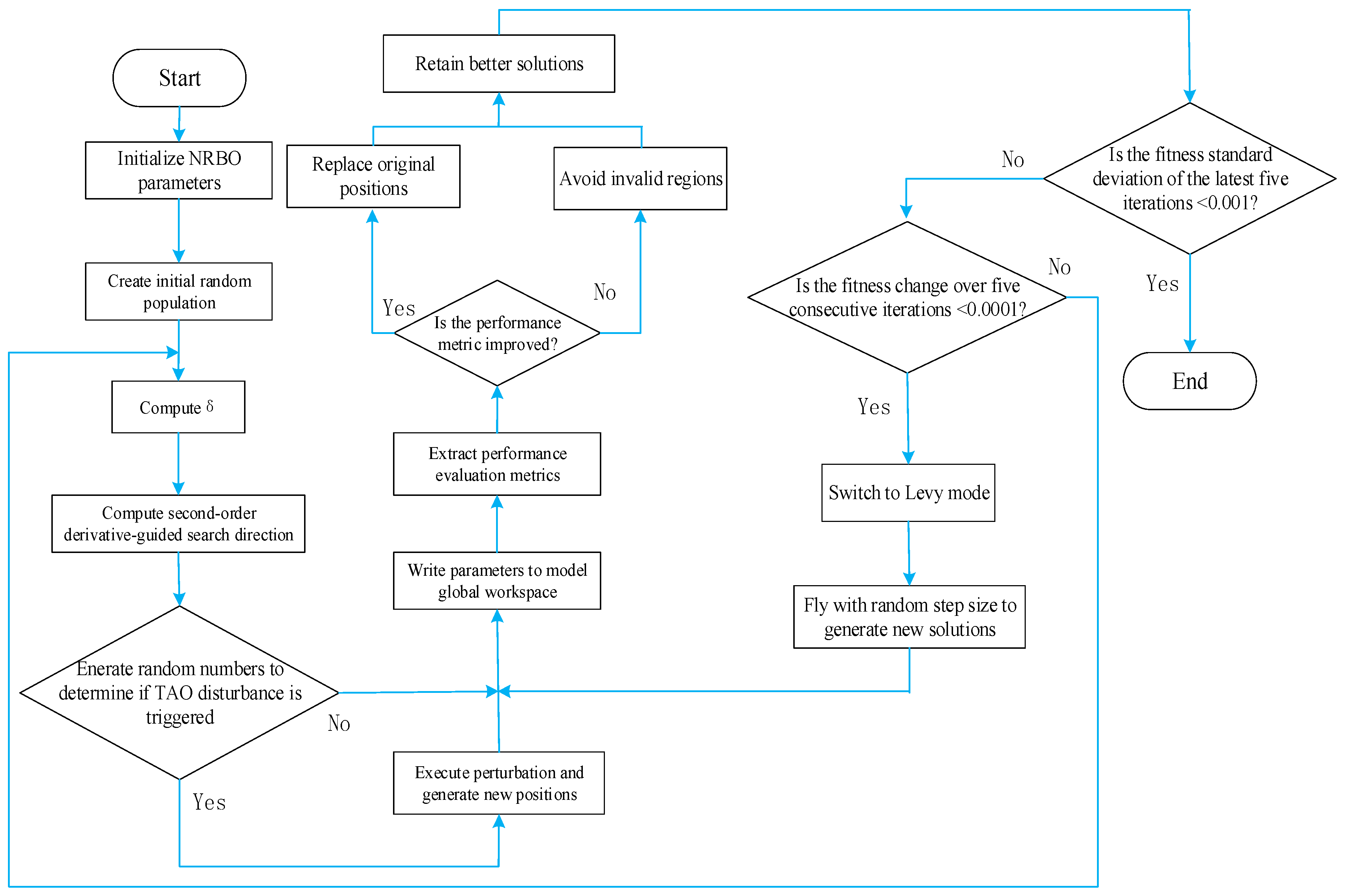
3.4. Design of Newton-Raphson-Based Optimizer
4. Simulation Experiments and Result Analysis
- (1)
- ADRC: Conventional active disturbance rejection controller.
- (2)
- F_ADRC: ADRC with optimized nonlinear function.
- (3)
- MADRC: F_ADRC with delay compensation module.
- (4)
- NRBO-MADRC: MADRC with NRBO-based parameter auto-tuning.
- (5)
- PSO_PID: PID optimized by particle swarm optimization.
- (6)
- MSMC (modified sliding mode controller): The original exponential convergence law of the sliding mode controller has been modified to the following form , thereby achieving better anti-interference performance and response speed.
