Improvement of Wheat and Barley Cultivation Through Seed Priming with UV, Ozone, and Nutripriming (Fe, Zn, and B)
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Physical Treatments
2.3. Nutripriming Treatments
2.4. In Vitro Experiments
2.5. Seed Tray Experiments
2.6. Field Experiments
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Treatments
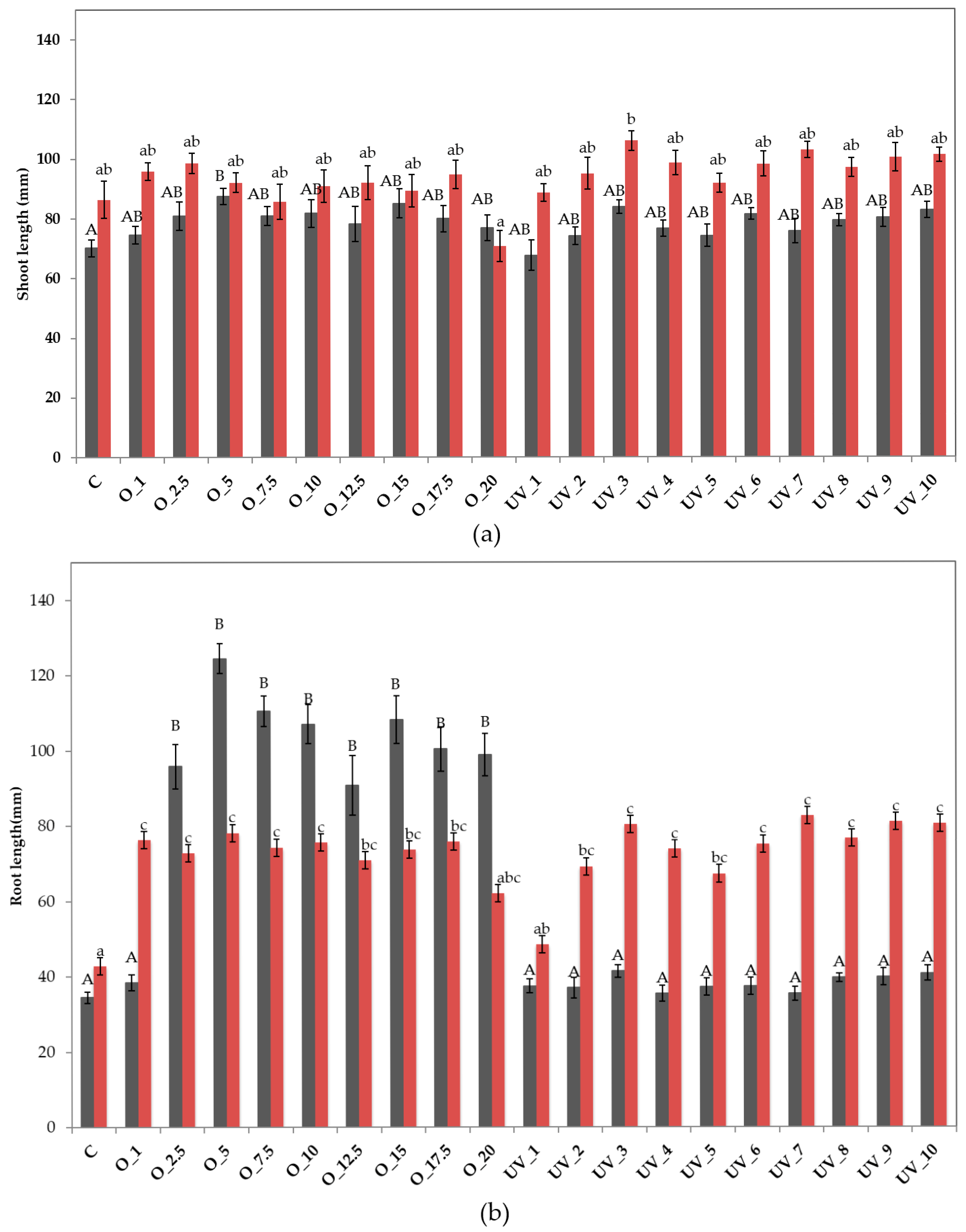
3.1.1. In Vitro Test
3.1.2. Seed Tray Test
3.1.3. Field Experiment
3.2. Nutripriming
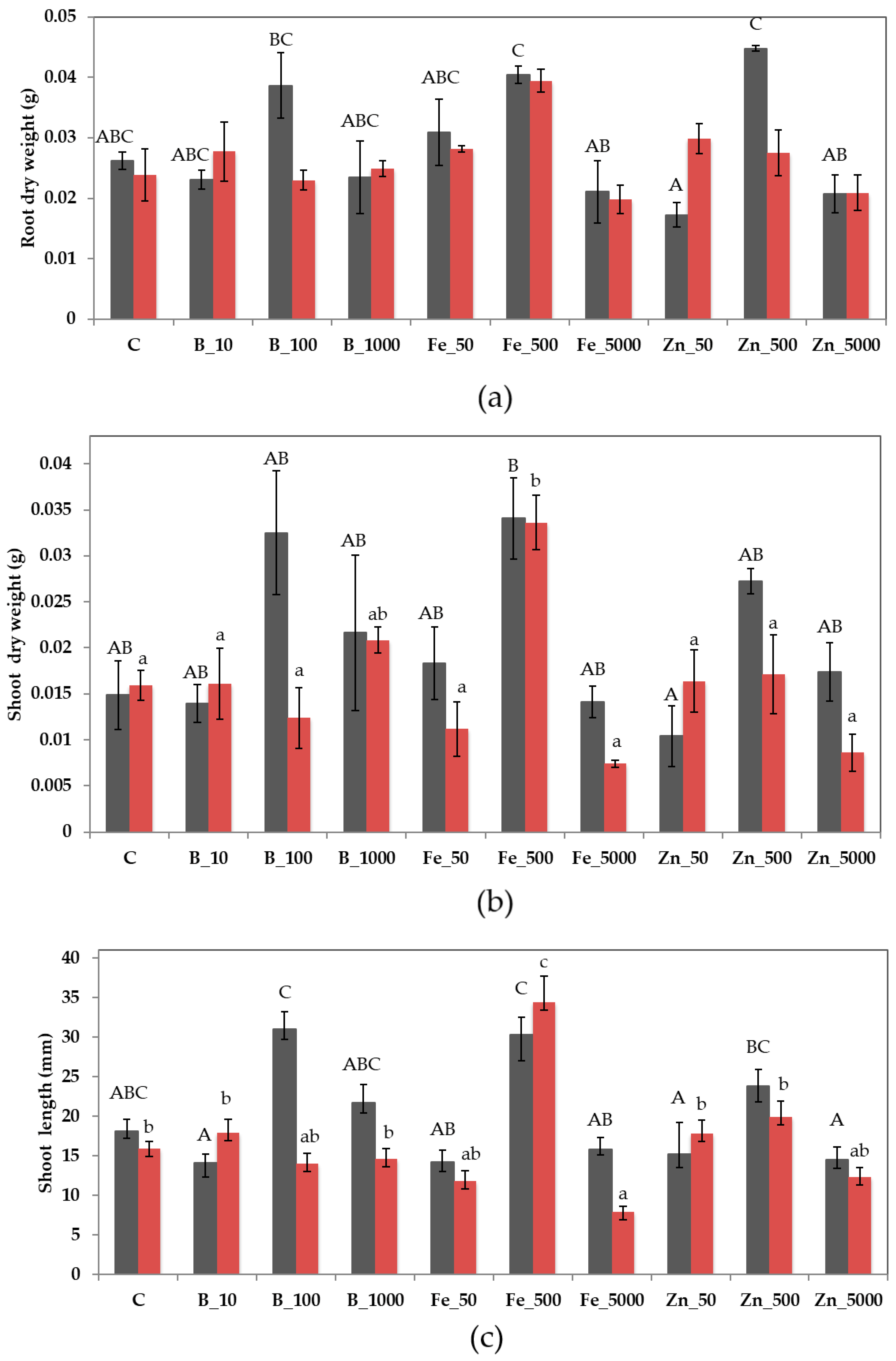
3.2.1. In Vitro Test
3.2.2. Seed Tray Test
3.2.3. Field Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Léridon, H. World population outlook: Explosion or implosion? Popul. Soc. 2020, 573, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, M.; Morley, T.; Rau, M.L.; Saghai, Y. A meta-analysis of projected global food demand and population at risk of hunger for the period 2010–2050. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.; Tignor, M.; Poloczanska, E.; Mintenbeck, K.; Alegría, A.; Craig, M.; Langsdorf, S.; Löschke, S.; Möller, V.; et al. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability Working Group II Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Farm to Fork Strategy. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/farm2fork_en (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Database. Available online: https://www.fao.org/statistics/en/ (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Hoque, M.N.; Islam, S. Comprehensive Review of the Quality and Processing Suitability of U.S. Hard Red Spring Wheat: Current Strategies, Challenges, and Future Potential Scope. Agriculture 2024, 14, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Mottaleb, K.A.; Sonder, K.; Donovan, J.; Braun, H.-J. Global trends in wheat production, consumption and trade. In Wheat Improvement: Food Security in a Changing Climate; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nikkhah, A. Barley grain for ruminants: A global treasure or tragedy. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.; Zannini, E.; Sahin, A.W.; Arendt, E.K. Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein. Foods 2021, 10, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Lafond, G.; May, W. Grain yield and water use: Relative performance of winter vs. spring cereals in east-central Saskatchewan. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2000, 80, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, A.; Sarwar, T.; Nawaz, A.; Ijaz, M.; Sattar, A.; Ahmad, S. Methods of Seed Priming. In Priming and Pretreatment of Seeds and Seedlings; Bahauddin Zakariya University: Layyah, Pakistan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolić, D.; Stanković, M.; Prokopijević, M.; Radotić, K. Effects of UV-A and UV-B Irradiation on Antioxidant Activity and Fluorescence Characteristics of Soybean (Glycine max L.) Seeds. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2022, 96, 2797–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Wang, R.; Ma, B.; Li, T.; Guan, C. UV-B-Priming Combined with the Soil Application of MWCNT Enhances Rice Growth Performance Under Salt Stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 3846–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbeles, D.; Milan, M.; Palmiano, D. Effects of Ultraviolet-C (UV-C) radiation on germination, seedling growth, and abiotic stress response in waxy corn (Zea mays L.). Acad. J. Biol. 2024, 46, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, K.; Dutta, P.; Sadhukhan, S. Seed priming with non-ionizing physical agents: Plant responses and underlying physiological mechanisms. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanello, R.; Puntel, R.; Garcia, W.; Dorneles, L. Mitigating salt stress by conditioning seeds with ultraviolet light (UV-C) in white oats (Avena sativa L.). