Abstract
Low-light image enhancement aims to restore images captured under extreme low-light conditions. Existing methods demonstrate that fusing Fourier transform magnitude and phase information within the RGB color space effectively improves enhancement results. Meanwhile, recent advances have demonstrated that certain color spaces based on human visual perception, such as Hue–Value–Intensity (HVI), are superior to RGB for enhancing low-light images. However, these methods neglect the key impact of the coupling relationship between spatial and frequency-domain features on image enhancement. This paper proposes a spatial–frequency-domain multi-scale fusion for low-light image enhancement by exploring the intrinsic relationships among the three channels of HVI space, which consists of a dual-path parallel processing architecture. In the spatial domain, a specifically designed multi-scale feature extraction module systematically captures comprehensive structural information. In the frequency domain, our model establishes deep coupling between spatial features and Fourier transform features in the I-channel. The effectively fused features from both domains synergistically drive an encoder–decoder network to achieve superior image enhancement performance. Extensive experiments on multiple public benchmark datasets show that the proposed method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both quantitative metrics and visual quality.
1. Introduction
Low-light image acquisition often encounters several major degradation issues, including insufficient brightness, pronounced noise, blurred details, and color distortion. These limitations significantly impair the practical performance of computer vision systems in critical application domains such as surveillance and autonomous driving [1,2], medical imaging analysis [3,4], and nighttime remote sensing [5,6]. To address these challenges, low-light image enhancement (LLIE) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14] has emerged as a fundamental and technically demanding research field in computer vision, which aims to reconstruct clear, natural-looking, and information-preserved visual content comparable to normal illumination conditions.
Recent years have witnessed significant advances in this field, where extensive works demonstrate that effectively leveraging frequency-domain information (particularly by fusing Fourier transform (FT) magnitude [12] and phase [13] within the RGB color space) can improve model performance. In addition, investigating color spaces that are highly consistent with human visual perception or that facilitate the separation of illumination components has emerged as a critical research direction. Existing studies have shown that other color spaces based on human visual perception, including Hue–Value–Intensity (HVI) [15], HSV [16,17], and YCbCr [18], demonstrate distinct advantages over conventional RGB space in characterizing illumination, color, and texture attributes, enabling new possibilities to design more effective LLIE models.
While the HVI color space has been adopted for low-light image enhancement, existing studies have insufficiently investigated the inherent correlations of its fundamental components: Hue (H), Value (V), and Intensity (I). Specifically, the Intensity channel, which is highly correlated with illumination, needs to be further studied in terms of how its characteristics can complement frequency-domain representations to improve restoration quality. For example, Figure 1 shows the restoration effects achieved by swapping the amplitude components (Amp) among the three HVI channels of a low-light and normal-light image pair in the Fourier domain while retaining their phase components (Pha). As shown in the figure, the Intensity (I) channel exhibits markedly greater responsiveness to Fourier-domain modifications. This finding validates that amplifying Fourier magnitude components specifically within the intensity channel of low-light images can deliver more effective brightness enhancement. However, existing methods exhibit inherent limitations in effectively integrating spatial and frequency-domain information. Unlike FourLLIE, which only uses Fourier transforms for global modeling, CIDNet’s multi-scale convolution lacks explicit frequency interaction, and diffusion/transformer methods often suffer from high computational costs or limited interpretability. Our method achieves deep spatial–frequency coupling in the HVI space’s I-channel. Through a dual-path architecture with adaptive fusion, it simultaneously recovers illumination and preserves details. The primary constraints include the inflexibility of spatial feature extraction across scales, coupled with the absence of a robust coupling mechanism between spatial features (notably high-frequency and phase-dependent local details) and frequency features (particularly amplitude-driven global illumination and structural information). These limitations emphasize the pressing need to develop a unified framework capable of jointly optimizing local detail preservation and global illumination, as well as structure enhancement, thereby achieving complementary synergy between dual-domain representations.