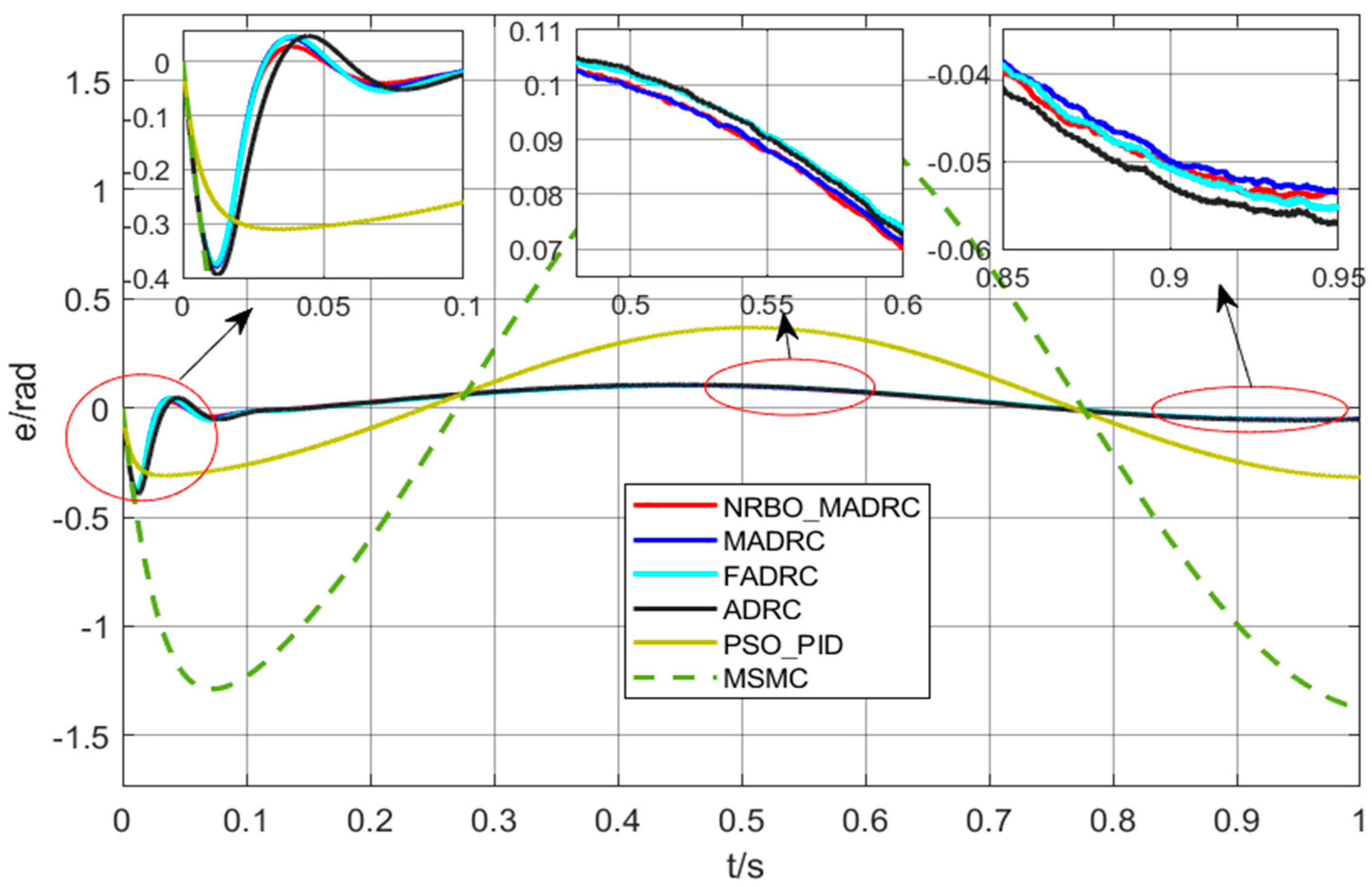
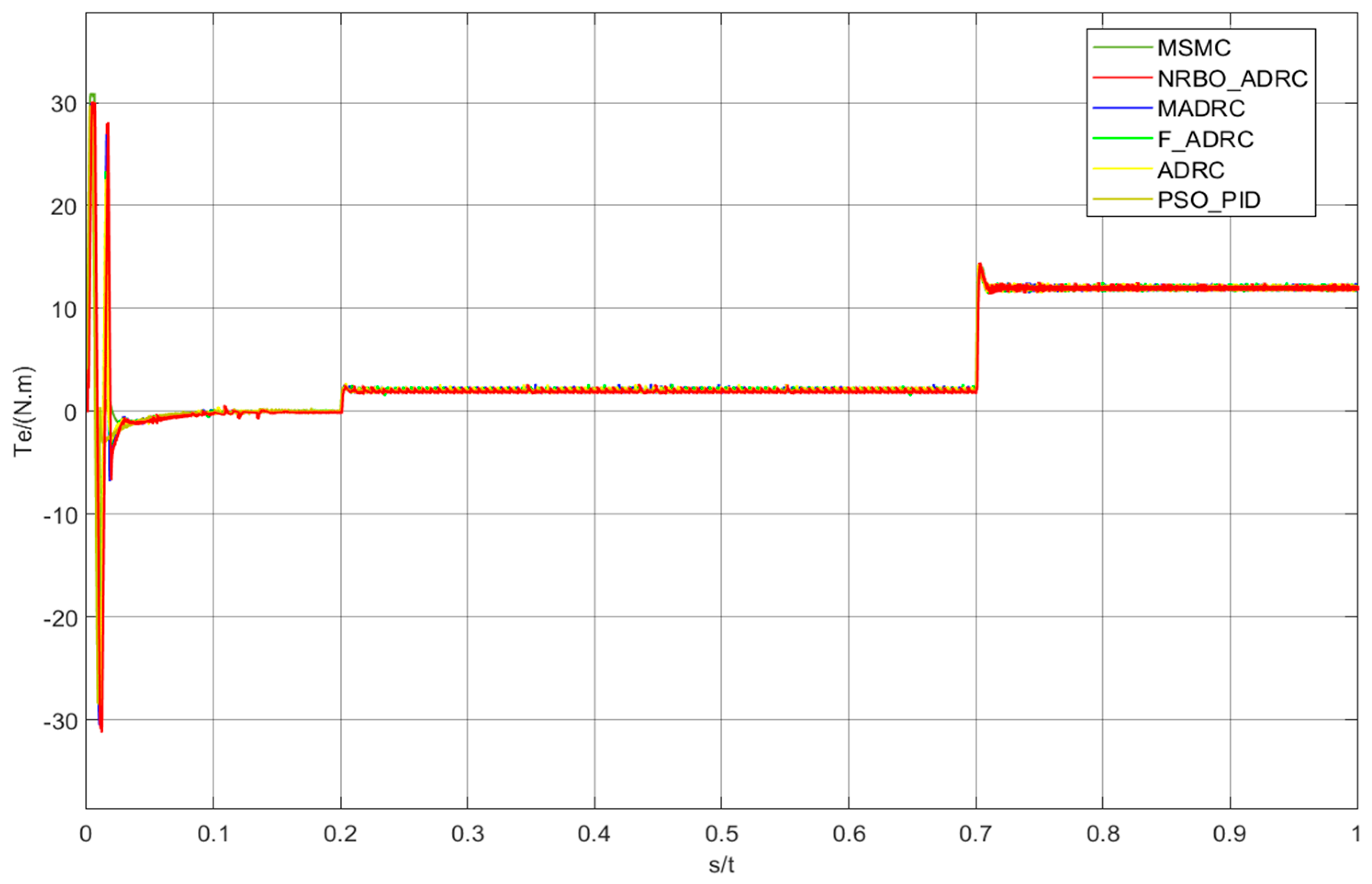
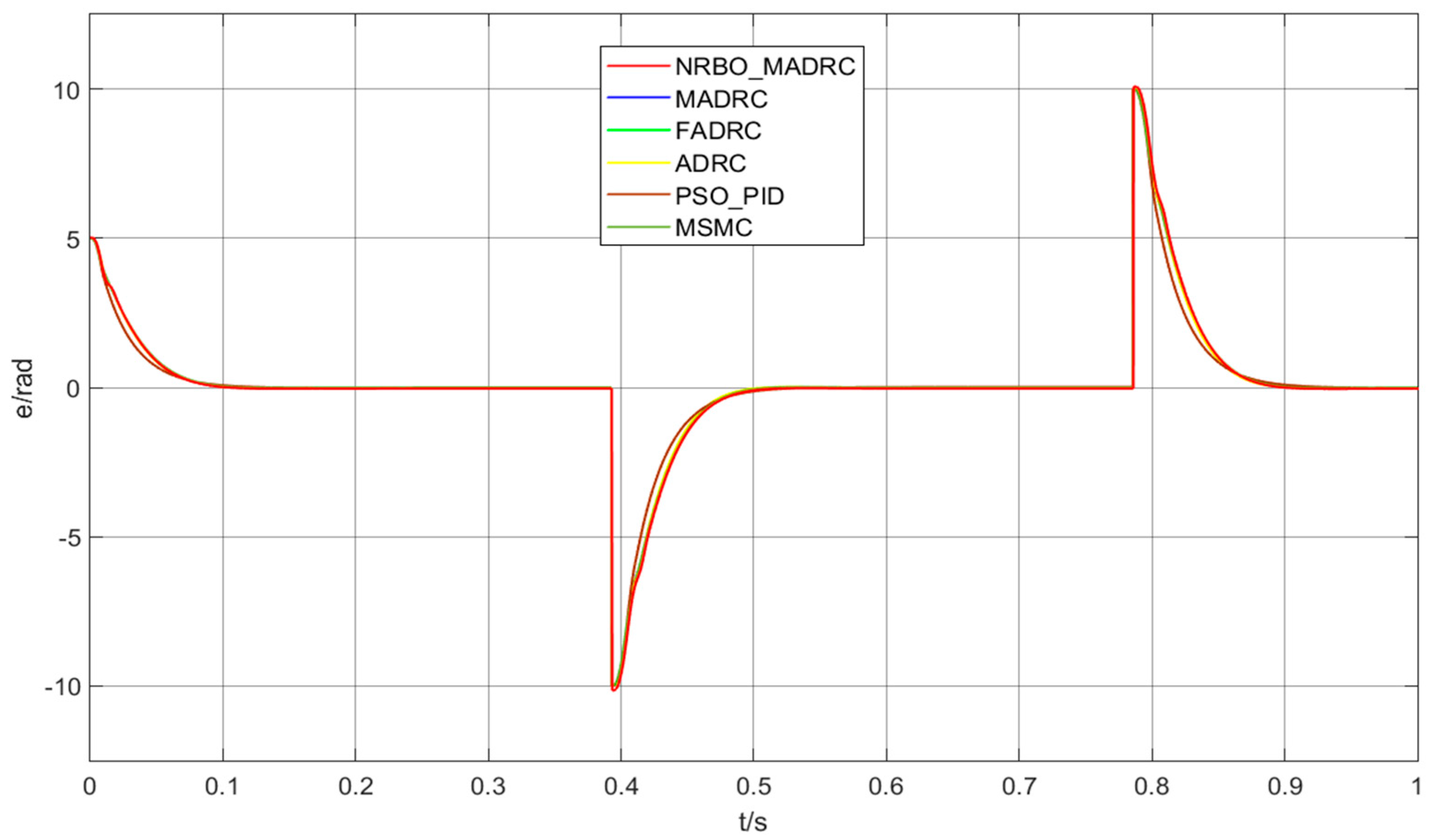