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2024, 87, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Tawfic, G.A.; Shehata, S.A.; Ali, S.R.; Hamid, O.A.A.; Ahmed, A.E.R.A.; El-Mogy, M.M. The effect of seed priming with UV and gamma rays on the growth, production, and storage ability of cauliflower heads. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2023, 51, 13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacharava, N.; Chanishvili, S.; Badridze, G.; Chkhubianishvili, E.; Janukashvili, N. Effect of seed irradiation on the content of antioxidants in leaves of Kidney bean, Cabbage and Beet cultivars. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2009, 3, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Thabet, M.; Abou-Zeid, M.; Safhi, F.; Alwutayd, K.; Khalifa, W. Ultraviolet-C irradiation of wheat grains induces seedling resistance to leaf rust and powdery mildew disease. Ital. J. Agron. 2023, 18, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maarouf-Bouteau, H.; and Bailly, C. Oxidative signaling in seed germination and dormancy. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdemir Evrendilek, G. Ozone Processing of Corn Grains: Effect on Seed Vigor and Surface Disinfection. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2023, 46, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeeva, V.; Zorina, E.; Bezgina, J.; Kolosova, O. Influence of ozone on germination and germinating energy of winter wheat seeds. Eng. Rural. Dev. 2018, 23, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Violleau, F.; Hadjeba, K.; Albet, J.; Cazalis, R.; Surel, O. Increase of corn seeds germination by oxygen and ozone treatment. In Proceedings of the IOA Conference and Exhibition, Valencia, Spain, 29 October 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, P.; Bose, B. Effects of various concentrations of boron on germination, seedling growth and sugar mobilization in wheat using boric acid primed seeds. J. Crop Weed 2023, 19, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singhal, R.K.; Kumar, N.; Bose, B. Micro-nutrient Seed Priming: A Pragmatic Approach Towards Abiotic Stress Management. In New Frontiers in Stress Management for Durable Agriculture; Rakshit, A., Singh, H.B., Singh, A.K., Singh, U.S., Fraceto, L., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahmani, B.; Ghassemi, K.; Ghassemi-Golezani, K.; Valizadeh, M.; Asl, V. Seed priming and seedling establishment of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Food Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Singhal, R.K.; Bose, B.; Chauhan, J.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Rajendran, K.; et al. Seed Priming with Mg(NO3)2 and ZnSO4 Salts Triggers the Germination and Growth Attributes Synergistically in Wheat Varieties. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Mahmood, A.; Römheld, V.; Neumann, G. Nutrient seed priming improves seedling development of maize exposed to low root zone temperatures during early growth. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 49, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atar, B.; Uygur, V.; Sukuşu, E. Effects of Priming with Copper, Zinc and Phosphorus on Seed and Seedling Composition in Wheat and Barley. Turk. J. Agric. Nat. Sci. 2020, 7, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Farooq, M.; Hussain, M.; Wakeel, A. Zinc seed priming improves stand establishment, tissue zinc concentration and early seedling growth of chickpea. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2019, 29, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Farooq, M.; Nawaz, A.; Rehman, A. Optimizing boron seed priming treatments for improving the germination and early seedling growth of wheat. J. Agric. Soc. Sci. 2012, 8, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, S.; Pavia, I.; Carvalho, A.