Assessment of the Accumulation of Certain Metals in Human Globus pallidus Using Particle-Induced X-Ray Emission (PIXE), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Microanalysis (EDX)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Particle-Induced X-Ray Emission (PIXE)
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Microanalysis (EDX)
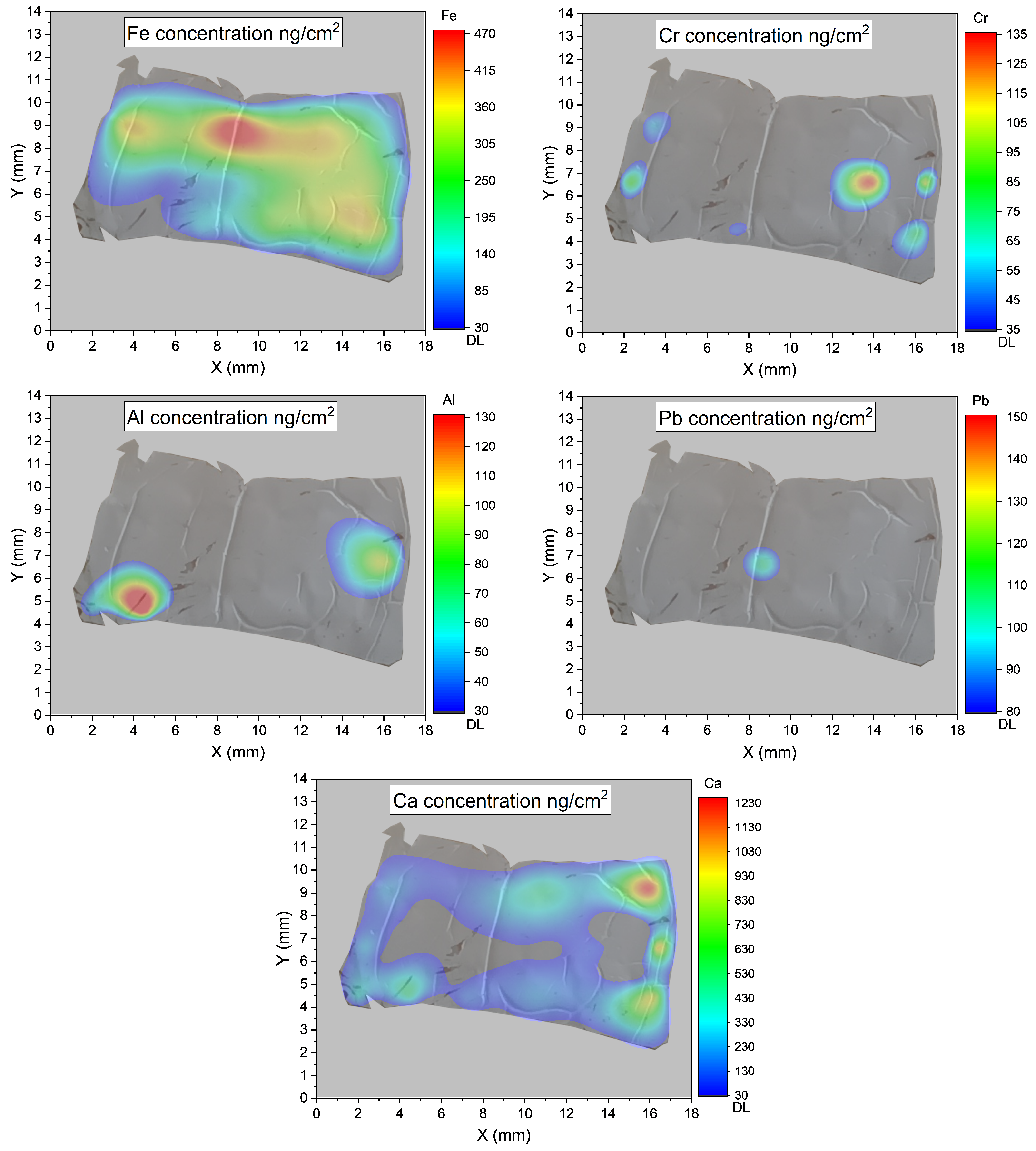
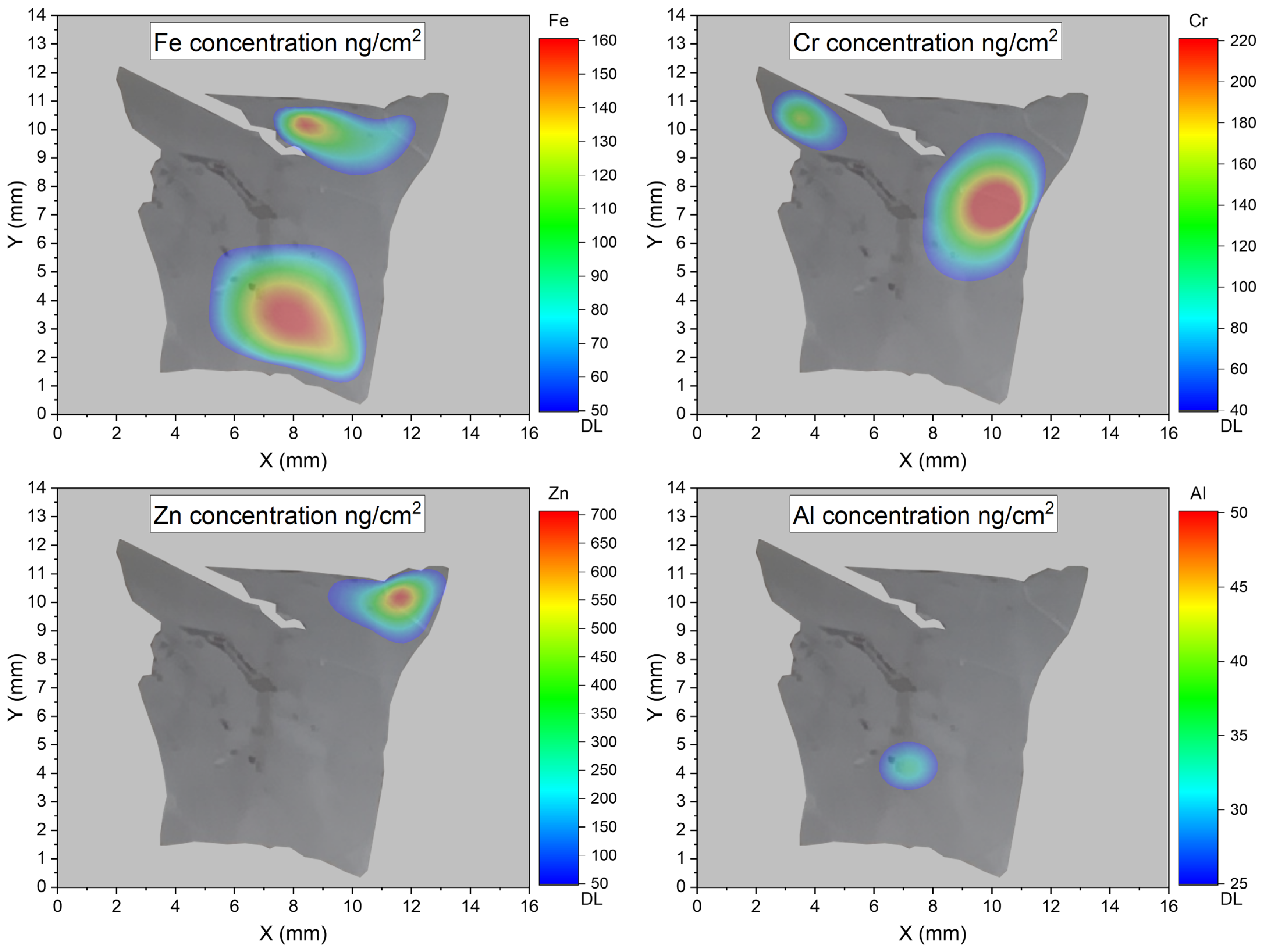
3. Results
PIXE Method
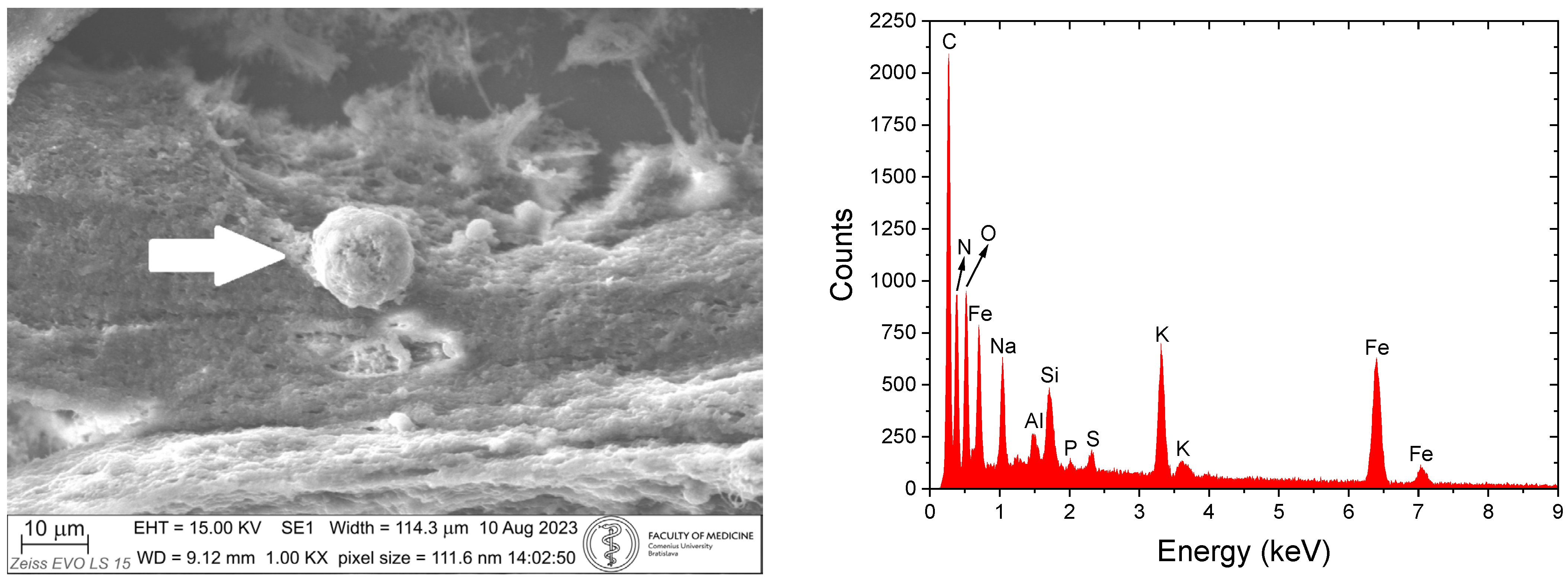
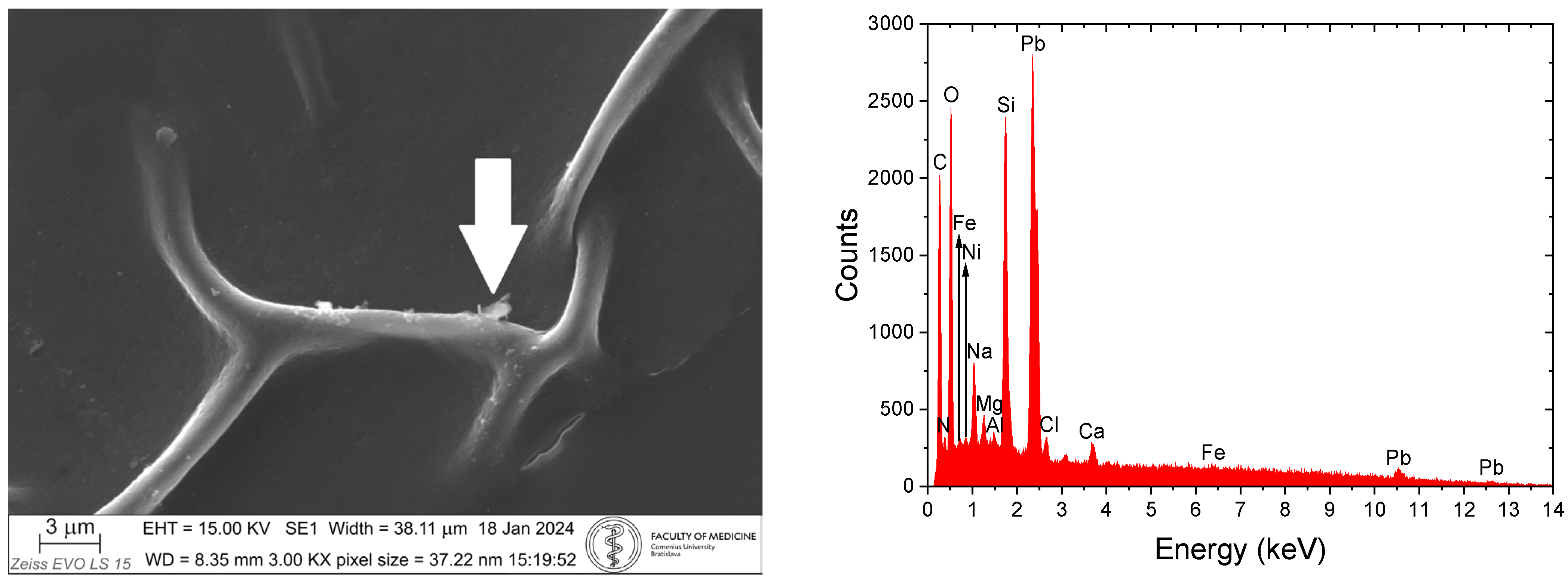
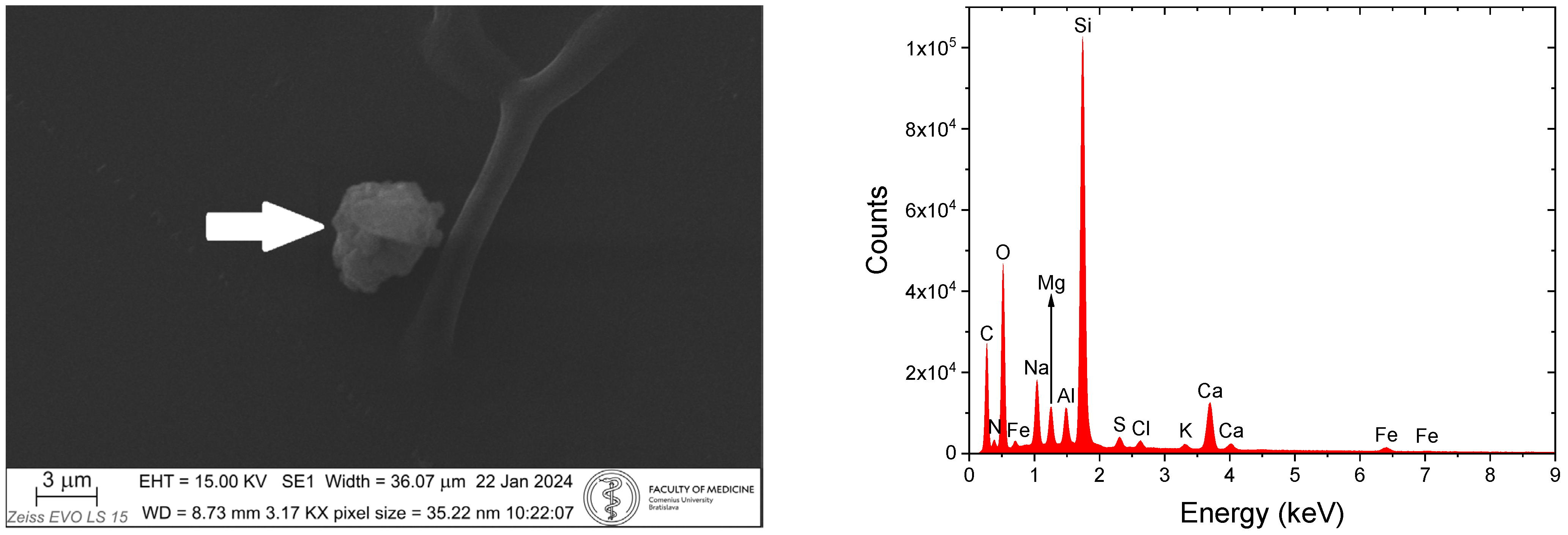
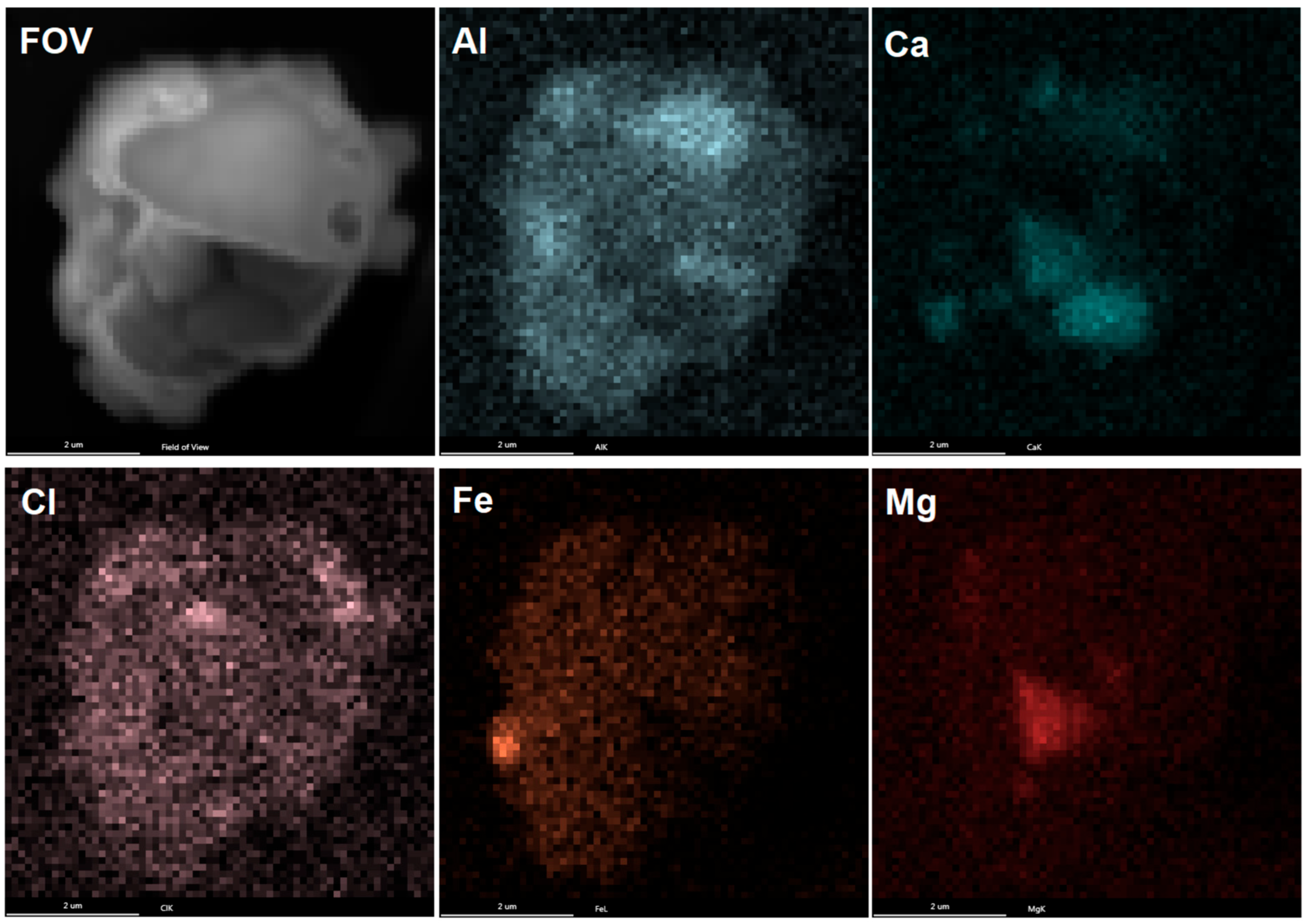
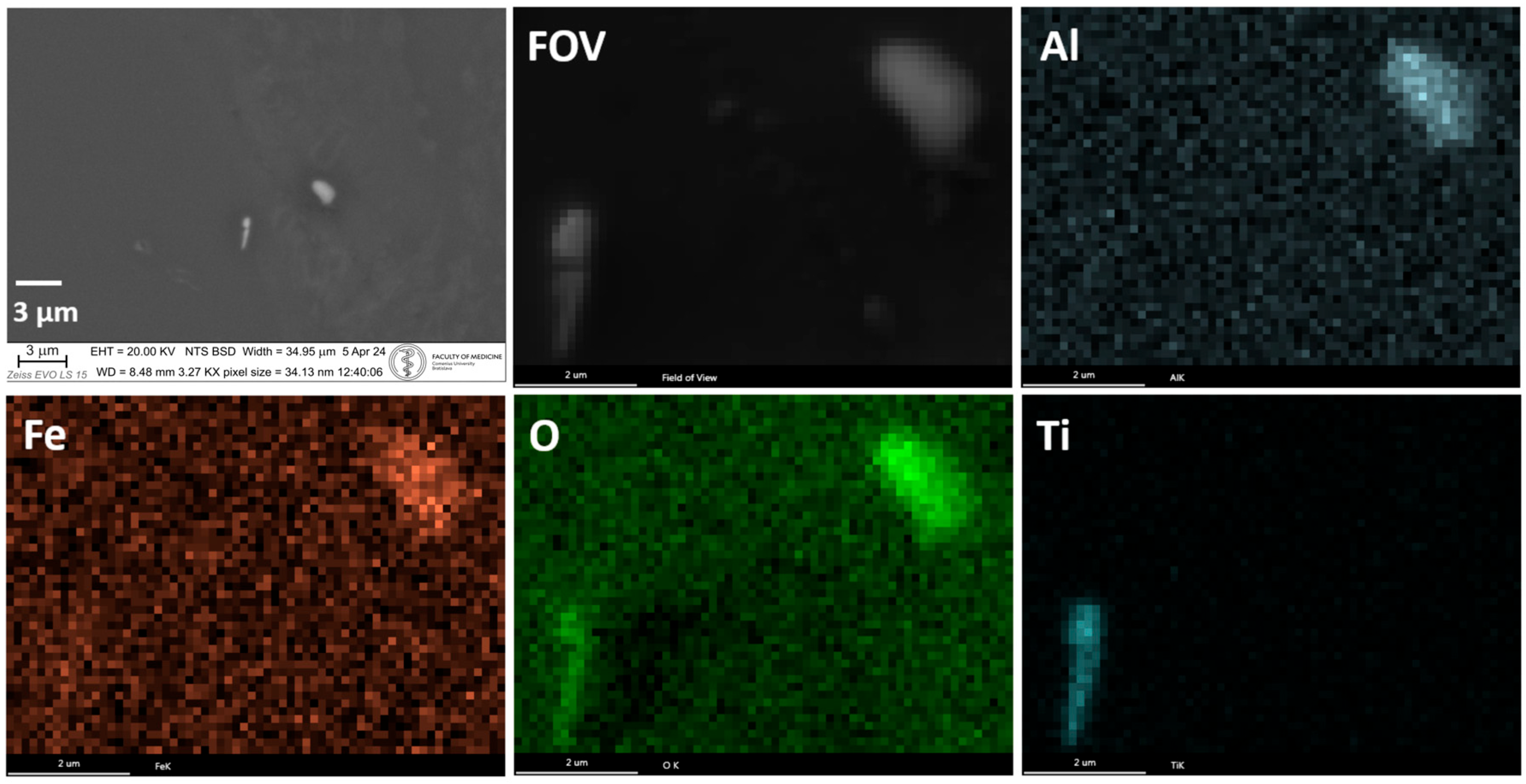
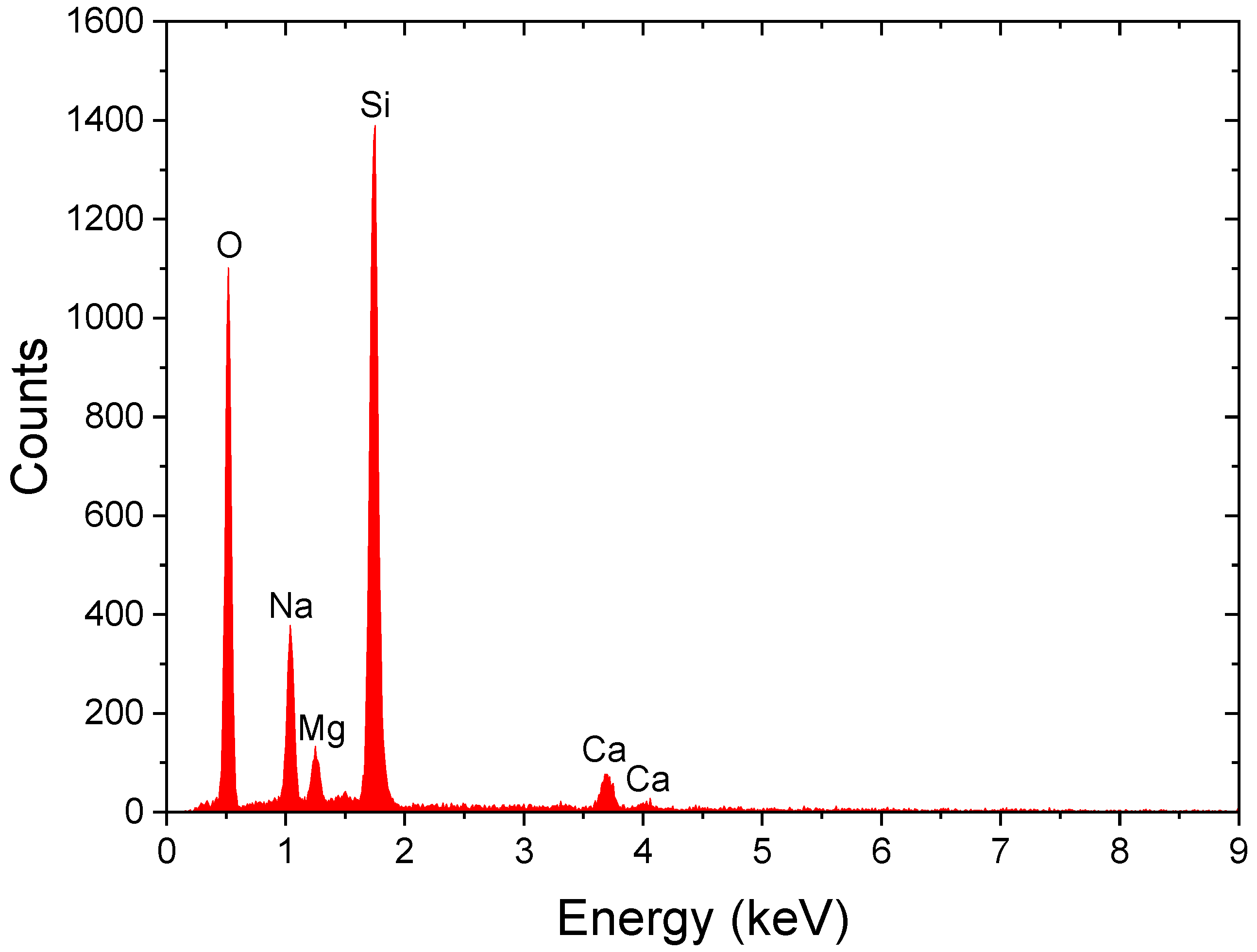
4. SEM-EDX Method
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pánik, J.; Kopáni, M.; Zeman, J.; Ješkovský, M.; Kaizer, J.; Povinec, P.P. Determination of Metal Elements Concentrations in Human Brain Tissues Using PIXE and EDX Methods. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 3, 2313–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopáni, M.; Pánik, J.; Filová, B.; Bujdoš, M.; Mišek, J.; KOHAN, M.; Jakuš, J.; Povinec, P.P. PIXE Analysis of Iron in Rabbit Cerebellum after Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. Bratisl. Med. J. 2022, 123, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Guelph. GupixWIN. Available online: https://www.physics.uoguelph.ca/about-gupix-and-gupixwin (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Zeman, J.; Ješkovský, M.; Kaiser, R.; Kaizer, J.; Povinec, P.P.; Staníček, J. PIXE Beam Line at the CENTA Facility of the Comenius University in Bratislava: First Results. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 311, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasniak, J.; Ješkovský, M.; Zeman, J.; Kontuľ, I.; Kaizer, J.; Sučák, K.; Povinec, P.P. Improvements in the PIXE System of the CENTA Laboratory with Application in the Contamination Studies of Tree Rings in Slovakia. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2024, 548, 165254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povinec, P.P.; Masarik, J.; Ješkovský, M.; Kaizer, J.; Šivo, A.; Breier, R.; Pánik, J.; Staníček, J.; Richtáriková, M.; Zahoran, M.; et al. Development of the Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Technology at the Comenius University in Bratislava. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2015, 361, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, K.G. Accelerator-Based Ion Beam Analysis—An Overview and Future Prospects. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuisma-Kursula, P. Accuracy, Precision and Detection Limits of SEM-WDS, SEM-EDS and PIXE in the Multi-Elemental Analysis of Medieval Glass. X-Ray Spectrom. 2000, 29, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.R.; Greenamyre, J.T. The Role of Environmental Exposures in Neurodegeneration and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 124, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottenfeld, D.; Beebe-Dimmer, J.L.; Buffler, P.A.; Omenn, G.S. Current Perspective on the Global and United States Cancer Burden Attributable to Lifestyle and Environmental Risk Factors. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 2013, 34, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Ho, Y.-S.; Chang, R.C.-C. The Pathogenic Effects of Particulate Matter on Neurodegeneration: A Review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshkin, M.P.; Petrovski, D.V.; Akulov, A.E.; Romashchenko, A.V.; Gerlinskaya, L.A.; Ganimedov, V.L.; Muchnaya, M.I.; Sadovsky, A.S.; Koptyug, I.V.; Savelov, A.A.; et al. Nasal Aerodynamics Protects Brain and Lung from Inhaled Dust in Subterranean Diggers, Ellobius talpinus. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20140919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-Y.; Cheng, T.-J.; Yang, D.-M.; Wang, C.-T.; Chiung, Y.-M.; Liu, P.-S. Demonstration of an Olfactory Bulb–Brain Translocation Pathway for ZnO Nanoparticles in Rodent Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 48, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, L.E.; Patchin, E.S.; Chiu, P.-L.; Brandenberger, C.; Smiley-Jewell, S.; Pinkerton, K.E. Nose-to-Brain Transport of Aerosolised Quantum Dots Following Acute Exposure. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formica, M.L.; Real, D.A.; Picchio, M.L.; Catlin, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; Paredes, A.J. On a Highway to the Brain: A Review on Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery Using Nanoparticles. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lin, G.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chai, E. A Review of Respirable Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5)-Induced Brain Damage. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 967174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Minko, T. Nanotherapeutics for Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery: An Approach to Bypass the Blood Brain Barrier. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, D.; Ali, A.; Md, S.; Baboota, S.; Sahni, J.K.; Ali, J. Insights into Direct Nose to Brain Delivery: Current Status and Future Perspective. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiankhaw, K.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. PM2.5 Exposure in Association with AD-Related Neuropathology and Cognitive Outcomes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, J.P.; Goldstein, G.W. Mechanisms of Lead Neurotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 41, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, J.; Kim, K.; Chakraborti, T.; Goldstein, G. Molecular Mechanisms of Lead Neurotoxicity. Neurochem. Res. 1999, 24, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbergeld, E.K. Mechanisms of Lead Neurotoxicity, or Looking beyond the Lamppost. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 3201–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, T.W.; Morel, F.M.M. A Biological Function for Cadmium in Marine Diatoms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4627–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffo, M.; Caruso, G.; La Fata, G.; Barresi, V.; Visalli, M.; Venza, M.; Venza, I. Heavy Metals and Epigenetic Alterations in Brain Tumors. Curr. Genom. 2015, 15, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Nanni, A.; Curcio, A.; Lombardi, G.; Somma, T.; Minutoli, L.; Caffo, M. Impact of Heavy Metals on Glioma Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Coppola, L.; Savarese, B.; Avilia, G.; Giarra, A.; Pagano, G.; Marano, A.; Trifuoggi, M.; Bifulco, M.; et al. Impacts of Environmental Pollution on Brain Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanjuk, A.; Lyndin, M.; Moskalenko, R.; Gortinskaya, O.; Lyndina, Y. The Role of Heavy Metal Salts in Pathological Biomineralization of Breast Cancer Tissue. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulson, B.G.; Szczepski, K.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Jaremko, L.; Emwas, A.-H.; Jaremko, M. Aggregation of Biologically Important Peptides and Proteins: Inhibition or Acceleration Depending on Protein and Metal Ion Concentrations. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckett, S. Abnormal Deposits of Chromium in the Pathological Human Brain. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1986, 49, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, L. Cations in Malignant and Benign Brain Tumors. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. Toxicol. 1996, 31, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plays, M.; Müller, S.; Rodriguez, R. Chemistry and Biology of Ferritin. Metallomics 2021, 13, mfab021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, P.; Elia, L.; Poli, M. Ferritin, Cellular Iron Storage and Regulation. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.A.; Connor, J.R. Nuclear Ferritin: A New Role for Ferritin in Cell Biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—General. Subj. 2010, 1800, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Hong, D.K.; Choi, B.Y.; Suh, S.W. Zinc in the Brain: Friend or Foe? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, M.; Cavazza, C. Structure, Function, and Biosynthesis of Nickel-dependent Enzymes. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1071–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambelli, B.; Ciurli, S. Nickel and Human Health. Met Ions Life Sci. 2013, 13, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopáni, M.; Kopániová, A.; Čaplovičová, M.; Marusčaková, L.; Šišovský, V.; Jakubovský, J. Iron and Its Relation to Glycoconjugates in Human Globus Pallidus. Bratisl. Med. J. 2014, 115, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S. An Overview of Biomineralization Processes and the Problem of the Vital Effect. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2003, 54, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasae, K.D.; Abolaji, A.O.; Faloye, T.R.; Odunsi, A.Y.; Oyetayo, B.O.; Enya, J.I.; Rotimi, J.A.; Akinyemi, R.O.; Whitworth, A.J.; Aschner, M. Metallobiology and Therapeutic Chelation of Biometals (Copper, Zinc and Iron) in Alzheimer’s Disease: Limitations, and Current and Future Perspectives. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 67, 126779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylinski, D.A. Biologically Controlled Mineralization in Prokaryotes. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2003, 54, 217–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazala, R.; Zoppellaro, G.; Kletetschka, G. Iron Level Changes in the Brain with Neurodegenerative Disease. Brain Multiphys 2023, 4, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschvink, J.L.; Kobayashi-Kirschvink, A.; Woodford, B.J. Magnetite Biomineralization in the Human Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7683–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Fan, K.; Yan, X. Iron Oxide Nanozyme: A Multifunctional Enzyme Mimetic for Biomedical Applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3207–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Hussain, S.; Jaffari, G.H.; Hanif, S.; Qureshi, M.N.; Zia, M. Fabrication of Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles under Different Spectral Lights Transforms Physio Chemical, Biological, and Nanozymatic Properties. Nano Trends 2023, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Bhatti, S.H.; Ali, Z.; Jaffari, G.H.; Khan, N.A.; Rizvi, Z.F.; Zia, M. Photoinduced Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Transformation of Morphological and Biological Response on Light Irradiance. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11783–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Zhu, C.; Gong, L.; Zhu, N.