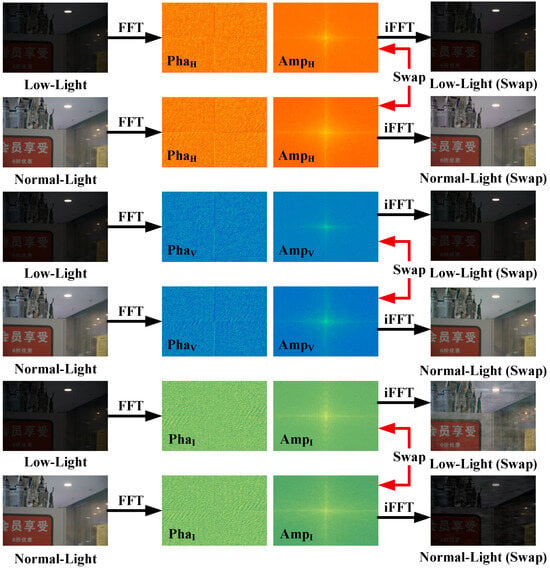
Figure 1.
The restoration effects achieved by swapping the amplitude components (Amp) among the three HVI channels of an image pair (low-light and normal-light) in the Fourier domain while retaining their phase components (Pha). “FFT” and “iFFT”, respectively, represent the Fourier transform and inverse Fourier transform.
This paper presents an HVI-based spatial–frequency-domain multi-scale fusion approach for low-light image enhancement, with its core innovation lying in two key aspects: (1) the exploration of the HVI color space’s I-channel characteristics and (2) the establishment of a novel coupling mechanism between I-channel information and Fourier frequency-domain components, where magnitude governs global illumination and contrast, and phase control structural and detailed information. This dual-domain integration synergistically addresses both illumination distribution recovery and high-frequency detail reconstruction, overcoming the limitations of conventional methods that are constrained to single processing domains or isolated channel operations. The proposed framework implements parallel dual-path processing, comprising a spatial path that employs multi-scale feature extraction to capture holistic structural characteristics through multi-context modeling, and a frequency path that performs deep I-channel–Fourier coupling to derive frequency representations enriched with illumination and structural priors. These complementary features are adaptively fused to drive an encoder–decoder network for final image reconstruction. The architecture ensures joint optimization of local textural details and global illumination and structure during image enhancement. The principal contributions of the proposed LLIE method are summarized as follows.
- This paper presents a novel mechanism for deep coupling between spatial features and Fourier transform features in the I-channel of HVI color space, which significantly enhances joint detail and illumination restoration through fusion of I-channel illumination characteristics with frequency-domain information.
- We develop a dual-path spatial–frequency fusion model that concurrently processes features via a multi-scale spatial module and a Fourier–Intensity coupling module and then employs adaptive fusion to drive an encoder–decoder network for joint local–global feature optimization.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple public benchmarks, conclusively validating the effectiveness and superiority of our model for low-light image enhancement.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Low-Light Image Enhancement Methods
Traditional low-light image enhancement approaches predominantly follow two technical trajectories: Histogram Equalization (HE) techniques [19,20,21,22,23] and Retinex theory [24,25,26,27,28,29]. HE-based methods primarily address inherent limitations such as over-enhancement and contrast distortion. For example, Arici et al. [21] proposed adaptive histogram modification through dual-criterion objective functions for controllable contrast enhancement. Lee et al. [22] developed contrast enhancement algorithms through hierarchical difference representations of 2D histograms that intensify adjacent-pixel grayscale difference modeling with constrained optimization to elevate objective quality and subjective visual effects. In addition, Wang et al. [23] introduced gamma-correction-fused histogram adjustment schemes, filling histogram valleys while smoothing peaks to alleviate traditional HE limitations. Meanwhile, Retinex-theoretic advancements focus on refining illumination–reflectance decomposition accuracy while suppressing noise. For example, Fu et al. [26] innovated exponential weighted gradient regularization beyond logarithmic variational models to rectify gradient imbalance and reduce detail loss in reflectance. Li et al. [27] established robust Retinex frameworks through explicit noise modeling and optimized regularization for superior noise handling. In addition, Xu et al. [28] advanced Structure–Texture-Aware Retinex models that leverage exponentiated local derivatives to generate structural and textural maps guiding decomposition regularization, achieving significant gains in both enhancement and color correction.