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Correia, C.; Lima-Brito, J. Seed priming with iron and zinc in bread wheat: Effects in germination, mitosis and grain yield. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Tahir, M.; Noor Us, S.; Shah, S.H.; Sarwar, G.; Manzoor, M. Seed priming with zinc ion on growth performance and nutrient acquisition of maize in aridisols. Pak. J. Bot. 2023, 55, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.-Y.; Zhu, H.-D.; Yin, K.-D.; Du, J.-D.; Zhang, Y.-X. Seed priming mitigates the effects of saline-alkali stress in soybean seedlings. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 77, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Atiqueur, R.; Aziz, T.; Habib, M. Boron Nutripriming Improves the Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzi, A.; Bostani, A.B. Morpho-physiological responses of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana bertoni) to various priming treatments under drought stress. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 4753–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.V.; Artés, H.F.D.A.; Artés, C.F. Evaluación de la calidad de granadas tratadas con UV-C y almacenadas en atmósfera controlada. In Proceedings of the V Congreso Iberoamericano de Tecnología Postcosecha y Agroexportaciones, Murcia, Spain, 29 May–1 June 2007; pp. 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Junta de Castilla y León. Clima de Castilla y León. Available online: https://conocecastillayleon.jcyl.es/web/es/geografia-poblacion/clima.html (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Martínez-Moreno, F.; Solís, I.; Igartua, E. Barley History and Breeding in Spain. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Cornejo, D.; Penas, A.; del Rio, S. Comparative Analysis of Precipitation Trends in Continental Spain over the Period 1961–2010. Int. J. Geobot. Res. 2013, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Wood, J.; Freemantle, N.; King, M.; Nazareth, I. Trap of trends to statistical significance: Likelihood of near significant P value becoming more significant with extra data. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2014, 348, g2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazim, S.K.; Ramadhan, M.N. Effects of physical and chemical seed priming techniques on seed germination and seedling growth of maize (Zea mays L.). Ann. Biol. 2023, 39, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Semenov, A.; Korotkova, I.; Sakhno, T.; Marenych, M.; Hanhur, V.; Liashenko, V.; Kaminsky, V. Effect of UV-C radiation on basic indices of growth process of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seeds in pre-sowing treatment. Acta Agric. Slov. 2020, 116, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughbakhch Pournavab, R.; Bacópulos Mejía, E.; Benavides Mendoza, A.; Salas Cruz, L.R.; Ngangyo Heya, M. Ultraviolet Radiation Effect on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Common Species from Northeastern Mexico. Agronomy 2019, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrateva, N.; Kasatkina, N.; Kuryleva, A.; Baturina, K.; Ilyasov, I.; Korepanov, R. Effect of treatment of seeds of grain crops by ultraviolet radiation before sowing. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 433, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, J.; kassem Issam, A.; Aghyad, S.; Abdulmunim, A.; Adnan, I.; Bassam, A.S. Priming of Long-Term Stored Cotton Seeds Using Combined UV-A, B and C Radiation and Its Influence on Germination. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 16, 82–94. [Google Scholar]