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qin, M.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y. Engineering Core–Shell Chromium Nanozymes with Inflammation-Suppressing, ROS-Scavenging and Antibacterial Properties for Pulpitis Treatment. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 13971–13986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | Gender | Age (Years) | Cause of Death | Post-Mortem Interval (Hours) | Occupation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Male | 53 | Cirrhosis | 7 | Teacher |
| S2 | Female | 69 | Heart failure | 10 | Lawyer |
| S3 | Female | 83 | Heart failure | 8 | Saleswoman |
| S4 | Male | 19 | Nephritis | 6 | Student |
| S5 | Male | 67 | Heart failure | 9 | Builder |
| S6 | Female | 72 | Thrombosis | 10 | Cook |
| Element | Symbol | Z | Κα [keV] | Κβ [keV] | Lα [keV] | Mα [keV] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | C | 6 | 0.277 | - | - | - |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 0.392 | - | - | - |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 0.525 | - | - | - |
| Sodium | Na | 11 | 1.041 | 1.071 | - | - |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 | 1.254 | 1.302 | - | - |
| Aluminium | Al | 13 | 1.487 | 1.557 | - | - |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 1.74 | 1.836 | - | - |
| Phosphorus | P | 15 | 2.014 | 2.139 | - | - |
| Sulphur | S | 16 | 2.308 | 2.464 | - | - |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 2.622 | 2.816 | - | - |
| Potassium | K | 19 | 3.314 | 3.59 | - | - |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | 3.692 | 4.013 | 0.341 | - |
| Titanium | Ti | 22 | 4.51 | 4.932 | 0.452 | - |
| Chrome | Cr | 24 | 5.415 | 5.947 | 0.573 | - |
| Iron | Fe | 26 | 6.404 | 7.058 | 0.705 | - |
| Nickel | Ni | 28 | 7.478 | 8.265 | 0.852 | - |