2.2. Deep-Learning-Based Low-Light Image Enhancement Methods
Despite persistent challenges in modeling complex scene dynamics and perceptual cues, which often lead to suboptimal brightness restoration, color fidelity loss, and noise amplification in extremely low-light conditions, deep-learning-based LLIE methods have demonstrated significant progress [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Guo et al. [38] proposed reference-free deep curve estimation using non-reference loss functions, bypassing paired or unpaired data requirements to effectively resolve illumination deficiency and noise suppression. Zheng et al. [39] developed UTVNet with learnable noise-level maps and unfolded variational modules for precise noise estimation/suppression in sRGB-space real-world images while enhancing detail robustness. Additionally, generative models exhibit growing potential: Yi et al. [40] introduced Diff-Retinex, combining Retinex decomposition with diffusion models via transformer-based separation and multi-path networks for detail recovery. Cai et al. [41] proposed a single-stage framework named Retinexformer, which is built on a lighting-guided transformer architecture designed to address remote dependency issues in image enhancement. In addition, Feng et al. [42] introduced a dual-branch framework called DiffLight, comprising a denoising enhancement branch that employs a diffusion model for initial noise reduction and brightness adjustment and a detail preservation branch that utilizes a lightweight transformer for recovering fine-grained details. The model further incorporates a Progressive Patch Fusion mechanism to mitigate block artifacts during ultra-high-definition (UHD) image processing.
Fourier frequency information has proven highly effective for low-light image enhancement [12,13,43,44,45,46,47,48,49], owing to its global representation capability and inherent illumination–structure decoupling properties. Recent advancements further exploit this potential through innovative architectures. For example, Huang et al. [47] introduced amplitude-phase dual-branch networks for explicit frequency-domain brightness–structure modeling, complemented by spatial–frequency interaction modules that enable efficient local–global learning with reduced parameters. For ultra-high-definition scenarios, Li et al. [48] achieved precise brightness–noise separation in Fourier space via cascaded low-high-resolution networks while concurrently contributing the first UHD-LL 4K real-paired dataset. Wang et al. [12] adopted dual-stage networks separately targeting global amplitude enhancement and local detail recovery. Zhang et al. [13] integrated infrared priors with luminance attention mechanisms for dual-stage multi-branch amplitude-phase refinement that elevates brightness–color–texture fidelity with concurrent noise suppression. In addition, Lv et al. [49] embedded Fourier amplitude-phase priors into pre-trained diffusion models, accomplishing joint low-light enhancement and deblurring via zero-shot learning independent of paired data or specific degradation assumptions.
3. Methods
3.1. Overall
This section presents the proposed HVI-based spatial–frequency-domain multi-scale fusion LLIE method (abbreviated as HVI-FourNet). As shown in Figure 2, HVI-FourNet adopts a dual-branch U-Net architecture. Its spatial-domain and frequency-domain branches, respectively, utilize SpaBlock and FourBlock to extract HVI features and intensity features in three encoding stages and three decoding stages. In each decoding stage, feature interaction enhancement is achieved through the Lighten Cross-Attention (LCA) [15] module, and the enhanced image is finally obtained after the inverse HVI transformation.
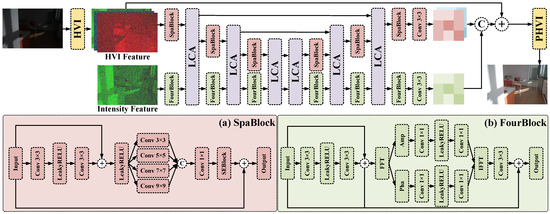
Figure 2.
The architecture of the proposed HVI-FourNet. The model adopts a dual-branch U-Net architecture. An input image is transformed into HVI space to extract HVI features, while the intensity features are separately extracted to form the other branch. The HVI feature branch employs SpaBlock for channel-wise feature extraction, while the intensity branch utilizes FourBlock for processing. An LCA module is then incorporated to interactively guide and enhance the features of both branches. After undergoing downsampling and upsampling stages, the final illumination-enhanced image is produced.