- Summerfelt, S. Ozonation and UV irradiation—An introduction and examples of current applications. Aquacult. Eng. 2003, 28, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kells, S.A.; Mason, L.J.; Maier, D.E.; Woloshuk, C.P. Efficacy and fumigation characteristics of ozone in stored maize. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2001, 37, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junta de Castilla y León. Inforiego: Información Meteorológica Para el Regante. Available online: http://www.inforiego.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Sciencia, M.; Creech, C.; Frels, K.; Easterly, A. Optimizing agronomic practices for hard winter wheat production in the Great Plains with respect to seeding rate, row spacing, and variety. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 2964–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, M.; Lu, W.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, F. Novel insights into the effect of drought stress on the development of root and caryopsis in barley. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fu, B.X. Inter-Relationships Between Test Weight, Thousand Kernel Weight, Kernel Size Distribution and Their Effects on Durum Wheat Milling, Semolina Composition and Pasta Processing Quality. Foods 2020, 9, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhaman, M.S.; Imran, S.; Rauf, F.; Khatun, M.; Baskin, C.C.; Murata, Y.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Seed Priming with Phytohormones: An Effective Approach for the Mitigation of Abiotic Stress. Plants 2021, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahbi Bellakanji, A.; Zribi, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Mougenot, B. Forecasting of Cereal Yields in a Semi-arid Area Using the Simple Algorithm for Yield Estimation (SAFY) Agro-Meteorological Model Combined with Optical SPOT/HRV Images. Sensors 2018, 18, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelamegam, R.; Sutha, T. UV-C Irradiation Effect on Seed Germination, Seedling Growth and Productivity of Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 430–443. [Google Scholar]
- Kharb, V.; Vivek, S.; Singh, D.S.; and Kalia, A. Influence of iron seed priming on seed germination, growth and iron content in rice seedlings. J. Plant Nutr. 2023, 46, 4054–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajouri, A.; Asgedom, H.; Becker, M. Seed priming enhances germination and seedling growth of barley under conditions of P and Zn deficiency. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2004, 167, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, R.; Basra, S. Seed Priming with Zinc Improves the Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Wheat. Seed Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaz, A.; Yoshida, C.; Gorni, P.; Freitas-Silva, L.; Araújo, T.; Ribeiro, C. Iron toxicity: Effects on the plants and detoxification strategies. Acta Bot. Bras. 2022, 36, e2021abb0131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, G. Effects of Drought Stress on Germination and Seedling Growth of Seed Primed with Boron in Spinach. J. Agric. Prod. 2024, 5, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumbal, S.; Ali, A.; Nasser Binjawhar, D.; Ullah, Z.; Eldin, S.M.; Iqbal, R.; Sher, H.; Ali, I. Comparative Effects of Hydropriming and Iron Priming on Germination and Seedling Morphophysiological Attributes of Stay-Green Wheat. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 23078–23088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nciizah, A.D.; Rapetsoa, M.C.; Wakindiki, I.I.C.; Zerizghy, M.G. Micronutrient seed priming improves maize (Zea mays) early seedling growth in a micronutrient deficient soil. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.Y.; Hawes, M.C.; Ottman, M.J. Drought-Tolerant Barley: I. Field Observations of Growth and Development. Agronomy 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurinak, J.J.; Thorne, D.W. Zinc Solubility Under Alkaline Conditions in a Zinc-Bentonite System. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1955, 19, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.; Davood, M.; Mohsen, V.; Behzad, S. Boric Acid Production from a Low-Grade Boron Ore with Kinetic Considerations. Mod. Chem. Appl. 2017, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, B.; Gervais, J.A.; Buhl, K.; Stone, D. Boric Acid Technical Fact Sheet; National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University Extension Services: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T. Seed priming with iron and zinc improves growth and yield of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Pure Appl. Biol. 2017, 6, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, G.; Nakhforoosh, A.; Kaul, H.-P. Management of crop water under drought: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 401–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briat, J.-F.; Dubos, C.; Gaymard, F. Iron nutrition, biomass production, and plant product quality. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Wheat | Barley | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | B (μg/g) | Fe (μg/g) | Zn (μg/g) | B (μg/g) | Fe (μg/g) | Zn (μg/g) |
| Control | 1.73 | 32.9 | 19.3 | 0.68 | 30.7 | 18.2 |
| B 1000 mg/L | 35.60 | 31.5 | 20.6 | 40.40 | 31.7 | 18.7 |
| B 100 mg/L | 6.70 | 37.0 | 22.1 | 4.86 | 26.6 | 16.9 |
| B 10 mg/L | 2.16 | 33.5 | 19.7 | 1.50 | 28.6 | 17.8 |
| Fe 5000 mg/L | 0.90 | 437.0 | 19.2 | 0.65 | 452.0 | 17.6 |
| Fe 500 mg/L | 0.76 | 89.3 | 19.4 | 0.67 | 105.0 | 18.6 |
| Fe 50 mg/L | 0.94 | 37.6 | 21.5 | 0.59 | 36.0 | 20.2 |
| Zn 5000 mg/L | 1.39 | 32.7 | >500 | 0.67 | 32.4 | >500 |
| Zn 500 mg/L | 1.09 | 29.2 | 94.7 | 0.75 | 27.8 | 95.8 |
| Zn 50 mg/L | 1.19 | 30.4 | 25.6 | 0.83 | 29.3 | 28.1 |
| Fe 500 mg/L+B 100 mg/L | 4.69 | 89.2 | 22.0 | 4.02 | 95.6 | 18.7 |
| Zn 500 mg/L+B 100 mg/L | 4.10 | 28.0 | 97.7 | 4.05 | 28.5 | 114 |
| Zn 500 mg/L+Fe 500 mg/L | 0.68 | 82.8 | 94.6 | 0.74 | 93.8 | 91.0 |
| Zn 500 mg/L+Fe 500 mg/L+B 100 mg/L | 4.11 | 93.4 | 106.0 | 3.75 | 84.4 | 85.2 |
| Wheat | Barley | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed Parameters | Degrees of Freedom | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value |
| Shoot length 7 DAS | 19 | 2.12 | 0.008 | 2.22 | 0.006 |
| Root length 7 DAS | 19 | 77.67 | <0.001 | 11.59 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | Shoot Length 7 DAS (mm) | Shoot Length 14 DAS (mm) | Root Length 14 DAS (mm) | Root Dry Weight 14 DAS (mg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Barley | Wheat | Barley | Wheat | Barley | Wheat | Barley | |
| Control | 56.90 ± 2 | 62.36 ± 5 | 98.03 ± 3 ab | 115.29 ± 5 | 140.78 ± 5 | 124.19 ±5 | 8.8 ± 0.9 | 10.5 ± 0.8 |
| UV | 61.45 ± 1 | 69.90 ± 3 | 100.70 ± 4 ab | 134.17 ± 4 | 131.45 ± 8 | 123.54 ± 4 | 10.1 ± 0.2 | 12.1 ± 0.8 |
| Oz | 52.60 ± 3 | 60.20 ± 5 | 92.46 ± 3 b | 116.36 ± 6 | 125.28 ± 5 | 119.13 ± 6 | 8.9 ± 1.1 | 11.7 ± 1.0 |
| UV+Oz | 58.69 ± 3 | 56.17 ± 5 | 104.96 ± 4 a | 118.00 ± 6 | 124.70 ± 7 | 119.58 ± 6 | 8.15 ± 4.4 | 11.9 ± 2.7 |
| SEM± | 1.31 | 2.27 | 1.68 | 2.79 | 3.12 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| F-value | 2.002 | 1.6 | 2.832 | 2.59 | 2.097 | 0.25 | 1.05 | 0.27 |
| p-value | 0.128 | 0.194 | 0.049 | 0.057 | 0.115 | 0.860 | 0.417 | 0.846 |
| Treatment | Number of Tillers (1 m2) | Plant Height (cm) | Fresh Aerial Biomass per m2 (g) | Dry Aerial Biomass per m2 (g) | Yield (Kg/ha) | TGW (g) | Bulk Density (Kg/hl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 578.7 ± 94 | 50.7 ± 3.8 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.48 ± 0.02 | 1930.5 ± 294 | 41.86 ± 3.0 | 71.23 ± 3.9 |