4.1. Sinusoidal Signal Tracking Under Load
4.2. Variable-Load Experiment Under Step Signal
4.3. No-Load Experiment Under Square Wave Signal
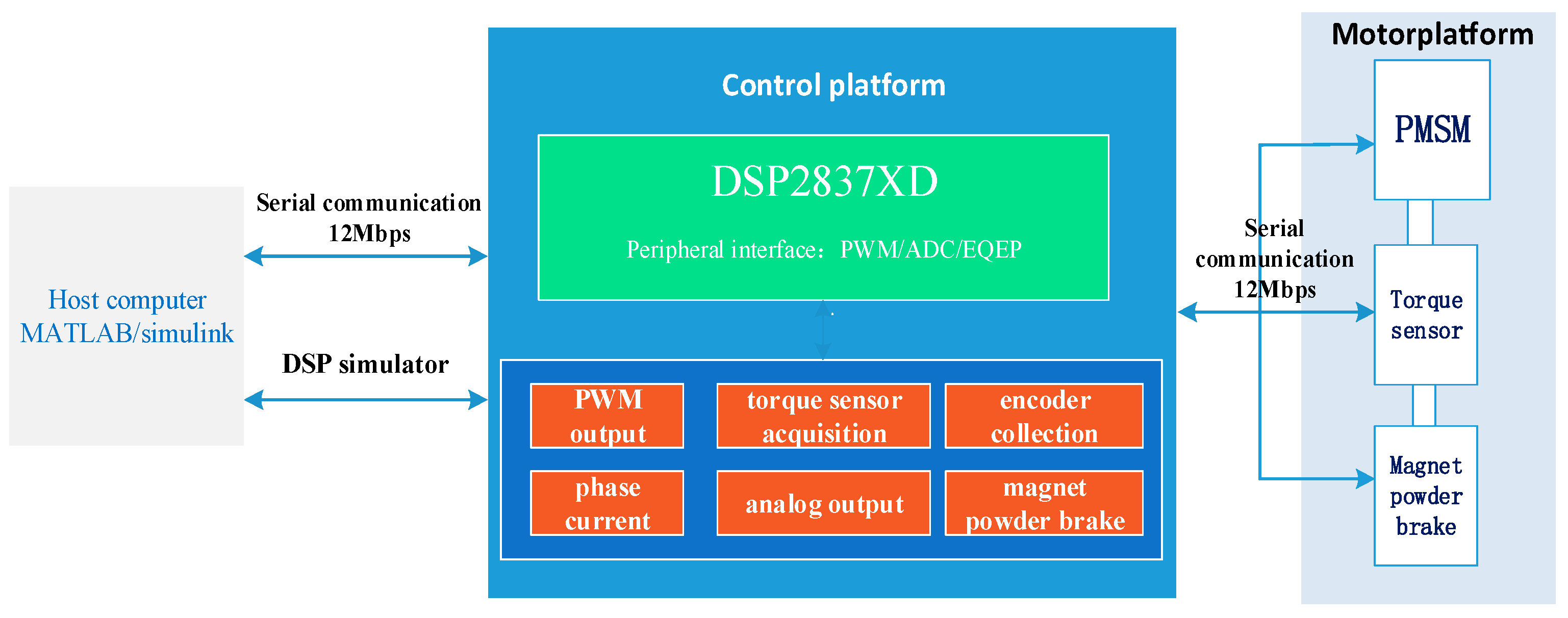
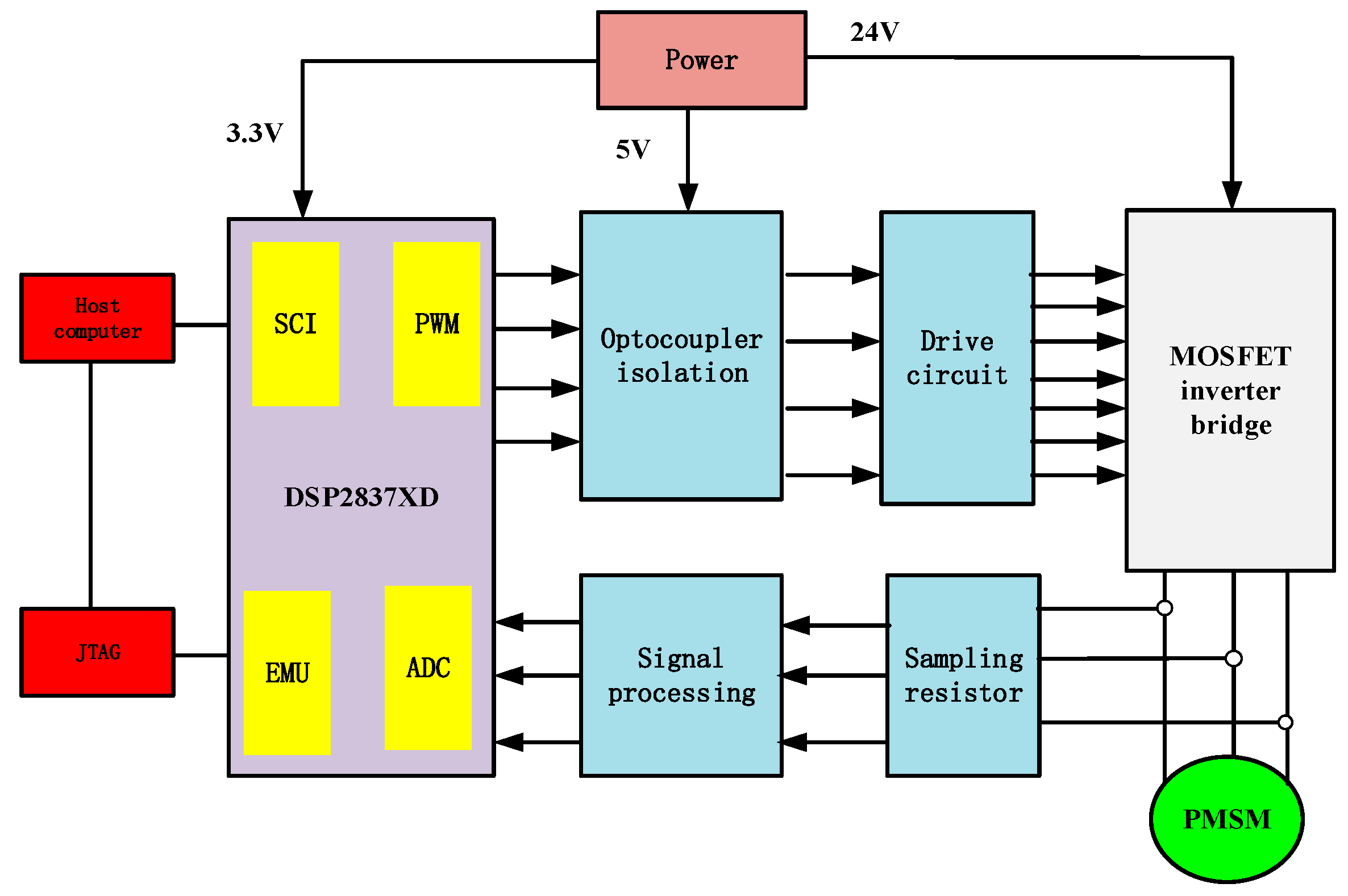
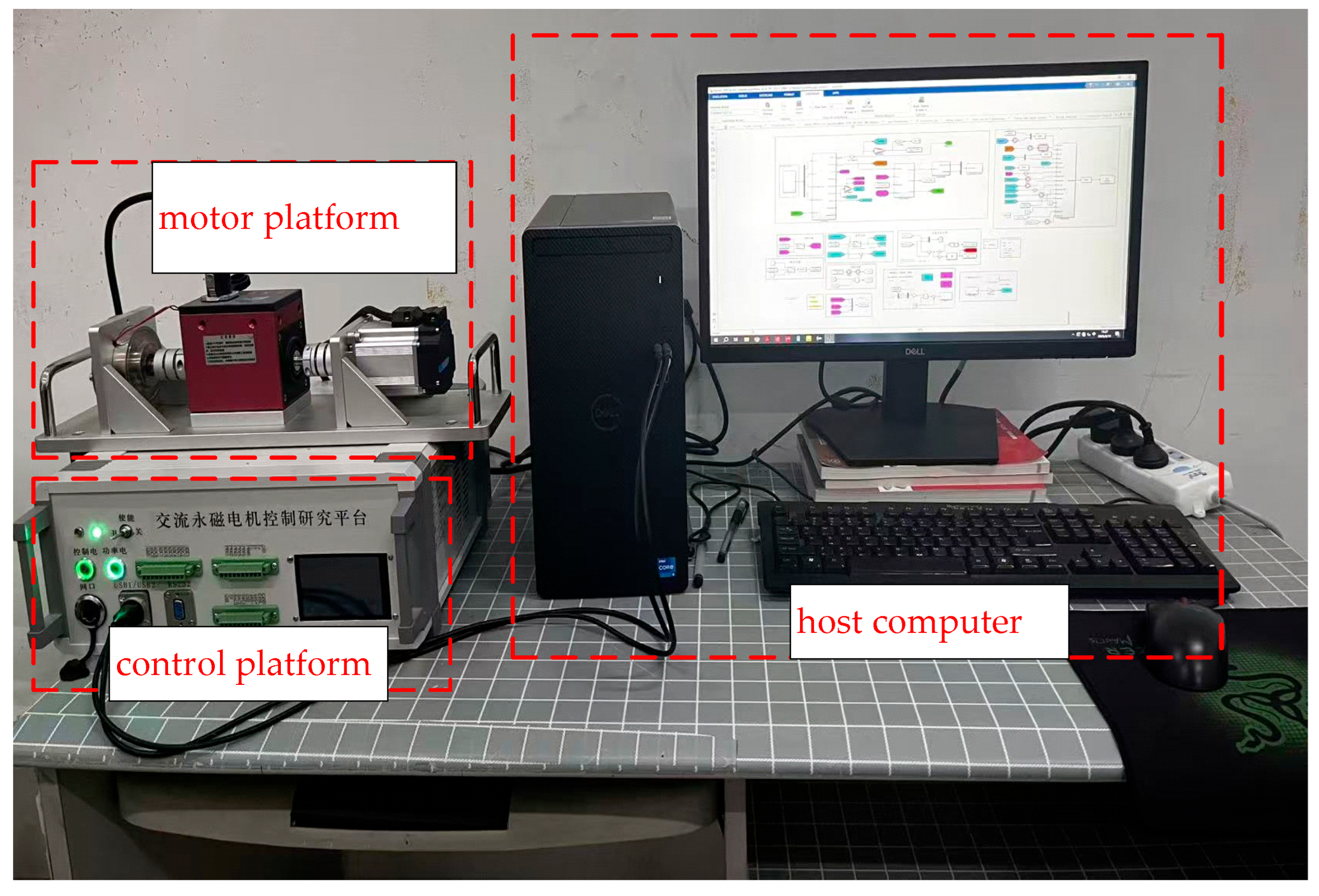