For an input low-light image , HVI-FourNet first transforms the input image from the sRGB space to the HVI space through the HVI transformation module [15] to obtain the HVI feature . Similar to [15], we continue to adopt the dual-branch design system, treating the intensity channels separately, and the intensity channel features are represented as . Subsequently, we, respectively, use 3 × 3 convolution operations on and to obtain the shallow feature and feature . In the encoding stage, extracts deep features () in the spatial-domain branch through three Spablocks. Meanwhile, extracts deep features () through three Fourblocks in the Fourier frequency-domain branch. After each encoding stage, the LCA [15] module is used to cross-guide and enhance the spatial and frequency-domain features. In the decoding stage, the encoded features and are first interactively enhanced through the LCA module and then enhanced, respectively, by SpaBlock and FourBlock to obtain the decoded features () and (). At the same time, the decoder fuses the corresponding encoder stage features through weighted skip connections to reduce information loss and optimize feature recovery. Then, and of the decoder’s dual-branch results are first processed through a 3 × 3 convolutional layer to generate the features and . Finally, and are concatenated and transformed through the inverse HVI transformation to generate the final predicted image . Then, the joint loss function is used to perform end-to-end optimization on the target enhanced image .
3.2. HVI Space Information
Firstly, we briefly introduce the HVI space transformation, originally proposed by Yan et al. [15]. For an input image , the transformation works as follows. First, convert each individual pixel p in to the HSV space. Its transformation process can be represented by , , and . To address red discontinuity artifacts, is decomposed into orthogonal components:
The resulting HVI mapping process , , and is shown as follows:
where the adaptive intensity collapse function suppresses black plane noise:
where is a trainable density parameter governing radial compression, and is a fixed hyperparameter. Finally, , , and can be concatenated to form the HVI feature .
3.3. SpaBlock
Figure 2a shows how the SpaBlock module enhances spatial feature extraction by using multi-scale convolution. This approach outperforms traditional CNNs by capturing both local details and global structures. For input features , processing occurs as follows. First, a base residual path ( convolution → LeakyReLU activation → convolution) processes the input. Its output is then combined with the original input through a residual connection:
To optimize efficiency and capacity, we reduce the dimensions from (C = 64) to (C/4 = 16) while progressively increasing the kernel sizes from to (in steps of 2). The m-th scale output yields . These multi-scale features are concatenated through convolution to obtain feature :
Finally, undergoes channel attention refinement through SEBlock [13] and fuses with the original input via residual connection, producing the enhanced output feature with strengthened spatial representation.
3.4. FourBlock
Figure 1 and foundational Fourier methods [47,48] demonstrate that intensity (I) channel features in HVI space can be effectively enhanced through Fourier-domain representation, which captures global context with low parameterization. Accordingly, we design the FourBlock module, which is shown in Figure 2b. For input features , a base residual path ( convolution → LeakyReLU activation → 3 × 3 convolution) processes the input , yielding locally enhanced feature through residual connection:
then undergoes a Fourier transform:
where and denote spatial and frequency coordinates, respectively, with components decomposed as
where and represent the real and imaginary part of , respectively. is converted into amplitude spectrum and phase spectrum . These components are separately modulated via independent subnetworks. The specific process is as follows:
Then, and are reconstructed into the spatial residual feature through the inverse FFT (iFFT). Finally, we introduce a two-stage residual fusion: first combines with local feature through element-wise addition and then fuses with the original input to produce the frequency-enhanced feature for the intensity channel.
3.5. Loss Function
Based on the optimization strategy [15], a composite loss function is jointly computed in both sRGB and HVI color spaces between the predicted image and the target image . Additionally, their corresponding HVI space mappings are, respectively, represented as and , and sRGB space mappings are, respectively, represented as and . This multi-objective framework minimizes discrepancies across four metrics in both two spaces:
where ( = 1.0) is a weighting hyperparameter to balance the losses in the two different color spaces. In each color space, we calculate the loss of the predicted image and the target image using Loss, Edge Loss, Perceptual Loss, and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) Loss, and the calculation formulas are as follows:
where (), (=50.0), (), and () are the weighting hyperparameters corresponding to the Norm Loss (), Edge Loss (), Perceptual Loss (), and SSIM Loss functions (), respectively.
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Metrics
We evaluate the proposed HVI-FourNet on four standard LLIE datasets: LOL-v1 [50], LOL-v2-Real [51], LOL-v2-Synthetic [51], and MIT-5K [52].
LOL. The LOL-v1 dataset [50] contains 485 training and 15 testing pairs captured under controlled conditions. Based on the LOL-v1 dataset, LOL-v2 expands both scale and diversity through two variants: LOL-v2-Real [51] (689 training and 100 testing pairs with authentic exposure variations) and LOL-v2-Synthetic [51] (900 training and 100 testing pairs with statistically matched luminance distributions), enabling comprehensive evaluation of real and synthetic scenarios.