| UV | 581.3 ± 88 | 46.7 ± 4.2 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 0.57 ± 0.07 | 1510.6 ± 180 | 49.46 ± 3.1 | 74.36 ± 1.0 |
| Oz | 509.3 ± 30 | 46.0 ± 3.5 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 0.52 ± 0.09 | 1795.0 ± 200 | 45.24 ± 0.2 | 70.28 ± 4.3 |
| UV+Oz | 557.3 ± 150 | 44.7 ± 2.1 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 1773.4 ± 238 | 47.79 ± 1.2 | 62.90 ± 5.5 |
| SEM± | 26.1 | 1.08 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 294.5 | 1.28 | 2.14 |
| Eta squared (η2) | 0.11 | 0.385 | 0.177 | 0.346 | 0.176 | 0.449 | 0.357 |
| F-value | 0.33 | 1.67 | 0.57 | 1.41 | 0.57 | 2.18 | 1.48 |
| p-value | 0.80 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.31 | 0.65 | 0.10 | 0.29 |
| Treatment | Number of Tillers (1 m2) | Plant Height (cm) | Fresh Aerial Biomass per m2 (g) | Dry Aerial Biomass per m2 (g) | Yield (Kg/ha) | TGW (g) | Test Weight (Kg/hl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 573.3 ± 78 | 50.7 ± 3.5 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 0.45 ± 0.01 ab | 1483.9 ± 71 | 53.75 ± 0.6 | 62.09 ± 2.9 |
| UV | 528.0 ± 48 | 55.0 ± 3.5 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 0.31 ± 0.04 a | 1437.9 ± 85 | 53.08 ± 1.5 | 61.49 ± 3.7 |
| Oz | 738.7 ± 76 | 54.3 ± 5.2 | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 0.52 ± 0.08 b | 1449.3 ± 211 | 56.85 ± 2.9 | 65.21 ± 2.3 |
| UV+Oz | 616.0 ± 28 | 53. 7 ± 2.6 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.34 ± 0.04 a | 1466.4 ± 196 | 50.91 ± 2.7 | 64.39 ± 3.11 |
| SEM± | 35.4 | 1.70 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 65.9 | 1.12 | 1.39 |
| Eta squared (η2) | 0.447 | 0.086 | 0.505 | 0.594 | 0.006 | 0.329 | 0.113 |
| F-value | 2.15 | 0.25 | 2.72 | 3.91 | 0.02 | 1.31 | 0.34 |
| p-value | 0.17 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 0.80 |
| Wheat | Barley | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed Parameters | Degrees of Freedom | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value |
| Root dry weight | 9 | 6.30 | <0.001 | 4.63 | 0.022 |
| Shoot dry weight | 9 | 3.49 | 0.010 | 6.78 | <0.001 |
| Shoot length | 9 | 11.76 | <0.001 | 9.96 | <0.001 |
| Crop | Water Conditions | Degrees of Freedom | χ2-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual nutrients | wheat | Normal | 3 | 0.26 | 0.97 |
| Deficit | 3 | 3.92 | 0.22 | ||
| barley | Normal | 3 | 1.13 | 0.77 | |
| Deficit | 3 | 3.3 | 0.35 | ||
| Combined nutrients | wheat | Normal | 4 | 1.67 | 0.79 |
| Deficit | 4 | 1.69 | 0.79 | ||
| barley | Normal | 4 | 2.96 | 0.56 | |
| Deficit | 4 | 3.87 | 0.42 |
| Treatment | Water | Shoot Length 7 DAS | Shoot Length 14 DAS | Shoot Dry Weight 14 DAS | Root Dry Weight 14 DAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | 4.20 ± 0.24 b | 7.60 ± 0.5 | 7.86 ± 0.6 | 7.19 ± 0.8 |
| D | 2.37 ± 0.6 a | 7.11 ± 0.6 | 7.68 ± 0.8 | 7.56 ± 1.3 | |
| B | N | 3.27 ± 0.4 ab | 6.63 ± 0.6 | 7.2 ± 0.8 | 5.98 ± 0.9 |
| D | 4.02 ± 0.3 b | 7.0 ± 0.3 | 7.87 ± 0.5 | 7.61 ± 0.7 | |
| Fe | N | 3.5 ± 0.4 b | 7.38 ± 0.4 | 7.43 ± 0.6 | 8.39 ± 0.6 |
| D | 3.65 ± 0.4 b | 7.28 ± 0.6 | 6.91 ± 0.8 | 8.40 ± 1.0 | |
| Zn | N | 3.78 ± 0.3 b | 6.9 ± 0.6 | 7.35 ± 0.7 | 9.93 ± 0.6 |
| D | 3.61 ± 0.4 b | 8.04 ± 0.4 | 7.69 ± 0.7 | 8.18 ± 0.8 | |
| Water (W) | F-value | 1.03 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| p-value | 0.31 | 0.54 | 0.87 | 0.91 | |
| Treatment (T) | F-value | 0.44 | 0.61 | 0.24 | 2.85 |
| p-value | 0.72 | 0.61 | 0.87 | 0.04 | |
| W × T | F-value | 4.00 | 0.88 | 0.29 | 1.37 |
| p-value | 0.009 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.26 |
| Treatment | Water | Shoot Length 7 DAS | Shoot Length 14 DAS | Shoot Dry Weight 14 DAS | Root Dry Weight 14 DAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | 4.02 ± 0.3 | 8.69 ± 0.3 | 7.35 ± 0.7 | 7.79 ± 0.7 a |