| Zinc | Zn | 30 | 8.639 | 9.572 | 1.012 | - |
| Lead | Pb | 82 | 74.97 | 84.936 | 10.552 | 2.346 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopáni, M.; Kosnáč, D.; Pánik, J.; Ješkovský, M.; Zeman, J.; Povinec, P.P.; Polák, Š. Assessment of the Accumulation of Certain Metals in Human Globus pallidus Using Particle-Induced X-Ray Emission (PIXE), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Microanalysis (EDX). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9897. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189897
Kopáni M, Kosnáč D, Pánik J, Ješkovský M, Zeman J, Povinec PP, Polák Š. Assessment of the Accumulation of Certain Metals in Human Globus pallidus Using Particle-Induced X-Ray Emission (PIXE), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Microanalysis (EDX). Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9897. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189897
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopáni, Martin, Daniel Kosnáč, Ján Pánik, Miroslav Ješkovský, Jakub Zeman, Pavel P. Povinec, and Štefan Polák. 2025. "Assessment of the Accumulation of Certain Metals in Human Globus pallidus Using Particle-Induced X-Ray Emission (PIXE), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Microanalysis (EDX)" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9897. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189897
APA StyleKopáni, M., Kosnáč, D., Pánik, J., Ješkovský, M., Zeman, J., Povinec, P. P., & Polák, Š. (2025). Assessment of the Accumulation of Certain Metals in Human Globus pallidus Using Particle-Induced X-Ray Emission (PIXE), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Microanalysis (EDX). Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9897. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189897