MIT-5K. This dataset [52] provides 5000 RAW images with five expert retouches (A–E). We use Expert C’s versions as the target images, with 4500 pairs for training and 500 for testing, to validate performance under complex illumination variations.
Metrics. For the objective assessment of enhanced image quality, this study employs three widely used metrics: Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) [53], and Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) [54]. PSNR measures the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of distorting noise, serving as a classic pixel-level distortion metric. SSIM evaluates the perceived structural similarity between two images based on luminance, contrast, and structure, offering a perception-aware comparison. To further capture human perceptual quality, we introduce LPIPS: a deep-learning-based metric that quantifies perceptual similarity using features extracted from a pre-trained AlexNet [55]. Lower LPIPS values indicate higher perceptual fidelity, while higher PSNR and SSIM values reflect better signal preservation and structural integrity, respectively.
4.2. Experiment Settings
In the process of training deep learning models, variations in input sizes across datasets and limitations in hardware resources necessitate a balance between computational efficiency and model performance. Consequently, we designed tailored training strategies based on the characteristics of each dataset and practical constraints. For real-captured datasets (LOL-v1 and LOL-v2-Real), we use random crops (batch size = 4, epochs = 800), while LOL-v2-Synthetic uses full-resolution inputs (batch size = 1, epochs = 500). For the MIT-5K dataset, we use random crop (batch size = 8, epoch = 1000). Our implementation uses PyTorch v1.13.0 on RTX 3090 GPU with Adam optimizer [56] ( = 0.9, = 0.999) and cosine-annealed learning rate [57] from to .
4.3. Comparison with State of the Arts
Quantitative comparison. The comprehensive experimental results presented in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 demonstrate that our proposed method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance across all evaluation metrics. On the LOL-v1 dataset, compared against 13 methods including classical approaches (BIMEF [58], FEA [59], LIME [60], MF [61], NPE [62], RetinexNet [50], and DSLR [63]) and recent deep learning models (KinD [64], RUAS [9], Uformer [65], Restormer [66], LLFormer [67], Diff-Retinex [40], LightenDiffusion [14], and CIDNet [15]), our approach not only achieves the highest PSNR of 24.33 (0.68 higher than LLFormer) but also demonstrates remarkable performance in both structural (0.855 SSIM) and perceptual (0.092 LPIPS) metrics.

Table 1.
Quantitative comparison on the LOL-v1 [50]. The best results are boldfaced, and the second-best ones are underlined.

Table 2.
Quantitative comparison on the LOL-v2-Real [51]. The best results are boldfaced, and the second-best ones are underlined.

Table 3.
Quantitative comparison on the LOL-v2-Synthetic [51]. The best results are boldfaced, and the second-best ones are underlined.

Table 4.
Quantitative comparison on the MIT-5K [52]. The best results are boldfaced, and the second-best ones are underlined.
For the LOL-v2 dataset, evaluated against 14 methods covering traditional techniques (MF [61], NPE [62], RetinexNet [50], and SGM [51]) and advanced networks (KinD [64], KinD++ [68], MIRNet [69], FECNet [47], Z_DCE [38], SNR-Aware [70], Bread [18], FourLLIE [12], and CIDNet [15]), our method exhibits exceptional adaptability to different data characteristics. The LOL-v2-Real results (24.32 PSNR/0.876 SSIM) reveal stable performance under authentic exposure variations, while the LOL-v2-Synthetic evaluation (25.86 PSNR/0.942 SSIM) confirms effective handling of synthetic artifacts. The marginal LPIPS difference (0.122 vs. 0.051) in LOL-v2-Real indicates potential directions for future perceptual quality improvement.
Benchmarked against 13 methods spanning classical algorithms (BIMEF [58], FEA [59], MF [61], NPE [62], SRIE [26], RetinexNet [50], and DSLR [63]) and deep learning approaches (KinD [64], Z_DCE [38], Z_DCE++ [64], RUAS [9], ELGAN [72], and CIDNet [15]), the MIT-5K results constitute the most compelling evidence of generalization capability. The 4.5 PSNR advantage over DSLR (24.74 vs. 20.24), combined with 15.2% LPIPS reduction from SRIE, demonstrates robust performance under complex illumination conditions that were not explicitly targeted during training. This cross-dataset effectiveness is further corroborated by the consistent average advantages (+1.14 PSNR, +0.016 SSIM, and −0.023 LPIPS) maintained across all evaluation scenarios, indicating that our method effectively addresses the challenges of low-light enhancement.