| D | 4.54 ± 0.3 | 10.02 ± 0.7 | 8.12 ± 0.6 | 8.99 ± 0.7ab | |
| B | N | 5.29 ± 0.2 | 8.65 ± 0.3 | 7.43 ± 0.7 | 11.25 ± 0.7 cd |
| D | 4.43 ± 0.4 | 9.67 ± 0.4 | 8.26 ± 0.6 | 9.72 ± 0.6 abc | |
| Fe | N | 5.24 ± 0.3 | 10.53 ± 0.4 | 9.45 ± 0.6 | 12.04 ± 0.5 d |
| D | 4.88 ± 0.4 | 10.01 ± 0.7 | 8.24 ± 1.1 | 10.48 ± 1.0 bcd | |
| Zn | N | 4.85 ± 0.3 | 9.01 ± 0.5 | 8.46 ± 0.7 | 7.69 ± 0.7 a |
| D | 4.72 ± 0.4 | 9.58 ± 0.4 | 12.12 ± 3.7 | 9.49 ± 0.8 abc | |
| Water (W) | F-value | 0.79 | 2.88 | 0.55 | 0.01 |
| p-value | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0.46 | 0.96 | |
| Treatment (T) | F-value | 2.02 | 2.68 | 1.28 | 7.29 |
| p-value | 0.11 | 0.049 | 0.28 | <0.001 | |
| W × T | F-value | 1.49 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 2.91 |
| p-value | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.037 |
| Treatment | Water | Shoot Length 7 DAS | Shoot Length 14 DAS | Shoot Dry Weight 14 DAS | Root Dry Weight 14 DAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | 3.37 ± 0.5 | 10.02 ± 0.6 | 14.02 ± 3.1 | 8.94 ± 1.9 |
| D | 2.02 ± 0.3 | 9.14 ± 0.5 | 7.34 ± 0.7 | 17.42 ± 2.7 | |
| Fe+B | N | 2.61 ± 0.4 | 9.15 ± 0.4 | 9.55 ± 0.8 | 10.55 ± 1.6 |
| D | 2.64 ± 0.3 | 8.25 ± 0.6 | 8.72 ± 0.6 | 17.06 ± 0.9 | |
| Zn+B | N | 2.34 ± 0.4 | 8.65 ± 0.5 | 12.30 ± 3.9 | 10.42 ± 1.5 |
| D | 1.94 ±0.3 | 7.9 ± 0.6 | 7.0 ± 0.6 | 17.75 ± 0.9 | |
| Zn+Fe | N | 2.37 ± 0.4 | 8.56 ± 0.7 | 8.35 ± 0.9 | 10.18 ±1.2 |
| D | 2.65 ± 0.3 | 8.55 ± 0.5 | 11.97 ± 2 | 15.57 ± 0.8 | |
| Zn+Fe+B | N | 2.54 ± 0.4 | 8.65 ± 0.8 | 11.23 ± 0.9 | 12.74 ± 1.4 |
| D | 2.25 ± 0.2 | 8.84 ± 0.4 | 9.7 ± 0.5 | 16.67 ± 0.9 | |
| Water (W) | F-value | 2.02 | 1.74 | 2.19 | 48.59 |
| p-value | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.14 | <0.001 | |
| Treatment (T) | F-value | 0.66 | 1.53 | 0.15 | 0.52 |
| p-value | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.96 | 0.72 | |
| W × T | F-value | 1.3 | 0.44 | 1.57 | 0.76 |
| p-value | 0.27 | 0.78 | 0.19 | 0.55 |
| Treatment | Water | Shoot Length 7 DAS | Shoot Length 14 DAS | Shoot Dry Weight 14 DAS | Root Dry Weight 14 DAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | 3.88 ± 0.4 | 12.14 ± 0.6 | 12.62 ± 0.9 | 19.1 ± 1.4 |
| D | 2.72 ± 0.4 | 9.76 ± 0.6 | 8.59 ± 0.8 | 17.25 ± 1.3 | |
| Fe+B | N | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 11.34 ± 0.4 | 10.93 ± 0.5 | 18.52 ± 1.2 |
| D | 2.39 ± 0.5 | 9.53 ± 0.7 | 7.92 ± 0.8 | 10.99 ± 1.3 | |
| Zn+B | N | 2.81 ± 0.4 | 10.01 ± 0.5 | 13.66 ± 0.7 | 20.69 ± 1.0 |
| D | 2.81 ± 0.5 | 9.96 ± 0.7 | 10.6 ± 0.6 | 14.78 ± 0.8 | |
| Zn+Fe | N | 3.15 ± 0.4 | 10.91 ± 0.5 | 11.46 ± 0.8 | 17.67 ± 1.1 |
| D | 2.52 ± 0.5 | 9.39 ± 0.8 | 9.27 ± 0.8 | 14.28 ± 1.1 | |
| Zn+Fe+B | N | 4.23 ± 0.3 | 12.11 ± 0.3 | 10.41 ± 0.6 | 22.81 ± 0.8 |
| D | 3.25 ± 0.3 | 10.54 ± 0.3 | 8.71 ± 0.4 | 13.48 ± 0.7 | |
| Water (W) | F-value | 6.49 | 14.95 | 38.01 | 18.90 |
| p-value | 0.01 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Treatment (T) | F-value | 2.21 | 1.74 | 4.42 | 1.13 |
| p-value | 0.07 | 0.15 | <0.001 | 0.34 | |
| W × T | F-value | 0.55 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 1.14 |
| p-value | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.34 |
| Treatment | Number of Tillers (1 m2) | Plant Height (cm) | Fresh Aerial Biomass (Kg) | Dry Aerial Biomass (Kg) | Yield (Kg/ha) | TGW (g) | SBD (Kg/hl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 578.7 ± 67 | 50.7 ± 2 | 2.226 ± 0.1 | 0.480 ± 0.1 | 1930.5 ± 294 | 41.86 ± 3.0 | 71.23 ± 3.9 |
| Hydropriming | 570.7 ± 143 | 49.0 ± 1 | 2.243 ± 0.3 | 0.497 ± 0.1 | 1728.7 ± 170 | 43.69 ± 0.8 | 73.72 ± 2.8 |
| B | 589.3 ± 88 | 51.0 ± 4 | 2.478 ± 0.6 | 0.533 ± 0.1 | 1734.4 ± 211 | 48.51 ± 2.0 | 80.17 ± 0.4 |