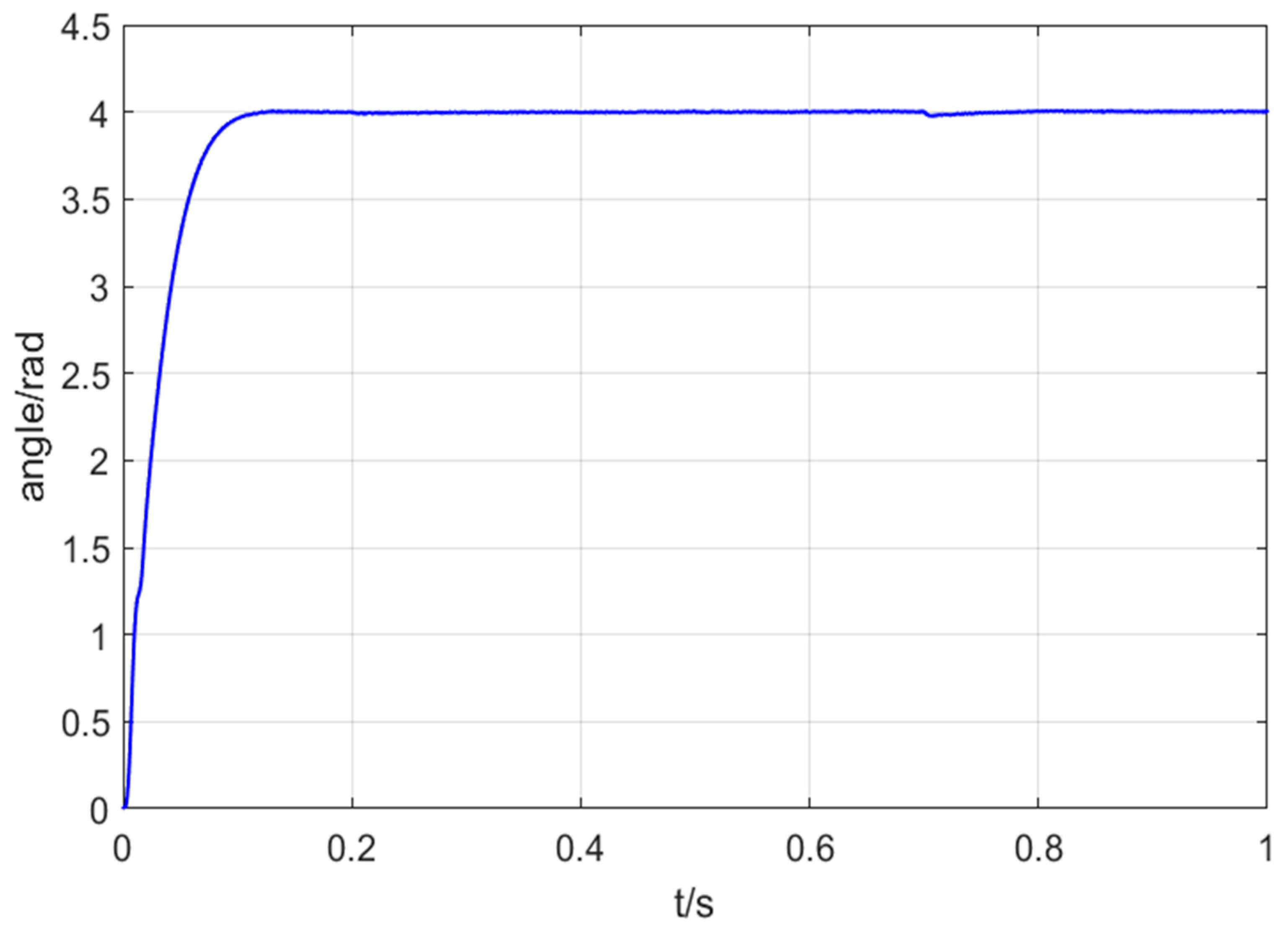
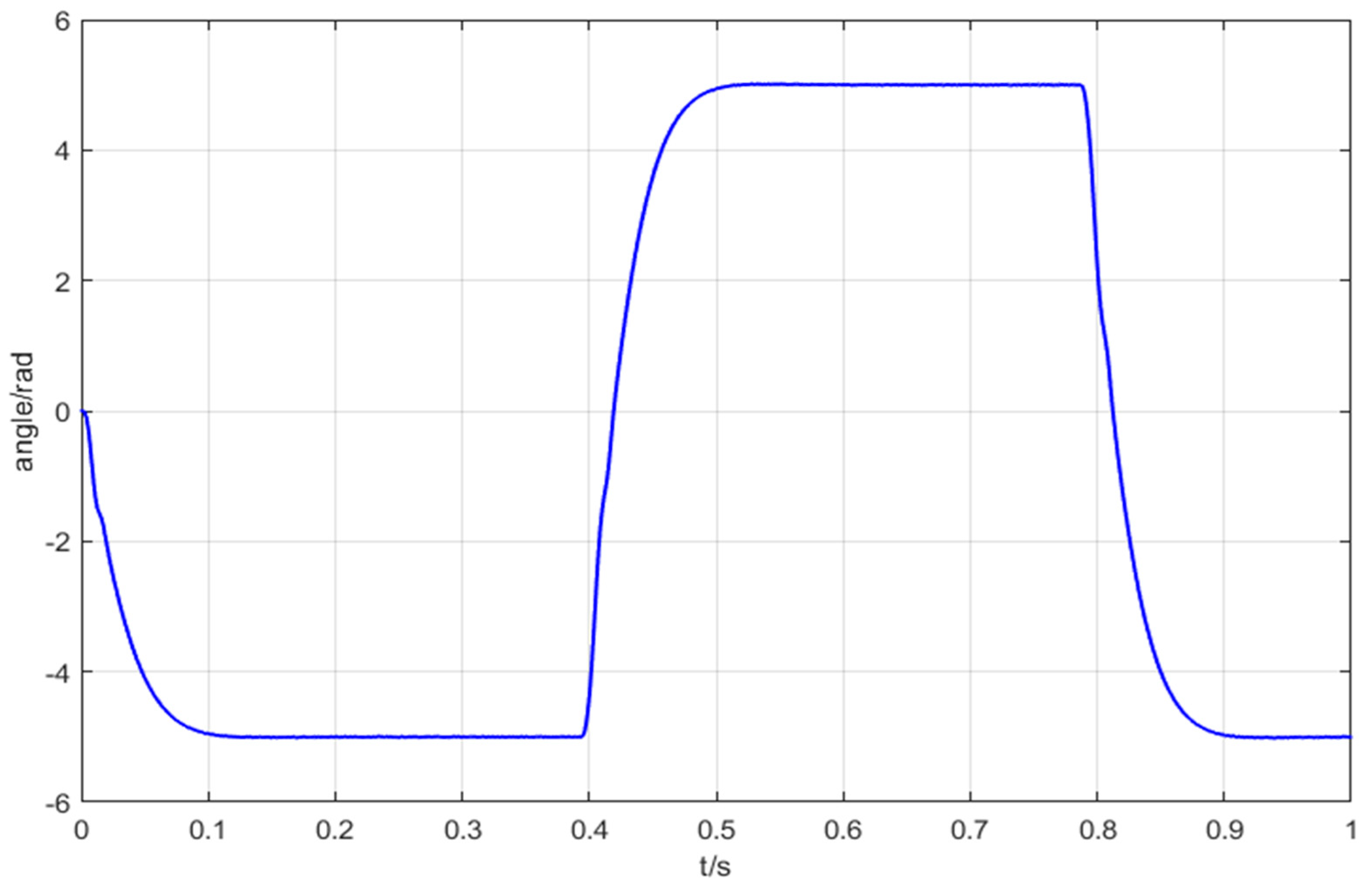
4.4. Prototype Experiment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The improved ADRC-based PMSM position control design can meet high-performance requirements under complex working conditions, thus achieving fast response, minimal overshoot, and strong disturbance rejection capability.