Moreover, our model maintains high computational efficiency, with a total of 3.55 M parameters and 19.53 G FLOPs. The two key modules, SpaBlock and FreBlock, contribute efficiently to this complexity, requiring only 83.87 K and 94.66 K parameters and 5.34 G and 5.64 G FLOPs, respectively.
Qualitative Comparison. To visualize the enhancement effect of our method, we randomly selected one image from each of the LOL-v1 [50], LOL-v2 [51], and MIT-5k [52] datasets for comparison. As demonstrated in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, our approach consistently generates predicted images that exhibit superior visual correspondence with the target images when compared against some state-of-the-art methods. The LOL-v1 dataset evaluation (Figure 3) reveals our method’s exceptional capability in recovering intricate details from severely underexposed areas, particularly in challenging scenarios involving wall textures and object surfaces, while simultaneously achieving remarkable noise suppression and artifact reduction, where RetinexNet [50], KinD [64], RUAS [9], Uformer [65], and LLFormer [67] show noticeable deficiencies. Moreover, our approach outperforms Restormer [66] and CIDNet [15] in terms of color fidelity and the generation of natural-looking daylight illumination. The slightly inferior illumination rendering of CIDNet, observable in the unnatural shadows on the upper cabinet area, is likely due to its limited ability in coordinating global and local illumination consistency. In contrast, our method preserves more coherent and natural lighting across the entire scene.

Figure 3.
Qualitative comparison in LOL-v1 [50].

Figure 4.
Qualitative comparison in LOL-v2-Real [51] (the first row) and LOL-v2-Synthetic [51] (the second row).

Figure 5.
Qualitative comparison in MIT-5K [52].
The comprehensive visual comparisons on LOL-v2 datasets (Figure 4) provide compelling evidence of our method’s advanced restoration capabilities. Both real and synthetic samples distinctly illustrate their superior performance in reconstructing structural details and achieving balanced illumination distribution, effectively avoiding common pitfalls of competing methods such as SNR-Aware’s [70] over-enhancement, FourLLIE’s [12] color casts, and CIDNet’s [15] unnatural smoothing effects. This balanced performance is particularly evident in handling complex shadow regions and fine textures where other methods tend to fail.
Most significantly, the MIT-5K benchmark results (Figure 5) highlight our method’s outstanding generalization capacity in real-world scenarios. It successfully addresses multiple challenges simultaneously: correcting color distortions (prevalent in RetinexNet [50], Z_DCE++ [71], and KinD [64]), overcoming insufficient enhancement (characteristic of SRIE [26] and DSLR [63] outputs), and eliminating artifacts (commonly observed in ELGAN [72] and CIDNet [15] results). The visual comparisons consistently demonstrate our method’s ability to produce naturally enhanced images with accurate color reproduction and well-preserved fine details, even in extremely low-light conditions with complex scene elements. These qualitative observations, corroborated by quantitative metrics, collectively validate the proposed method’s effectiveness in delivering perceptually superior low-light enhancement across diverse real-world and synthetic scenarios.
4.4. Ablation Study
The ablation study performed on the LOL-v2-Real dataset provides quantitative validation for the individual contributions of each core module in our architecture. As clearly evidenced in Table 5, the removal of the FourBlock module results in a substantial performance degradation, manifesting as a 0.78 dB PSNR decrease (from 24.32 to 23.54) accompanied by a 0.011 SSIM reduction, which unequivocally confirms its pivotal role in advanced feature representation and structural detail recovery. Parallel observations emerge from the SpaBlock module ablation, which induces a 0.017 SSIM deterioration and 0.015 LPIPS increment relative to the complete model, quantitatively demonstrating its essential function in maintaining spatial coherence and perceptual quality. Most significantly, the complete model achieves optimal performance across all metrics (24.32 PSNR, 0.876 SSIM, and 0.122 LPIPS), confirming that both modules synergistically enhance illumination adjustment, detail restoration, and perceptual fidelity. These results robustly justify the architectural design choices.