| Fe | 650.7 ± 8 | 50.0 ± 2 | 3.057 ± 0.2 | 0.720 ± 0.1 | 1832.3 ± 224 | 41.88 ± 1.0 | 73.62 ± 3.7 |
| Zn | 490.7 ± 32 | 50.0 ± 1 | 2.374 ± 0.2 | 0.557 ± 0.1 | 1670.5 ± 195 | 42.80 ± 1.0 | 65.49 ± 5.5 |
| Fe+B | 605.3 ± 98 | 48.7 ± 2 | 2.298 ± 0.3 | 0.507 ± 0.1 | 1820.5 ± 100 | 48.94 ± 1.3 | 76.63 ± 0.3 |
| Zn+B | 464.0 ± 66 | 44.7 ± 3 | 2.098 ± 0.4 | 0.480 ± 0.1 | 1617.0 ± 83 | 44.80 ± 2.5 | 72.11 ± 1.2 |
| Zn+Fe | 560.0 ± 85 | 49.0 ± 2 | 2.651 ± 0.2 | 0.613 ± 0.1 | 1547.6 ± 119 | 43.64 ± 1.4 | 76.03 ± 2.3 |
| Zn+Fe+B | 514.7 ± 29 | 47.3 ± 3 | 1.807 ± 0.2 | 0.393 ± 0.1 | 1417.4 ± 96 | 43.47 ± 1.6 | 65.64 ± 7.0 |
| SEM± | 63.30 | 2.32 | 0.32 | 0.07 | 239.1 | 1.77 | 3.78 |
| Eta squared (η2) | 0.277 | 0.239 | 0.350 | 0.417 | 0.161 | 0.492 | 0.423 |
| F-value | 0.86 | 0.71 | 1.21 | 1.61 | 0.43 | 2.18 | 1.65 |
| p-value | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.89 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
| Treatment | Number of Tillers (1 m2) | Plant Height (cm) | Fresh Aerial Biomass (Kg) | Dry Aerial Biomass (Kg) | Yield (Kg/ha) | TGW (g) | SBD (Kg/hl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 573.3 ± 98 | 50.7 ± 3.5 | 2.337 ± 0.1 | 0.450 ± 0.01 | 1483.97 ± 71 | 53.75 ± 0.6 | 62.1 ± 2.9 |
| Hydropriming | 714.7 ± 35 | 60.3 ± 1.8 | 3.260 ± 0.3 | 0.523 ± 0.04 | 1833.77 ± 96 | 52.41 ± 0.3 | 62.2 ± 3.2 |
| B | 680.0 ± 74 | 56.0 ± 2.5 | 2.337 ± 0.2 | 0.407 ± 0.05 | 1785.00 ± 99 | 53.27 ± 1.8 | 63.0 ± 4.4 |
| Fe | 696.0 ± 75 | 52.0 ± 4.2 | 2.440 ± 0.3 | 0.430 ± 0.05 | 1750.80 ± 257 | 49.79 ± 4.5 | 67.1 ± 7.0 |
| Zn | 701.3 ± 64 | 55.3 ± 7.7 | 2.567 ± 0.6 | 0.480 ± 0.12 | 1360.17 ± 290 | 53.85 ± 1.3 | 63.9 ± 4.4 |
| Fe+B | 698.7 ± 16 | 59.0 ± 2.3 | 3.098 ± 0.5 | 0.480 ± 0.10 | 1612.10 ± 127 | 54.10 ± 0.8 | 60.5 ± 4.0 |
| Zn+B | 829.3 ± 43 | 59.7 ± 0.9 | 3.437 ± 0.6 | 0.567 ± 0.10 | 1460.80 ± 24 | 53.22 ± 2.0 | 60.2 ± 6.4 |
| Zn+Fe | 616.0 ± 74 | 57.7 ± 5.4 | 2.218 ± 0.4 | 0.347 ± 0.05 | 2057.60 ± 363 | 49.94 ± 2.3 | 67.1 ± 5.8 |
| Zn+Fe+B | 837.3 ± 19 | 56.7 ± 6.0 | 3.142 ± 0.6 | 0.503 ± 0.07 | 1321.77 ± 129 | 57.45 ± 0.9 | 73.2 ± 5.7 |
| SEM± | 27.99 | 4.36 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 211.3 | 2.03 | 5.04 |
| Eta squared (η2) | 0.322 | 0.206 | 0.326 | 0.259 | 0.374 | 0.363 | 0.231 |
| F-value | 1.07 | 0.59 | 1.09 | 0.79 | 1.35 | 1.28 | 0.68 |
| p-value | 0.43 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iglesias-Ganado, Á.; Martín-García, J.; Poveda, J.; López-Sainz, M.F.; Sánchez-Gómez, T.; Santamaría, O. Improvement of Wheat and Barley Cultivation Through Seed Priming with UV, Ozone, and Nutripriming (Fe, Zn, and B). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9988. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189988
Iglesias-Ganado Á, Martín-García J, Poveda J, López-Sainz MF, Sánchez-Gómez T, Santamaría O. Improvement of Wheat and Barley Cultivation Through Seed Priming with UV, Ozone, and Nutripriming (Fe, Zn, and B). Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9988. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189988
Chicago/Turabian StyleIglesias-Ganado, Álvaro, Jorge Martín-García, Jorge Poveda, María Felicidad López-Sainz, Tamara Sánchez-Gómez, and Oscar Santamaría. 2025. "Improvement of Wheat and Barley Cultivation Through Seed Priming with UV, Ozone, and Nutripriming (Fe, Zn, and B)" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9988. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189988
APA StyleIglesias-Ganado, Á., Martín-García, J., Poveda, J., López-Sainz, M. F., Sánchez-Gómez, T., & Santamaría, O. (2025). Improvement of Wheat and Barley Cultivation Through Seed Priming with UV, Ozone, and Nutripriming (Fe, Zn, and B). Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9988. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189988