- (2)
- The ADRC parameter self-tuning based on the NRBO eliminates the need for manual parameter adjustment, reduces implementation complexity, improves tuning accuracy, and further enhances the overall control performance of the ADRC.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, T.; Yang, M.; Wang, G. Sensorless full-speed domain control of permanent magnet synchronous motors based on pulse frequency injection and fuzzy super-spiral sliding mode observer. Power Tools 2024, 4, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Ming, Y.; Wang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, D. Precise position control based on resonant controller and second-order sliding mode observer for PMSM-driven feed servosystem. IEEE. Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yu, H.; Li, W.; Meng, F.; Liu, X.; Yao, M. FMSS improved sliding mode control strategy based on feedback exact linearization decoupling. Electr. Power Eng. Technol. 2023, 42, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, R.; Shi, P.; Ou, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S. New adaptive sliding mode and parameter identification control for permanent magnet synchronous motors. J. Electr. Power Syst. Autom. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, S. Sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on second-order low-pass filtering. Coal Mine Mach. 2013, 34, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, I.; Sharma, V. Analysis of different control schemes of PMSM motor and also a comparison of FOPI and PI controller for sensorless MSVPWMM scheme. e-Prime—Advances in Electrical Engineering. Electron. Energy 2023, 6, 100359. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, M.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, L. An improved adaptive finite-time super-twisting sliding mode observer for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. Actuators 2024, 13, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumantri, B.; Uchiyama, N.; Sano, S. Generalized super-twisting sliding mode control with a nonlinear sliding surface for robust and energy-efficient controller of a quad-rotor helicopter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 231, 2042–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, D.; Ren, L.; Han, J.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Research on speed sensorless control strategy of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on fuzzy super-twisting sliding mode observer. Sci. Prog. 2024, 107, 368504241228106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, H.; Yu, X. Practical terminal sliding mode control and its applications in servo systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhao, X. A novel robust adaptive nonsingular fast integral terminal sliding mode controller for permanent magnet linear synchronous motors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, K.; Cheng, M. Deadbeat Predictive Control for Position Servo Permanent Magnet Motor. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2023, 38, 5176–5184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, L. Adaptive sliding mode position control for permanent magnet linear motor based on periodic disturbance learning. J. Electr. Mach. Control. 2021, 25, 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, B.; Ai, B.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y. Nonlinear active disturbance rejection control of hydraulic turbine regulating system considering dead zone. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2023, 42, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Paek, S.-Y.; Kong, Y.-S.; Pak, S.-H.; Kang, J.-S.; Yun, J.-N.; Kil, H.-I.; Hwang, C.-J. Robust optimal tuning of a reduced active disturbance rejection controller based on first-order plus dead time model approximation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Han, J.; Chen, G.; Cheng, Y.; Song, C. Fuzzy self-tuning fractional order PD permanent magnet synchronous motor speed control based on torque compensation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Jia, N.; She, J.; Dai, W.; Zhou, R.; Liu, W.; Li, X. Robust model-free super-twisting sliding mode control method based on extended sliding mode disturbance observer for PMSM drive system. Control. Eng. Pract. 2023, 139, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Ataei, M.; Ekramian, M. Continuous nonsingular terminal sliding mode control based on adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer for uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatics 2019, 109, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y. Disturbance/Uncertainty Estimation and Attenuation Techniques in PMSM Drives—A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 3273–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. Using Sign Function and Absolute Function to Construct Nonlinear Function. Control. Eng. China 2008, S2, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. Nonlinear State Error Feedback Control Law—NLSEF. Control. Decis. 1995, 03, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. The “Extended State Observer” of a Class of Uncertain Systems. Control. Decis. 1995, 1, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhang, R. Error analysis of second-order expansion state observer. Syst. Sci. Math. 1999, 4, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Qi, G.; Liu, G. Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Power Electron. 2024, 58, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Fan, J. A Composite Control Strategy of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Active Disturbance Rejection. Electr. Mach. Control. Appl. 2023, 50, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Wu, S.; Han, S.; Cui, S. Application of Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Controller for Sensorless Control of Internal Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Qiao, W.; Qu, L. An Enhanced Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Rotor Position Sensorless Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 6175–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X. Auto Disturbance Rejection Tracking Control of Electro-hydraulic Position Servo System Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2021, 40, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. ADRC controller optimization design based on improved PSO algorithm for attitude control of helicopter. Inf. Commun. 2019, 4, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Ju, Y.; Liu, G. Nonlinear auto disturbance rejection control via the improved shark smell optimization for permanent magnet synchronous motor. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 44, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Sowmya, R.; Premkumar, M.; Jangir, P. Newton-Raphson-based optimizer: A new population-based metaheuristic algo-rithm for continuous optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 128, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Madonski, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, W. Composite Control Design for Systems With Uncertainties and Noise Using Combined Extended State Observer and Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 4119–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z. Enhanced ADRC Position Servo System Based on Fourth-Order ESO. Master’s Thesis, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Ran, Q.; Zhao, S. Vector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Auto Disturbance Rejection and Improved ESO. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2023, 9, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, R.; Xiang, C. Synchronous Control of High-Speed Train Lift Wing Angle of Attack Drive System Based on Active Disturbance Rejection. Electr. Mach. Control. Appl. 2023, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chai, Q. Research on the Vector Control Strategy of PMSM Based on ADRC + Advanced Repeat Control. Power Electron. 2020, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Lin, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, P. Improved Nonlinear Backstepping Active Disturbance Rejection Position Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2023, 7, 73–78. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, D. Research on Position Tracking Performance Optimization of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910467
Xu Y, Huang Z, Liu D. Research on Position Tracking Performance Optimization of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910467
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yu, Zihao Huang, and Dejun Liu. 2025. "Research on Position Tracking Performance Optimization of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910467
APA StyleXu, Y., Huang, Z., & Liu, D. (2025). Research on Position Tracking Performance Optimization of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Control. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910467