Table 5.
Ablation study on the LOL-v2-Real dataset [51].
The ablation study on loss functions demonstrates the critical importance of our multi-term loss formulation. Removing the entire loss weighting scheme (sRGB only) leads to noticeable drops in PSNR and SSIM. Most notably, ablating the Norm Loss causes a catastrophic performance collapse, confirming its role as the foundational reconstruction constraint. The Edge Loss () and Perceptual Loss (), respectively, contribute to structural preservation and perceptual quality as their removal increases LPIPS. While the SSIM Loss () slightly improves PSNR, its individual contribution is less dominant. The full model achieves the best balance across all metrics, validating the effectiveness of the combined loss function.
5. Conclusions
Based on the intrinsic advantages of the HVI color space for decoupling illumination and chromatic information, the proposed a novel low-light image enhancement framework, HVI-FourNet, which establishes deep coupling between spatial-domain and Fourier frequency-domain representations through a dual-path architecture. The method effectively integrates multi-scale spatial features and global frequency priors, achieving superior performance both quantitatively and visually across multiple benchmarks. However, the approach entails higher computational and memory costs and may perform suboptimally under extreme noise or motion blur. Future work will focus on enabling real-time processing, extending the model to video sequences, supporting UHD images, and incorporating perceptual quality metrics for further enhancement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and H.Z. (Huiying Zheng); methodology, Y.Z. and H.Z. (Hancheng Zhu); software, Y.Z.; validation, X.X.; formal analysis, H.Z. (Hancheng Zhu); investigation, Y.Z.; resources, Y.Z.; data collection, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.Z. (Huiying Zheng) and X.X.; visualization, Y.Z.; supervision, H.Z. (Hancheng Zhu); project administration, H.Z. (Hancheng Zhu); funding acquisition, H.Z. (Hancheng Zhu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62101555) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20210488).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The experiment uses four public LLIE datasets, which are available in the LOL-v1 [50], LOL-v2-Real [51], LOL-v2-Synthetic [51], and MIT-5K [52].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, T.; Segu, M.; Postels, J.; Wang, Y.; Van Gool, L.; Schiele, B.; Tombari, F.; Yu, F. SHIFT: A synthetic driving dataset for continuous multi-task domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21371–21382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yurtsever, E.; Fossaert, J.; Zhou, X.; Zimmer, W.; Cui, Y.; Zagar, B.L.; Knoll, A.C. A Survey on Autonomous Driving Datasets: Statistics, Annotation Quality, and a Future Outlook. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 7138–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Marinescu, R.; Dalca, A.V.; Bonkhoff, A.K.; Bretzner, M.; Rost, N.S.; Golland, P. 3D-StyleGAN: A style-based generative adversarial network for generative modeling of three-dimensional medical images. In Proceedings of the MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, Strasbourg, France, 1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cap, Q.H.; Fukuda, A.; Iyatomi, H. A practical framework for unsupervised structure preservation medical image enhancement. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, J.; Ray, N.; Schubert, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Chao, D. Small-object detection in remote sensing images with end-to-end edge-enhanced GAN and object detector network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, H. Exploring Distortion Prior With Latent Diffusion Models for Remote Sensing Image Compression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5623713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U.; Koh, Y.J.; Kim, C.S. Global and local enhancement networks for paired and unpaired image enhancement. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Jang, H.; Ha, N.; Sohn, K. Deep low-contrast image enhancement using structure tensor representation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10561–10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Yi, P.; Lu, T.; Lin, C.W. Degrade is upgrade: Learning degradation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, W.; Tan, R.T. Unsupervised night image enhancement: When layer decomposition meets light-effects suppression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 404–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Jin, Z. Fourllie: Boosting low-light image enhancement by fourier frequency information. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October 2023; pp. 7459–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, M.; Lv, H. DMFourLLIE: Dual-stage and multi-branch fourier network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 7434–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Luo, A.; Liu, X.; Han, S.; Liu, S. Lightendiffusion: Unsupervised low-light image enhancement with latent-retinex diffusion models. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Pang, G.; Shi, K.; Wu, P.; Dong, W.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Hvi: A new color space for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 5678–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yang, J.; Kasabov, N. Low illumination video image enhancement. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 3900613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Di, X.; Zhang, B.; Ji, R.; Wang, C. Better than reference in low-light image enhancement: Conditional re-enhancement network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 31, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, Q. Low-light image enhancement via breaking down the darkness. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizer, S.M.; Amburn, E.P.; Austin, J.D.; Cromartie, R.; Geselowitz, A.; Greer, T.; ter Haar Romeny, B.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Zuiderveld, K. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1987, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, E.D.; Zong, S.; Hemminger, B.M.; DeLuca, M.; Johnston, R.E.; Muller, K.; Braeuning, M.P.; Pizer, S.M. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization image processing to improve the detection of simulated spiculations in dense mammograms. J. Digit. Imaging 1998, 11, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, T.; Dikbas, S.; Altunbasak, Y. A histogram modification framework and its application for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, C.; Kim, C.S. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2D histograms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 5372–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L. An effective histogram modification scheme for image contrast enhancement. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2017, 58, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Woodell, G.A. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.u.; Jobson, D.J.; Woodell, G.A. Retinex processing for automatic image enhancement. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, Z. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2828–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hou, Y.; Ren, D.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Shao, L. Star: A structure and texture aware retinex model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 5022–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Tan, J.; Li, Y. Multi-purpose oriented single nighttime image haze removal based on unified variational retinex model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1643–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Liu, B.; Lu, F. Fast enhancement for non-uniform illumination images using light-weight CNNs. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; You, S.; Fu, Y. Learning temporal consistency for low light video enhancement from single images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4967–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5637–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, L.; You, S. LE-GAN: Unsupervised low-light image enhancement network using attention module and identity invariant loss. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 240, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Ma, K.K. Learning a simple low-light image enhancer from paired low-light instances. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22252–22261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pan, C.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, C.; Shen, H.T. Learning semantic-aware knowledge guidance for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhu, Z.; Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Yuan, H. Global structure-aware diffusion process for low-light image enhancement. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 79734–79747. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, J.; Xuan, Z.; Yang, R.; Hao, Y.; Zou, F.; Lin, F.; Han, S. R2rnet: Low-light image enhancement via real-low to real-normal network. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 90, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Shi, D.; Shi, W. Adaptive unfolding total variation network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4439–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L.; Ma, J. Diff-retinex: Rethinking low-light image enhancement with a generative diffusion model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 12302–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Bian, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Timofte, R.; Zhang, Y. Retinexformer: One-stage retinex-based transformer for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 12504–12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hou, S.; Lin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, P.; Dong, W.; Sun, J.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Difflight: Integrating content and detail for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–18 June 2024; pp. 6143–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q. A fourier-based framework for domain generalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14383–14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoli, D.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Fourier space losses for efficient perceptual image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2360–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dai, B.; Wu, W.; Loy, C.C. Focal frequency loss for image reconstruction and synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 13919–13929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, X.; Zhou, M.; Huang, Z.; Peng, J.; Zha, Z.J. Exploring Fourier Prior for Single Image Rain Removal. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-22), Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022; pp. 935–941. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yan, K.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xiong, Z. Deep fourier-based exposure correction network with spatial-frequency interaction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.L.; Zhou, M.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Feng, R.; Loy, C.C. Embedding fourier for ultra-high-definition low-light image enhancement. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11831. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, B.; Li, C.; Nie, L. Fourier priors-guided diffusion for zero-shot joint low-light enhancement and deblurring. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 25378–25388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkovsky, V.; Paris, S.; Chan, E.; Durand, F. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Sgdr: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Z.; Li, G.; Gao, W. A bio-inspired multi-exposure fusion framework for low-light image enhancement. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00591. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Pang, Y.; Wen, J. Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 Posters, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 26–30 July 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Ding, X.; Paisley, J. A fusion-based enhancing method for weakly illuminated images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 129, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.M.; Li, B. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kim, W. DSLR: Deep stacked Laplacian restorer for low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cun, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Uformer: A general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17683–17693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Shen, T.; Luo, W.; Stenger, B.; Lu, T. Ultra-high-definition low-light image enhancement: A benchmark and transformer-based method. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Beyond brightening low-light images. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1013–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H.; Shao, L. Learning enriched features for real image restoration and enhancement. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 492–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C.W.; Jia, J. Snr-aware low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17714–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Z. Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).